Hydrogel Applications for Cultural Heritage Protection: Emphasis on Antifungal Efficacy and Emerging Research Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fungal Species and Deterioration Mechanisms in Cultural Heritage
3. Hydrogels for Paper Relic Protection
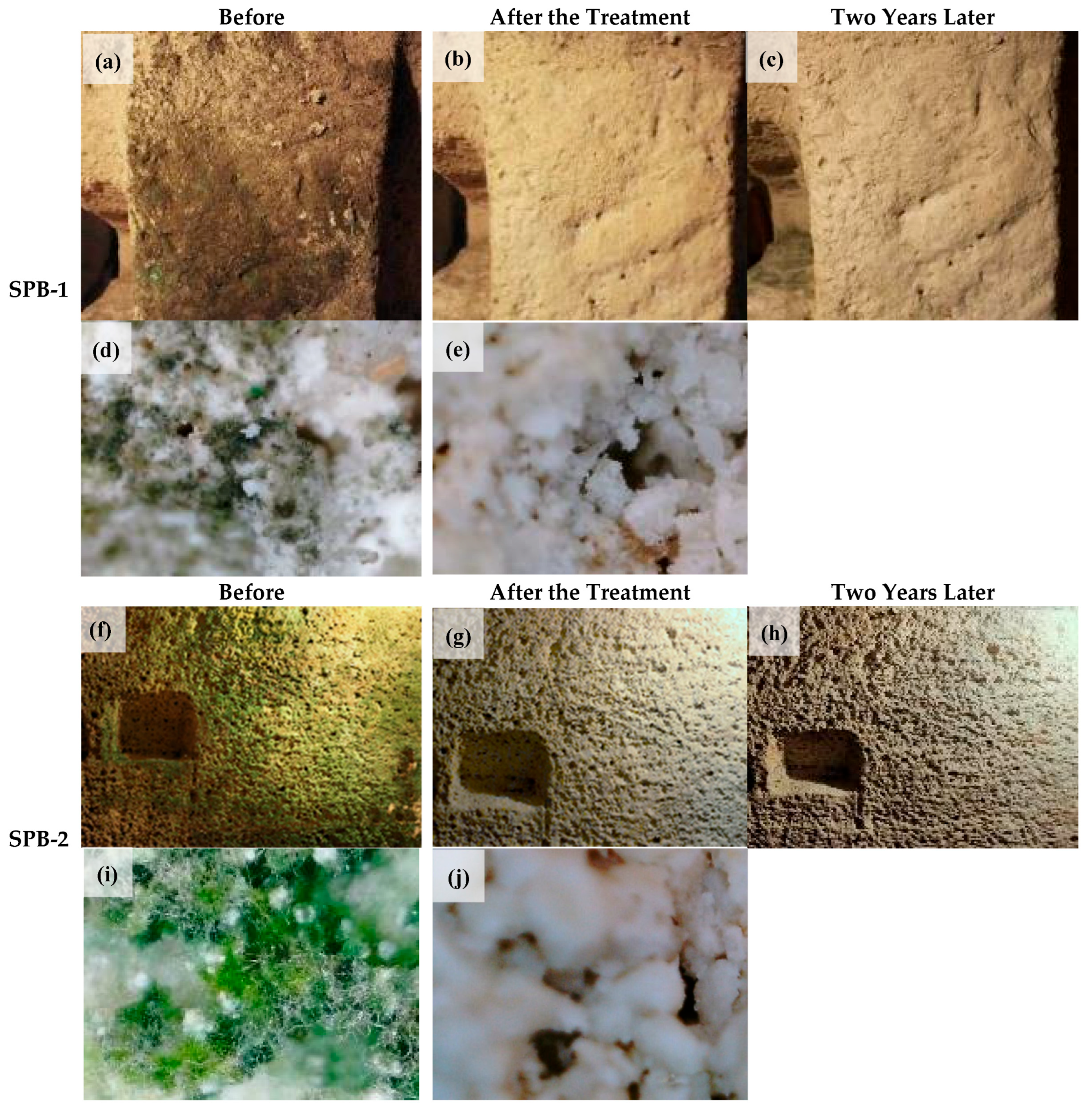
4. Hydrogels for Mural Conservation
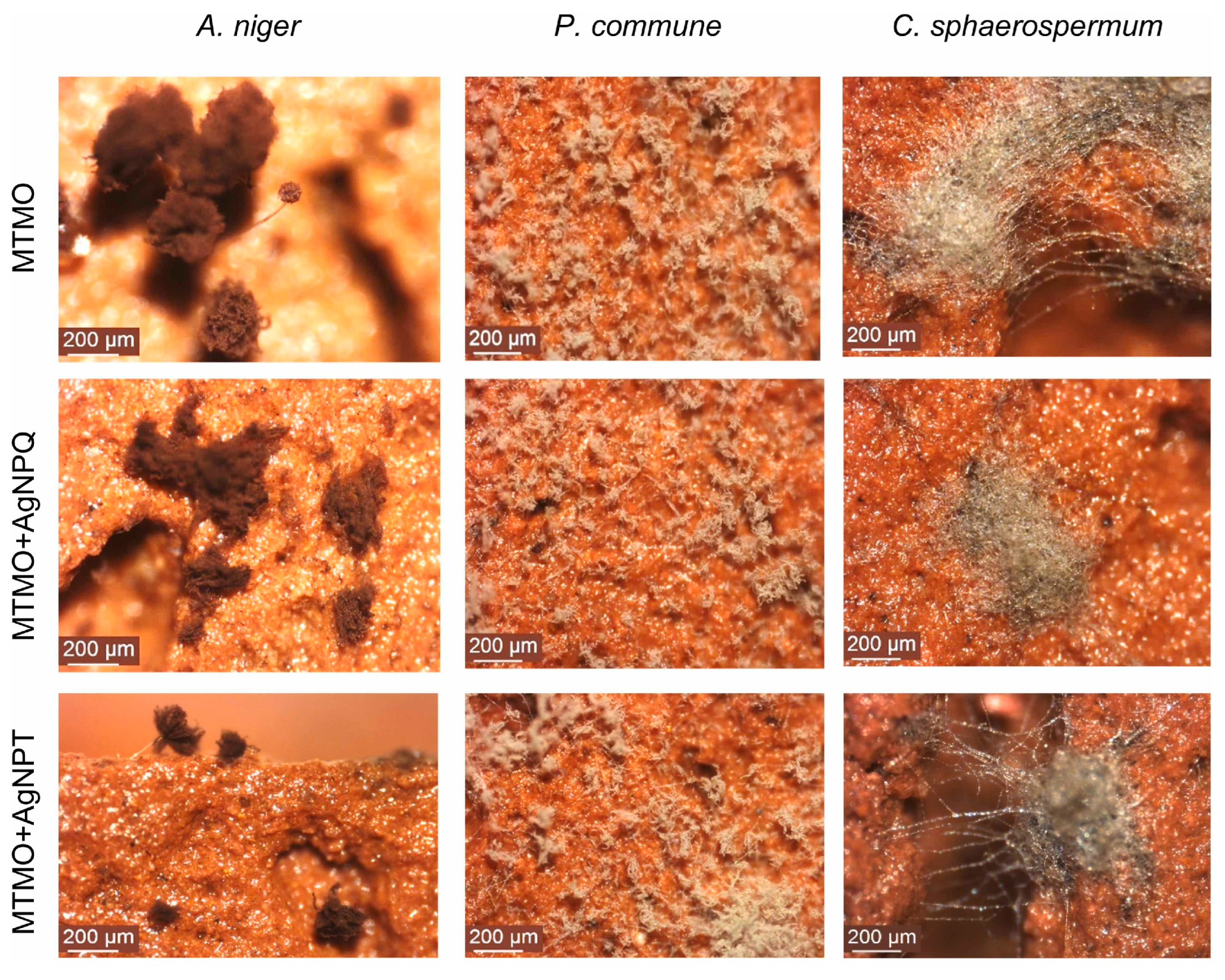
5. Hydrogels for Ancient Ceramic Conservation
6. Other Important Cultural Relics
6.1. Hydrogels for Stone Cultural Relics
6.2. Hydrogels for Bone and Keratinous Cultural Relics
6.3. Hydrogels for Wooden Cultural Relics
7. Removal Methods of Hydrogels and Their Impact on Cultural Heritages
8. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| semi-IPN | semi-interpenetrating network |
| PVA | Poly(vinyl alcohol) |
| PHEAA | Poly(N-(2-hydroxyethyl)acrylamide |
| SGs | Soft gels |
| RGs | Rigid gels |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| BH | Bentonite-based hydrogel |
| PAM | Polyacrylamide |
| AgNPs | Silver nanoparticles |
References
- Yu, P.K. Cultural relics, intellectual property, and intangible heritage. Temple Law Rev. 2008, 81, 433–506. [Google Scholar]
- Walsham, A. Introduction: Relics and Remains; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010; Volume 206, pp. 9–36. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X.; Ma, X.; Wen, J.; Chen, Y.; Fan, M. Growth characteristics of fungi isolated from unearthed wooden cultural relics. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2022, 44, 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Sterflinger, K. Fungi: Their role in deterioration of cultural heritage. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2010, 24, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterflinger, K.; Pinzari, F. The revenge of time: Fungal deterioration of cultural heritage with particular reference to books, paper and parchment. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Wu, F.; Tian, T.; He, D.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, J.; Duan, Y.; Ma, D.; Wang, W.; Feng, H. Fungal diversity and its contribution to the biodeterioration of mural paintings in two 1700-year-old tombs of China. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2020, 152, 104972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, T.P.D.; Ismail, I.; Aziz, I.R. Biodeterioration and biodegradation of cultural & religious heritage made of paper as a wood derivative. J. Islam Sci. 2022, 9, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, X.; Ma, K.; Guo, P.; Sun, Q.; Jia, S.; Pan, J. Analysis and control of fungal deterioration on the surface of pottery figurines unearthed from the tombs of the Western Han Dynasty. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 956774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Biological Disease Survey of Open Stone Relics in Ningbo Area. Int. J. Front. Sociol. 2023, 5, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Pan, X.; Ge, Q.; Ma, Q.; Li, Q.; Fu, T.; Hu, C.; Zhu, X.; Pan, J. Identification of fungal communities associated with the biodeterioration of waterlogged archeological wood in a Han dynasty tomb in China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Jiang, Y.; Xin, M. Study on Lipopeptide Antifungal Agents for Cultural Relics. In Proceedings of the 1st International Biology and Medicine Conference, Jakarta, Indonesia, 11–12 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi, P.; Verma, R.K.; Jain, N. Fungal degradation of cultural heritage monuments and management options. Curr. Sci. 2021, 121, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Chin, S.; Benedict, A.C.; Ghazali, S.; Yang, L. A comprehensive review of weathering patterns and protective materials for stone relics. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Proceedings of the 7th International Conference of Chemical Engineering & Industrial Biotechnology, Putrajaya, Malaysia, 27–29 August 2024; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2025; p. 012004. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y. Study on Protection Measures and Risk Management Strategies for Cultural Relics and Artworks. Adv. Econ. Manag. Polit. Sci. 2023, 53, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; He, C.; Zhang, G.; Xu, R.; Zhan, H.; Wu, F.; He, D. Study on the control effectiveness of relative humidity by various ventilation systems for the conservation of cultural relics. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, B. Biocides for the control of mosses on stone cultural relics. Stud. Conserv. 2023, 68, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakakhel, M.A.; Wu, F.; Gu, J.D.; Feng, H.; Shah, K.; Wang, W. Controlling biodeterioration of cultural heritage objects with biocides: A review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 143, 104721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petraretti, M.; Siciliano, A.; Carraturo, F.; Cimmino, A.; De-Natale, A.; Guida, M.; Pollio, A.; Evidente, A.; Masi, M. An Ecotoxicological Evaluation of Four Fungal Metabolites with Potential Application as Biocides for the Conservation of Cultural Heritage. Toxins 2022, 14, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, S.; Guilbaud-Chéreau, C.; Hoschtettler, P.; Stefan, L.; Bianco, A.; Ménard-Moyon, C. Preparation and optimization of agarose or polyacrylamide/amino acid-based double network hydrogels for photocontrolled drug release. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 255, 127919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, X.; Peng, H.; Zhu, X.; Huang, J.; Ran, M.; Ma, L.; Sun, X. A chitosan-coated lentinan-loaded calcium alginate hydrogel induces broad-spectrum resistance to plant viruses by activating Nicotiana benthamiana calmodulin-like (CML) protein 3. Plant Cell Environ. 2023, 46, 3592–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Ménard-Moyon, C.; Bianco, A. Carbon and 2D nanomaterial smart hydrogels for therapeutic applications. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2025, 14, 20250156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xiang, S.; Wang, J.; Luo, X.; Du, C.; Sun, X. Long-Acting Sustained-Release Hydrogel for Soil-Borne Pathogen Control in Chinese Herbal Medicine. J. Polym. Environ. 2024, 32, 6311–6319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Patel, D.; Hickson, B.; DesRochers, J.; Hu, X. Recent progress in biopolymer-based hydrogel materials for biomedical applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Gu, Y.; Su, B.; Sun, X.; Chen, Q. Alginate–Nanosilver Hydrogels: A Self-Dissolving System for Comprehensive Preservation of Waterlogged Wooden Artifacts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 16091–16103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, R.; Ning, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, X.; Zhu, J. PVA Composite Hydrogel Film for Rust Removal of an Ancient Chinese Fragile Bronze Artifact. Langmuir 2025, 41, 5312–5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Zheng, L.; Li, S.; Fan, X.; Shen, S.; Hu, D. Electrochemical removal of stains from paper cultural relics based on the electrode system of conductive composite hydrogel and PbO2. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zha, J.; Han, X.; Wang, H. Temporary consolidation of marine artifact based on polyvinyl alcohol/tannic acid reversible hydrogel. Polymers 2023, 15, 4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Lei, Y.; Kaya, M.G.A.; Goh, K.L.; Tang, K. Identification, deterioration, and protection of organic cultural heritages from a modern perspective. NPJ Herit. Sci. 2025, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Yin, L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, M.; Sun, M.; Hu, C.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Pan, J. Fungal community analysis and biodeterioration of waterlogged wooden lacquerware from the Nanhai no. 1 shipwreck. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Ding, J.; Zhao, X.; Dong, W.; Lu, Z.; Li, X. Preparing a microemulsion-loaded hydrogel for cleaning wall paintings and coins. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Lv, H.; Wu, H.; Wu, H.; Yuan, Z.; Xu, Q.; Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Shi, Y.; Xiao, L.; et al. Dual-Janus Hydrogel Composite for Moisturizing and Antimicrobial Conservation of Bone Relics. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 10274–10283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadd, G.M.; Fomina, M.; Pinzari, F. Fungal biodeterioration and preservation of cultural heritage, artwork, and historical artifacts: Extremophily and adaptation. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2024, 88, e00200-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrić, N.; Spremo, N.; Vraneš, M.; Belić, S.; Karaman, M.; Kovačević, S.; Karadžić, M.; Podunavac-Kuzmanović, S.; Korolija-Crkvenjakov, D.; Gadžurić, S. New protic ionic liquids for fungi and bacteria removal from paper heritage artefacts. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 17905–17912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, M.H.; AlHarbi, M.; Elsehemy, I.A.; Haggag, W.M.; Refaat, B.M.; Ali, S.M.; Elkelish, A. Natural Inhibitory Treatment of Fungi-Induced Deterioration of Carbonate and Cellulosic Ancient Monuments: Isolation, Identification and Simulation of Biogenic Deterioration. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 2049–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, A.C.; Sequeira, S.O.; Macedo, M.F. Fungi in archives, libraries, and museums: A review on paper conservation and human health. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 45, 686–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gámez-Espinosa, E.; Deyá, C.; Cabello, M.; Bellotti, N. Control of fungal deterioration of ceramic materials by green nanoadditives-based coatings. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2023, 36, 101069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriele, F.; Bruno, L.; Casieri, C.; Ranaldi, R.; Rugnini, L.; Spreti, N. Application and monitoring of oxidative alginate–biocide hydrogels for two case studies in “The Sassi and the Park of the Rupestrian Churches of Matera”. Coatings 2022, 12, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, B.; Liu, N.; Liu, X.; Teri, G.; Liu, P.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Cao, J. Mould prevention of archive packaging based microenvironment intervention and regulation. J. Cult. Herit. 2022, 57, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embacher, J.; Zeilinger, S.; Kirchmair, M.; Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Neuhauser, S. Wood decay fungi and their bacterial interaction partners in the built environment—A systematic review on fungal bacteria interactions in dead wood and timber. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2023, 45, 100305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastouri, A.; Efhamisisi, D.; Lexa, M.; Oladi, R.; Gholinejad-Pirbazari, A.; Torabi, H.; Zeidler, A.; Frigione, M. Biological-degradation, lignin performance and physical-chemical characteristics of historical wood in an ancient tomb. Fungal Biol. 2025, 129, 101588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhao, C.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chang, G.; He, L.; Pan, A. Insight into a bentonite-based hydrogel for the conservation of sandstone-based cultural heritage: In situ formation, reinforcement mechanism, and high-durability evaluation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 52459–52466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, H.; Yue, E.; Yu, L. Preservation and Conservation of Chinese Traditional Paper-Based Cultural Relics. Polym. Bull. 2024, 24, 1003. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Y. Chemical Conservation of Paper-Based Cultural Heritage. Molecules 2024, 30, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lan, X.; Bai, X. Study on the biological hazards and control measures of the Dunhuang manuscripts. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Proceedings of the 2020 the 4th International Conference on Agricultural and Food Science, Istanbul, Turkey, 28–30 October 2020; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; p. 012012. [Google Scholar]
- Stratigaki, M.; Armirotti, A.; Ottonello, G.; Manente, S.; Traviglia, A. Fungal and bacterial species richness in biodeteriorated seventeenth century Venetian manuscripts. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yao, J.; Yan, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Y. Reversible deacidification and preventive conservation of paper-based cultural relics by mineralized bacterial cellulose. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 13091–13102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, J.; Wang, S.; Dai, Z.; Qin, S.; Mei, S.; Zhang, W.; Guo, R. Preventive conservation of paper-based relics with visible light high-transmittance ultraviolet blocking film based on carbon dots. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 678, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Pan, L.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, B.; Hu, Y. Preparation of agnps/oregano essential oil composite film and its antibacterial application in the conservation of paper relics. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 160, 112008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, P.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H. Nanocomposites composed of modified natural polymer and inorganic nanomaterial for safe, high-efficiency, multifunctional protection of paper-based relics. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2023, 66, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, R.; Wu, P.; Quan, M. CMC-Ca (OH)2-TiO2 Nanocomposite for Paper Relics Multifunctional Restoration: Strengthening, Deacidification, UV Effect Resistance, and Antimicrobial Protection. Coatings 2024, 14, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balliana, E.; Marchand, M.; Di-Matteo, V.; Ballarin, B.; Cassani, M.C.; Panzavolta, S.; Zendri, E. Application of Zinc-Based Metal-Organic Framework ZIF-8 on Paper: A Pilot Study on Visual Appearance and Effectiveness. Polymers 2025, 17, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiah, T.C. Applying chitosan to increase the fungal resistance of paper-based cultural relics. Taiwan J. For. Sci. 2009, 24, 285–294. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzuca, C.; Micheli, L.; Cervelli, E.; Basoli, F.; Cencetti, C.; Coviello, T.; Iannuccelli, S.; Sotgiu, S.; Palleschi, A. Cleaning of paper artworks: Development of an efficient gel-based material able to remove starch paste. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 16519–16528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertasa, M.; Canevali, C.; Sansonetti, A.; Lazzari, M.; Malandrino, M.; Simonutti, R.; Scalarone, D. An in-depth study on the agar gel effectiveness for built heritage cleaning. J. Cult. Herit. 2021, 47, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonelli, N.; Poggi, G.; Chelazzi, D.; Giorgi, R.; Baglioni, P. Poly (vinyl alcohol)/poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) hydrogels for the cleaning of art. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 536, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrangelo, R.; Chelazzi, D.; Poggi, G.; Fratini, E.; Pensabene-Buemi, L.; Petruzzellis, M.L.; Baglioni, P. Twin-chain polymer hydrogels based on poly (vinyl alcohol) as new advanced tool for the cleaning of modern and contemporary art. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 7011–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Severini, L.; Titubante, M.; Gong, D.; Micheli, L.; Mazzuca, C.; Gong, Y. Gellan gum hydrogel as an aqueous treatment method for Xuan paper. Restaur. Int. J. Preserv. Libr. Arch. Mater. 2021, 42, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, M.; Dong, W.; Zhang, J. Fabrication of Salecan/poly (AMPS-co-HMAA) semi-IPN hydrogels for cell adhesion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Gan, D.; Soubrier, M.; Chiang, H.; Yan, L.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Yu, S.; Xia, Y.; et al. Bioadhesive and conductive hydrogel-integrated brain-machine interfaces for conformal and immune-evasive contact with brain tissue. Matter 2022, 5, 1204–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Nie, Z.; Yu, H.; Xu, J.; Xu, L.; Chen, Q. Protective cleaning of Chinese paper artworks with strong hydrogels: An interfacial adhesion perspective. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2023, 66, 2681–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrulas, R.V.; Nunes, A.D.; Sequeira, S.O.; Casimiro, M.H.; Corvo, M.C. Cleaning fungal stains on paper with hydrogels: The effect of pH control. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2020, 152, 104996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, X. Current progress on murals: Distribution, conservation and utilization. Herit. Sci. 2023, 11, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertasa, M.; Ricci, C.; Scarcella, A.; Zenucchini, F.; Pellis, G.; Croveri, P.; Scalarone, D. Overcoming challenges in street art murals conservation: A comparative study on cleaning approach and methodology. Coatings 2020, 10, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglioni, P.; Chelazzi, D.; Giorgi, R.; Baglioni, P.; Chelazzi, D.; Giorgi, R. Cleaning of wall paintings and stones. Nanotechnol. Conserv. Cult. Herit. A Compend. Mater. Tech. 2015, 61–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.R.A. Sodium dodecyl sulfate micro-emulsion as a smart cleaning agent for archeological manuscripts: Surface investigations. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2021, 136, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemam, E. Cleaning of Wall Paintings by Polyvinyl Alcohol–Borax/Agarose (PVA–B/AG) Double Network Hydrogels: Characterization, Assessment, and Applications; University of Antwerp: Antwerp, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Khaksar-Baghan, N.; Koochakzaei, A.; Hamzavi, Y. An overview of gel-based cleaning approaches for art conservation. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wu, C.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, B. Toward a non-invasive cleaning of the wall painting using polyelectrolyte hydrogel. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2023, 66, 2213–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senserrich-Espunes, R.; Anzani, M.; Rabbolini, A.; Font-Pagès, L. L’intervento con i gel di Agar sulle pitture murali del trecento nella capella di Sant Miquel, al monastero reale di Santa Maria de Pedralbes di Barcelona. In XIII Congresso Nazionale IGIIC–Lo Stato Dell’arte–Centro Conservazione E Restauro La Venaria Reale–Torino; Lo Stato dell’Arte 13: Venaria, Italy, 2015; pp. 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Sonaglia, E.; Schifano, E.; Augello, S.; Sharbaf, M.; Marra, F.; Montanari, A.; Dini, L.; Sarto, M.S.; Uccelletti, D.; Santarelli, M.L. Ozone-loaded bacterial cellulose hydrogel: A sustainable antimicrobial solution for stone cleaning. Cellulose 2024, 31, 9847–9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lian, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Self-shaping microemulsion gels for cultural relic cleaning. Langmuir 2021, 37, 11474–11483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Du, C.; Hua, Y.; Zhang, J.; Peng, R.; Yao, X. Synthesis and characterization of loaded Nano/zinc oxide composite hydrogels intended for anti-mold coatings on bamboo. Bioresources 2019, 14, 7134–7147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coad, B.R.; Kidd, S.E.; Ellis, D.H.; Griesser, H.J. Biomaterials surfaces capable of resisting fungal attachment and biofilm formation. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaretti, A.; Cuvillier, L.; Sciutto, G.; Guilminot, E.; Joseph, E. Biologically derived gels for the cleaning of historical and artistic metal heritage. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, R.; Palla, F. Plant essential oils as biocides in sustainable strategies for the conservation of cultural heritage. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
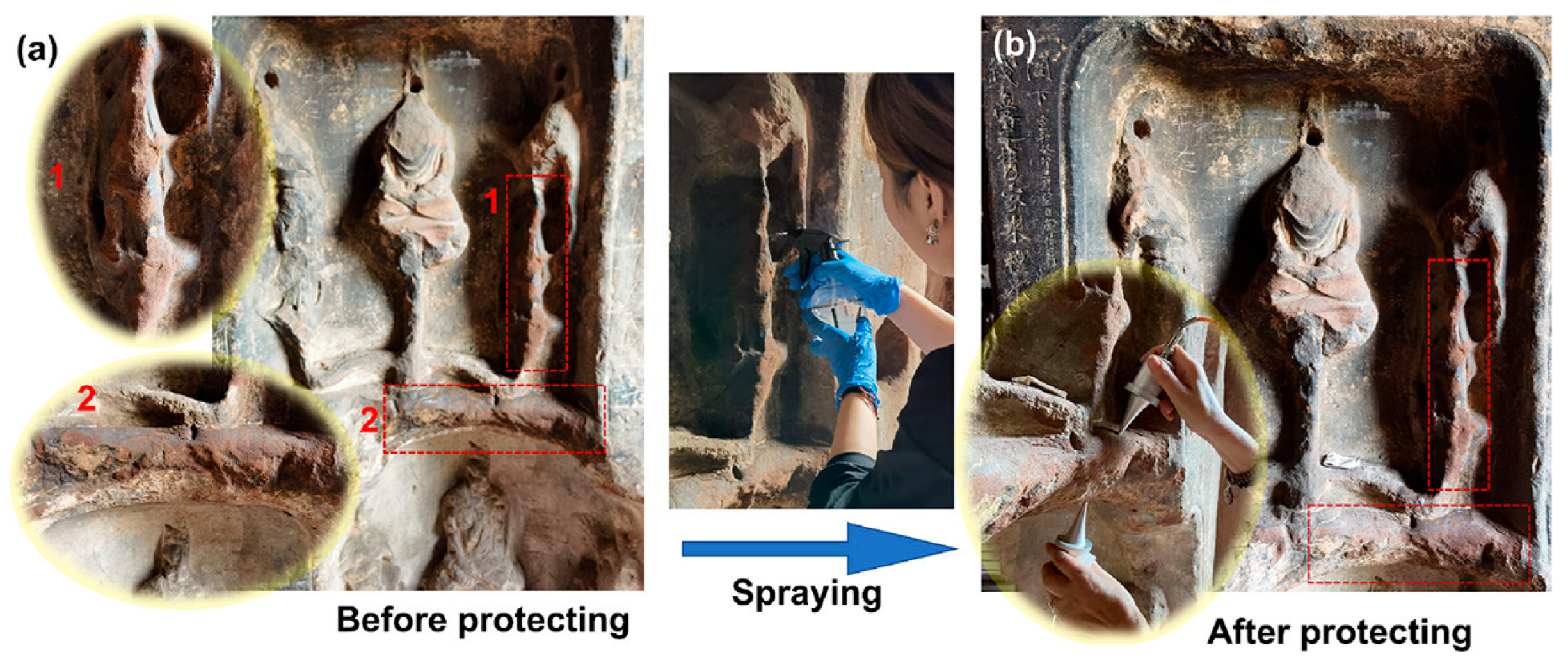


| Major Fungal Taxon | Key Deterioration Materials | Main Degradation Mechanisms | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascomycota | Aspergillus spp. | Paper, Murals, Textiles, Leather, Ancient Ceramics, Stone (covering nearly all kinds of biodeteriorated objects of cultural heritage) | 1. Organic cultural materials (paper, textiles, leather, etc.) (1) Enzymatic degradation (primary mechanism): Fungi secrete extracellular enzymes to decompose organic components in cultural heritage. (2) Acidic metabolites. (3) Discoloration and Metabolite Contamination. 2. Inorganic cultural materials (murals, stone artifacts, metals) (1) Biogenic acid erosion: Secretes organic acids to dissolve carbonates (e.g., CaCO3 in murals). (2) Biofilm disruption. (3) Metal corrosion. 3. Synergistic environmental effects (1) Humidity-dependent activity. (2) Microbial symbiosis(e.g., enhanced degradation through bacterial synergism). | [8,34,35,36,37] |
| Penicillium spp. | ||||
| Cladosporium spp. | ||||
| Fusarium spp. | [35,38] | |||
| Alternaria spp. | [35] | |||
| Trichoderma spp. | [35,38,39] | |||
| Chaetomium spp. | [35,37] | |||
| Zygomycota | Mucor spp. | Textiles, Paper, Ancient Ceramics | 1. Physical biofilm formation. 2. Mild organic acid secretion. | [8] |
| Basidiomycota | Brown (e.g.: Serpula lacrymans)—and white-rot (e.g.: Schizophyllum commune) decay fungi | Wood (highly specialized) | Decompose and utilize lignin, cellulose, and hemicellulose. | [24,40,41] |
| Lichens (a symbiotic partnership between a fungus and a phototrophic organism) | Stone Monuments, Buildings, Cement and Mortar | 1. Chemical degradation (Dominant Mechanism) (1) Organic acid corrosion. (2) Chelation. 2. Physical mechanical deterioration 3. Biomineralization deposition | [33,35,42] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, M.; Xiang, S.; Tang, H. Hydrogel Applications for Cultural Heritage Protection: Emphasis on Antifungal Efficacy and Emerging Research Directions. Gels 2025, 11, 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080606
Chen M, Xiang S, Tang H. Hydrogel Applications for Cultural Heritage Protection: Emphasis on Antifungal Efficacy and Emerging Research Directions. Gels. 2025; 11(8):606. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080606
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Meijun, Shunyu Xiang, and Huan Tang. 2025. "Hydrogel Applications for Cultural Heritage Protection: Emphasis on Antifungal Efficacy and Emerging Research Directions" Gels 11, no. 8: 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080606
APA StyleChen, M., Xiang, S., & Tang, H. (2025). Hydrogel Applications for Cultural Heritage Protection: Emphasis on Antifungal Efficacy and Emerging Research Directions. Gels, 11(8), 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080606






