Abstract
The soil-borne fungus Dactylonectria torresensis is the most common causal agent of black-foot disease in Europe. However, there is a lack of understanding on how this fungus can provoke plant symptoms. In this study, we sequenced, annotated and analyzed the genomes of three isolates of D. torresensis collected from asymptomatic vine, weed and soil. Sequenced genomes were further compared to those of 27 fungal species including root and aerial pathogens, white rot degraders, indoor biodeterioration agents, saprotrophs, dark septate endophytes and mycorrhiza. Strains of D. torresensis present genomes with between 64 and 65 Mbp and with up to 18,548 predicted genes for each strain. Average Nucleotide Identity (ANI) shows that strains are different according to genome contents. Clusters of orthologous groups were compared, and clusters of genes related to necroses were particularly detected in all strains of D. torresensis (necrosis inducing peptides and proteins, and ethylene inducing peptides) as well as several genes involved in resistance against fungicides frequently used in viticulture such as copper. Interestingly, an expanded high number of genes related to carbohydrate-active enzymes were detected in each Dactylonectria strain, especially those related to glycoside hydrolases that could be involved in penetration of plant tissues or pathogenicity. An increased number of candidate genes for CAZyme classes AA9 and AA3-1 supports the ability of strains to efficiently degrade plant material. High numbers of genes of D. torresensis related to secretome and small secreted proteins were further characterized. Moreover, the presence of several gene clusters such as fujikurin-like genes was detected and were normally found in Fusarium fujikuroi, that have been linked to fungal pathogenicity. The phenotypes of the three strains investigated showed further difference in light response. We found that Dactylonectria strains have an increased number of photoreceptor encoding genes and we showed sequence alterations. Altogether, the results highlight several gene clusters present in D. torresensis strains that could be linked to endophytic lifestyle, pathogenicity, plant maceration and degradation of plant tissues as well as adaptation to soil contaminated with metals and metalloids and light response.
1. Introduction
The soil-borne fungus Dactylonectria torresensis is the most common causal agent of black-foot disease in Europe [1,2,3], one of the most important destructive diseases in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.), which has a devastating effect on grapevine production worldwide [4]. It is well known that D. torresensis is common in the soil and causes infection of grafted vines after some months of growth in nursery soils and in young vineyards, especially during the first five years after planting [1,2]. Young vines affected by D. torresensis generally appear normal at planting but differences in vigour become marked with reduced trunk growth, shortened internodes, and reduced foliage/canopy. Foliar symptoms may appear as small leaves with interveinal chlorosis, followed by necrosis and early defoliation [5]. Removal of the rootstock bark of declining plants reveals further black discolouration and necrosis of wood tissues that develop from the base of the rootstock. Below ground, symptoms include reduced total root biomass, low numbers of feeder roots, and black, sunken and necrotic root lesions [4].
Although the disease cycle of D. torresensis on grapevines has not been specifically studied, the behavior of Cylindrocarpon-like asexual morphs on other hosts [6,7] has indicated that conidia and chlamydospores are likely to be produced on the diseased roots and stem bases of infected vines. The conidia are apparently dispersed in soil water and the chlamydospores can allow the organism to survive in the soil for a number of years [8]. Previous research reports have shown that contact between these spores and the grapevine roots or callused stem bases results in high rates of infection [9,10]. Infection can occur through the small wounds made when roots on the callused cuttings break off during the planting process or through the incomplete callusing of the basal ends of the cuttings [4].
Concerning Dactylonectria, an alternative that has been poorly addressed is that these fungi associated with black-foot disease have a dual role: a pathogenic lifestyle on certain plants and a non-pathogenic one on others. For instance, Agustí-Brisach et al. [11] reported isolation of Dactylonectria macrodidyma complex, which comprehends Dactylonectria alcacerensis, D. estremocensis, D. macrodidyma, D. novozelandica and D. torresensis, from 26 of 52 asymptomatic weed species growing in propagation field nurseries and vineyards, with these strains being pathogenic to grapevine seedlings in potted assays. Langenhoven et al. [12] isolated several black-foot disease fungi from asymptomatic plants in South Africa, including grapevine, cereals and brasicaceous crops. Recently, Berlanas et al. [13] reported the occurrence of 13 species associated with black-foot disease from the asymptomatic inner tissues of surface sterilized secondary roots of grapevine grafted plants ready to be sold to growers in Spain. The fact that plant pathogens can be non-pathogenic endophytes on other plants has important implications, such as asymptomatic plants inadvertently serving as reservoirs of inoculum and potentially initiating epidemics in other crops [14], or even serving as sources of hidden diversity of plant-pathogenic species.
Regardless of biological, chemical, or cultural measures, no effective management strategies for D. torresensis are currently available to avoid fungal infection and/or to eliminate this pathogen once plants are infected [15]. Despite the importance and necessity of controlling black-foot disease, the molecular mechanisms of pathogenesis in grapevine and other secondary hosts, and the genetic basis for host specificity are still poorly understood. To date, most investigations into the nature of host-specific adaptations have focused on differences between species of plant pathogens, while fewer studies have been conducted to investigate and explain the intraspecific diversity of host-specific adaptations. In addition, no genomic and transcriptomic studies have been conducted for D. torresensis on grapevines although the genome sequence of its sister species D. macrodidyma was made public by Malapi-Wight et al. [16].
Although single genome analysis facilitates better insights into the biology of a pathogen, comparative analysis of multiple genomes can often reveal a significantly greater amount of information on the physiology and evolution of a pathogen [17]. In this study, we analyzed the genomes of three isolates of D. torresensis collected from asymptomatic vine and weed, and soil. The main objectives of this study were to (i) identify the genomic characteristics of these fungi, (ii) understand the genetic variation among the sequenced species, (iii) identify genes potentially involved in niche specialization within species, (iv) to identify fungal adaptations to the endophytic or pathogenic lifestyles, and (v) to identify unique and shared genes and pathways related to virulence in D. torresensis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Strains and Culture Collection
Fungal strains included in the study were isolated from the weed species Solanum nigrum (BV-745), grapevine rootstock 110 Richter (BV-666) and soil samples (BV-349) collected in 2017 in a single grapevine nursery field in Mendavia (Navarra, Spain) (Figure 1A). Isolation from weed and grapevine were made from the asymptomatic endosphere tissue of roots. Sections of externally symptomless roots (1–2 cm long and 1–3 mm diameter) were cut, washed under running tap water, surface disinfested for 1 min in a 1.5% sodium hypochlorite solution, and washed twice with sterile distilled water. The bark was carefully peeled out and the endosphere tissue was plated onto malt extract agar (MEA; Biokar-Diagnostics, Zac de Ther, France) supplemented with streptomycin sulfate (MEAS) at 0.4 g.L–1 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). Isolation from soil samples were performed by plating them onto the Glucose-Faba Bean Rose Bengal Agar (GFBRBA) semi-selective culture medium as described by Berlanas et al. [2]. All isolates were single-spored in order to obtain pure cultures and stored in filter paper at −20 °C.
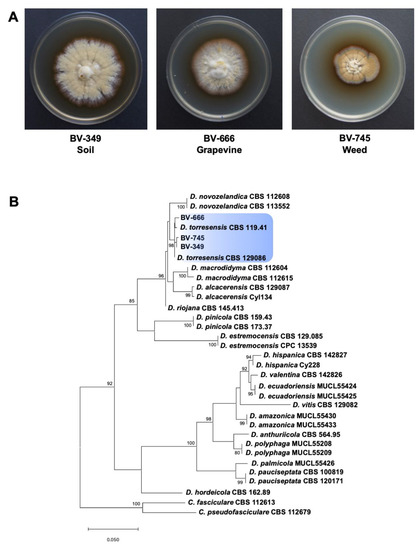
Figure 1.
(A) Colony morphology of Dactylonectria torresensis strains isolated from soil, weed or grapevine. (B) Maximum likelihood phylogeny of Dactylonectria spp. as estimated from the alignment of the histone H3 gene sequences. Maximum likelihood bootstrap percentages are indicated at the nodes. Support values less than 70% bootstrap are omitted. The tree was rooted to Campylocarpon fasciculare (CBS 112613) and Ca. pseudofasciculare (CBS 112679). The scale bar indicates 0.05 expected changes per site.
2.2. DNA Isolation and Fungal Identification
Fungal strains BV-349, BV-666 and BV-745 were grown on potato dextrose agar (PDA; Conda Laboratories, Madrid, Spain) plates for 7 days at room temperature. Mycelium was scraped from plates with the scalpel, transferred to the mortar and grinded with pestle in liquid nitrogen to get fine powder. One hundred mg of powder was taken for the DNA isolation using DNeasy Plant Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) following manufacturer procedure as described by Berlanas et al. [13]. Obtained DNA was cleaned and concentrated using Amicon Ultra-0.5 mL Centrifugal Filters for DNA and Protein Purification and Concentration with cut off 30 kDa (Millipore-Merck, Bedford, MA, USA).
The identification of black-foot pathogens was made by sequencing part of the histone H3 gene. PCR conditions and sequence analysis were performed according to Berlanas et al. [13]. Maximum Likelihood (ML) was performed on the individual gene alignment in MEGA v. 6 [18] using the best fit model as estimated with the Bayesian information criterion in jModelTest 2.1.10 [19]. Branch support was calculated from 1000 bootstrap replicates for dataset. Campylocarpon fasciculare (CBS 112613) and Ca. pseudofasciculare (CBS 112679) were used as outgroups in the phylogenetic analysis.
2.3. Genome Sequencing and Assembly
Fungal genomes were sequenced with Illumina NextSeq 500 using the V2 reagent kit (2 × 150 bp) and generating a total of 50 million PE reads (LGC Genomics GmbH, Berlin). Illumina raw data were checked with FastQC [20] and possible PhiX contaminant sequences removed with Bowtie2 [21]. The presence of adapters was checked, reads were quality filtered and trimmed using Trimmomatic v.0.36 [22]. Genome assembly was carried out with SPAdes v.3.11.1 in careful mode, with k-mer size 21, 33, 55, 77, 99, 127 [23]. Contig coverage was assessed by mapping corrected reads against the assembled contigs with Bowtie 2 and BAM files were read with QualiMap v.2.2.1 [24]. Small contigs (<500 bp) with low coverage (<2×) were removed. The presence of contaminant contigs was ascertained using BlobTools v.1.0.1 [25] and the genome assembly quality of filtered contigs was evaluated with QUAST v.4.6.0 [26]. Genome completeness reconstruction was assessed with BUSCO v.3.0.2 [27]. Taxonomic affiliation was confirmed by targeting and extracting the complete Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) with ITSx v.1.1 [28] and locally aligning the sequence (blastn) against the UNITE web-based database (https://unite.ut.ee/) [29].
2.4. Average Nucleotide Identity
Previously available genome sequences of other related fungal organisms, later included in the comparative analysis, were downloaded from the NCBI repository with the ncbi-genome-download Python script [30]. Whole genome relatedness of de-novo assembled genomes and downloaded genomes were assessed using Average Nucleotide Identity (ANI) analysis with BLAST method [31]. The selected fungi had at least one of the following features in common with D. torresensis: root colonization (including pathogenic, beneficial endophytic and mycorrhizal colonization), plant pathogenesis and plant biomass degradation. These fungi were: Ilyonectria destructans C1, Ilyonectria mors-panacis g3b [32], Dactylonectria macrodidyma JAC15-245 [16], Botrytis cinerea B05.10 [33], Fusarium graminearum PH-1 [34], Leptosphaeria maculans JN3 [35], Magnaporthe oryzae 70-15 [36], Serendipita indica DSM 11,827 [37], Ustilago bromivora UBRO v3 [38], Botryosphaeria dothidea LW030101 [39], Trichoderma reesei QM6a [40], Phaeomoniella chlamydospora UCRPC4 [41], Rhizoctonia solani AG-3 [42], Tulasnella calospora AL13/4D [43], Phaeoacremonium minimum UCRPA7 [44], Phaeoacremonium sp. FL0889 (Joint Genomics Institute [JGI], http://fungalgenomes.org), Serpula lacrymans S7.3 [45], Phanerochaete chrysosporium ATCC 20,696 [46], Rhizophagus irregularis DAOM 181,602 [47], Laccaria bicolor S238N-H82 [48], Tuber melanosporum Mel28 [49], Phaeomoniella chlamydospora RR-HG1 [50], Cadophora malorum Mo12 [51], Oidiodendron maius Zn [43], Periconia macrospinosa DSE2036 [52], Verticilium dahliae Vdsl17 [53] and Nectria haemotococca mpVI [54].
2.5. Gene Prediction and Genome Annotation
The gene prediction of de-novo assembled genomes was conducted in Maker v.3.00.0 [55] generating a consensus prediction based on the following strategy: (1) low-complexity (simple) and interspersed (complex) repetitive elements were masked with RepeatMasker v.4.0.5; (2) ab-initio unsupervised gene finding was made with GeneMark-ES v.4.32 [56]; (3) a gene prediction based on precomputed Fusarium graminearum model was performed with Augustus v.3.2.3 [57]. The sequences of the previously available fungal genomes were either de-novo annotated or re-annotated, using data accessible from the JGI (https://jgi.doe.gov/). The gene prediction was executed in Maker, combining the following information: GeneMark-ES ab-initio gene prediction, available proteins from same or related organisms, existing Augustus gene prediction models from related fungal taxa.
Amino acid FASTA files were then annotated with the accelerated blastp implemented in DIAMOND v.0.9.24.125 using the NCBI fungal protein RefSeq database.
2.6. Functional Annotation of Predicted Genes
Functional annotation was carried out using a local installation of the whole eukaryotic orthologous eggNOG v.4.5.1 database [58]. Carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes) were classified in Dactylonectria strains BV-349, BV-666 and BV-745 using the dbCAN Hmmer-based classification system with E-Value < 1 × 10−15, coverage > 0.35 [59] at http://bcb.unl.edu/dbCAN2/. Similar annotation was done for 27 fungal genomes including root pathogens, aerial pathogens, trunk or cane pathogens, white rot degraders, indoor biodeterioration agents, saprotrophs, dark septate endophytes and mycorrhiza. All positive hits were manually examined for final validation. All CAZyme classes, including Glycoside Hydrolases (GH), Carbohydrate Esterases (CE), Glycoside Transferases (GT), Polysaccharide Lyases (PL) and Carbohydrate-Binding Modules (CBM) were considered. Circos online software at http://mkweb.bcgsc.ca/tableviewer/was further used for data visualization and comparison of CAZymes with other fungi.
The secretome tool software http://genomics.cicbiogune.es/SECRETOOL/ was also utilized for general secretome analysis and small secreted proteins (ssp) using the default settings for eucaryotic genomes. Comparisons were further carried out with the data from the 27 other fungal genomes.
Antismash analysis was finally performed for prediction of genes related to secondary metabolites (https://fungismash.secondarymetabolites.org/).
2.7. Analysis of Growth and Light Response
Strains were cultivated on malt extract (3% w/v), Mandels Andreotti minimal medium [60] or synthetic nutrient poor agar (SNA) medium [61] in daylight (12 h:12 h cycles of light and darkness) or constant darkness for 72 h for assessment of hyphal extension and light response. Fungal growth on Petri dishes were documented photographically.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fungal Strains
A phylogenetic analysis was performed with Dactylonectria strains isolated from the weed species Solanum nigrum (BV-745), grapevine rootstock 110 Richter (BV-666) and soil samples (BV-349) to identify them at species-level. The Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) best-fit nucleotide substitution model identified by jModelTest was Hasegawa-Kishino-Yano model (HKY) with gamma distributed with invariant sites rates (G + I) for the Dactylonectria analysis. Alignment of 31 Dactylonectria sequences resulted in a 540-character dataset. The three isolates clustered strongly (>98%) with the type specimens of D. torresensis (CBS 129,086 and CBS 119.41) (Figure 1B). Strains BV-666 and BV-745 were isolated from asymptomatic vine and weed, respectively. Recent studies have suggested that black-foot fungi have a non-pathogenic endophytic phase [12,13] and may become pathogenic to grapevine after different abiotic and/or biotic stresses conditions and thus, they are considered as latent pathogens in grapevine. Several factors have been reported to be determinants in triggering pathogenicity in an endophyte that was previously asymptomatic, such as the nutrient status, changes in plant gene expression, habitat, host genotype or the locally occurring abiotic stresses that might reduce host fitness, resulting in bias of this delicate equilibrium and thus influencing the symptom expression in plants [62]. Abiotic stress factors in new plantations and grapevine nursery fields include water stress, J-rooting, winter-kill, waterlogging, soil compaction, nutrition deficiency and/or overcropping [15].
3.2. Genomes
The genomes of three D. torresensis strains isolated from grapevine, weed or soil were sequenced and annotated. Strain BV-349 has a genome size of 64.42 Mb (GC content: 50.67%) while strain BV-666 and strain BV-745 have 65.33 Mb (GC content: 50.17%) and 64.21 Mb (GC content: 50.23%), respectively and with 19,102 predicted proteins for strain BV-349, 19,090 for strain BV-666, and 18,724 for strain BV-745 (Table 1). Single-copy ortholog analysis reported a genome assembly completeness of 98.6% for strain BV-349, 98.3% for BV-666 and 99.0% for BV-745. ANI analysis showed that strains are different at genome level (Supplementary File 1: Figure S1). The number of transposon-related proteins in the three strains is 117, 139 and 143, respectively.

Table 1.
Genome statistics of Dactylonectria strains.
3.3. COG Categories and Eggnog Analysis
Using COG categories and eggnog database, we analyzed each group of gene categories (Table 2) and searched which potential genes could be involved in pathogenicity or endophytism. Each strain contains genes related to ethylene induced peptide-related gene and necrosis inducing protein (NPP1) (Table 3). A high number of genes related to carbohydrate-actives enzymes were further detected in each strain. Other interesting genes to highlight were genes related to heavy metal or metalloid resistance such as copper, cadmium and others that could be detected in a vineyard (Table 3). Other genes of interest were those related to salicylate hydrolase, which degrades salicylic acid normally involved in signalling of plant defense reaction, siderophore as an iron chelator and auxin as a phytohormone (Table 3). Only a few fungal salicylate hydroxylase enzymes have been reported such as in the endophyte Epichloë festucae or in the pathogen Fusarium graminearum causing Fusarium head blight (FHB) [63]. Salicylate hydroxylase enzymatic activities have been also found in Trichosporon cutaneum and other Fusarium spp. [64,65]. Interestingly, no symptom was recorded in the weed and vine and the strains were established as non-pathogenic endophytes, suggesting the possibility that degradation of salicylic acid is a factor on how Dactylonectria strains avoid plant defense reaction.

Table 2.
Clusters of ortholog groups of Dactylonectria strains.

Table 3.
Genes related to pathogenicity, metal resistance or other properties in Dactylonectria genomes.
3.4. CAZymes
A high number of genes related to carbohydrate metabolism was detected in the genomes of all three Dactylonectria strains investigated. Previously, CAZyme encoding genes were shown to have roles during infection of plants by fungal pathogens [39]. Therefore, we further analyzed the genomes of Dactylonectria strains BV-349, BV-666, BV-745 for CAZymes related genes. The strains contain 1140, 1116, and 1133 genes encoding putative CAZymes, respectively (Table 3).
As for many fungi, among CAZymes related genes, the Glycoside Hydrolase (GH) superfamily is the most represented class in the three Dactylonectria strains (Figure 2). We found that some GH genes were represented by a number of genes >20 as for GH78 (Figure 2) corresponding to α-L-rhamnosidase/rhamnogalacturonan α-L-rhamnohydrolase/L-Rhap-α-1,3-D-Apif -specific α-1,3-L-rhamnosidase). Also, GH43 was over-represented. GH43 has functions like β-xylosidase/α-L-arabinofuranosidase/xylanase/α-L-arabinofuranosidase/exo-β-1,3-galactanase/β-D-galactofuranosi-dase. GH3 was also highly represented in each genome and corresponds to β-glucosidase/xylan 1,4-β-xylosidase/β-glucosylceramidase/β-N-acetylhexosaminidase/α-L-arabinofuranosidase/isoprime-verose-producing oligoxyloglucan hydrolase/coniferin β-glucosidase/exo-1,3-1,4-glucanase or β-N-acetylglucosaminide phosphorylases (Figure 2). Additionally, GH28 was highly present (Figure 2). GH28 has potential activities like polygalacturonase/α-L-rhamnosidase/rhamno-galacturonase/rhamnogalacturonan α-1,2-galacturono-hydrolase/endo-xylogalacturonan hydrolase. Lastly, GH18 (chitinase/lysozyme/endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase/peptidoglycan hydrolase/Nod factor hydrolase/xylanase inhibitor/concanavalin B or narbonin), GH16 (xyloglucan/xyloglucosyltransferase/β-agarase/κ-carrageenase/xyloglucanase/β-porphyranase/hya-luronidase/endo-β-1,4-galactosidase/chitin β-1,6-glucanosyltransferase), and GH109 (α-N-acetylgalactosaminidase) were also represented by a number of genes >20 (Figure 2).
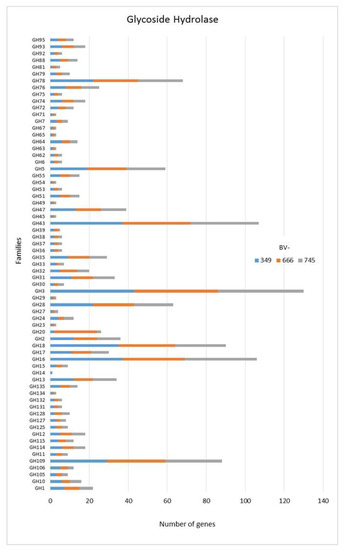
Figure 2.
Numbers of genes related to glycoside hydrolases in Dactylonectria torresensis strains BV-349, BV-666, BV-745.
In addition to GH, polysaccharide lyase related genes (PCWDE) were also detected in the three genomes of D. torresensis with PL1 being the most present family followed by PL3, PL4, PL9 and others (PL6, 7, 11, 14, 20, 22, 26; Figure 3). Genes related to glycosyl transferase (GT1, GT2, GT4), carbohydrate esterase (CE10), carbohydrate binding module (CBM67, CBM50) and auxiliary activities (AA7, AA3) were also further highly present in the three genomes (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). Of those, particularly the expansion in GT1, PL1 and PL3 gene families was found to be characteristic for plant pathogenic fungi [66].
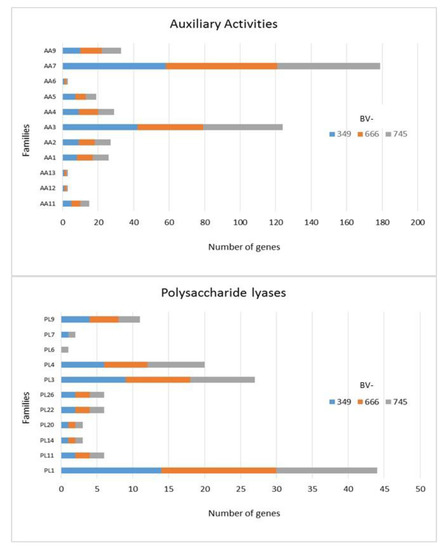
Figure 3.
Numbers of genes related to auxiliary activities and polysaccharide lyases in Dactylonectria torresensis strains BV-349, BV-666, BV-745.
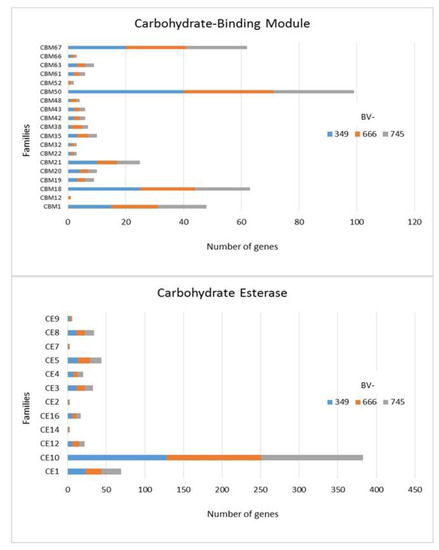
Figure 4.
Numbers of genes related to carbohydrate-binding modules and carbohydrate esterases in Dactylonectria torresensis strains BV-349, BV-666, BV-745.
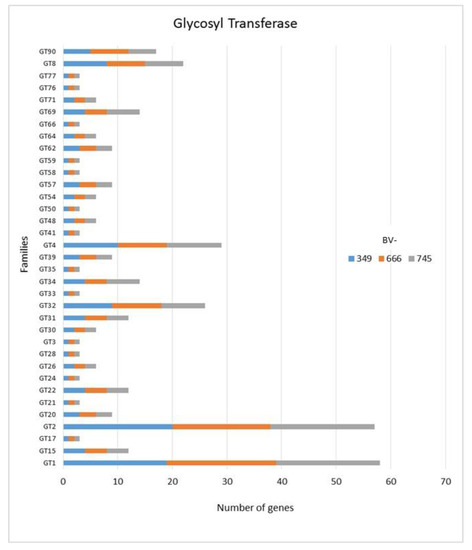
Figure 5.
Numbers of genes related to glycosyl transferases in Dactylonectria torresensis strains BV-349, BV-666, BV-745.
As only small differences were recorded between the strains for either genes related to glycoside hydrolases (Figure 2), auxiliary activities and polysaccharide lyases (Figure 3), carbohydrate-binding modules, carbohydrate esterases (Figure 4) or glycosyl transferases (Figure 5), more information were searched in relation/differences of Dactylonectria strains to other fungi. Circos simulation shows relationship between the percentages of CAZymes genes shared by Dactylonectria strains and also with other black-foot fungi (Supplementary File 2: Figure S2). CAZyme numbers appears as significantly higher in Dactylonectria spp. than the average for the other 27 fungal genomes (Figure 6), which agrees with characteristics of plant pathogens [66].
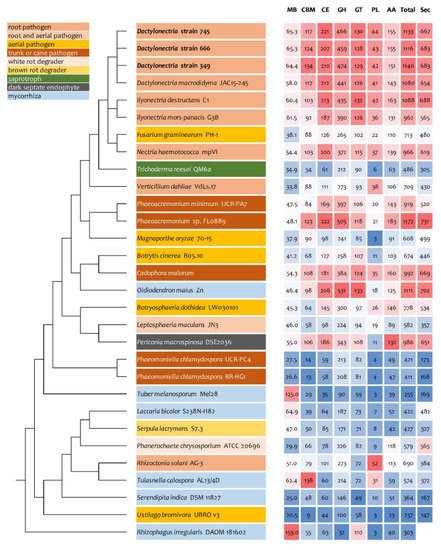
Figure 6.
Comparative analyses of genome size, numbers of genes related to carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZyme) and secretome in Dactylonectria torresensis strains BV-349, BV-666, BV-745 to known fungal pathogens, saprotrophs or symbionts. CBM: Carbohydrate-Binding Module, CE: Carbohydrate Esterase, GH: Glycoside Hydrolase, GT: Glycosyl Transferase, PL: Polysaccharide lyases, AA: Auxiliary Activity, Total: total number of CAZymes, Sec: number of secreted proteins.
In comparison to Dactylonectria strains described in this study, the dark septate endophyte Oidiodendron maius Zn has a total of 1111 genes related to CAZymes and the trunk disease pathogen Phaeoacremonium sp. FL0889 1172 (Figure 6). The highest score was also related to black-foot pathogens such as Dactylonectria macrodidyma JAC15-245 (1080 genes), and Ilyonectria destructans C1 (1088). Other genomes had genes numbers between 237 and 992.
The fact that these three genomes possess a high number of CAZymes and PCWDE domains suggests that the strains have a broad spectrum of enzymes as weapons for degrading plant cell-wall and to establish themselves as endophytes inside plant tissues as well as to macerate root tissues. Several genomic studies have indeed indicated that a high amount of CAZyme and PCWDE-related genes is linked to non-pathogenic or pathogenic endophytes [43,52,67].
3.5. Genes Involved in Oxidative Degradation of Plant Biomass
CAZyme gene analysis revealed the characteristic expansions in gene families implicated in infection and pathogenicity [39,66]. Here, in particular the increased number of GH43 encoding genes, but also of auxiliary functions suggest a role of the competence to degrade lignocellulose in pathogenicity of Dactylonectria spp. Therefore, we investigated the genomic content for the presence of AA3-1, AA9 and AA14 members. The AA9 family represents an efficient group of lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases (LPMOs) of high biotechnological relevance [68] due to their contribution to cellulose degradation, but also xyloglucan degradation was shown for this family [69]. A contribution of LPMOs to lignin degradation was reported as well [70] For AA14 LPMOs, only recently a high efficiency in boosting wood saccharification was shown [71]. LPMOs degrade lignocellulosic biomass via an oxidative mechanism, that requires an electron donor [72]. Cellulose dehydrogenases (CDHs) of the family AA3-1 are known to reduce LPMOs in nature and are hence crucial for their function [73]. Hence, the combination of these LPMOs and CDHs along with the fact that LPMOs were also found to be efficient under anaerobic conditions [74], make them ideal candidates for virulence factors of Dactylonectria.
For AA14, a Blastp search of the 321 Sordariomycetes genomes in Mycocosm (https://mycocosm.jgi.doe.gov) with the characterized Pyconoporus coccineus AA14 proteins [71] revealed putative homologues (e-values around 1E-38) in only about half of the Sordariomycetes species so far sequenced. In only a few cases, two putative homologues were detected. In the three Dactylonectria strains investigated here, we found one putative homologue each, but with amino acid identities around 25% and similarities around 31% to P. coccineus AA14a and AA14b. Since for those proteins no functional domains were characterized yet, a comparable functionality of the Dactylonectria homologues remains to be confirmed.
Members of the class AA9 (formerly GH61) are particularly important for oxidative degradation of plant biomass. Dactylonectria strains BV-666 and BV-745 contain twelve homologues with the respective domain, while BV-349 only has ten putative LPMOs of class AA9 (Supplementary File 3: Figure S3).
Analysis of putative cellobiose dehydrogenases, which fuel LPMO efficiency, was done in comparison of characterized homologues from www.cazy.org. A strikingly high number of putative homologues was detected in the Dactylonectria strains, with four in BV-349 and BV-666 and even five in BV-745, while for example N. crassa contains 2 and T. reesei none. However, their functionality as cellobiose dehydrogenases remains to be confirmed.
In summary, while the functionality of the additional homologues remains to be experimentally confirmed along with their expression in vivo, the high number of putative CDH and AA9 encoding genes supports the role of Dactylonectria as a pathogen with an efficient machinery for wood degradation. Despite important possible contributions of other factors to virulence, a clear difference for the three strains according to their isolation site (soil, grapevine, weed) could not be deduced from abundance of genes predominantly associated with wood degradation.
3.6. Analyses of Secretome and Small Secreted Proteins (SSP)
High numbers of genes of D. torresensis corresponding to secretome and a larger size of small secreted proteins were further characterized in the three genomes of Dactylonectria (with number between 683 and 687 secreted proteins and 251–260 for SSP) (Figure 6 and Figure 7). Comparison showed that dark septate endophytes Pericornia macrospinosa DSE2036 and Oidiodendron maius Zn as well as trunk disease pathogen Cadophora malorum, Phaeoacremonium sp. FL0889, and black-foot pathogens Dactylonectria macrodidyma JAC15-245, as well as Ilyonectria destructans C1 had a similar range of genes related to secretome (650–731) (Figure 6). Small secreted proteins play important roles in pathogenicity of fungal-plant interactions and in symbiosis [52,75,76,77]. The large numbers of secreted proteins in Dactylonectria strains show also potential roles in pathogenicity.
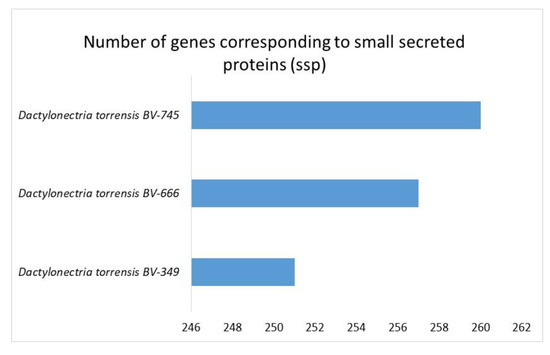
Figure 7.
Numbers of genes in Dactylonectria torresensis strains BV-349, BV-666, BV-745 corresponding to small secreted proteins (ssp).
3.7. Antismash Analyses
One of the crucial weapons for fungal plant pathogen is the production of phytotoxic compounds [78]. Fungal antismash analysis was used to search in the genomes’ gene clusters encoding key enzymes such as NRPS (non-ribosomal peptide synthetase), PKS (polyketide synthase), HYBRID PKS-NRPS and others. Dactylonectria strains were found to contain a significant number of genes encoding key secondary metabolism biosynthesis enzymes (Table 4). Interestingly, biosynthetic gene clusters for echinocandin B (antifungal lipopeptide inhibiting the synthesis of glucan), brefeldin (antiviral metabolite) and asperfuranone (a polyketide) were detected in the Dactylonectria genomes, except in BV-349 for echinocandin B (Table 4). Surprisingly, a fujikurin biosynthetic gene cluster was also detected in all three genomes with percentage of similarity between 83 and 100% to known gene cluster (Table 4). Fujikurin has been isolated from an endophytic Fusarium species [79] and phytopathogens and highlights were made on a possible role of this metabolite as a phytopathogenic virulence determinant [80]. Other fujikurin-like clusters were also detected in opportunistic pathogens such as Aureobasidium pullulans and Scedosporium spp., in the saprophyte Endocalyx cinctus (saprophyte in dead palms), in the ericoid mycorrhizal fungus Cairneyella variabilis, in Paecilomyces hepiali (entomopathogenic fungus associated with plants) and Ophiostoma sp. responsible of Dutch elm disease [81]. The presence of this gene cluster, but with a configuration different from the one of Fusarium fujikuroi, a species complex belonging to Nectriaceae [82] (Supplementary File 4: Figure S4) suggests that this secondary metabolite could allow several fungal species to interact with plants, as phytopathogens or non-pathogenic endophytes.

Table 4.
Antismach analysis of Dactylonectria genomes.
3.8. Light Response
Light has a profound impact on physiology and metabolism of fungi [83] and in particular also on regulation of plant cell-wall degradation [84,85], which may be relevant for pathogenicity of Dactylonectria. Light and photoreceptors impact circadian rhythmicity as well and recently a connection of fungal circadian rhythmicity of pathogenicity was detected [86,87]. We noticed that the three strains investigated in this study show phenotypic differences when grown in light (Figure 8A). Especially, BV-666 showed a clear reaction to changing light conditions when it was grown in daylight (light:dark 12 h:12 h). Differences in hyphal extension between daylight and darkness were obvious on xylan (BV-745) or cellulose (BV-349) (Figure 8B). Therefore, we were interested if these differences are reflected in the genomes of these strains. We analyzed blue light photoreceptor candidates of all three Dactylonetria strains and found that the photoresponse machinery of these fungi is more complex than that of N. crassa or T. reesei. Besides homologues of ENV1/VVD and BLR2/WC-2, Dactylonectria spp. have an additional, close homologue to BLR1/WC-1, representing the crucial PAS/LOV photoreceptors. Moreover, we found two further proteins related to and sharing similar domains with BLR1/WC1 (Figure 8C). All Dactylonectria proteins containing a putative PAS/LOV (Per-ARNT-Sim/Light, oxygen or voltage) domain also comprised the conserved sequence NCRFLQ which is considered crucial for light responses [88], except for one of them (Figure 8D), where the sequence is altered to NCRLLQ. Then, we tested whether alterations in the sequences of the detected photoreceptors would correlate with the altered light response we had observed. Indeed, aligning the sequences revealed that in BV-666, three of the four photoreceptor homologues showed alterations in one or more amino acids (Figure 8E), which is in accordance with an altered response to daylight (Figure 8A). However, since these alterations did not occur in functional domains like phosphorylation or myristoylation sites, we could not assign a possible relevance. Since BV-666 was isolated from grapevine, further work to evaluate whether the detected alterations may have affected association with the plant and hence virulence, could provide insight into the relevance of the extended photoresponse system of Dactylonectria on pathogenicity.
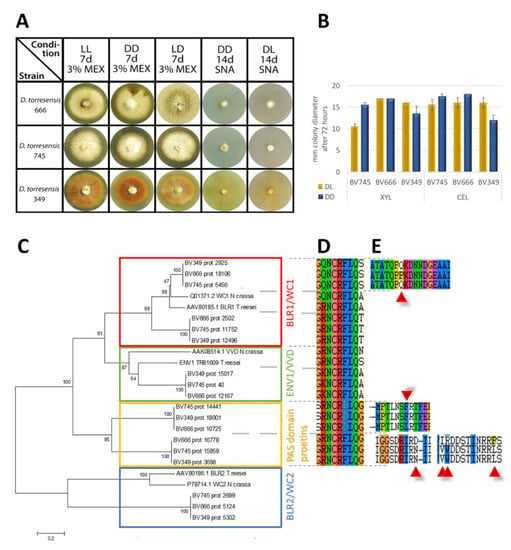
Figure 8.
Light response and photoreceptors in Dactylonectria. (A) Growth characteristics of mycelia grown on 3% (w/v) malt extract (MEX) or SNA medium in daylight (DL; 12:12 dark:light cycles) or constant darkness (DD) for 7 days. For strain BV-666 formation of rings is visible on both media. (B) Analysis of hyphal extension upon growth on Mandels Andreotti minimal medium (Mandels 1978) with 1% (w/v) xylan or cellulose in daylight (DL) or constant darkness (DD). Errorbars reflect standard deviation of two biological replicates. (C) Phylogenetic analysis of photoreceptor homologues in Dactylonectria. The evolutionary history was inferred using the minimum evolution method (Eck and Dayhoff 1966). The bootstrap consensus tree inferred from 500 replicates is taken to represent the evolutionary history of the taxa analyzed (Felsenstein 1985). Phylogenetic analyses were conducted in MEGA4 (Tamura et al. 2007). GenBank accession numbers of reference proteins are given with the protein names and species. (D) Encoded amino acids in the genomic region of the NCRFLQ conserved motif in the proteins shown in the phylogenetic tree. (E) Alterations in the amino acid sequence at different loci of proteins shown in the phylogenetic tree.
The sequence differences in the photoreceptors described above may impact circadian rhythms already, but in addition we analyzed the sequence of FREQUENCY (FRQ), which is crucial for circadian rhythmicity in N. crassa [89]. However, we did not detect any differences in FRQ between the strains.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we analyzed genomes of D. torresensis strains from three different habitats such as soil, weed, and grapevine. Overall, there was a similar genome content in the strains with genes related to necrosis, heavy metal/metalloid resistance, salicylic acid degradation, and a high number of CAZymes related to glycoside hydrolases that could be involved in non-pathogenic endophytism or pathogenicity. Analysis of photoreceptors revealed an increased number as well as specific mutations in one strain, indicating an increase relevance of light perception and potentially integration with other signals in Dactylonectria compared to other ascomycetes. High numbers of genes related to secretome and small secreted proteins were further detected. However, small differences were recorded between the three genomes. Our analysis also demonstrates the presence of several gene clusters with some as fujikurin-like genes that have been linked to fungal pathogenicity. We further detected high numbers of genes related to CAZyme families and high numbers of transposons. This finding is further represented by CAZymes associated with wood degradation.
The fact that D. torresensis can be a non-pathogenic endophyte on weeds or grapevine has important implications. The potential role of asymptomatic hosts may include not only preservation of a viable inoculum source quantitatively during for example, crop rotation in grapevine nursery fields, but also in shaping the genetic structure of the pathogen population qualitatively, which may have significant implications for disease management. This finding also highlights the urgent need to implement early, accurate and specific in planta detection and quantification of D. torresensis to prevent the spread of black-foot disease in grapevine propagation material. The future direction of research on black-foot needs to investigate: (i) how these fungi colonize roots of secondary hosts or grapevine and establish themselves inside, and (ii) what triggers latent black-foot fungi to transition from a non-pathogenic endophyte to a pathogenic endophyte, and cause disease symptoms in grapevine.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2309-608X/6/4/255/s1, Figure S1: Average Nucleotide Identity (ANI). Figure S2: circular network plot of CAZymes categories and their percentages shared in Dactylonectria torresensis strains (top) and with other black-foot pathogens (below). A: CBM, B: CE, C: GH, D: GT, E: PL, F: AA, G: BV-745, H: BV-666, I: BV-349, J: Ilyonectria destructans C1, K: Ilyonectria mors-panacis G3B, L: Dactylonectria macrodidyma JAC15-245. Figure S3: phylogenetic analysis of AA9 candidates of Dactylonectria. The evolutionary history was inferred using the maximum parsimony method (Eck and Dayhoff 1966). The bootstrap consensus tree inferred from 500 replicates is taken to represent the evolutionary history of the taxa analyzed (Felsenstein 1985). Phylogenetic analyses were conducted in MEGA4 (Tamura et al., 2007). GenBank accession numbers of reference proteins are given with the protein names and species. Figure S4: antismash analyses of fujikurin-like genes in Dactylonectria torresensis strains BV-349, BV-666, BV-745.
Author Contributions
L.A.; M.G., S.C., M.S., S.B. and C.B. performed the bioinformatic analyses; S.B. performed plate assays for light response and phenotype, L.A., M.G., S.C., M.S., S.B. and D.G. interpreted the results; S.C. and D.G. drafted the manuscript; all authors read, revised and approved the manuscript; D.G. acquired the funding; C.B., M.d.P.M.-D. and E.D.-L. maintained the fungal cultures, and generated the DNA for genome sequencing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was funded by CAR (Government of La Rioja, Spain), under the project “Development of Microsatellite Markers to Study the Genetic Diversity of Dactylonectria torresensis Populations in Spain” (project number R-05-18).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to B. Nikolic from AIT Austrian Institute of Technology for DNA extraction of the fungi. M.P. Martínez-Diz and C. Berlanas were supported by the FPI-INIA program from the INIA. D. Gramaje was supported by the Ramón y Cajal Program, Spanish Government (RYC-2017-23098). We acknowledge support of the publication fee by the CSIC Open Access Publication Support Initiative through its Unit of Information Resources for Research (URICI). We would like to thank authors of published or publicly available genomes that were used in this study, especially the genome data produced by the Joint Genome Institute.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Availability of Data and Materials
This Whole Genome Shotgun (WGS) Project has been deposited at DDBJ/ENA/GenBank under the accessions VYKH00000000 (D. torresensis isolate BV-349), VYKG00000000 (isolate BV-666) and VYKF00000000 (isolate BV-745). The versions described in this paper are version VYKH01000000, VYKG01000000 and VYKF01000000, respectively. This Dactylonectria torresensis Genome Sequencing and Assembly Project was submitted under BioProject PRJNA566152.
Abbreviations
Average Nucleotide Identity (ANI); Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes (CAZymes); Carbohydrate Esterases (CE); Carbohydrate-Binding Modules (CBM); Fusarium Head Blight (FHB); Glucose-Faba Bean Rose Bengal Agar (GFBRBA); Glycoside Hydrolases (GH); Glycoside Transferases (GT); Hasegawa-Kishino-Yano model (HKY); Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS); Malt Extract Agar (MEA); Polysaccharide Lyases (PL); and Potato Dextrose Agar (PDA).
References
- Reis, P.; Cabral, A.; Nascimento, T.; Oliveira, H.; Rego, C. Diversity of Ilyonectria species in a young vineyard affected by black foot diseases. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2013, 52, 335–346. [Google Scholar]
- Berlanas, C.; López-Manzanares, B.; Gramaje, D. Estimation of viable propagules of black-foot disease pathogens in grapevine cultivated soils and their relation to production systems and soil properties. Plant Soil 2017, 417, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlucci, A.; Lops, F.; Mostert, L.; Halleen, F.; Raimondo, M.L. Occurrence fungi causing black foot on young grapevines and nursery rootstock plants in Italy. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2017, 56, 10–39. [Google Scholar]
- Agustí-Brisach, C.; Armengol, J. Black-foot disease of grapevine: An update on taxonomy, epidemiology and management strategies. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2013, 52, 245–261. [Google Scholar]
- Gramaje, D.; Armengol, J. Fungal trunk pathogens in the grapevine propagation process: Potential inoculum sources, detection, identification, and management strategies. Plant Dis. 2011, 95, 1040–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, C.D. The genus Cylindrocarpon. Mycol. Pap. (CMI) 1966, 104, 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Brayford, D. Cylindrocarpon . In Methods for Research on Soilborne Phytopathogenic Fungi; Singleton, L.L., Mihail, J.D., Rush, C.M., Eds.; APS Press: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 1993; pp. 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Petit, E.; Barriault, E.; Baumgartner, E.; Wilcox, W.F.; Rolshausen, P.E. Cylindrocarpon species associated with black-foot of grapevine in northeastern United States and southeastern Canada. Am. J. Enol. Viticult. 2011, 62, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rego, C.; Nascimento, T.; Oliveira, H. Characterisation of Cylindrocarpon destructans isolates from grapevines in Portugal. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2001, 40, S343–S350. [Google Scholar]
- Halleen, F.; Crous, P.W.; Petrini, O. Fungi associated with healthy grapevine cuttings in nurseries, with special reference to pathogens involved in the decline of young vines. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2003, 32, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustí-Brisach, C.; Gramaje, D.; León, M.; García-Jiménez, J.; Armengol, J. Evaluation of vineyard weeds as potential hosts of black-foot and petri disease pathogens. Plant Dis. 2011, 95, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langenhoven, S.D.; Halleen, F.; Spies, C.F.J.; Stempien, E.; Mostert, L. Detection and quantification of black foot and Crown and root rot pathogens in grapevine nursery soils in the Western Cape of South Africa. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2018, 57, 519–537. [Google Scholar]
- Berlanas, C.; Ojeda, S.; López-Manzanares, B.; Andrés-Sodupe, M.; Bujanda, R.; del Pilar Martínez-Diz, M.; Díaz-Losada, E.; Gramaje, D. Occurrence and diversity of black-foot disease fungi in symptomless grapevine nursery stock in Spain. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallad, G.E.; Bhat, R.G.; Koike, S.T.; Ryder, E.J.; Subbarao, K.V. Weedborne reservoirs and seed transmission of Verticillium dahliae in lettuce. Plant Dis. 2005, 89, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramaje, D.; Úrbez-Torres, J.R.; Sosnowski, M.R. Managing grapevine trunk diseases with respect to etiology and epidemiology. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 12–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malapi-Wigth, M.; Salgado-Salazar, C.; Demer, J.; Veltri, D.; Crouch, J.A. Draft genome sequence of Dactylonectria macrodidyma, a plant-pathogenic fungus in the Nectriaceae. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e00278-15. [Google Scholar]
- Guttman, D.; McHardy, A.C.; Schulze-Lefert, P. Microbial genome-enabled insights into plant-microorganism interactions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 5, 797–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FASTQC. A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2010. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 9 September 2019).
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okonechnikov, K.; Conesa, A.; García-Alcalde, F. Qualimap 2: Advanced multi-sample quality control for high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 292–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laetsch, D.R.; Koutsovoulos, G.; Booth, T.; Stajich, J.; Kumar, S. BlobTools v1.0.1. Zenodo 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simão, F.A.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ioannidis, P.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Ryberg, M.; Hartmann, M.; Branco, S.; Wang, Z.; Godhe, A.; De Wit, P.; Sánchez-García, M.; Ebersberger, I.; de Sousa, F.; et al. Improved software detection and extraction of ITS1 and ITS2 from ribosomal ITS sequences of fungi and other eukaryotes for analysis of environmental sequencing data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2013, 4, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, R.H.; Larsson, K.H.; Taylor, A.F.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Jeppesen, T.S.; Schigel, D.; Kennedy, P.; Picard, K.; Glöckner, F.O.; Tedersoo, L. The UNITE database for molecular identification of fungi: Handling dark taxa and parallel taxonomic classifications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D259–D264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, K. Kblin/Ncbi-Genome-Download. 2019. Available online: https://github.com/kblin/ncbi-genome-download (accessed on 13 September 2019).
- Pritchard, L. Widdowquinn/Pyani. 2019. Available online: https://github.com/widdowquinn/pyani (accessed on 13 September 2019).
- Zhu, B.; Wang, S.; Mi, C.-Y.; Yang, R.-H.; Zen, G.-H.; Hu, X.-F. Genome sequence resource for Ilyonectria mors-panacis, causing rusty root rot of Panax notoginseng. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staats, M.; van Kan, J.A. Genome update of Botrytis cinerea strains B05.10 and T4. Eukaryot. Cell. 2012, 11, 1413–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.; Urban, M.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E. Annotation of Fusarium graminearum (PH-1) Version 5.0. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e01479-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutreux, F.; Da Silva, C.; D’Agata, L.; Couloux, A.; Gay, E.J.; Istace, B.; Lapalu, N.; Lemainque, A.; Linglin, J.; Noel, B.; et al. De novo assembly and annotation of three Leptosphaeria genomes using Oxford Nanopore MinION sequencing. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, R.A.; Talbot, N.J.; Ebbole, D.J.; Farman, M.L.; Mitchell, T.K.; Orbach, M.J.; Thon, M.; Kulkarni, R.; Xu, J.-R.; Pan, H.; et al. The genome sequence of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Nature 2005, 434, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccaro, A.; Lahrmann, U.; Güldener, U.; Langen, G.; Pfiffi, S.; Biedenkopf, D.; Wong, P.; Samans, B.; Grimm, C.; Basiewicz, M.; et al. Endophytic life strategies decoded by genome and transcriptome analyses of the mutualistic root symbiont Piriformospora indica. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabe, F.; Bosch, J.; Stirnberg, A.; Guse, T.; Bauer, L.; Seitner, D.; Rabanal, F.A.; Czedik-Eysenberg, A.; Uhse, S.; Bindics, J.; et al. A complete toolset for the study of Ustilago bromivora and Brachypodium sp. as a fungal-temperate grass pathosystem. Elife 2016, 5, e20522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lian, S.; Li, B.; Lu, H.; Dong, X.; Wang, C. Draft Genome Sequence of Botryosphaeria dothidea, the Pathogen of Apple Ring Rot. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e01142-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia-Ling, C.; Huang, C.-H.; Chen, C.-L.; Tung, S.-Y.; Wang, T.-F. Trichoderma reesei complete genome sequence, repeat-induced point mutation, and partitioning of CAZyme gene clusters. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 170. [Google Scholar]
- Morales-Cruz, A.; Amrine, K.C.H.; Blanco-Ulate, B.; Lawrence, D.P.; Travadon, R.; Rolshausen, P.E.; Baumgartner, K.; Cantu, D. Distinctive expansion of gene families associated with plant cell wall degradation, secondary metabolism, and nutrient uptake in the genomes of grapevine trunk pathogens. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibberg, D.; Genzel, F.; Verwaaijen, B.; Blom, J.; Rupp, O.; Goesmann, A.; Zrenner, R.; Grosch, R.; Pühler, A.; Schlüter, A. Draft genome sequence of the potato pathogen Rhizoctonia solani AG3-PT isolate Ben3. Arch. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1065–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, A.; Kuo, A.; Nagy, L.G.; Morin, E.; Barry, K.W.; Buscot, F.; Canbäck, B.; Choi, C.; Cichocki, N.; Clum, A.; et al. Convergent losses of decay mechanisms and rapid turnover of symbiosis genes in mycorrhizal mutualists. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Ulate, B.; Rolshausen, P.; Cantu, D. Draft genome sequence of the Ascomycete Phaeoacremonium aleophilum strain UCR-PA7, a causal agent of the Esca disease complex in grapevines. Genome Announc. 2013, 1, e00390-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastwood, D.; Floudas, D.; Binder, M.; Majcherczyk, A.; Schneider, P.; Aerts, A.; Asiegbu, F.O.; Baker, S.E.; Barry, K.; Bendiksby, M.; et al. The plant cell wall-decomposing machinery underlies the functional diversity of forest fungi. Science 2011, 333, 762–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, D.S.T.; Larrondo, L.F.; Putnam, N.; Gelpke, M.D.S.; Huang, K.; Chapman, J.; Helfenbein, K.G.; Ramaiya, P.; Detter, J.C.; Larimer, F.; et al. Genome sequence of the lignocellulose degrading fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium strain RP78. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisserant, E.; Malbreil, M.; Kuo, A.; Kohler, A.; Symeonidi, A.; Balestrini, R.; Charron, P.; Duensing, N.; Frey, N.F.D.; Gianinazzi-Pearson, V.; et al. Genome of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus provides insight into the oldest plant symbiosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20117–20122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plett, J.M.; Gibon, J.; Kohler, A.; Duffy, K.; Hoegger, P.J.; Velagapudi, R.; Han, J.; Kuees, U.; Grigoriev, I.V.; Martin, F. Phylogenetic, genomic organization and expression analysis of hydrophobin genes in the ectomycorrhizal basidiomycete Laccaria bicolor. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2012, 49, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, F.; Kohler, A.; Murat, C.; Balestrini, R.; Coutinho, P.M.; Jaillon, O.; Montanini, B.; Morin, E.; Noel, B.; Percudani, R.; et al. Perigord black truffle genome uncovers evolutionary origins and mechanisms of symbiosis. Nature 2010, 464, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonielli, L.; Compant, S.; Strauss, J.; Sessitsch, A.; Berger, H. Draft genome sequence of Phaeomoniella chlamydospora strain RR-HG1, a grapevine trunk disease (Esca)-related member of the Ascomycota. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e00098-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rédou, V.; Kumar, A.; Hainaut, M.; Henrissat, B.; Record, E.; Barbier, G.; Burgaud, G. Draft genome sequence of the Deep-Sea Ascomycetous filamentous fungus Cadophora malorum Mo12 from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge reveals its biotechnological potential. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00467-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, D.G.; Németh, J.B.; Barry, K.; Hainaut, M.; Henrissat, B.; Johnson, J.; Kuo, A.; Lim, J.H.P.; Lipzen, A.; Nolan, M.; et al. Comparative genomics provides insights into the lifestyle and reveals functional heterogeneity of dark septate endophytic fungi. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klosterman, S.J.; Subbarao, K.V.; Kang, S.; Veronese, P.; Gold, S.E.; Thomma, B.P.H.J.; Chen, Z.; Henrissat, B.; Lee, Y.-H.; Park, J.; et al. Comparative genomics yields insights into niche adaptation of plant vascular wilt pathogens. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.J.; Rounsley, S.D.; Rodriguez-Carres, M.; Kuo, A.; Wasmann, C.C.; Grimwood, J.; Schmutz, J.; Taga, M.; White, G.J.; Zhou, S.; et al. The genome of Nectria haematococca: Contribution of supernumerary chromosomes to gene expansion. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, C.; Yandell, M. MAKER2: An annotation pipeline and genome-database management tool for second-generation genome projects. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ter-Hovhannisyan, V.; Lomsadze, A.; Chernoff, Y.O.; Borodovsky, M. Gene prediction in novel fungal genomes using an ab initio algorithm with unsupervised training. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 1979–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanke, M.; Keller, O.; Gunduz, I.; Hayes, A.; Waack, S.; Morgenstern, B. AUGUSTUS: Ab initio prediction of alternative transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W435–W439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta-Cepas, J.; Szklarczyk, D.; Forslund, K.; Cook, H.; Heller, D.; Walter, M.C.; Rattei, T.; Mende, D.R.; Sunagawa, S.; Kuhn, M.; et al. eggNOG 4.5: A hierarchical orthology framework with improved functional annotations for eukaryotic, prokaryotic and viral sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D286–D293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Mao, X.; Yang, J.; Chen, X.; Mao, F.; Xu, Y. dbCAN: A web resource for automated carbohydrate-active enzyme annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W445–W451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandels, M.; Andreotti, R. Problems and challenges in the cellulose to cellulase fermentation. Proc. Biochem. 1978, 13, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Crous, P.W.; Verkleij, G.J.M.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Samson, R.A. (Eds.) Fungal Biodiversity; CBS Laboratory Manual Series; Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.M.; Oelmüller, R. Mutualism or parasitism: Life in an unstable continuum. What can we learn from the mutualistic interaction between Piriformospora indica and Arabidopsis thaliana? Rev. Endocytobiosis Cell Res. 2009, 19, 81–111. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, G.; Naumann, T.A.; Vaughan, M.M.; McCormick, S.; Usgaard, T.; Kelly, A.; Ward, T.J. Characterization of a Fusarium graminearum salicylate hydroxylase. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graminha, M.A.S.; Rocha, E.M.F.; Prade, R.A.; Martinez-Rossi, N.M. Terbinafine resistance mediated by salicylate 1-monooxygenase in Aspergillus nidulans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 3530–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodge, A.G.; Wackett, L.P. Metabolism of bismuth subsalicylate and intracellular accumulation of bismuth by Fusarium sp. strain BI. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Xu, J.R. Comparative analysis of fungal genomes reveals different plant cell wall degrading capacity in fungi. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohm, R.A.; Feau, N.; Henrissat, B.; Schoch, C.L.; Horwitz, B.A.; Barry, K.W.; Condon, B.J.; Copeland, A.C.; Dhillon, B.; Glaser, F.; et al. Diverse lifestyles and strategies of plant pathogenesis encoded in the genomes of eighteen Dothideomycetes fungi. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1003037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrêa, T.L.; dos Santos, L.V.; Pereira, G.A. AA9 and AA10: From enigmatic to essential enzymes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, Y.; Várnai, A.; Ishida, T.; Sunagawa, N.; Petrovic, D.M.; Igarashi, K.; Jellison, J.; Goodell, B.; Alfredsen, G.; Westereng, B.; et al. A Lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase with broad xyloglucan specificity from the brown-rot fungus Gloeophyllum trabeum and its action on cellulose-xyloglucan complexes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 6557–6572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Ma, F.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Yu, H. A lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase from a white-rot fungus drives the degradation of lignin by a versatile peroxidase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02803-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couturier, M.; Ladevèze, S.; Sulzenbacher, G.; Ciano, L.; Fanuel, M.; Moreau, C.; Villares, A.; Cathala, B.; Chaspoul, F.; Frandsen, K.E.; et al. Lytic xylan oxidases from wood-decay fungi unlock biomass degradation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018, 14, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kracher, D.; Scheiblbrandner, S.; Felice, A.K.G.; Breslmayr, E.; Preims, M.; Ludwicka, K.; Haltrich, D.; Eijsink, V.G.H.; Ludwig, R. Extracellular electron transfer systems fuel cellulose oxidative degradation. Science 2016, 352, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiblbrandner, S.; Ludwig, R. Cellobiose dehydrogenase: Bioelectrochemical insights and applications. Bioelectrochemistry 2020, 131, 107345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, T.H.F.; Eijsink, V.G.H.; Horn, S.J. The use of lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases in anaerobic digestion of lignocellulosic materials. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffaele, S.; Kamoun, S. Genome evolution in filamentous plant pathogens: Why bigger can be better. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plett, J.M.; Kemppainen, M.; Kale, S.D.; Kohler, A.; Legué, V.; Brun, A.; Tyler, B.M.; Pardo, A.G.; Martin, F. A secreted effector protein of Laccaria bicolor is required for symbiosis development. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, R.J.; Thon, M.R.; Hacquard, S.; Amyotte, S.G.; Kleemann, J.; Torres, M.F.; Damm, U.; Buiate, E.A.; Epstein, L.; Alkan, N.; et al. Lifestyle transitions in plant pathogenic Colletotrichum fungi deciphered by genome and transcriptome analyses. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amselem, J.; Cuomo, C.A.; Van Kan, J.A.L.; Viaud, M.; Benito, E.P.; Couloux, A.; Coutinho, P.M.; De Vries, R.P.; Dyer, P.S.; Fillinger, S.; et al. Genomic analysis of the necrotrophic fungal pathogens Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Botrytis cinerea. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, S.F.; Clardy, J. CR377, a new pentaketide antifungal agent isolated from an endophytic fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1447–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiemann, P.; Sieber, C.M.K.; Von Bargen, K.W.; Studt, L.; Niehaus, E.-M.; Espino, J.J.; Huß, K.; Michielse, C.B.; Albermann, S.; Wagner, D.; et al. Deciphering the cryptic genome: Genome-wide analyses of the rice pathogen Fusarium fujikuroi reveal complex regulation of secondary metabolism and novel metabolites. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbaraini, N.; Andreis, F.C.; Thompson, C.E.; Guedes, R.L.M.; Junges, Â.; Campos, T.; Staats, C.C.; Vainstein, M.H.; De Vasconcelos, A.T.R.; Schrank, A. Genome-wide analysis of secondary metabolite gene clusters in Ophiostoma ulmi and Ophiostoma novo-ulmi reveals a fujikurin-like gene cluster with a putative role in infection. Front Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Bargen, K.W.; Niehaus, E.-M.; Krug, I.; Bergander, K.; Würthwein, E.-U.; Tudzynski, B.; Humpf, H.U. Isolation and structure elucidation of fujikurins A-D: Products of the PKS19 gene cluster in Fusarium fujikuroi. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1809–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrochano, L.M. Light in the fungal world: From photoreception to gene transcription and beyond. Ann. Rev. Genet. 2019, 53, 149–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmoll, M. Regulation of plant cell degradation by light in Trichoderma. Fungal Biol. Biotechnol. 2018, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stappler, E.; Dattenböck, C.; Tisch, D.; Schmoll, M. Analysis of light- and carbon-specific transcriptomes implicates a class of G-protein-coupled receptors in cellulose sensing. mSphere 2017, 2, e00089-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, J. How light affects the life of Botrytis. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2017, 106, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hevia, M.A.; Canessa, P.; Müller-Esparza, H.; Larrondo, L.F. A circadian oscillator in the fungus Botrytis cinerea regulates virulence when infecting Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8744–8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosson, S.; Moffat, K. Structure of a flavin-binding plant photoreceptor domain: Insights into light-mediated signal transduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 2995–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Y. Mechanism of the Neurospora circadian clock, a FREQUENCY-centric view. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).