Abstract
Alpinia oxyphylla is a traditional Chinese medicinal plant with a medicinal history of more than 1700 years. Ring leaf blight (RLB) disease, caused by pestalotioid species, is an important disease of A. oxyphylla, seriously affecting the yield and quality of its fruits. The causal agent of RLB disease has not been systematically identified or characterized yet. In this study, thirty-six pestalotioid strains were isolated from the leaves and stems of A. oxyphylla that was collected from six cities of Hainan province, China. Based on the multi-locus phylogeny (ITS, tef-1α and tub2) and morphological characteristic analyses, seventeen species belonging to three genera (Neopestalotiopsis, Pestalotiopsis and Pseudopestalotiopsis) were identified, and six new species (N. baotingensis, N. oblatespora, N. olivaceous, N. oxyphylla, N. wuzhishanensis and N. yongxunensis) were described. Pathogenicity tests revealed that strains of Neopestalotiopsis species caused more severe ring leaf blight on A. oxyphylla than strains of Pestalotiopsis and Pseudopestalotiopsis under wounded inoculation conditions.
1. Introduction
Alpinia oxyphylla belongs to the family Zingiberaceae and is an important Chinese herbal plant, with a medicinal history dating back 1700 years [1]. As an edible herb, the traditional medicinal effects of A. oxyphylla’s fruit mainly include warming the kidney, stopping spermatorrhea, arresting polyuria, warming the spleen as well as stopping diarrhea and excess saliva [2,3]. Moreover, the essential oil of A. oxyphylla has various effects including antibacterial, anticancer, antioxidant, vasodilation and improved immunity [4]. A. oxyphylla likes to grow in warm and humid environmental conditions and is commonly planted under rubber trees, areca trees and other economic forests as a semi-shade plant [5,6,7]. A. oxyphylla is mainly distributed in southern China, such as in Hainan, Guangdong and Guangxi provinces. Among them, Hainan, with abundant rainfall and high temperatures, is the most important planting area for A. oxyphylla, accounting for 90% of the total output in China [8,9,10].
The occurrence of diseases causes serious losses to the production and quality of A. oxyphylla. Ring leaf blight (RLB) is an important disease of A. oxyphylla that occurs from the seedling to the fruiting stage, mainly infecting old leaves. The disease often extends from the leaf edge or tip, forming irregular, reddish-brown spots with alternating dark and light brown wavy concentric rings and obvious yellow halos around the periphery of the disease spots, on which numerous small black conidiomata of the pathogen are scattered. The pathogen of this disease can be transmitted through wind and rain, mainly invading through wounds. The high temperature and rainy season contribute to the occurrence of RLB disease, and the high incidence of this disease is from August to September. Under suitable conditions, the proportion of diseased plants can reach more than 50%, and the area of the diseased spots can reach 1/3–1/2 of the leaf surface, even the entire leaf, which has an impressive impact on the growth of A. oxyphylla [11,12].
The pathogen of RLB disease was first reported as Pestalotia palmarum in 1986 [11]. Subsequently, the classification status of P. palmarum was adjusted to the genus Pestalotiopsis, while Pestalotia and Pestalotiopsis were used confusingly in descriptions of A. oxyphylla diseases [13]. The ring brown spot (RBS) disease of A. oxyphylla was caused by Pestalosphaeria alpinia, a sexual morph of pestalotioid fungi [14]. As asexual fungi, most pestalotioid species lack the sexual morphs Pestalosphaeria [15]. Most of pestalotioid species are important plant pathogens and are also commonly found as endophytes or saprophytes, being mainly distributed throughout tropical and temperate regions [16,17,18]. Pestalotioid species can infect the leaves, shoots, flowers, fruits or other parts of plants and cause a variety of diseases in multiple economic crops, including leaf spots, gray blight, shoot dieback, trunk diseases, dry flowers and fruit rot [17,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. Hence, pestalotioid species causing disease in A. oxyphylla need to be reidentified and characterized based on their fungal diversity, molecular systematics and pathogenicity.
The development of a molecular phylogenetic analysis overcomes the limitation of overlapping conidial measurements in the traditional taxonomy of pestalotioid species [16,17,27,28]. In 2014, two novel genera, Neopestalotiopsis and Pseudopestalotiopsis, were segregated from Pestalotiopsis based on conidial characters and multi-locus phylogenetic analyses. The combined sequences of the ITS, tub2 and tef-1α genes were used to construct phylogenetic trees, which become an important basis for distinguishing different species within the genera Pestalotiopsis, Neopestalotiopsis and Pseudopestalotiopsis. Morphologically, Neopestalotiopsis can be easily differentiated from Pestalotiopsis and Pseudopestalotiopsis by the versicolorous median cells of the conidia, and Pseudopestalotiopsis is different from Pestalotiopsis with its three darker, concolorous median cells [17]. Through these methods, many novel pestalotioid species isolated from different plants have been introduced in recent years [19,22,29,30,31,32,33,34].
Therefore, the objective of this study is to clarify the types, characteristics and pathogenicities of pestalotioid species related to disease in A. oxyphylla of Hainan, China.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection, Fungi Isolation and Morphological Examination
Fresh leaves of A. oxyphylla with typical ring spots and stems with irregular cloud-like spots were collected from the main planted areas at ten townships in six cities of Hainan province, including Baoting, Ledong, Qiongzhong, Sanya, Wanning and Wuzhishan in 2022. Small pieces (5 mm × 5 mm) of leaves or stems were cut from the junctions of diseased and healthy areas, disinfected with 3% sodium hypochlorite for 3 min, then 75% ethanol for 30 s and subsequently washed with sterilized water three times. The treated tissue pieces were dried on sterilized blotting paper and then placed on PDA plates (containing 100 μg/mL streptomycin, 50 μg/mL kanamycin and 100 μg/mL ampicillin). The plates were cultured at room temperature and examined daily for 7 days; then, the marginal mycelia with different morphologies on each plate were transferred to fresh PDA; subsequently, the pestalotioid strains were purified using single-spore culturing according to the results of the ITS sequence analysis.
The pestalotioid strains usually sporulated at room temperature on PDA after 10–20 days. The conidiomata were observed using a dissecting microscope (CNOPTEC, SZ680, Chongqing, China), and the characteristics of spores and conidiophores were observed using an optical microscope (CNOPTEC, DV320, Chongqing, China). All the morphological characteristics of the spores were photographed and measured for at least 30 individuals using OPTPro v.6.1.1.67. The images were processed using Adobe Photoshop CS6. The pure cultures of isolated fungal strains were stored in the seed health center of China Agricultural University.
2.2. DNA Extraction, Gene Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analyses
DNA was extracted from fresh fungal mycelia using the Biomed genomic DNA extraction kit (Biomed, Beijing, China). The partial sequences of three genes (ITS, tef-1α and tub2) were amplified. The PCR was performed according to Table 1, and the PCR products were purified and sequenced at Beijing Tsingke Biotech (Beijing, China).

Table 1.
PCR primers and procedures used in this study.
The nucleotide sequences were checked using Chromas2.4.1 and then analyzed using the BLAST tool on the NCBI platform to assess the closest phylogenetic matches. All related sequences determined using BLAST or referenced previous studies were downloaded from GenBank (Table 2). MAFFT v.7 (https://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/software/, accessed on 15 October 2023) was used to align each locus sequence, and MEGA v.11 was used to manually improve the sequences. The three final aligned gene sequences were concatenated using SequenceMatrix (13 May 2024) [40].

Table 2.
The strain information and gene accession numbers for pestalotioid species used in this study.
The phylogenetic analyses of the combined sequences were carried out using maximum-likelihood (ML) and Bayesian inference (BI) methods. The ML analysis was performed on the CIPRES web portal (https://www.phylo.org, accessed on 31 October 2023) using RAxML-HPC BlackBox 8.2.10, with a GTRGAMMA substitution model and 1000 bootstrap replicates [91]. The BI analysis was implemented using MrBayes v.3.2.7 [92], and MrModeltest 2.2 [92] was used to seek the best-fit nucleotide substitution models for each gene. Two Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods were run for 1,000,000 generations, and trees were sampled every 1000th generation. The first 25% of trees, standing for the burn-in phase of the analyses, were discarded, and the remaining trees were estimated to be the posterior probabilities. The ML tree and BI tree were viewed using Figtree v.1.4.4. and modified using WPS Office v.12.1.0.16729.
The new species can be further confirmed through PHI (Pairwise Homoplasy Index) analysis, which can also be used to analyze the species’ boundaries and related taxa [93]. The PHI test was completed using SplitsTree v.4 [94,95], and a value over 0.05 revealed no significant recombination in the dataset. The relationships among closely related species were shown using splits graphs through the LogDet transformation and split decomposition.
2.3. Pathogenicity Test
The pathogenicity of the fungi was tested using the wound inoculation method. Fresh and healthy leaves of A. oxyphylla measuring 30–40 cm long were collected from the field. The surface of the leaves was disinfected by spraying them with 75% ethanol and then washed three times with sterile water. Each fungal isolate was inoculated on 6 sites per leaf with 3 leaf replicates. A piece of mycelium (6 mm diameter), which was taken from the margin of a fresh colony cultured to 2/3 of the PDA plate’s diameter, was placed on the wound of injured leaf using a sterilized needle. A piece of PDA without mycelium was used as the control. The inoculated leaves were placed in a box and cultured in the incubator at 26 °C and 600 LUX, with a 16 h/8 h LED light/dark cycle. After 5 days, disease symptoms were recorded, the lesion area was measured using ImageJ v.1.53c and the data were analyzed using SPSS Statistics 24. The re-isolated fungi from the disease lesion were identified and tested using Koch’s postulates.
3. Results
3.1. Phylogenetic Analyses
A total of 36 pestalotioid isolates were obtained from the leaves (32 isolates) and stems (4 isolates) of A. oxyphylla from six cities in Hainan province. Based on the ITS sequence and color of the intermediate cells of the conidia, 36 strains were classified into three genera, of which 32 strains belong to Neopestalotiopsis, 2 strains belong to Pestalotiopsis and 2 strains belong to Pseudopestalotiopsis.
The phylogenetic tree of Neopestalotiopsis contained 145 taxa, with 2 outgroup taxa (Pestalotiopsis colombiensis and P. diversiseta). A total of 1404 characters, including gaps (503 for ITS, 469 for tef-1a and 432 for tub2), were included in the phylogenetic analysis. For the Bayesian inference, the HKY + G model with a gamma-distributed rate was selected for ITS, the HKY + G model with a gamma-distributed rate was selected for tef1-a and the HKY + I + G model with an invgamma-distributed rate was selected for tub2. Similar tree topologies were acquired using the ML and BI methods, and the best scoring ML tree is shown in Figure 1. The phylogenetic tree depicts 32 Neopestalotiopsis taxa isolated from A. oxyphylla, revealing 6 novel species.

Figure 1.
RAxML tree of Neopestalotiopsis isolates based on ITS, tef-1α and tub2 sequences. The roots of this tree are Pestalotiopsis diversiseta MFLUCC 12-0287 and P. colombiensis CBS 118553. The strains isolated in this study are marked in red. Ex-type strains are marked with T. ML bootstrap values ≥ 50% and BI probabilities (in red) ≥ 0.90 are displayed at the nodes.
The phylogenetic tree of Pestalotiopsis comprised 78 taxa, with the outgroup taxon N. cubana CBS 600.96. A total of 1457 characters, including gaps (505 for ITS, 495 for tef-1a and 457 for tub2), were included in the phylogenetic analysis. For the Bayesian inference, the GTR + I + G model with an invgamma-distributed rate was selected for ITS, the GTR + G model with a gamma-distributed rate was selected for tef1-a and the GTR + I + G model with an invgamma-distributed rate was selected for tub2. Similar tree topologies were obtained using the ML and BI methods, and the best scoring ML tree is shown in Figure 2. The phylogenetic tree depicts two Pestalotiopsis strains isolated from A. oxyphylla, clustered with the type species of P. hydei.
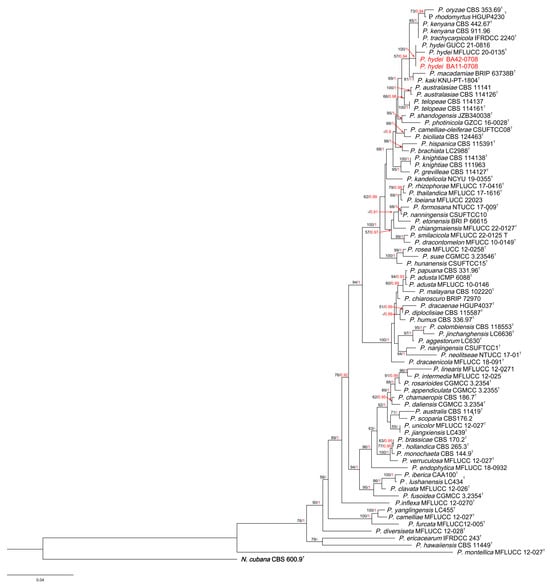
Figure 2.
RAxML tree of Pestalotiopsis isolates based on ITS, tef-1α and tub2 sequences. The root of this tree is N. cubana CBS 600.9. The strains isolated in this study are marked in red. Ex-type strains are marked with T. ML bootstrap values ≥ 50% and BI probabilities (in red) ≥ 0.90 are displayed at the nodes.
The alignment of Pseudopestalotiopsis contained 35 taxa, with P. trachicarpicola OP068 as the outgroup taxon. A total of 1392 characters, including gaps (521 for ITS, 442 for tef-1a and 429 for tub2), were included in the phylogenetic analysis. For the Bayesian inference, the HKY + G model with a gamma-distributed rate was selected for ITS, the HKY + G model with a gamma-distributed rate was selected for tef1-a and the HKY + I model with a propinv-distributed rate was selected for tub2. Similar tree topologies were obtained using the ML and BI methods, and the best scoring ML tree is shown in Figure 3. The phylogenetic tree depicts two Pseudopestalotiopsis taxa isolated from A. oxyphylla, clustered with the type species of Ps. avicenniae and Ps. myanmarina, respectively.
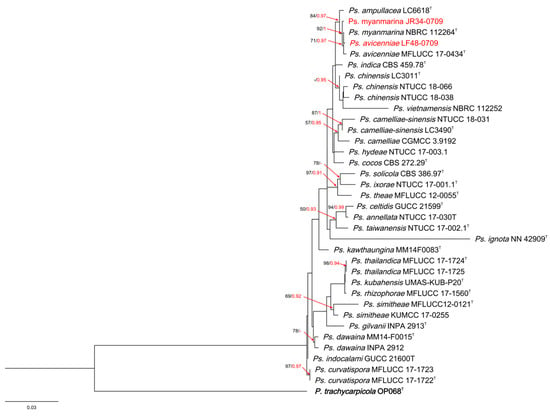

Figure 3.
RAxML tree of Pseudopestalotiopsis isolates based on ITS, tef-1α and tub2 sequences. The root of this tree is P. trachycaroicola OP068. The strains isolated in this study are marked in red. Ex-type strains are marked with T. ML bootstrap values ≥ 50% and BI probabilities (in red) ≥ 0.90 are displayed at the nodes.
3.2. PHI Analyses
The results of the PHI test indicate no obvious recombination (Φw = 0.1064) among N. baotingensis SX41-0706, N. oblatespora YJ11-0708 and their closely related species N. saprophytica MFLUCC 12-0282, N. paeoniea CBS 318.74, N. hydeana MFLUCC 20-0132, N. egyptiaca CBS 140162, N. guajavicola FMBCC 11.4 and N. mesopotamica CBS 299.74 (Figure 4a). And there is no significant recombination (Φw = 0.0786) between N. olivaceous LF25-0709 and its closely related species N. amomi HKAS 124563, N. zingiberis GUCC 21001 and N. magna MFLUCC 12-0652 (Figure 4b). N. yongxunensis YX101-0708, N. wuzhishanensis YX116-0708 and their closely taxa have no significant recombination according to the PHI test results (Φw = 0.1103) (Figure 4c).
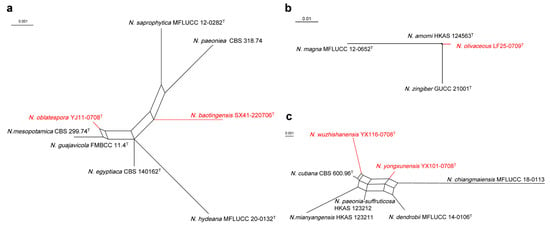
Figure 4.
Split graphs showing the results of the PHI test of new (a) N. baotingensis SX41-0706, N. oblatespora YJ11-0708, (b) N. olivaceous LF25-0709, and (c) N. yongxunensis YX101-0708 and N. wuzhishanensis YX116-0708 with their most closely related species. The new species in each graph is shown in red font. Ex-type strains are marked with “T”.
3.3. Taxonomy
Based on the multi-locus phylogeny (ITS, tef-1α and tub2) and morphological characteristic analyses, 17 species were identified. Three Neopestalotiopsis strains failed to acquire spores and were not identified as specific species. Six new species are described below. The conidial dimensions of the identified isolates in this study and their closely related strains are shown in Table 3.
Neopestalotiopsis baotingensis X.F. Cui and Z.G. Hao, sp. nov. (Figure 5).
MycoBank: MB854050.
Etymology: It is named in reference to the first collection city of Baoting in Hainan Province.
Holotype: SX41-0706.
Description:
The conidiomata on PDA are solitary or aggregated, globose and dark. The conidiophores often degenerated to conidiogenous cells. Conidiogenous cells are spherical and hyaline. The conidia are fusiform, straight to slightly curved, 18–26 × 5–7.2 μm ( = 23.2 × 6.3 μm) and have four septa. The basal cell is conical to obtuse, hyaline, thin and smooth walled and is 3.2–6.2 μm long ( = 4.5 μm). The three median cells are 12–17.3 μm ( = 14.8 μm), verruculose, versicolored, pale brown to dark brown and the septa and periclinal walls are darker than the rest of the cell. The second cell from the base is pale brown to brown, is paler than the two other cells and is 3.2–5.5 μm long ( = 4.4 μm). The third cell is brown to dark brown, darker than the two other cells and is 4–6 μm long ( = 4.9 μm). The fourth cell is brown to dark brown and 4–6 μm long ( = 5 μm). The apical cell is 2.5–5 μm long ( = 3.8 μm) and cylindric to subcylindric, with 2–4 tubular appendages on it, often 2–3, arising from its apex, which are unbranched and 3–30.5 μm long ( = 19.7 μm). The single basal appendage is unbranched, tubular, centric and 2.5–10 μm long ( = 6.3 μm). A sexual morph was not observed.
Culture characteristics: The colony reached 70 mm in diameter on PDA after 4 days of growth at room temperature. The colony was off white, with dense aerial hyphae on the surface with crenate edges, and its reverse was lemon yellow.
Material examined: The sample originated in China, Hainan Province, Baoting city, Shiling Township, Shuixian village, from leaf spots of A. oxyphylla, which was collected on 6 July 2022 by X.F. Cui and Z.G. Hao (SX41-0706, holotype); the ex-type came from Hainan Province, Wuzhishan city, Shuiman Township, Yongxun village, from spots on the stem base of A. oxyphylla, which was collected on 8 July 2022 by X.F. Cui and Z.G. Hao (YJ34-0708);
Notes: Two strains of Neopestalotiopsis baotingensis were isolated from two cities in Hainan, SX41-0706 and YJ34-0708, with well-supported clusters (ML = 81%, BI = 1). N. baotingensis is closely related to N. saprophytica (MFLUCC 12-0282) in the phylogenetic analysis. The conidiophores of N. baotingensis often degenerated to conidiogenous cells, while those of N. saprophytica were unbranched or irregularly branched; N. baotingensis is shorter than N. saprophytica (N. baotingensis 18–26 μm, = 23.2 μm vs. N. saprophytica 22–30 μm, = 24.9 μm); N. baotingensis has shorter apical appendages (N. baotingensis 3–30.5 μm, = 19.7 μm vs. N. saprophytica 23–35 μm, = 27.3 μm). Additionally, there was an 21 bp difference for ITS~tef-1α~tub2 between N. baotingensis and N. saprophytica (4/452 in ITS; 16/746 in tef-1α and 1/415 in tub2). The PHI test for N. baotingensis revealed that there is no obvious recombination between N. baotingensis and its closely related taxa. Therefore, N. baotingensis is classified as a new species in this study.

Table 3.
The conidial dimensions of pestalotioid species related to this study.
Table 3.
The conidial dimensions of pestalotioid species related to this study.
| Species | Isolate Number | Conidial Size (μm) | Apical Appendages (μm) | Basal Appendages | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Length | ||||
| N. baotingensis | SX41-0706 | 18–26 × 5–7.2 | 2–4 | 3–30.5 | 2.5–10 |
| N. saprophytica | MFLUCC 12-0282 | 22–30 × 5–6 | 2–4 | 23–35 | 4–7 |
| N. brachiata | SX31-0706 | 18.5–25.3 × 5.5–7.5 | 1–3 | 3.7–38.7 | 2.5–8 |
| N. brachiata | MFLUCC 17-1555 | 18.5–25 × 5.5–6 | 1–3 | 9.5–33 | 4–9 |
| N. coffeae-arabicae | BL32-0708 | 19.2–25.3 × 5.3–7 | 2–4 | 10.9–22.6 | 1.4–5.4 |
| N. coffeae-arabicae | LF51-0709 | 17.8–24.2 × 5–7 | 2–4 | 6.6–21.6 | 2.5–6.8 |
| N. coffeae-arabicae | NM42-0706 | 17.5–23.8 × 5.8–7.8 | 2–4 | 12.7–31 | 2.7–9.2 |
| N. coffeae-arabicae | HGUP4019 | 16–20 × 5–7 | 2–4 | 11–16 | 3–5 |
| N. cubana | MH51-0708 | 19.7–30 × 5–6.8 | 2–4 | 15.5–32.2 | 4–7.5 |
| N. cubana | YX112-0708 | 21–29 × 5.6–7.3 | 2–4 | 18.7–36.5 | 3.3–10.3 |
| N. cubana | CBS 600.96 | 20–25 × 8–9.5 | 2–4 | 21–27 | 4–7 |
| N. oblatespora | YJ11-0708 | 18–23.2 × 5.5–6.7 | 2–4 | 10–26.5 | 2–9 |
| N. guajavicola | FMBCC 11.4 | 23.3 × 6.5 | 2–3 | 21.8 | 4.4 |
| N. olivaceous | LF25-0709 | 21.5–33.8 × 5.5–7.7 | 2–5 | 9.5–22.5 | (0) 1.2–4.8 |
| N. amomi | HKAS 124563 | 18–30 × 4–7 | 2–3 | 7–17 | 2–5 |
| N. zingiberis | GUCC 21001 | 21–31 × 6–9.5 | 1–3 | 12–15 | 0–6 |
| N. oxyphylla | LF55-0709 | 18.8–23.5 × 5.3–7.0 | 2–4 | 10–25.3 | 2.5–8 |
| N. aotearoa | CBS 367.54 | 21–28 × 6.5–8.5 | 2–3 | 5–12 | 1.5–4 |
| N. elaeidis | MFLUCC 15-0735 | 10–20 × 3–7 | 2–3 | 10–20 | (0) 2–6 |
| N. petila | MFLUCC 17-1738 | 21–26.5 × 6–7 | 2–3 | 22–29 | 3–8 |
| N. piceana | CBS 394.48 | 19.5–25 × 7.5–9 | 3 | 21–31 | 6–23 |
| N. samarangensis | MFLUCC 12-0233 | 18–21 × 6.5–7.5 | 3 | 12–18 | 3.5–5.2 |
| N. rosicola | NM47-0706 | 16.9–24.6 × 5.5–7.2 | 2–4 | 10–25 | 1.7–7 |
| N. rosicola | CFCC 51992 | 20.2–25.5 × 5.5–8 | 2–4 | 17–22.8 | 2–9.5 |
| N. vaccinii | JR31-0709 | 14.5–20.6 × 5.5–7.4 | 2–3 | 10–22.5 | 1.3–5.1 |
| N. vaccinii | CAA1059 | 20.9 × 6.4 | 2–3 | 8.9–25.3 | 1.7–6.6 |
| N. hispanica | CBS 147686 | 24.4–25.3 × 7.2–7.8 | 3–4 | 19.5–22.6 | 5.1–15.5 |
| N. wuzhishanensis | YX116-0708 | 19.5–26.5 × 4.5–6.3 | 1–3 | 9–20.8 | (0) 0.8–3.8 |
| N. mianyangensis | UESTCC 22.0006 | 19–23 × 5.5–7 | 3 | 5.5–11 | 3–4 |
| N. yongxunensis | YX101-0708 | 18.2–25.5 × 5.8–7.5 | 2–4 | 10.5–24.7 | 1.7–7 |
| N. dendrobii | MFLUCC 14-0106 | 20.5–23 × 6.5–7.5 | 2–3 | 5–6.5 | NA |
| N. paeonia-suffruticosa | CGMCC3.23554 | 20–23 × 9–11 | 3–4 | 22.5–34 | 3.5–7.5 |
| P. hydei | BA11-0708 | 20.3–27.8 × 4.5–6.6 | 1–3 | 3.4–17.2 | 1–9.5 |
| P. hydei | MFLUCC 20-0135 | 18–35 × 3–6 | 1–3 | 3–12 | 2–8 |
| Ps. avicenniae | LF48-0709 | 20.8–30.7 × 5.8–7.9 | 1–3 | 17.2–33.3 | 2–7.8 |
| Ps. avicenniae | MFLUCC 17-0434 | 22.5–26.5 × 5.5–6 | 1–3 | 15.5–28.5 | 3–4 |
| Ps. myanmarina | JR34-0709 | 25.4–34.8 × 5.8–7.4 | 2–3 | 18.1–36.9 | 2.7–7 |
| Ps. myanmarina | NBRC 11226 | 31–38.5 × 6.5–9 | 2–3 | 22.5–38.5 | NA |
The strains in this study are indicated in bold font. NA: not available.
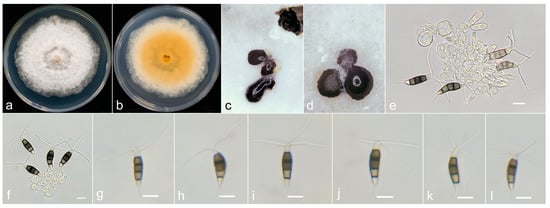
Figure 5.
Neopestalotiopsis baotingensis (SX41-0706, holotype). (a,b) Colony on PDA (above and reverse), (c,d) conidiomata on PDA, (e,f) conidiogenous cells and (g–l) conidia. Scale bars = 10 μm.
Neopestalotiopsis oblatespora X.F. Cui and Z.G. Hao, sp. nov. (Figure 6).
MycoBank: MB854051.
Etymology: The name refers to the spore morphology.
Holotype: YJ11-0708.
Description:
Conidiomata were not observed on PDA. The conidiophores are often monopodial, branched and colorless. The conidia are oblate, straight, scarcely curved, 18–23.2 × 5.5–6.7 μm ( = 20.2 × 6.2 μm) and have four septa. The basal cell is conical to subcylindrical, pale brown or hyaline, thin and smooth walled and is 2.5–4.5 μm long ( = 3.2 μm). The three median cells are 12–15 μm ( = 13.6 μm), nearly concolorous or versicolored and brown to dark brown, with the septa and periclinal walls darker than the rest of the cell. The second cell from the base is brown to dark brown and 3.7–6 μm long ( = 4.7 μm). The third cell is dark brown and 3–5 μm long ( = 4.2 μm). The fourth is dark brown and 3.5–5.3 μm long ( = 4.4 μm). The apical cell is 2.5–4 μm long ( = 3.2 μm), conical, hyaline, thin and smooth walled. There are 2–4 tubular appendages on the apical cell (often 3) arising from the apex of the apical cell, which are unbranched and 10–26.5 μm long ( = 18 μm). The single basal appendage is unbranched, tubular, centric or lateral and 2–9 μm long ( = 5.6 μm). A sexual morph was not observed.
Culture characteristics: The colonies reached 70 mm in diameter after 4 days on PDA at room temperature, and had serrated-edge, off-white, sparse aerial hyphae on the surface appearing to radiate, turning grey after sporulation.
Material examined: The sample originated in China, Hainan Province, Wuzhishan city, Shuiman Township, Yongxun village, from spots on the stem base of A. oxyphylla, which was collected on 8 July 2022 by X.F. Cui and Z.G. Hao (YJ11-0708);
Notes:
Based on multigene analyses, Neopestalotiopsis oblatespora is closely related to Neopestalotiopsis guajavicola (FMBCC 11.4), with only a 2 bp difference between them (1/476 in ITS; 1/378 in tef-1α). However, N. oblatespora is distinct from N. guajavicola, with a sporulation structure (branched conidiophores of N. oblatespora vs. conidiomata of N. guajavicola), smaller spores (N. oblatespora: 18–23.2 × 5.5–6.7 μm, = 20.2 × 6.2 μm vs. N. guajavicola 21.7–24.9 × 6–7 μm, = 23.3 × 6.5 μm) and shorter apical appendages (N. oblatespora: 10–26.5 μm, = 18 μm vs. N. guajavicola: 19.1–24.5 μm, = 21.8 μm); additionally, N. oblatespora has 2–4 apical appendages, while N. guajavicola has 2–3 appendages. Moreover, N. oblatespora has no significant recombination with its closely taxa according to the PHI test. Therefore, N. oblatespora is classified as a new species in the present study.

Figure 6.
Neopestalotiopsis oblatespora (YJ11-0708, holotype). (a,b) Colony on PDA (above and reverse), (c) conidia pile on PDA, (d,e) conidiophores and (f–k) conidia. Scale bars = 10 μm.
Neopestalotiopsis olivaceous X.F. Cui and Z.G. Hao, sp. nov. (Figure 7).
MycoBank: MB854052.
Etymology: The name refers to the color of the colony.
Holotype: LF25-0709.
Description:
Conidiomata were not observed on PDA. The conidia sometimes aggregate, becoming globose, dark green piles. The conidiophore are branched, with spore scars. The conidia are fusiform, straight to obviously irregularly curved, 21.5–33.8 × 5.5–7.7 μm ( = 26.5 × 6.3 μm) and have four septa. The basal cell is conical, hyaline or pale olive, smooth, thin walled and 2.7–6.2 μm long ( = 4.5 μm). The three median cells are 14 to 21.7 μm long ( = 17 μm), pale olivaceous to olivaceous, concolorous and have a rugose wall, with septa darker than the rest of the cell. The second cell from the base is pale olivaceous to olivaceous and 3.3 to 8.5 μm long ( = 5.9 μm). The third cell is pale olivaceous to olivaceous and 4 to 6.5 μm long ( = 5.1 μm). The fourth cell is pale olivaceous to olivaceous and 4 to 6.5 μm long ( = 5.4 μm). The apical cell is 3.5 to 5.5 μm long ( = 4.5 μm), hyaline, and conic to acute, with 2 to 5 (often 3–4) tubular appendages on the apical cell, which are inserted at different loci in a crest at the apex of the apical cell, unbranched and 9.5 to 22.5 μm ( = 14 μm) long. A single basal appendage, which is occasionally absent, is unbranched, tubular, centric or lateral and 1.2 to 4.8 μm ( = 2.4 μm) long. A sexual morph was not observed.
Culture characteristics: The colonies reached 70 mm in diameter on PDA after 7 days of growth at room temperature. The colonies appeared circular, white above and medium dense, with aerial hyphae on the flat surface; its reverse was olivaceous, gradually deepening over time.
Material examined: The sample originated in China, Hainan Province, Qiongzhong city, Changzheng Township, Luofan village, from leaf spots of A. oxyphylla, which was collected on 9 July 2022 by X.F. Cui and Z.G. Hao (LF25-0709, holotype); the ex-type originated in Hainan Province, Baoting city, Shiling Township, Shuixian village, from leaf spots of A. oxyphylla, which was collected on 6 July 2022 by X.F. Cui and Z.G. Hao (SX33-0706); the sample originated in Hainan Province, Wuzhishan city, Shuiman Township, Yongxun village, from leaf spots of A. oxyphylla, which was collected on 8 July 2022 by X.F. Cui and Z.G. Hao (YX45-0708).
Notes: Three strains of Neopestalotiopsis olivaceous were isolated from three cities in Hainan, LF25-0709, SX33-0706 and YX45-0708, with well-supported clusters (ML = 99%, BI = 1). N. olivaceous clusters a sister group with N. amomi (HKAS 124563) and N. zingiberis (GUCC 21001). Molecularly, N. olivaceous can be differentiated from N. amomi (HKAS 124563) and N. zingiberis (GUCC 21001), according to ITS~tef-1α~tub2 (1/471 of ITS and 5/328 of TEF with N. amomi; 3/447 of ITS, 14/719 of TUB and 13/358 of TEF with N. zingiberis). Morphologically, N. olivaceous is distinguished with longer conidia (21.5–33.8 μm of N. olivaceous vs. 18–30 μm of N. amomi and 21–31 μm of N. zingiberis), different numbers of apical appendages (2–5 tubular appendages for N. olivaceous vs. 2–3 for N. amomi and 1–3 for N. zingiberis) and longer apical appendages (N. olivaceous with 9.5–22.5 μm vs. N. amomi with 7–17 μm and N. zingiberis with 12–15 μm). The results of the PHI test showed no significant recombination among N. olivaceous and its closely related taxa. Thus, N. olivaceous is classified as a new species in the present study.

Figure 7.
Neopestalotiopsis olivaceous (LF25-0709, holotype). (a,b) Colony on PDA (above and reverse), (c) conidia pile on PDA, (d) conidiophores and (e–l) conidia. Scale bars = 10 μm.
Neopestalotiopsis oxyphylla X.F. Cui and Z.G. Hao, sp. nov. (Figure 8).
MycoBank: MB854053.
Etymology: It is named in reference to the host species, Alpinia oxyphylla.
Holotype: LF55-0709.
Description:
The conidiomata are solitary or aggregated, globose and dark, often immersed in PDA. The conidiophores are distinct, often degenerated to conidiogenous cells. Conidiogenous cells are spherical and hyaline. The conidia are fusiform, straight to slightly curved, 18.8–23.5 × 5.3–7.0 μm ( = 21 × 6.2 μm) and have four septa. The basal cell is conical to subcylindrical, hyaline, thin and smooth walled and is 2.3–5 μm long ( = 3.9 μm). The three median cells are 11.3–15 μm ( = 13 μm), versicolored and brown to dark brown, with septa and periclinal walls that are darker than the rest of the cell and a wall with verrucae. The second cell from the base is pale brown, paler than the other two cells and 3.3–5.2 μm long ( = 4.1 μm). The third cell is dark brown, darker than the other two and 3.5–5.0 μm long ( = 4.1 μm); the fourth is pale brown to brown and 3.7–5.4 μm long ( = 4.4 μm). The apical cell is 2.8–5 μm long ( = 3.8 μm), conic to acute, hyaline, thin and smooth walled, with 2–4 tubular appendages on the apical cell (often 2–3) arising from the apex of the apical cell, which are occasionally branched, flexuous and 10–25.3 μm long ( = 18.6 μm). The single basal appendage is unbranched, tubular, centric and 2.5–8 μm long ( = 5 μm). A sexual morph was not observed.
Culture characteristics: The colonies reached 70 mm in diameter after 9 days on PDA at room temperature, with circular-edge, off-white, dense, central aerial hyphae on the raised surface, with a filiform margin, black fruiting bodies and a reverse similar in color.
Material examined: The sample originated in China, Hainan Province, Qiongzhong city, Changzheng Township, Luofan village, from leaf spots of A. oxyphylla, which was collected on 9 July 2022 by X.F. Cui and Z.G. Hao (LF55-0709, holotype); the ex-type was from Hainan Province, Wuzhishan city, Maoyang Township, Maohui village, from stem base spots of A. oxyphylla, which was collected on 8 July 2022 by X.F. Cui and Z.G. Hao (MJ31-0708); the ex-type originated in Hainan Province, Baoting city, Nanmao Shengli Farm, from leaf spots of A. oxyphylla, which was collected on 6 July 2022 by X.F. Cui and Z.G. Hao (NM44-0706).
Notes:
Based on multigene analyses, Neopestalotiopsis oxyphylla is closely related to N. brachiata (MFLUCC 17-1555), N. elaeidis (MFLUCC 15-0735), N. petila (MFLUCC 17-1738), N. aotearoa (CBS 367.54) and N. piceana (CBS 394.48), with only 0–2 bp difference among them. However, N. oxyphylla is distinct from N. elaeidis, with larger spores (N. oxyphylla: 18.8–23.5 × 5.3–7.0 μm, = 21 × 6.2 μm vs. N. elaeidis 10–20 × 3–7 μm, = 16 × 5.5 μm) and thinner spores (N. oxyphylla: 5.3–7.0 μm vs. N. aotearoa: 6.5–8.5 μm and N. piceana 7.5–9 μm); N. oxyphylla has different numbers of apical appendages (N. oxyphylla: 2–4; N. brachiata: 1–3; N. aotearoa, N. elaeidis and N. petila: 2–3; N. piceana: 3) and shorter apical appendages (N. oxyphylla: 10–25.3 μm vs. N. brachiata: 9.5–33; N. petila: 22–29 μm, N. piceana: 21–31 μm), but they are longer than those of N. aotearoa (5–12 μm). In addition, N. oxyphylla has shorter basal appendages (N. oxyphylla: 2.5–8 μm vs. N. piceana: 6–23 μm). Therefore, N. oxyphylla is classified as a new species in the present study.
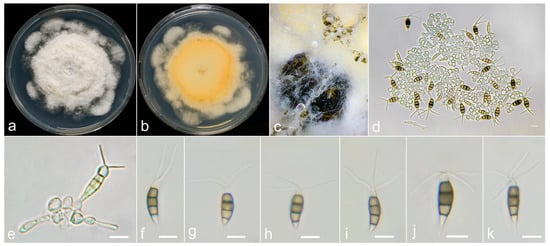
Figure 8.
Neopestalotiopsis oxyphylla (LF55-0709, holotype). (a,b) Colony on PDA (above and reverse), (c) conidiomata on PDA, (d,e) conidiogenous cells, and (f–k) conidia. Scale bars = 10 μm.
Neopestalotiopsis wuzhishanensis X.F. Cui and Z.G. Hao, sp. nov. (Figure 9).
MycoBank: MB854054.
Etymology: It is named in reference to the first collection city of Wuzhishan in Hainan province.
Holotype: YX116-0708.
Description:
The conidiomata on the PDA are solitary, globose and dark. The conidiophores often degenerated to conidiogenous cells. Conidiogenous cells are unclear. The conidia arefusiform, straight, scarcely curved, 19.5–26.5 × 4.5–6.3 μm ( = 22.4 × 5.2 μm) and have four septa. The basal cell is conical to subcylindrical, hyaline, thin and smooth walled and is 2.8–5.5 μm long ( = 4.2 μm). The three median cells are 12.8–16 μm ( = 14.4 μm), nearly concolorous, pale brown and hyaline, with septa and periclinal walls darker than the rest of the cell. The second cell from the base is pale brown and 4–6.2 μm long ( = 5.1 μm). The third cell is pale brown and 3.5–5.2 μm long ( = 4.4 μm); the fourth is pale brown and 3.8–6.3 μm long ( = 4.7 μm). The apical cell is 2.7–5.5 μm long ( = 3.6 μm), conic to acute, hyaline, thin and smooth-walled, with 1–3 tubular appendages on the apical cell (often 1–2) arising from the apex of the apical cell, which are unbranched, straight to flexuous and 9–20.8 μm long ( = 15.4 μm). There is a single or no basal appendage, which is unbranched, tubular, centric and 0.8–3.8 μm long ( = 1.9 μm). A sexual morph is not observed.
Culture characteristics: The colonies reached 70 mm in diameter after 12 days on PDA at room temperature, with circular-edge, white, medium-dense, aerial hyphae on the flat surface, with a filiform margin, black and fruiting bodies. And its reverse was lemon yellow.
Material examined: The sample originated in China, Hainan Province, Wuzhishan city, Shuiman Township, Yongxun village, from leaf spots of A. oxyphylla, which was collected on 8 July 2022 by X.F. Cui and Z.G. Hao (YX116-0708).
Notes:
Neopestalotiopsis wuzhishanensis clusters a sister group to Neopestalotiopsis cubana (CBS 600.96), while N. wuzhishanensis is different from N. cubana depending on ITS, tef-1α and tub2 sequences (3/481 in ITS, 2/434 in tef-1α and 3/715 in tub2). Additionally, there are remarkabe discrepancies in the morphological characteristics: N. wuzhishanensis is thinner (N. wuzhishanensis: 4.5–6.3 μm, = 5.2 μm vs. N. cubana 8–9.5 μm, = 8.8 μm) and shorter in its apical appendages (N. wuzhishanensis: 9–20.8 μm, = 15.4 μm vs. N. cubana: 21–27 μm, = 24 μm) and base appendage (N. wuzhishanensis: 0.8–3.8 μm, = 1.9 μm vs. N. cubana: 4–7 μm); additionally, the three median cells of N. wuzhishanensis are paler than N. cubana; furthermore, N. cubana has 1–3 apical appendages, while N. cubana carries 2–4 appendages. The results of the PHI test showed that N. wuzhishanensis has no significant recombination with its closely related taxa. Therefore, N. wuzhishanensis is classified as a new species in the present study.
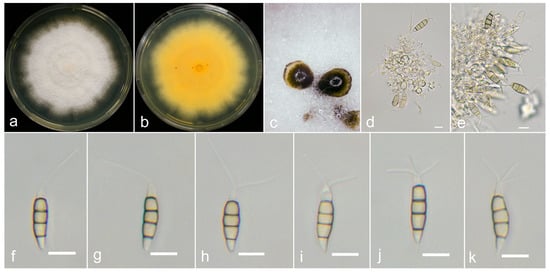
Figure 9.
Neopestalotiopsis wuzhishanensis (YX116-0708, holotype). (a,b) Colony on PDA (above and reverse), (c) conidiomata on PDA, (d,e) conidiogenous cells and (f–k) conidia. Scale bars = 10 μm.
Neopestalotiopsis yongxunensis X.F. Cui and Z.G. Hao, sp. nov. (Figure 10).
MycoBank: MB854055.
Etymology: The name refers to the first collection village of Yongxun in Hainan Province.
Holotype: YX101-0708.
Description:
The conidiomata on the PDA are solitary or aggregated, globose, dark and embedded or semi-immersed. The conidiophores often degenerated to conidiogenous cells. Conidiogenous cells are unclear. The conidia are fusiform, straight to curved, 18.2–25.5 × 5.8–7.5 μm ( = 21.6 × 6.6 μm) and have four septa. The basal cell is conical, hyaline, thin and smooth walled and is 3.0–5.2 μm long ( = 4.1 μm). The three median cells are 12–15.2 μm ( = 13.7 μm), versicolored, pale brown to brown and have septa and periclinal walls that are darker than the rest of the cell; the second cell from the base is pale brown, paler than the other two cells and is 3.5–5.3 μm long ( = 4.3 μm). The third cell is brown, darker than the other two and is 3.8–5.3 μm long ( = 4.6 μm). The fourth cell is brown and 4.0–5.2 μm long ( = 4.6 μm). The apical cell is 2.5–5.0 μm long ( = 3.7 μm), conic to subcylindrical, hyaline, thin and smooth walled, with 2–4 tubular appendages on the apical cell arising from the apex of the apical cell, which are filiform, unbranched, straight to flexuous and 10.5–24.7 μm long ( = 18.2 μm). The single basal appendage is unbranched, tubular, centric and 1.7–7 μm long ( = 4.2 μm). A sexual morph is not observed.
Culture characteristics: The colonies reached 70 mm in diameter after 4 days on PDA at room temperature, with a circular-edge, white, dense aerial mycelium on the surface; the reverse was similar in color. The fruiting bodies were black, mostly under the hyphae and were visible on the back.
Material examined: The sample originated in China, Hainan Province, Wuzhishan city, Shuiman Township, Yongxun village, from leaf spots of A. oxyphylla, which was collected on 8 July 2022 by X.F. Cui and Z.G. Hao (YX101-0708);
Notes:
Neopestalotiopsis yongxunensis is related to N. dendrobii (MFLUCC 14-0106) and N. paeonia-suffruticosa (HKAS 123212), as shown in the phylogenetic analysis, while N. yongxunensis can be differentiated from N. dendrobii and N. paeonia-suffruticosa depending on ITS, tef1-α and tub2 sequences, showing a 7 bp difference (2/284 in tef1-α and 5/416 in tub2) with N. dendrobii and 10 bp difference (9/440 in tef1-α and 1/715 in tub2) with N. paeonia-suffruticosa. In addition, there are remarkable discrepancies in the morphological characteristics: N. yongxunensis is thinner in its conidia (N. yongxunensis: 5.8–7.5 μm, = 6.6 μm vs. N. paeonia-suffruticosa: 9–11 μm, = 9.5 μm), has different numbers of apical appendages (N. yongxunensis 2–4 vs. N. paeonia-suffruticosa 3–4) and shorter apical appendages (N. yongxunensis: 10.5–24.7 μm vs. N. paeonia-suffruticosa 22.5–34 μm), while N. yongxunensis differs from N. dendrobii in having longer apical appendages (N. yongxunensis: 10.5–24.7 μm vs. N. dendrobii 5–6.5 μm) with different numbers (N. yongxunensis 2–4 vs. N. dendrobii 2–3). Furthermore, the PHI test indicated that there is no significant recombination between N. yongxunensis and its closely related species. Therefore, N. yongxunensis is classified as a new species in the present study.
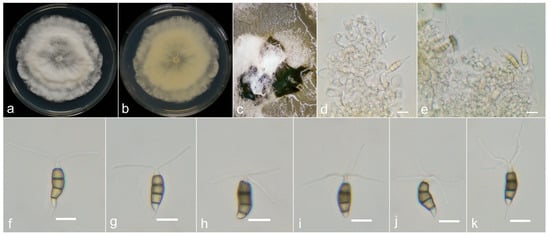
Figure 10.
Neopestalotiopsis yongxunensis (YX101-0708, holotype). (a,b) Colony on PDA (above and reverse), (c) conidiomata on PDA, (d,e) conidiogenous cells and (f–k) conidia. Scale bars = 10 μm.
3.4. Pathogenicity Assay
Sixteen of the twenty tested pestalotioid isolates were able to cause typical brown lesions after inoculation, while the other four isolates did not, including Neopestalotiopsis sp.4 MH133-0708, N. coffeae-arabicae NM42-0706, N. oblatespora YJ11-0708 and Neopestalotiopsis sp.3 SX11-0706. The lesion areas measured 5 days after inoculation were 54.02, 13.86, 15.57, 4.65, 11.08, 117.40, 100.63, 82.31, 8.55, 80.25, 32.03, 7.02, 104.86, 84.48, 102.04 and 16.17 mm2 for isolates of P. hydei BA11-0708, Ps. myanmarina JR34-0709, Ps. avicenniae LF48-0709, N. coffeae-arabicae BL32-0708, N. coffeae-arabicae LF51-0709, N. cubana MH51-0708, N. cubana YX112-0708, N. wuzhishanensis YX116-0708, N. yongxunensis YX101-0708, N. baotingensis SX41-0706, N. vaccinii JR31-0709, N. rosicola NM47-0706, N. oxyphylla LF55-0709, N. brachiata SX31-0706, Neopestalotiopsis sp.5 XC11-0709 and N. olivaceous LF25-0709, respectively (Figure 11). The morphology of the purified fungi re-isolated from the lesion after inoculation was identical with those of the isolates used for inoculation, which were also confirmed using PCR and gene sequences. The results of the pathogenicity and phylogenetic analysis showed that the strains close to N. cubana and N. brachiata had a stronger pathogenicity (Figure 1 and Figure 11B).
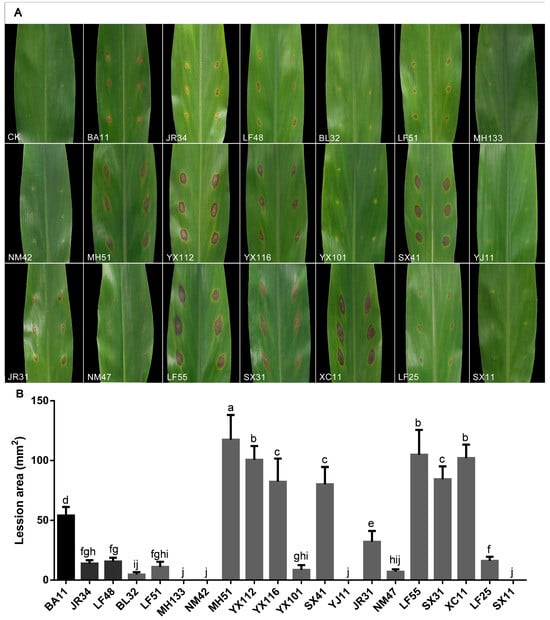
Figure 11.
Pathogenicity test results of 20 pestalotioid species on Alpinia oxyphylla leaves. (A) Symptoms on leaves after 5 days. Icons in figures, in sequence, are CK, P. hydei BA11-0708, Ps. myanmarina JR34-0709, Ps. avicenniae LF48-0709, N. coffeae-arabicae BL32-0708, N. coffeae-arabicae LF51-0709, Neopestalotiopsis sp.4 MH133-0708, N. coffeae-arabicae NM42-0706, N. cubana MH51-0708, N. cubana YX112-0708, N. wuzhishanensis YX116-0708, N. yongxunensis YX101-0708, N. baotingensis SX41-0706, N. oblatespora YJ11-0708, N. vaccinii JR31-0709, N. rosicola NM47-0708, N. oxyphylla LF55-0709, N. brachiata SX31-0706, Neopestalotiopsis sp.5 XC11-0709, N. olivaceous LF25-0709 and Neopestalotiopsis sp.3 SX11-0706. (B) Pathogenicity of the isolates was evaluated by measuring the area of the necrotic lesions after 5 days. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of the mean. Significant differences (p < 0.05) are indicated with different letters according to Duncan’s multiple range test. The abscissa designation corresponds sequentially to (A), excluding “CK”.
4. Discussion
In this study, 36 pestalotioid strains were isolated. According to the multi-locus phylogeny (ITS, tef-1α and tub2) and morphological characteristics analyses, one Pestalotiopsis sp, two Pseudopestalotiopsis spp., and fourteen Neopestalotiopsis spp. were identified. Six new species (N. baotingensis, N. oblatespora, N. olivaceous, N. oxyphylla, N. wuzhishanensis and N. yongxunensis) were described. Among the 36 strains, the isolation frequency of N. coffeae-arabicae and N. cubana was 16.67% for both, higher than the others; additionally, N. coffeae-arabicae, N. olivaceous and N. oxyphylla were isolated from five, three and three cities separately, with a wider distribution in Hainan than others. This is the first systematic report of Neopestalotiopsis, Pestalotiopsis and Pseudopestalotiopsis fungi relating to A. oxyphylla in its main planted area.
The development of molecular biology has greatly facilitated the identification of microorganisms, and the phylogeny analyses of combined ITS, tef-1α and tub2 can better distinguish Neopestalotiopsis, Pestalotiopsis and Pseudopestalotiopsis. For example, in this study, N. olivaceous and N. wuzhishanensis do not conform to the morphological characteristics of the versicolorous median cells depicted in Neopestalotiopsis. This phenomenon was also mentioned by Sun et al. [18], so the phylogeny analyses can overcome the discrimination of the three genera only by the intermediate cell color. While the three gene sequences of N. oxyphylla, N. aotearoa and N. brachiata are closely similar, only with 0–2 bp difference in the combined sequence, and between N. oblatespora and N. guajavicola, with 2 bp difference, they have obvious discrepancies in their morphological characteristics. A similar phenomenon was observed between N. alpapicalis MFLUCC 17-2544T and N. rhizophorae MFLUCC 17-1551T [41]. Therefore, more gene fragments need to be introduced in order to further differentiate closely related species of pestalotioid fungi.
RLB is an important disease in the cultivation process of A. oxyphylla, according to previous reports. Its pathogen was reported as Pestalotia palmarum in 1986 [11], now classified as Pestalotiopsis palmarum, while the RBS disease, with similar symptoms to RLB disease, was caused by Pestalosphaeria alpinia, the sexual morph of pestalotioid, as reported in 1994 [15]. Perhaps due to the differences in the classification method and limitations in the sample size, P. palmarum and P. alpinia were not isolated in this study, which explained the potential diversity of pestalotioid fungi in this host that need to be further explored. In addition, the symptoms of RLB and RBS disease are similar, with both caused by pestalotioid fungi with different morphs, so it is recommended to merge the two diseases into one for future research and disease management.
The pathogenicity tests of 20 pestalotioid strains showed that most species can cause obvious symptoms on the leaves, indicating the diversity of the pathogen of RLB disease, and the Neopestalotiopsis species (lesion area over 75 mm2 for 7 species) tended to infect A. oxyphylla and caused more serious disease than Pestalotiopsis (lesion area of about 50 mm2) and Pseudopestalotiopsis (less than 50 mm2 for both). The reports of the disease caused by Neopestalotiopsis fungi have been more frequent in recent years [18]. In addition, all pathogenicity tests were carried out with a single cultivar of A. oxyphylla and constant environmental conditions. As we all know, both differences in varieties and changes in the environmental conditions can affect the occurrence of diseases. Therefore, more studies need to be performed on different varieties under different environmental conditions.
What is worth noting is that most of the pestalotioid species have a broad range of hosts, and one species of pestalotioid fungi can infect several economic plants, while a plant can be harmed by several pestalotioid fungi. For example, N. cubana can infect rubber trees [96], Camellia oleifera [19] and Ixora chinensis [97], and a new leaf fall disease of rubber trees was caused by N. aotearoa, N. cubana and N. formicarum [96]. A. oxyphylla is a semi-shade plant mainly planted in rubber tree forests. In this study, six strains of N. cubana, one strain of Neopestalotiopsis sp.3 SX11-0706 clustered with N. formicarum and five strains (N. oxyphylla, N. brachiata and Neopestalotiopsis sp.5 XC11-0709) closely related to N. aotearoa were isolated. Thus, it suggests that some pestalotioid species may infect both the rubber tree and A. oxyphylla. The promotion of medicinal plant cultivation under forest trees should be carried out with attention to the occurrence of cross-infection diseases in order to prevent them.
A comprehensive understanding of the species and genetic diversity of pathogens is the foundation for sustainable disease management. Since there is no research about the resistance varieties of A. oxyphylla to RLB disease, the strains with different characteristics and pathogenicities that were isolated in this study may provide a material basis for the subsequent screening of resistant varieties, including highly active biological and chemical agents friendly to the environment.
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, X.C.; Methodology, Z.H. and Y.L. (Yingbin Li); Resources, X.C., Z.H. and J.Z.; Software, S.S.; Supervision, J.L., Y.L. (Yixiang Liu) and L.L.; Visualization, M.C.; Writing—original draft, X.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Major Science and Technology Project in Yunnan Province (202102AE090042-02) and the leading fund project of the Sanya Research Institute of China Agricultural University (SYND-2022-11).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All sequence data are available in NCBI GenBank following the accession numbers in the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Qiu, L.Y. Investigation of Germplasm Resources of Alpinia oxyphylla Miq. in Hainan Island. Master’s Thesis, Hainan University, Hainan, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Alpiniae oxyphyllae Fructus; The Medicine Science and Technology Press of China: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zheng, Y.L.; Hu, X.J.; Hu, X.L.; Lv, W.W.; Lv, D.; Chen, J.J.; Wu, M.L.; Song, Q.C.; Shentu, J.Z. Ethnopharmacological uses, phytochemistry, biological activities, and therapeutic applications of Alpinia oxyphylla Miguel: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 224, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.H.; Xu, P.; Chen, F.; Tan, Y.F.; Duan, J.A. Anti-diarrheal constituents of Alpinia oxyphylla. Fitoterapia 2013, 89, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.Z.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, L.Y.; Xian, Q.Q.; Sun, P.Z.; Du, Z.Y. Geographical distribution and prediction of potential region of Alpinia oxyphylla Miq. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2018, 46, 1–3+8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F. Exploration of Metabolites and Related Genes of Volatile Oil from Wild Alpinia oxyphylla Miq. in Hainan Province; Central University for Nationalities: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.Z.; Liufu, Y.Q.; Lin, S.C.; Xian, S.Q. Analysis of the basic biological characteristics and high yield cultivation techniques of Alpinia oxyphylla Miq. South China Agric. 2018, 12, 27+29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, Y.G.; Yang, H.G.; Yao, G.L.; Zhang, J.F.; Yu, J.; Yang, D.M.; Chen, P. The current planting situation and industrial development countermeasures of Alpinia oxyphylla Miq. in Hainan Province. Mod. Hortic. 2021, 44, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.M. Analysis of biological characteristics and environment for high production of Alpinia oxyphylla. Chin. J. Mod. Appl. Pharm. 1992, 5, 205–207. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.X.; Ren, B.L.; Wang, M.Y.; Wang, Q.L.; Yang, Q.; Tang, H.; Wang, Z.N. Present situation and development strategy of Alpinia oxyphylla. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2019, 44, 1960–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.Q.; Chen, J.J. Three important new diseases of Alpinia oxyphylla Miq. Chin. J. Trop. Agric. 1986, 3, 50–53. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.R.; Zhou, J.; Wu, X.P.; Lei, X.T. The main diseases and pests of Alpinia oxyphylla and their prevention and control. China Trop. Agric. 2012, 48, 56–58. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, M.Y.; Zeng, X.P.; Rui, K.; Wang, H.F.; Chen, M.C. The occurrence and control of the leaf blight disease of Alpinia oxyphylla in Hainan Island. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2015, 655, 170–171. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, P.K. Fungal Diseases of Cultivated Medicinal Plants in Guangdong Province; Guangdong Science and Technology Press: Guangzhou, China, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Guo, L.D.; Chukeatirote, E.; Bahkali, A.H.; Hyde, K.D. Pestalotiopsis-morphology, phylogeny, biochemistry and diversity. Fungal Divers. 2011, 50, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Guo, L.D.; Cai, L.; Chukeatirote, E.; Wu, W.P.; Sun, X.; Crous, P.W.; Bhat, D.J.; McKenzie, E.H.C.; Bahkali, A.H.; et al. A multi-locus backbone tree for Pestalotiopsis, with a polyphasic characterization of 14 new species. Fungal Divers. 2012, 56, 95–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Hyde, K.D.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Xu, J.; Crous, P.W. Pestalotiopsis revisited. Stud. Mycol. 2014, 79, 121–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.R.; Jayawardena, R.S.; Sun, J.E.; Wang, Y. Pestalotioid species associated with medicinal plants in southwest China and Thailand. Microbiol. Spectrum 2023, 11, e0398722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.L.; Yang, Q.; Li, H. Morphology, phylogeny, and pathogenicity of pestalotioid species on Camellia oleifera in China. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diogo, E.; Goncalves, C.I.; Silva, A.C.; Valente, C.; Braganca, H.; Phillips, A.J.L. Five new species of Neopestalotiopsis associated with diseased Eucalyptus spp. in Portugal. Mycol. Prog. 2021, 20, 1441–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.F.; Chen, T.H.; Liu, S.D. Bioactivity of antifungal substance iturin a produced by Bacillus subtilis strain BS-99-H against Pestalotiopsis eugeniae, a causal pathogen of wax apple fruit rot. Plant Pathol. Bull. 2010, 19, 225–233. [Google Scholar]
- Prasannath, K.; Shivas, R.G.; Galea, V.J.; Akinsanmi, O.A. Neopestalotiopsis species associated with flower diseases of Macadamia integrifolia in Australia. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, I.; Chung, C.L.; Lin, S.R.; Hung, T.H.; Shen, T.L.; Hu, C.Y.; Hozzein, W.N.; Ariyawansa, H.A. Cryptic diversity, molecular systematics, and pathogenicity of genus Pestalotiopsis and allied genera causing gray blight disease of tea in Taiwan, With a description of a new Pseudopestalotiopsis species. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 425–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Larignon, P.; Hyde, K.D.; Al-Sadi, A.M.; Liu, Z.Y. Characterization of Neopestalotiopsis, Pestalotiopsis and Truncatella species associated with grapevine trunk diseases in France. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2016, 55, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoubi, N.; Soleimani, M.J. Strawberry fruit rot caused by Neopestalotiopsis iranensis sp nov., and N. mesopotamica. Curr. Microbiol. 2016, 72, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamorro, M.; Aguado, A.; De los Santos, B. First report of root and crown rot caused by Pestalotiopsis clavispora (Neopestalotiopsis clavispora) on strawberry in Spain. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeewon, R.; Liew, E.C.Y.; Hyde, K.D. Phylogenetic relationships of Pestalotiopsis and allied genera inferred from ribosomal DNA sequences and morphological characters. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2002, 25, 378–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeewon, R.; Liew, E.C.Y.; Simpson, J.A.; Hodgkiss, I.J.; Hyde, K.D. Phylogenetic significance of morphological characters in the taxonomy of Pestalotiopsis species. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 27, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualberto, G.F.; Catarino, A.D.; Sousa, T.F.; Cruz, J.C.; Hanada, R.E.; Caniato, F.F.; Silva, G.F. Pseudopestalotiopsis gilvanii sp. nov. and Neopestalotiopsis formicarum leaves spot pathogens from guarana plant: A new threat to global tropical hosts. Phytotaxa 2021, 489, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.K.; Yang, Q.; Sun, Y.R.; Zeng, X.Y.; Jayawardena, R.S.; Hyde, K.D.; Wang, Y. Additions to Neopestalotiopsis (Amphisphaeriales, Sporocadaceae) fungi: Two new species and one new host record from China. Biodivers. Data J. 2022, 10, e90709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.L.; Dissanayake, A.J.; Zhang, T.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Liu, J.K. Identification and pathogenicity of pestalotioid fungi associated with woody oil plants in Sichuan Province, China. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prematunga, C.J.; You, L.Q.; Gomdola, D.; Balasuriya, A.; Yang, Y.H.; Jayawardena, R.S.; Luo, M. An addition to pestalotioid fungi in China: Neopestalotiopsis fragariae sp. nov. causing leaf spots on Fragaria × ananassa. Asian J. Mycol. 2022, 5, 220–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; He, Y.K.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Y. Two new Pseudopestalotiopsis species isolated from Celtis sinensis and Indocalamus tessellatus plants in southern China. Phytotaxa 2022, 543, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zeng, X.Y.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Q.; He, Y.K.; Wang, Y. Two new species of Neopestalotiopsis from southern China. Biodivers. Data J. 2021, 9, e70446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols; Academic Press, Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Carbone, I.; Kohn, L.M. A method for designing primer sets for speciation studies in filamentous ascomycetes. Mycologia 1999, 91, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, K.; Kistler, H.C.; Cigelnik, E.; Ploetz, R.C. Multiple evolutionary origins of the fungus causing Panama disease of banana: Concordant evidence from nuclear and mitochondrial gene genealogies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2044–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, N.L.; Donaldson, G.C. Development of primer sets designed for use with the PCR to amplify conserved genes from filamentous ascomycetes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odonnell, K.; Cigelnik, E. Two divergent intragenomic rDNA ITS2 types within a monophyletic lineage of the fungus Fusarium are nonorthologous. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1997, 7, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, G.; Lohman, D.J.; Meier, R. SequenceMatrix: Concatenation software for the fast assembly of multi-gene datasets with character set and codon information. Cladistics 2011, 27, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norphanphoun, C.; Jayawardena, R.S.; Chen, Y.; Wen, T.C.; Meepol, W.; Hyde, K.D. Morphological and phylogenetic characterization of novel pestalotioid species associated with mangroves in Thailand. Mycosphere 2019, 10, 531–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Cheewangkoon, R.; Gentekaki, E.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Brahmanage, R.S.; Hyde, K.D. Neopestalotiopsis alpapicalis sp. nov. a new endophyte from tropical mangrove trees in Krabi Province (Thailand). Phytotaxa 2019, 393, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, J.D.P.; Machado, A.R.; Firmino, A.L.; Rosado, A.W.C.; de Souza, C.A.F.; de Souza-Motta, C.M.; Freire, K.; Paiva, L.M.; Magalhaes, O.M.C.; Pereira, O.L.; et al. Mycological diversity description I. Acta Bot. Bras. 2018, 32, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Fan, X.; Tian, C. Identification and characterization of leaf-inhabiting fungi from Castanea Plantations in China. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Tibpromma, S.; Zhang, F.; Xu, J.C.; Chethana, K.W.T.; Karunarathna, S.C.; Mortimer, P.E. Neopestalotiopsis cavernicola sp. nov. from Gem Cave in Yunnan Province, China. Phytotaxa 2021, 512, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibpromma, S.; Hyde, K.D.; McKenzie, E.H.C.; Bhat, D.J.; Phillips, A.J.L.; Wanasinghe, D.N.; Samarakoon, M.C.; Jayawardena, R.S.; Dissanayake, A.J.; Tennakoon, D.S.; et al. Fungal diversity notes 840–928: Micro-fungi associated with Pandanaceae. Fungal Divers. 2018, 93, 1–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Geng, K.; Zhang, B.; Hyde, K.D.; Zhao, W.S.; Wei, J.G.; Kang, J.C.; Wang, Y. Two new species of Pestalotiopsis from Southern China. Phytotaxa 2013, 126, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Crous, P.W.; Jiang, N.; Fan, X.; Liang, Y.; Tian, C. Diversity of Sporocadaceae (pestalotioid fungi) from rosa in China. Persoonia 2022, 49, 201–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.Y.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Chen, B.W.; Hyde, K.D.; McKenzie, E.H.C.; Chomnunti, P.; Kang, J.C. Endophytic pestalotioid taxa in Dendrobium orchids. Phytotaxa 2019, 419, 268–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crous, P.W.; Wingfield, M.J.; Le Roux, J.J.; Richardson, D.M.; Strasberg, D.; Shivas, R.G.; Alvarado, P.; Edwards, J.; Moreno, G.; Sharma, R.; et al. Fungal Planet description sheets: 371-399. Persoonia 2015, 35, 264–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konta, S.; Tibpromma, S.; Karunarathna, S.C.; Samarakoon, M.C.; Steven, L.S.; Mapook, A.; Boonmee, S.; Senwanna, C.; Balasuriya, A.; Eungwanichayapant, P.D.; et al. Morphology and multigene phylogeny reveal ten novel taxa in Ascomycota from terrestrial palm substrates (Arecaceae) in Thailand. Mycosphere 2023, 14, 107–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul Haq, I.; Ijaz, S.; Khan, N.A. Genealogical concordance of phylogenetic species recognition-based delimitation of Neopestalotiopsis species associated with leaf spots and fruit canker disease affected guava plants. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 58, 1301–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, R.; Liu, S.; Mu, T.; Zhang, X.; Xia, J. Morphological and phylogenetic analyses reveal two new species of Sporocadaceae from Hainan, China. MycoKeys 2022, 88, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, E.F.S.; Da Silva, M.; Barros, M.V.P.; Kasuya, M.C.M. Neopestalotiopsis hadrolaeliae sp. nov., a new endophytic species from the roots of the endangered orchid Hadrolaelia jongheana in Brazil. Phytotaxa 2019, 416, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huanaluek, N.; Jayawardena, R.S.; Maharachchikum-Bura, S.S.N.; Harishchandra, D.L. Additions to pestalotioid fungi in Thailand: Neopestalotiopsis hydeana sp. nov. and Pestalotiopsis hydei sp. nov. Phytotaxa 2021, 479, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinsanmi, O.A.; Nisa, S.; Jeff-Ego, O.S.; Shivas, R.G.; Drenth, A. Dry flower disease of macadamia in Australia caused by Neopestalotiopsis macadamiae sp. nov. and Pestalotiopsis macadamiae sp. nov. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.; Guo, L.D.; Chukeatirote, E.; Hyde, K.D. Improving the backbone tree for the genus Pestalotiopsis; addition of P. steyaertii and P. magna sp. nov. Mycol. Prog. 2014, 13, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crous, P.W.; Wingfield, M.J.; Chooi, Y.H.; Gilchrist, C.L.M.; Lacey, E.; Pitt, J.I.; Roets, F.; Swart, W.J.; Cano-Lira, J.F.; Valenzuela-Lopez, N.; et al. Fungal Planet description sheets: 1042-1111. Persoonia 2020, 44, 301–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Bonthond, G.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Cai, L.; Crous, P.W. Sporocadaceae, a family of coelomycetous fungi with appendage-bearing conidia. Stud. Mycol. 2019, 92, 287–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverio, M.L.; Calvacanti, M.A.d.Q.; Silva, G.A.d.; Oliveira, R.J.V.d.; Bezerra, J.L. A new epifoliar species of Neopestalotiopsis from Brazil. Agrotropica 2016, 28, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crous, P.W.; Summerell, B.A.; Swart, L.; Denman, S.; Taylor, J.E.; Bezuidenhout, C.M.; Palm, M.E.; Marincowitz, S.; Groenewald, J.Z. Fungal pathogens of Proteaceae. Persoonia 2011, 27, 20–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiwan, N.; Jeewon, R.; Pem, D.; Jayawardena, R.S.; Nazurally, N.; Mapook, A.; Promputtha, I.; Hyde, K.D. Fungal species from Rhododendron sp.: Discosia rhododendricola sp. nov, Neopestalotiopsis rhododendricola sp. nov. and Diaporthe nobilis as a new host record. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyawansa, H.A.; Hyde, K.D. Additions to Pestalotiopsis in Taiwan. Mycosphere 2018, 9, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Hilario, S.; Pinto, G.; Alves, A. Diversity and pathogenicity of pestalotioid fungi associated with blueberry plants in Portugal, with description of three novel species of Neopestalotiopsis. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2022, 162, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorenza, A.; Gusella, G.; Aiello, D.; Polizzi, G.; Voglmayr, H. Neopestalotiopsis siciliana sp. nov. and N. rosae causing stem lesion and dieback on avocado plants in Italy. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardena, R.S.; Liu, M.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Zhang, W.; Xing, Q.; Hyde, K.D.; Nilthong, S.; Li, X.; Yan, J. Neopestalotiopsis vitis sp. nov. causing grapevine leaf spot in China. Phytotaxa 2016, 258, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Tibpromma, S.; Hughes, A.C.; Chethana, K.W.T.; Wijayawardene, N.N.; Dai, D.Q.; Du, T.Y.; Elgorban, A.M.; Stephenson, S.L.; Suwannarach, N.; et al. Culturable mycota on bats in central and southern Yunnan Province, China. Mycosphere 2023, 14, 497–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Hou, L.w.; Raza, M.; Cai, L. Pestalotiopsis and allied genera from Camellia, with description of 11 new species from China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R.; Bao, D.F.; Shen, H.W.; Su, X.J.; Li, Y.X.; Luo, Z.L. Endophytic Pestalotiopsis species associated with Rhododendron in Cangshan Mountain, Yunnan Province, China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1016782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crous, P.W.; Boers, J.; Holdom, D.; Osieck, E.R.; Steinrucken, T.V.; Tan, Y.P.; Vitelli, J.S.; Shivas, R.G.; Barrett, M.; Boxshall, A.G.; et al. Fungal Planet description sheets: 1383–1435. Persoonia 2022, 48, 261–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyawansa, H.A.; Hyde, K.D.; Jayasiri, S.C.; Buyck, B.; Chethana, K.W.T.; Dai, D.Q.; Dai, Y.C.; Daranagama, D.A.; Jayawardena, R.S.; Lucking, R.; et al. Fungal diversity notes 111-252-taxonomic and phylogenetic contributions to fungal taxa. Fungal Divers. 2015, 75, 27–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiwan, N.; Wanasinghe, D.N.; Mapook, A.; Jayawardena, R.S.; Norphanphoun, C.; Hyde, K.D. Novel species of Pestalotiopsis fungi on Dracaena from Thailand. Mycology 2020, 11, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.K.; Hyde, K.D.; Jones, E.B.G.; Ariyawansa, H.A.; Bhat, D.J.; Boonmee, S.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; McKenzie, E.H.C.; Phookamsak, R.; Phukhamsakda, C.; et al. Fungal diversity notes 1–110: Taxonomic and phylogenetic contributions to fungal species. Fungal Divers. 2015, 72, 1–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.; Maharachchikumbura, S.; Thambugala, K.; Bhat, D.J.; Hyde, K.D. Morpho-molecular taxonomic studies reveal a high number of endophytic fungi from Magnolia candolli and M. garrettii in China and Thailand. Mycosphere 2021, 12, 163–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.Z.; Maharachchikumbura, S.; Tian, Q.; Hyde, K.D. Pestalotiopsis species on ornamental plants in Yunnan Province, China. Sydowia 2013, 65, 113–128. [Google Scholar]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Chukeatirote, E.; Guo, L.D.; Crous, P.W.; Mckenzie, E.H.C.; Hyde, K.D. Pestalotiopsis species associated with Camellia sinensis (tea). Mycotaxon 2013, 123, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, P.; Gonçalves, M.F.M.; Pinto, G.; Silva, B.; Martín-García, J.; Diez, J.J.; Alves, A. Three novel species of fungi associated with pine species showing needle blight-like disease symptoms. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2022, 162, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, K.D.; Jeewon, R.; Chen, Y.-J.; Bhunjun, C.S.; Calabon, M.S.; Jiang, H.-B.; Lin, C.-G.; Norphanphoun, C.; Sysouphanthong, P.; Pem, D.; et al. The numbers of fungi: Is the descriptive curve flattening? Fungal Divers. 2020, 103, 219–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Lee, S.Y.; Jung, H.Y. Pestalotiopsis kaki sp. nov., a novel species isolated from persimmon tree (Diospyros kaki) Bark in Korea. Mycobiology 2020, 49, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Liu, J.K.; Hyde, K.D.; Nanayakkara, R.R.; Zhu, G.S.; Liu, Z.Y. Fungi from Asian Karst formations I. Pestalotiopsis photinicola sp nov., causing leaf spots of Photinia serrulata. Mycosphere 2017, 8, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harishchandra, D.L.; Aluthmuhandiram, J.V.S.; Yan, J.; Hyde, K.D. Molecular and morpho-cultural characterisation of Neopestalotiopsis and Pestalotiopsis species associated with ornamental and forest plants in China. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 7, 352–362. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; McKenzie, E.H.C.; Hyde, K.D. A novel species of Pestalotiopsis causing leaf spots of Trachycarpus fortunei. Cryptogam. Mycol. 2012, 33, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.G.; Phan, C.K.; Wang, L.; Xu, T.; Luo, J.T.; Sun, X.; Guo, L.D. Pestalotiopsis yunnanensis sp. nov., an endophyte from Podocarpus macrophyllus (Podocarpaceae) based on morphology and ITS sequence data. Mycol. Prog. 2013, 12, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Guo, L.D.; Liu, Z.Y.; Hyde, K.D. Pseudopestalotiopsis ignota and Ps. camelliae spp. nov associated with grey blight disease of tea in China. Mycol. Prog. 2016, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, A.d.M.; Hanada, R.E.; de Queiroz, C.A.; Sousa, T.F.; Lima, Í.N.; Gasparotto, L.; da Silva, G.F. First report of Pseudopestalotiopsis dawaina causing spots in Caryota mitis in Brazil. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozawa, S.; Ando, K.; Phay, N.; Watanabe, K. Pseudopestalotiopsis dawaina sp. nov. and Ps. kawthaungina sp. nov.: Two new species from Myanmar. Mycol. Prog. 2018, 17, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, I.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Hyde, K.D.; Ariyawansa, H.A. Molecular phylogeny, morphology and pathogenicity of Pseudopestalotiopsis species on Ixora in Taiwan. Mycol. Prog. 2018, 17, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lateef, A.A.; Sepiah, M.; Bolhassan, M.H. Description of Pseudopestalotiopsis kubahensis sp. nov., a new species of microfungi from Kubah National Park, Sarawak, Malaysia. Curr. Res. Environ. Appl. Mycol. 2015, 5, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozawa, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yen, L.T.H.; Hop, D.V.; Phay, N.; Ando, K.; Watanabe, K. Identification of two new species and a sexual morph from the genus Pseudopestalotiopsis. Mycoscience 2017, 58, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Tangthirasunun, N.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Jiang, Y.L.; Xu, J.J.; Hyde, K.D.; Wang, Y. Novel Pestalotiopsis species from Thailand point to the rich undiscovered diversity of this chemically creative genus. Cryptogam. Mycol. 2014, 35, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.T.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES science gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In Proceedings of the Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaedvlieg, W.; Binder, M.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Summerell, B.A.; Carnegie, A.J.; Burgess, T.I.; Crous, P.W. Introducing the consolidated species concept to resolve species in the Teratosphaeriaceae. Persoonia 2014, 33, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruen, T.C.; Philippe, H.; Bryant, D. A simple and robust statistical test for detecting the presence of recombination. Genetics 2006, 172, 2665–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huson, D.H.; Bryant, D. Application of phylogenetic networks in evolutionary studies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pornsuriya, C.; Chairin, T.; Thaochan, N.; Sunpapao, A. Identification and characterization of Neopestalotiopsis fungi associated with a novel leaf fall disease of rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis) in Thailand. J. Phytopathol. 2020, 168, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, Y.W.; Tan, H.T.; Khaw, Y.S.; Li, S.F.; Chong, K.P. First report of Neopestalotiopsis cubana causing leaf blight on Ixora chinensis in Malaysia. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).