Abstract
Penicillium expansum is the predominant causal agent causing blue mold in postharvest fresh Codonopsis pilosula during storage. The pathogen reduces the yield and affects the quality of C. pilosula and even generates patulin, threatening human health. In this study, postharvest fresh, healthy C. pilosula was sprayed with P. expansum, and the control effect of ozone on postharvest diseases of C. pilosula was studied, and the effect of ozone on the contents in the main active ingredients of C. pilosula was compared; finally, the effect of ozone on reactive oxygen species (ROS) metabolism in C. pilosula was analyzed. The results showed that 2 mg L−1 ozone application significantly inhibited the occurrence of postharvest blue mold caused by P. expansum, reduced weight loss rate, controlled the accumulation of patulin and maintained the contents of the main active components in C. pilosula. The study will provide a theoretical basis for ozone treatment to control the occurrence of postharvest diseases of C. pilosula.
1. Introduction
Codonopsis pilosula is a perennial herb of Campanulaceae [1], whose main active ingredients are lobetyolin, codonopsine, volatile oil, flavonoids, phytol and polysaccharides [2]. Phenylpropanoid glycosides are a major functional component isolated from the dried roots of C. pilosula. These compounds have rich medicinal value [3], which can enhance immunity [4], improve microcirculation [5], enhance hematopoietic function [6], and have obvious improvement effects on diabetes, liver protection and base repair [7].
Gansu Province is the dominant producer of C. pilosula in China, with a planting area of 50,000 hm2 and a yield of 558,000 tons [8]. However, with the continuous expansion of C. pilosula planting area, the disease of C. pilosula caused by pathogenic fungi has gradually become more obvious, which seriously affects the yield and quality of C. pilosula. The infection caused by pathogenic fungi not only leads to the loss of Chinese medicinal materials, but also causes mycotoxin contamination in Chinese medicinal materials, which seriously reduces the quality of Chinese medicinal materials and impairs their therapeutic effect, and even endangers the health of patients.
Penicillium expansum is a predominant causal agent, which was isolated from the blue mold of fresh C. pilosula during storage by our research team [9]. The infection of P. expansum not only leads to the occurrence of postharvest blue mold in C. pilosula, but also produces patulin with carcinogenic, teratogenic and mutagenic effects [10]. Many countries have stipulated the maximum limit of patulin in food. The European Union (EU) and the US Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) have stipulated that the maximum limit of patulin in fruit juice drinks is 50 μg/L [11]. However, there is no report on the stipulated limit of patulin in Chinese medicinal materials. As a traditional Chinese medicine for both medicine and food, the quality of C. pilosula is closely related to the health of patients. At present, the wide application of chemical synthetic fungicides not only leads to the resistance of pathogens, but also raises the problems of chemical residues, environmental pollution and the safety of medicinal materials.
As an excellent strong oxidant, the most significant feature of ozone is that it can be decomposed into O2 and singlet oxygen atom without any residue after application; therefore, ozone is called non-polluting disinfectant [12]. Ozone not only has a strong ability to kill various fungi, but can also reduce the accumulation of mycotoxins and degrade pesticide residue to a certain extent [13]. Ozone is widely applied in the prevention and control of postharvest diseases of fruits and vegetables [14]. The mechanism of ozone involved in postharvest disease control is that, on the one hand, ozone can directly affect the growth and development of the pathogenic fungus by destroying the cell structure; on the other hand, ozone treatment can induce resistance to the pathogen by activating the active oxygen metabolism (ROS) of the host plant to increase the antioxidant enzymatic activity, then avoid excessive accumulation of reactive oxygen species. Evidence has shown that ozone treatment controlled postharvest diseases of kiwifruit by inhibiting the growth of Botrytis cinerea and P. expansum and increased the activity of defense-related enzymes [15]. However, the effect of ozone treatment on the control of blue mold, patulin accumulation and the main active ingredient contents of fresh C. pilosula, as well as the possible mechanism of action, are rarely reported.
In this study, the effects of ozone treatment on the disease development, weight loss rate, and patulin accumulation of C. pilosula were firstly investigated by spraying inoculation P. expansum spore suspension. The influence of ozone exposure on the changes of the main active ingredients in C. pilosula after P. expansum inoculation was determined. Finally, the possible action mechanism was analyzed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Fresh C. pilosula samples were purchased from C. pilosula planting base in Min County (location 35° N and 104° E), Gansu Province of China. Roots with a similar size and without obvious pest or mechanical damage were collected in November 2021, taken to the Chemical Biology Laboratory in Gansu Agricultural University and stored at room temperature for further experiment.
P. expansum was isolated and purified from the tissue of C. pilosula with typical symptoms of the blue mold of C. pilosula by our research team and identified by morphology and molecular biology [16], and was stored at 4 °C for later use.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Spore Suspension
P. expansum spore suspension was prepared based on the method of Luo et al. [15]. 10 mL sterile water (containing 0.01 mL Tween 80) was added to P. expansum cultured for 7 days. The concentration of the filtered spore suspension was adjusted to 1 × 106 spores mL−1.
2.2.2. Ozone Treatment Method
The healthy roots of C. pilosula were disinfected with 1% sodium hypochlorite for 5 min, washed with sterile distilled water to remove sodium hypochlorite remaining on the surface of the roots, and dried naturally in the air. The above prepared 1 × 106 spores mL−1 P. expansum spore suspension was evenly sprayed on the surface of C. pilosula (spray volume of 3 mL). After 2 h of inoculation, ozone treatment was performed by ozone generator (OSAN, Aoshan Huanbao Technology Industry Co., Ltd., Dalian, China). In our previous study, we did a preliminary experiment on the ozone concentration screening. The results showed that 2 mg L−1 of the ozone concentration had the optimal inhibition effect on the disease development [17]. Therefore, the C. pilosula inoculated with P. expansum was treated with 2 mg L−1 ozone gas in a tightly sealed air bottle (diameter 20 cm, height 25 cm) for 0, 1 and 2 h, respectively.
2.2.3. Analysis of Incidence of the Blue Mold and Patulin Accumulation of C. pilosula during Different Storage Periods
C. pilosula inoculated with P. expansum was treated with ozone at different times, and then kept at 15 °C and 50% RH. The incidence was observed every 7 days and the disease index (formula (1)) and disease incidence (formula (2)) were calculated [18]; the disease classification standards are shown in Table S1 (Supplementary Materials, Table S1).
Disease index = [(Diseased plants at each level × Number of plants at that
level)/(Total number of plants × Highest disease level)] × 100%,
level)/(Total number of plants × Highest disease level)] × 100%,
Disease incidence= (Diseased plants investigated/Total plants investigated)
× 100%,
× 100%,
The C. pilosula inoculated with P. expansum but not treated with ozone was used as a control. The samples were collected every 7 days for patulin analysis. Patulin accumulation was determined based on the method by Lv [19].
2.2.4. Determination of Weight Loss Rate of C. pilosula during Different Storage Periods
The C. pilosula inoculated with P. expansum was treated with ozone for 0, 1 and 2 h, respectively, then packaged with sterile bags and kept at room temperature (15 °C, 50% RH). The weight of the treated C. pilosula was weighed by analytical balance every 7 days. The weight loss rate was calculated based on the following formula (3).
Weight loss rate = [Initial weight(W1) − Storage time node
weight(W2)]/[Initial weight(W1)] × 100%,
weight(W2)]/[Initial weight(W1)] × 100%,
2.2.5. Analysis of Main Active Ingredients in C. pilosula Inoculated with P. expansum during Different Storage Periods
The single standard solutions of main active ingredients were prepared as follows: 1 mg lobetyolin, 0.5 mg syringin, 0.5 mg lobetyolin I, 0.5 mg atractylenolide I, 0.5 mg atractylenolide II and 0.5 mg atractylenolide III were dissolved separately in 5 mL methanol to obtain the six single standard stock solutions. The mixed standard solution was done as follows: the above-mentioned single standard solutions were accurately measured and transferred into the 10 mL volumetric flask, and methanol was added to obtain the mixed standard solution of the above six main active ingredients.
Chromatographic conditions: (Supplementary Materials, Table S2).
The preparation of C. pilosula samples was carried out according to the above Section 2.2.3 method. A 1.0 g sample of powder was accurately weighed, transferred into a centrifuge tube to extract with 25 mL methanol, vortexed in a vortex mixer for 3 min, then ultrasonically extracted at 20 °C (40 kHz, 150 W) for 30 min. The extract was obtained and centrifuged at 4 °C, 5000× g for 5 min. The supernatant was evaporated and concentrated to dryness at 45 °C. The residue was redissolved with methanol and transferred to a 5 mL volumetric flask. Methanol was added to a constant volume of 5 mL and, finally, filtered through a 0.45 µm organic microporous membrane to further HPLC analysis.
2.2.6. Analysis of ROS Metabolism in C. pilosula Inoculated with P. expansum during Different Storage Periods
The production of superoxide anion (O2−.) and the content of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) were determined according to the method of Bao et al. [20]. The production of O2−. content was expressed as nmol/g FW (fresh weight). H2O2 content was expressed as mmol/g FW.
NADPH oxidase (NOX) activity was determined using NADPH oxidase kit (Suzhou Keming Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Suzhou, China). NOX activity was expressed as U/g FW. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity was determined using superoxide dismutase kit (Suzhou Keming Biotechnology Co., Ltd. China Suzhou Limited). SOD activity was expressed as U/g FW. Catalase (CAT) activity was determined referring to the Fan et al. [21] method. CAT activity was expressed as U/min/g FW. Peroxidase (POD) activity was determined referring to the method of Venisse et al. [22]. POD activity was expressed as ΔOD470/min/g FW.
2.2.7. Determination of Cell Membrane Permeability
Cell membrane permeability was measured and calculated according to the method of Chen et al. [23].
2.2.8. Determination of Malondialdehyde Content
Malondialdehyde (MDA) content was determined according to the method of Li et al. [24].
2.2.9. Data Statistics and Analysis
The experimental data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. SPSS 26.0 statistical analysis software was used for data processing. The significance of the difference was expressed at the p < 0.05 level, and the software Origin 2022 was used for mapping.
3. Results
3.1. Ozone Treatment Controlled the Development of the Blue Mold of C. pilosula
Ozone treatment significantly (p < 0.05) inhibited the occurrence of the blue mold of in C. pilosula during the postharvest storage period (Figure 1A). With the extension of storage time, the disease incidence and disease index showed an increasing trend. For example, on the 7th day of storage after treatment, the control group had obvious root disease with 1~2 mm granular mold spots on the surface, while the same symptoms were observed on the 14th day of storage for the ozone treatment group; that is to say, compared with the control group, the development of the disease was delayed by 7 days. On the 42th day of storage, the disease incidence of the control group increased rapidly; almost all samples were infected and some sample roots were decayed or worse, with soft rot and obvious mildew on the surface of roots. However, compared with the control group, the disease incidence of the ozone treatment group was significantly lower than that of the control group, and the longer the ozone treatment time, the better the inhibition of blue mold of C. pilosula. As shown in Figure 1B, on the 42nd day, the disease incidence of the ozone treatment 1 h group and the ozone treatment 2 h group was 13.9% and 30.5% lower than those of the control group, respectively. On the 56th day of storage, the control group displayed severe symptoms of disease, the incidence of which was 21.3% higher than that of the ozone treatment 2 h group (Figure 1C). In brief, ozone treatment significantly inhibited the expansion of the blue mold of C. pilosula caused by P. expansum and delayed the disease incidence of C. pilosula, and the longer the ozone treatment time, the better the inhibition effect that was obtained.
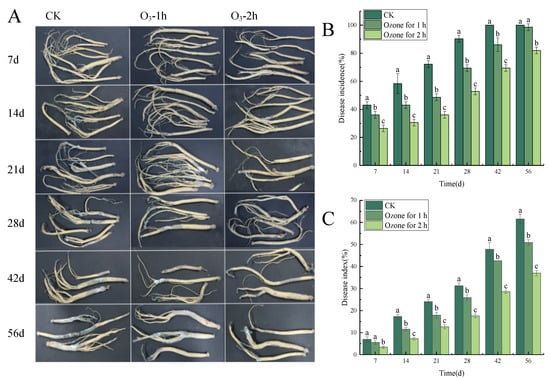
Figure 1.
Effects of ozone treatment on the disease incidence and disease index of the blue mold of C. pilosula during different storage periods. (A): Pictures of disease symptoms of C. pilosula samples during different storage periods; (B): Disease incidence; (C): Disease index. Bars indicate standard error. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.2. Ozone Treatment Suppressed the Weight Loss Rate of C. pilosula Inoculated with P. expansum
Ozone fumigation treatment alleviated the weight loss of C. pilosula to some extent. The weight loss rate of C. pilosula in the control group and the ozone treatment group increased with the prolongation of storage time; especially during days 0–14 of storage, the weight loss rate of C. pilosula increased rapidly. Nevertheless, the weight loss rate increased slowly from the 14th to the 28th day after treatment. From the 28th day to the end of storage, the weight loss rate increase tended to be gentle. The weight loss rate in the control group was 62.81% on the 28th day of storage, while in the ozone treatment group it was 61.79% (1 h) and 60.00% (2 h), respectively. At the end of storage, the weight loss rate in the control group reached 64.51%, while the weight loss rate in the ozone treatment group was 63.28% (1 h) and 61.20% (2 h), respectively (Figure 2).
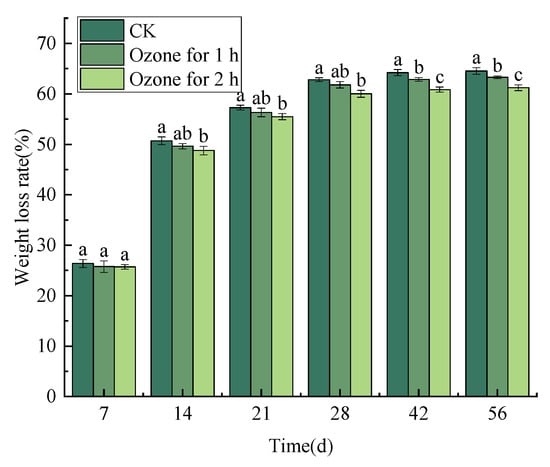
Figure 2.
Effect of ozone treatment on weight loss rate of C. pilosula inoculated with P. expansum. Bars indicate standard error. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.3. Effect of Ozone Treatment on Patulin Accumulation in C. pilosula Inoculated with P. expansum
Ozone treatment significantly (p < 0.05) reduced the accumulation of patulin in C. pilosula inoculated with P. expansum. The infection of P. expansum led to the accumulation of patulin (PAT) in the tissue of the bule mold of C. pilosula. With the increase in storage time, the content of PAT in the tissue of C. pilosula increased continuously, and the increasing trend in the control group was significantly greater than that in the ozone treatment group; the longer the ozone treatment time, the more obvious the inhibitory effect that was found. For example, on the 56th day of inoculation with P. expansum, the PAT content of the control group was 3.61 µg/g, while the PAT content of the ozone treatment 1 h and 2 h groups were 2.39 µg/g and 1.63 µg/g, respectively, and the PAT toxin content decreased by 33.06% and 54.85%, respectively (Figure 3).
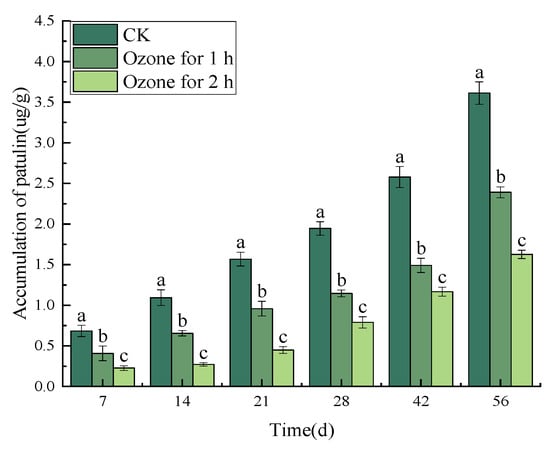
Figure 3.
Effect of ozone treatment on patulin accumulation in C. pilosulain inoculated with P. expansum. Bars indicate standard error. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.4. Ozone Treatment Maintained the Content of Main Active Ingredients in C. pilosula Inoculated with P. expansum
Ozone application markedly inhibited the P. expansum infection and effectively maintained the main active ingredients in C. pilosula. In the present study, the six main active ingredients of codonopatin, tangshenoside I, syringin, atractylenolide III, atractylenolide I, and atractylenolide II were detected in the tissue of C. pilosula by HPLC (Supplementary Materials, Figure S1). The change of contents for six active ingredients in C. pilosula inoculated with P. expansum in ozone treatment group and control group were shown in Figure 4. Compared with the control group, the four main active ingredients of codonopatin, tangshenoside I, syringin, atractylenolide III in C. pilosula after the ozone treatment maintained a good level (the darker the color, the higher the relative content of the ingredient was observed); however, the two active ingredients of atractylenolide I and atractylenolide II almost could not be detected after ozone treatment. In addition, as shown in Figure 4B, the correlation analysis presented that codonopatin was significantly positively correlated with tangshenoside I, syringin, atractylenolide III, and atractylenolide I; there was a significant positive correlation between tangshenoside I and syringin, atractylenolide III, and atractylenolide I. Syringin was significantly positively correlated with atractylenolide III (the darker the color, the stronger the correlation).
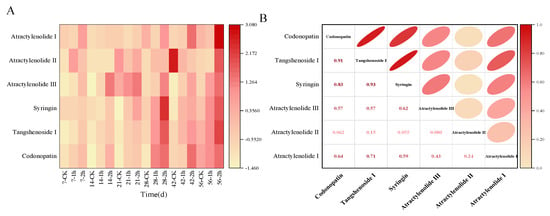
Figure 4.
Effect of ozone treatment on the content of the main active ingredients of the blue mold of C. pilosula. (A) Thermography; (B) Analysis of relationship.
After different concentrations of ozone treatment, the content of the main active ingredients of codonopatin, tangshenoside I syringin and atractylenolide III (atractylenolide I and atractylenolide II was too low to be detected) was maintained in the C. pilosula tissue (Figure 5). In general, the infection of P. expansum led to a reduction in the content of lobetyolin, lobetyolin I, syringin and atractylenolide III. However, ozone treatment inhibited the growth of P. expansum, and maintained the content of codonopatin, tangshenoside I, syringin and atractylenolide III to a certain extent.
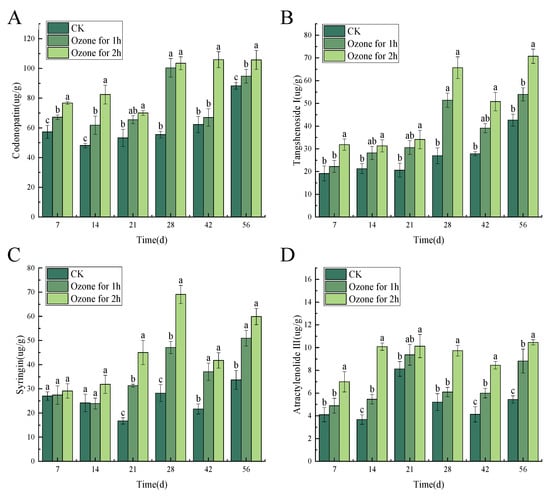
Figure 5.
Effect of ozone treatment on the content of four main active ingredients of the blue mold of C. pilosula. Bars indicate standard error. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05). (A) lobetyolin; (B) lobetyolin I; (C) syringin; (D) atractylenolide III.
The principal component analysis of the main active ingredients of C. pilosula at different storage periods showed that the characteristic values of codonopatin, tangshenoside I and syringin were 3.79, 1.03 and 0.58, respectively. The cumulative contribution rate of codonopatin, tangshenoside I and syringin reached 89.83%. The codonopatin, tangshenoside I and syringin can be used as the evaluation indexes of the main active ingredients of C. pilosula at different storage times. According to the results of principal component analysis, the principal component score coefficient matrix was obtained. Taking the variance contribution rate of the top three principal components of codonopatin, tangshenoside I and syringin as the weight, the principal component comprehensive score was calculated: comprehensive score (H) = (63.08707 × F1 + 17.12968 × F2 + 9.61508 × F3)/89.83183. According to the comprehensive score of principal components, we can know the ranking (Supplementary Materials, Table S3). Combined with the PCA score diagram of the principal components in Figure 6, the score of the ozone treatment 2 h group on the 56th day was the highest, and the score of the control group on the 14th day was the lowest. The comprehensive evaluation and distribution results of the main active components of C. pilosula were highest in the ozone treatment 2 h group, followed by the ozone treatment 1 h group, and the control group had the lowest comprehensive score. The higher the score, the better the retention effect of the active components of C. pilosula. It can be seen from the results of the score that the active components of C. pilosula after ozone treatment were significantly higher than those of the control group.
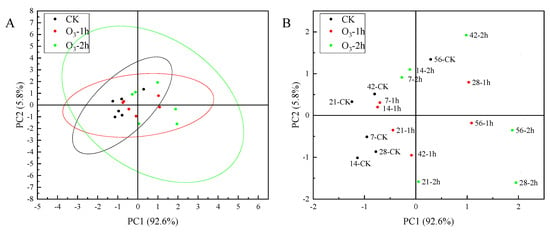
Figure 6.
PCA score scatter plot of C. pilosula samples. (A). Load chart. (B). Score chart.
3.5. Ozone Treatment Activated ROS Metabolism in C. pilosula Inoculated with P. expansum
3.5.1. Ozone Treatment Suppressed the Accumulation of O2−. and H2O2 in the Inoculated C. pilosula
Compared with the untreated control group, the ozone treatment significantly (p < 0.05) reduced the contents of O2−. and H2O2 in C. pilosula inoculated with P. expansum. The analysis of the O2−. production content of the inoculated P. expansum showed that there was a significant difference between the control group and the ozone treatment group (p < 0.05). However, the content of O2−. generally increased with the increase of storage time and reached a peak on the 56th day of storage. The ozone treatment for 1 h and 2 h decreased by 19.40% and 33.33%, respectively, compared with the control group (Figure 7A). The content of H2O2 increased first, then decreased, and reached a peak on the 42nd day. After 1 h and 2 h of ozone treatment, the content of H2O2 in C. pilosula decreased by 41.04% and 68.66%, respectively, compared with the control (Figure 7B).
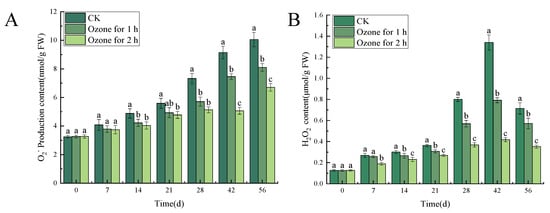
Figure 7.
Effects of ozone treatment on O2−. production content (A) and H2O2 content (B) in C. pilosula. Bars indicate standard error. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.5.2. Ozone Treatment Increased the Activities of NOX, SOD, CAT and POD in C. pilosula
The result showed that ozone treatment significantly (p < 0.05) increased the activities of NOX, SOD, CAT and POD. There were significant differences between ozone-treated and control groups in NOX activity in C. pilosula during different times after inoculation with P. expansum. NOX activity generally increased with the prolongation of storage time. The NOX activity in the ozone treatment 2 h group reached a peak of 126.25 U/g FW on the 56th day of storage, which was significantly higher than that in the control group (24.24%) and the ozone treatment 1 h group (10.10%), and NOX activity in the ozone treatment 1 h group was significantly higher than that in the control group (15.73%) (Figure 8A). Similar results were observed in the activities of SOD, CAT and POD. SOD activity gradually increased with the extension of storage time and was markedly higher in the ozone treatment 2 h group than in the control group (12.91%) and the 1 h treatment group (4.99%), respectively, on the 56th day (Figure 8B). CAT activity in the ozone treatment group reached a peak on the 42nd day of storage, and activity in the ozone treatment 2 h group was significantly higher than in the control group (26.46%) and ozone treatment 1 h group (13.06%) (Figure 8C). A similar changing trend was found in POD activity (Figure 8D).
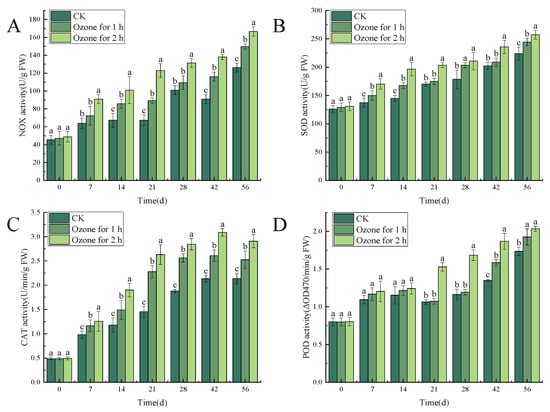
Figure 8.
The effect of ozone treatment on the activities of NOX (A), SOD (B), CAT (C) and POD (D) in C. pilosula. Bars indicate standard error. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.6. Effects of Ozone Treatment on Cell Membrane Permeability and MDA Content in C. pilosula
Compared with the untreated control group, the ozone treatment significantly (p < 0.05) reduced cell membrane permeability and MDA content of C. pilosula tissue. Cell membrane permeability and MDA content are employed to evaluate the cell membrane integrity of plant tissues. The cell membrane permeability in ozone-treated C. pilosula inoculated with P. expansum was significantly lower than it was in the control group. Similarly, the MDA content was also significantly lower than it was in the control group (p < 0.05), and the cell membrane permeability and MDA content decreased with the prolongation of ozone treatment time. After 56 days of inoculation, the cell membrane permeability in ozone-treated groups for 1 h and 2 h, respectively, decreased by 16.57% and 22.15%, when compared with the control group (Figure 9A). The MDA content in ozone-treated groups for 1 h and 2 h decreased by 32.35% and 38.87%, respectively, compared with the control group (Figure 9B).
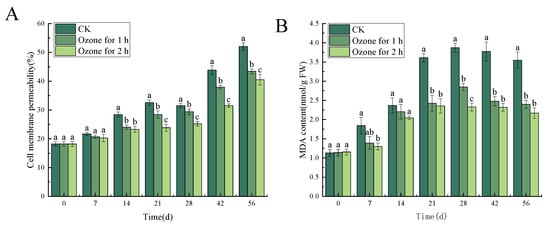
Figure 9.
Effects of ozone treatment on cell membrane permeability (A) and MDA content (B) in C. pilosula. Bars indicate standard error. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
4.1. Ozone Treatment Inhibits the Occurrence of the Blue Mold of C. pilosula
Our previous studies suggested that P. expansum is the main pathogen causing fresh C. pilosula blue mold during the postharvest storage period, which seriously impairs the quality of the fresh C. pilosula after harvest [19]. In this study, it was found that 2 mg L−1 ozone fumigation treatment significantly reduced the disease incidence of the blue mold of C. pilosula, inhibited the development of the blue mold of C. pilosula, reduced the accumulation of patulin, and alleviated the weight loss of C. pilosula to some extent. The longer the ozone treatment time, the more significant the effect that was observed. The PAT content in the ozone treatment for 2 h group was 1.63 µg/g on the 56th day of inoculation with P. expansum; compared with the control group, the PAT content decreased by 54.85% and the accumulation of toxins was greatly reduced but it still exceeded the maximum tolerable daily intake of 0.4 µg/kg stipulated by the Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) of the World Health Organization [25]. Luo et al. [15] also indicated that gaseous ozone application significantly reduced the disease incidence of postharvest kiwifruit, maintained high fruit hardness and prolonged fruit shelf life. Similarly, Li et al. [10] suggested that ozone treatment not only significantly inhibited the growth of potato dry rot caused by F. sulphureum, but also controlled diacetoxyscirpenol accumulation. Smila et al. [26] found that ozone water (1.5 mg L−1 for 2 min) treatment directly acted on P. expansum, P. digitatum, P. italicum, Botrytis cinerea and Rhizopus stolonifer, and the killing rate of the above spores was 95–100%, which showed that ozone treatment can reduce the degree of pathogen infection to the host, suppress the disease incidence, and, ultimately, control the occurrence of postharvest diseases by inhibiting the growth of pathogenic fungi. In fact, in addition to the direct inhibitory effect, ozone treatment also can stimulate ROS metabolism and induce hosts’ resistance, and, finally, control the disease development. It has been shown that appropriate concentration of ozone treatment can effectively delay the browning of mushrooms by increasing the activities of POD, SOD and CAT, maintain a high level of total phenols and soluble protein content, and reduce the total number of colonies, molds and yeasts in mushrooms [27].
4.2. Effect of Ozone Treatment on the Content of Main Effective Components in C. pilosula Inoculated with P. expansum
As we know, the medicinal value of C. pilosula is mainly reflected in its main active ingredients. The main active ingredients of C. pilosula are codonopatin, tangshenoside I, syringin, atractylenolide III, atractylenolide I, and atractylenolide II, which can enhance immunity, microcirculation and hematopoietic function, and have obvious improvement effects on diabetes, liver protection and base repair. In this study, P. expansum infection, while impairing the quality of C. pilosula and producing patulin, significantly influenced these active ingredients; in particular, P. expansum infection significantly reduced the content of codonopsis glycosides, which may be related to the consumption of codonopsis glycosides in C. pilosula tissue due to fungal growth and metabolism [28]. Xi et al. [29] found that ozone treatment effectively reduced the infection of pathogenic fungus to Angelica sinensis, inhibited the development of disease and reduced the accumulation of mycotoxins. Hu et al. [30] also found that the content of flavonoid glycosides in Radix Astragali was significantly reduced after Aspergillus flavus infection. Ozone application markedly inhibited P. expansum infection and effectively maintained the main active ingredients in C. pilosula. For instance, the content of codonopatin, tangshenoside I, syringin and atractylenolide III were well maintained, and the content of atractylenolide III in particular significantly increased; however, the contents of atractylenolide I and atractylenolide II decreased. We speculate that the active ingredients of atractylenolide I and atractylenolide II convert into atractylenolide III under the action of ozone. For instance, under the action of ozone, the hydrogen on the ninth double bond of atractylenolide I and the ninth carbon atom of atractylenolide II undergoes a series of chemical reactions to form hydroxyl groups, thereby obtaining atractylenolide III (Figure 10).
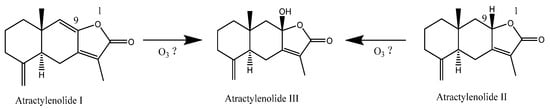
Figure 10.
Schematic diagram of active ingredient transformation of C. pilosula.
4.3. Effects of Ozone Treatment on ROS Metabolism in C. pilosula Tissue
Reactive oxygen species (such as O2−. and H2O2) is the by-product during the interaction between plant and pathogen, and ROS at the appropriate concentration acts as signal molecules to mediate downstream signaling pathways and regulate the host’s defense response [31]. However, high concentrations of ROS will attack the host’s plasma membrane structure and cause lipid peroxidation, which ultimately leads to cell membrane damage and pathogen invasion, eventually leading to disease occurrence. In the present study, the ozone treatment significantly reduced the contents of O2−. and H2O2 in C. pilosula inoculated with P. expansum, when compared with the untreated control group. The reason may be that, when P. expansum infected C. pilosula, the tissue of C. pilosula suffered biological stress, which resulted in the increase of the content of O2−. and H2O2. When the content of O2−. and H2O2 exceeds the range of the oxidative defense of C. pilosula, the lipid peroxidation of C. pilosula cell membrane leads to oxidative damage, reduces cell activity, accelerates the invasion of pathogen, and is conducive to the decay and deterioration of C. pilosula. However, ozone application, on the one hand, inhibits the growth of pathogens, and once the growth of pathogens is inhibited, the development of disease will be controlled. More importantly, ozone treatment stimulates ROS metabolism in plant tissue and maintains oxidative homeostasis. It is well known that NOX and SOD are the main enzymes that produce O2−. and H2O2. NOX mainly regulates the production of O2−., and SOD catalyzes the disproportionation reaction of O2−. to produce H2O2 and O2. CAT and POD further decompose H2O2 into H2O and O2, thus protecting cells from ROS damage. In this study, the activities of NOX, SOD, CAT and POD increased with the prolongation of storage time, and in the ozone treatment group were significantly higher than in the control group, which promoted the antioxidant system and maintained the steady state of C. pilosula tissue cells. This result is consistent with Lin et al. [32], who found that ozone treatment significantly increased the activities of SOD, CAT and POD, improved the resistance against disease, maintained postharvest quality and prolonged shelf life of postharvest Toona sinensis. Therefore, we infer that, although ozone stimulates the accumulation of ROS, at the same time, ozone application increased the activities of the antioxidant enzymes, which is attributed to eliminating or removing the excessive ROS, to avoid the membrane lipid peroxidation due to ROS excessive accumulation.
As we expected, ozone treatment reduced cell membrane permeability and MDA content of C. pilosula tissue. The result agreed with the report by Liang et al. [33], who found that ozone treatment maintained the hardness of postharvest tomatoes by reducing cell membrane permeability and inhibiting the accumulation of MDA, thereby prolonged the shelf life of tomatoes. Similarly, Wang et al. [34] also suggested that fresh-cut kiwifruit treated with 1 mg/L ozone for 10 min significantly inhibited the activity of cell wall polysaccharide degrading enzymes, reduced MDA content, maintained protopectin and cellulose levels, and delayed fruit softening and decay.
5. Conclusions
Ozone treatment at a concentration of 2 mg L−1 for 2 h significantly reduced the P. expansum infection, alleviated the weight loss of C. pilosula, and suppressed the accumulation of patulin. Ozone treatment maintained the contents of the main active ingredients of lobetyolin, lobetyolin I, syringin and atractylenolide III. The mechanism is attributed to ozone treatment stimulating ROS metabolism of C. pilosula tissues, enhanced the activity of SOD, NOX, POD and CAT, which avoided the oxidative stress caused by the excessive accumulation of O2−. and H2O2 in the tissues, better maintained the integrity of the cell membrane, consequently improved the resistance of C. pilosula against P. expansum, and inhibited the occurrence of postharvest blue mold and maintained the main active ingredients of C. pilosula. This study provides a theoretical basis for ozone treatment to inhibit the growth of P. expansum and control postharvest diseases of Chinese herbal medicine. In follow-up studies, the molecular mechanism of ozone treatment to suppress the growth of P. expansum, inhibit the accumulation of patulin and manage the blue mold of C. pilosula needs to be further studied.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jof10030163/s1, Figure S1: Chromatograms separation by HPLC for the main active ingredients in C. pilosula.; Table S1: Disease classification standard; Table S2: Mobile phase gradient elution procedure; Table S3: Principal component eigenvalues, variance contribution rate and cumulative variance contribution rate.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.C., Z.L., Q.L., D.Z. and H.X.; methodology, J.C.; software, J.C.; validation, Z.L., Q.L., D.Z. and S.S.; formal analysis, S.S. and Y.B.; investigation, S.S.; resources, H.X. and S.S.; data curation, J.C.; writing—original draft preparation, J.C. and Q.L.; writing—review and editing, H.X.; visualization, D.Z.; supervision, S.S. and Y.B.; project administration, H.X.; funding acquisition, H.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Project of Enterprise Supporting Plan (grant no. (2022CYZC-45), Education Department of Gansu Province), the youth supervisor supporting fund (grant no. (GAUQDFC-2021–09)) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. (32060566)).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lodi, R.S.; Dong, X.; Jiang, C.; Sun, Z.; Deng, P.; Sun, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Mesa, A.; Huang, X.; et al. Antimicrobial activity and enzymatic analysis of endophytes isolated from Codonopsis pilosula. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2023, 99, fiad071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.E.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, H.M.; Ahn, J.-H.; Jung, I.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Choi, J.-H.; Jang, D.S. Chemical constituents of the roots of Codonopsis lanceolata. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2018, 41, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Qi, Y.; Wei, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, P. The effective approach for the quality control of Codonopsis radix based on quality markers of immune activity. J. Sep. Sci. 2022, 45, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.Z.; Zhang, C.; Jing, L.R.; Feng, M.; Yang, Y. The structural characterization and immune modulation activities comparison of Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharide (CPPS) and Selenizing cpps (sCPPS) on mouse in vitro and vivo. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 160, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, X.; Fan, J.; Hou, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Han, J.; Hu, F. Isolation, characterization and immunomodulatory activity of oligosaccharides from Codonopsis pilosula. J. Funct. Foods. 2020, 72, 104070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.Z. Study on the pharmacological effects and clinical application of Dangshen Tonic. China Health Stand. Manag. 2015, 22, 130–131. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.M.; Liu, J.S.; Wang, M.; Cao, T.T.; Qi, Y.D.; Zhang, B.G.; Liu, H.T.; Sun, X.B.; Xiao, P.G. Quantitative and HPLC fingerprint analysis combined with chemometrics for quality evaluation of Codonopsis Radix processed with different methods. Chinese Herb. Med. 2019, 11, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, M.; Jo, S.R.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, M.S. UPLC-QTOF-MS-Based metabolomics and antioxidant capacity of Codonopsis lanceolata from different geographical origins. Foods 2023, 12, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ngea, G.L.N.; Godana, E.A.; Shi, Y.; Lanhuang, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; Yang, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H. Recent advances in Penicillium expansum infection mechanisms and current methods in controlling P. expansum in postharvest apples. Crit. Rev. Food. Sci. 2023, 63, 2598–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Cui, R.; Zhang, F.; Meng, X.H.; Liu, B.J. Current situation and future challenges of patulin reduction—A review. Food Control 2022, 138, 108996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.F.; Wei, W.N.; Zhou, W.Y.; Li, H.X.; Rao, S.Q.; Gao, L.; Yang, Z.Q. Prevention and detoxification of patulin in apple and its products: A review. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 110034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarron, E.; Pascale, G.W.; Thierry, A. Ozone treatments for preserving fresh vegetables quality: A Critical Review. Foods 2021, 10, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, T.Y.; Li, C.; Wu, Z.X. Effects of ozone treatment on pesticide residues in food: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Pandiselvam, R.; Kothakota, A.; Ishwarya, S.P.; Zalpouri, R.; Mahanti, N.K. Impact of ozone treatment on food polyphenols—A comprehensive review. Food Control 2022, 142, 109207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, A.W.; Bai, J.Q.; Li, R.; Fang, Y.M.; Li, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, L.; Liang, J.; Huang, T.Z.; Kou, L.P. Effects of ozone treatment on the quality of kiwifruit during postharvest storage affected by Botrytis cinerea and Penicillium expansum. J. Phytopathol. 2019, 167, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durairaj, K.; Velmurugan, P.; Vedhanayakisri, K.A.; Chang, W.-S.; Senthilkumar, P.; Choi, K.-M.; Lee, J.-H.; Oh, B.-T. Molecular and phenotypic characterization of pathogenic fungal strains isolated from ginseng root rot. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 104, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.L.; Zhang, R.; Xue, H.L.; Bi, Y. Ozone controls potato dry rot development and diacetoxyscirpenol accumulation by targeting the cell membrane and affecting the growth of Fusarium sulphureus. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2023, 199, 112222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarsaiya, S.; Jain, A.; Jia, Q.; Fan, X.K.; Shu, F.X.; Chen, Z.W.; Zhou, Q.N.; Shi, J.H.; Chen, J.S. Molecular identification of endophytic fungi and their pathogenicity evaluation against dendrobium nobile and dendrobium officinale. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Yang, X.; Xue, H.; Nan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Bi, Y.; Shang, S. Isolation of main pathogens causing postharvest disease in fresh Codonopsis pilosula during different storage stages and ozone control against disease and mycotoxin accumulation. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, G.; Bi, Y.; Li, Y.; Kou, Z.; Hu, L.; Ge, Y.; Wang, D. Overproduction of reactive oxygen species involved in the pathogenicity of Fusarium in potato tubers. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2014, 86, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.C.; Li, W.X.; Hu, X.L. Effect of micro-vacuum storage on active oxygen metabolism, internal browning and related enzyme activities in Laiyang pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Reld). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 72, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venisse, J.; Gullner, S.G.; Brisset, M.N. Evidence for the involvement of an oxidative stress in the initiation of infection of pear by Erwinia amylovora. Plant Physiol. 2001, 125, 2164–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, J.; Lin, H.; Lin, M.; Lin, Y.; Wang, H.; Hung, Y.-C. Salicylic acid treatment suppresses Phomopsis longanae Chi-induced disease development of postharvest longan fruit by modulating membrane lipid metabolism. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 164, 111168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Han, L.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Nie, J. Dynamic degradation of penconazole and its effect on antioxidant enzyme activity and malondialdehyde content in apple fruit. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 300, 111053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Du, Y.M.; Jiao, W.X.; Fu, M.R. Effects of fruit tissue pH value on the Penicillium expansum growth, patulin accumulation and distribution. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, 16881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simla, S.; Boontang, B.; Harakotr, B. Anthocyanin content, total phenolic content, and antiradical capacity in different ear components of purple waxy corn at two maturation stages. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2016, 10, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chang, M.C.; Meng, J.L.; Liu, J.Y.; Cheng, Y.F.; Feng, C.P. Effect of ozone treatment on the quality and enzyme activity of Lentinus edodes during cold storage. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, 14557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Q.; Chen, Y.; Zong, Y.Y.; Xu, X.D.; Tian, S.P. Dissection of patulin biosynthesis, spatial control and regulation mechanism in Penicillium expansum. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 1124–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.H.; Yang, D.Y.; Xue, H.L.; Liu, Z.G.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Shang, S. Isolation of the main pathogens causing postharvest disease in fresh Angelica sinensis during different storage stages and impacts of ozone treatment on disease development and mycotoxin production. Toxins 2023, 15, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.C.; Kong, W.J.; Liu, Q.T.; Liu, H.M.; Zhao, G.; Yang, M.H. Study on the influence of Aspergillus flavus contamination on the quality of Radix Astragali and its storage condition optimization. Mod. Chin. Med. 2015, 17, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Shetty, N.P.; Jørgensen, H.L.; Jensen, J.D.; Collinge, D.B.; Shetty, H.S. Roles of reactive oxygen species in interactions between plants and pathogens. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2008, 121, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H.; Chen, C.K.; Luo, H.X.; Xu, W.T.; Zhang, H.J.; Tian, J.J.; Ju, R.H.; Wang, L.Q. The combined effect of ozone treatment and polyethylene packaging on postharvest quality and biodiversity of Toona sinensis (A.Juss.) M.Roem. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 154, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.Z.; Ji, L.L.; Chen, C.K.; Wang, C.R. Effects of ozone treatment on the storage quality of post-harvest tomato. Int. J. Food Eng. 2018, 14, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Li, Y.X.; Yang, S.H.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Gao, S.Y.; Wu, Z.X. Mechanism of ozone treatment in delayed softening of fresh-cut kiwifruit during storage. Postharvest Bio. Technol. 2023, 201, 112469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).