Abstract
The development of Natural Language Processing applications tailored for diverse Arabic-speaking users requires specialized Arabic corpora, which are currently lacking in existing Arabic linguistic resources. Therefore, in this study, a multidialectal parallel Arabic corpus is built, focusing on the travel and tourism domain. By leveraging the text generation and dialectal transformation capabilities of Large Language Models, an initial set of approximately 100,000 parallel sentences was generated. Following a rigorous multi-stage deduplication process, 50,010 unique parallel sentences were obtained from Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) and five major Arabic dialects—Saudi, Egyptian, Iraqi, Levantine, and Moroccan. This study presents the detailed methodology of corpus generation and refinement, describes the characteristics of the generated corpus, and provides a comprehensive statistical analysis highlighting the corpus size, lexical diversity, and linguistic overlap between MSA and the five dialects. This corpus represents a valuable resource for researchers and developers in Arabic dialect processing and AI applications that require nuanced contextual understanding.
1. Introduction
Arabic is among the most widely spoken languages globally, with over 450 million speakers in nearly 25 countries across the Middle East and North Africa [1]. Despite its global reach and significance, Arabic is one of the morphologically richest languages [2]. While Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) functions as a formal written and spoken language used in education, official communications, and the media, it is rarely used in daily conversations. Most Arabic speakers communicate in regional dialects, such as Egyptian, Levantine, Gulf, Iraqi, and Maghrebi Arabic, which vary widely across geographical, social, and cultural lines [3,4]. These dialects differ substantially from MSA and each other in terms of phonology, syntax, morphology, and lexicon. This variation is so pronounced that speakers of different dialects occasionally struggle to understand one another, leading to issues of mutual unintelligibility [5].
This linguistic diversity poses a significant challenge to the development of inclusive and dialect-aware Natural Language Processing (NLP) systems [6]. Digital applications, such as voice assistants, customer support bots, and search engines, are increasingly expected to interact with users in their native dialects. However, most existing Arabic NLP resources focus primarily on MSA, leading to poor generalization and degraded performance when models are exposed to dialectal inputs in real-world scenarios. The absence of high-quality, large-scale, domain-specific corpora for Arabic dialects is a key bottleneck in advancing this field.
Over the past two decades, many Arabic language resources have been developed to support NLP tasks, including the Arabic Gigaword corpus [7], CALLHOME Egyptian Arabic corpus [8], and MADAR corpus [9]. LDC [10] and ELRA [11] provide most resources for different languages, including Arabic and its dialects, and each has made significant contributions to Arabic language processing. While foundational, many efforts either exclude dialects or focus narrowly on a single variety, often relying on manual data collection and annotation processes which are time-consuming and difficult to scale [12]. Furthermore, the lack of domain specificity in the existing corpora limits their practical applicability in sectors such as tourism, healthcare, and e-commerce, where user interactions are highly contextual.
Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) offer promising alternatives for corpus construction [13,14,15,16]. These models exhibit exceptional abilities to generate coherent and contextually appropriate texts across various languages and dialects, facilitating rapid synthetic data creation with minimal manual intervention [17,18,19,20]. Prior studies (e.g., [21]) have explored the use of LLMs for text generation in low-resource languages. However, their utility in structured, multidialectal Arabic corpus creation remains underexplored [22,23].
Despite these advantages, the use of LLMs has limitations [24]. As they can generate incorrect content, humans must validate their outputs to confirm domain relevance and check linguistic authenticity.
This study addresses this gap by demonstrating how LLMs can be effectively leveraged to generate high-quality idiomatic dialectal variants aligned with MSA. We built a parallel, multidialectal Arabic corpus focusing on the “travel and tourism” domain—an application area that presents a rich context for studying dialectal variation owing to its frequent use of spontaneous, user-generated queries involving bookings, destinations, and local services. By leveraging LLMs to generate consistent translations across MSA and major Arabic dialects, the proposed corpus addresses several limitations of existing resources. It provides multidialectal coverage, ensures domain specificity, can be efficiently scaled with minimal manual intervention, and supports downstream tasks such as machine translation. Moreover, classification and dialect identification enhance the robustness and inclusivity of the Natural Language Understanding (NLU) system.
This study details the corpus-building methodology, including prompt design, LLM configuration, and generation strategy, along with a detailed refinement process that ensures uniqueness, consistency, and linguistic diversity. A comprehensive statistical analysis of the corpus was conducted by examining the sentence length, lexical overlap, and dialectal divergence. The proposed dataset addresses a critical gap in Arabic NLP resources by offering scalable multidialectal and domain-specific data to support various downstream tasks, including machine translation, classification, and dialect identification.
2. Methodology
This study adopted a systematic, multi-stage methodology to build a high-quality, parallel, multidialectal Arabic corpus tailored to the travel and tourism domain. We employed Gemini 1.5 pro [25], a multilingual LLM, because of its multilingual performance and effective handling of Arabic and its dialects. We selected Gemini because it consistently produces stable output formatting and offers easily controlled generation parameters and uniform tokenization. This simplifies creating dialectal corpora. Compared to other LLMs such as GPT, Claude, and LLaMA, Gemini LLM presents stable output formatting, convenient generation parameters, and consistent tokenization across dialects, making it highly appropriate for generating reliable and high-quality synthetic dialectal corpora.
Gemini offers powerful support for structured outputs and function-calling supports stable corpus creation [26,27]. Moreover, Gemini architecture has Mixture-of-Experts (MoE), which helps scale to larger token budgets and multimodal inputs, improving efficiency for long-context generation [27].
Recent studies, including [28,29], demonstrate that Gemini performs competitively on the Arabic language and its dialect. This indicates its appropriateness to create synthetic Arabic dialects corpora. Although GPT (with its different versions) remains great in general reasoning tasks [30], Gemini’s structure makes it the most suitable model for the goals of this study.
This approach leverages the generative capabilities of LLMs for initial data creation and follows rigorous quality control procedures—including dialectal transformation, incremental data management, and deduplication—to ensure the reliability, consistency, and linguistic diversity of the corpus.
2.1. Domain Specification
The “travel and tourism” domain was selected owing to its high practical relevance and its growing prominence in interactive NLP applications, such as virtual assistants, booking systems, and multilingual customer service. To define the domain scope, a taxonomy of subtopics was constructed by analyzing publicly available travel corpora, tourism websites, and multilingual customer service queries. The thematic taxonomy ensured comprehensive topical coverage, encompassing hotel and flight bookings, tourist attractions and activities, transportation and navigation, restaurants and dining experiences, common traveler interactions (e.g., asking for directions and inquiring about prices or services), and the resolution of typical travel-related issues. This taxonomy guided the development of a keyword set and scenario bank, forming the foundation for prompt engineering in the initial data generation phase.
2.2. Initial Sentence Generation
The initial dataset was automatically generated in MSA using the Gemini LLM, which offers robust Arabic language support. Prompts were manually designed to elicit domain-relevant sentences featuring diverse linguistic styles and sentence structures (e.g., interrogative, imperative, and descriptive). Special attention was paid to syntactic and lexical diversity, with prompt variations designed to avoid repetitive sentence structures and vocabulary. The generated data included realistic user queries, service-related requests, informative statements, and context-specific utterances.
2.3. Dialectal Transformation
Following the generation of sentences in MSA, each sentence was converted into five primary Arabic dialects via additional prompting of the Gemini LLM. The target dialects were Saudi, Egyptian, Iraqi, Levantine (with emphasis on Syrian and Lebanese), and Moroccan. These five dialects were selected to provide broad geographic and linguistic coverage within the Arab world as they are widely utilized and studied in Arabic dialect-related NLP research, with available linguistic resources. This selection maintains a balanced foundation for future expansion to add additional dialects. The transformation prompts were designed to preserve the original semantic content while ensuring authentic dialectal usage. Each dialectical version reflects the localized grammatical structures, idiomatic expressions, and vocabulary typical of the target variety. Where necessary, the prompts included speaker role definitions and context scenarios to improve pragmatic alignment.
2.4. Deduplication and Data Refinement
Considering the inherent risk of content overlap owing to LLM sampling behavior, a multi-stage deduplication process was employed to ensure that the final corpus only included unique and semantically distinct entries. The initial generation comprised approximately 100,000 parallel sentence sets, each containing an MSA sentence and its corresponding dialectal transformation, ensuring diverse dialectal variants for each MSA sentence.
2.4.1. Stage 1: MSA-Based Filtering and Deduplication
The first stage focused on filtering and deduplicating MSA sentences by performing a first-pass deduplication process on the MSA set, which identified and removed redundant MSA sentences. This ensured a duplicate-free MSA corpus and established a reliable foundation for subsequent dialectal transformations.
2.4.2. Stage 2: Parallel Entry Deduplication
The second stage of deduplication ensured that each unique MSA sentence retained only one complete parallel entry, including all dialectal variants (five dialects in total). This step was crucial to ensure consistency and uniqueness, as it prevented the redundancy of multiple dialectal variants for the same MSA sentence. Consequently, only one parallel set of MSA and dialectal variants was maintained for each unique MSA sentence.
2.4.3. Final Output:
After applying the multi-stage deduplication process, the final dataset comprised 50,010 fully parallel and unique sentences. Each row in the dataset contains a single MSA sentence and its five corresponding dialectal variants.
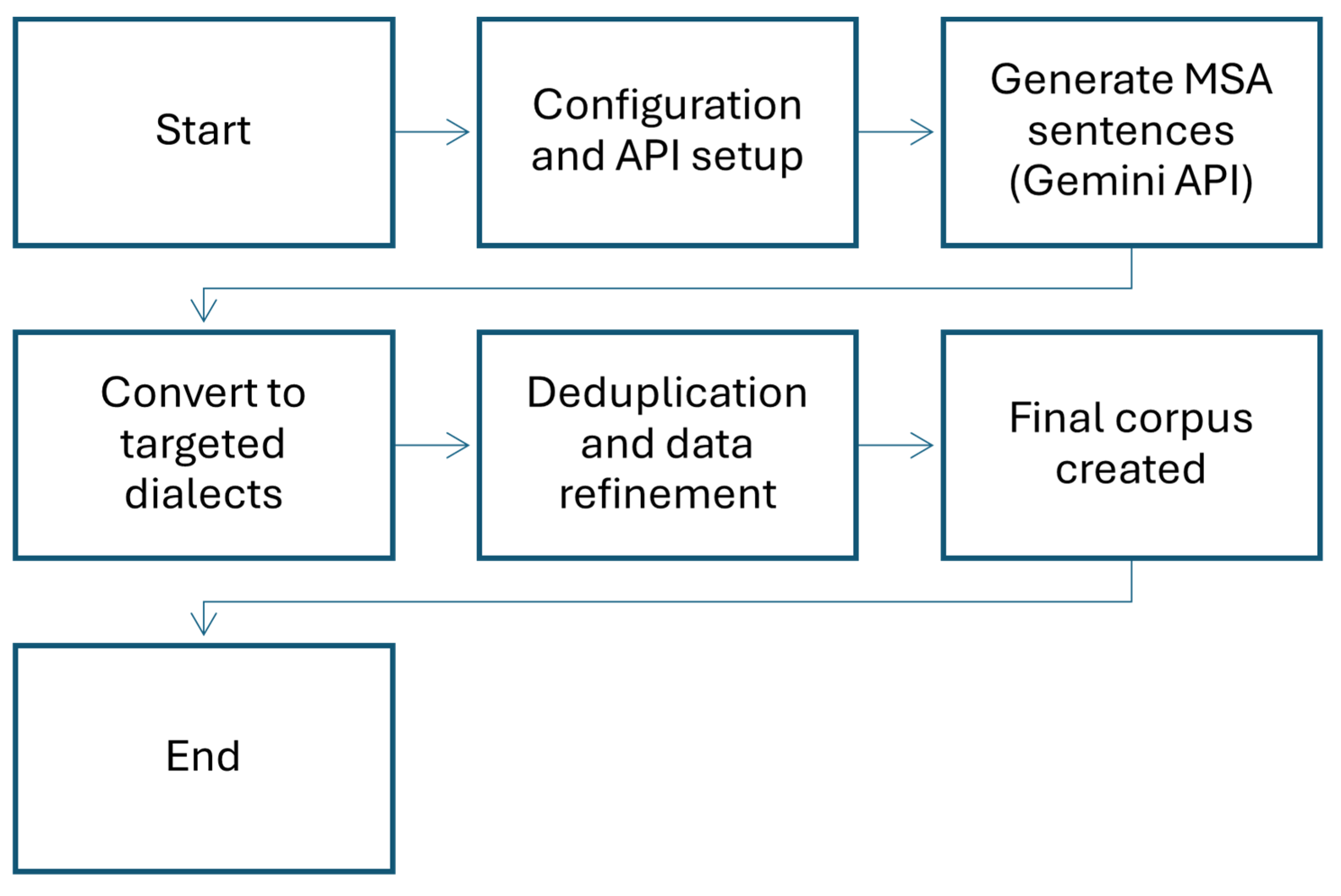
This refined data filtering and validation approach is critical for achieving a high-quality, multidialectal resource that minimizes noise and redundancy while preserving linguistic diversity and cross-dialectal comparability. Figure 1 illustrates the overall process, starting from configuration and ending with corpus creation.
Figure 1.
Flowchart illustrating the overall process.
3. Results
The constructed corpus comprised 50,010 parallel sentence sets, each aligned across six Arabic dialects—MSA, Saudi, Egyptian, Iraqi, Levantine, and Moroccan. Table 1 shows examples of selected sentences from the resulting corpus. Each MSA sentence was idiomatically translated into its dialectal counterparts using prompt-based LLM generation to ensure semantic alignment and natural usage for each variety. The resulting corpus constitutes a valuable multilingual resource for studying cross-dialectal variation, training multidialectal NLP systems, and improving the performance of dialect-specific applications in the travel and tourism domain.

Table 1.
Examples of selected sentences from the resulting corpus.
3.1. Corpus Characteristics
The final corpus exhibited notable characteristics in terms of scale, linguistic coverage, and thematic focus. Starting with approximately 100,000 generated sentences, a rigorous multi-stage deduplication process was applied to eliminate redundancies and ensure semantic uniqueness. This filtering yielded a clean and balanced set of 50,010 sentence sets, each containing a single MSA sentence and five dialectal variants (as shown in Table 1).
For dialectal coverage, the corpus provides broad dialectal coverage across major Arabic-speaking regions in North Africa and the Middle East, ensuring a wide linguistic representation. Thematic consistency was maintained throughout the corpus by focusing exclusively on the “travel and tourism” sector, ensuring that vocabulary and expressions reflected domain-relevant scenarios, such as bookings, navigation, accommodations, and local inquiries.
3.2. Preliminary Statistical Analysis of the Corpus
Although each variety included an equal number of sentence pairs (n = 50,010), the preliminary analysis revealed variations in lexical richness and sentence structure across dialects. The Moroccan dialect showed the highest lexical diversity in the corpus (TTR = 3.68%) and the longest average sentence length, indicating both a richer vocabulary and more verbose expressions compared to the other dialects. Conversely, the MSA sentences tended to be shorter and more syntactically concise (as Table 2 shows).

Table 2.
Preliminary statistical metrics of the multidialectal corpus.
3.2.1. Frequency Distribution of Words and N-Grams
A frequency analysis of unigrams and bigrams further underscores the lexical divergence between MSA and dialects. While certain thematic elements are preserved across varieties, such as common verbs of intent or travel-related nouns, the surface forms differ substantially. Examples include MSA ‘أريد’ (I want) and ‘هل’ (Is/Are?) vs. dialectal variants ‘أبغى’ (Saudi), ‘عايز’ (Egyptian), ‘بدي’ (Levantine), and ‘بغيت’ (Moroccan), which are used extensively in their respective dialects. The bigram and trigram analysis reflected similar patterns. The phrase ‘أبحث عن فندق’ (I search for a hotel) in MSA appeared with the following dialectal transformations: ‘أدوّر عن فندق’ (Saudi/Iraqi), ‘بدوّر على فندق’ (Egyptian), ‘عم دوّر على فندق’ (Levantine), and ‘كنقلّب على أوطيل/فندق’ (Moroccan). Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7 show the most frequent words in the corpus. The size of each word corresponds to its frequency, allowing for intuitive recognition of which words dominate the corpus. Such an analysis can identify key dialectal markers, frequent function words, and culturally specific expressions that distinguish this type from Standard Arabic or other dialects.

Figure 2.
A visualization of the most frequent words in MSA.

Figure 3.
A visualization of the most frequent words in the Egyptian dialect.

Figure 4.
A visualization of the most frequent words in the Iraqi dialect.

Figure 5.
A visualization of the most frequent words in the Levantine dialect.

Figure 6.
A visualization of the most frequent words in the Moroccan dialect.

Figure 7.
A visualization of the most frequent words in the Saudi dialect.
3.2.2. Sentence Length Distribution Analysis
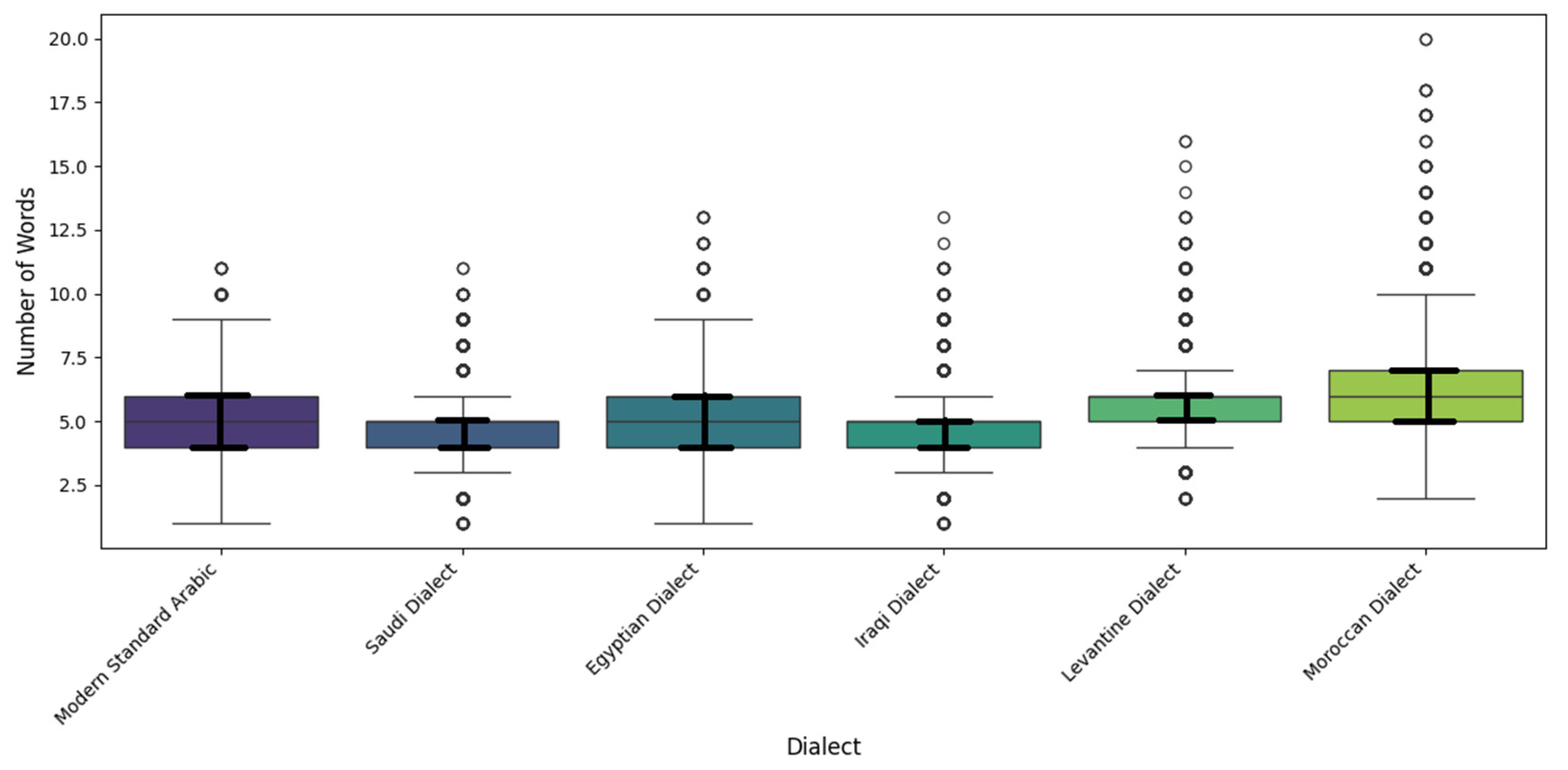
An in-depth analysis of sentence length distributions revealed low variability across dialects, with sentence lengths clustering around the mean. Minimum lengths ranged from 0 to 1 tokens (with edge cases likely due to cleaning artifacts), and maximum lengths ranged from 11 (MSA and Saudi dialect) to 19 tokens (Moroccan). The standard deviations for sentence lengths in the tokens ranged from 1.24 to 1.55. The Moroccan dialect notably stands out for its relatively longer and more variable sentence structures (with an average of 6.24 tokens and a maximum length of 19 tokens), as shown in Table 2 and Figure 8.
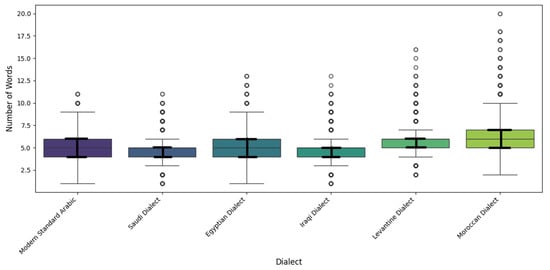
Figure 8.
Sentence length distribution across dialects.
3.2.3. Lexical Overlap Between MSA and Dialects
A lexical overlap analysis was performed to quantify the degree of vocabulary shared between MSA and each dialect. Table 3 presents the percentages of shared and unique words in each dialect compared to MSA.

Table 3.
Lexical overlap between MSA and dialects.
Table 3 shows a clear gradient in lexical divergence. The Saudi dialect shares the most vocabulary with MSA, whereas the Moroccan dialect shares the least. Moreover, nearly 6500 tokens in Moroccan Arabic are unique to the dialect and do not appear in the MSA column. The most frequent unique Moroccan terms include ‘بغيت’ (I want), ‘واش’ (Is/Are?), ‘شي’ (a/some), ‘غادي’ (going to), and ‘كاين’ (there is), reflecting high lexical distinctiveness. These fundamental differences have direct implications on the development of NLP models, particularly for lexically distant dialects (such as Moroccan), where greater linguistic variability poses additional challenges for model accuracy and generalization.
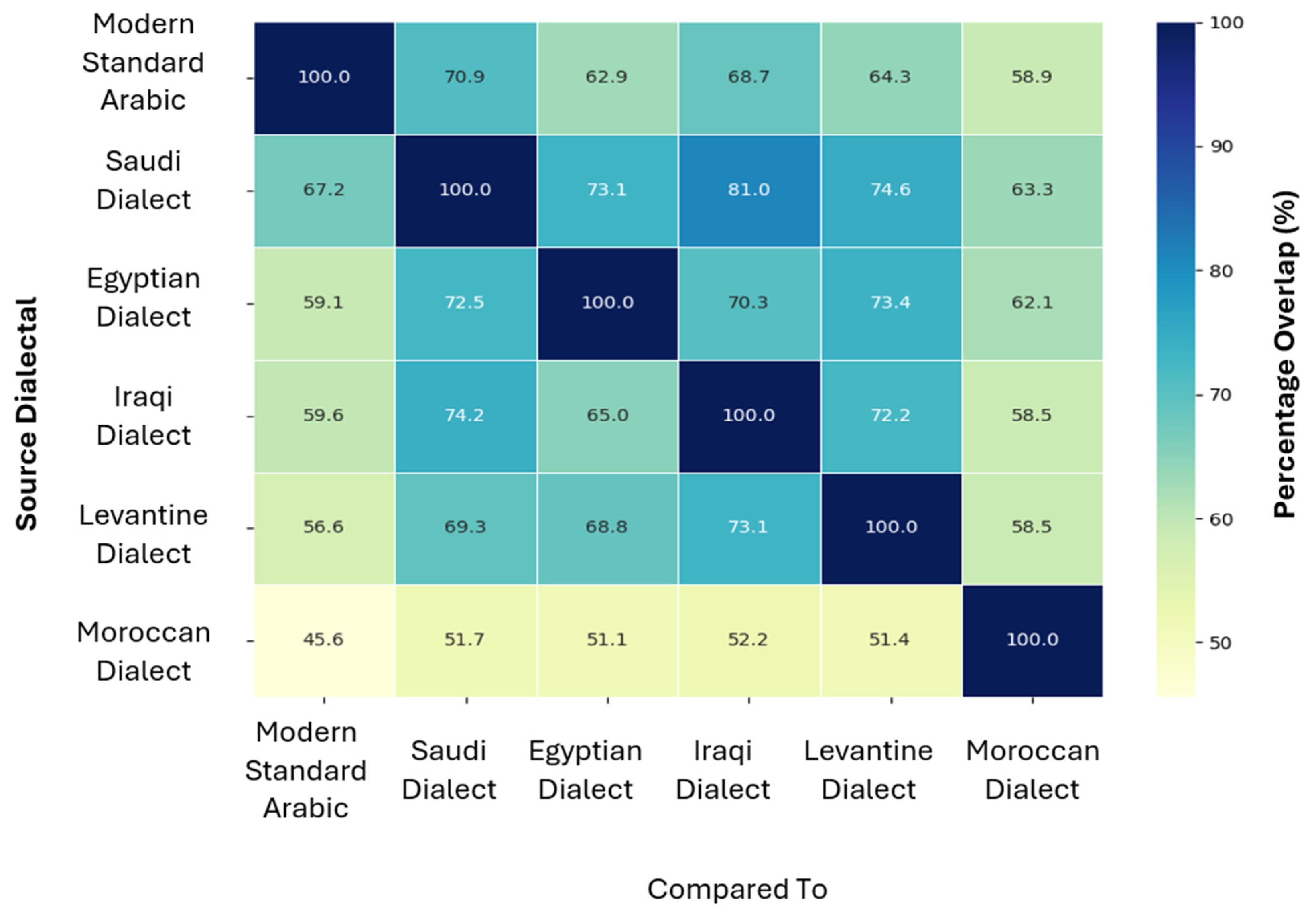
Figure 9 shows a lexical overlapping heat map. Among MSA and the dialects, Iraqi and Saudi dialects showed the highest mutual overlap (81% and 74.2%, respectively), indicating a shared vocabulary base. Conversely, Moroccan exhibited greater lexical distances from MSA.
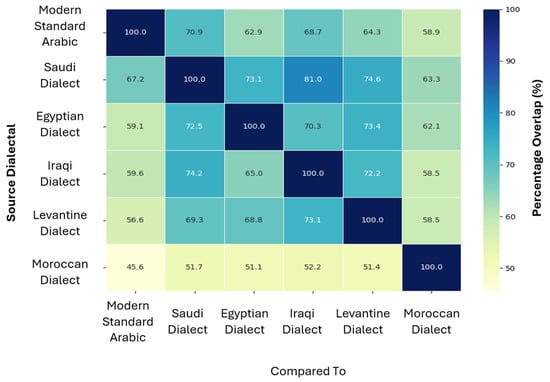
Figure 9.
Lexical overlap between dialects.
4. Discussion
The construction and analysis of this multidialectal Arabic corpus offer valuable insights into the current capabilities and future potential of large-scale domain-specific language resource development, particularly for under-represented Arabic dialects. By focusing on the travel and tourism domain, this study highlights both the practical requirements of real-world applications and the linguistic diversity that robust NLP systems must accommodate.
One of the key contributions of this study is that it demonstrates the scalability and practicality of using the Gemini 1.5 pro LLM for the generation and transformation of Arabic text [25]. This aligns with broader trends in the use of LLMs for zero- and few-shot learning, where instruction-tuned LLMs can produce coherent, dialect-appropriate, and semantically faithful outputs with minimal task-specific fine-tuning [31]. In contrast to traditional corpus construction methods that rely on labor-intensive annotation or semi-automated bootstrapping [32,33], this LLM-based approach allows for rapid, controlled generation of parallel sentence sets with high linguistic fidelity.
The prompting strategies employed consistent semantic alignment across dialects while allowing for natural, idiomatic variations. This aligns with prior research showing that instruction-tuned models can be effectively directed to produce structured, coherent multilingual outputs [34,35]. However, inherent issues in LLM sampling—particularly content redundancy—necessitate multi-stage deduplication, and purification steps are critical for addressing the inherent repetition and redundancy issues that can increase with LLM outputs [36]. The final corpus, comprising 50,010 unique parallel sentences, demonstrated that high-volume, domain-targeted corpus creation using current-generation LLMs is feasible and effective. This approach can be extended to other domains, dialects, or languages.
To ensure the reliability of the generated corpora, a data quality validation process was applied. A native Arabic speaker and a bilingual annotator reviewed a random sample of the dataset manually. They checked each sentence pair checked according to some of the main criteria (adequacy and consistency alongside fluency and coherence), as mentioned in [37].
Additionally, automated checks were performed to detect duplicated entries and formatting inconsistencies. The evaluation results showed that the selected samples met the required quality standards, confirming the overall reliability of the synthetic corpus. However, translated sentences can have several variants, as there are many ways to say the same thing in Arabic, which is a common challenge in all languages.
4.1. Dialectal Coverage and Linguistic Diversity
The analysis revealed clear lexical, syntactic, and morphological distinctions between the five dialects represented in the corpus. A lexical overlap analysis confirmed the established linguistic intuitions: dialects such as Saudi and Iraqi share a higher proportion of vocabulary with MSA, whereas Moroccan diverges substantially. These findings have direct implications for the development of novel NLP models and highlight the necessity of dialect-specific training data, confirming the importance of multidialectal corpora in enabling robust and inclusive Arabic NLP tools [6,38].
Additionally, the observed variations in sentence length and token diversity indicate different expressive strategies across dialects. Moroccan Arabic consistently features longer and more lexically diverse constructions for semantically equivalent content. This aligns with previous linguistic studies on the Moroccan divergence from both MSA and other spoken varieties [39]. These distinctions highlight the need for dialect-sensitive modeling strategies, especially when managing structurally and lexically distinct dialects. Traditional corpus-building methods often fail to capture such diversity on scale, reinforcing the value of the proposed LLM-based methodology [40,41].
This study uses an LLM to create a parallel dialectal Arabic corpus that is synthetic but linguistically balanced, with focus on a specific domain, i.e., travel and tourism.
Many studies (e.g., [15]) have exploited GPT or other LLMs to generate synthetic data and have used LLM prompts to generate and evaluate an English corpus. Our work focuses on enriching an existing resource in the context of Arabic, a morphologically rich and highly diverse language, and its dialects.
Our methodology aligns with [19,20], as they use synthetic data to overcome data scarcity in low-resource contexts. However, to build a dataset, we use prompts and domains rather than a pseudo-parallel translation dataset.
As the dialects reflect cultural differences, the corpora in this research align with [21], which focuses on the cultural alignment of Large Language Models.
To summarize, while existing studies emphasize automated creation, scalability, or bias analysis, our results illustrate that using LLM prompts to generate synthetic data can produce a linguistically and morphologically rich Arabic dialect corpus.
4.2. Limitations
Despite these strengths, this study has several limitations. First, although the LLM was effective in generating dialectal transformations, minor inconsistencies or overgeneralizations may exist, particularly in dialects with lower digital representations or ambiguous orthographic standards (e.g., Moroccan or Iraqi Arabic). Second, dialect boundaries are often fluid, and intra-dialectal variations are not explicitly captured in this corpus. While the current selection of dialects provides wide regional coverage, future work must expand the dialectal granularity by including subregional varieties. Although it has strong capabilities in the context of Arabic and its dialects, Gemini demonstrates limited sensitivity to few dialectal nuances, often normalizing informal expressions or misunderstanding region-specific languages. It also displays, in very few places, inconsistencies in handling dialectal spellings and code-switching between Arabic and its dialects.
This corpus provides a valuable resource for advancing Arabic NLP and improving language technologies in diverse Arabic-speaking communities, including dialect identification, MSA-to-dialect translation, dialect chatbots, ASR for dialects, and dialect summarization tasks.
In our future work, we will focus on expanding the corpus size and include other domains such as healthcare, customer service chatbots, law, and education. We will also incorporate additional dialects and sub-regional dialectal variations and use the corpus to evaluate dialectal language models. In addition, we will perform deeper linguistic analyses focused on phenomena such as code-switching.
5. Conclusions
This study proposed an approach that combines the generative capabilities of LLMs with a rigorous deduplication process to construct a multidialectal parallel Arabic corpus in the travel and tourism domain. The final dataset consisted of 50,010 unique parallel sentences aligned across MSA and five major Arabic dialects—Saudi, Egyptian, Iraqi, Levantine, and Moroccan. This high-quality corpus advances our understanding of Arabic linguistic variation and supports the development of dialect-aware NLP systems.
The corpus was refined using a multi-stage deduplication process, reducing the initial dataset of 100,000 sentences into a clean and consistent set of 50,010 parallel entries. The data exhibit significant lexical diversity across dialects, particularly in vocabulary and sentence structure. Notably, the Moroccan dialect demonstrated the highest lexical divergence from MSA, whereas the Saudi and Egyptian dialects showed closer alignment. These differences highlight the challenges in and opportunities for developing NLP models that can handle the full spectrum of Arabic dialects.
Our analysis revealed clear patterns in sentence length and lexical overlap. While sentence lengths were relatively consistent across dialects, the Moroccan dialect featured longer and more variable sentence constructions. Lexical overlap analysis revealed the substantial divergence between MSA and dialects such as Moroccan, which contain unique vocabulary elements that are absent in MSA. These findings have important implications for future NLP tasks.
The corpora are freely available for researchers under an open-source license. With appropriate processing, these corpora can be used to train models for dialect-specific applications, such as sentiment analysis models, chatbots, NER systems, and dialect identification technologies.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during the current study are deposited in the Zenodo repository and can be accessed via https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17776617 (accessed on 1 December 2025). The copyright of the dataset remains with the author (© 2025), and it is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0). All analyses were conducted using publicly available Python 3 libraries, as described in Section 2.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- United Nations Arabic Language Day. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/observances/arabiclanguageday?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Habash, N. Introduction to Arabic Natural Language Processing; Hirst, G., Ed.; Synthesis Lectures on Human Language Technologies; Morgan & Claypool: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Alsudais, A.; Alotaibi, W.; Alomary, F. Similarities between Arabic Dialects: Investigating Geographical Proximity. Inf. Process Manag. 2022, 59, 102770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, M. Diglossia in Arabic A Comparative Study of the Modern Standard Arabic and Egyptian Colloquial Arabic. Glob. J. Hum.-Soc. Sci. 2012, 12, 23–35. [Google Scholar]
- Bouamor, H.; Alshikhabobakr, H.; Mohit, B.; Oflazer, K. A Human Judgement Corpus and a Metric for Arabic MT Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qata, 25–29 October 2014; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2014; pp. 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelali, A.; Darwish, K.; Durrani, N.; Mubarak, H. Farasa: A Fast and Furious Segmenter for Arabic. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Demonstrations, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–17 June 2016; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, R.; Graff, D.; Chen, K.; Kong, J.; Maeda, K. Arabic Gigaword, 5th ed.; Abacus Data Network: Del Mar, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Canavan, A.; Zipperlen, G.; Graff, D. CALLHOME Egyptian Arabic Speech; Linguistic Data Consortium: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bouamor, H.; Habash, N.; Salameh, M.; Zaghouani, W.; Rambow, O.; Abdulrahim, D.; Obeid, O.; Khalifa, S.; Eryani, F.; Erdmann, A.; et al. MADAR: A Large-Scale Multi-Arabic Dialect Applications and Resources Project. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2018), Miyazaki, Japan, 7–12 May 2018; European Language Resources Association (ELRA): Miyazaki, Japan, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- LDC Linguistic Data Consortium. Available online: https://www.ldc.upenn.edu/ (accessed on 5 October 2025).
- ELRA ELRA Catalogue of Language Resources. Available online: https://catalogue.elra.info/en-us/ (accessed on 5 October 2025).
- Besdouri, F.Z.; Zribi, I.; Belguith, L.H. Arabic Automatic Speech Recognition: Challenges and Progress. Speech Commun. 2024, 163, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, C.; Marttinen Larsson, M. Large Corpora and Large Language Models: A Replicable Method for Automating Grammatical Annotation. Linguist. Vanguard 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, S. Using Early LLMs for Corpus Linguistics: Examining ChatGPT’s Potential and Limitations. Appl. Corpus Linguist. 2024, 4, 100089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busker, T.; Choenni, S.; Bargh, M.S. Exploiting GPT for Synthetic Data Generation: An Empirical Study. Gov. Inf. Q. 2025, 42, 101988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea-Trigo, M.; Botella-López, C.; Martínez-del-Amor, M.Á.; Álvarez-García, J.A.; Soria-Morillo, L.M.; Vegas-Olmos, J.J. Synthetic Corpus Generation for Deep Learning-Based Translation of Spanish Sign Language. Sensors 2024, 24, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Li, L.; Ma, Z.; Lee, S.; Yu, H.; Hemphill, L. A Bibliometric Review of Large Language Models Research from 2017 to 2023. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2024, 15, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, H.; Khan, A.U.; Qiu, S.; Saqib, M.; Anwar, S.; Usman, M.; Akhtar, N.; Barnes, N.; Mian, A. A Comprehensive Overview of Large Language Models. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2025, 16, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imankulova, A.; Sato, T.; Komachi, M. Filtered Pseudo-Parallel Corpus Improves Low-Resource Neural Machine Translation. ACM Trans. Asian Low-Resour. Lang. Inf. Process. 2020, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YirMibEşoğlu, Z.; Güngör, T. Morphologically Motivated Input Variations and Data Augmentation in Turkish-English Neural Machine Translation. ACM Trans. Asian Low-Resour. Lang. Inf. Process. 2023, 22, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlKhamissi, B.; ElNokrashy, M.; Alkhamissi, M.; Diab, M. Investigating Cultural Alignment of Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Bangkok, Thailand, 11–16 August 2024; Long papers. Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2024; Volume 1, pp. 12404–12422. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Shenaifi, N.; Azmi, A.M.; Hosny, M. Advancing AI-Driven Linguistic Analysis: Developing and Annotating Comprehensive Arabic Dialect Corpora for Gulf Countries and Saudi Arabia. Mathematics 2024, 12, 3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Haff, K.; Jarrar, M.; Hammouda, T.; Zaraket, F. Curras + Baladi: Towards a Levantine Corpus. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth Language Resources and Evaluation Conference (LREC 2022), Marseille, France, 20–25 June 2022; European Language Resources Association: Marseille, France, 2022; pp. 769–778. [Google Scholar]
- Shumailov, I.; Shumaylov, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Papernot, N.; Anderson, R.; Gal, Y. AI Models Collapse When Trained on Recursively Generated Data. Nature 2024, 631, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Google Gemini. Available online: https://gemini.google.com/ (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- Team, G.; Anil, R.; Borgeaud, S.; Alayrac, J.-B.; Yu, J.; Soricut, R.; Schalkwyk, J.; Dai, A.M.; Hauth, A.; Millican, K.; et al. Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.11805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, P.; Lei, V.I.; Burnell, R.; Bai, L.; Gulati, A.; Tanzer, G.; Vincent, D.; Pan, Z.; Wang, S.; Lenc, C.; et al. Gemini 1.5: Unlocking Multimodal Understanding across Millions of Tokens of Context. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.05530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldawsari, M.; Dawood, O. AraEventCoref: An Arabic Event Coreference Dataset and LLM Benchmarks. ACM Trans. Asian Low-Resour. Lang. Inf. Process. 2025, 24, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, M.A.; Abouzahir, C.; Kharouf, L.; Al-Eisawi, W.; Shamout, F.E.; Habash, N. MedArabiQ: Benchmarking Large Language Models on Arabic Medical Tasks. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning for Healthcare (ML4HC), Rochester, MN, USA, 15 August 2025; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Sallam, M.; Al-Mahzoum, K.; Almutawaa, R.A.; Alhashash, J.A.; Dashti, R.A.; AlSafy, D.R.; Almutairi, R.A.; Barakat, M. The performance of OpenAI ChatGPT-4 and Google Gemini in virology multiple-choice questions: A comparative analysis of English and Arabic responses. BMC Res. Notes 2024, 17, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.X.; Zhou, K.; Li, J.; Tang, T.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y.; Min, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Z.; et al. A Survey of Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.18223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeman, K.; Lee, M. Automatic Building of Arabic Multi Dialect Text Corpora by Bootstrapping Dialect Words. In Proceedings of the Communications, Signal Processing, and their Applications (ICCSPA), 2013 1st International Conference on Communications, Signal Processing and Their Applications, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 12–14 February 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Biemann, C.; Shin, S.-I.; Choi, K.-S. Semiautomatic Extension of CoreNet Using a Bootstrapping Mechanism on Corpus-Based Co-Occurrences. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Computational Linguistics—COLING’04, Geneva, Switzerland, 23–27 August 2004; Association for Computational Linguistics: Morristown, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 1227–1232. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, H.W.; Hou, L.; Longpre, S.; Zoph, B.; Tay, Y.; Fedus, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Dehghani, M.; Brahma, S.; et al. Scaling Instruction-Finetuned Language Models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.11416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Bommasani, R.; Lee, T.; Tsipras, D.; Soylu, D.; Yasunaga, M.; Zhang, Y.; Narayanan, D.; Wu, Y.; Kumar, A.; et al. Holistic Evaluation of Language Models. Transactions on Machine Learning Research (TMLR). arXiv 2023, arXiv:2211.09110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.B.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language Models Are Few-Shot Learners. Proc. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. (NeurIPS) 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- van der Lee, C.; Gatt, A.; van Miltenburg, E.; Wubben, S.; Krahmer, E. Best Practices for the Human Evaluation of Automatically Generated Text. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Natural Language Generation, Tokyo, Japan, 29 October–1 November 2019; van Deemter, K., Lin, C., Takamura, H., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Tokyo, Japan, 2019; pp. 355–368. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Twairesh, N.; Al-Khalifa, H.; Al-Salman, A.; Al-Ohali, Y. AraSenTi-Tweet: A Corpus for Arabic Sentiment Analysis of Saudi Tweets. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 117, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouamor, H.; Habash, N.; Oflazer, K. A Multidialectal Parallel Corpus of Arabic. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’14), Reykjavik, Iceland, 26 May 2014; European Language Resources Association (ELRA): Paris, France; pp. 1240–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Bowker, L.; Pearson, J. Working with Specialized Corpora; Studies in Corpus Linguistics; John Benjamins Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 6, ISBN 9789027222774. [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair, J. Corpus, Concordance, Collocation; Describing English Language; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1991; ISBN 9780194371445. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).