Large Language Models in Healthcare and Medical Applications: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Review Design and Rationale
2.2. Literature Search Strategy
2.3. Study Selection Criteria
2.3.1. Inclusion Criteria
- Peer-reviewed articles, conference papers, and preprints focusing on LLM applications in healthcare or medicine.
- Publications from 2015 onward.
- Studies describing, evaluating, or benchmarking LLMs in clinical, educational, research, or administrative healthcare contexts.
2.3.2. Exclusion Criteria
- Non-English publications.
- Studies unrelated to healthcare or lacking sufficient methodological detail.
- Editorials, commentaries, and duplicate records.
2.4. Data Extraction and Synthesis
- Source: Refers to the original study or publication cited in the review, providing the foundational reference for the findings presented.
- LLMs Used: Specifies the large language models or AI systems analyzed or implemented in the respective studies (e.g., GPT-4, Med-PaLM, BioGPT, LLaMA, etc.).
- Highlight: Summarizes the core focus or contributions of the study, such as advancements in clinical decision support, diagnostic reasoning, or medical education.
- Application Area: Indicates the specific domain or healthcare context in which the LLMs were applied, such as diagnostics, patient care, clinical decision support, medical education, or drug discovery.
2.5. Limitations of the Review
3. Background on Large Language Models
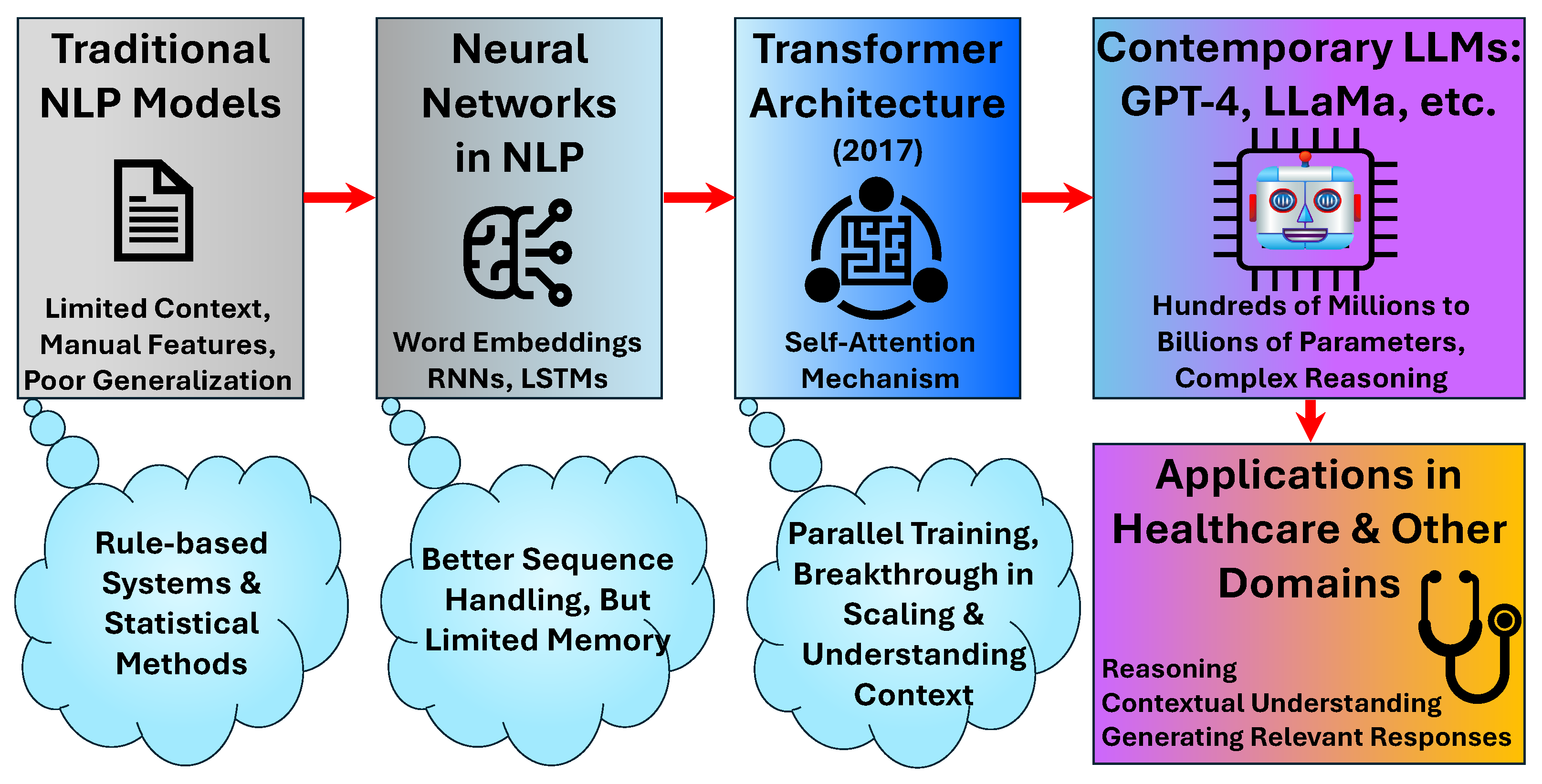
3.1. Evolution and Architectural Foundations
3.2. Foundational Models and Healthcare Adaptation
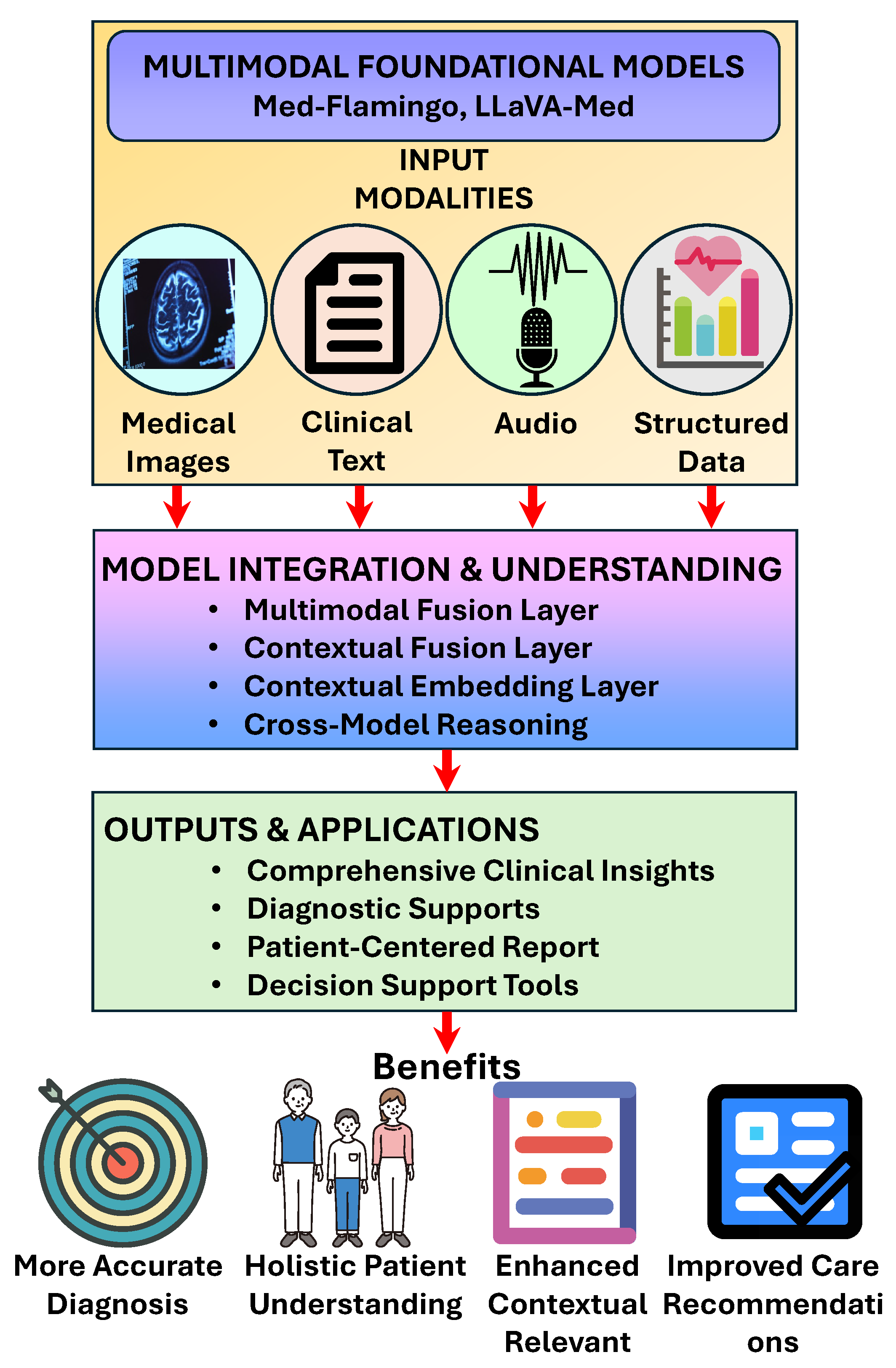
3.3. Multimodal Capabilities
4. Methodology of LLMs in Healthcare
4.1. Data Acquisition and Pre-Training
4.2. Fine-Tuning and Adaptation
4.3. Prompt Engineering and In-Context Learning
5. Applications of LLMs in Healthcare
5.1. Clinical Decision Support and Diagnostics
5.2. Medical Education and Training
5.3. Patient Care and Communication
5.4. Medical Literature Analysis and Research Support
5.5. Drug Discovery and Development
5.6. Radiology and Medical Imaging
5.7. Clinical Documentation and Administrative Support
6. Evaluation Frameworks and Benchmarks
6.1. Performance Metrics and Assessment Approaches
6.2. Human-Centered Evaluation
6.3. Reproducibility and Validation Challenges
6.4. Empirical Evaluation and Benchmarking
6.5. User-Centered and Clinician-Involved Studies
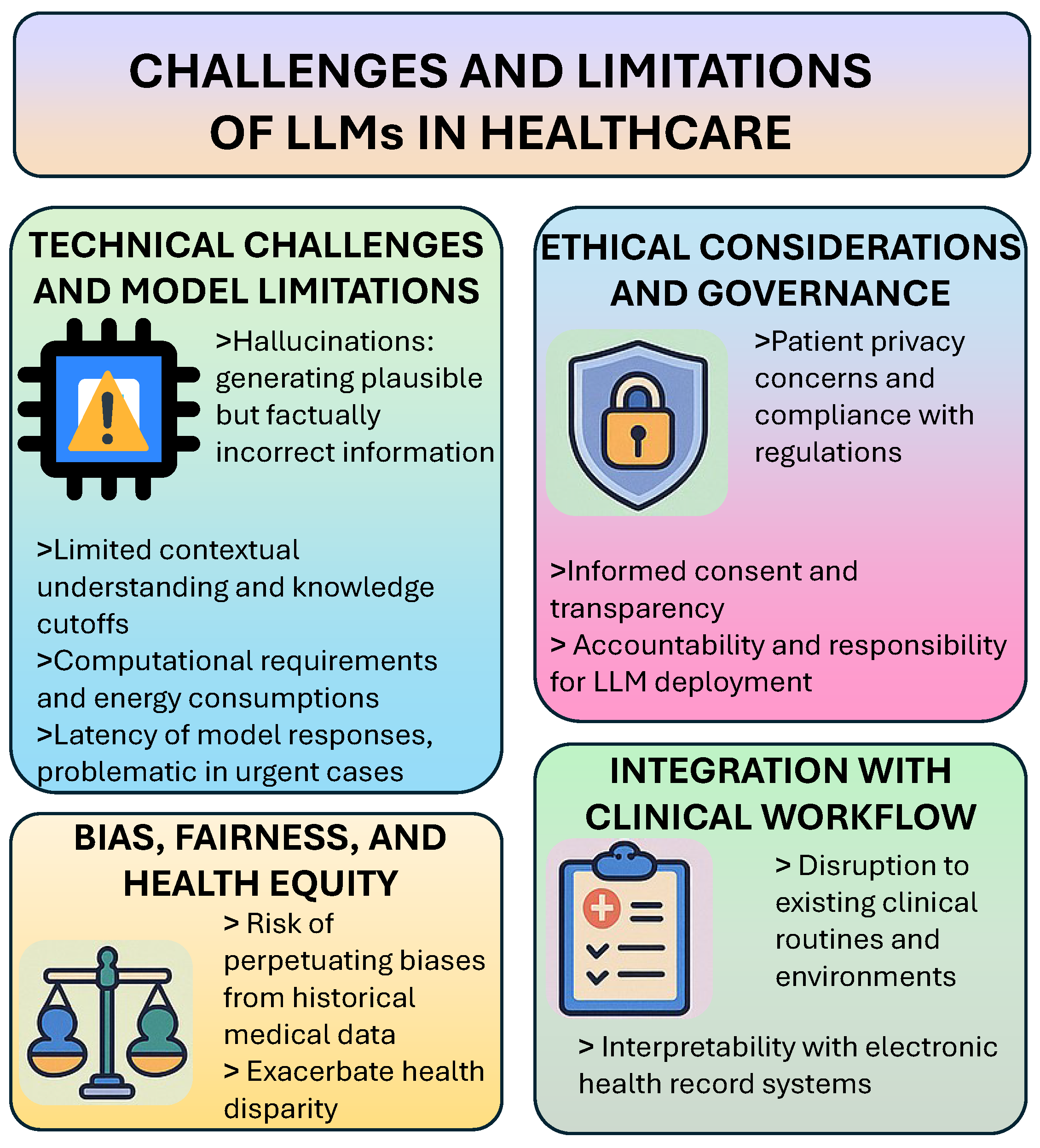
7. Challenges and Limitations
7.1. Data Diversity and Heterogeneity in Healthcare
- Curated and Representative Datasets: Building and utilizing datasets that reflect multiple languages, cultures, and demographic groups is essential. This includes collecting multilingual medical corpora and integrating data from varied healthcare environments [76].
- Domain Adaptation and Fine-Tuning: LLMs can be fine-tuned on region- or institution-specific data to capture local nuances in language and practice, improving model relevance and accuracy for specific settings [76].
7.2. Technical Challenges and Model Limitations
7.3. Ethical Considerations and Governance
7.4. Explainability and Interpretability of LLM Outputs
- Chain-of-Thought Prompting: This technique encourages models to articulate their reasoning step by step, mirroring clinical decision-making and making conclusions more transparent and verifiable [77].
- Attention Visualization: Visualization tools highlight which parts of the input data the model focused on, providing insights into the decision-making process and identifying potential errors or concerns [78].
7.5. Bias, Fairness, and Health Equity
7.6. Integration with Clinical Workflow
8. Future Directions
8.1. Multimodal and Domain-Specific Advancements
8.2. Human–AI Collaboration Models
8.3. Regulatory Frameworks and Standard Development
8.4. Patient-Centered Design and Participatory Approaches
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnsen, M. Large Language Models (LLMs); Maria Johnsen: Trondheim, Norway, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Yan, X.; Zhang, K.; Liu, D.; Cui, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Cao, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; et al. The application of large language models in medicine: A scoping review. Iscience 2024, 27, 109713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, S. Large language models in medical and healthcare fields: Applications, advances, and challenges. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazi, Z.A.; Peng, W. Large Language Models in Healthcare and Medical Domain: A Review. Informatics 2024, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Meng, X.; Yan, X.; Ji, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; et al. Revolutionizing health care: The transformative impact of large language models in medicine. J. Med. Internet Res. 2025, 27, e59069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, F.; Hoffmann, L.; Rueger, C.; van Dijk, E.H.; Kader, R.; Ortiz-Prado, E.; Makowski, M.R.; Saba, L.; Hadamitzky, M.; Kather, J.N.; et al. Current applications and challenges in large language models for patient care: A systematic review. Commun. Med. 2025, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arksey, H.; O’malley, L. Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 2005, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levac, D.; Colquhoun, H.; O’brien, K.K. Scoping studies: Advancing the methodology. Implement. Sci. 2010, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Mao, R.; Lin, Q.; Ruan, Y.; Lan, X.; Feng, M.; Cambria, E. A survey of large language models for healthcare: From data, technology, and applications to accountability and ethics. Inf. Fusion 2025, 118, 102963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spotnitz, M.; Idnay, B.; Gordon, E.R.; Shyu, R.; Zhang, G.; Liu, C.; Cimino, J.J.; Weng, C. A survey of clinicians’ views of the utility of large language models. Appl. Clin. Inf. 2024, 15, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xue, X.; Gao, P.; Jin, Z.; Hu, M.; Wu, Y.; Ying, X. A survey of datasets in medicine for large language models. Intell. Robot. 2024, 4, 457–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wu, C.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Yuan, Y. A Survey of LLM-based Agents in Medicine: How far are we from Baymax? arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.11211. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhou, Z.; Lyu, H.; Wang, Z. Large language models-powered clinical decision support: Enhancing or replacing human expertise? Intell. Med. 2025, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Bao, P.; Yuan, J.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. Large language models illuminate a progressive pathway to artificial intelligent healthcare assistant. Med. Plus 2024, 1, 100030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jussupow, E.; Spohrer, K.; Heinzl, A.; Gawlitza, J. Augmenting medical diagnosis decisions? An investigation into physicians’ decision-making process with artificial intelligence. Inf. Syst. Res. 2021, 32, 713–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojesomo, A.; Seghier, M.; Hadjileontiadis, L.; AlShehhi, A. Revolutionizing Disease Diagnosis with Large Language Models: A Systematic Review. Res. Sq. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karttunen, P. Large Language Models in Healthcare Decision Support. Bachelor’s Thesis, Tampere University, Tampere, Finland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Almubark, I. Exploring the Impact of Large Language Models on Disease Diagnosis. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 8225–8238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, J.C.L.; Jin, L.; Elangovan, K.; Lim, G.Y.S.; Lim, D.Y.Z.; Sng, G.G.R.; Ke, Y.; Tung, J.Y.M.; Zhong, R.J.; Koh, C.M.Y.; et al. Development and testing of a novel large language model-based clinical decision support systems for medication safety in 12 clinical specialties. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.01741. [Google Scholar]
- Castaneda, C.; Nalley, K.; Mannion, C.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Blake, P.; Pecora, A.; Goy, A.; Suh, K.S. Clinical decision support systems for improving diagnostic accuracy and achieving precision medicine. J. Clin. Bioinform. 2015, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, A.; PourNejatian, N.; Shin, H.C.; Smith, K.E.; Parisien, C.; Compas, C.; Martin, C.; Costa, A.B.; Flores, M.G.; et al. A large language model for electronic health records. npj Digit. Med. 2022, 5, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, T.; Su, Q.; Liu, Y.; Kang, C.; Lyu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Nie, Y.; Pan, Y. Application of large language models in disease diagnosis and treatment. Chin. Med. J. 2025, 138, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holley, K.; Mathur, M. LLMs and Generative AI for Healthcare: The Next Frontier; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Jiang, S.; Xu, L.; Liu, K.; Li, H.; Xing, G.; Chen, H.; Jiang, X.; Yan, Z. Drhouse: An llm-empowered diagnostic reasoning system through harnessing outcomes from sensor data and expert knowledge. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2024, 8, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, B.; Viswanath, K. Integration of machine learning and deep learning in medical and healthcare education. In Applications of Parallel Data Processing for Biomedical Imaging; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2024; pp. 148–174. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Alrazaq, A.; AlSaad, R.; Alhuwail, D.; Ahmed, A.; Healy, P.M.; Latifi, S.; Aziz, S.; Damseh, R.; Alrazak, S.A.; Sheikh, J.; et al. Large language models in medical education: Opportunities, challenges, and future directions. JMIR Med. Educ. 2023, 9, e48291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safranek, C.W.; Sidamon-Eristoff, A.E.; Gilson, A.; Chartash, D. The role of large language models in medical education: Applications and implications. JMIR Med. Educ. 2023, 9, e50945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, H.C.; Upperman, J.S.; Robinson, J.R. A systematic review of large language models and their implications in medical education. Med. Educ. 2024, 58, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez, T.M.; Xu, Y.; Boudreau, J.D.; Kow, A.W.C.; Bello, F.; Van Phuoc, L.; Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Leung, G.K.K.; Lan, Y.; et al. Harnessing the potential of large language models in medical education: Promise and pitfalls. J. Am. Med. Inf. Assoc. 2024, 31, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.Q.; Feng, L.Y.; Ye, J.G.; Zou, J.G.; Zheng, Y.F. Accelerating the integration of ChatGPT and other large-scale AI models into biomedical research and healthcare. MedComm Future Med. 2023, 2, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almansour, M.; Alfhaid, F.M. Generative artificial intelligence and the personalization of health professional education: A narrative review. Medicine 2024, 103, e38955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domrös-Zoungrana, D.; Rajaeean, N.; Boie, S.; Fröling, E.; Lenz, C. Medical Education: Considerations for a Successful Integration of Learning with and Learning about AI. J. Med. Educ. Curric. Dev. 2024, 11, 23821205241284719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, F.; Wang, X.; Fu, Q.; Ren, W. Ethical considerations and fundamental principles of large language models in medical education. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e60083. [Google Scholar]
- Lema, K.g. Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) for Medical Education and Training. AfricArxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.; Sukumaran, R.; Cook, T.S. Efficient healthcare with large language models: Optimizing clinical workflow and enhancing patient care. J. Am. Med. Inf. Assoc. 2024, 31, 1436–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Tan, T.F.; Lu, W.; Thirunavukarasu, A.J.; Ting, D.S.W.; Liu, N. Large language models in health care: Development, applications, and challenges. Health Care Sci. 2023, 2, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ZareiNejad, M.; Tavana, P. Application of Generative AI in Patient Engagement. In Application of Generative AI in Healthcare Systems; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; p. 119. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, X.; Yao, B.; Zhang, S.; Rogers, E.; Intille, S.; Shara, N.; Gao, G.G.; Wang, D. Talk2Care: Facilitating asynchronous patient-provider communication with large-language-model. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.09357. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, R.; Alkhnbashi, O.S.; Hammoudeh, M. Optimizing Large Language Models for Arabic Healthcare Communication: A Focus on Patient-Centered NLP Applications. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2024, 8, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannhardt, N. Improving Patient Access and Comprehension of Clinical Notes: Leveraging Large Language Models to Enhance Readability and Understanding. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Djulbegovic, B.; Guyatt, G.H. Progress in evidence-based medicine: A quarter century on. Lancet 2017, 390, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, W.; Donald, A. Evidence based medicine: An approach to clinical problem-solving. BMJ 1995, 310, 1122–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazdin, A.E. Evidence-based treatment and practice: New opportunities to bridge clinical research and practice, enhance the knowledge base, and improve patient care. Am. Psychol. 2008, 63, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rane, N.L.; Tawde, A.; Choudhary, S.P.; Rane, J. Contribution and performance of ChatGPT and other Large Language Models (LLM) for scientific and research advancements: A double-edged sword. Int. Res. J. Mod. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2023, 5, 875–899. [Google Scholar]
- Nydén, M.; Bika, D. New Medicines Design, Development and Commercialization in the Era of AI. In Proceedings of the LMDE Conference, Athens, Greece, 19–20 June 2023; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 137–155. [Google Scholar]
- Doron, G.; Genway, S.; Roberts, M.; Jasti, S. New Horizons: Pioneering Pharmaceutical R&D with Generative AI from lab to the clinic–an industry perspective. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.12482. [Google Scholar]
- Harrer, S.; Menard, J.; Rivers, M.; Green, D.V.; Karpiak, J.; Jeliazkov, J.R.; Shapovalov, M.V.; del Alamo, D.; Sternke, M.C. Artificial intelligence drives the digital transformation of pharma. In Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Practice; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 345–372. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Mastouri, M.; Zhang, Y. Accelerating drug discovery, development, and clinical trials by artificial intelligence. Med 2024, 5, 1050–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doron, G.; Genway, S.; Roberts, M.; Jasti, S. Generative AI: Driving productivity and scientific breakthroughs in pharmaceutical R&D. Drug Discov. Today 2024, 30, 104272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Chen, L.; Ke, L.; Dou, B.; Zhang, C.; Feng, H.; Zhu, Y.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, B.; Wei, G. A review of transformers in drug discovery and beyond. J. Pharm. Anal. 2024, 101081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwal, A.; Ansari, A.; Ahmad, I.; Azad, A.K.; Kumarasamy, V.; Subramaniyan, V.; Wong, L.S. Generative artificial intelligence in drug discovery: Basic framework, recent advances, challenges, and opportunities. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1331062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Huang, N.; Li, G.; Li, X.; Wu, J.C.; Yang, S. Artificial intelligence in drug development. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.h.; Lu, Z.h.; Wang, T.; Liu, F. Large language models facilitating modern molecular biology and novel drug development. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1458739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oniani, D.; Hilsman, J.; Zang, C.; Wang, J.; Cai, L.; Zawala, J.; Wang, Y. Emerging opportunities of using large language models for translation between drug molecules and indications. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W. Machine Learning for Drug Discovery and Beyond. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Champaign, IL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- AlSaad, R.; Abd-Alrazaq, A.; Boughorbel, S.; Ahmed, A.; Renault, M.A.; Damseh, R.; Sheikh, J. Multimodal large language models in health care: Applications, challenges, and future outlook. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e59505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbareia, R.; Omar, M.; Soffer, S.; Glicksberg, B.S.; Nadkarni, G.N.; Klang, E. Visual-textual integration in LLMs for medical diagnosis: A preliminary quantitative analysis. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 27, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Wei, J.; Sun, L.; Yu, B.; Chang, G.; Liu, D.; Zhang, S.; Yao, Z.; Xu, M.; Bu, L. A survey on advancements in image-text multimodal models: From general techniques to biomedical implementations. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 178, 108709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, L.; Lu, X.; Xu, Y. The role of large language models in medical image processing: A narrative review. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2023, 14, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutbi, M. Artificial intelligence-based applications for bone fracture detection using medical images: A systematic review. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayaz, M.; Khan, M.; Saqib, M.; Khelifi, A.; Sajjad, M.; Elsaddik, A. MedVLM: Medical Vision-Language Model for Consumer Devices. In IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Jin, Y.; Guan, Z.; Li, T.; Qin, Y.; Qian, B.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.F.; et al. Visual–language foundation models in medicine. Vis. Comput. 2024, 41, 2953–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, N.; Ora, M.; Agarwal, A.; Yang, T.; Bathla, G. A Review of The Opportunities and Challenges with Large Language Models in Radiology: The Road Ahead. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, T.; Basch, P.; Barr, M.; Yackel, T.; Medical Informatics Committee of the American College of Physicians. Clinical documentation in the 21st century: Executive summary of a policy position paper from the American College of Physicians. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhou, J.; Gao, Z.; Hua, W.; Fan, L.; Yu, H.; Hagen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Assimes, T.L.; Hemphill, L.; et al. A scoping review of using large language models (LLMs) to investigate electronic health records (EHRs). arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.03066. [Google Scholar]
- Saadat, S.; Khalilizad Darounkolaei, M.; Qorbani, M.; Hemmat, A.; Hariri, S. Enhancing Clinical Documentation with AI: Reducing Errors, Improving Interoperability, and Supporting Real-Time Note-Taking. Infosci. Trends 2025, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, B.; Boyle, A.; Marfo, N.; Tangamornsuksan, W.; Steen, J.P.; McKechnie, T.; Lee, Y.; Mayol, J.; Antoniou, S.A.; Thirunavukarasu, A.J.; et al. Large Language Models for Chatbot Health Advice Studies: A Systematic Review. JAMA Netw. Open 2025, 8, e2457879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A. A Survey on Security and Privacy of Multimodal LLMs—Connected Healthcare Perspective. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 4–8 December 2023; pp. 1807–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, K.; Tu, T.; Gottweis, J.; Sayres, R.; Wulczyn, E.; Amin, M.; Hou, L.; Clark, K.; Pfohl, S.R.; Cole-Lewis, H.; et al. Toward expert-level medical question answering with large language models. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhimani, M.; Miller, A.; Agnew, J.D.; Ausin, M.S.; Raglow-Defranco, M.; Mangat, H.; Voisard, M.; Taylor, M.; Bierman-Lytle, S.; Parikh, V.; et al. Real-World Evaluation of Large Language Models in Healthcare (RWE-LLM): A New Realm of AI Safety & Validation. medRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, T.Y.C.; Sivarajkumar, S.; Kapoor, S.; Stolyar, A.V.; Polanska, K.; McCarthy, K.R.; Osterhoudt, H.; Wu, X.; Visweswaran, S.; Fu, S.; et al. A framework for human evaluation of large language models in healthcare derived from literature review. npj Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Cao, W.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, P.; Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Tian, F. Human-centered design and evaluation of AI-empowered clinical decision support systems: A systematic review. Front. Comput. Sci. 2023, 5, 1187299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirunavukarasu, A.J.; Ting, D.S.J.; Elangovan, K.; Gutierrez, L.; Tan, T.F.; Ting, D.S.W. Large language models in medicine. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1930–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Garadi, M.; Mungle, T.; Ahmed, A.; Sarker, A.; Miao, Z.; Matheny, M.E. Large Language Models in Healthcare. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.04748. [Google Scholar]
- Milasheuski, U.; Barbieri, L.; Tedeschini, B.C.; Nicoli, M.; Savazzi, S. On the impact of data heterogeneity in federated learning environments with application to healthcare networks. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Conference on Artificial Intelligence (CAI), Singapore, 25–27 June 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1017–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, E.; Parwani, A.; Baig, M.M.; Singh, R. Challenges and barriers of using large language models (LLM) such as ChatGPT for diagnostic medicine with a focus on digital pathology—A recent scoping review. Diagn. Pathol. 2024, 19, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehandru, N.; Miao, B.Y.; Almaraz, E.R.; Sushil, M.; Butte, A.J.; Alaa, A. Evaluating large language models as agents in the clinic. npj Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswat, D.; Bhattacharya, P.; Verma, A.; Prasad, V.K.; Tanwar, S.; Sharma, G.; Bokoro, P.N.; Sharma, R. Explainable AI for healthcare 5.0: Opportunities and challenges. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 84486–84517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaddad, A.; Peng, J.; Xu, J.; Bouridane, A. Survey of explainable AI techniques in healthcare. Sensors 2023, 23, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, H.W.; Ooi, C.P.; Seoni, S.; Barua, P.D.; Molinari, F.; Acharya, U.R. Application of explainable artificial intelligence for healthcare: A systematic review of the last decade (2011–2022). Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 226, 107161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasu, P.N.; Sandhya, N.; Jhaveri, R.H.; Raut, R. From blackbox to explainable AI in healthcare: Existing tools and case studies. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, 8167821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Source | LLMs Used | Highlight | Application Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| M. Johnsen [1] | GPT-4, LLaMA | Overview of foundational LLM concepts and applications | General overview |
| X. Meng et al. [2] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Med-PaLM | Comprehensive scoping review of LLM applications in medicine | Medical applications |
| D. Wang and S. Zhang [3] | ChatGPT, GPT-3.5, GPT-4 | Review of applications, advances, and challenges of LLMs in healthcare | Medical and healthcare fields |
| Z. A. Nazi and W. Peng [4] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Med-PaLM | Comprehensive review of LLMs in healthcare and medicine | Healthcare and medical domain |
| K. Zhang et al. [5] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Med-PaLM | Analysis of transformative impact of LLMs on healthcare | Medicine and healthcare transformation |
| F. Busch et al. [6] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Claude | Systematic review of LLM applications and challenges in patient care | Patient care |
| K. He et al. [9] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Med-PaLM, Llama-2 | Survey focusing on data, technology, applications, accountability and ethics | Healthcare ethics and accountability |
| M. Spotnitz et al. [10] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Claude | Survey of clinicians’ perspectives on LLM utility | Clinical utility assessment |
| D. Zhang et al. [11] | ChatGPT, Med-PaLM, GatorTron | Survey of medical datasets for training and evaluating LLMs | Medical datasets |
| W. Wang et al. [12] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Claude, BioMistral | Survey of LLM-based agents in medicine | Medical agents |
| J. Li et al. [13] | ChatGPT, Med-PaLM, Med-Gemini | Analysis of whether LLMs enhance or replace human expertise | Clinical decision support |
| M. Yuan et al. [14] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Claude | Progressive pathway towards AI healthcare assistants | Healthcare assistants |
| E. Jussupow et al. [15] | Early GPT models, BERT | Investigation of physicians’ decision-making with AI | Medical diagnosis |
| A. Bojesomo et al. [16] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Med-PaLM | Systematic review of LLMs for disease diagnosis | Disease diagnosis |
| P. Karttunen [17] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Llama-2 | Analysis of LLMs for healthcare decision support | Healthcare decision support |
| I. Almubark [18] | ChatGPT, Med-PaLM, Med-Gemini | Impact of LLMs on disease diagnosis | Disease diagnosis |
| J. C. L. Ong et al. [19] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Claude | Development of LLM-based CDSS for medication safety | Medication safety |
| C. Castaneda et al. [20] | Pre-LLM AI systems | CDSS for diagnostic accuracy and precision medicine | Diagnostic accuracy |
| X. Yang et al. [21] | GatorTron | Development of LLM specifically for electronic health records | Electronic health records |
| X. Yang et al. [22] | ChatGPT, Med-PaLM, Med-Gemini | Applications of LLMs in diagnosis and treatment | Disease diagnosis and treatment |
| K. Holley and M. Mathur [23] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Claude, Gemini | Exploration of LLMs and generative AI as next frontier in healthcare | Healthcare innovation |
| B. Yang et al. [24] | DrHouse system | LLM-empowered diagnostic reasoning system using sensor data and expert knowledge | Diagnostic reasoning |
| B. Santhosh and K. Viswanath [25] | GPT-3.5, GPT-4, BERT | Integration of ML and DL in medical education | Medical education |
| A. Abd-Alrazaq et al. [26] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Bard | Opportunities and challenges of LLMs in medical education | Medical education |
| C. W. Safranek et al. [27] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Claude | Applications and implications of LLMs in medical education | Medical education |
| H. C. Lucas et al. [28] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Med-PaLM | Systematic review of LLMs and implications for medical education | Medical education |
| T. M. Benítez et al. [29] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Claude | Promise and pitfalls of LLMs in medical education | Medical education |
| D. Q. Wang et al. [30] | ChatGPT, Bard, LLaMA | Accelerating integration of ChatGPT into biomedical research | Biomedical research |
| M. Almansour and F. M. Alfhaid [31] | GPT-4, Claude, Gemini | Personalization of health professional education using generative AI | Health professional education |
| W. Qian [55] | Early GPT models, BERT | Machine learning applications for drug discovery | Drug discovery |
| Source | LLMs Used | Highlight | Application Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| D. Domrös-Zoungrana et al. [32] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Med-PaLM | Considerations for integrating AI in medical education | Medical education |
| L. Zhui et al. [33] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Claude | Ethical considerations of LLMs in medical education | Medical education ethics |
| K. g Lema [34] | GPT-4, Claude, Gemini | AGI applications for medical education and training | Medical education and training |
| S. Tripathi et al. [35] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Claude | Optimizing clinical workflow and patient care with LLMs | Clinical workflow optimization |
| R. Yang et al. [36] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Llama-2 | Development, applications, and challenges of LLMs in healthcare | Healthcare applications |
| M. ZareiNejad and P. Tavana [37] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Claude | Applications of generative AI for patient engagement | Patient engagement |
| Z. Yang et al. [38] | Talk2Care | Facilitating asynchronous patient–provider communication using LLMs | Patient–provider communication |
| R. Mohammad et al. [39] | Arabic-adapted ChatGPT, Arabic GPT | Optimizing LLMs for Arabic healthcare communication | Multilingual healthcare communication |
| N. Mannhardt [40] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Llama-2 | Enhancing readability of clinical notes using LLMs | Clinical note comprehension |
| N. L. Rane et al. [44] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Bard | Performance of ChatGPT for scientific and research advancements | Medical research |
| B. Huo et al. [67] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, Claude | Systematic review of LLM chatbots for health advice | Health advice |
| M. Nydén and D. Bika [45] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, AlphaFold | Medicine design and development in the AI era | Drug development |
| G. Doron et al. [46] | GPT-4, AlphaFold, ESMFold | Pioneering pharmaceutical R&D with generative AI | Pharmaceutical R&D |
| S. Harrer et al. [47] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, AlphaFold | AI driving digital transformation in pharmaceutical industry | Pharma transformation |
| Y. Zhang et al. [48] | ChatGPT, AlphaFold, ESMFold | Accelerating drug discovery and clinical trials with AI | Drug discovery |
| G. Doron et al. [49] | GPT-4, AlphaFold, Chroma | Driving productivity in pharmaceutical R&D with generative AI | Pharmaceutical productivity |
| J. Jiang et al. [50] | GPT-4, BERT, RoBERTa | Review of transformer models in drug discovery | Drug discovery |
| A. Gangwal et al. [51] | GPT-4, ProtGPT2, AlphaFold | Framework, advances, challenges of generative AI in drug discovery | Drug discovery |
| K. Zhang et al. [52] | ChatGPT, GPT-4, AlphaFold | AI applications in drug development | Drug development |
| X.h. Liu et al. [53] | ChatGPT, AlphaFold, ESMFold | LLMs facilitating molecular biology and drug development | Molecular biology and drug development |
| D. Oniani et al. [54] | GPT-4, MolGPT, ChemLLM | Using LLMs for translation between drug molecules and indications | Drug indication mapping |
| R. AlSaad et al. [56] | GPT-4V, Gemini Pro, Claude 3 | Applications and challenges of multimodal LLMs in healthcare | Multimodal healthcare |
| R. Agbareia et al. [57] | GPT-4V, Med-Flamingo, LLaVA-Med | Quantitative analysis of visual–textual integration in LLMs for diagnosis | Medical diagnosis |
| R. Guo et al. [58] | Med-Flamingo, LLaVA-Med, PMC-CLIP | Survey of image–text multimodal models in biomedicine | Biomedical imaging |
| D. Tian et al. [59] | Med-Flamingo, LLaVA-Med, RadBERT | Role of LLMs in medical image processing | Medical image processing |
| M. Kutbi [60] | GPT-4V, RadBERT, PandaGPT | AI applications for bone fracture detection in medical images | Bone fracture detection |
| M. Ayaz et al. [61] | MedVLM | Vision–language models for medical applications in consumer devices | Medical image understanding |
| C. Liu et al. [62] | Med-Flamingo, LLaVA-Med, BioMedCLIP | Foundation models combining visual and language capabilities for medicine | Medical multimodality |
| N. Soni et al. [63] | ChatCAD, RadGPT, Radiology-GPT | Opportunities and challenges of LLMs in radiology | Radiology |
| M. A. Rahman [68] | GPT-4V, Gemini Pro, Claude 3 | Security and privacy considerations for multimodal LLMs in healthcare | Healthcare security |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maity, S.; Saikia, M.J. Large Language Models in Healthcare and Medical Applications: A Review. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060631
Maity S, Saikia MJ. Large Language Models in Healthcare and Medical Applications: A Review. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(6):631. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060631
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaity, Subhankar, and Manob Jyoti Saikia. 2025. "Large Language Models in Healthcare and Medical Applications: A Review" Bioengineering 12, no. 6: 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060631
APA StyleMaity, S., & Saikia, M. J. (2025). Large Language Models in Healthcare and Medical Applications: A Review. Bioengineering, 12(6), 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060631









