Abstract
In this review paper, we perform a comprehensive review of the current state of the art, worldwide applications, and modifications of the Snowmelt Runoff Model (SRM). Snow is a significant element of the hydrologic cycle and is sometimes regarded as the primary source of streamflow in watersheds at high latitudes and altitudes. Quantitative assessment of snowmelt runoff is crucial for real-world applications, including runoff projections, reservoir management, hydro-electricity production, irrigation techniques, and flood control, among others. Numerous hydrological modeling software have been developed to simulate snowmelt-derived streamflow. The SRM is one of the well-known modeling software developed to simulate snowmelt-derived streamflow. The SRM simulates snowmelt runoff with fewer data requirements and uses remotely sensed snow cover extent. This makes the SRM appropriate for use in data-scarce locations, particularly in remote and inaccessible mountain watersheds at higher elevations. It is a conceptual, deterministic, semi-distributed, and degree-day hydrological model that can be applied in mountainous basins of nearly any size. Recent advancements in remote sensing integration and climate model coupling have significantly enhanced the model’s ability to estimate snowmelt runoff. Additionally, numerous studies have recently improved the traditional SRM, further enhancing its capabilities. This paper highlights some of the global SRM research, focusing on the working of the model, input parameters, remote sensing data availability, and modifications to the original model.
Keywords:
modeling; runoff; watershed; snowmelt; snowmelt runoff model (SRM); applications; modifications 1. Introduction
The hydrological cycle comprises various complex phenomena, like evapotranspiration, condensation, precipitation, infiltration, snowmelt, and runoff. The water cycle in mountain watersheds above 40° N and below 40° S is primarily dominated by snow accumulation and ablation [1,2,3]. Snowmelt-driven runoff contributes up to 75% of the total streamflow discharge in the mountainous regions of the western United States [4]. Therefore, snowmelt plays a major role in the hydrological cycle and contributes significantly to streamflow in such watersheds. Quantitative assessment of snowmelt runoff plays a crucial role in the accurate prediction of streamflow, floods, effective hydropower management, and optimal freshwater resource allocation [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. Therefore, it is imperative to develop reliable methods for estimating snowmelt runoff to enhance our ability to mitigate the risks associated with floods and efficiently manage water resources. Numerous hydrological models have been developed over the years to estimate snowmelt-derived streamflow [14].
Based on the relevant research, we have summarized and discussed various categories of these models [15,16]. Depending on the type of outcome, snowmelt models can be classified as either deterministic or stochastic. Deterministic models can predict only a single value of snowmelt-derived streamflow for given input variables and specified sets of parameters, while stochastic models predict a range of possible streamflow estimates based on the statistical variation of the input variables. Most of the models currently in use fall under the deterministic category. Deterministic models can be further classified as either lumped-parameter or distributed models. Lumped-parameter models were the first to be developed for deriving streamflow based on snowmelt. These models treat the entire watershed as a homogeneous unit. Distributed models allow the user to divide a watershed into subunits or grid points. This property gives distributed models an advantage over lumped-parameter models, since different environmental/climatic scenarios, like precipitation, can be applied to corresponding subunits. For example, the amount of precipitation in a watershed’s northern part may be greater or less than that in the southern part. By dividing the watershed into sub-basins, the spatial variation of precipitation can be accounted for in distributed models. Statistical models have been used to predict seasonal streamflow using measured snowpack depth and precipitation data. However, statistical models are at a disadvantage in cases of severe drought/floods, where current data may be skewed compared to historical data. Model selection depends on specific applications. To estimate the total streamflow volume for the entire runoff season, statistical models yield better results, while deterministic models are more accurate for estimating streamflow at smaller time steps. Based on the physics behind computation, models can be classified as statistical, conceptual, or physical. Statistical models rely on the statistical relationship between input variables and outcomes and therefore can only be used for ideal cases. Conceptual models establish relationships between variables and parameters and use corresponding equations to compute streamflow. Physical models are primarily based on mass and energy balance computations. As technology and computational abilities have advanced, so too have snowmelt runoff simulation models. A new category of snowmelt models is now available, i.e., data-driven models [17,18,19]. These models primarily apply machine learning methods and can provide an in-depth analysis of snowpack by automatically selecting appropriate parameters from different sources. Data-driven models have advantages over physically based models in quickly identifying patterns and correlations from the given data without relying on specific physical equations [19].
Many snowmelt models have been developed since 1970, some being more and others less computationally intensive. Depending on how energy balance is handled, some snowmelt models use temperature index methods [20,21], while others use energy balance equations [22,23]. Some models are more snow-physics-based, in which snowmelt due to temperature rise is considered alongside effects due to changes in the physical properties of snow, such as microstructure and refreezing. These models allow for the investigation of flow and transport processes within the snowpack and are widely used in snow hydrology research and avalanche warning systems [24,25]. These snowmelt models include SNOBAL [26], the Utah Energy Balance model (UEB) [27], the Hydrological Simulation Program—FORTRAN (HSPF) [28], the monthly runoff simulating model UTHBAL [29,30], the Soil Water Assessment Tool (SWAT), etc. A simple yet robust temperature index-based Snowmelt Runoff Model (SRM) was developed based on the principles of snowmelt induced by increasing air temperature [31]. A FORTRAN model was developed to simplify the SRM modeling process for beginners in the EXSRM model [32]. Snowmelt models such as the Snow Thermal Model (SNTHERM89) [33] and SNOWPACK [24] have been developed based on energy balance equations. These models are increasingly common in snow engineering and provide more detailed information on the vertical distribution of snow. A Snow-water Equivalent-based model (SWE Hydro) was developed, which incorporated microwave observations from the AMSR-E sensor to estimate the streamflow that was case-studied in the Pelly and Stewart Rivers [34]. The SRM model developed by Martinec in 1975 [31] was further improved by incorporating the Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) data assimilation approach [35]. This study analyzed the streamflow in the Tamor River basin in the Eastern Himalayas between 2002 and 2006 [35]. Another snowmelt model, the International Centre for Theoretical Physics’ (ICTP) Regional Climatic Model (RecCM3), was applied over the western US to predict the early occurrence of snowmelt and snowmelt-derived stream hazards caused by the increase in temperature due to global warming [36]. Another snowmelt model was developed to integrate snow cover and snow depth for the estimation of the snow-water equivalent and snowmelt runoff in the Langtang catchment area in the central Himalayas [37].
The last several decades have also seen the development and use of numerous applications of machine learning techniques, like Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs), the Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS), gene expression programming (GEP), etc. [38,39], to hydrology, including snowmelt runoff modeling. For instance, ANNs and the ANFIS were used [38] to model snowmelt runoff in the Taleghan, Alborz. Another model was created [40] utilizing a deep learning long short-term memory (LSTM) network for snowmelt-driven discharge modeling in a Himalayan basin.
The Snowmelt Runoff Model (SRM) is one of the renowned models used to simulate snowmelt runoff. The SRM is a deterministic, conceptual, physical, and semi-distributed model [3,41,42]. The SRM can simulate snowmelt runoff even with scarcely available climate data [7]. The SRM has been successfully used in numerous studies worldwide under diverse topographic and hydroclimatic conditions. The SRM has served several purposes, from climate change simulations to quality assessment of remote sensing data, as well as quantitative assessment of water resources and hydropower.
In this review paper, we perform a comprehensive review of the working principles of the SRM and its worldwide applications. Additionally, the SRM has witnessed numerous modifications and enhancements in recent years. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, a review and consolidation of SRM modifications has not yet been performed. Therefore, this study provides important insights into SRM’s principle, applications, and modifications, highlighting the significance of the SRM even after 50 years of its inception, and in a machine learning- and artificial intelligence-focused scientific community. The authors believe that this paper brings the reader to the forefront of the current state of the art of SRM research and opens a pathway towards further improvements in the SRM.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 discusses in detail the working principles of the SRM, Section 3 explains the collection of input data for the SRM, Section 4 explains the required parameters, and Section 5 focuses on the improvements and expansions of the SRM. Section 6 provides the summary and concluding remarks.
2. Snowmelt Runoff Model
The Snowmelt Runoff Model (SRM) was developed by [31]. It is a temperature index model, meaning that the snowmelt is simulated primarily based on the air temperature of the zone. The SRM works via the degree-day method, which involves the computation of daily snowmelt depth using the number of degree days (which is the temperature above a given threshold (generally 0 °C is considered ideal) multiplied by 1 day) and the degree-day factor [42]. The SRM model has been made user-friendly in the WinSRM software, which is a Graphical User Interface (GUI)-based software. It is an open-source software that can be easily accessed from the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) website (https://www.ars.usda.gov/research/software/download/?softwareid=7&modecode=80-42-05-10 (accessed on 17 June 2025)). Detailed descriptions can be found in the user manuals [43,44]. The SRM has served different purposes, from estimating the snowmelt runoff to predicting the future streamflow considering the climate change scenario [45,46,47,48]. The SRM has played a significant role in water resource engineering, as it has enabled the estimation of streamflow from snow cover and temperature data. The SRM does not account for situational circumstances, such as rain-on-snow events, snow metamorphism (such as SNOWPACK [24]), or microclimatic surges, which limit its ability to assess the changes within the snowpack or provide micro-scale snowmelt simulations. However, the simple nature of the SRM allows for precise simulations of snowmelt on a macro scale. Due to its relative simplicity, the SRM can be used even in in situ data-scarce regions, giving it an advantage in remote high-elevation areas [7]. Its simplicity, along with its ability to divide a larger watershed into multiple elevation zones and simulate streamflow with scarce data availability, makes the SRM a robust and unique tool to simulate the snowmelt runoff virtually in any watershed around the world.
The SRM has been used widely over 100 basins in 29 countries with varying watershed areas, ranging from 0.76 km2 to 917,444 km2 [3,14,16,41,45,49,50]. The SRM has been proven more accurate as compared to other similar models [45,51] and is easy to use due to a simplified equation [16]. The SRM can be used for short-term, as well as long-term, simulations of snowmelt runoff. The SRM forecasts daily streamflow based on Equation (1) [31,43,44]:
where Q is the estimated zonal streamflow, n is the number of the day, n+1 is the number of the next day, cn is the value of the runoff coefficient for the nth day, Tn is the number of degree-days of the nth day (°C.day), ΔT is the conversion of the measured temperature into the temperature measured at the hypsometric elevation (°C), Sn is the fractional snow cover for the nth day, Pn is the precipitation of the nth day (cm), A is the area of the concerned zone (km2), and k is the factor of the recession coefficient, based on the constants X and Y. All variables and parameters are discussed in detail in Section 3 and Section 4, respectively. The units by themselves would calculate Q in the units of cm.km2/day. The desirable unit for the streamflow is either m3/s or ft3/s. The equation uses the conversion factor of 10,000/86,400 to convert the units to m3/s. It is clear from the above equation that the model calculates the streamflow for the (n + 1)th day from the nth day. This means that the model will calculate the streamflow for any day, given the streamflow for the previous day. The streamflow for the first day of simulation is called the base flow, which must be given manually to initiate the modeling process.
The model assessment of the SRM consists of two metrics. The first metric is the Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency of the Nash–Sutcliffe Coefficient (NSE, R2) [52]. The Nash–Sutcliffe Coefficient is the statistical coefficient used extensively in hydrology, which determines the goodness of fit between observed and simulated values. The equation for NSE is given as follows [52]:
where Qi is the daily observed streamflow, Qi′ is the daily simulated streamflow, and is the average of the observed streamflow. An NSE of 1 is the best possible value, indicating a perfect match between observed and estimated streamflow; an NSE of 0 indicates that the model is no better than using the average of the observed streamflow as a predictor. A negative NSE indicates that the model performs worse than using the average data as a predictor.
The second metric is the volume difference (DV). It is the percentage volume difference between the observed and estimated total seasonal runoff. The equation for DV is as follows:
where V is the total observed volume and V′ is the total estimated volume. A value of DV close to 0 indicates a good agreement between the total observed and estimated runoff volumes. A positive DV indicates a lower estimated volume than the observed volume, and a negative DV indicates a higher estimated volume than the observed volume.
Since the hydrological parameters are dynamic and can vary to a great extent both spatially and temporally, the SRM needs to be calibrated for each watershed to obtain the watershed-specific values of parameters. Generally, data from the first few years of the desired period is used to calibrate the model and obtain the values of all parameters. Upon calibration, the obtained parameters are directly used for model simulation for later years to predict streamflow. Comparison of the predicted streamflow and the observed streamflow for a certain period of time is performed for validation. If the values of the two metrics yield reasonable values (NSE > 0.5; Dv < 10%), the model is said to be validated successfully.
Literature Review
Snow cover is vulnerable to climate change, particularly to the increase in temperature. The state of the SRM, input variables, parameters, and climate change scenario have been reviewed, and the results from previous studies have been compiled [45]. The status of the SRM applications over the Kashmir Himalayas was reviewed in [53], which focused on two widely researched watersheds in Kashmir: the Sind basin and the Lidder watershed. Due to the sheer volume of the studies carried out and the publications using the SRM (research/review papers), citing all of them is not feasible. Thus, we summarize a few representative ones in Table 1. We primarily used Google Scholar to find relevant studies. Additionally, we attempted to include the studies carried out over a wide range of spatio-temporal settings around the world.

Table 1.
Summarized application of SRM in various watersheds.
Another application of the SRM is to assess the quality of remotely sensed snow cover data. Runoff prediction is one of the most useful capabilities of a GIS system, which might be used to detect floods, anticipate the flow of pollutants in water, or aid in reservoir management [63]. Ever since its inception, airborne remotely sensed snow cover has been assessed by the SRM [66,67]. Later on, advances in remote sensing technology have made the satellite-acquired remotely sensed global snow cover data available for free and open source, prompting numerous publications to assess the quality of satellite-derived snow cover data using the SRM. Demonstration of applications of Landsat, Satellite Pour l’Observation de la Terre (SPOT), and NOAA-AVHRR satellite-derived snow cover data over 13 watersheds can be found in a study conducted in the Alps region using the SRM [67]. MODIS has been operational since 2000. MODIS provides daily and 8-day snow cover products, which are preprocessed and ready to use. An assessment of the quality of the MODIS-acquired daily snow cover data was performed by comparing the MODIS- and National Operational Hydrologic Remote Sensing Center (NOHRSC)-derived snow cover maps. The Rio Grande basin was used as a case study, and the MODIS snow cover data was found to be of sufficient quality to be used for streamflow prediction using the SRM [68]. The MODIS Terra and Aqua datasets over the Beas basin were combined, and the derived snow cover data were used with the SRM between 2015 and 2018 to predict the streamflow and perform a preliminary analysis of the contribution of snowmelt to the Beas River [69]. The MODIS data is continuously enhanced, with updated versions released from time to time, the latest being version 6.1, released in 2021. However, the visible and near-infrared data acquisition nature of the MODIS sensor renders it unable to predict the snow extent under cloud cover [70]. A spatio-temporal combination approach by integrating MODIS Terra-, MODIS Aqua-, and Landsat-derived snow cover data to reduce the cloud cover was proposed and utilized over the Balkhab River basin in Afghanistan, with a significant increase in the estimated snow cover area [71]. The MODIS cloud gap-free data product was released in 2020, the quality of which was assessed by integrating it with Landsat data over the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau [70] and over the Hutubi River basin [72]. All of these publications have utilized the snow cover data in the SRM to predict streamflow. Thus, the SRM can be used to validate the snow cover data. Various remotely sensed hydrological data, including MODIS-acquired snow cover and temperature and the Tropical Rainfall Measurement Mission (TRMM)-derived precipitation data, in addition to the in situ-measured air temperature data, were used to simulate the snowmelt-derived runoff in the Taleghan watershed in Iran [73]. The results show that the remotely sensed data provided better estimates of runoff prediction than those obtained by using the in situ weather station-derived meteorological data [73]. This study highlights the SRM’s ability to assess the quality of not only the remotely sensed snow cover data, but also other meteorological data. Considering the numerous applications of the SRM, it becomes crucial to understand the input variables and parameters to accurately predict the desired streamflow. The next section explains the input variables required in the SRM.
3. Input Variables for SRM
The SRM requires three input variables for functioning, namely, temperature, precipitation, and fractional snow-covered area. Table 2 provides a list of readily available remote sensing product sources for these three variables. The most important variable in estimating streamflow is the change in snow cover area. When the snow starts to melt, the areal extent of snow decreases, and thus the fractional snow-covered area also decreases. The plot of this change in fractional snow cover is called the Snow cover depletion curve (SDC). A steep slope of the SDC indicates rapid snowmelt, while a shallow plot indicates moderate snowmelt. Sometimes, the SDC increases even during the snowmelt season, indicating the occurrence of storms. Instantaneous SDC values need to be removed from the SDC in order to prevent overestimation of the SDC [43,44]. Historically, the SDC was derived based on the data gathered by weather stations or the aerial photographs taken from aircraft. However, in both cases, the data were scarce either spatially (weather stations) or temporally (aircraft). Moreover, many mountain regions in the world do not allow easy and feasible installation and maintenance of weather stations in the high-altitude regions. Nowadays, satellite imagery is used to derive the SDC (Table 2). Satellite imagery has proved time and again to be very effective in operational snow cover monitoring. MODIS is a sensor aboard NASA’s Terra and Aqua satellites. MODIS acquires data in the optical region of the electromagnetic spectrum and delivers it in the form of daily or 8-day products. The development of the Normalized Difference Snow Index (NDSI) allows the user to download the snow cover data directly instead of raw data. The MODIS data can be downloaded from NASA Earth Data Search (https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov/search (accessed on 17 June 2025)) cost-free, and the processing of acquired data is relatively simple. The downloaded data requires a moderate level of preprocessing before it can be used for the estimation of the SDC. Figure 1 demonstrates the accumulation and depletion of spatial snow cover over time during the water year 2011 in the Morony watershed, Montana, USA, acquired by the MODIS/Terra 8-day snow cover product.

Table 2.
A list of readily available remote sensing product sources for temperature, precipitation, and fractional snow-covered area.
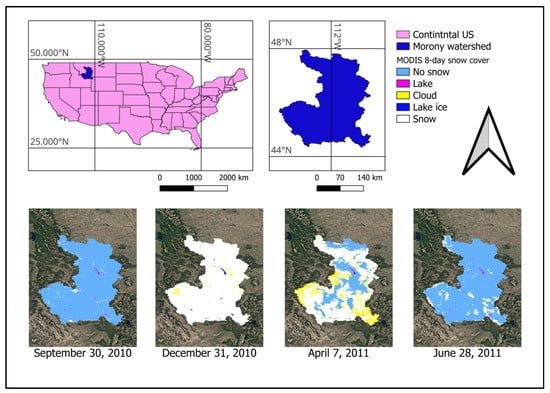
Figure 1.
Demonstration of snow cover accumulation and depletion over the Morony watershed during the water year 2011.
The amount of snow on the ground changes frequently at lower altitudes compared to higher altitudes. This is because the daytime temperatures in the lower zones are much higher than those at higher elevations, causing the snow to melt. As the elevation of the zone increases, the average daily temperature decreases, resulting in constant and substantial snow cover. As an example, Figure 2 demonstrates the presence of substantial snow cover with elevation rise in the Morony watershed, Montana, USA. The watershed, which has an elevation range of ~860 m–~3418 m, was divided into six elevation zones of 500 m each. Zone 1 is the lowest-elevation zone (860–1000 m), resulting in the fluctuating snow cover, while Zone 6 is the highest-elevation zone (1001–3418 m), where the snow cover is present throughout the winter and only depletes during the summer.
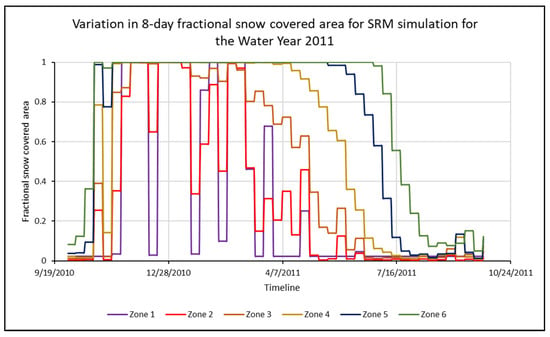
Figure 2.
Variation in 8-day fractional snow-covered area in six elevation zones of the Morony watershed for the water year 2011.
The next input variable to consider is precipitation. Precipitation is responsible for any runoff, rain-derived or snowmelt-derived. NASA’s Tropical Rainfall Measurement Mission (TRMM) sensor detects worldwide precipitation and provides daily precipitation data (Table 2). The TRMM precipitation data can be downloaded from NASA Earthdata Search (https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov/search?q=TRMM (accessed on 17 June 2025)), and it is also free. TRMM data also requires a moderate level of preprocessing, and precipitation graphs can be derived from the processed data. However, the 25 km spatial resolution of the TRMM impedes the user’s ability to monitor finer areas or watersheds with a smaller areal extent. Using the weather station data would give the users more freedom and a finer resolution. When using the data from weather stations, consideration should be given to the difference between the elevation of weather stations and the hypsometric elevation of the zone. If using only one weather station per zone, the elevation must be as close as possible to the hypsometric elevation of the zone. It is possible that zones at higher elevations may not have any weather stations. In such cases, linear extrapolation of the precipitation values from the other weather stations may be used. Moreover, since the model is based primarily on changes in the snow-covered area, the limited availability of precipitation has little effect on the model simulations. Figure 3 shows the random nature of the precipitation observed at five Global Historical Climatological Network (GHCN) stations. Since the weather station was unavailable at zone 6, the precipitation for zone 6 was extrapolated using the precipitation from other weather stations.
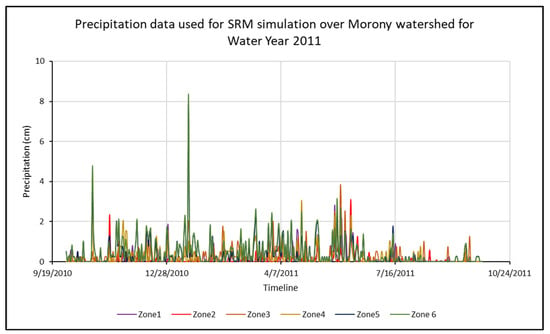
Figure 3.
Precipitation variation in the six elevation zones of the Morony watershed during the water year 2011.
The last required input variable is the air temperature. Temperature changes are required for the determination of the number of degree days and degree-day factor, which is discussed in detail in Section 4. Numerous spaceborne sensors, such as MODIS, operate in the thermal infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum and thus acquire spectral radiance, which is then converted into Land Surface Temperature (LST, Table 2). However, since the air temperature is required as an SRM input, a correction needs to be performed to convert the LST into air temperature. Since the land–air temperature difference varies throughout the world, there is no global equation that can be directly used to convert the LST into air temperature. Therefore, using the air temperature observed by weather stations seems a better fit. There are many datasets available for weather station data in the United States, namely the National Weather Service (https://www.weather.gov/nwr/station_listing (accessed on 17 June 2025)), National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI) (https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/ (accessed on 17 June 2025)), etc., which simultaneously provide temperature and precipitation data. Using the temperature and precipitation data from the same weather station on any given day is advised to equalize any errors induced by a change in acquisition site. Figure 4 shows the sample temperature data at the Morony watershed for all zones for the water year 2011. As the elevation increases, the temperature decreases due to the temperature lapse rate. Therefore, the temperature in higher-elevation zones (such as Zone 6) is lower than that in lower-elevation zones (such as Zone 1).
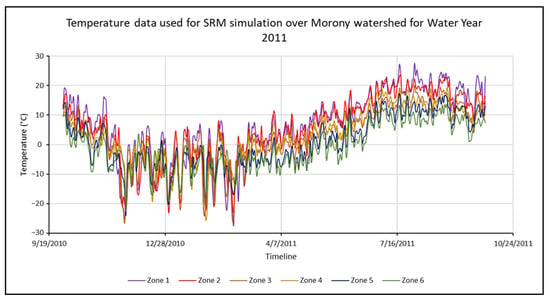
Figure 4.
Temperature variation in the six elevation zones of the Morony watershed during the water year 2011.
Some studies have also utilized the MODIS-derived LST data to calculate the air temperature using the Near-Surface Temperature Lapse Rate (NLR) [78,79]. For instance, Ref. [79] demonstrates the linear relationship between MODIS-derived monthly Land Surface Temperature and Emissivity (LSTE) data (MOD11C3) and observed air temperature data, which was exploited by integrating the local linear equation parameters with MOD11C3 to derive the air temperature.
4. Parameters Required for the SRM
The SRM requires nine different parameters, namely, critical temperature, degree-day factor, temperature lapse rate, runoff coefficient for snowmelt, runoff coefficient for rain, recession coefficients X and Y, lag time, and rainfall contributing area. These parameters are calculated hydrologically or generated from measurements while taking into consideration the physical laws, basin features, and theoretical or empirical regression connections. Some of these parameters are dynamic, meaning that a particular set of parameter values might not be appropriate for the entire timeline [80]. In addition, due to extreme variation in geographical conditions, the parameters are generally not transferable between multiple watersheds [81]. All these parameters have been reviewed in detail [82]. Each parameter is explained here, starting with the critical temperature.
4.1. Critical Temperature (TCRIT)
Critical temperature is the parameter required to determine if the precipitation is in the form of rain or snow. If the local air temperature is greater than the critical temperature, the precipitation is considered rain; otherwise, the precipitation is considered snow. The TCRIT can vary significantly depending on the topographical and climatic conditions. Studies, such as [83], determine the percentage of snow precipitation using the precipitation sub-model. On the other hand, studies, such as [84], use the logistic curve equation to estimate the percentage of snow precipitation. Determining the amount of snow precipitation using such methods provides estimates of snow when obtaining the TCRIT may not be feasible. Additionally, TCRIT essentially acts as a boundary between snow and rain, which may not always be the case. Therefore, using methods such as the precipitation sub-model or logistic curve may reduce inaccurate estimates of snow precipitation. Currently, the SRM only employs TCRIT, and assessment of other snow precipitation estimation methods in the SRM has future research potential.
4.2. Degree-Day Factor (DDF, α)
The degree-day factor (also referred to as the melt factor) is required for the calculation of snowmelt depth. The model follows a linear relationship between the snowmelt depth and air temperature [15] and thus is easier to use and adapt to climate change scenarios. The SRM uses the following equation to calculate the melt depth [43,44]:
where ‘M’ is the daily snowmelt depth (cm), ‘α’ is the degree-day factor (cm °C−1 d−1), and ‘T’ is the number of degree-days (°C d). A comparison of degree-day values with the daily drop in the snow water equivalent, as determined by a radioactive snow gauge, snow pillow, or snow lysimeter, can be used to assess degree-day ratios. In the absence of comprehensive data, an empirical relationship can be used to determine the degree-day factor [44,85]:
where ρs and ρw are the densities of snow and water, respectively. Depending on the snow density, the α can vary to a great extent, since denser snow will need a higher number of degree days to melt, and vice versa.
M = α×T,
4.3. Temperature Lapse Rate (γ)
The SRM distributes point-based data of the daily average air temperature to the hypsometric mean elevation of each elevation zone using temperature lapse rates. The hypsometric elevation of a zone or watershed is the elevation above and below which the watershed area is equally divided. It means that 50% of the watershed will be at a lower elevation than the hypsometric elevation, while the remaining 50% of the watershed will be at a higher elevation than that. Thus, the hypsometric elevation is considered the middle point of the zone or watershed, and therefore data from weather stations at any elevation is converted to the hypsometric elevation to generalize it over the entire zone or watershed. If the weather station is not located at the hypsometric elevation of the zone, the temperature lapse rate is used to calculate the temperature at the hypsometric elevation. Typically, a lapse rate of 0.65 °C per 100 m is used in SRM simulations.
4.4. Runoff Coefficient for Snowmelt (CS)
When the snowpack starts to melt, the meltwater first percolates through the snowpack, and once the pores are filled, the water yields into the runoff. However, not all the meltwater yields into runoff. Thus, the runoff coefficient for snowmelt is the ratio of the volume of runoff caused by snowmelt to the volume of snow melted. In its mathematical form, the runoff coefficient for snowmelt can be calculated as
where CS is the runoff coefficient of snowmelt, Vrunoff is the volume of actual runoff, and Vsnowmelt is the volume of actual snowmelt.
4.5. Runoff Coefficient for Rain (CR)
The runoff coefficient for rain is the ratio of runoff due to rain to the total rainfall. It greatly depends on the surface conditions and ranges between 0 and 1. For example, if the surface is heavily vegetated, much of the precipitated rainwater may be retained by the vegetation, and the overall runoff will decrease. In this case, the runoff coefficient will be relatively lower. On the other hand, if the surface is barren land with little to no infiltration capacity (like concrete), most or all of the rainfall will flow as runoff. In this case, the runoff coefficient will be a higher value closer to 1. Thus, mathematically, the runoff coefficient for rain can be calculated by
where CR is the coefficient of runoff for rain, Q is the volume of runoff, and P is the volume of precipitation. Generally, the runoff coefficient is higher at the beginning of the snowmelt period due to the snow coverage. As the snow melts, underlying land emerges, and the infiltration increases, resulting in a decrease in the runoff coefficient [82]. If the runoff simulations do not initially succeed, the runoff coefficient must often be adjusted [44].
4.6. Recession Coefficients X and Y
The recession coefficients X and Y are used as the parameters to calculate the overall recession coefficient k. The recession coefficient shows the decrease in discharge during a dry time. The lower envelope line connecting all points represents the k values when Qn and Qn+1 are plotted against one another on a log–log plot. Mathematically, the recession coefficient k can be calculated by the following equation [43,44]:
where k is the overall recession coefficient, Qn+1 is the streamflow of the (n + 1)th day, and Qn is the streamflow of the nth day. Alternatively, k can also be calculated using the recession coefficients X and Y as follows [44]:
where kn+1 is the recession coefficient of the (n + 1)th day, Qn is the streamflow of the nth day, and X and Y are the recession coefficients. Since the recession coefficient represents the recession in flow due to the watershed’s extent, the k value is generally higher for larger watersheds and vice versa. Since k corresponds to the recession in snowmelt runoff, the maximum recession that can occur on any day is 100% streamflow of the previous day. Therefore, the value of k must always be lower than 1. Therefore, in the case of unnaturally high k values, a k value of 0.99 is substituted to prevent impossible results.
kn+1 = XQn−Y,
4.7. Time Lag
The time lag is used to simulate the lag in time between temperature rise and streamflow rise due to snowmelt. The time lag essentially indicates a fraction of temperature and precipitation data for the nth and (n + 1)th day to be used to simulate the discharge of the (n + 1)th day. The SRM GUI provides numerous time lag options, ranging from 6 to 24 h. A time lag of 18 h suggests that 100% of the temperature and precipitation of the nth day are used to simulate the snowmelt runoff on the (n + 1)th day [44].
4.8. Rainfall Contributing Area (RCA)
There are two approaches to treating precipitation identified as rain. In the initial scenario (option 0), it is believed that snow that is typically dry and deep will retain any rain that falls on it; therefore, only the runoff from the areas without snow contributes to the overall runoff. When the snow cover ripens later, option 1 should be selected. If rain occurs on the ripe snow cover, it is expected that the same quantity of water is released from the snowpack, resulting in rain from the whole area being part of the runoff.
4.9. SRM Parameter Values Used in the Literature, Calibration, and Validation
Table 3 shows a comprehensive review of the parameters used for model calibration by numerous previous studies. It should be noted, however, that each scenario is unique, and the parameters may not show any correlation concerning the time and location of the study area.

Table 3.
SRM parameters used by numerous studies.
Determining the appropriate values for the set of model parameters is a highly complex task, since parameters may change with time, and it may not be possible to physically determine the value of each parameter. Generally, and practically, the values of the model parameters are obtained by calibration to minimize the objective function. A Progressive Segmented Optimization Algorithm (PSOA) was developed, and its applicability was validated over the Manasi River basin between 2001 and 2012 [91]. The PSOA outperformed the original SOA algorithm and was better suited for calibration of the SRM [91]. The PSOA determines the parameters of one water year based on the batch calibration of all the previous water years [91]. The Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) algorithm can also be used to perform the calibration for the SRM [3].
5. Modification of SRM and Prospects
The first version of the SRM was published in 1975, but many modified or expanded versions have been developed ever since. The Snowmelt Runoff Model (SRM) was initially a FORTRAN model developed to be run on an IBM 370-series mainframe computer. Many modifications have been made to the SRM since its inception in 1975. Martinec et al. (1983) created the first computerized version of the concept [43]. A Java version of the SRM was created by Hannes Kleindienst as part of the HYDLP project. The standard degree-day factor method was improved to the restricted degree-day factor method, which, along with the number of degree days and degree-day factor, considered the longwave and shortwave radiation received by the snowpack. The results from the Dischma basin were improved by this method [42].
Furthermore, the model has been enhanced by many researchers for better performance and applicability in different settings. An improved temperature index model was created using the new melt rate calculation method, incorporating shortwave solar radiation, snow albedo, and the degree-day factor [92]. To reflect the snowmelt process more accurately, the SRM was modified to use accumulated active temperature rather than daily average temperature [93]. Moreover, an additional algorithm modification was also added to enable the SRM to output the snow cover series and snow water equivalent, which can then be used for long-term snow cover series simulation.
The SRM radiation model was developed to simulate snowmelt runoff in the Iranian Taleghan watershed [94]. The simulation accuracy was substantially enhanced, and the snow hydrological behaviors in the watershed region were more accurately described by incorporating the radiation element into the model [94]. The conventional SRM model with a finer zonation based on aspect and slope (SRM+AS model) was developed, incorporating topographic elements like aspect and slope for simulating snowmelt [95]. As a result of adequate parameterization, careful input data selection, and data preparation, the SRM + AS model’s performance is slightly better than the traditional SRM model [95]. The traditional SRM primarily works on the degree-day approach and is only applicable for pristine watersheds. The SRM does not consider artificial flow regulation and flow alteration due to reservoir/irrigation-based activities. An expansion of the traditional SRM, the Expanded SRM (E-SRM), was developed to recover the natural flow regime altered by reservoir operations by incorporating multi-year batch processing, nested iterator, and seasonal divider algorithms, and integrating the SRM with a parsimonious regulation-correction methodology [96]. The E-SRM was applied to the Morony watershed in Montana, USA, and the results showed that incorporating the regulated flow significantly improved the SRM’s performance in predicting the naturalized streamflow [96]. A following study was performed to incorporate the hydropower-predicting component within the SRM, which is named the Snowmelt Runoff-Driven Hydropower Model (SRDHM) [97]. The SRDHM is designed to predict the hydropower generation potential through Run-of-River (ROR) hydropower plants by considering the remotely sensed snow cover and in situ observed temperature and precipitation data. The SRDHM also incorporates the hypothesis that not all of the water inflow to the dam barrier is utilized for hydropower; a majority of the water will bypass the hydropower plant through the spillway. Therefore, only a fraction of the incoming streamflow will be utilized for hydropower generation. The SRDHM uses a novel parameter called the ‘Turbine Flow Factor’ to simulate the behavior of water diversion. Additionally, the SRDHM is capable of simulating the snowmelt runoff and associated hydropower potential at pristine, regulated, and ungauged locations, since the baseflow is calculated by the model using the streamflow from the closest upstream and downstream gauge stations [97]. These modifications and enhancements to the SRM aim to improve its accuracy, applicability, and capability to simulate snowmelt runoff and associated processes.
The SRM was originally a temperature index, semi-distributed snowmelt estimating model. A Spatially-distributed Snowmelt Runoff Model (SDSRM) was developed, which, along with the original runoff predictions, also generates various snow-physics parameters such as snow density, snow depth, snow water equivalent, degree days, net solar radiation, snowmelt depth, rain-induced runoff, snow-induced runoff, total runoff, and evapotranspiration as a time series [98]. The developed SDSRM was applied over the Nuranang and Mago watersheds in Arunachal Pradesh, India [98]. The SDSRM was also applied over the Digang, Mago, and Subansiri basins in Arunachal Pradesh, where it was determined that the annual temporal variation in snow parameters was gradual in the Dibang and Subansiri basins, whereas the variation in snow parameters was expeditious in the Mago basin [99]. The SDSRM was even further modified to incorporate glacier melt by the development of the Spatially Distributed Snowmelt and Glacier Melt Runoff Model (SDSGRM) [100]. The SDSGRM was also applied over the glaciated Mago River in Arunachal Pradesh, suggesting potential applications in data-scarce regions [100].
Since its inception in 1975, the SRM has been used extensively in numerous publications worldwide, indicating that applications of the SRM are endless, from estimating the streamflow for agricultural use to estimating the hydropower based on the streamflow estimates. Advances in the satellite-acquired free and open-source remotely sensed data have enabled the utilization of the SRM almost globally. Now, advances in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) technology have enabled the use of UAVs for fine-resolution data collection. This has opened new avenues of research in snowmelt runoff modeling, and research is encouraged in the modeling of snowmelt by acquiring real-time air and ground temperature, along with high-resolution snow cover data. The development of UAV-based Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) has also enabled the estimation of daily increase/decrease in snow depth, which can help enhance the degree-day factor to higher accuracy. Similarly, more research is encouraged to expand our understanding of the parameters used in the SRM. Hydrological models are complex, and the parameters are dynamic and change spatially and temporally. More research is encouraged to simplify the behavior of the parameters. Integration of the SRM with other climatic models may also expand its applications.
6. Summary and Conclusions
In regions where the accumulation of snow and its melting makes a significant contribution to the hydrological cycle, snowmelt runoff modeling becomes a crucial part of hydrological research and water resource management. In mountainous areas like the western United States, runoff due to snowmelt accounts for up to 75% of the total streamflow volume. According to prior research investigations, temperature and precipitation are the primary factors influencing the snowmelt process.
The SRM model, which is a temperature index model created to simulate snow melt runoff, has been effectively used for various regions of the world. The main factors influencing its extensive use are its simple model structure, correctness, easily accessible input parameters, and excellent computational efficiency. Three input variables necessary for SRM to function are temperature, precipitation, and fractional snow cover. Among these variables, the change in snow cover area has the most significant influence. To run an SRM simulation, a variety of input parameters like the temperature lapse rate, critical temperature, degree day factor, lag time, snowmelt runoff coefficients, rainfall runoff coefficients, and the recession coefficients are required. These parameters are highly dynamic and change spatially and temporally.
The SRM can estimate streamflow and assess how climate change is affecting runoff in mountainous watersheds with improved climatic variable input and parameter selection techniques. The model’s effective implementation in mountainous basins with a snow-dominated environment is made possible by the growing accessibility of remote sensing data. Although it has its limits, new developments in the coupling of climate models and remote sensing have improved its capabilities for precise snowmelt runoff estimation. For accurate results when using the SRM, proper calibration, validation, and uncertainty analysis are crucial.
By utilizing remote sensing data, GIS tools, field measurements, and innovative model parameterization techniques, additional research is required to model snowmelt runoff for data-scarce mountainous watersheds where only limited hydro-meteorological data are available. Continued research and advancement in this area are important for improving our understanding of snowmelt processes and their implications for water resources.
Author Contributions
Investigation, N.B., R.K. and M.Q.; resources. X.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, N.B., R.K. and M.Q.; writing—review and editing, N.B., R.K., R.M.N. and X.Z.; funding acquisition, X.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partly funded by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) grant number G104-21-W8414, and The APC was funded by Montana Technological University.
Acknowledgments
N.B. would like to thank Montana Water Center, Montanaview, and the Billings Geophysical Society for scholarships and fellowships towards his PhD degree. The authors would also like to express their sincere gratitude towards anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions towards the improvement of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funding agency did not play any role in the outcome of this review.
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Meaning |
| SRM | Snowmelt Runoff Model |
| MODIS | Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer |
| AMSR-E | Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer |
| UEB | Utah Energy Balance model |
| HSPF | Hydrological Simulation Program—FORTRAN |
| SNTHERM89 | Snow Thermal Model |
| MCMC | Markov Chain Monte Carlo |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| ANFIS | Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System |
| GEP | Gene Expression Programming |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| MT | Montana |
| NSE | Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency |
| Dv | Volume difference |
| NOAA | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration |
| AVHRR | Advanced Very High-Resolution Radiometer |
| SPOT | Satellite Pour l’Observation de la Terre |
| NOHRSC | National Operational Hydrologic Remote Sensing Center |
| SDC | Snow Cover Depletion |
| NASA | National Aeronautics and Space Administration |
| NDSI | Normalized Difference Snow Index |
| TRMM | Tropical Rainfall Measurement Mission |
| LST | Land Surface Temperature |
| NCEI | National Centers for Environmental Information |
| SOA | Segmented Optimization Algorithm |
| PSOA | Progressive Segmented Optimization Algorithm |
| GUI | Graphic User Interface |
| ROR | Run-of-River |
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
| LiDAR | Light Detection and Ranging |
References
- Adam, J.; Hamlet, A.; Lettenmaier, D. Implications of global climate change for snowmelt hydrology in the twenty-first century. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2009, 23, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudu, S.; Cui, C.; Saydi, M.; King, J. Application of snowmelt runoff model (SRM) in mountainous watersheds: A review. Water Sci. Eng. 2012, 5, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemens, K.; Dibike, Y.; Shrestha, R.; Prowse, T. Runoff projection from an alpine watershed in Western Canada: Application of a snowmelt runoff model. Water 2021, 13, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuyovich, C.; Jacobs, J.; Daly, S. Comparison of passive microwave and modeled estimates of total watershed SWE in the continental United States. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 9088–9102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brubaker, K.; Rango, A. A new version of the snowmelt runoff model incorporating radiation. Environ. Prof. 1997, 19, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, R. Snowmelt runoff models. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 1999, 23, 205–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. Satellite snow cover mapping and snowmelt runoff modelling in Beas basin. IAHS 1991, 205, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Bao, A. Modelling snowmelt runoff under climate change scenarios in an ungauged mountainous watershed, Northwest China. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013, 808565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmens, K.; Ramage, J. Recent changes in spring snowmelt timing in the Yukon River basin detected by passive microwave satellite data. Cryosphere 2013, 7, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Parajka, J.; Tian, Q.; Blöschl, G. Estimating degree-day factors from MODIS for snowmelt runoff modeling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 4773–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griessinger, N.; Seibert, J.; Magnusson, J.; Jonas, T. Assessing the benefit of snow data assimilation for runoff modeling in Alpine catchments. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 3895–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuyovich, C.; Jacobs, J.; Hiemstra, C.; Deeb, E. Effect of spatial variability of wet snow on modeled and observed microwave emissions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Tiwari, R.; Kumar, K.; Rautela, K. Statistical evaluation of snow accumulation and depletion from remotely sensed MODIS snow time series data using the SARIMA model. AQUA-Water Infrastruct. Ecosyst. Soc. 2023, 72, 348–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Manzoor, S.; Mahrukh. Modelling of snowmelt runoff across the Himalayan Region. J. Agrometeorol. 2022, 24, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWalle, D.; Rango, A. Principles of Snow Hydrology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Cui, M.; Wan, J.; Zhang, S. A review on snowmelt models: Progress and prospect. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Vanrolleghem, P. Including snowmelt in influent generation for cold climate WRRFs: Comparison of data-driven and phenomenological approaches. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2022, 8, 2087–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.; Elias, E.; Carroll, K.; Brown, C. Exploring random forest machine learning and remote sensing data for streamflow prediction: An alternative approach to a process-based hydrologic modeling in a snowmelt-driven watershed. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kedam, N.; Sharma, K.V.; Mehta, D.J.; Caloiero, T. Advanced machine learning techniques to improve hydrological prediction: A comparative analysis of streamflow prediction models. Water 2023, 15, 2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huss, M.; Farinotti, D.; Bauder, A.; Funk, M. Modelling runoff from highly glacierized alpine drainage basins in a changing climate. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 3888–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, R.; Rai, S.; Jain, S.; Kumar, B.; Dobhal, D. Assessment of snowmelt run-off modelling and isotope analysis: A case study from the western Himalaya, India. Ann. Glaciol. 2013, 54, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, E. Sensitivity of the European hydrological system snow models. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. Publ. 1982, 138, 222–231. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, M.; Wang, L.; Koike, T.; Xue, Y.; Hirabayashi, Y. Improving the snow physics of WEB-DHM and its point evaluation at the SnowMIP sites. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 2577–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehning, M.; Bartelt, P.; Brown, B.; Fierz, C.; Satyawali, P. A physical SNOWPACK model for the Swiss avalanche warning: Part II. Snow microstructure. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2002, 35, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vionnet, V.; Brun, E.; Morin, S.; Boone, A.; Faroux, S.; Le Moigne, P.; Martin, E.; Willemet, J. The detailed snowpack scheme Crocus and its implementation in SURFEX v7. 2. Geosci. Model Dev. 2012, 5, 773–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, D.; Dozier, J.; Davis, R. Climate and energy exchange at the snow surface in the alpine region of the Sierra Nevada: 1. Meteorological measurements and monitoring. Water Resour. Res. 1992, 28, 3029–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarboton, D.; Luce, C. Utah Energy Balance Snow Accumulation and Melt Model (UEB) (63); Utah Water Research Laboratory: Logan, UT, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Bicknell, B.; Imhoff, J.; Kittle, J., Jr.; Donigian, A., Jr.; Johanson, R. Hydrological Simulation Program-FORTRAN.; User’s manual for release, 11; US EPA: Athens, GA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Loukas, A.; Mylopoulos, N.; Vasiliades, L. A modeling system for the evaluation of water resources management strategies in Thessaly, Greece. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 1673–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliades, L.; Mastraftsis, I. A monthly water balance model for assessing streamflow uncertainty in hydrologic studies. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2023, 25, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinec, J. Snowmelt-runoff model for stream flow forecasts. Hydrol. Res. 1975, 6, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engman, E.; Martinec, J.; Rango, A. EXSRM, an Expert System for Snowmelt Runoff Model (SRM); IAHS Publication: Wellingford, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, R.E. A One-Dimensional Temperature Model for a Snow Cover: Technical Documentation for SNTHERM89: Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory (U.S.), and Engineer Research and Development Center (U.S.) 1991. Available online: https://erdc-library.erdc.dren.mil/items/81b728f7-84b5-4ef8-e053-411ac80adeb3 (accessed on 17 June 2025).
- Ramage, J.; Semmens, K. Reconstructing snowmelt runoff in the Yukon River basin using the SWEHydro model and AMSR-E observations. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 2563–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panday, P.; Williams, C.; Frey, K.; Brown, M. Application and evaluation of a snowmelt runoff model in the Tamor River basin, Eastern Himalaya using a Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) data assimilation approach. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 5337–5353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauscher, S.; Pal, J.; Diffenbaugh, N.; Benedetti, M. Future changes in snowmelt-driven runoff timing over the western US. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L16703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stigter, E.; Wanders, N.; Saloranta, T.; Shea, J.; Bierkens, M.; Immerzeel, W. Assimilation of snow cover and snow depth into a snow model to estimate snow water equivalent and snowmelt runoff in a Himalayan catchment. Cryosphere 2017, 11, 1647–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafakhah, M.; Sedighi, F.; Javadi, M. Modeling the rainfall-runoff data in snow-affected watershed. Int. J. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2014, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birbal, P.; Azamathulla, H.; Leon, L.; Kumar, V.; Hosein, J. Predictive modelling of the stage–discharge relationship using Gene-Expression Programming. Water Supply 2021, 21, 3503–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, S.; Zhao, Z.; Li, B.; Lu, L.; Fu, D.; Shi, X.; Tang, B.; Qi, H. Snowmelt-driven streamflow prediction using machine learning techniques (LSTM, NARX, GPR, and SVR). Water 2020, 12, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, K.; Martinec, J. Remote Sensing in Snow Hydrology: Runoff Modelling, Effect of Climate Change; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kustas, W.; Rango, A.; Uijlenhoet, R. A simple energy budget algorithm for the snowmelt runoff model. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 1515–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinec, J.; Rango, A.; Major, E. The Snowmelt-Runoff Model (SRM) User’s Manual (No. REPT-83B0251); New Mexico State University: Las Cruces, NM, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Martinec, J.; Rango, A.; Roberts, R. Snowmelt Runoff Model (SRM) User’s Manual; New Mexico State University Press: Las Cruces, NM, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rango, A. Worldwide testing of the snowmelt runoff model with applications for predicting the effects of climate change. Hydrol. Res. 1992, 23, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekeli, A.; Akyurek, Z.; Sorman, A.; Sensoy, A.; Sorman, A. Using MODIS snow cover maps in modeling snowmelt runoff process in the eastern part of Turkey. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.; Romshoo, S.; Bhat, M. Estimation of snowmelt runoff using snowmelt runoff model (SRM) in a Himalayan watershed. World J. Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Tenzin, J.; Ongsomwang, S. Snowmelt runoff analysis and impact assessment of temperature change in the upper Punatsang Chu basin, Bhutan. Suranaree J. Sci. Technol. 2015, 22, 511–528. [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker, K.; Rango, A.; Kustas, W. Incorporating radiation inputs into the snowmelt runoff model. Hydrol. Process. 1996, 10, 1329–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, M.; Masood, A.; Mushtaq, H.; Bukhari, S.; Ahmad, B.; Tahir, A. Exploring climate change impacts during first half of the 21st century on flow regime of the transboundary kabul river in the hindukush region. J. Water Clim. Change 2020, 11, 1521–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, B.; Chevallier, P.; Andréassian, V.; Tahir, A.; Arnaud, Y.; Neppel, L.; Bajracharya, O.; Budhathoki, K. Comparison of two snowmelt modelling approaches in the DudhKoshi basin (eastern Himalayas, Nepal). Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.; Sutcliffe, J. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, S.; Sarif, M. Status on snow cover area, mass balance, glacial area loss, surface velocities and applications of snowmelt runoff model over Kashmir Himalayas and Upper Indus Basin: A review. Polar Sci. 2024, 42, 101075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, M.; Apfl, G. Remote sensing, geographic information systems and snowmelt runoff models—An integrated approach; IAHS: Wellingford, UK,, 1997; pp. 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Rango, A.; Martinec, J. Areal extent of seasonal snow cover in a changed climate. Hydrol. Res. 1994, 25, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Cheng, G. A test of Snowmelt Runoff Model (SRM) for the Gongnaisi River basin in the western Tianshan Mountains, China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 2253–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, V.; Roy, P. Estimation of snowmelt runoff in Beas Basin, India. Geocarto Int. 2005, 20, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Ju, Q.; Yu, Z.; Hao, J.; Gu, H.; Gu, H.; Li, W. Simulation of snowmelt runoff and sensitivity analysis in the Nyang River Basin, southeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Nat. Hazards 2019, 99, 931–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, M.; Sabaghzadeh, M.; Niazkar, M. Evaluation of Snowmelt Impacts on Flood Flows Based on Remote Sensing Using SRM Model. Water 2023, 15, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzi, S.; Sadeghian, M. Application of Snow Melt Runoff Model in a Mountainous Basin of Iran. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2016, 4, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Nabi, G.; Poomee, M.; Ashraf, A. Snowmelt runoff prediction under changing climate in the Himalayan cryosphere: A case of Gilgit River Basin. Geosci. Front. 2017, 8, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddam, V.; Kulkarni, A.; Gupta, A. Assessment of snow-glacier melt and rainfall contribution to stream runoff in Baspa Basin, Indian Himalaya. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Manzoor, S.; Vishwakarma, D.; Al-Ansari, N.; Kushwaha, N.; Elbeltagi, A.; Sushanth, K.; Prasad, V.; Kuriqi, A. Assessment of climate change impact on snowmelt runoff in himalayan region. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, H.; Siwar, C.; Mokhtar, M.; Lahlou, F.; Kanniah, K.; Al-Ansari, T. Snow runoff modelling in the upper Indus River Basin and its implication to energy water food nexus. Ecol. Model. 2024, 498, 110871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Zhang, Y.; Majeed, U.; Rashid, I. Runoff modelling and quantification of supraglacial debris impact on seasonal streamflow in the highly glacierized catchments of the western Karakoram in Upper Indus Basin, Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinec, J. Evaluation of air photos for snowmelt-runoff forecasts. In Proceedings of the International Symposia on the Role of Snow and Ice in Hydrology, Banff, AB, Canada, 6–20 September 1972; IAHS Press: Wallingford, UK; Volume 2, pp. 915–926. [Google Scholar]
- Seidel, K.; Martinec, J. Hydrological applications of Satellite Snow Cover mapping in the swiss Alps. In Proceedings of the EARSeL-LISSIG-Workshop Observing Our Cryosphere from Space, Bern, Switzerland, 11–13 March 2002; Volume 80. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Klein, A.; Over, T. A comparison of MODIS and NOHRSC snow-cover products for simulating streamflow using the Snowmelt Runoff Model. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2005, 19, 2951–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajuria, V.; Kumar, M.; Gunasekaran, A.; Rautela, K. Snowmelt runoff estimation using combined terra-aqua MODIS improved snow product in Western Himalayan River Basin via degree day modelling approach. Environ. Chall. 2022, 8, 100585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, B.; Gao, X.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Li, R. Validation of Cloud-Gap-Filled Snow Cover of MODIS Daily Cloud-Free Snow Cover Products on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussainzada, W.; Lee, H.; Bhanage, V.; Khpalwak, G. Sensitivity of snowmelt runoff modelling to the level of cloud coverage for snow cover extent from daily MODIS product collection 6. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 36, 100835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Liu, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, K. Adaptability of MODIS Daily Cloud-Free Snow Cover 500 m Dataset over China in Hutubi River Basin Based on Snowmelt Runoff Model. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghdi, M.; Vafakhah, M.; Moosavi, V. Improving Snowmelt Runoff Model (SRM) Performance Incorporating Remotely Sensed Data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2024, 52, 1841–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, G.; Hall, D.; Salomonson, V. MODIS snow products user guide. NASA Goddard Space Flight Cent. Rep 2006, 80, 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Riggs, G.; Hall, D.; Salomonson, V. A snow index for the Landsat thematic mapper and moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer. In Proceedings of the IGARSS’94-1994 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 8–12 August 1994; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1944. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z. MODIS Land Surface Temperature Products Users’ Guide; Institute for Computational Earth System Science, University of California: Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Avdan, U.; Jovanovska, G. Algorithm for automated mapping of land surface temperature using LANDSAT 8 satellite data. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 1480307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, L.; Shrestha, M.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; Zhou, J.; Yang, K.; Lu, H.; Chen, D. Improving snow process modeling with satellite-based estimation of near-surface-air-temperature lapse rate. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 12,005–12,030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Peng, D.; Gu, Y.; Luo, X.; Pang, B.; Zhu, Z. Temperature lapse rate estimation and snowmelt runoff simulation in a high-altitude basin. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, T. Parameterization of the snowmelt runoff model for the Salt-Verde System, Arizona during drought conditions. J. Ariz.-Nev. Acad. Sci. 2006, 38, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinze, P.; Azam, M. On the transferability of snowmelt runoff model parameters: Discharge modeling in the Chandra-Bhaga Basin, western Himalaya. Front. Water 2023, 4, 1086557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinec, J.; Rango, A. Parameter values for snowmelt runoff modelling. J. Hydrol. 1986, 84, 197–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semádeni-Davies, A. Monthly snowmelt modelling for large-scale climate change studies using the degree day approach. Ecol. Ecol. Model. 1997, 101, 303–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, C.; Chang, H.; Staneva, M.; Kostov, D. A simplified basin model for simulating runoff: The Struma River GIS. Prof. Geogr. 2001, 53, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinec, J. The degree-day factor for snowmelt runoff forecasting. IUGG General Assembly of Helsinki. IAHS Comm. Surf. Waters 1960, 51, 468–477. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, R.; Ren, L.; Cheng, W.; Yu, Z. Application of hydrological models in a snowmelt region of Aksu River Basin. Water Sci. Eng. 2008, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xie, H.; Yao, T.; Li, H.; Duan, S. Quantitative water resources assessment of Qinghai Lake basin using Snowmelt Runoff Model (SRM). J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 976–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, A.; Sarkar, A.; Sharma, N. Snowmelt Runoff Modeling in an Indian Himalayan River Basin using WinSRM, RS & GIS. Water Energy Int. 2015, 58, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Pangali Sharma, T.; Zhang, J.; Khanal, N.; Prodhan, F.; Paudel, B.; Shi, L.; Nepal, N. Assimilation of snowmelt runoff model (SRM) using satellite remote sensing data in Budhi Gandaki River Basin, Nepal. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, J.; Xu, C.; Xia, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, J. Parameter uncertainty of a snowmelt runoff model and its impact on future projections of snowmelt runoff in a data-scarce deglaciating river basin. Water 2019, 11, 2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Du, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Feng, X.; Zheng, W.; Li, Z.; Xu, C. A progressive segmented optimization algorithm for calibrating time-variant parameters of the snowmelt runoff model (SRM). J. Hydrol. 2018, 566, 470–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Williams, M. Snowmelt runoff modelling in an arid mountain watershed, Tarim Basin, China. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 3931–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Chen, X.; Li, L.; Bao, A.; de la Paix, M. Incorporating accumulated temperature and algorithm of snow cover calculation into the snowmelt runoff model. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 3589–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafakhah, M.; Nouri, A.; Alavipanah, S. Snowmelt-runoff estimation using radiation SRM model in Taleghan watershed. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudu, S.; Sheng, Z.; Cui, C.; Saydi, M.; Sabzi, H.; King, J. Integration of aspect and slope in snowmelt runoff modeling in a mountain watershed. Water Sci. Eng. 2016, 9, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwat, N.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, L.; Nagisetty, R.; Shaw, G.; Apple, M.; Clotfelter, J. Snowmelt Runoff Model (SRM) for Regulated Watersheds with Regulation Correction. J. Appl. Water Sci. 2025; Under review. [Google Scholar]
- Bhagwat, N. Snowmelt Runoff Driven Hydropower Modelling Based on Spaceborne Remotely Sensed and Ground Weather Network Data. Doctoral Dissertation, Montana Technological University, Butte, MT, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/openview/e2d7c1aacb9d1926efdbec5c54573d83/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=18750&diss=y (accessed on 17 June 2025).
- Rajkumari, S.; Chiphang, N.; Kiba, L.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Bhadra, A. Development and application of a spatially distributed snowmelt runoff model for limited data condition. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vese, M.; Nunchhani, V.; Samjetsabam, G.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Bhadra, A. Analyzing Snow Parameters Dynamics in Arunachal Pradesh’s Glaciated River Basins Through Spatially Distributed Snowmelt Runoff Model (SDSRM): Dibang, Mago and Subansiri. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2024, 52, 1589–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunchhani, V.; Chiphang, N.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Bhadra, A. Development of a Spatially Distributed Snow and Glacier Melt Runoff Model (SDSGRM) for data scarce high-altitude river basins. Environ. Model. Softw. 2024, 175, 106004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).