Abstract
Background: Chronic pruritus is a debilitating condition associated with a wide range of dermatologic, systemic and psychogenic etiologies. In patients with chronic pruritus that is refractory to conventional therapy, symptoms can significantly decrease quality of life by contributing to anxiety, sleep disturbances, and in many cases depression. Recent studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of mirtazapine in relieving chronic itch that is refractory to standard first-line therapies. Methods: We searched PubMed for English-language articles containing the words (“pruritus” or “itch”) AND “antidepressant” and then conducted a systematic review of the current literature to summarize the efficacy of mirtazapine in treating chronic itch. Results: All studies reported a reduction in itch intensity following the administration of mirtazapine. Conclusion: Collectively, these studies suggest the potential for mirtazapine to relieve chronic itch attributed to dermatological causes and malignancies. As, such mirtazapine may be an option for patients with chronic pruritus that is refractory to typical first-line treatments.
Keywords:
mirtazapine; chronic; pruritus; itch; refractory; treatment; noradrenergic; serotonergic; antihistaminergic; antidepressant Dear Editor,
Chronic pruritus is a common condition that can interfere with sleep and diminish overall quality of life. The current management of chronic itch is directed at the underlying cause, which can be dermatologic, systemic or psychogenic in nature [1]. First-line therapy typically begins with topical emollients, topical corticosteroids, and antihistamines. GABA-receptor modulators, opioid agonists/antagonists and phototherapy can be used for patients with refractory pruritus [1].
Recalcitrant itch is a distressing symptom for which a safe and effective agent is needed [2,3]. Recent studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of oral antidepressants in relieving chronic itch associated with dermatologic, systemic and psychogenic causes [4,5]. Mirtazapine, a dual noradrenergic and serotonergic antidepressant with antihistaminergic properties, is one such antidepressant that has demonstrated effectiveness in reducing itch severity. As an H1, 5HT2 and 5HT3-receptor blocker, mirtazapine may be an alternative therapy for pruritus that is refractory to first-line therapies. Mirtazapine is believed to centrally reduce itch by antagonizing a2-adrenergic receptors [6,7]. Aside from having a wide therapeutic index, mirtazapine is rarely known to cause the initial anxiety and nausea associated with other antidepressants effective in treating chronic itch [2,8]. To assess the efficacy of mirtazapine for the treatment of chronic pruritus, we therefore performed a systematic review of the current literature using PubMed for English-language articles containing the words (“pruritus” or “itch”) AND “antidepressant.” The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) flow chart is shown in Figure 1. All studies reported a reduction in itch intensity following the administration of mirtazapine. Collectively, these studies suggest the potential for mirtazapine to relieve chronic itch attributed to dermatological causes and malignancies (Table 1).
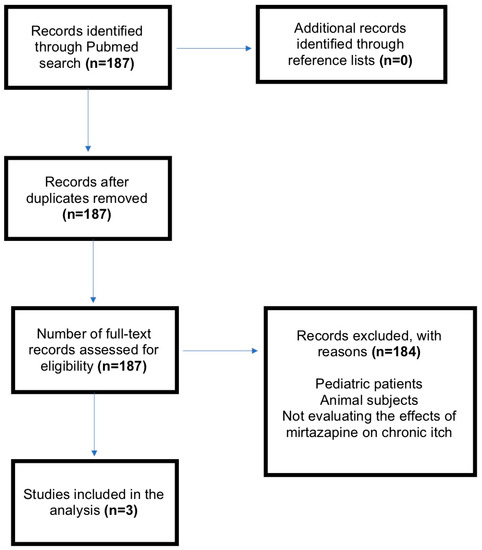
Figure 1.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) flow-chart. n, number of articles; Mirtazapine.

Table 1.
Summary of studies examining the effects of mirtazpine in treating chronic pruritus. * Determined based on the Oxford Centre for Evidence-based Medicine (CEBM) Levels of Evidence. Mirtazapine; CS, case series; CR, case report.
There are several limitations to this review. Of the studies evaluated, most were case series or case reports. Larger, randomized controlled trials are still needed to draw definitive conclusions regarding mirtazapine’s effectiveness in reducing itch. The studies included used a wide variety of outcome measures to evaluate itch intensity, which limits our ability to directly compare outcomes. Given the significant psychological burden of chronic pruritus, the placebo effect may have also affected perceived outcomes [9].
Mirtazapine is currently FDA-approved for the treatment of major depressive disorder. The main side effects of mirtazapine are heavy sedation, weight gain and hypercholesterolemia [10]. Mirtazapine is contraindicated in patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) given the increased risk of serotonin syndrome [6]. Prior to prescribing mirtazapine, physicians should obtain a baseline lipid panel, liver function tests, and fasting blood glucose levels [11]. The FDA-approved starting dose for mirtazapine is 15 mg orally every night for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) [7,11]. Physicians should counsel patients to report any signs of worsening depression or suicidal ideations upon the initiation of treatment or as a result of dosage changes. It is also advised that physicians schedule a follow-up appointment six-weeks after initiating treatment to evaluate for clinical improvement, drug reactions, or adverse effects.
In conclusion, mirtazapine may be an option for patients with chronic pruritus that is refractory to typical first-line treatments, but future randomized controlled trials are needed to determine the efficacy of therapy, optimal dosing regimens, and the types of chronic pruritus that benefit most from treatment with oral antidepressants.
Author Contributions
R.K., E.B. and S.G.K. conceived and designed the study; R.K. and E.B. conducted the literature review; R.K., E.B., J.G.Z. and S.G.K. analyzed the data; R.K. and E.B. prepared the original draft of the manuscript. R.K. and M.B. reviewed and edited the manuscript; J.G.Z. and S.G.K. supervised the analysis and writing of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
Shawn G. Kwatra is on the advisory board for Menlo and Trevi Therapeutics and has received grant funding from Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals. The other author(s) have no conflicts of interest to declare. The content in this manuscript has not been published or submitted for publication elsewhere. All authors have contributed significantly, and are in agreement with the content of the manuscript.
References
- Dhand, A.; Aminoff, M.J. The neurology of itch. Brain 2014, 137, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.P.; Frandsen, J.L.; Walsh, D.; Andresen, S.; Taylor, S. Mirtazapine for Pruritus. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2003, 25, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Sinha, V.R. Antidepressants as antipruritic agents: A review. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018, 28, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boozalis, E.; Khanna, R.; Kwatra, S.G. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for the treatment of chronic pruritus. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2018, 29, 812–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boozalis, E.; Khanna, R.; Zampella, J.G.; Kwatra, S.G. Tricyclic antidepressants for the treatment of chronic pruritus. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2019, 6, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.J.; Girouard, S.D.; Carlberg, V.M.; Mostaghimi, A. Effective use of mirtazapine for refractory pruritus associated with carcinoma en cuirasse. BMJ Support. Palliat. Care 2016, 6, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hundley, J.L.; Yosipovitch, G. Mirtazapine for reducing nocturnal itch in patients with chronic pruritus: A pilot study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2004, 50, 889–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.P.; Dickerson, E.D.; Pappagallo, M.; Benedetti, C.; Grauer, P.A.; Lycan, J. Mirtazepine: Heir apparent to amitriptyline? Am. J. Hosp. Palliat. Med. 2001, 18, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Laarhoven, A.I.M.; van der Sman-Mauriks, I.M.; Donders, A.R.T.; Pronk, M.C.; van de Kerkhof, P.C.M.; Evers, A.W.M. Placebo Effects on Itch: A Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials of Patients with Dermatological Conditions. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 1234–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, H.; Mennella, C.; Magid, M.; Stamu-O’Brien, C.; Kroumpouzos, G. Psychocutaneous disease: Pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 76, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drugs, A. REMERON ® (Mirtazapine) Tablets. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2007/020415s019,021208s010lbl.pdf (accessed on 29 June 2019).
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).