Abstract
Considering that electronic wastes (e-wastes) have been recently recognized as a potent environmental and human threat, the present study aimed to assess the potential risk of personal computer motherboards (PCMBs) leaching into aquatic media, following a real-life scenario. Specifically, PCMBs were submerged for 30 days in both distilled water (DW) and artificial seawater (ASW). Afterwards, PCMBs leachates were chemically characterized (i.e., total organic carbon, ions, and trace elements) and finally used (a) for culturing freshwater (Chlorococcum sp. and Scenedesmus rubescens) and saltwater (Dunaliella tertiolecta and Tisochrysis lutea) microalgae for 10 days (240 h), (b) as the exposure medium for mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis (96 h exposure), and (c) for performing the Cytokinesis Block Micronucleus (CBMN) assay in human lymphocytes cultures. According to the results, PCMBs could mediate both fresh- and marine algae growth rates over time, thus enhancing the cytotoxic, oxidative, and genotoxic effects in the hemocytes of mussels (in terms of lysosomal membrane impairment, lipid peroxidation, and NO content and micronuclei formation, respectively), as well as human lymphocytes (in terms of MN formation and CBPI values, respectively). The current findings clearly revealed that PCMBs leaching into the aquatic media could pose detrimental effects on both aquatic organisms and human cells.
Keywords:
algae; e-waste; genotoxicity; hemocytes; human lymphocytes; leachates; motherboard; mussels; stress indices; trace elements 1. Introduction
It is well known that human-derived pollutants can threaten environmental and human health, thus undermining the social-economic sustainability and prosperity [,]. In this context, great effort is systematically carried out for minimizing the environmental and human risk of main waste streams, like municipal and industrial wastes, as well as leachates from open dumpsites and landfills. However, electronic wastes (e-wastes), which have become one of the largest and ever-increasing waste streams worldwide [], are of great concern since their rational and environmentally sound management (i.e., recycle, reuse, and appropriate transport) is quite complex and remains problematic []. The latter is more evident in some developing countries (mainly in Africa and Asia), where legal loopholes and ineffective environmental policies still exist, and the Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and Their Disposal in third countries (i.e., South Africa and Asia) is violated [,].
E-wastes refer to all the electric and electronic equipment, along with their parts, which are discarded with no intention of reusing them []. The annual production of e-wastes (i.e., obsolete, or non-functional computer components, such as monitors, motherboards, keyboards, mouse, mobile phones and chargers, compact discs, headphones, television sets, air conditioners, and refrigerators, among others) is estimated at almost 50 million tons (Mts) by 2021, showing increasing trends overtime []. Most e-wastes are not recycled and disposed together with conventional wastes [,]. In fact, there is evidence that only 20% (almost 8.9 Mt) of the collected e-wastes are properly recycled, with approximately 40 Mts to end up in dumpsites and landfills, where they are either buried or burnt [,]. In all cases, their entrance into the environment is considered inevitable through leaching and transport with water, air and soil, thus contaminating both surface and groundwater bodies, as well as coastal basins [,]. For instance, several monitoring studies performed near e-waste treatment and workshop sites in developing countries revealed air, soil, and surface waters contamination with e-waste leaching components, mainly heavy metals ([,,,,,], as well as other toxic substances such as dioxins, polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), polychlorinated biphenyl (PCBs), brominated flame retardants (BFRs), polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin furans (PCDD/Fs) [].
Among e-wastes, personal computers (PCs) are of great concern, due to their short life and replacement, almost every two-three year []. Specifically, PC motherboards (PCMBs) represent the biggest printed circuit boards, including basic operational parts (i.e., capacitors, central processing unit/CPU, battery, external connectors and memory slots among others). PCMBs account for almost 6–9% of the total weight of PCs [], and possess high concentrations of heavy metals, like Ag, As, Au, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Hg, Mn, Ni, Pb, Se, U, and Zn, as well as uranium, bromine, Rare Earth Elements (REEs). and Platinum Group Metals (PGMs, like Ir, Pd, Pt and Rh), whose leaching could be harmful to both aquatic biota and human health [,,,]. Moreover, it has been recently reported that inappropriate handling or primitive recycling processes of e-wastes could lead to the release of dioxins, polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), as well as radioactive isotopes [,], thus being responsible for air, soil, and water resources contamination [].
Despite discrepancies, different e-waste leaching methods like the total threshold limit concentration (TTLC) test, the toxicity characteristic leaching procedure (TCLP), as well as the synthetic precipitation leaching procedure (SPLP), have been performed so far, based on different acid and/or low-pH conditions, e-waste crushing, agitation/extraction processes, and time intervals [,,,,]. However, although these methods are considered quite efficient to assess the leachability of toxic substances, like metal ions, more realistic and environmentally relevant testing methods, including both chemical and biological approaches, are highly recommended for assessing the real environmental and human impact of e-waste leaching components, following their direct disposal into water bodies [].
Considering the latter and in accordance with the Agenda 2030 for Sustainable Development, which pointed out e-waste potent threat to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SGDs), like the assurance of (a) the good health and well-being, through the reduction of chemicals in water (Goal 3), (b) aquatic ecosystems protection (Goal 14), and (c) the access to clean water (Goal 6) [], the main goal of the present study was to assess the biological effects of personal computer motherboards (PCMBs) leachates on fresh- and marine species, as well as on human lymphocytes, following a more realistic scenario. In the light of this, PCMBs were submerged for 30 days in both distilled water (DW) and artificial seawater (ASW) and thereafter PCMBs leachates, chemically characterized in a first step (i.e., total organic carbon, ions and trace elements), were used for performing biological tests. Specifically, algal bioassays with freshwater and saltwater algal species (i.e., Chlorococcum sp. and Scenedesmus rubescens as well as Dunaliella tertiolecta and Tisochrysis lutea T. ISO, respectively) were performed to assess the impact of PCMBs leachate on their growth. Moreover, mussels of the species Mytilus galloprovincialis were also used for assessing PCMBs leachate mediated cellular and oxidative effects, via the estimation of lysosomal membrane integrity (in terms of Neutral red Retention Time/NRRT assay), superoxide anions (•O2−), and nitric oxide (in terms of nitrite/NO2−) generation, as well as the extent of lipid peroxidation (in terms of malondialdehyde/MDA) in mussel hemolymph/hemocytes. Furthermore, since the presence of genotoxic compounds into PCMB leachates is of great concern, the formation of micronuclei (MN assay) in mussel hemocytes was estimated and further compared with the cytogenotoxic effects occurred in human lymphocytes (via the application of the Cytokinesis Block Micronucleus/CBMN assay), bearing in mind that the quality of the aquatic sources is undoubtedly related to human health.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
No permits were required for performing experiments with algae and mussels. The application of the CBMN method using human lymphocytes was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the University of Patras (Ref. No. 6344/26.6.2020).
2.2. PC Motherboards, Chemical and Reagents
Obsolete personal computer motherboards (PCMBs) were used for performing the experimental procedure (see Figure S1). All reagents and solvents used were of the highest analytical grade and purity. The chelating polymer resin SPR-IDA (Suspended Particulate Reagent—Iminodiacetate) as a 10% w/v suspension in deionized water was supplied by CETAC. For the preparation of reagents and standards, freshly prepared ultrapure water (18.2 MΩ × cm) was used from Barnstead NANOpure Infinity and eVOQUA systems. Ultrapure hydrochloric acid (HCl, 30%), suprapur® nitric acid (HNO3, 65%), and suprapur® ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH, 25%) were purchased from Merck. Multi-element stock solution, single-element stock solutions of Hg and P as well as ICP-MS Internal Std Mix (Bi, Ge, In, Li, Lu, Rh, Sc, Tb) were obtained from Agilent.
2.3. PCMBs Handling and Experimental Procedure
Batch-like leaching tests were performed using discarded/obsolete PCMBs, with no intention of reusing them. In brief, 2 similar PCMBs were submerged in static tanks (final volume 15L, with one PCMB per tank), containing (a) well-aerated distilled water (DW; pH 7.2 ± 1.4, dissolved oxygen: 7–8 mg L−1; salinity <0.05, temperature 17–18 °C), and (b) artificial seawater (ASW: pH 8.2 ± 1, dissolved oxygen: 7–8 mg L−1; salinity 35, temperature 17–18 °C). No size reduction or dismantling of the PCMBs components was conducted before and during the test. DW selection as leaching medium was based on its further usage for preparing algal culture medium and conducting CBMN assay, thus avoiding interferences and equivocal results, while the CPBM leaching period was 30 days, according to previous studies that showed the presence of PCMBs leaching chemicals into the aquatic media [,]. In parallel, tanks containing PCMB-free DW and/or ASW were used as reference ones. Afterwards, PCMBs were removed, and small volumes/aliquots of each tank (PCMB leachates) were used for chemical characterization.
From each tank, four portions (1000 mL in each case) of either PCMB-free or PCMB-DW leachate (N = 4 in each case) were used (a) for the preparation of the freshwater algal culture (BG-11) and (b) for performing the Cytokinesis Block Micronucleus (CBMN) assay in human lymphocytes cultures. Similarly, relevant portions of PCMB-free and PCMB-ASW were used for (a) the preparation of the saltwater algal culture media, while the rest (almost 10 L) was used for the maintenance/exposure of mussels, respectively (see also Figure S1).
2.4. Characterization of Leachates
Total organic carbon (TOC), ions (Cl−, NO2−, NO3−, PO43−, Br−) and a battery of trace elements (i.e., Al, P, Cr, Mn, Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn, Se, As, Ag, Cd, Sn, Hg, Tl, Pb) were determined in both DW and ASW leaching media, with or without the presence of PCMBs. Ions were determined by an ICS-1500 ion chromatography by Dionex, using an IonPac AS9-HC analytical column (4 × 250 mm) with Na2CO3 (9 mmol L−1) as eluent and flow rate 1 mL min−1. TOC was determined by a TOC-VCSH analyzer by Shimadzu. The TOC value was calculated by subtraction of the inorganic carbon (IC) value from the total carbon (TC) of each sample.
Trace elements were determined by an Agilent 8900 Triple Quadrupole ICP-MS/MS (Agilent Technologies, Tokyo, Japan) with an Agilent SPS4 Autosampler and an Agilent Integrated Sample Introduction System (ISIS). For the determination of metals, the employed method was based on ISO 17294-2 testing protocols [,]. The operating parameters are shown in Table S1. Multi-element and single-element stock solutions were diluted to create the calibration curves. The calibration standards and samples were finally prepared in an acid matrix of 2.5% v/v HNO3 and 0.5% v/v HCl. Linear regression was confirmed for all selected elements (R2 > 0.999). The limits of quantification of our method, including the preparation and analysis steps, are presented in Table S2.
Before the analysis of the leachates, the chelating polymer resin SPR-IDA (Suspended Particulate Reagent—Iminodiacetate) as a 10% w/v suspension in deionized water was used for preconcentration/matrix elimination of ASW. The reagent consisted of 10-micron diameter polymer beads derivatized with the chelating agent iminodiacetate. Then, 45 mL of the ASW sample was transferred to a centrifuge tube and 300 μL of the SPR-IDA (suspended particulate reagent iminodiacetate) in the form of a 10% w/v suspension were pipetted directly in the sample. The tube was capped, and the contents were mixed. As the samples were preserved with high-purity nitric at a pH of 1.6, high-purity ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH, 25%) was added in two steps (75 μL + 60 μL) to adjust the pH to approximately 8. After each addition of NH4OH, the samples were well mixed. The SPR-IDA beads were then allowed to settle for approximately one hour. Thereafter, the samples were placed in a centrifuge and spun at 2000 rpm for 10 min. The supernatants were carefully discarded, avoiding any loss of the resins that adhere to the bottom of the tubes. A solution of ultrapure water adjusted to pH 8 with high purity NH4OH was then added to the 45-mL mark of the sample tubes and the contents well mixed. The beads were allowed to settle, centrifuged, and the resulting supernatant liquid carefully discarded. Then, 1.5 mL aliquot of 7% v/v high-purity nitric acid was added to the bead residue to extract any bound metal ions []. Finally, the extract was diluted to 9 mL with ultrapure water.
2.5. Algal Bioassays
Algal strains of the freshwater species Chlorococcum sp. (strain SAG 22.83), and Scenedesmus rubescens (strain SAG 5.95) (Göttingen, Germany), as well as the saltwater species Dunaliella tertiolecta (CCAP19/6B) and Tisochrysis lutea (T. ISO strain CCAP 927, formerly listed as Isochrysis sp., Isochrysis galbana) were used for performing algal bioassays. In all cases, fresh- and salt-water algal strains were maintained and cultured in sterilized flasks, containing filtered DW enriched with BG-11 medium (24 ± 1 °C, pH 8.3 ± 0.3), and filtered ASW enriched with f/2 medium without Si (20 ± 1 °C, pH 8.3 ± 0.3, salinity 35) [,], under constant illumination (4300 lx). At the late logarithmic phase, a proper amount of each algal strain (1 × 104 cells mL−1) was transferred in conical sterilized flasks (volume 200 mL), containing PCBM-free (control cultures) or PCMB-utilized culture media (BG-11 and f/2 prepared with appropriate portions of filtered PCBM leachate in each case). Algal cell number was daily recorded for a period of 240 h (10 days), using a Neubauer hemocytometer, while the growth (μ) and the inhibition rate (%I) were determined according to well-known guidelines and protocols with some modifications []. The results are expressed as the mean ± SD from four measurements in each case.
2.6. Mussel Collection and Handling
Mussel species Mytilus galloprovincialis (5–6 cm long, almost 1 year old) were collected from a mussel farm, located in a well-monitored and characterized nature reserve area (north side of Korinthiakos Gulf, Galaxidi, Greece). The selection of the current area was based on previous studies that showed negligible levels of inorganic and organic pollution [,,]. Mussel collection was performed in February 2020, thus avoiding any interference of spawning with the obtained stress indices [,].
Mussels were transferred and laboratory acclimated for 7 days in static tanks (final volume 200 L per tank) containing aerated, recirculated with UV-sterilized and filtered artificial seawater (ASW, temperature 18 ± 1 °C, salinity 35, pH 8.0 ± 0.7, oxygen saturation > 90%). No mortality was observed throughout the acclimation period. Mussels were maintained without feeding during the acclimation period and then daily fed with Tisochrysis lutea (almost 2 × 106 cells mL−1).
2.6.1. Mussel Exposure
Before the onset of the experimental procedure, groups of mussels (20 individuals per group) were placed in two static tanks, each containing 10 L of CPBM-free ASW (control group of mussels) and 10L of CPBM- ASW leachate (CPBM-treated group of mussels) and further maintained for 4 days (96 h), without feeding, under the conditions mentioned above. Following 24 h of the onset and after the end (96 h) of the experimental procedure, ten individuals per group of mussels (control and CPBM-treated) were removed and finally used for performing stress indices analysis.
In any case, almost 10 mL of hemolymph were withdrawn from the posterior adductor muscle of 10 individuals (N = 10; 1 mL mussel−1; control- and CPBM-treated), using a sterile 1 mL syringe with an 18 G1/2′′ needle, containing equal volume of Alseve buffer []. A small portion of hemolymph from each mussel per group was used for the determination of lysosomal membrane stability in mussel hemocytes (using the neutral red retention time/NRRT) assay) and the cytogenetic analysis of DNA integrity (using the micronuclei/MN assay) (N = 10 in any case). The remaining mussel hemolymph was divided into 3 subgroups (each subgroup contained pooled hemolymph from 3 individuals per group of mussels) and further used for determining superoxide radicals, nitric oxide (in terms of nitrites) and MDA content.
2.6.2. Estimation of Lysosomal Membrane Stability and MN Frequency in Mussel Hemocytes (NRRT and MN Assays)
Both assays were performed according to the procedures and criteria proposed by UNEP/RAMOGE [] with minor modifications. In brief, 40–50 μL of hemolymph from each individual per group of mussels (N = 10) were spread on slides, transferred to a lightproof humidity chamber, and allowed to attach. In the case of the NRRT assay, all slides (cell monolayers) were incubated with 40 μg mL−1 of the cationic dye neutral red probe (NR) for 15 min in dark. Afterwards, the slides were examined under a light microscope every 15 min (at least 200 granular hemocytes examined in each slide). The period between the NR probe application and the appearance of the first evidence of dye loss from the lysosomes to the cytosol of at least 50% of the examined cells, represented the NRR time for each mussel. NRRT values (expressed as min) are the mean NRR time value ± SD from the analysis of 10 slides, each corresponding to hemolymph extracted by everyone per group of mussels.
For MN assay, all slides (containing agranular hemocytes) were fixed in methanol: acetic acid (3:1), stained with Giemsa (3% v/v), and mounted in Canada balsam, before counting under a light microscope (100× magnification, using immersion oil). At least 1000 hemocytes per slide were examined for the detection of micronucleated cells (MN), thus excluding apoptotic and necrotic ones. The results (in terms of ‰ MN frequencies) are the mean ± SD from the analysis of 10 slides, each corresponding to hemolymph extracted by everyone per group of mussels.
2.6.3. Determination of Superoxide Anions (•O2−) in Mussel Hemocytes
Superoxide anions (•O2−) detection and measurement in mussel hemocytes were spectrophotometrically performed, using nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) as previously reported by Pipe et al. [] with some modifications. In brief, almost 1 mL of pooled hemolymph from each mussel subgroup was centrifuged (150× g, 10 min, 4 °C) and the collected hemocytes were suspended in 1 mL TBS buffer (0.05 M Tris–chloride buffer, pH 7.6, containing 2% NaCl), containing 1 mg mL−1 of NBT. Following incubation for 2 h in the dark, cell suspensions were centrifuged (150× g, 10 min, 4 °C), washed twice with 300 μL TBS to remove extracellular NBT, and finally fixed with 300 μL of 70% methanol for 10 min. Thereafter, samples were centrifuged and air-dried for 5 min at room temperature. Afterwards, 1 mL of extraction fluid (2 M KOH in DMSO) was added and after incubation for 30 min, samples were measured spectrophotometrically at 620 nm (spectrophotometer PerkinElmer 551). The results are mean ± SD from 3 different measurements, performed in duplicate (technical replicates, N = 3 × 2), and expressed as OD620 nm per milligram of protein, commonly measured using the Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250-based assay [].
2.6.4. Determination of NO in Mussel Hemocytes
The detection and measurement of nitric oxides (NO, in terms of nitrites, NO2−) in mussel hemocytes were performed by the Griess reaction []. Specifically, 500 μL of pooled hemolymph from each mussel subgroup were centrifuged at 150× g for 10 min at 4 °C and the supernatant was removed carefully. Thereafter, 500 μL of 1% sulfanilic acid in 5% phosphoric acid were added to each sample, incubated at room temperature for 10 min and 500 μL of 0.1% N-napthyl-ethylene- diamine in 5% phosphoric acid was finally added. After 15 min of incubation, the optical density at 548 nm was measured. The molar concentration of nitrite in each sample was determined from standard curves with known concentrations of sodium nitrite (1–100 μmol L−1). The results are mean ± SD from 3 different measurements, performed in duplicate (technical replicates, N = 3 × 2) and expressed as nmol NO per milligram of protein.
2.6.5. Evaluation of MDA Content in Mussel Hemolymph
Lipid peroxidation was measured in the hemocytes of mussels as malondialdehyde (MDA) equivalents, which represent a reliable indicator of oxidative damage/stress []. The peroxidation of membrane lipids (in terms of malondialdehyde/MDA equivalents) in the mussels’ hemolymph was measured according to the method described by Vlahogianni and Valavanidis []. In brief, 1 mL of pooled hemolymph from each mussel subgroup was centrifuged (150× g, 10 min, 4 °C) and the supernatant was diluted in 2 mL of trichloroacetic acid (TCA)–thiobarbituric acid (TBA)–HCl [(15%, w/v TCA; 0.375%, w/v TBA in HCl 0.25 N), containing 0.02% (w/v) of butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) to prevent further peroxidation process. After heating for 15 min at 90 °C, all samples were cooled at room temperature, centrifuged at 300× g for 10 min, and finally measured at 535 nm. A molar extinction coefficient (1.5 × 105 M−1 cm−1) [] was used for the determination of the MDA concentration. The results are mean ± SD from 3 different measurements, performed in duplicate (technical replicates, N = 3 × 2) and expressed as nmol MDA per milligram of protein.
2.7. Cytokinesis Block Micronucleus (CBMN) Assay in Human Lymphocytes
The cytotoxic and/or genotoxic potential of CPBM leachate was assayed in human lymphocytes, via the Cytokinesis Block Micronucleus (CBMN) assay, using cytochalasin-B. The latter is considered as a reliable tool for assessing the presence of cytogenotoxic substances in aquatic media and highly recommended in case of hardly treated mixtures of hazardous substances or priority aquatic pollutants [,,,,].
The CBMN assay was performed according to the standard procedures []. Specifically, whole blood samples were collected from healthy and non- smoking male donors (20 and 25 years old), previously declared that they were not exposed to radiation, drug treatment, or any viral infection in the recent past. A small portion of whole blood (0.5 mL) per donor, was added to 6.5 mL Ham’s F-10 medium, containing 1.5 mL fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 0.3 mL phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) for the stimulation of cell division. Appropriate volumes of each CPBM-DW leaching portion were added in culture volume (8.8 mL) 24 h after culture initiation, to obtain final concentrations of 0.2, 1, 5, and 10% v/v, which are in accordance with previous studies regarding the cytogenotoxic effects of effluents and leachates [,,]. The verification of the CBMN assay method was performed with the use of the cyto-genotoxic mitomycin C (0.05 μg mL−1) (positive control, data not shown). After 44 h of incubation, cytochalasin-B (Cyt-B, final concentration of 6 μg mL−1) was added to block cytokinesis of dividing cells. Cultures were incubated at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 for 72 h and then cells were harvested and collected by centrifugation. A mild hypotonic treatment with a 3:1 solution of Ham’s medium and milli-Q H2O was left for 3 min at room temperature which was followed by 10 min fixation (for at least 3 times) with a fresh 5:1 solution of methanol/acetic acid.
Slides with cells were stained with DAPI and microscopically scored (100× magnification, using immersion oil). The MN formation in almost 4000 binucleated cells was scored in each case (1000 cells per culture in each case) (see also Figure S2). Cytotoxicity was calculated by Cytokinesis Block Proliferation index (CBPI), after counting at least 2000 cells in each case (500 cells per culture in each case), according to Equation (1) []:
The results are mean ± SD from 4 independent measurements. Each measurement was performed in duplicate (technical replicates).
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS 25 (IBM Inc., Armonk, NY, USA, 2019) software package. Data sets were checked for homogeneity of variance (Levene’s test of equality of error variances, SPSS Inc. 16) and the significant differences among variables obtained in control and CPBM-treated bioassays were assessed non-parametrically, using the Mann–Whitney u-test (p < 0.05).
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Leachates
The chemical analysis of samples showed significant differences in both DW and ASW in the presence or the absence of CPMB (Table 1).

Table 1.
Determination of ions, total organic carbon (TOC), and trace elements in DW and ASW in the presence or the absence of CPMB. Results (expressed as mg L−1 in case of ions and TOC, and as μg L−1 in case of trace elements) are mean ± SD from 3 different measurements. Values that share the same letter differ from each other (Bonferroni, p < 0.05).
Specifically, CPMB- DW leachates showed significantly increased levels of Cl−, Br−, and TOC, as well as trace elements, like P, Ni, Cu, Zn, and Sn, compared to those determined in CPMB-free DW, where levels were low and/or undetectable (below LOQ values) in most cases. On the other hand, CPBM-ASW leachates showed the presence of Br−, and TOC, as well as Cr, Ni and Sn. In both CPMB leachates, levels of both NO2−, NO3−, PO43− and trace elements, such as Fe, Mn, Se, As, Ag, Cd, Hg, Tl, and Pb were lower than LOQ values.
3.2. Effects of CPBM Leaching on Freshwater and Saltwater Algal Species
According to the results, freshwater algal species treated with CPBM- DW leachate showed different growth rates over time. Specifically, Chlorococcum sp. showed negligible growth rate alterations, with slight attenuation of CPBM leachate inhibitory potential over time (Figure 1A, Table 2A).
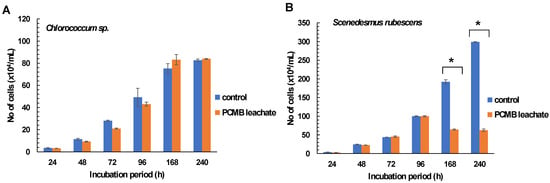
Figure 1.
Effects of PCMB-DW leachate in algal species (A) Chlorococcum sp. and (B) Scenedesmus rubescens. The results (in terms of number of cells × 104 mL−1) are mean ± SDs from 4 independent experiments. Asterisks (*) indicate significant difference between control and e-waste treated algae (Mann–Whitney u-test, p < 0.05).

Table 2.
Effects of PCMB leachate in freshwater algal species (A) Chlorococcum sp., (B) Scenedesmus rubescens, (C) Dunaliella tertiolecta and (D) Tisochrysis lutea. The results, in terms of growth rate values (μ) and % inhibition rate values (% I) are mean ± SDs from 4 independent experiments. Values that share the same letter differ from each other (Mann–Whitney u-test, p < 0.05).
On the contrary, in the case of Scenedesmus rubescens, although the significant 24 h growth arrest (24 h %I = 21.2± 6.31) declined over time (till 96 h), further treatment showed significantly lower growth rates (high % inhibition rates and low algal densities) than the control (Figure 1B, Table 2B).
Similarly, lower growth rates and algal density were observed in Dunaliella tertiolecta treated in CPBM-utilized culture media (48–240 h), while in the case of Tisochrysis lutea significantly higher inhibitory rates were observed after treatment for 168 and 240 h (Figure 2A,B, Table 2C,D).
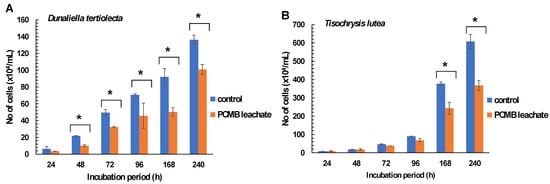
Figure 2.
Effects of PCMB-ASW leachate in algal species (A) Dunaliella tertiolecta and (B) Tisochrysis lutea. The results (in terms of number of cells × 104 mL−1) are mean ± SDs from 4 independent experiments. Asterisks (*) indicate significant difference between control and e-waste treated algae (Mann–Whitney u-test, p < 0.05).
3.3. CPBM Leaching Mediated Effects on Mussels
Regarding mussel exposure to CPBM-ASW leachate, no mortality was observed during the exposure period. However, the results showed significantly lower NRRT values in hemocytes of mussels after the onset (24 h) as well as at the end (96 h) of the exposure period, thus indicating an acute lysosomal membrane destabilization, compared to those that occurred in control mussels (Figure 3). On the other hand, •O2− levels remains constant, with a significant increase of NO levels to be observed in hemocytes of 96 h treated mussels (Figure 4A,B). Similarly, an enhanced peroxidation of lipids was observed in the hemolymph of mussels exposed for 24 and 96 h to CPBM leachate (Figure 4C). Interestingly, the latter was characterized by genotoxic potential, as revealed by the high MN frequencies observed in mussel hemocytes (Figure 5).
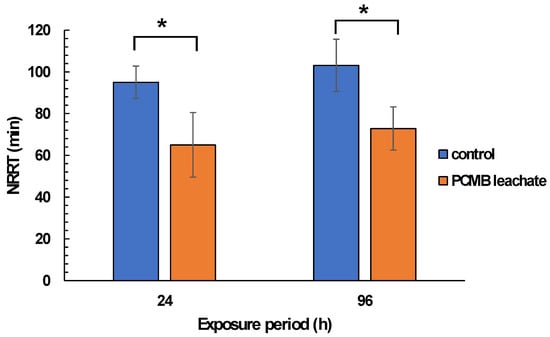
Figure 3.
Lysosomal membrane stability (in terms of NRRT values) in hemocytes of mussels exposed to PCMB-ASW for 96 h. The results (expressed as min) are mean± SDs for 10 individuals in each case. Asterisks (*) indicate significant difference from the respective control (Mann–Whitney u-test, p < 0.05).
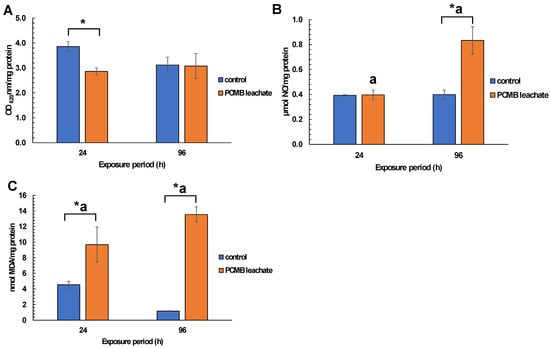
Figure 4.
Determination of (A) superoxide anions (O2−), (B) nitric oxides (in terms of NO2−), and (C) lipid peroxidation (in terms of MDA equivalents) in hemocytes/hemolymph of mussels exposed to PCMB-ASW for 96 h. The results (expressed as OD620 nm mg protein−1, μmol NO mg protein−1, and nmol MDA mg protein−1, respectively) are mean ± SD from 3 different measurements (each measurement was performed in duplicate) in all cases. Asterisks (*) indicate significant difference from the respective control. Values that share the same letter differ from each other (Mann–Whitney u-test, p < 0.05).
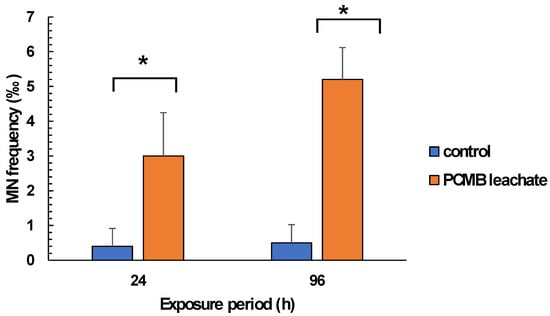
Figure 5.
Determination MN frequencies in hemocytes of mussels exposed to PCMB-ASW for 96 h. Values are mean ± SD obtained after analysis of samples derived from 10 individuals of each group of mussels. Asterisks (*) indicate significant difference from the respective control. Values that share the same letter differ from each other (Mann–Whitney u-test, p < 0.05).
3.4. CPBM Leaching Mediated Effects on Human Lymphocytes (CBMN Assay)
Considering the CBMN assay, the results showed the CPBM leachate cytotoxic and genotoxic potential against human lymphocytes. Specifically, cells treated with different concentrations of CPBM leachate (0.2–10% v/v) showed lower CBPI values, compared to those that occurred in control (Figure 6A). Moreover, cells treated with CPBM leachate at concentrations ranged from 1 to 10% v/v showed a significant induction of MN formation, with almost a 2-fold increase to be observed in cells treated with the highest CPBM leachate concentration (Figure 6B,C).
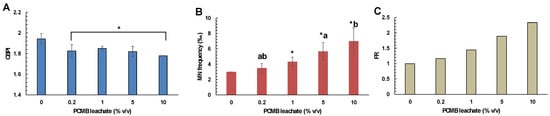
Figure 6.
Determination of (A) cytotoxic (in terms of CBPI values) and (B,C) genotoxic (in terms of MN frequency and frequency ratio) effects of PCMB-DW leachate on human lymphocytes. The results are mean ± SD from 4 different measurements in all cases. Asterisks (*) indicate significant difference from the respective control. Values that share the same letter differ from each other (Mann–Whitney u-test, p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
4.1. PCMB Chemical Substances in Leaching Media
Based on a real-life scenario, the present study revealed that the direct disposal of PCBMs into fresh- and saltwater bodies could lead to the release of different types of chemical substances, even after a leaching period of 30 days. Similarly, Lithner et al. [] reported that different discarded electronic products can leach toxic compounds during a short-term (3 days) period of leaching into pure water (pH 7, 23 °C), while Almeida et al. [] reported that PCMBs trace elements could be leached into DW (pH 4.8) even after the first days of a prolonged leaching period (120 days). According to the latter, it seems reasonable to suggest that even under mild leaching conditions, in terms of constant temperature and natural to alkaline pH values ((pH 7–8, 17 °C), inorganic anions, trace elements, and organic toxicants can be leached by PCMBs into both media tested. The latter was supported by the increased levels of total organic carbon (TOC) measured in both leaching media, as well as the high levels of Cl−, Br− and trace elements, such as Al, Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, and Sn.
Bromide ions (Br−) concentrations measured in both PCMB-DW and PCMB-ASW leachates were within the range of values reported by Almeida et al. [] (1.21 mg/L), following a leaching period of 120 days, with Br− concentrations almost 1 mg/L to be obtained only after 30 days of leaching. The latter supports previous evidence that Br−, mainly derived by halogenated organic pollutants (HOPs) like brominated flame retardants (BFRs) typically encountered in MBs, is likely to be one of the major e-waste pollutants in aquatic media []. Additionally, the presence of Al, Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, and Sn as main elements in MBs components (i.e., capacitors, processors, etc.) has been recently reported [,,]. Although different types of organic chemical substances were not measured, the high levels of TOC could depict the presence of organic toxicants, mainly released during the PCMB leaching process. The latter could be detrimental for biota, due to organic carbon’s ability to form complexes with metals and nutrients, thus acting as a substrate for microbial production []. Moreover, the increased levels of Cl− mainly derived from chlorinated flame retardants (CFRs) commonly used to produce MB capacitors, could react with organic carbon precursors to form trihalomethane that is harmful to aquatic biota and human [], but more studies are needed for elucidate the latter.
Differences among the number and the amount of trace elements and inorganic and organic substances leached into DW and ASW is not surprising. In fact, since there is evidence that their leaching depends on both the method and media used, small changes in pH values, metal mobility and chemical form, the presence of organic compounds and corrosion time intervals [,,,], their presence could be over- or underestimated, depending on the procedure currently used. The latter could lead to the suggestion that the number and the amount of those substances could not be comparable to their presence in solid e-wastes, representing only a small fraction of leaching substances (including both organic and inorganic compounds) that currently occurred after the application of acid-based e-waste leaching methods (i.e., TTLC, TCLP, SPLP methods) [,,]. However, their presence, even under mild leaching conditions currently performed, following corrosion [], is of great environmental concern, thus giving rise to their detrimental biological effects [,].
4.2. Biological Effects of PCMB Leachates
Until now, previous studies were focused on the assessment of e-waste ability to promote mortality in tested organisms, as well as challenged species ability to accumulate e-waste leaching substances into their tissues. However, data regarding the assessment of non-lethal mediated effects of e-wastes on species from different trophic levels are scarce. In fact, given that e-waste is considered as a complex mixture of chemical substances, whose inhibitory, synergistic, and additive interactions are questioned and hardly assessed, the investigation of e-waste mediated biological effects requires a battery of biological tests and assays, commonly related with different species as well as aspects of organism function []. To this end, the present study showed that PCMB leaching into DW and ASW could affect algal growth, marine mussels, and human health.
4.2.1. Effects on Algal Species Growth and Survival
Algae, representing key producers in the aquatic ecosystems, are ideal biological models for alarming disturbances in water quality due to the presence of different types of chemicals, wastes and leachates ([,,,,]. To this end, algae cultured in PCMB leachate-utilized media showed differential responses in their growth and algal cell densities, thus revealing the deterioration of culture media due to chemical substances leaching from PCMB. Considering algal cell densities and growth rates over time, Chlorococcum sp. seemed to be less vulnerable towards PCMB leachate, as revealed by the negligible changes of algal cell density and growth rate, while Scenedesmus rubescens, bearing different growth rate showed a significant decline of algal cell density over time. Similarly, both saltwater species Dunaliella tertiolecta and Tisochrysis lutea showed a significant decline in their growth and cell density over time, thus revealing their sensitivity.
Despite the absence of data regarding algal response against such a mixture of contaminants (present in e-waste leachates), differences between algae could be due to cell size, the presence of cell wall, as well as species ability to absorb and eliminate contaminants. For example, algae with cell wall, like Chlorococcum sp., could be less vulnerable to chemical substances, thus bearing higher growth rates after prolonged exposure periods, probably due to adaptation and metabolic regulations [,]. On the other hand, the presence of hazardous substances at levels almost critical for growth could inhibit or prompt algal growth [,], depending on the elimination rates of the tested species []. Moreover, there is evidence that chemical substances could disturb cell wall integrity, thus leading to cell division dysfunction [,], before algal adaptation occurs over time, as revealed by PCMB-treated Scenedesmus rubescens low growth rates and cell density. In case of wall-free Dunaliella tertiolecta and Tisochrysis lutea, the absence of cell wall could make them sensitive to chemical substances, which in turn could lead to lower growth rate and density almost after a short period of exposure [,], as revealed by the results of the present study. However, more studies are needed for verifying the exact mechanisms linked to algal behavior against e-waste leachates, bearing in mind the complex nature of those type of wastes, as well as the presence of different types of chemical substances and interactions among them.
4.2.2. Cellular and Oxidative Effects on Hemolymph/Hemocytes of Mussel Mytilus Galloprovincialis
The determination of stress indices in hemolymph of the species Mytilus galloprovincialis is widely used for assessing the type of pressure aquatic ecosystems are faced with, as well as the adverse effects of different types of pollutants (either alone or in mixtures) with great precision and reproducibility [,,,]. Since mussel hemocytes represent the main immune defensive cells in bivalves [] the present study showed for the first time that PCMBs leaching into marine media (ASW) could disturb hemocyte lysosomal membrane integrity. The latter is of great interest, considering that lysosomes constitute the main cellular organelles of sequestration and detoxification of xenobiotics, while their functional membrane impairment by different types of single or mixtures of both inorganic and organic chemicals could lead to cellular damage [,,]. In fact, given that abiotic factors (i.e., pH, dissolved oxygen, and salinity) remained constant during the experimental period, lysosomal membrane impairment could be related to the uptake of PCMB leaching toxic substances, which in turn lead to the loss of membrane integrity, the release of lysosomal content into the cytoplasm, and the concomitant cellular death, a process that could affect the overall health status of the organism, as previously mentioned [,].
In accordance with the latter, the increased levels of both NO and MDA revealed the enhancement of oxidative-like stress in challenged mussels, possibly due to the presence of pro-oxidant PCBM leaching substances, like metals and lipophilic organic compounds. The latter was further reinforced by previous studies, regarding the oxidative potential of e-waste chemicals and their ability to disrupt immune processes [,]. In particular, although both NO and/or •O2−, formed by aerobic metabolism in mitochondria and microsomes, or the stimulation of immune mechanisms, like the respiratory burst in mussel hemocytes, could be vital for cell protection against oxidant injury, NO overproduction has been linked to many aspects of cellular damage, like peroxidation of membrane lipids, mainly via the formation of hydroxyl radicals (HO) and the toxic intermediate peroxynitrite (ONOO−) (see [] and references therein), a fact that was further revealed by the results of the present study.
4.2.3. Cytogenotoxic Effects on Mussel Hemocytes and Human Lymphocytes
Interestingly, the significant increase of MN frequency in mussel hemocytes as well as the cytotoxic (in terms of low CBPI values) and genotoxic (in terms of high MN frequency values) effects currently observed in human lymphocytes, revealed the presence of cytogenotoxic compounds into the leaching media even under mild leaching conditions currently used. In fact, the enhanced levels of lipid peroxides and NO could merely explain the observed genotoxic effects in mussel hemocytes [], but the presence of e-waste leaching components could be also responsible for the induction of severe cyto-genotoxicity in challenge organisms. The latter was reinforced by previous studies that reported e-waste leaching components’ ability to oxidize nucleobases, and thus induce DNA methylation, and dysfunction of DNA repair [,,]. Moreover, Grant et al. [] reported that e-waste leaching substances, such as Polybrominated diphenyl ethers, PAHs, Cr, Ni, and Al, could enhance the formation of nuclear abnormalities in both animals and human beings, a fact that was also confirmed by cytogenetic studies performed in residents of e-waste heavily polluted areas [,,]. Moreover, Uba et al. [] recently reported that the existence of metal–DNA interactions could disturb the cell cycle and the mitotic process in Allium cepa. On the other hand, high levels of organic compounds, as indicated by the high levels of TOC, and Cl− could lead to the formation of THM-derived carcinogenic and mutagenic intermediates [,], thus increasing the risk posed by the release of e-wastes into aquatic media. However, considering the difficulties in determining each e-waste leaching component into the receiving media, further studies are important to elucidate the mechanism(s) of e-waste leachate mediated genotoxic effects.
5. Conclusions
The present study firstly revealed that PCMBs direct disposal into fresh- and saltwater bodies (mild leaching conditions) could be detrimental not only for aquatic biota but also for human health, via the leaching of both inorganic and organic chemical substances, as well as trace elements of environmental concern. Accordingly, it was mentioned that PCMB leachates could affect both fresh- and saltwater algal biomass and growth rates, a fact that could be linked with disturbances on water quality and the ecological relevance of those key producers of the aquatic ecosystems. The latter was further reinforced by the significant cellular, oxidative, and genotoxic effects firstly observed in challenged mussels of the species Mytilus galloprovincialis, as well as human lymphocytes, thus indicating the pressure aquatic ecosystems and human beings are faced with, due to the presence of oxidative and cytogenetic PCMB leaching chemical substances. However, the number and the amount of those PCMB leaching chemical substances could merely represent the true environmental and human impact, since more leaching compounds could be also released, following pH changes due to natural water acidification (i.e., acid rain fallout) and/or the increased trend of e-waste disposal over time. To this end, more studies are needed for elucidating the pH-dependent leachability of e-waste derived trace elements in the presence or absence of organic substances, as well as their potential impact, thus enriching scientific and public awareness in favor of natural sources protection and the concomitant human health.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/toxics9070166/s1, Supplementary Figures and Tables are available in SM File (Figures S1 and S2, Tables S1 and S2).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.D.; methodology, S.D.; software, S.D.; validation, S.D., M.A., D.V. and I.N.; formal analysis, S.D., M.K., G.K., M.A. and A.E.; investigation, M.K. and G.K.; data curation, S.D., M.A., D.V., A.E. and I.N.; writing—original draft preparation, S.D.; writing—review and editing, S.D. and I.N.; visualization, S.D., M.A., D.V. and I.N.; supervision, S.D.; project administration, S.D.; funding acquisition, S.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki. The application of the CBMN method using human lymphocytes was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the University of Patras (Ref. No. 6344/26.6.2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Akrokeramos Sewerage Laboratory of Athens Water Supply and Sewerage Company (EYDAP SA) for ICP-MS/MS analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- United Nations. The Sustainable Development Goals 2018 Report; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Fuller, R.; Acosta, N.J.R.; Adeyi, O.; Arnold, R.; Basu, N.; Baldé, A.B.; Bertollini, R.; Bose-O’Reilly, S.; Boufford, J.I.; et al. The Lancet Commission on pollution and health. Lancet 2018, 391, 462–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- UNEP. E-Waste. Volume I: Inventory Assessment Manual; Division of Technology, Industry, and Economics, International Environmental Technology Center, Osaka/Shiga, United Nations Environment Program. 2007. Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/handle/20.500.11822/7857 (accessed on 11 September 2016).
- Baldé, C.P.; Forti, V.; Gray, V.; Kuehr, R.; Stegmann, P. The Global E-Waste Monitor—2017; United Nations University (UNU): Bonn, Germany; International Telecommunication Union (ITU): Geneva, Switzerland; International Solid Waste Association (ISWA): Vienna, Austria, 2017; pp. 978–992, ISBN Electronic Version. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP. Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and their Disposal; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 1992; Available online: http://www.basel.int/Portals/4/Basel%20Convention/docs/text/BaselConventionText-e.pdf (accessed on 14 October 2014).
- Step Initiative. Solving the E-Waste Problem (Step) White Paper, One Global Definition of E-Waste; Step Initiative: Bonn, Germany, 2014; Available online: http://www.step-initiative.org/files/step/_documents/StEP_WP_One GlobalDefinitionofE-waste_20140603_amended.pdf (accessed on 9 May 2017).
- Ladou, J.; Lovegrove, S. Export of electronics equipment waste. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2008, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Achal, V. Environmental and health impacts due to e-waste disposal in China—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 139745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Needhidasan, S.; Agarwal, S.G. A review on properties evaluation of bituminous addition with E-waste plastic powder. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 22, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Resource Conservation and Recovery. Electronic Waste in the United States through 2009; EPA 530-R-11-002; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas, R.; Cardoso, C.E.; Costa, S.; Morais, T.; Moleiro, P.; Lima, A.F.; Soares, M.; Figueiredo, S.; Agueda, T.L.; Rocha, P.; et al. New insights on the impacts of e-waste towards marine bivalves: The case of the rare earth element Dysprosium. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 113859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.H.; Wu, S.C.; Deng, W.J.; Yu, X.Z.; Luo, Q.; Leung, A.O.W.; Wong, A.S. Export of toxic chemicals–a review of the case of uncontrolled electronic-waste recycling. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 149, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pradhan, J.K.; Kumar, S. Informal e-waste recycling: Environmental risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in Mandoli industrial area, Delhi, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 7913–7928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awasthi, A.K.; Zeng, X.; Li, J. Environmental pollution of electronic waste recycling in India: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 211, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.; Cai, Z.W.; Wong, M.H. Environmental contamination from electronic waste recycling at Guiyu, southeast China. J. Mater. Cycl. Waste 2006, 8, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.O.W.; Luksemburg, W.; Wong, A.; Wong, M. Spatial distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in soil and combusted residue at Guiyu, an electronic waste recycling site in Southeast China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2730–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.O.W.; Duzgoren-Aydin, N.S.; Cheung, K.C.; Wong, M.H. Heavy metals concentrations of surface dust from e-waste recycling and its human health implications in southeast China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2674–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, X.-J.; Huang, L.-Q.; Tao, L.; Zeng, Y.-H.; Mai, B.-X. Halogenated organic pollutants in aquatic, amphibious, and terrestrial organisms from an e-waste site: Habitat-dependent accumulation and maternal transfer in watersnake. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, B.H. E-waste: An assessment of global production and environmental impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 408, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kida, A. Elemental analysis methods including rare metals in used products. JSMCWM 2010. Available online: http://jsmcwm.or.jp/recycle/4KidaNIES.pdf (accessed on 9 July 2010). (In Japanese).
- Almeida, C.; Grosselli, M.; González, P.; Martínez, D.; Gil, R. Batch leaching tests of motherboards to assess environmental contamination by bromine, platinum group elements and other selected heavy metals. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, C.A.; Gomes, L.P. Physical and chemical characterization and recycling potential of desktop computer waste, without screen. J. Clean Prod. 2018, 184, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib Al Razi, K.M. Resourceful recycling process of waste desktop computers: A review study. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 110, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Pan, B.; Wang, L.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Nie, X. Adverse effects in Daphnia magna exposed to e-waste leachate: Assessment based on life trait changes and responses of detoxification-related genes. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lincoln, J.D.; Ogunseitan, O.A.; Shapiro, A.A.; Saphores, J.-D.M. Leaching assessments of hazardous materials in cellular telephones. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2572–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Method 1311: Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure (TCLP). Available online: http://www.epa.gov/wastes/hazard/testmethods/sw846/pdfs/1311.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2011).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Method 1311: Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure, SW-846 Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Wastes. 1992. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/epawaste/hazard/testmethods/sw846/online/index.htm (accessed on 9 July 1992).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Identification and Listing of Hazardous Waste; The Code of Federal Regulations; Office of Federal Register, National Archives and Records Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; Title 40, Chapter 1, Part 261. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Method 1312: Synthetic Precipitation Leaching Procedure, SW-846 Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Wastes. 1994. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/epawaste/hazard/testmethods/sw846/online/index.htm (accessed on 1 September 1994).
- Puckett, J.; Smith, T.C. Exporting Harm: The High-Tech Trashing of Asia; Basel Action Network: Seattle, WA, USA, 2002; Available online: http://www.ban.org/E-waste/technotrashfinalcomp.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2006).
- Lithner, D.; Halling, M.; Dave, G. Toxicity of electronic waste leachates to Daphnia magna: Screening and toxicity identification evaluation of different products, components, and materials. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 62, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 17294-1: 2004. Water Quality—Application of Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS)—Part 1: General Guidelines. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/32957.html (accessed on 1 September 2004).
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 17294-1: 2016. Water Quality—Application of Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS)—Part 2: Determination of Selected Elements Including Uranium Isotopes. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/62962.html (accessed on 1 September 2016).
- Smith, F.; Doeschot, P. Use of the SPR-IDA Reagent for the Determination of Trace Metals in a Coastal Seawater Reference Material; APPLICATION NOTE: SPR-IDA-001; Teledyne Technologies, Inc.: Omaha, NE, USA, 2014; Available online: https://www.teledynecetac.com/products/nebulizers/spr-ida (accessed on 9 July 2021).
- Tsarpali, V.; Harbi, K.; Dailianis, S. Physiological response of the green microalgae Dunaliella tertiolecta against imidazolium ionic liquids [bmim][BF4] and/or [omim][BF4]: The role of salinity on the observed effects. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloukinioti, M.; Politi, A.; Kalamaras, G.; Dailianis, S. Feeding regimes modulate biomarkers responsiveness in mussels treated with diclofenac. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 156, 104919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organization for the Economic Cooperation and Development. Test No. 201: Freshwater Alga and Cyanobacteria, Growth Inhibition Test; OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsarpali, V.; Belavgeni, A.; Dailianis, S. Investigation of toxic effects of imidazolium ionic liquids, [bmim][BF4] and [omim][BF4], on marine mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis with or without the presence of conventional solvents, such as acetone. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 164, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toufexi, E.; Tsarpali, V.; Efthimiou, I.; Vidali, M.S.; Vlastos, D.; Dailianis, S. Environmental and human risk assessment of landfill leachate: An integrated approach with the use of cytotoxic and genotoxic stress indices in mussel and human cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Fernández, C.; Lacroix, C.; Paul-Pont, I.; Le Grand, F.; Albentosa, M.; Bellas, J.; Viñas, L.; Campillo, J.A.; Hegaret, H.; Soudant, P. Effect of diet quality on mussel biomarker responses to pollutants. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 177, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politakis, N.; Belavgeni, A.; Efthimiou, I.; Charalampous, N.; Kourkouta, C.; Dailianis, S. The impact of expired commercial drugs on non-target marine species: A case study with the use of a battery of biomarkers in hemocytes of mussels. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNEP/Ramoge. Manual on the Biomarkers Recommended for the MED POL Biomonitoring Programme; UNEP: Athens, Greece, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Pipe, R.K.; Coles, J.A.; Carissan, F.M.M.; Ramanathan, K. Copper induced immunomodulation in the marine mussel, Mytilus edulis. Aquat. Toxicol. 1999, 46, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grintzalis, K.; Georgiou, C.D.; Schneider, Y.J. An accurate and sensitive Coomassie brilliant blue G-250-based assay for protein determination. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 480, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, L.C.; Wagner, D.A.; Glogowski, J.; Skipper, P.L.; Wishnok, J.S.; Tannenbaum, S. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and (15N) nitrate in biological fluids. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 126, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavazzi, B.; Di Pierro, D.; Amorini, A.M.; Fazzina, G.; Tuttobene, M.; Giardina, B.; Lazzarino, G. Energy metabolism and lipid peroxidation of human erythrocytes as a function of increased oxidative stress. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlahogianni, T.H.; Valavanidis, A. Heavy-metal effects on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defence enzymes in mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis. Chem. Ecol. 2007, 23, 361–371. [Google Scholar]
- Wills, E.D. Lipid peroxide formation in microsomes. Biochem J. 1969, 113, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zegura, B.; Heath, E.; Cernoša, A.; Filipic, M. Combination of in vitro bioassays for the determination of cytotoxic and genotoxic potential of wastewater, surface water and drinking water samples. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Xiang, L.; Luan, H.; Wei, Y.; Ren, H.; Chen, P. The health concern of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in a notorious e-waste recycling site. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 186, 109817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charalampous, N.; Kindou, A.; Vlastos, D.; Tsarpali, V.; Antonopoulou, M.; Konstantinou, I.; Dailianis, S. A multidisciplinary assessment of river surface water quality in areas heavily influenced by human activities. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 69, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFu, H.; RuiRui, C.; EnHui, Z.; Na, C.; Bo, Y.; HuaHong, S.; MinSheng, H. Toxicity bioassays for water from black-odor rivers in Wenzhou, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 1731–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlastos, D.; Dailianis, S.; Kindou, A.; Antonopoulou, M.; Gianni, A.; Zacharias, I. Assessing the environmental/human risk of potential genotoxicants in water samples from lacustrine ecosystems: The case of lakes in Western Greece. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organization for the Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). Test No. 487: In Vitro Mammalian Cell Micronucleus Test; OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vlastos, D.; Antonopoulou, M.; Lavranou, A.; Efthimiou, I.; Dailianis, S.; Hela, D.; Lambropoulou, D.; Paschalidou, A.K.; Kassomenos, P. Assessment of the toxic potential of rainwater precipitation: First evidence from a case study in three Greek cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.-I.; Lee, S.-H.; Osako, M. Leaching of brominated flame retardants from TV housing plastics in the presence of dissolved humic matter. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, P.J.; Molot, L.A. Effect of landscape form on export of dissolved organic carbon, iron, and phosphorus from forested stream catchments. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 2591–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health Canada. Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality; Minister of Public Works and Government Services Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Keith, A.; Keesling, K.; Fitzwater, K.K.; Pitchel, J.; Houy, D. Assessment of Pb, Cd, Cr and Ag leaching from electronics waste using four extraction methods. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2008, 43, 1717–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Richardson, J.B.; Niu, X.; Jackson, O.J.; Laster, J.D.; Walker, A.K. Dynamic leaching test of personal computer components. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, Y.C.; Townsend, T.G. Leaching of lead from computer printed wire boards and cathode ray tubes by municipal solid waste landfill leachates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4778–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Król, A.; Mizerna, K.; Bożym, M. An assessment of pH-dependent release and mobility of heavy metals from metallurgical slag. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Richardson, J.; Walker, A.; Yuan, P. TCLP heavy metal leaching of personal computer components. J. Environ. Eng. 2006, 132, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musson, S.; Jang, Y.; Townsend, T.; Chung, I. Characterization of lead leachability from cathode ray tubes using the toxicity characteristic leaching procedure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 4376–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagan, R.; Dubey, B.; Bitton, G.; Townsend, T. Aquatic toxicity of leachates generated from electronic devices. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 53, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dailianis, S. Environmental impact of anthropogenic activities: The use of mussels as a reliable tool for monitoring marine pollution. In Mussels: Anatomy, Habitat and Environmental Impact; McGevin, L.E., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 43–72. [Google Scholar]
- American Society for Testing and Materials. Standard Guide for Conducting Static 96-h Toxicity Tests with Microalgae; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1996; Volume 11.05. [Google Scholar]
- Tsiaka, P.; Tsarpali, V.; Ntaikou, I.; Kostopoulou, M.N.; Lyberatos, G.; Dailianis, S. Carbamazepine-mediated pro-oxidant effects on the unicellular marine algal species Dunaliella tertiolecta and the hemocytes of mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 1208–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbi, K.; Makridis, P.; Koukoumis, C.; Papadionysiou, M.; Vgenis, T.; Kornaros, M.; Ntaikou, I.; Giokas, S.; Dailianis, S. Evaluation of a battery of marine speciesbased bioassays against raw and treated municipal wastewaters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Li, H. Aquatic toxicity of heavy metal-containing wastewater effluent treated using vertical flow constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cáceres, T.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Toxicity of fenamiphos and its metabolites to the Cladoceran Daphnia carinata: The influence of microbial degradation in natural waters. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1264–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dai, X.K.; Wei, J. Toxicity of the xenoestrogen nonylphenol and its biodegradation by the alga Cyclotella caspia. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 1662–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Yao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Chu, H. The influence of four pharmaceuticals on Chlorella pyrenoidosa culture. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, L.Y.; Li, Y.B.; Wang, X.L.; Liang, S.K.; Zhu, C.J.; Han, X.R. The influence of biosurfactant on the growth of Prorocentrum donghaiense. China Environ. Sci. 2004, 6, 692–696. [Google Scholar]
- Charalampous, N.; Grammatikopoulos, G.; Kourmentza, C.; Kornaros, M.; Dailianis, S. Effects of Burkholderia thailandensis rhamnolipids on the unicellular algae Dunaliella tertiolecta. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsarpali, V.; Dailianis, S. Investigation of landfill leachate toxic potency: An integrated approach with the use of stress indices in tissues of mussels. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 124–125, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danellakis, D.; Ntaikou, I.; Kornaros, M.; Dailianis, S. Olive oil mill wastewater toxicity in the marine environment: Alterations of stress-indices in tissues of mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 101, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.C. Bivalves. In Invertebrates Blood Cells; Ratcliffe, N.A., Rowley, A.F., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2001; pp. 233–300. [Google Scholar]
- Dailianis, S.; Domouhtsidou, G.P.; Raftopoulou, E.; Kaloyianni, M.; Dimitriadis, V.K. Evaluation of neutral red retention assay, micronucleus test, acetylcholinesterase activity and a signal transduction molecule (cAMP) in tissues of Mytilus galloprovincialis (L.) in pollution monitoring. Mar. Environ. Res. 2003, 56, 443–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, M.R.; Friedl, F.E. Effects of fungicide on in vitro hemocytes viability, phagocytosis and attachment in the American oyster, Crassostrea virginica. Aquaculture 1992, 107, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazzoli, C.; Orisakwe, O.E.; Dragone, R.; Mantovani, A. Diagnostic health risk assessment of electronic waste on the general population in developing countries’ scenarios. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2010, 30, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cao, J.; Li, K.Q.; Miao, X.H.; Li, G.; Fan, F.Y.; Zhao, Y.C. Chromosomal aberrations and DNA damage in human populations exposed to the processing of electronics waste. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2009, 16, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dailianis, S. Production of superoxides and nitric oxide generation in haemocytes of mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lmk.) after exposure to cadmium: A possible involvement of Na+/H+ exchanger in the induction of cadmium toxic effects. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 27, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Kaur, B.; Kalina, I.; Popov, T.A.; Georgieva, T.; Garte, S.; Binkova, B.; Sram, R.J.; Taioli, E.; Farmer, P.B. Effects of environmental air pollution on endogenous oxidative DNA damage in humans. Mutat. Res. 2007, 620, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, K.; Goldizen, F.C.; Sly, P.D.; Brune, M.N.; Neira, M.; van den Berg, M. Health consequences of exposure to e-waste: A systematic review. Lancet Glob. Health 2013, 1, E350–E361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, S.; Yang, F.X.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Hui, Y.; Li, J.G.; Liu, A.L.; Wu, Y.N.; Lu, W.Q.; Xu, Y. Elevated levels of urinary 8-hydroxy-20-deoxyguanosine in male electrical and electronic equipment dismantling workers exposed to high concentrations of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans, poly- brominated diphenyl ethers, and polychlorinated biphenyls. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4202–4207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perkins, D.N.; Drisse, M.B.; Nxele, T.; Sly, P.D. E-waste: A global hazard. Ann. Glob. Health 2014, 80, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uba, B.O.; Okoye, E.L.; Nweke, B.G.; Ibeneme, C.P. Evaluation of the Ecotoxicity Potentials of E-Waste Using Selenastrum capricornutum (Microalga), Eisenia fetida (Earth Worm) and Allium cepa (Onion Bulb) as Bioindicators. Asian J. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. 2020, 3, 20–31. [Google Scholar]
- Reckhow, D.A.; Singer, P.C. Chlorination by-products in drinking waters: From formation potentials to finished water concentrations. J. Am. Water Work Assoc. 1990, 82, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).