Wild Zebrafish Sentinels: Biological Monitoring of Site Differences Using Behavior and Morphology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Location & Subjects
2.2. Ethics Statement
2.3. Data Collection & Analysis
3. Results
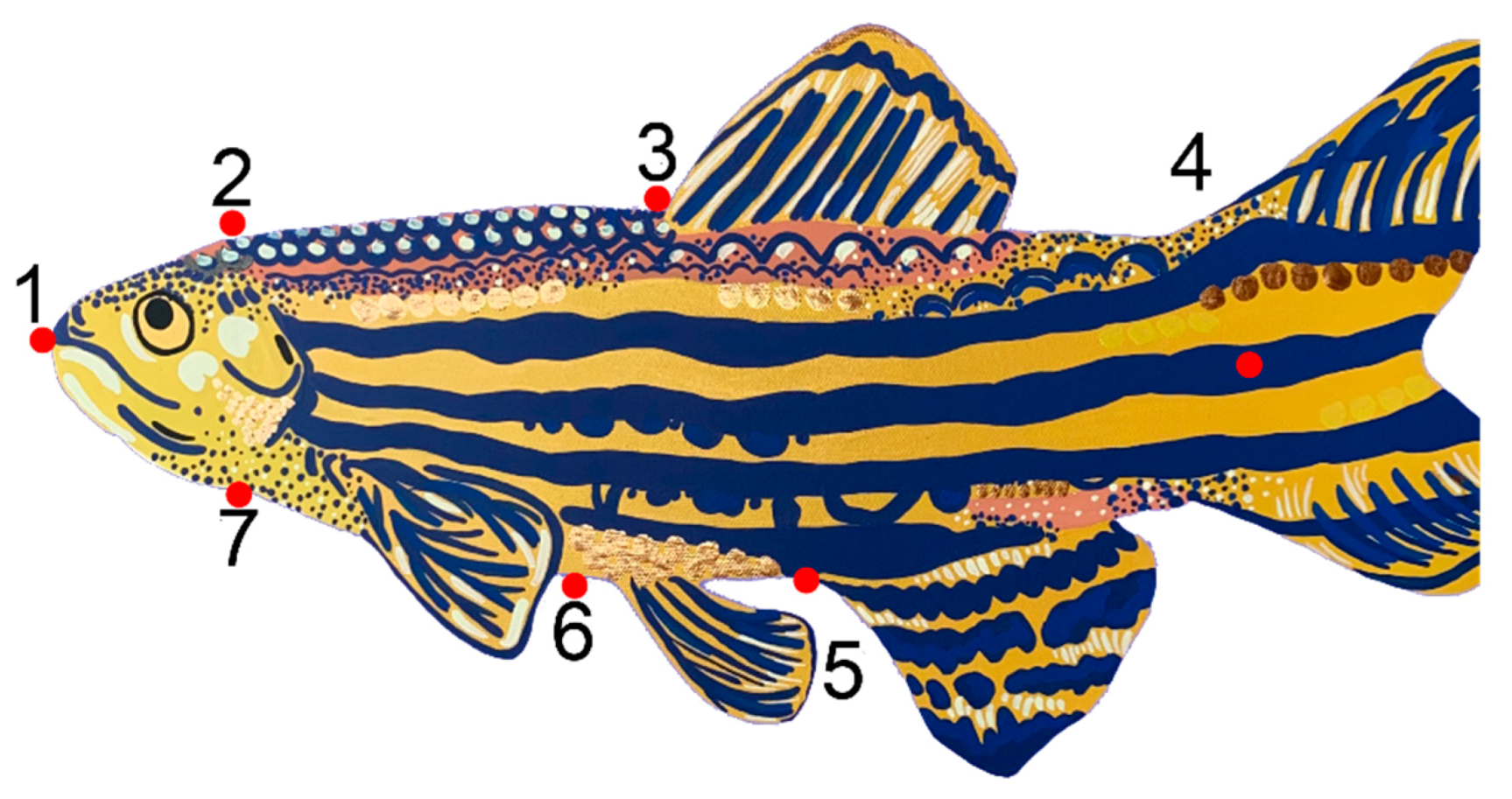
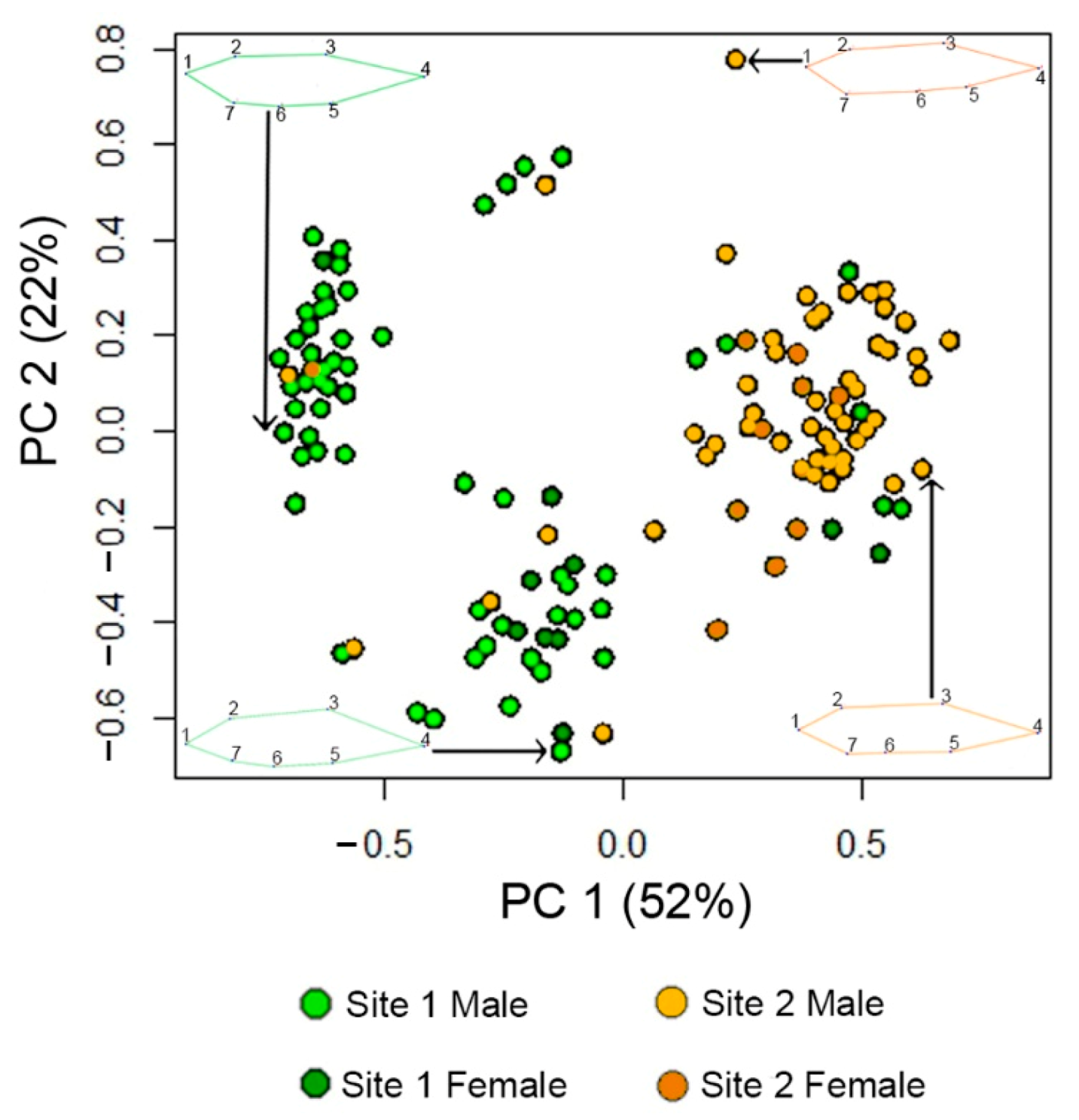
3.1. Fish Body Shape Is Distinct between Sites
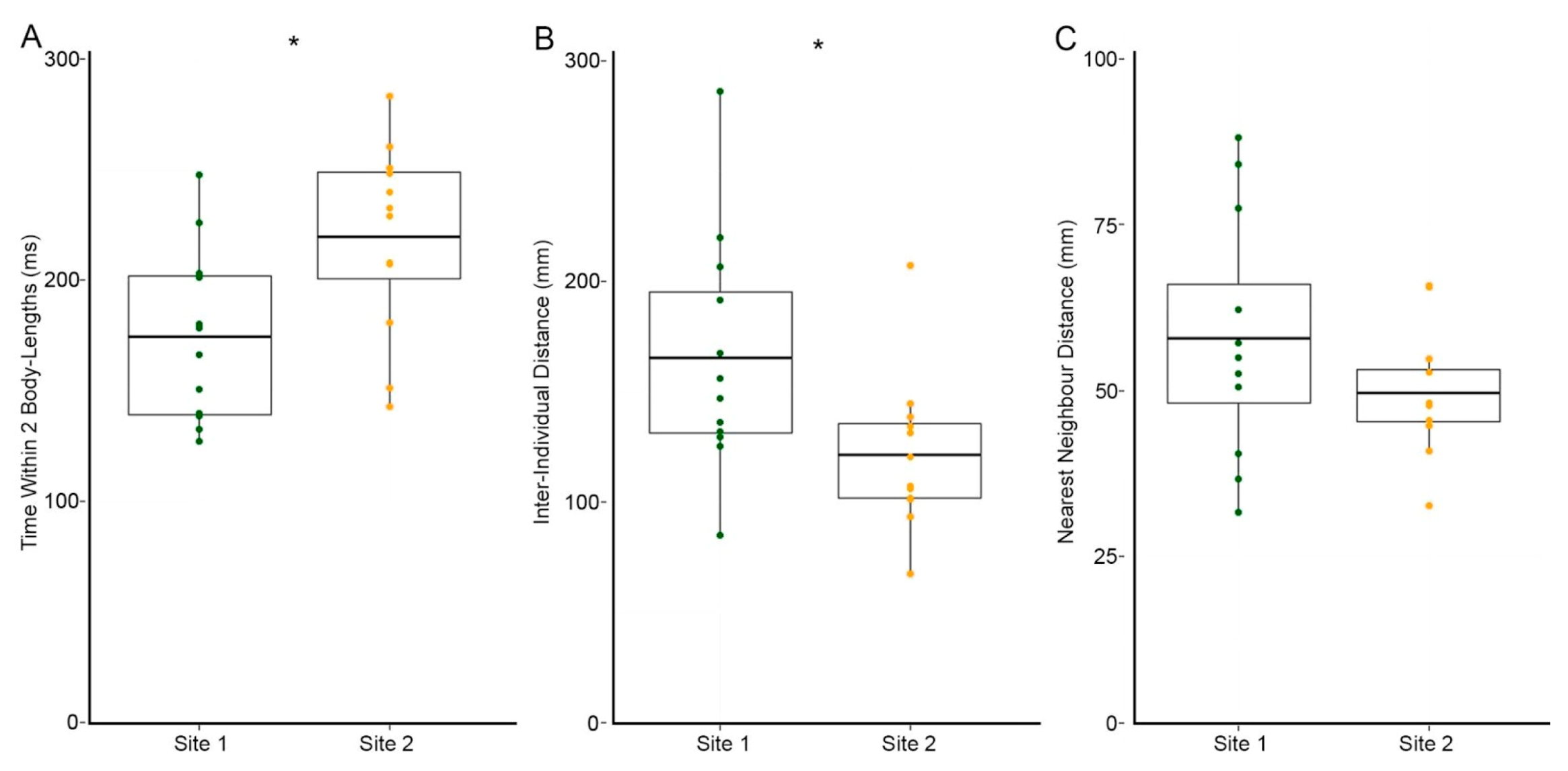
3.2. Site 2 Fish Are More Cohesive Than Site 1 Fish
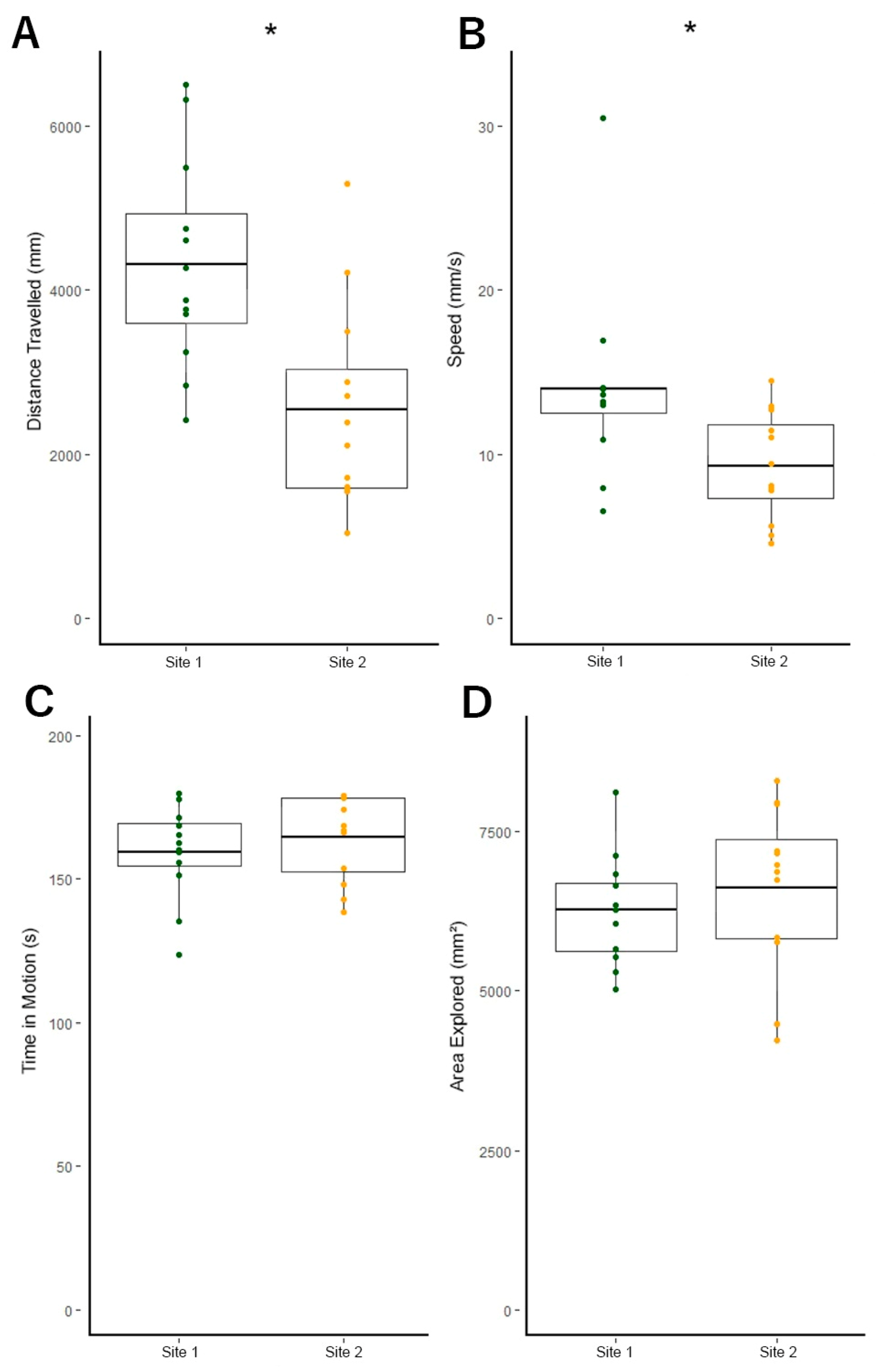
3.3. Site 1 Fish Are More Active Than Site 2 Fish
4. Discussion
Additional Thoughts on Using Wild Zebrafish as Sentinels
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foley, J.A.; DeFries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K.; et al. Global Consequences of Land Use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Fuller, R.; Acosta, N.J.R.; Adeyi, O.; Arnold, R.; Basu, N.; Baldé, A.B.; Bertollini, R.; Bose-O’Reilly, S.; Boufford, J.I.; et al. The Lancet Commission on Pollution and Health. Lancet 2018, 391, 462–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oldenborgh, G.J.; Krikken, F.; Lewis, S.; Leach, N.J.; Lehner, F.; Saunders, K.R.; van Weele, M.; Haustein, K.; Li, S.; Wallom, D.; et al. Attribution of the Australian Bushfire Risk to Anthropogenic Climate Change. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 21, 941–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniewski, D.; Marriner, N.; Cheddadi, R.; Morhange, C.; Ontiveros, M.Á.C.; Fornós, J.J.; Giaime, M.; Trichon, V.; Otto, T.; Luce, F.; et al. Recent Anthropogenic Climate Change Exceeds the Rate and Magnitude of Natural Holocene Variability on the Balearic Islands. Anthropocene 2020, 32, 100268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Wang, L.; Lin, A.; Yu, D.; Yuan, M.; Li, C. Distinguishing the Impacts of Climate Change and Anthropogenic Factors on Vegetation Dynamics in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; Pahl-Wostl, C.; Bunn, S.E.; Lawford, R. Global Water, the Anthropocene and the Transformation of a Science. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, F.; Malik, M. Factors Affecting Water Pollution: A Review. J. Ecosyst. Ecography 2017, 7, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häder, D.-P.; Banaszak, A.T.; Villafañe, V.E.; Narvarte, M.A.; González, R.A.; Helbling, E.W. Anthropogenic Pollution of Aquatic Ecosystems: Emerging Problems with Global Implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, Y.; Franklin, J.; Seddon, N.; Solan, M.; Turner, M.G.; Field, C.B.; Knowlton, N. Climate Change and Ecosystems: Threats, Opportunities and Solutions. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 375, 20190104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Xie, Z.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Zeng, Y.; Xie, J.; Xie, Z.; Jia, B.; Qin, P.; et al. Global River Water Warming Due to Climate Change and Anthropogenic Heat Emission. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2020, 193, 103289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, I.T.; Rogers, J.; Graham, A. Water Security under Severe Drought and Climate Change: Disparate Impacts of the Recent Severe Drought on Environmental Flows and Water Supplies in Central California. J. Hydrol. X 2020, 7, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, M.; Hale, R.; Parris, K.M.; Swearer, S.E. Impacts of Human-Induced Environmental Change in Wetlands on Aquatic Animals. Biol. Rev. 2018, 93, 529–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, B.A.; Kominoski, J.S.; Adams, H.E.; Jones, S.E.; Kane, E.S.; Loecke, T.D.; Mahaney, W.M.; Martina, J.P.; Prather, C.M.; Robinson, T.M.P.; et al. Direct and Terrestrial Vegetation-Mediated Effects of Environmental Change on Aquatic Ecosystem Processes. BioScience 2010, 60, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Williamson, C.E.; Dodds, W.; Kratz, T.K.; Palmer, M.A. Lakes and Streams as Sentinels of Environmental Change in Terrestrial and Atmospheric Processes. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambrick, H.; Dear, K.; Woodruff, R.; Hanigan, I.; McMichael, A. The Impacts of Climate Change on Three Health Outcomes: Temperature-Related Mortality and Hospitalisations, Salmonellosis and Other Bacterial Gastroenteritis, and Population at Risk from Dengue; Australian Government: Canberra, Australia, 2008.
- Reid, G.K.; Gurney-Smith, H.J.; Marcogliese, D.J.; Knowler, D.; Benfey, T.; Garber, A.F.; Forster, I.; Chopin, T.; Brewer-Dalton, K.; Moccia, R.D.; et al. Climate Change and Aquaculture: Considering Biological Response and Resources. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2019, 11, 569–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Ebi, K. Preventing and Mitigating Health Risks of Climate Change. Environ. Res. 2019, 174, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paavola, J. Health Impacts of Climate Change and Health and Social Inequalities in the UK. Environ. Health 2017, 16, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorensen, C.; Murray, V.; Lemery, J.; Balbus, J. Climate Change and Women’s Health: Impacts and Policy Directions. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, K.; Blashki, G.; Wiseman, J.; Burke, S.; Reifels, L. Climate Change and Mental Health: Risks, Impacts and Priority Actions. Int. J. Ment. Health Syst. 2018, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipp, A.; Cunsolo, A.; Gillis, D.; Sawatzky, A.; Harper, S.L. The Need for Community-Led, Integrated and Innovative Monitoring Programmes When Responding to the Health Impacts of Climate Change. Int. J. Circumpolar Health 2019, 78, 1517581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinth, P.; Mahesh, G.; Panwar, Y. Mapping of Zebrafish Research: A Global Outlook. Zebrafish 2013, 10, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornet, C.; Calzolari, S.; Miñana-Prieto, R.; Dyballa, S.; van Doornmalen, E.; Rutjes, H.; Savy, T.; D’Amico, D.; Terriente, J. ZeGlobalTox: An Innovative Approach to Address Organ Drug Toxicity Using Zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Langdon, P.; Chen, X.; Huang, C.; Yan, Y.; Yang, J.; Zeng, L. Regime Shifts in Shallow Lake Ecosystems along an Urban-Rural Gradient in Central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Luo, X.; Jin, C.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J.C. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Vegetation Phenology along the Urban–Rural Gradient in Coastal Dalian, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 54, 126784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickards, N.; Thomas, T.; Kaelin, A.; Houghton-Carr, H.; Jain, S.K.; Mishra, P.K.; Nema, M.K.; Dixon, H.; Rahman, M.M.; Horan, R.; et al. Understanding Future Water Challenges in a Highly Regulated Indian River Basin—Modelling the Impact of Climate Change on the Hydrology of the Upper Narmada. Water 2020, 12, 1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Central Water Commission. Status of Trace & Toxic Metals in Indian Rivers; Ministry of Jal Shakti, Department of Water Resources, River Development, and Ganga Rejuvenation: New Delhi, India, 2019.
- Aitken, S.N.; Yeaman, S.; Holliday, J.A.; Wang, T.; Curtis-McLane, S. Adaptation, Migration or Extirpation: Climate Change Outcomes for Tree Populations. Evol. Appl. 2008, 1, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, B.P.; Al-Janabi, B.; Broszeit, S.; Cioffi, R.; Kumar, A.; Aranguren-Gassis, M.; Bailey, A.; Green, L.; Gsottbauer, C.M.; Hall, E.F.; et al. Evolution of Marine Organisms under Climate Change at Different Levels of Biological Organisation. Water 2014, 6, 3545–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, D.; Narciso, L.; Cabral, H.N.; Vinagre, C. Thermal Tolerance and Potential Impacts of Climate Change on Coastal and Estuarine Organisms. J. Sea Res. 2012, 70, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Both, C.; Bouwhuis, S.; Lessells, C.M.; Visser, M.E. Climate Change and Population Declines in a Long-Distance Migratory Bird. Nature 2006, 441, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyeman, J.; Schlosberg, D.; Craven, L.; Matthews, C. Trends and Directions in Environmental Justice: From Inequity to Everyday Life, Community, and Just Sustainabilities. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2016, 41, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, L. Geographies of Race and Ethnicity II: Environmental Racism, Racial Capitalism and State-Sanctioned Violence. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2017, 41, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuelke-Leech, B.-A. A Model for Understanding the Orders of Magnitude of Disruptive Technologies. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 129, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Coolsaet, B.; Corbera, E.; Dawson, N.M.; Fraser, J.A.; Lehmann, I.; Rodriguez, I. Justice and Conservation: The Need to Incorporate Recognition. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 197, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerin, G.R.; Wen, H.; Lowe, A.J. Leaf Morphology Shift Linked to Climate Change. Biol. Lett. 2012, 8, 882–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCauley, S.J.; Hammond, J.I.; Mabry, K.E. Simulated Climate Change Increases Larval Mortality, Alters Phenology, and Affects Flight Morphology of a Dragonfly. Ecosphere 2018, 9, e02151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claireaux, G.; Webber, D.; Kerr, S.; Boutilier, R. Physiology and Behaviour of Free-Swimming Atlantic Cod (Gadus Morhua) Facing Fluctuating Salinity and Oxygenation Conditions. J. Exp. Biol. 1995, 198, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, T.C.; Blum, M.J.; Heins, D.C. Morphological Responses of a Stream Fish to Water Impoundment. Biol. Lett. 2010, 6, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cureton, J.C.; Broughton, R.E. Rapid Morphological Divergence of a Stream Fish in Response to Changes in Water Flow. Biol. Lett. 2014, 10, 20140352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruitwagen, G.; Hecht, T.; Pratap, H.B.; Wendelaar Bonga, S.E. Changes in Morphology and Growth of the Mudskipper (Periophthalmus Argentilineatus) Associated with Coastal Pollution. Mar. Biol. 2006, 149, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.L.; Hawkins, W.E.; Overstreet, R.M.; Brown-Peterson, N.J. Morphological Deformities as Biomarkers in Fish from Contaminated Rivers in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2009, 6, 2307–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquin, L.; Petitjean, Q.; Côte, J.; Laffaille, P.; Jean, S. Effects of Pollution on Fish Behavior, Personality, and Cognition: Some Research Perspectives. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beever, E.A.; Hall, L.E.; Varner, J.; Loosen, A.E.; Dunham, J.B.; Gahl, M.K.; Smith, F.A.; Lawler, J.J. Behavioral Flexibility as a Mechanism for Coping with Climate Change. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2017, 15, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebacher, F.; Post, E. Climate Change Impacts on Animal Migration. Clim. Change Responses 2015, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ludsin, S.A.; Mason, D.M.; Adamack, A.T.; Brandt, S.B.; Zhang, X.; Kimmel, D.G.; Roman, M.R.; Boicourt, W.C. Hypoxia-Driven Changes in the Behavior and Spatial Distribution of Pelagic Fish and Mesozooplankton in the Northern Gulf of Mexico. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2009, 381, S80–S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfakianakis, D.G.; Leris, I.; Laggis, A.; Kentouri, M. The Effect of Rearing Temperature on Body Shape and Meristic Characters in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Juveniles. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2011, 92, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallare, A.V.; Schirling, M.; Luckenbach, T.; Köhler, H.-R.; Triebskorn, R. Combined Effects of Temperature and Cadmium on Developmental Parameters and Biomarker Responses in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Embryos. J. Therm. Biol. 2005, 30, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriyampola, P.S.; Sykes, D.J.; Khemka, A.; Shelton, D.S.; Bhat, A.; Martins, E.P. Water Flow Impacts Group Behavior in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Behav. Ecol. 2017, 28, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limonta, G.; Mancia, A.; Benkhalqui, A.; Bertolucci, C.; Abelli, L.; Fossi, M.C.; Panti, C. Microplastics Induce Transcriptional Changes, Immune Response and Behavioral Alterations in Adult Zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, S.J.; Thomas, B.S.; Jonz, M.G. Aquatic Surface Respiration and Swimming Behaviour in Adult and Developing Zebrafish Exposed to Hypoxia. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 1777–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Bhat, A. Morphological Divergences and Ecological Correlates among Wild Populations of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Environ. Biol. Fishes 2017, 100, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.-J.; Jia, Y.-F.; Chen, N.; Bian, W.-P.; Li, Q.-K.; Ma, Y.-B.; Chen, Y.-L.; Pei, D.-S. Zebrafish as a Model System to Study Toxicology: Zebrafish Toxicology Monitoring. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrionuevo, W.R.; Burggren, W.W. O2 Consumption and Heart Rate in Developing Zebrafish (Danio Rerio): Influence of Temperature and Ambient O2. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1999, 276, R505–R513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, R.L.; Sajadi, H.; Abraham, J.; Grundy, M.A.; Gerhard, G.S. The Effects of Temperature Reduction on Gene Expression and Oxidative Stress in Skeletal Muscle from Adult Zebrafish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2004, 138, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ton, C.; Stamatiou, D.; Liew, C.-C. Gene Expression Profile of Zebrafish Exposed to Hypoxia during Development. Physiol. Genom. 2003, 13, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization. Water Quality—Determination of the Acute Lethal Toxicity of Substances to a Freshwater Fish [Brachydanio Rerio Hamilyon-Buchanan (Teleostei, Cyprinidae)]—Part 1: Static Method; ISO 7346-1; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, J.R.; Benson, S.A. Inconsistent Ethical Regulation of Larval Zebrafish in Research. J. Fish Biol. 2020, 97, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engeszer, R.E.; Patterson, L.B.; Rao, A.A.; Parichy, D.M. Zebrafish in the Wild: A Review of Natural History and New Notes from the Field. Zebrafish 2007, 4, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laale, H.W. The Biology and Use of Zebrafish, Brachydanio Rerio in Fisheries Research. J. Fish Biol. 1977, 10, 121–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welcomme, R.L. International Introductions of Inland Aquatic Species; FAO Fish: Rome, Italy, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard, V.L. Behavior and Ecology of the Zebrafish, Danio Rerio; University of Leeds: Leeds, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, A. Patterns in the Distribution of Freshwater Fishes in Rivers of Central Western Ghats, India and Their Associations with Environmental Gradients. Hydrobiologia 2004, 529, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, R.; Gerlach, G.; Lawrence, C.; Smith, C. The Behaviour and Ecology of the Zebrafish, Danio Rerio. Biol. Rev. 2008, 83, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Geological Survey. “Danio Rerio”. Nonindigenous Aquatic Species; Tech. Pap.; United States Geological Survey: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2013; Volume 294, 318p.
- Trigueiro, N.S.; Canedo, A.; Braga, D.L.; Luchiari, A.C.; Rocha, T.L. Zebrafish as an Emerging Model System in the Global South: Two Decades of Research in Brazil. Zebrafish 2020, 17, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Mondal, D.; Das, B.; Sengupta, M.K.; Ahamed, S.; Hossain, M.A.; Samal, A.C.; Saha, K.C.; Mukherjee, S.C.; Dutta, R.N.; et al. Status of Groundwater Arsenic Contamination in All 17 Blocks of Nadia District in the State of West Bengal, India: A 23-Year Study Report. J. Hydrol. 2014, 518, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha Mazumder, D.N.; Chakraborty, A.K.; Ghose, A.; Gupta, J.D.; Chakraborty, D.P.; Dey, S.B.; Chattopadhyay, N. Chronic Arsenic Toxicity from Drinking Tubewell Water in Rural West Bengal. Bull. World Health Organ. 1988, 66, 499–506. [Google Scholar]
- Mazumder, D.N.G.; Deb, D.; Biswas, A.; Saha, C.; Nandy, A.; Das, A.; Ghose, A.; Bhattacharya, K.; Mazumdar, K.K. Dietary Arsenic Exposure with Low Level of Arsenic in Drinking Water and Biomarker: A Study in West Bengal. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2014, 49, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelton, D.S.; Shelton, S.G.; Daniel, D.K.; Raja, M.; Bhat, A.; Tanguay, R.L.; Higgs, D.M.; Martins, E.P. Collective Behavior in Wild Zebrafish. Zebrafish 2020, 17, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suriyampola, P.S.; Shelton, D.S.; Shukla, R.; Roy, T.; Bhat, A.; Martins, E.P. Zebrafish Social Behavior in the Wild. Zebrafish 2016, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteley, A.R.; Bhat, A.; Martins, E.P.; Mayden, R.L.; Arunachalam, M.; Uusi-Heikkilä, S.; Ahmed, A.T.A.; Shrestha, J.; Clark, M.; Stemple, D.; et al. Population Genomics of Wild and Laboratory Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 4259–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IndiKosh. Available online: https://indikosh.com/vill/324229/jhinaidanga (accessed on 24 October 2020).
- BIS. Drinking Water—Specification (Second Revision of IS 10500: 2012); Doc: FAD 14; Bureau of Indian Standards: New Delhi, India, 2012.
- World Health Organization. Exposure to Arsenic: A Major Public Health Concern; WHO/CED/PHE/EPE/19.4.1; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Chromium in Drinking Water; WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/04; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Lead in Drinking-Water; WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/09/Rev/1; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Iron in Drinking-Water; WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/08; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, A.; De, C.; Das, D. The Study of Correlation between Physico-Chemical Parameters and Ichthyofaunal Diversity at Raidak River Flowing through the Coochbehar District of West Bengal, India. Cosmos 2019, 9, 9155–9168. [Google Scholar]
- Egan, R.J.; Bergner, C.L.; Hart, P.C.; Cachat, J.M.; Canavello, P.R.; Elegante, M.F.; Elkhayat, S.I.; Bartels, B.K.; Tien, A.K.; Tien, D.H.; et al. Understanding Behavioral and Physiological Phenotypes of Stress and Anxiety in Zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 205, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, N.; Gerlai, R. From Schooling to Shoaling: Patterns of Collective Motion in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Zhang, H.; Klaminder, J.; Brodin, T.; Andersson, P.L.; Andersson, M. ToxTrac: A Fast and Robust Software for Tracking Organisms. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Zhang, H.; Klaminder, J.; Brodin, T.; Andersson, M. ToxId: An Algorithm to Track the Identity of Multiple Animals. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, M.L. Interrater Reliability: The Kappa Statistic. Biochem. Med. 2012, 22, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- R Studio Team. R Studio: Integrated Development for R; R Studio, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zelditch, M.L.; Swiderski, D.L.; Sheets, H.D.; Fink, W.L. Geometric Morphometrics for Biologists; Elsevier Academic Press: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rohlf, F.J. TpsUtil; Department of Ecology and Evolution, State University of New York: Stony Brook, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rohlf, F.J. TpsDig; Department of Ecology and Evolution, State University of New York: Stony Brook, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen, C.E.; Annunziato, K.M.; Cooper, K.R. Behavioral, Morphometric, and Gene Expression Effects in Adult Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Embryonically Exposed to PFOA, PFOS, and PFNA. Aquat. Toxicol. Amst. Neth. 2016, 180, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suriyampola, P.S.; Eason, P.K. The Effects of Landmarks on Territorial Behavior in a Convict Cichlid, Amatitlania Siquia. Ethology 2015, 121, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlf, F.J. TpsRelw; Department of Ecology and Evolution, State University of New York: Stony Brook, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, D.; Collyer, M.; Kaliontzopoulou, A. Geomorph: Software for Geometric Morphometric Analyses. R Package Version 3.2.1. 2015. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=geomorph (accessed on 31 October 2020).
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHenry, M.J.; Lauder, G.V. Ontogeny of Form and Function: Locomotor Morphology and Drag in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). J. Morphol. 2006, 267, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Duan, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Gong, Z.; Wang, L. Barrier Function of Zebrafish Embryonic Chorions against Microplastics and Nanoplastics and Its Impact on Embryo Development. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 395, 122621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.C.; Seebacher, F. Bisphenols Alter Thermal Responses and Performance in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Conserv. Physiol. 2021, 9, coaa138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallauer, J.; Geng, X.; Yang, H.-C.; Shen, J.; Tsai, K.-J.; Liu, Z. The Effect of Chronic Arsenic Exposure in Zebrafish. Zebrafish 2016, 13, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H.; Peng, T.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Fan, C.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, F.; Meng, X. Role of Neurexin2a in Lead-Induced Locomotor Defect in Developing Zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 194, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, B.D.; Pereira, T.C.B.; Altenhofen, S.; Nabinger, D.D.; Ferreira, P.M.; Bogo, M.R.; Bonan, C.D. Antibiotic Drugs Alter Zebrafish Behavior. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 242, 108936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignet, C.; Devier, M.-H.; Le Menach, K.; Lyphout, L.; Potier, J.; Cachot, J.; Budzinski, H.; Bégout, M.-L.; Cousin, X. Long-Term Disruption of Growth, Reproduction, and Behavior after Embryonic Exposure of Zebrafish to PAH-Spiked Sediment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 13877–13887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyche, J.L.; Nourizadeh-Lillabadi, R.; Almaas, C.; Stavik, B.; Berg, V.; Skåre, J.U.; Alestrøm, P.; Ropstad, E. Natural Mixtures of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POP) Increase Weight Gain, Advance Puberty, and Induce Changes in Gene Expression Associated with Steroid Hormones and Obesity in Female Zebrafish. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2010, 73, 1032–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribas, L.; Liew, W.C.; Díaz, N.; Sreenivasan, R.; Orbán, L.; Piferrer, F. Heat-Induced Masculinization in Domesticated Zebrafish Is Family-Specific and Yields a Set of Different Gonadal Transcriptomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E941–E950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilescu, M.; Demnerová, K.; Aamand, J.; Agathos, S.; Fava, F. Emerging Pollutants in the Environment: Present and Future Challenges in Biomonitoring, Ecological Risks and Bioremediation. New Biotechnol. 2015, 32, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmer, S.; Moore, F.B.-G.; Bagatto, B. The Effects of Chronic Developmental Hypoxia on Swimming Performance in Zebrafish. J. Fish Biol. 2006, 69, 1885–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, E.H.H.; Yu, R.M.K.; Wu, R.S.S. Hypoxia Affects Sex Differentiation and Development, Leading to a Male-Dominated Population in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 3118–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, T.; Bhat, A. Population, Sex and Body Size: Determinants of Behavioural Variations and Behavioural Correlations among Wild Zebrafish Danio Rerio. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 170978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, L.; Knörr, S.; Keiter, S.; Nagel, T.; Segner, H.; Braunbeck, T. Prochloraz Causes Irreversible Masculinization of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 16417–16422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, Í.F.S.; Souza, T.M.; Vieira, L.R.; Marchi, F.C.; Nascimento, A.P.; Farias, D.F. Toxicity Testing of Pesticides in Zebrafish-a Systematic Review on Chemicals and Associated Toxicological Endpoints. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 10185–10204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberge, J.-M.; Angelstam, P. Usefulness of the Umbrella Species Concept as a Conservation Tool. Conserv. Biol. 2004, 18, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinkat, G.; Cabral, J.S.; Darwall, W.; Ficetola, G.F.; Fisher, J.L.; Giling, D.P.; Gosselin, M.-P.; Grossart, H.-P.; Jähnig, S.C.; Jeschke, J.M.; et al. Flagship Umbrella Species Needed for the Conservation of Overlooked Aquatic Biodiversity. Conserv. Biol. J. Soc. Conserv. Biol. 2017, 31, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inderjit; Weston, L.A. Are Laboratory Bioassays for Allelopathy Suitable for Prediction of Field Responses? J. Chem. Ecol. 2000, 26, 2111–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfuss, H.L.; Furlong, E.T.; Phillips, P.J.; Scott, T.-M.; Kolpin, D.W.; Cetkovic-Cvrlje, M.; Lesteberg, K.E.; Rearick, D.C. Complex Mixtures, Complex Responses: Assessing Pharmaceutical Mixtures Using Field and Laboratory Approaches. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, A.J. Toxicological Testing in Laboratories Is Not Ecological Testing of Toxicology. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 1995, 1, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.J.; Teraoka, H.; Heideman, W.; Peterson, R.E. Zebrafish as a Model Vertebrate for Investigating Chemical Toxicity. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 86, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Gebhardt, M.; Stewart, A.M.; Cachat, J.M.; Brimmer, M.; Chawla, J.S.; Craddock, C.; Kyzar, E.J.; Roth, A.; Landsman, S.; et al. Towards a Comprehensive Catalog of Zebrafish Behavior 1.0 and Beyond. Zebrafish 2013, 10, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tal, T.; Yaghoobi, B.; Lein, P.J. Translational Toxicology in Zebrafish. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2020, 23–24, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvan, M.J., III; Sonntag, D.M.; Cmar, C.B.; Cook, R.S.; Curran, M.A.; Miller, G.L. Oxidative Stress in Zebrafish Cells: Potential Utility of Transgenic Zebrafish as a Deployable Sentinel for Site Hazard Ranking. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 274, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambino, K.; Chu, J. Zebrafish in Toxicology and Environmental Health. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2017, 124, 331–367. [Google Scholar]
- Wittwehr, C.; Aladjov, H.; Ankley, G.; Byrne, H.J.; de Knecht, J.; Heinzle, E.; Klambauer, G.; Landesmann, B.; Luijten, M.; MacKay, C.; et al. How Adverse Outcome Pathways Can Aid the Development and Use of Computational Prediction Models for Regulatory Toxicology. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2017, 155, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suriyampola, P.S.; Cacéres, J.; Martins, E. Effects of Short-Term Turbidity on Sensory Preference and Behaviour of Adult Fish. Anim. Behav. 2018, 146, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, D.J.; Suriyampola, P.S.; Martins, E.P. Recent Experience Impacts Social Behavior in a Novel Context by Adult Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Villemereuil, P.; Gaggiotti, O.E.; Mouterde, M.; Till-Bottraud, I. Common Garden Experiments in the Genomic Era: New Perspectives and Opportunities. Heredity 2016, 116, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacci, D.; Proestou, D.; Champlin, D.; Martinson, J.; Waits, E.R. Genetic Basis for Rapidly Evolved Tolerance in the Wild: Adaptation to Toxic Pollutants by an Estuarine Fish Species. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 5467–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esbaugh, A.J.; Brix, K.V.; Grosell, M. Na+ K+ ATPase Isoform Switching in Zebrafish during Transition to Dilute Freshwater Habitats. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 286, 20190630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piferrer, F.; Beaumont, A.; Falguière, J.-C.; Flajšhans, M.; Haffray, P.; Colombo, L. Polyploid Fish and Shellfish: Production, Biology and Applications to Aquaculture for Performance Improvement and Genetic Containment. Aquaculture 2009, 293, 125–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzen, K.; Beveridge, M.C.M.; Mangel, M. Cultured Fish: Integrative Biology and Management of Domestication and Interactions with Wild Fish. Biol. Rev. 2012, 87, 639–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schell, C.J.; Dyson, K.; Fuentes, T.L.; Des Roches, S.; Harris, N.C.; Miller, D.S.; Woelfle-Erskine, C.A.; Lambert, M.R. The Ecological and Evolutionary Consequences of Systemic Racism in Urban Environments. Science 2020, 369, eaay4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, K.; Eichhorn, M.; Griffiths, M. Decolonizing Field Ecology. Biotropica 2019, 51, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazlett, M.A.; Henderson, K.M.; Zeitzer, I.F.; Drew, J.A. The Geography of Publishing in the Anthropocene. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 2020, 2, e270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, B.L. Lessons from Microbes: What Can We Learn about Equity from Unculturable Bacteria? mSphere 2020, 5, e01046-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liboiron, D.M. Plastic Demands Land. That’s a Function of Colonialism. Available online: https://www.teenvogue.com/story/how-plastic-is-a-function-of-colonialism (accessed on 31 October 2020).
- Goodwin, N.R. Five Kinds of Capital: Useful Concepts for Sustainable Development. Available online: https://ageconsearch.umn.edu/record/15595 (accessed on 30 October 2020).
- Duff, N.M.; Sommerfeld, R.E.; Litvak, M.K. Discriminating Sex in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Using Geometric Morphometrics. Zebrafish 2019, 16, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutte, A.H.; Nazario, L.R.; Majolo, J.H.; Pereira, T.C.B.; Altenhofen, S.; Dadda, A.; Bogo, M.R.; Da Silva, R.S. Persistent Increase in Ecto-5′-nucleotidase Activity from Encephala of Adult Zebrafish Exposed to Ethanol during Early Development. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2018, 70, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, A.; Rahaman, M.; Suzuki, R.-T.; Murono, Y.; Tokumoto, T. Next-Generation and Further Transgenerational Effects of Bisphenol A on Zebrafish Reproductive Tissues. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, S. The Four Steps to the Epiphany: Successful Strategies for Products That Win; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, J.; Engel, J.S. Models of Innovation: Startups and Mature Corporations. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2007, 50, 94–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citigroup. Closing the Racial Inequality Gaps, the Economic Cost of Black Inequality in the U.S.; Citi GPS, Global Perspectives & Solutions: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Berkes, F.; Ross, H. Community Resilience: Toward an Integrated Approach. Soc. Nat. Resour. 2013, 26, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerow, S.; Newell, J.P.; Stults, M. Defining Urban Resilience: A Review. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 147, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Site | Site 1 | Site 2 |
|---|---|---|
| District | Cooch Behar | Nadia |
| Pollutants | As <0.01 mg/L [27] Iron (2.3–6.5 mg/L), Lead (0–16.6 μg/L) [27], minimal human-made debris | As, 0.1 mg/L–0.5mg/L [67,69], Iron (0–9.1 mg/L), Chromium (0–147.8 μg/L) [27], abundant human-made debris: plastic bottles, styrofoam plates, bags, shoes [52] |
| Water use | People were observed bathing, washing clothes and irrigating crops with water from the field site | People tried to minimize contact with the water. When contact was made with water people described burning and itching sensations. |
| Land use | Homes, rice cultivation, sand mining, livestock grazing, unpaved roads | Homes, buildings, shops, paved roads |
| Water Flow | Flowing [71] | Stagnant [71] |
| pH | 7.4 [71] | 6.9–7.8 [70,71] |
| Total Dissolved Solids (ppt) | 0.2 [71] | 0.3 [70,71] |
| Dissolved Oxygen (ppm) | 3.2–5.4 [79] | 1.5 [52] |
| Nitrate (ppm) | 0.0 [70] | 0.0 [70] |
| Nitrite (ppm) | 0.5 [70] | 0.0 [70] |
| Temperature (°C) | 19–25.6 [71] | 21.4–25.6 [70,71] |
| Elevation (m) | 12.2 [71] | 41.4 [70,71] |
| Substrate | Mud [71] | Silt [71] |
| Predation Pressure | less [71] | greater [71] |
| Population Density | ~700 persons/km² [52] | ~1250 persons/km² [52] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kelly, J.R.; Shelton, S.G.; Daniel, D.K.; Bhat, A.; Mondal, R.; Nipple, F.; Amro, H.; Bower, M.E.; Isaac, G.; McHaney, G.; et al. Wild Zebrafish Sentinels: Biological Monitoring of Site Differences Using Behavior and Morphology. Toxics 2021, 9, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9070165
Kelly JR, Shelton SG, Daniel DK, Bhat A, Mondal R, Nipple F, Amro H, Bower ME, Isaac G, McHaney G, et al. Wild Zebrafish Sentinels: Biological Monitoring of Site Differences Using Behavior and Morphology. Toxics. 2021; 9(7):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9070165
Chicago/Turabian StyleKelly, Jeffrey R., Sierra G. Shelton, Danita K. Daniel, Anuradha Bhat, Rubina Mondal, Fahren Nipple, Halima Amro, Myra E. Bower, Gabriel Isaac, Gillian McHaney, and et al. 2021. "Wild Zebrafish Sentinels: Biological Monitoring of Site Differences Using Behavior and Morphology" Toxics 9, no. 7: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9070165
APA StyleKelly, J. R., Shelton, S. G., Daniel, D. K., Bhat, A., Mondal, R., Nipple, F., Amro, H., Bower, M. E., Isaac, G., McHaney, G., Martins, E. P., & Shelton, D. S. (2021). Wild Zebrafish Sentinels: Biological Monitoring of Site Differences Using Behavior and Morphology. Toxics, 9(7), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9070165







