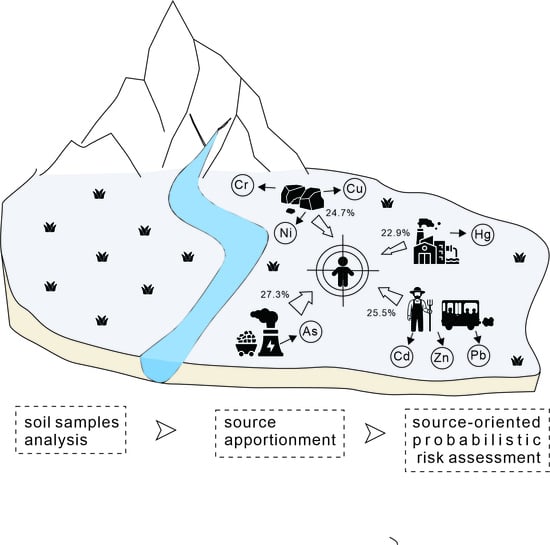
Spatial Analysis, Influencing Factors, and Source-Oriented Probabilistic Health Risks of Potential Toxic Elements in High Geological Background Soil in Central and Southern Shandong Peninsula, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
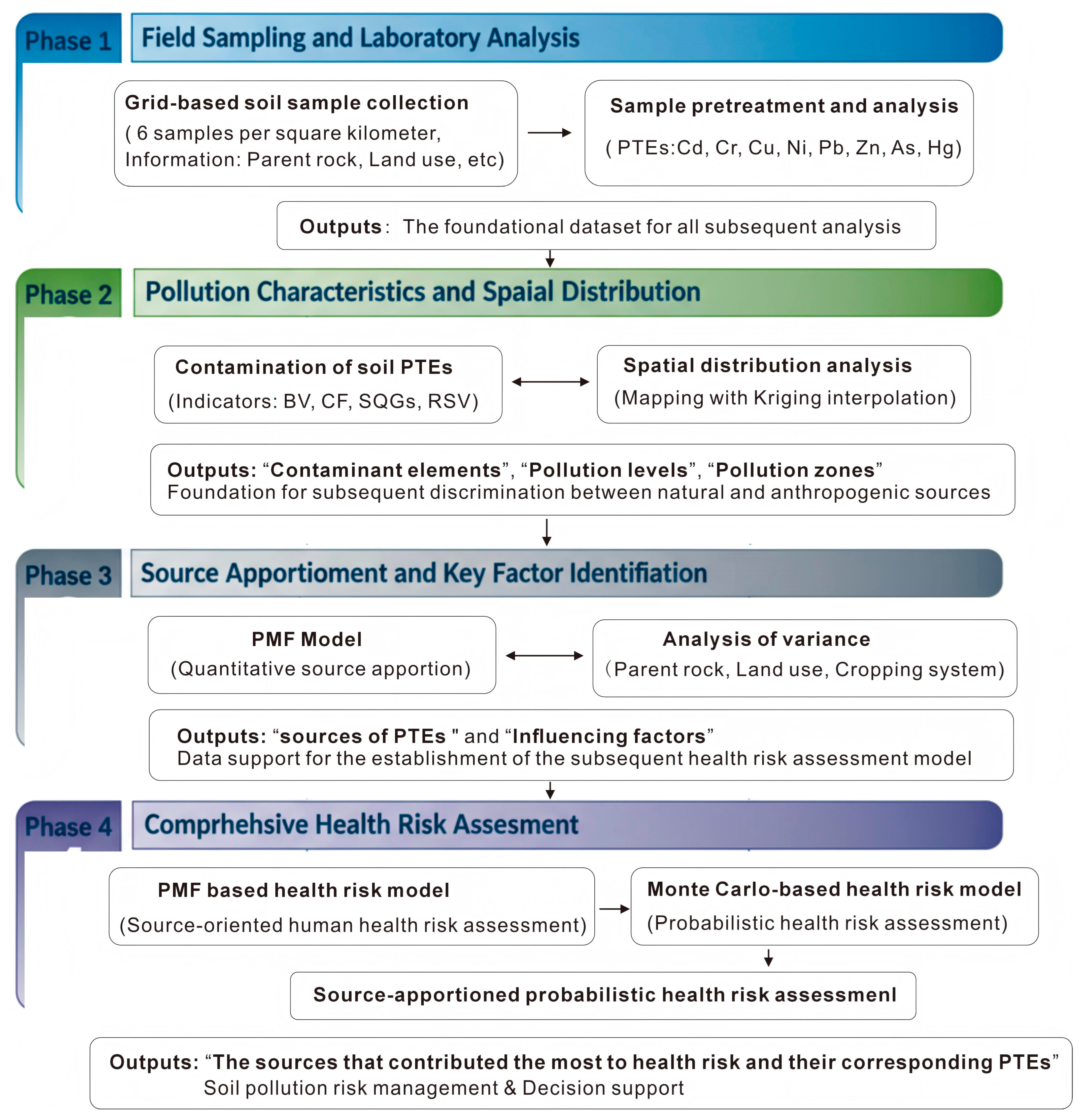
2. Materials and Methods
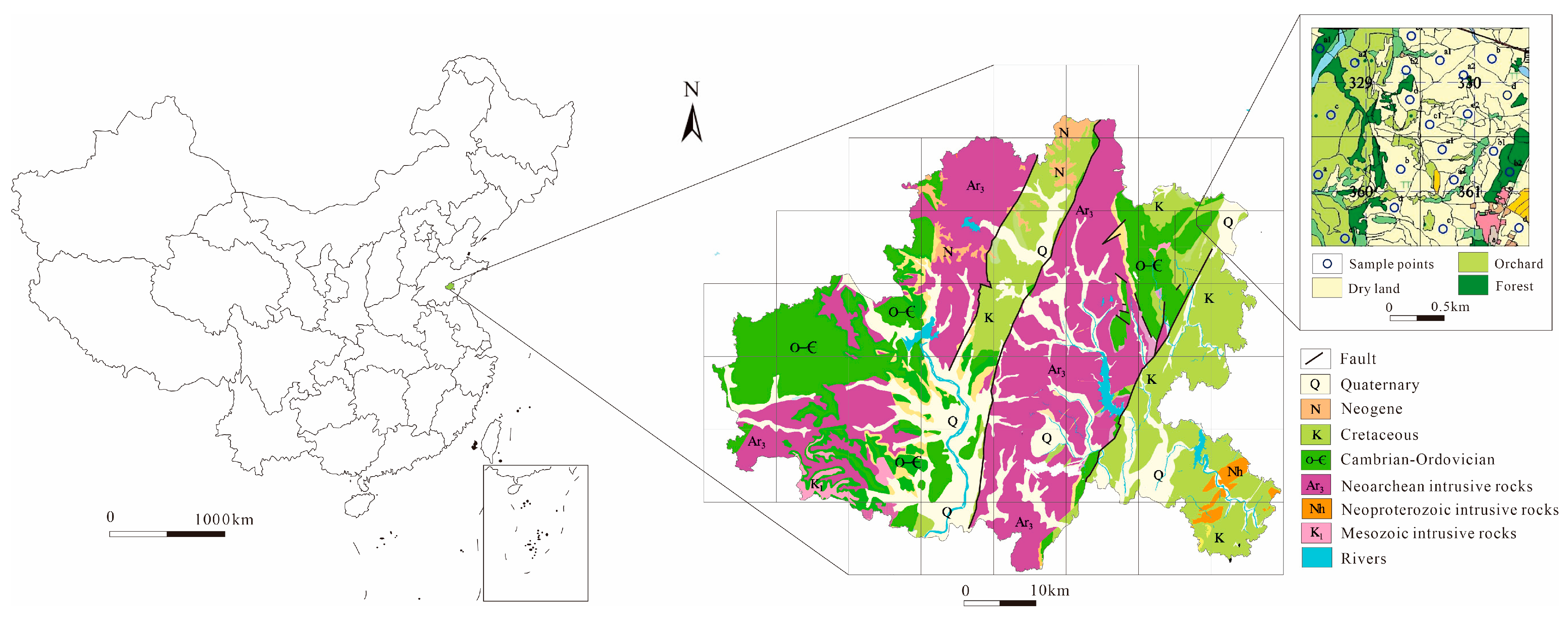
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Sampling Collection and Preparation
2.3. Sample Chemical Analysis
2.4. Contamination Factor (CF)
2.5. Sediment Quality Guidelines (SQGs)
2.6. Positive Matrix Factorization Model (PMF)
2.7. Source-Oriented Probabilistic Health Risk Model
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Concentration and Contamination of Soil PTEs
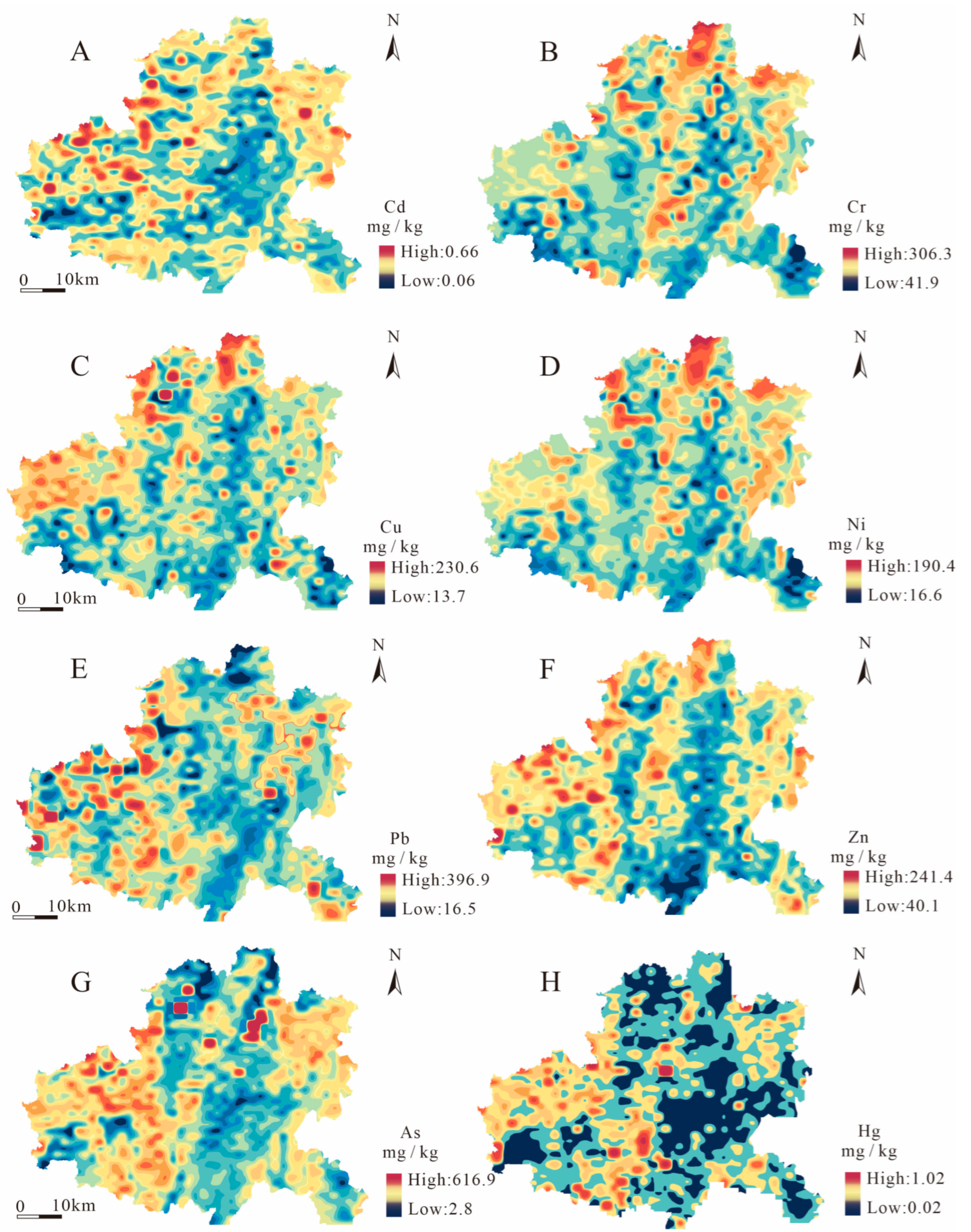
3.2. Spatial Distribution of PTEs
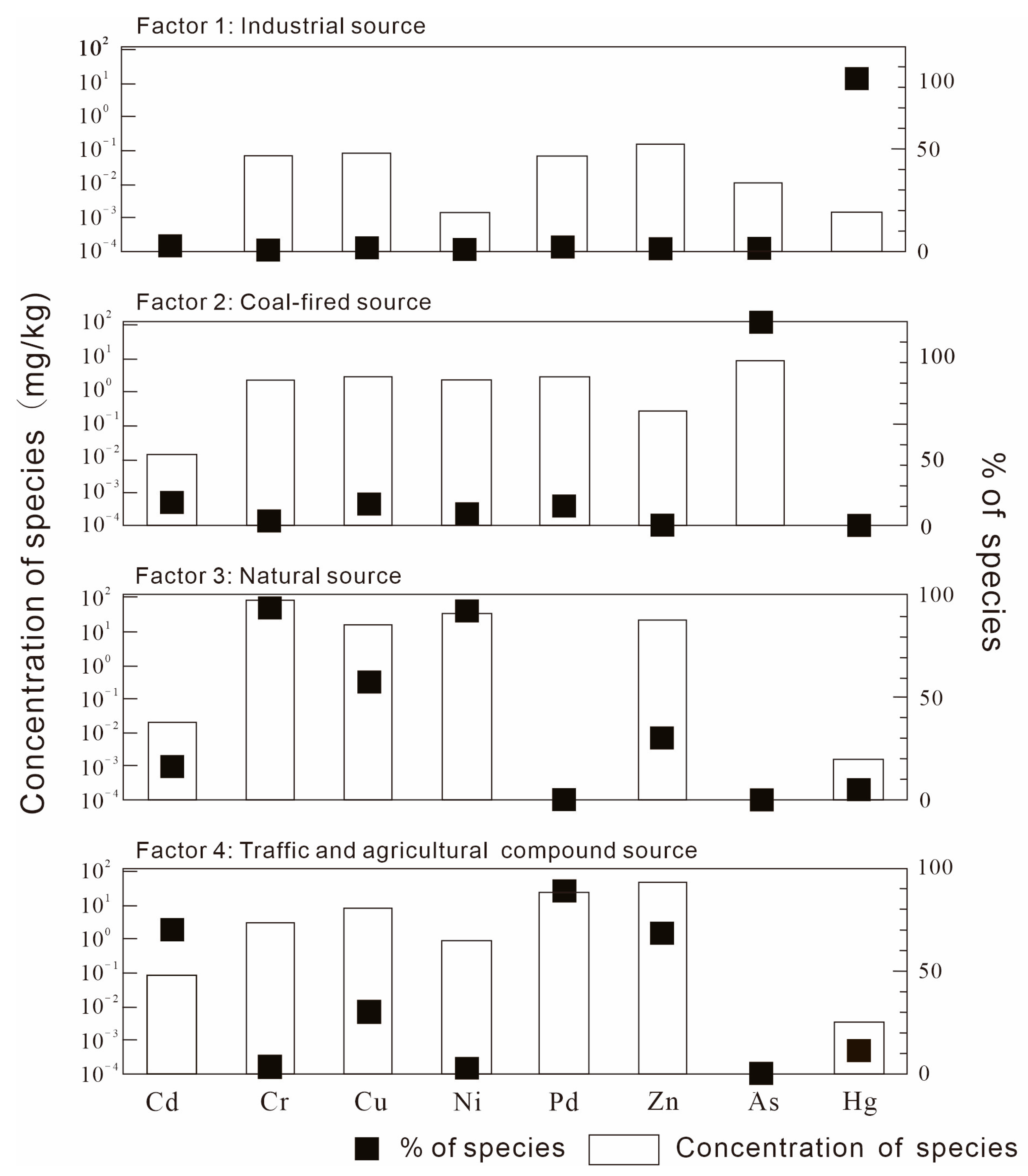
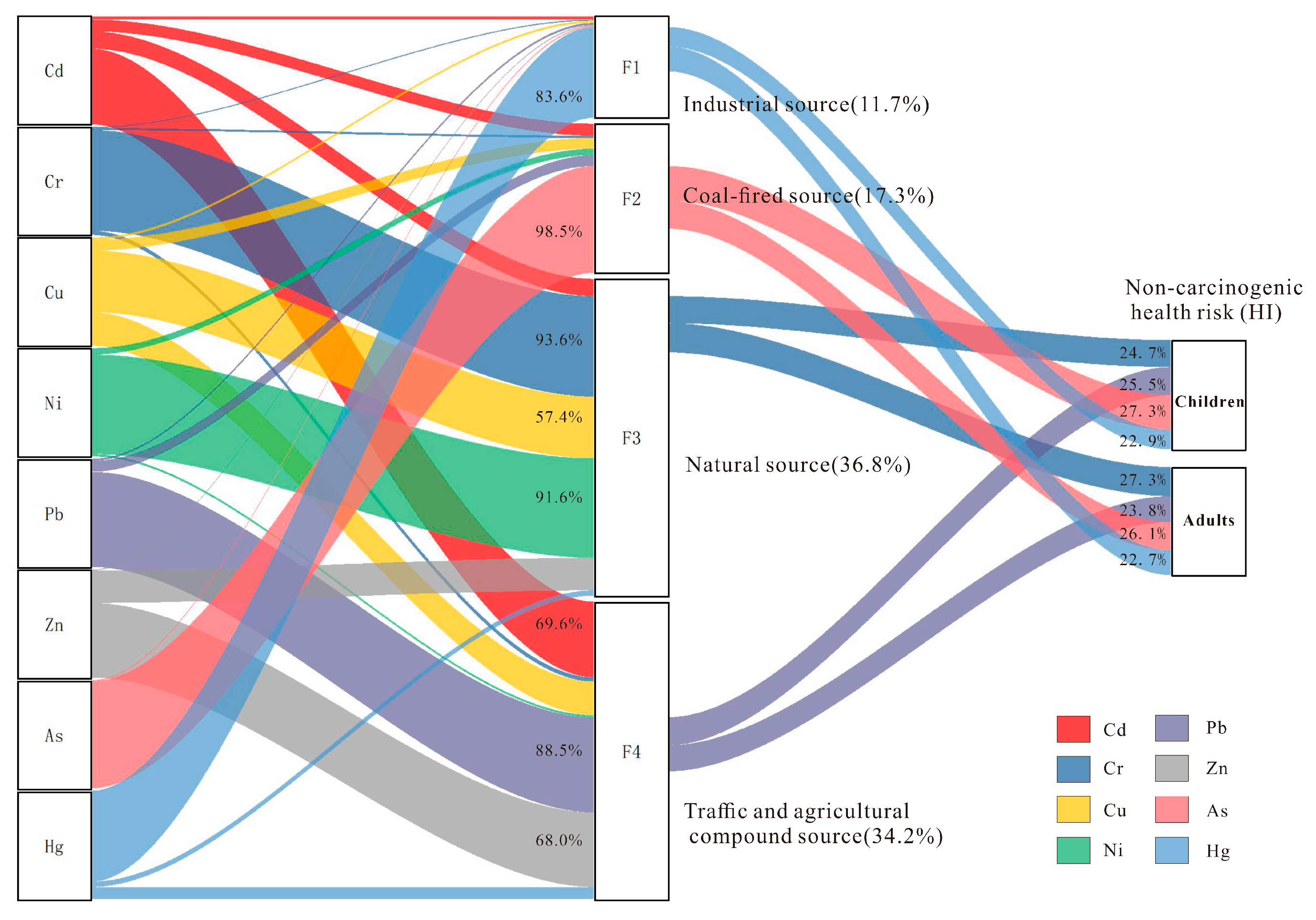
3.3. Source Apportionment
3.4. Determination of Key Factors on PTEs Accumulation in Soil
3.4.1. Parent Rocks
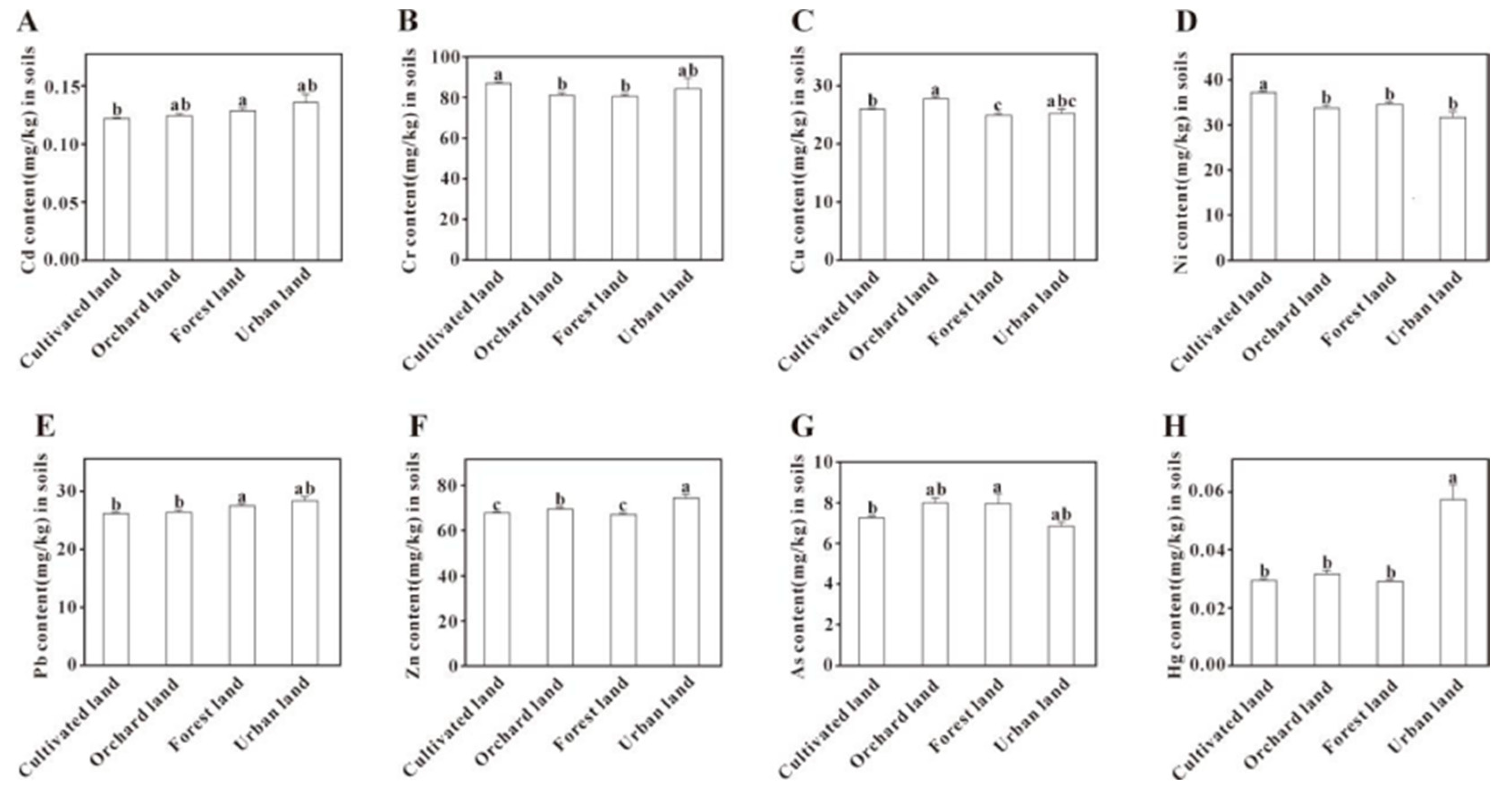
3.4.2. Land Use Type
3.4.3. Cropping System
3.5. Concentration-Oriented Health Risk Assessment Base on PMF
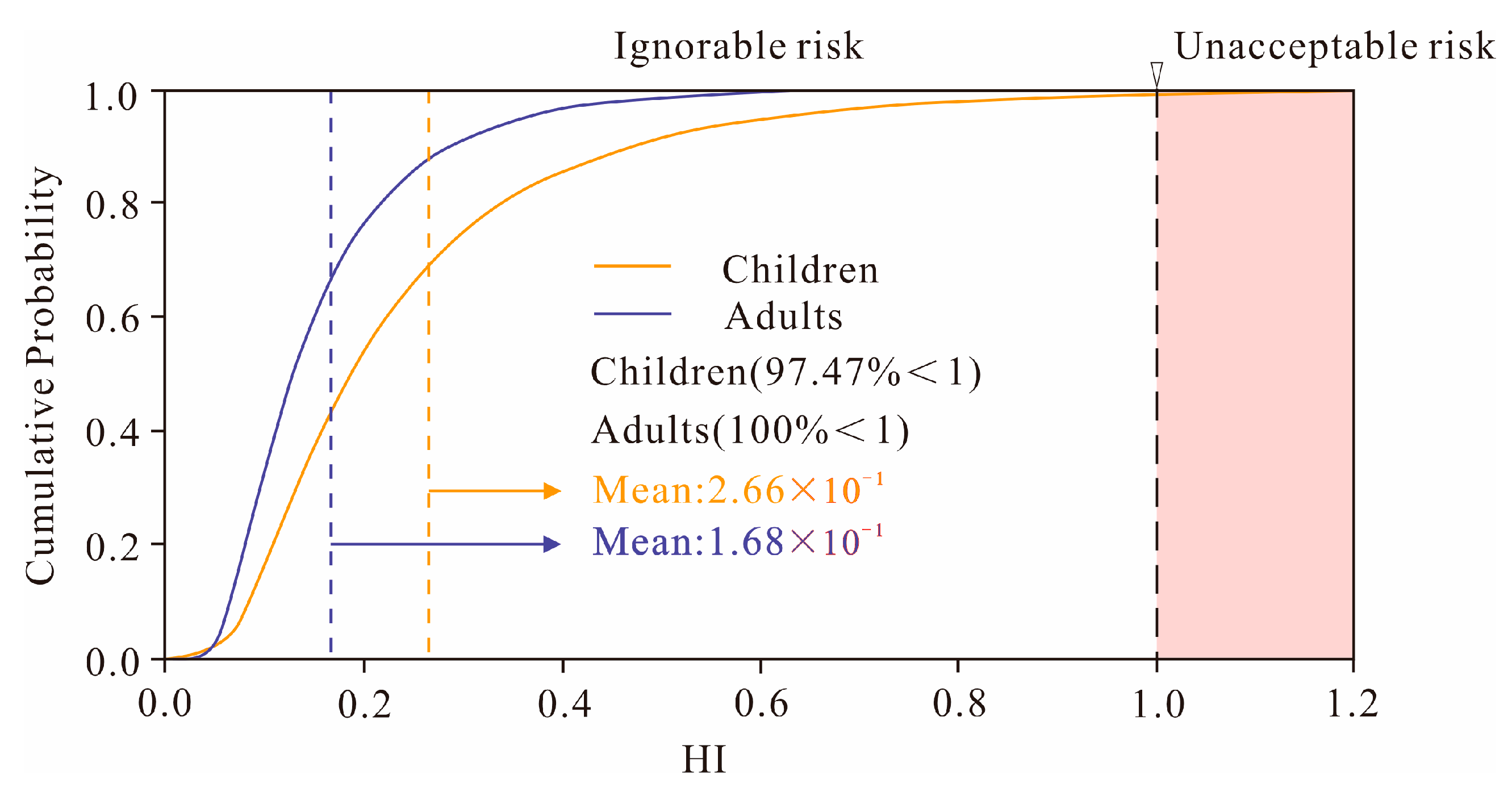
3.6. Probabilistic Health Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PTEs | Potential toxic elements |
| PMF | Positive matrix factorization |
| CF | Contamination Factor |
| SQGs | Sediment quality guidelines |
| ERM | Effects Range-Median |
| ERL | Effects Range-Low |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
References
- Chen, H.; Teng, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Li, T.; He, Z.; Yang, X. Current status of agricultural soil pollution by heavy metals in China: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 3034–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.J.; Tang, Z.; Song, J.J.; Huang, X.Y.; Wang, P. Toxic metals and metalloids: Uptake, transport, detoxification, phytoremediation, and crop improvement for safer food. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angon, P.B.; Islam, M.S.; Kc, S.; Das, A.; Anjum, N.; Poudel, A.; Suchi, S.A. Sources, effects and present perspectives of heavy metals contamination: Soil, plants and human food chain. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Lee, S.S.; Zhang, M.; Tsang, Y.F.; Kim, K.H. Heavy metals in food crops: Health risks, fate, mechanisms, and management. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, Z.; Zulkafflee, N.S.; Mohd Redzuan, N.A.; Selamat, J.; Ismail, M.R.; Praveena, S.M.; Toth, G.; Abdull Razis, A.F. Understanding Potential Heavy Metal Contamination, Absorption, Translocation and Accumulation in Rice and Human Health Risks. Plants 2021, 10, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q.; Guo, L.; Hang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, J.; Tao, T.; Liu, Q.; Ding, C. Risk assessment and source tracing of heavy metals in major rice-producing provinces of Yangtze River Basin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, K.; Xi, X.; Niu, R.; Ren, C.; Wang, C. Spatial-temporal analysis and background value determination of molybdenum concentration in basins with high molybdenum geochemical background—A case study of the upper Yi River basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ren, B.; Deng, X.; Yin, W.; Xie, Q.; Cai, Z.; Zou, H. Black shale bedrock control of soil heavy metal typical high geological background in China Loushao Basin: Pollution characteristics, source and Influence assessment based on spatial analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 477, 135072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Chen, B.; Huang, C.; Lu, X.; Zou, R.; Wei, Y. Potentially Toxic Element Migration Characteristics and Bioavailability in Soils of the Black Shale Region, Western Zhejiang Province, China. Toxics 2025, 13, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, C. Natural and Human Factors Affect the Distribution of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution: A Review. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2020, 231, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Wen, Y.; Bostick, B.C.; Wen, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhuo, X.; et al. New strategy for exploring the accumulation of heavy metals in soils derived from different parent materials in the karst region of southwestern China. Geoderma 2022, 417, 115806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, Q.; Lu, W.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wu, L.; Zhang, N.; et al. Contamination levels of and potential risks from metal(loid)s in soil-crop systems in high geological background areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, T.; Perkins, R.B.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Ning, Z. Geogenic cadmium pollution and potential health risks, with emphasis on black shale. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 176, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parviainen, A.; Loukola-Ruskeeniemi, K. Environmental impact of mineralised black shales. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 192, 65–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Ling, S.; Wu, X.; Li, X. Geochemical accumulation and source tracing of heavy metals in arable soils from a black shale catchment, southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kierczak, J.; Pędziwiatr, A.; Waroszewski, J.; Modelska, M. Mobility of Ni, Cr and Co in serpentine soils derived on various ultrabasic bedrocks under temperate climate. Geoderma 2016, 268, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithanage, M.; Kumarathilaka, P.; Oze, C.; Karunatilake, S.; Seneviratne, M.; Hseu, Z.Y.; Gunarathne, V.; Dassanayake, M.; Ok, Y.S.; Rinklebe, J. Occurrence and cycling of trace elements in ultramafic soils and their impacts on human health: A critical review. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 104974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.H.V.; da Silva, F.B.V.; da Silva, Y.; de Lima Veloso, V.; de Sousa, M.G.F.; de Souza Junior, V.S.; Echevarria, G.; do Nascimento, C.W.A. Integrating environmental, ecological and human health risk assessments for heavy metals in tropical ultramafic soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Hedding, D.W.; Nel, W.; Ji, J.; Chen, J. Geochemical behavior and potential health risk of heavy metals in basalt-derived agricultural soil and crops: A case study from Xuyi County, eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 139058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.S.; Ao, M.; Geng, K.R.; Chen, J.Q.; Deng, T.H.; Li, J.J.; Guan, Z.T.; Mo, B.L.; Liu, T.; Yang, W.J.; et al. Enrichment and speciation of chromium during basalt weathering: Insights from variably weathered profiles in the Leizhou Peninsula, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Guan, Y.; Nel, W.; Xu, C. Heavy metal migration and lithium isotope fractionation under extreme weathering of basalt on tropical Hainan Island, China. Appl. Geochem. 2024, 175, 106163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, S.-i.; Takeda, A.; Nunohara, K.; Tsuchiya, N. Red soils derived from limestone contain higher amounts of trace elements than those derived from various other parent materials. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2013, 59, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Ji, J.; Yang, Z.; Han, H.; Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W. Cadmium risk in the soil-plant system caused by weathering of carbonate bedrock. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, Y.G.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.B.; Li, K.Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Xing, H.; Wei, M.Q. Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metal elements in rock-soil in the mountainous areas of Southwest China: A case study of Xichang. Geol. J. 2023, 58, 3866–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Qu, S.; Nel, W.; Ji, J. The influence of natural weathering on the behavior of heavy metals in small basaltic watersheds: A comparative study from different regions in China. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Song, C.; Chen, Z.; Guan, H.; Xing, D.; Gao, T.; Sun, J.; Ning, Z.; Xiao, T. Geochemical factors controlling the mobilization of geogenic cadmium in soils developed on carbonate bedrocks in Southwest China. Geoderma 2023, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hou, Q.; Yang, Z.; Yu, T. The spatial distribution pattern and influencing factors of chromium (Cr) in topsoil of eastern and central China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 495, 138925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, T.; Li, J.; Bruun Hansen, H.C.; Shaheen, S.M.; Antoniadis, V.; Bolan, N.; Rinklebe, J. Integrated assessment of the impact of land use types on soil pollution by potentially toxic elements and the associated ecological and human health risk. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 299, 118911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Guan, Q.; Shao, W.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Li, H.; Sun, Y. A joint method to quantify source contributions of heavy metals to ecological and human health risks in oasis farmland soil. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2021, 85, 1600–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xie, M.; Li, G.; Lin, S.; Wang, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. A spatial source-oriented and probability-based risk-assessment framework for heavy metal and PAH contamination of urban soils in Guangzhou, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 482, 136500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Fang, Q.; Zhou, Y. Implementation of an integrated health risk assessment coupled with spatial interpolation and source contribution: A case study of soil heavy metals from an abandoned industrial area in Suzhou, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 36, 2633–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Li, K.; Guo, G.; Ju, T. Source-specific health risks apportionment of soil potential toxicity elements combining multiple receptor models with Monte Carlo simulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yu, J.; Yang, K.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Qiao, S. Source Apportionment and Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements Based on PCA and PMF Model in Black Soil Area of Hailun City, Northeast China. Toxics 2024, 12, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Du, Q.; Guan, Q.; Luo, H.; Shan, Y.; Shao, W. A Monte Carlo simulation-based health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils of an oasis agricultural region in northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Cao, H.; Du, P.; Ren, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, H. Source-oriented probabilistic health risk assessment of soil potentially toxic elements in a typical mining city. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CNEMC. Natural Background Values of Soil Elements in China; Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990; pp. 334–379. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pang, X.; Dai, J.; Hu, X.; Song, Z.; Yu, C.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; et al. Background values of soil geochemistry in Shandong Province. Shandong Land. Resour. 2018, 34, 39–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Ren, L.; Bao, L. Cumulative Risk Assessment of Soil-Crop Potentially Toxic Elements Accumulation under Two Distinct Pollution Systems. Minerals 2022, 12, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, I.U.; Muhammad, S.; Faisal, S.; Rehman, I.U.; Ali, W. Heavy metal(loid)s contamination and ecotoxicological hazards in coal, dust, and soil adjacent to coal mining operations, Northwest Pakistan. J. Geochem. Explor. 2024, 256, 107332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.R.; Macdonald, D.D.; Smith, S.L.; Calder, F.D. Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ. Manag. 1995, 19, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. EPA Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) 5.0 Fundamentals and User Guide. 2014. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-02/documents/pmf_5.0_user_guide.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2019).
- Paatero, P.; Tapper, U. Positive matrix factorization: A non-negative factor model with optimal utilization of error estimates of data values. Environmetrics 2006, 5, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, F.L.; Li, K.N.; Ouyang, D.; Zhou, J.W.; Luo, Y.T.; Zhang, H.B. Sources apportionments of heavy metal(loid)s in the farmland soils close to industrial parks: Integrated application of positive matrix factorization (PMF) and cadmium isotopic fractionation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, Z.X.; Dong, K.; Hui, F.J.; Wang, D.Q.; Huang, Y.C. Pollution Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Soils Using Characterization and Microbiological Analysis: The Case of a Rare and Precious Metal Mining Site in Wuzhou, Guangxi. Toxics 2025, 13, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.-H.; Cai, L.-M.; Wen, H.-H.; Hu, G.-C.; Chen, L.-G.; Luo, J. An integrated approach to quantifying ecological and human health risks from different sources of soil heavy metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Huang, S.; Wang, M.; Wu, J.; Su, J.; Lin, K.; Chen, X.; He, T.; Li, Y.; Sha, C.; et al. Source-oriented health risk assessment and priority control factor analysis of heavy metals in urban soil of Shanghai. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Xie, Y.; Feng, X.; Wu, K.; Li, X.; Wu, P. Multi-source apportionment of soil heavy metals and spatial heterogeneity of associated risks in overlapping zones with high geological background and mining-smelting activities. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 385, 127079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.B.; Tang, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, C.Q.; Wang, W.J. Contamination of heavy metal(loid)s in groundwater around mining and smelting area: Quantitative source-oriented health risk assessment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2025, 47, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proshad, R.; Abedin Asha, S.M.A.; Abedin, M.A.; Chen, G.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Tan, R.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Z. Pollution area identification, receptor model-oriented sources and probabilistic health hazards to prioritize control measures for heavy metal management in soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 369, 122322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund Volume I: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A); Interim Final; US Environment Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- GB15618-2018; Soil Environmental Quality-Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. Chinese Environment Protection Administration (CEPA): Beijing, China, 2018. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/trhj/201807/t20180703_446029.shtml (accessed on 10 March 2016).
- Callén, M.S.; de la Cruz, M.T.; López, J.M.; Navarro, M.V.; Mastral, A.M. Comparison of receptor models for source apportionment of the PM10 in Zaragoza (Spain). Chemosphere 2009, 76, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Cheng, Z.; Su, L.; Liu, M. Quantitative source apportionment of heavy metals in cultivated soil and associated model uncertainty. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 215, 112150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, S.; Hui, M.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Duan, L.; Luo, Y. New Insight into Atmospheric Mercury Emissions from Zinc Smelters Using Mass Flow Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 3532–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Pascual, M.J.; Vega, C.M.; Andrade, N.; Fernandez, L.E.; Silman, M.R.; Torrents, A. Hg distribution and accumulation in soil and vegetation in areas impacted by artisanal gold mining in the Southern Amazonian region of Madre de Dios, Peru. Chemosphere 2024, 361, 142425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Gao, J.; Tong, Y.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, S.; Li, G.; Yue, T. Advances in the sources, chemical behaviour, and whole process distribution of Hg, As, and Pb in the iron and steel smelting industry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, R.; Nayak, A.K.; Shukla, A.K.; Rao, K.S.; Gautam, P.; Lal, B.; Tripathi, R.; Shahid, M.; Panda, B.B.; Kumar, A.; et al. Impairment of soil health due to fly ash-fugitive dust deposition from coal-fired thermal power plants. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhao, Y.; Hao, R. Arsenic emission and distribution characteristics in the ultra-low emission coal-fired power plant. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 36814–36823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkonen, H.G.; Dasika, R.; Drake, J.A.; Wallis, C.J.; Clarke, B.O.; Reichman, S.M. Evaluation of environmental and anthropogenic influences on ambient background metal and metalloid concentrations in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parthasarathy, P.; Asok, M.; Ranjan, R.K.; Swain, S.K. Bioavailability and risk assessment of trace metals in sediments of a high-altitude eutrophic lake, Ooty, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 18616–18631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Han, G.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q. Suspended Sediments Quality Assessment in a Coastal River: Identification of Potentially Toxic Elements. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakmak, D.; Saljnikov, E.; Mrvic, V.; Jakovljevic, M.; Marjanovic, Z.; Sikiric, B.; Maksimovic, S. Soil properties and trace elements contents following 40 years of phosphate fertilization. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Lou, C.; Zhai, W.; Tang, X.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Murtaza, R.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, J. Increased occurrence of heavy metals, antibiotics and resistance genes in surface soil after long-term application of manure. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Z.; Williams, G.D.Z.; Dwyer, G.S.; Gatiboni, L.; Duckworth, O.W.; Vengosh, A. Evidence for the accumulation of toxic metal(loid)s in agricultural soils impacted from long-term application of phosphate fertilizer. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoffer, J.T.; Sauvé, S.; Neaman, A.; Ginocchio, R. Role of Leaf Litter on the Incorporation of Copper-Containing Pesticides into Soils Under Fruit Production: A Review. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 20, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, J.; Nawab, J.; Faiq, M.E.; Ullah, S.; Alam, A.; Ahmad, I.; Ali, S.W.; Khan, S.; Ahmad, I.; Muhammad, A.; et al. Multi-geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and source apportionment of potentially toxic elements in urban children’s park soils in Pakistan: A risk assessment study. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 311, 119961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.M.; Jiang, H.H.; Luo, J. Metals in soils from a typical rapidly developing county, Southern China: Levels, distribution, and source apportionment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 19282–19293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, I.J.; Almond, P.C.; Eger, A.; Stone, J.O.; Montgomery, D.R.; Malcolm, B. Rapid soil production and weathering in the Southern Alps, New Zealand. Science 2014, 343, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Wen, J.; Zhang, S.; Wu, C.; Ouyang, H.; Hu, N.; Li, X.; Qiu, X. The coupling of sulfide and Fe-Mn mineral promotes the migration of lead and zinc in the redox cycle of high pH floodplain soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 472, 134546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Ji, J.; Zhang, C.; Huang, C.; Lu, X.; Yang, Z. The degree of soil arsenic background enrichment by carbonate weathering is mainly controlled by climate in large spatial scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genova, G.; Della Chiesa, S.; Mimmo, T.; Borruso, L.; Cesco, S.; Tasser, E.; Matteazzi, A.; Niedrist, G. Copper and zinc as a window to past agricultural land-use. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 126631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Feng, X.B.; Qiu, G.L.; Shang, L.H.; Li, Z.G. Mercury pollution in Asia: A review of the contaminated sites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoffer, J.T.; Solari, F.; Petit-Dit-Grezeriat, L.; Pelosi, C.; Ginocchio, R.; Yanez, C.; Mazuela, P.; Neaman, A. The downside of copper pesticides: An earthworm’s perspective. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 31, 16076–16084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neaman, A.; Schoffer, J.-T.; Navarro-Villarroel, C.; Pelosi, C.; Peñaloza, P.; Dovletyarova, E.; Schneider, J. Copper contamination in agricultural soils: A review of the effects of climate, soil properties, and prolonged copper pesticide application in vineyards and orchards. Plant Soil. Environ. 2024, 70, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Ren, B.Z.; Deng, X.P.; Yin, W.; Xie, Q.; Cai, Z.Q.; Zou, H. Potential toxic elements (PTEs) in rhizosphere soils and crops under a black shale high geological background: Pollution characteristics, distribution and risk assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 165, 112236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Yang, S.; Luo, S. Source analysis and health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural land of multi-mineral mining and smelting area in the Karst region—A case study of Jichangpo Town, Southwest China. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Lou, Z.; Sheng, M.; Xiaonan, L.; Ren, Z.; Xiao, R. Source-oriented stochastic health risk assessment of toxic metals in soil via a hybrid model and Monte Carlo simulation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 286, 117209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA (The United States Environmental Protection Agency). Supplemental Guidance for Developing Soil Screening Levels for Superfund Sites; OSWER9355.4-24. Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2001.
- Qing, X.; Yutong, Z.; Shenggao, L. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risk in urban soils of steel industrial city (Anshan), Liaoning, Northeast China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 120, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEPPRC (Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China) and MLRPRC (Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China), 2014. Bulletin on National Survey of Soil Contamination. Available online: http://www.zhb.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/qt/201404/t20140417_270670.htm (accessed on 12 October 2019). (In Chinese)
- DB11/T656-2009; Environmental Site Assessment Guideline. Jilin University: Changchun, China, 2009.
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Reference Dose (RfD): Description and Use in Health Risk Assessments. In Background Document 1A. Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS); 1993. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/iris/reference-dose-rfd-description-and-use-health-risk-assessments (accessed on 12 October 2019).
- USEPA (The United States Environmental Protection Agency). Exposure Factors Handbook 2011 Edition (Final); EPA/600/R-09/052F; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- USEPA (The United States Environmental Protection Agency). CASRN 7440-50-8US EPA, S., 1999. Soil Screening Guidance: Technical Background Document |Superfund| US EPA. 1991. Available online: https://dam.assets.ohio.gov/image/upload/epa.ohio.gov/Portals/30/rules/VAP-Support-Document-Final.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2019).
- USEPA (The United States Environmental Protection Agency). Risk assessment guidance for superfund. In Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A); EPA/540/1-89/002; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Risk Based Screening Table-Generic, Summary Table. 2015. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/risk/risk-based-screening-table-generic-tables (accessed on 31 January 2016).
- Yang, S.; He, M.; Zhi, Y.; Chang, S.X.; Gu, B.; Liu, X.; Xu, J. An integrated analysis on source-exposure risk of heavy metals in agricultural soils near intense electronic waste recycling activities. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chao, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, A.; Cao, H. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.H.; Zhang, D.G.; Wang, Y.T. Probabilistic Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Intake via Vegetable Consumption around Pb/Zn Smelters in Southwest China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R.; Wang, Q.; Miao, Y.; Jiao, L.; Shoaib, M.; Shen, Z. Temporal variations of levels and sources of health risk associated with heavy metals in road dust in Beijing from May 2016 to April 2018. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 129434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhao, J.; Chang, S.X.; Collins, C.; Xu, J.; Liu, X. Status assessment and probabilistic health risk modeling of metals accumulation in agriculture soils across China: A synthesis. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Geng, X.; Zhao, M.; Sun, T.; Fan, Z. Health risk assessment of heavy metal(loid)s in park soils of the largest megacity in China by using Monte Carlo simulation coupled with Positive matrix factorization model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Parameters | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | As | Hg | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (mg/kg) | 0.13 | 85.0 | 26.0 | 36.2 | 26.8 | 68.4 | 7.6 | 0.03 | 6.58 | |
| Min. (mg/kg) | 0.03 | 5.0 | 3.5 | 3.3 | 3.7 | 7.5 | 0.4 | 0.003 | 4.1 | |
| Max. (mg/kg) | 6.80 | 1641.5 | 870.0 | 728.8 | 948.5 | 790.4 | 1880.2 | 4.22 | 8.1 | |
| SD | 0.1 | 57.66 | 16.85 | 29.26 | 21.73 | 28.11 | 15.83 | 0.06 | 0.7 | |
| CV% | 76% | 68% | 65% | 81% | 81% | 41% | 208% | 192% | 11% | |
| BV a [37] (mg/kg) | 0.097 | 61.0 | 22.6 | 26.9 | 26 | 74.2 | 11.2 | 0.065 | 7.7 | |
| BV b [38] (mg/kg) | 0.132 | 62.0 | 22.6 | 27.1 | 23.6 | 63.3 | 8.6 | 0.031 | 7.32 | |
| SQGs [42] (mg/kg) | ERL | 1.2 | 81 | 34 | 21 | 47 | 150 | 8.2 | 0.15 | - |
| ERM | 9.6 | 370 | 270 | 52 | 218 | 410 | 70 | 0.71 | - | |
| SV [53] | pH ≤ 5.5 | 0.3 | 150 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 200 | 40 | 1.3 | - |
| 5.5 ≤ pH ≤ 6.5 | 0.3 | 150 | 50 | 70 | 90 | 200 | 40 | 1.8 | - | |
| 6.5 ≤ pH ≤ 7.5 | 0.3 | 200 | 100 | 100 | 120 | 250 | 30 | 2.4 | - | |
| pH > 7.5 | 0.6 | 250 | 100 | 190 | 170 | 300 | 25 | 3.4 | - | |
| Sources | Non-Cancer Hazard Quotient (HQ) | Hazard Index (HI) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | As | Hg | ||
| Industrial | 4.2 × 10−4 | 6.6 × 10−3 | 1.9 × 10−3 | 4.9 × 10−3 | 2.3 × 10−2 | 6.6 × 10−4 | 7.5 × 10−2 | 4.3 × 10−4 | 1.13 × 10−1 |
| Coal-fired | 4.7 × 10−4 | 7.3 × 10−3 | 2.1 × 10−3 | 5.5 × 10−3 | 2.5 × 10−2 | 7.3 × 10−4 | 9.2 × 10−2 | 3.0 × 10−4 | 1.33 × 10−1 |
| Natural source | 4.4 × 10−4 | 8.9 × 10−3 | 2.3 × 10−3 | 7.1 × 10−3 | 2.5 × 10−2 | 7.7 × 10−4 | 7.6 × 10−2 | 2.9 × 10−4 | 1.21 × 10−1 |
| Traffic-agricultural source | 4.8 × 10−4 | 6.6 × 10−3 | 2.2 × 10−3 | 5.8 × 10−3 | 2.7 × 10−2 | 7.8 × 10−4 | 8.2 × 10−2 | 3.1 × 10−4 | 1.25 × 10−1 |
| Total | 1.8 × 10−3 | 3.0 × 10−2 | 8.4 × 10−3 | 2.3 × 10−2 | 9.9 × 10−2 | 2.9 × 10−3 | 3.3 × 10−1 | 1.3 × 10−3 | 4.96 × 10−1 |
| Sources | Non-Cancer Hazard Quotient (HQ) | Hazard Index (HI) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | As | Hg | ||
| Industrial | 1.6 × 10−4 | 1.3 × 10−2 | 2.2 × 10−4 | 5.8 × 10−4 | 2.9 × 10−3 | 8.0 × 10−5 | 8.6 × 10−3 | 6.4 × 10−5 | 2.56 × 10−2 |
| Coal-fired | 1.7 × 10−4 | 1.4 × 10−2 | 2.4 × 10−4 | 6.5 × 10−4 | 3.2 × 10−3 | 8.9 × 10−5 | 1.1 × 10−2 | 4.5 × 10−5 | 2.94 × 10−2 |
| Natural | 1.8 × 10−4 | 1.7 × 10−2 | 2.7 × 10−4 | 8.4 × 10−4 | 3.1 × 10−3 | 9.5 × 10−5 | 8.8 × 10−3 | 4.3 × 10−5 | 3.03 × 10−2 |
| Traffic-agricultural source | 1.7 × 10−4 | 1.3 × 10−2 | 2.5 × 10−4 | 6.8 × 10−4 | 3.3 × 10−3 | 9.4 × 10−5 | 9.3 × 10−3 | 5.1 × 10−5 | 2.68 × 10−2 |
| Total | 6.8 × 10−4 | 5.7 × 10−2 | 9.8 × 10−4 | 2.8 × 10−3 | 1.3 × 10−2 | 3.6 × 10−4 | 3.7 × 10−2 | 2.0 × 10−4 | 1.12 × 10−1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, L.; Lou, Y.; Sun, Z. Spatial Analysis, Influencing Factors, and Source-Oriented Probabilistic Health Risks of Potential Toxic Elements in High Geological Background Soil in Central and Southern Shandong Peninsula, China. Toxics 2025, 13, 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110945
Wan F, Zhang X, Li Y, Liu S, Li J, Zhao C, Zhang L, Lou Y, Sun Z. Spatial Analysis, Influencing Factors, and Source-Oriented Probabilistic Health Risks of Potential Toxic Elements in High Geological Background Soil in Central and Southern Shandong Peninsula, China. Toxics. 2025; 13(11):945. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110945
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Fang, Xiuwen Zhang, Yan Li, Shenglin Liu, Jianwei Li, Chuang Zhao, Lin Zhang, Yanhong Lou, and Zeqiang Sun. 2025. "Spatial Analysis, Influencing Factors, and Source-Oriented Probabilistic Health Risks of Potential Toxic Elements in High Geological Background Soil in Central and Southern Shandong Peninsula, China" Toxics 13, no. 11: 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110945
APA StyleWan, F., Zhang, X., Li, Y., Liu, S., Li, J., Zhao, C., Zhang, L., Lou, Y., & Sun, Z. (2025). Spatial Analysis, Influencing Factors, and Source-Oriented Probabilistic Health Risks of Potential Toxic Elements in High Geological Background Soil in Central and Southern Shandong Peninsula, China. Toxics, 13(11), 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110945