Highlights
What are the main findings?
- BPA exposure impairs learning and memory and reduces synaptic plasticity (e.g., lower dendritic spine density), even at low concentrations; several effects are dose-dependent and, in some cases, sex-dependent.
- In animal and cellular models, BPA triggers oxidative/nitrosative stress, apoptosis, autophagy dysfunction, cytoskeletal alterations, and pathway changes involving AMPK, HO-1, and nNOS/Keap1/Nrf2.
- In human hESC-derived neurons, BPA reduces neuritogenesis, disrupts synaptic proteins (e.g., PSD-95; AMPAR alterations), and increases intracellular Ca2+, consistent with nitro-oxidative stress–driven neurotoxicity.
- Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) partially mitigates BPA-induced cognitive and molecular changes in mice, improving behavior and restoring antioxidant and synaptic pathway markers.
What is the implication of the main finding?
- BPA displays clinically relevant neurotoxic potential even below previously accepted regulatory limits, underscoring the need to reassess safety thresholds, strengthen public policies restricting BPA use, and prioritize safer alternatives particularly for pregnant women, children, and chronically exposed populations.
Abstract
Introduction: Bisphenol A (BPA) is a synthetic compound widely used in plastics and epoxy resins, and human exposure is virtually unavoidable. Numerous studies indicate that even doses below current regulatory limits may elicit neurotoxic effects, impairing learning, memory, and synaptic plasticity. Methodology: This mini-review. Searches were conducted in PubMed, the Virtual Health Library (VHL/BVS), and ScienceDirect, using MeSH descriptors related to “Bisphenol A,” “Neurotoxicity Syndromes,” “Central Nervous System,” and “Prefrontal Cortex,” combined with Boolean operators. We included studies published between 2007 and 2025, available in English, Portuguese, or Spanish, and focused on the neurotoxic effects of BPA. After screening and application of the eligibility criteria, twelve articles were selected. Results: The analyzed studies show that BPA exposure, even at low concentrations, compromises neuronal survival, dendritic density, and synaptic plasticity. In animal models, cognitive deficits were observed in memory and learning tasks, associated with increased oxidative stress and alterations in molecular pathways such as AMPK, HO-1, and nNOS/Keap1/Nrf2. In cell cultures, BPA induced apoptosis, autophagy dysfunction, cytoskeletal reorganization, and loss of synaptic proteins. The effects were dose-dependent and, in some cases, sex-dependent. Conclusions: BPA exhibits significant neurotoxic potential, affecting both the development and function of the central nervous system. These findings underscore the need to revise current safety limits and reinforce the importance of public policies regulating BPA use, as well as encouraging the search for safer alternatives.
1. Introduction
Bisphenol A (BPA) is one of the most ubiquitous synthetic chemical compounds in contemporary society and is widely used as a monomer in the production of polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins materials found in the inner lining of most food cans and in dental sealants. Human exposure to BPA has become virtually unavoidable, as heat and extreme environmental conditions (such as acidic or basic media) accelerate the hydrolysis of the ester bonds linking its monomers, thereby facilitating the release of the substance into foods and beverages and, consequently, increasing the risk of contamination [1].
In parallel with these exposure mechanisms, international regulatory agencies have established safety limits [2]. Reports indicate that the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) set the tolerable daily intake (TDI) at approximately 0.2 ng/kg body weight per day, a lifetime exposure parameter representing a substantial reduction from the previously adopted limit of up to 4 µg BPA/kg/day.
Even within such safety limits, experimental evidence from animal models shows that BPA exposure can impair brain development, cognitive functions, and behavior and may even be associated with the emergence of mental disorders such as schizophrenia [3,4]. Although much of the literature focuses on neurotoxic effects resulting from perinatal exposure and on mechanisms modulating its impact on neurodevelopment [5], recent studies suggest that BPA also exerts adverse effects on the adult brain, an area for which toxicogenomic evidence remains scarce [6].
Furthermore, several studies indicate that BPA interferes with both reproductive and non-reproductive behaviors, such as playful interactions and performance on learning tasks in female and male rodents. These findings, unexpected for a xenobiotic estrogen, are consistent with observations of dendritic spine synapse loss [7].
Moreover, investigations show that BPA, even at doses below the daily exposure limit recommended by agencies such as the EPA, can impair the synaptogenic response to 17β-estradiol in the hippocampus of ovariectomized female rats [8]. Inhibition of estrogen-induced dendritic spine synaptogenesis is associated with cognitive deficits, particularly in individuals with physiologically reduced levels of this hormone, as observed in postmenopausal women [9].
Taken together, these findings underscore the need for public policies aimed at promoting health and preventing risks associated with BPA exposure through stricter regulations on the production, commercialization, and use of such compounds. In this context, the present study aimed to conduct a mini-review of the literature on the neurotoxic effects of bisphenol A, with an emphasis on potential clinical conditions associated with exposure to this compound.
2. Methodology
This mini-review was conducted in a manner similar to that described by Gomes et al. [10]. Searches were performed in PubMed, the Virtual Health Library (VHL/BVS), and ScienceDirect. We predefined a mechanistic scope: inclusion was restricted to primary experimental studies (in vitro/in vivo) that evaluated bisphenol A (BPA) alone (or BPA ± a single modulator when the BPA effect could be isolated) and reported quantitative cellular/synaptic outcomes in neural cells (human or animal, primary cultures or cell lines) and/or brain structures, with emphasis on the prefrontal cortex (PFC) and hippocampus (e.g., neuritogenesis, dendritic spines, synaptic proteins, ROS/RNS, apoptosis/autophagy, PKC/ERK/CREB pathways, PSD-95, AMPAR/NMDAR). Search terms followed MeSH headings: bisphenol A, neurotoxicity syndromes, central nervous system, and prefrontal cortex. Boolean operators AND and OR were used to construct the combinations listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Search strategy.
Regarding the eligibility criteria established, inclusion: original experimental study (in vitro/in vivo) with BPA alone or BPA ± one isolable modulator; neural models (neural cells and/or cortical/hippocampal tissues); quantitative cellular/synaptic outcomes; PFC/hippocampus or neural cultures with plasticity endpoints; publication period 2007–2025; full text available; languages English, Portuguese, or Spanish.
Exclusion: reviews, editorials, and letters; epidemiological/observational studies without cellular/synaptic analysis; multiple co-exposures when the BPA effect could not be isolated; non-neural models; behavior-only studies without cellular correlation; no full text; outside the period/language limits; duplicates; misaligned with the study objective; and grey literature.
Screening was conducted on the Rayyan (QCRI) platform with three reviewers. Each reviewer was blinded to the others’ decisions. In cases of impasse or a tie, the final adjudication was referred to a third reviewer. In total, 149 articles were identified from PubMed (n = 110), the Virtual Health Library (VHL/BVS) (n = 11), and ScienceDirect (n = 28). In the first filtering stage, which involved the initial screening of titles and abstracts, 88 records were excluded for the following reasons: reviews; studies exclusively epidemiological or behavioral in nature; out of scope; language or time-frame restrictions; and lack of full text. After this stage, 61 articles remained. In the second filtering stage, which consisted of full-text assessment of these 61 articles, 49 were excluded for the following reasons: absence of quantitative cellular or synaptic outcomes (n = 17); multiple co-exposures without isolating the effect of BPA (n = 9); non-neural model or outside the PFC–hippocampus/neuronal scope (n = 8); behavioral or epidemiological focus only (n = 11); and no access to full text (n = 4). Consequently, 12 studies were included, as shown in the flow diagram below (Figure 1). The included studies are presented in Section 3.
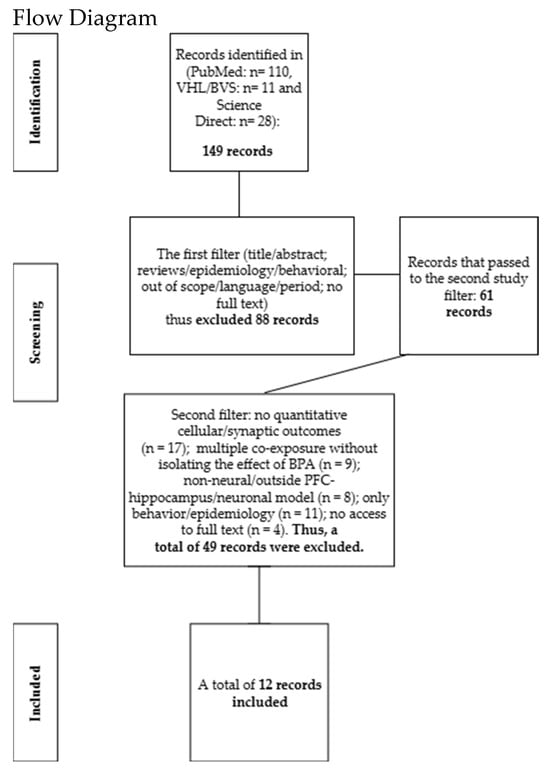
Figure 1.
149 records identified; first screening excluded 88 (61 advanced). Second screening excluded 49 for methodological and scope reasons. Final sample: 12 studies included.
3. Results
With regard to the results presented in this mini-review, a summary table was prepared compiling data from in vitro studies and research involving neuronal structures. As shown in Table 2, the selected articles were organized according to the following criteria: author/year, methodology, BPA dosage, neurotoxicity, and conclusion.

Table 2.
Compendium.
3.1. Bisphenol A-Induced Neurotoxicity: Evidence from Cell Cultures
This section addresses bisphenol A (BPA)-induced neurotoxicity in neural cell cultures. In this context, the experiment conducted by Wang et al. [14] primarily aimed to investigate the effects of chronic BPA exposure on glutamatergic neurons derived from human stem cells. To this end, the authors cultured these neurons and applied an increasing sequence of BPA concentrations (0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, and 10 μM). Additionally, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, 0.1%) was used as the control solution. The exposure period ranged from 3 to 14 days, with the first three days designated for the assessment of short-term effects and 14 days for the analysis of long-term effects, representing continuous exposure to BPA.
From a morphological perspective, neurite outgrowth progressively decreased as BPA concentrations increased. In parallel, there was a significant reduction in cell viability at concentrations between 0.5 and 10 μM. Doses equal to or greater than 1 μM induced dendritic degeneration as well as cell body enlargement. Functionally, there was a marked upregulation of synaptophysin (SYN) and PSD-95, changes commonly associated with neuropsychiatric disorders. In addition, increased expression of AMPA receptors and the GRIP1 protein was observed, accompanied by a reduction in GluA2, which led to elevated intracellular calcium levels and the activation of cleaved caspase-3, a typical marker of apoptosis. Finally, the tested BPA concentrations promoted increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reduced antioxidant markers, contributing to heightened oxidative stress and cellular impairment.
Consistent with these findings, the experiments conducted by Lee et al. [15] sought to explore the mechanisms underlying BPA neurotoxicity, with particular emphasis on cell viability and neuronal differentiation. For this purpose, N2a cells, which possess a high differentiation potential, were employed. BPA concentrations of 0–9 μM, 10 μM, and 100 μM were tested. All concentrations were evaluated for 24 h, and the 100 μM dose was additionally assessed at early time points (5 to 60 min) and extended up to 14 days. At concentrations between 0 and 9 μM, no significant alterations or evidence of BPA-induced toxicity were observed. However, at doses ≥ 10 μM, a decline in cell viability became evident. At 100 μM, the most pronounced effects were observed, including marked viability loss, increased cellular debris, decreased culture density, impaired and fragmented neurites, activation of the apoptotic cascade, accumulation of autophagic vesicles, substantial ROS elevation, and reduced antioxidant activity. The authors concluded that BPA induces progressive, dose-dependent neuronal degeneration, confirming its neurotoxic potential.
Similarly, Cho et al. [16] evaluated the neurotoxic effects of BPA in neural tissues using primary cortical neurons. These cells were exposed to BPA at 50, 100, and 200 μM after seven days of culture for a period of five days. Concentrations of 50 and 100 μM did not induce evident cytotoxicity, whereas 200 μM resulted in neuronal death, marked impairment of neurite outgrowth, reduced cell viability, loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, and increased intracellular ROS levels. The authors concluded that 200 μM BPA exerts clear and severe neurotoxic effects.
Along the same line, Yin et al. [17] investigated neural plasticity and cytoskeletal integrity in Neuro-2a cells exposed to BPA. Cultures were divided into three groups: a negative control (culture medium), a DMSO control (0.001%), and treatment groups exposed to BPA (50, 100, 150, and 200 μM) for 24 h. Samples treated with 50 and 100 μM showed no significant changes in viability or morphofunctional parameters. However, at 150 μM, there was a notable reduction in cell viability, along with loss of membrane integrity, mitochondrial and nuclear alterations, and decreased levels of key markers such as SYP, drebrin (Dbn), MAP2, and Tau. At 200 μM, these effects were even more pronounced, culminating in extensive neuronal death, see Figure 2.
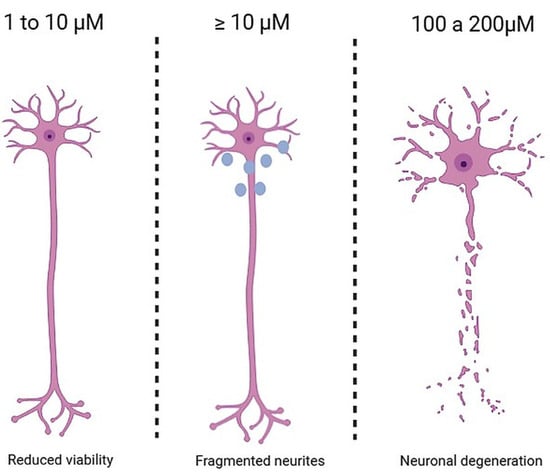
Figure 2.
Effects of BPA dose on neuronal tissue. Legend: The figure illustrates, from left to right, the progressive neurotoxic effects of BPA. At 1–10 μM, neural cells exhibit reduced viability or minimal toxic alterations; at concentrations ≥ 10 μM, neurite fragmentation and impaired outgrowth appear; at 100–200 μM, there is pronounced neuronal degeneration and significant neurotoxicity.
Moving toward a broader perspective on neural structures and functions, Zhang et al. [13] investigated the effects of low BPA doses on neural development in postnatal rodents. Animals were exposed to BPA via intraperitoneal injections at low (0.5 μg/kg), moderate (50 μg/kg), and high (5000 μg/kg) doses, in addition to a non-exposed control group. To evaluate complex neural structures and functions, such as those of the hippocampus, the authors performed Y-maze testing to assess memory and Golgi-Cox staining to analyze dendritic morphology. The results revealed that low and moderate doses caused impairments in learning and memory and reduced dendritic complexity, while high doses produced severe memory deficits and almost complete loss of dendritic growth.
Supporting these findings, Wu et al. [12] investigated whether BPA exposure increases oxidative stress and consequently impairs cognitive function. BPA was administered in drinking water at 0.1 μg/mL and 0.2 μg/mL for eight weeks. Animals underwent behavioral tests, including the Morris water maze, object recognition, and the shuttle box, to assess memory. The results showed that 0.1 μg/mL exposure caused mild spatial memory impairments, while 0.2 μg/mL led to pronounced deficits in spatial memory, recognition, and avoidance learning. These findings reinforce those of Zhang et al., confirming that even very low BPA doses impair learning and memory.
Finally, Kim et al. [11] examined the neurotoxic effects of BPA on the rodent hippocampus. Animals were exposed to BPA for two weeks at 1, 5, and 20 mg/kg/day. Analyses included proliferation and survival of new cells in the dentate gyrus, cerebral and hippocampal perfusion, and spatial learning and memory testing. The results demonstrated that 20 mg/kg/day BPA caused substantial cellular loss in the hippocampus and severe impairments in memory and learning.
Advancing to studies involving low BPA concentrations aligned with the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) tolerable daily intake (TDI, ~0.2 ng/kg/day), the experiment by Kiso-Farnè et al. [18] aimed to determine whether low BPA doses disrupt corticogenesis and neuronal differentiation in human neural stem cells. Human neural stem cell models were exposed to 0.1, 1, 10, and 100 nM for 2, 4, 7, and 12 days in vitro, followed by immunocytochemistry and quantitative cell analysis. The findings indicated altered cellular differentiation and proliferation, especially at 100 nM, where there was a significant reduction in SOX2 after 4–7 days and notable morphological changes.
Similarly, Pang et al. [20] compared the toxicity of BPA and its analogues (BPS and BPB) in murine hippocampal neurons, focusing on oxidative stress, apoptosis, and cell proliferation. Concentrations ranged from 1 nM to 100 μM, with oxidative stress assessed after 6 h, apoptosis after 24–48 h, and proliferation after 7 days. The study showed that even low doses increased oxidative stress; BPS was the least toxic, while BPA and BPB significantly reduced proliferation and triggered cell death at higher doses.
Corroborating these findings, Liang et al. [21] examined BPA and six derivatives (BPS, BPE, BPF, BPB, BPAF, and BPZ) in human neuronal cells, investigating viability, differentiation, and neurite morphology. Cell viability was tested at 0.001–300 μM for 24 h, while neurite length and differentiation were assessed at 1, 10, and 100 nM for eight days. Toxicity was notable only at high concentrations (>25 μM); however, even low doses (1–100 nM) significantly reduced neurite length, suggesting functional impairment without overt cell death. Among the derivatives, BPAF and BPB were the most toxic, whereas BPS was the least harmful.
Finally, Flores et al. [19] investigated the impact of BPA on the cholinergic system, including neuronal death, neural plasticity, and signaling pathways. Both in vivo and in vitro experiments were conducted. In male rodents, a single dose of 40 μg/kg BPA was administered and evaluated after 48 h, revealing selective neuronal loss and necrosis in cholinergic nuclei. In vitro, basal forebrain cholinergic neurons were exposed to 0.001–1 μM BPA for 1–14 days, demonstrating dose-dependent cell death, marked degeneration, loss of synaptic proteins, and dysfunction of cholinergic and glutamatergic pathways.
3.2. Teratogenic Potential of Bisphenol A in the Central Nervous System and Its Interference with Synaptic Plasticity in the Prefrontal Cortex and Hippocampus
Experimental studies in animal models have demonstrated that prenatal exposure to estrogenic endocrine disruptors, such as bisphenol A (BPA), is associated with significant teratogenic effects. This has raised increasing concern within the fields of neuroscience and environmental neurotoxicology regarding the implications of BPA for neural development [3].
Xing et al. [22] reported that BPA, either alone or in combination with genistein, induces neural tube malformations in rat embryos, particularly affecting the prosencephalon. These effects were dose-dependent and revealed a negative synergistic interaction between the compounds, amplifying damage to central nervous system (CNS) development. Converging lines of evidence indicate that BPA, a widely used endocrine disruptor, possesses teratogenic potential in the CNS, particularly by impairing synaptic plasticity in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus [23,24,25]. Exposure to BPA during critical periods of neurogenesis may disrupt neuronal migration and maturation, leading to persistent morphofunctional alterations and an increased risk of neuropsychiatric disorders [26].
BPA exposure during vulnerable developmental windows, such as gestation and early childhood, has been linked to morphological and functional changes in the CNS. Studies have shown that BPA reduces neuronal populations while increasing glial cell numbers in the cerebral cortex and impairs the self-renewal and differentiation of neural progenitors, leading to long-lasting behavioral and cognitive deficits [23]. In the hippocampus, BPA interferes with synapse formation and maintenance, reduces dendritic spine density, and impairs synaptic transmission, resulting in memory and learning impairments [6,24,27].
GABAergic neurotransmission, essential for emotional and psychophysiological regulation, is also disrupted by BPA exposure. BPA has been shown to increase the expression of cytochrome P450 and tryptophan hydroxylase genes in the prefrontal cortex while reducing 5α-reductase expression in females, indicating a sexually dimorphic response in adult rats [25]. Moreover, BPA decreases mRNA levels of CaMKII subunits, a protein critical for memory consolidation and synaptic plasticity [28].
From a pathophysiological perspective, BPA has been implicated in the suppression of potassium-chloride cotransporter 2 (KCC2) gene expression, essential for the developmental switch in GABAergic activity from excitatory to inhibitory. This suppression may compromise synaptic organization and cortical architecture [29]. BPA also disrupts both pre- and postsynaptic mechanisms, decreasing glutamate release, reducing dendritic spine density, and downregulating NMDA and AMPA receptors, which are vital for synaptic plasticity and long-term potentiation (LTP). In the prefrontal cortex, BPA blocks the synaptogenic response normally induced by sex hormones such as testosterone and estradiol, preventing the physiological synaptic increase these steroids promote [6,25,30]. Reported that BPA blocks estradiol-dependent memory consolidation in ovariectomized female rats, leading to object recognition deficits.
In nonhuman primates, even low BPA levels, comparable to typical human exposure, have been shown to reduce excitatory synapses and impair working memory, with partial recovery after compound withdrawal [25]. Brain estrogens, derived from androgens, play a fundamental role in neural development [31], yet BPA disrupts the development of midbrain dopaminergic neurons and hippocampal synapses in rodents [32,33]. In primates, gestational BPA exposure has resulted in abnormalities in the fetal ventral midbrain and hippocampus. In juveniles, however, no morphological or cognitive alterations were detected, suggesting that BPA’s effects are developmental stage-dependent [25]. Furthermore, BPA acts as a modulator of estrogen receptors, exhibiting both agonistic and antagonistic activity, and displays antiandrogenic properties, further disrupting synaptic plasticity [5].
At the molecular level, BPA alters intracellular signaling pathways, including the NMDAR/PSD-95–PTEN/AKT axis, thereby affecting the expression of synaptic proteins and transcription factors linked to autism spectrum disorders and neuroplasticity. These molecular alterations are associated with anxiety- and depression-like behaviors, cognitive impairments, and a potentially increased risk of autism spectrum disorders, particularly following perinatal exposure [34,35].
Given this evidence, it is crucial to prioritize research employing long-term, low-dose exposure models that more accurately reflect human environmental contact with BPA and its analogues (e.g., BPF, BPAF, and BPS). Such approaches would better simulate continuous, lifelong exposure scenarios. Additionally, there is a clear need to use advanced human-relevant models, including brain organoids, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and multi-omics technologies (transcriptomics, epigenomics, metabolomics), to identify early neurodevelopmental alterations and behavioral outcomes. Equally important is the expansion of epidemiological studies to improve biomonitoring and cumulative risk assessment, especially in relation to real-world exposure levels, including concentrations below the recently revised tolerable daily intake (TDI) set by EFSA (0.2 ng/kg/day). Finally, future efforts should focus on exploring neuroprotective strategies and assessing the comparative safety of BPA substitutes, thereby supporting stronger regulatory frameworks and more effective public health interventions.
4. Conclusions
Therefore, evidence from studies using both human neuronal cell cultures and animal models consistently indicates the neurotoxic potential of bisphenol A (BPA). This compound exerts deleterious effects by disrupting cellular structure and function across a wide range of exposure levels. Notably, human embryonic neuronal cells and animal neural systems exposed to concentrations between 1 and 10 μM exhibit morphological alterations, including impaired neuritic outgrowth, neurite fragmentation, and dendritic retraction. At doses ≥ 100 μM, BPA becomes markedly cytotoxic, triggering cellular apoptosis via apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) in a caspase-3-independent manner and blocking autophagic flux through the HO-1/AMPK pathway. In addition, oxidative stress is exacerbated, accompanied by dysregulation of calcium homeostasis, collectively leading to significant neuronal damage and weakening of synaptic integrity and plasticity.
These converging findings clearly demonstrate that BPA-induced cellular injury leads to nervous system dysfunction, including hippocampal impairment and cognitive deficits. Of particular note, exposures between 1 and 50 μM for 14 days or longer reduce hippocampal neurogenesis and severely impair spatial memory. At ≥100 μM, the neurotoxic effects are more pronounced, resulting in extensive neuronal death.
In summary, this mini-review underscores that BPA is a concentration-dependent neurotoxicant: lower doses produce subtle but measurable neural alterations, whereas higher doses lead to profound structural and functional damage. Importantly, BPA can compromise neural architecture, intracellular signaling, and memory processes. Future research should therefore prioritize standardized, long-term exposure models and robust behavioral assessments in both experimental systems and humans to strengthen causal inference and inform regulatory safety thresholds.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.V.d.A.F., T.d.S.T., J.S.B., A.C.M.O.R., G.C.d.L., S.V.G.J., G.B.S.L., J.L.F., A.B.d.S., L.N.d.S., R.R.d.S.J., M.I.K., E.F.P., E.G.C.d.N., T.A.A.d.M.F. and F.P.G.; Methodology, G.C.d.L., S.V.G.J., R.R.d.S.J., M.I.K., E.F.P. and T.A.A.d.M.F.; Validation, T.d.S.T., J.S.B., A.C.M.O.R., G.C.d.L., S.V.G.J., G.B.S.L., J.L.F., L.N.d.S., R.R.d.S.J., M.I.K., E.F.P., E.G.C.d.N. and T.A.A.d.M.F.; Investigation, L.V.d.A.F., T.d.S.T., J.S.B., A.C.M.O.R., G.B.S.L., J.L.F., A.B.d.S. and L.N.d.S.; Data curation, L.V.d.A.F., T.d.S.T., J.S.B., A.C.M.O.R., G.C.d.L., G.B.S.L., J.L.F., A.B.d.S. and L.N.d.S.; Writing—original draft preparation, L.V.d.A.F., T.d.S.T., A.C.M.O.R. and G.B.S.L.; Writing—review and editing, L.V.d.A.F., T.d.S.T., J.S.B., G.C.d.L., S.V.G.J., J.L.F., A.B.d.S., L.N.d.S., R.R.d.S.J., M.I.K., E.F.P., E.G.C.d.N., T.A.A.d.M.F. and F.P.G.; Visualization, L.V.d.A.F., T.d.S.T., A.C.M.O.R., G.B.S.L. and A.B.d.S.; Supervision, R.R.d.S.J., M.I.K., E.F.P., E.G.C.d.N., T.A.A.d.M.F. and F.P.G.; Project administration, S.V.G.J., R.R.d.S.J., E.G.C.d.N. and F.P.G.; Funding acquisition, J.S.B., E.G.C.d.N., T.A.A.d.M.F. and F.P.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES), Brazil.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable, as the study does not directly involve human participants or animals and was conducted using publicly available secondary data.
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived or not applicable, as this is a review study; therefore, obtaining individual consent does not apply. It is noted that this type of study uses publicly available data previously collected in accordance with ethical principles.
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript is a mini-review; no new data were generated or analyzed. All information supporting the reported results derives from previously published studies, cited in the References and accessible through public repositories/databases (e.g., PubMed, Virtual Health Library [BVS], and ScienceDirect). No additional datasets are available.
Conflicts of Interest
No conflicts of interest declared by the authors.
References
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Hauser, R.; Marcus, M.; Olea, N.; Welshons, W.V. Human exposure to bisphenol A (BPA). Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 24, 139–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buoso, E.; Masi, M.; Limosani, R.V.; Oliviero, C.; Saeed, S.; Iulini, M.; Passoni, F.C.; Racchi, M.; Corsini, E. Endocrine Disrupting Toxicity of Bisphenol A and Its Analogs: Implications in the Neuro-Immune Milieu. J. Xenobiot. 2025, 15, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, C.A.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Farabollini, F.; Newbold, R.R.; Rubin, B.S.; Talsness, C.E.; Vandenbergh, J.G.; Walser-Kuntz, D.R.; Saal, F.S.V. In vivo effects of bisphenol A in laboratory rodent studies. Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 24, 199–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.S. Effects of Bisphenol-A and Other Endocrine Disruptors Compared With Abnormalities of Schizophrenia: An Endocrine-Disruption Theory of Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2009, 35, 256–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolstenholme, J.T.; Rissman, E.F.; Connelly, J.J. The role of Bisphenol A in shaping the brain, epigenome and behavior. Horm. Behav. 2011, 59, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inagaki, T.; Frankfurt, M.; Luine, V. Estrogen-Induced Memory Enhancements Are Blocked by Acute Bisphenol A in Adult Female Rats: Role of Dendritic Spines. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 3357–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farabollini, F.; Porrini, S.; Della Seta, D.; Bianchi, F.; Dessì-Fulgheri, F. Effects of perinatal exposure to bisphenol A on sociosexual behavior of female and male rats. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110 (Suppl. 3), 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foehr, E.D.; Bohuslav, J.; Chen, L.F.; DeNoronha, C.; Geleziunas, R.; Lin, X.; O’MAhony, A.; Greene, W.C. The NF-kappa B-inducing kinase induces PC12 cell differentiation and prevents apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 34021–34024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Santos, C.; Ferrer, I.; Reiriz, J.; Viñals, F.; Barrachina, M.; Ambrosio, S. MPP+ increases alpha-synuclein expression and ERK/MAP-kinase phosphorylation in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Brain Res. 2002, 935, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, F.T.D.S.; Andrade, A.V.D.D.; Moura Melo, P.K.; Júnior, R.R.D.S.; Souza, D.L.S.D.; Tavares, É.A.F.; Sena, I.G.D.; Fernandes, T.A.A.D.M.; Morais, P.L.A.D.G.; Fonseca, I.A.T.; et al. The Effects of the Association Between a High-Fat Diet and Physical Exercise on BDNF Expression in the Hippocampus: A Comprehensive Review. Life 2025, 15, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.E.; Park, H.R.; Gong, E.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, J. Exposure to bisphenol A appears to impair hippocampal neurogenesis and spatial learning and memory. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 3383–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wei, W.; Sun, Q.; Wen, D.; Jia, L. Protective effect of alpha-lipoic acid on bisphenol A-induced learning and memory impairment in developing mice: nNOS and keap1/Nrf2 pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 154, 112307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kuang, H.; Luo, Y.; Liu, S.; Meng, L.; Pang, Q.; Fan, R. Low-dose bisphenol A exposure impairs learning and memory ability with alterations of neuromorphology and neurotransmitters in rats. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chang, L.; Aguilar, J.S.; Dong, S.; Hong, Y. Bisphenol-A exposure induced neurotoxicity in glutamatergic neurons derived from human embryonic stem cells. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Hsieh, C.F.; Wang, J.Y. Bisphenol a Induces Autophagy Defects and AIF-Dependent Apoptosis via HO-1 and AMPK to Degenerate N2a Neurons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.H.; Kim, A.H.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.; Lee, W.J.; Chang, S.C.; Lee, J. Sensitive neurotoxicity assessment of bisphenol A using double immunocytochemistry of DCX and MAP2. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2018, 41, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Hua, L.; Chen, L.; Hu, D.; Li, J.; An, Z.; Tian, T.; Ning, H.; Ge, Y. Bisphenol-A exposure induced neurotoxicity and associated with synapse and cytoskeleton in Neuro-2a cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2020, 67, 104911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiso-Farnè, K.; Yaoi, T.; Fujimoto, T.; Itoh, K. Low Doses of Bisphenol A Disrupt Neuronal Differentiation of Human Neuronal Stem/Progenitor Cells. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 2022, 55, 193–202. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, A.; Moyano, P.; Sola, E.; García, J.M.; García, J.; Frejo, M.T.; Guerra-Menéndez, L.; Labajo, E.; Lobo, I.; Abascal, L.; et al. Bisphenol-A Neurotoxic Effects on Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Neurons In Vitro and In Vivo. Biology 2023, 12, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Q.; Li, Y.; Meng, L.; Li, G.; Luo, Z.; Fan, R. Neurotoxicity of BPA, BPS, and BPB for the hippocampal cell line (HT-22): An implication for the replacement of BPA in plastics. Chemosphere 2019, 226, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Yin, N.; Liang, S.; Yang, R.; Liu, S.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, G.; Faiola, F. Bisphenol A and several derivatives exert neural toxicity in human neuron-like cells by decreasing neurite length. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 135, 111015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Shang, L.; Liu, R.; Wei, X.; Jiang, J.; Hao, W. Embryotoxic and teratogenic effects of the combination of bisphenol A and genistein on in vitro cultured postimplantation rat embryos. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 115, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowski, R.N.; Wise, L.M.; Park, P.Y.; Schantz, S.L.; Juraska, J.M. Early exposure to bisphenol A alters neuron and glia number in the rat prefrontal cortex of adult males, but not females. Neuroscience 2014, 279, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsworth, J.D.; Jentsch, J.D.; Groman, S.M.; Roth, R.H.; Redmond, E.D.; Leranth, C. Low circulating levels of bisphenol-A induce cognitive deficits and loss of asymmetric spine synapses in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and hippocampus of adult male monkeys. J. Comp. Neurol. 2015, 523, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, B.; Sánchez, P.; Torres, J.M.; Ortega, E. Effects of adult exposure to bisphenol a on genes involved in the physiopathology of rat prefrontal cortex. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanganu-Opatz, I.L. Between molecules and experience: Role of early patterns of coordinated activity for the development of cortical maps and sensory abilities. Brain Res. Rev. 2010, 64, 160–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, R.E.; Luine, V.; Khandaker, H.; Villafane, J.J.; Frankfurt, M. Adolescent bisphenol-A exposure decreases dendritic spine density: Role of sex and age. Synapse 2014, 68, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisman, J.; Yasuda, R.; Raghavachari, S. Mechanisms of CaMKII action in long-term potentiation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, M.; Berglund, K.; Hanna, M.; Guo, J.U.; Kittur, J.; Torres, M.D.; Abramowitz, J.; Busciglio, J.; Gao, Y.; Birnbaumer, L.; et al. Bisphenol A delays the perinatal chloride shift in cortical neurons by epigenetic effects on the Kcc2 promoter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4315–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leranth, C.; Hajszan, T.; Szigeti-Buck, K.; Bober, J.; MacLusky, N.J. Bisphenol A prevents the synaptogenic response to estradiol in hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of ovariectomized nonhuman primates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14187–14191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roselli, C.E.; Liu, M.; Hurn, P.D. Brain Aromatization: Classic Roles and New Perspectives. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2009, 27, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Ye, Y.; Li, T.; Chen, L.; Tian, D.; Luo, Q.; Lu, M. Bisphenol-A rapidly promotes dynamic changes in hippocampal dendritic morphology through estrogen receptor-mediated pathway by concomitant phosphorylation of NMDA receptor subunit NR2B. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 249, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Masuo, Y.; Ishido, M. Neurotoxicity of endocrine disruptors: Possible involvement in brain development and neurodegeneration. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B 2011, 14, 346–369. [Google Scholar]
- Kanlayaprasit, S.; Saeliw, T.; Thongkorn, S.; Panjabud, P.; Kasitipradit, K.; Lertpeerapan, P.; Songsritaya, K.; Yuwattana, W.; Jantheang, T.; Jindatip, D.; et al. Sex-specific impacts of prenatal bisphenol A exposure on genes associated with cortical development, social behaviors, and autism in the offspring’s prefrontal cortex. Biol. Sex Differ. 2024, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Kang, Y.; Bai, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. Perinatal Exposure to Bisphenol A Impairs Cognitive Function via the Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Signaling Pathway in Male Rat Offspring. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/tox.24007 (accessed on 1 October 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).