Anti-Obesity Effects of Pea Peptides Modified by Steam Explosion on Obese Mice: Regulation of Gut Microbiota and Glucose Metabolism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of SE-PP
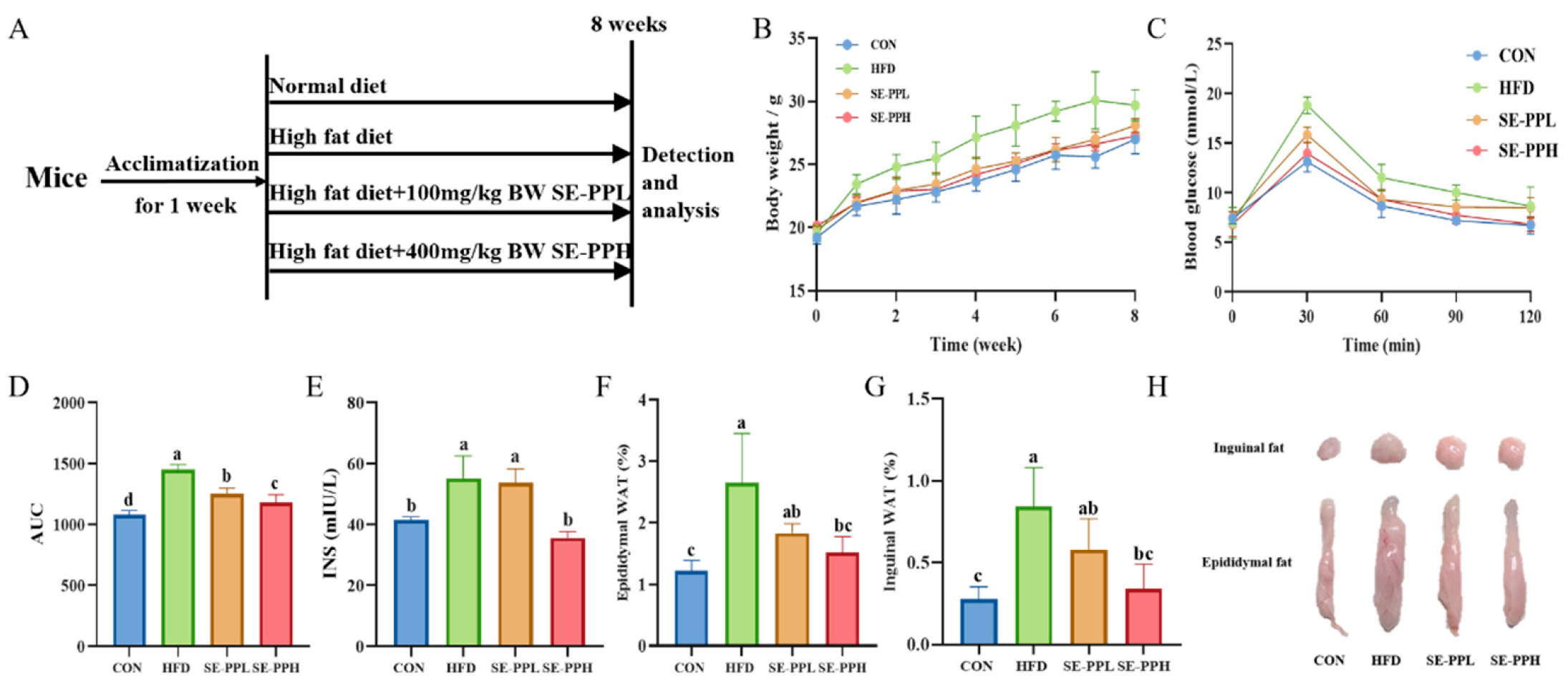
2.3. Animal Experiment Design
2.4. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
2.5. Histological Analysis
2.6. Immunohistochemistry
2.7. Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.8. Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis
2.9. Western Blot Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
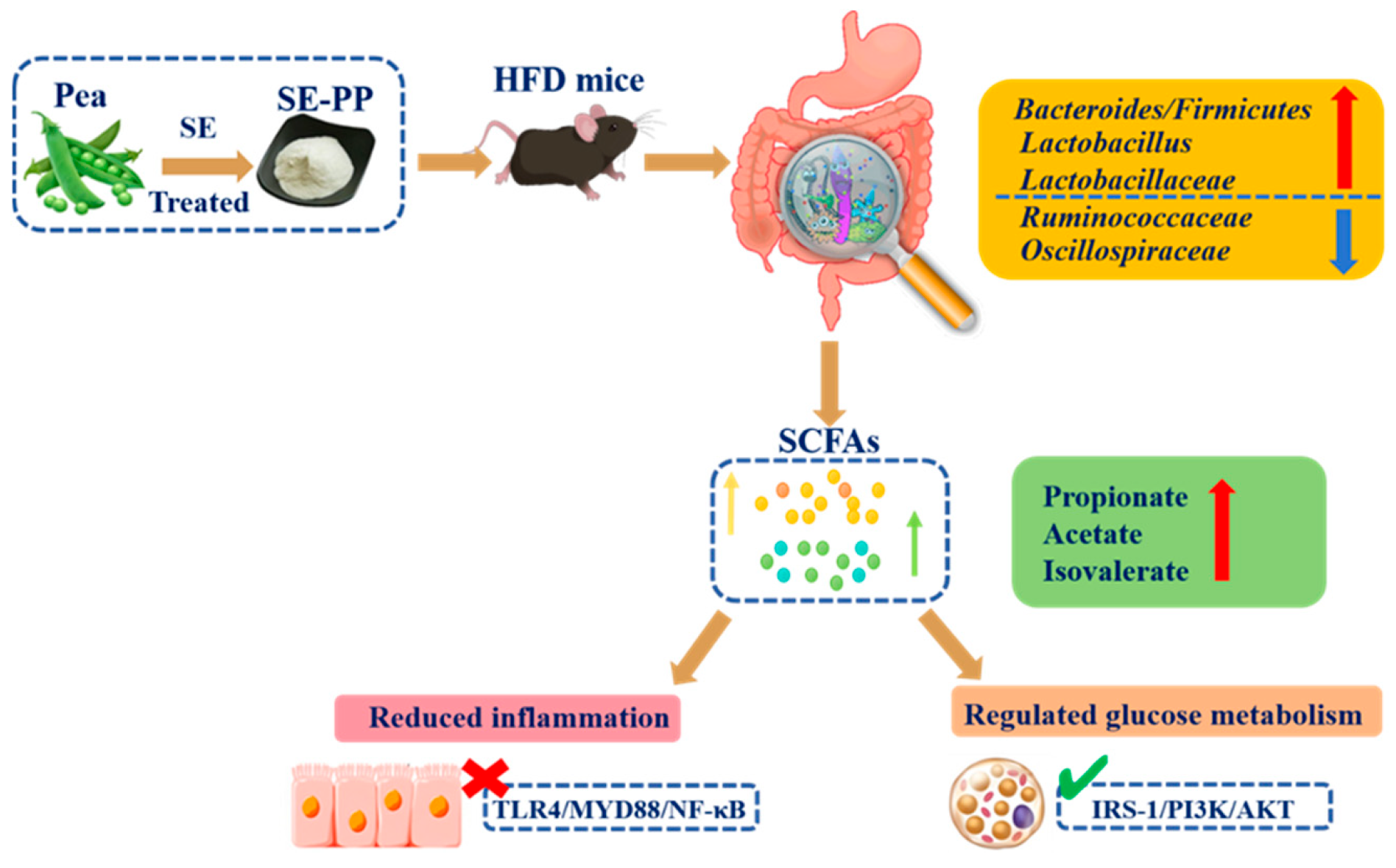
3.1. The Effect of SE-PP on Body Weight, Fat Mass Index and Blood Glucose of Mice
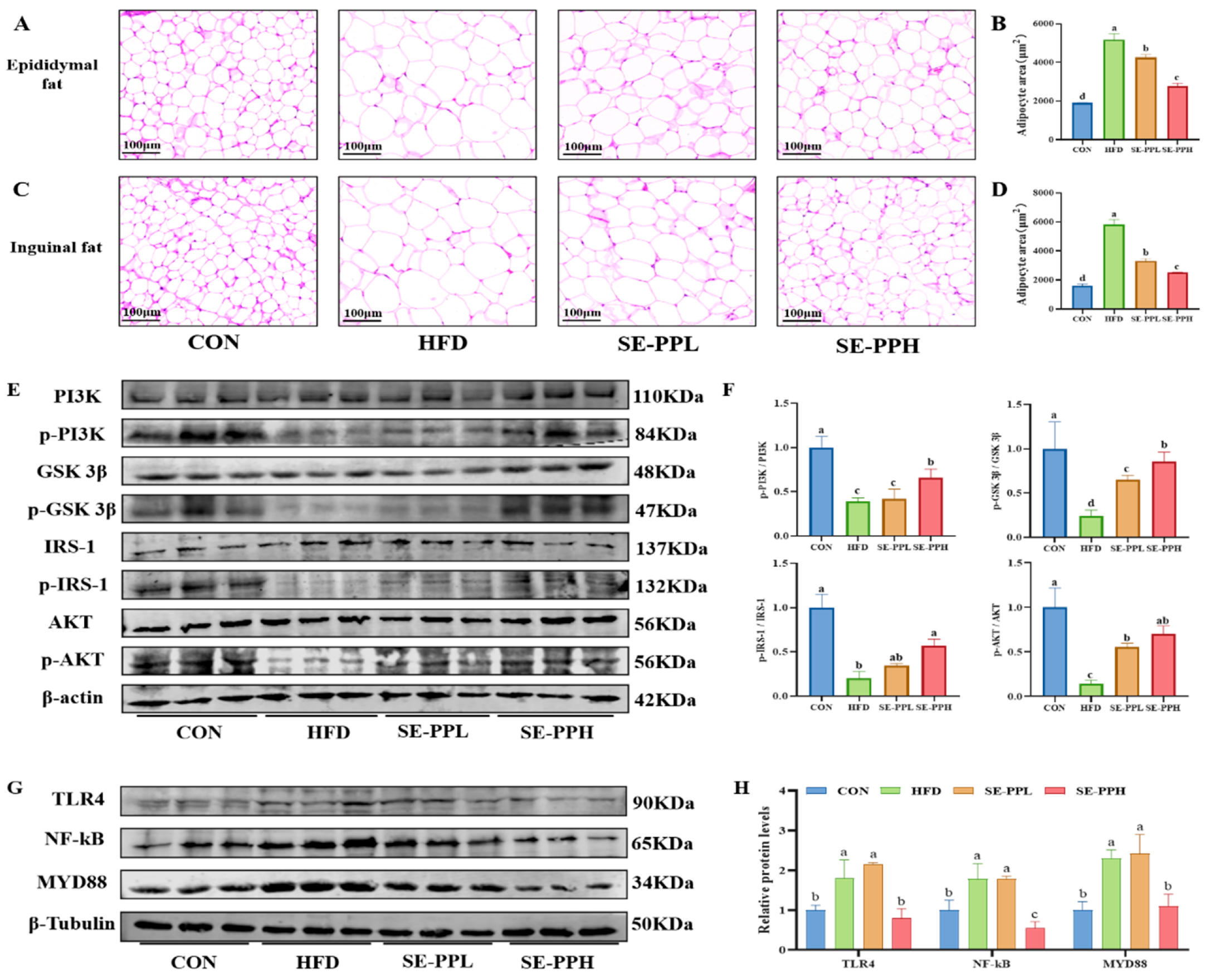
3.2. The Effect of SE-PP on Insulin Resistance and Inflammatory Response in Adipose Tissue Induced by HFD
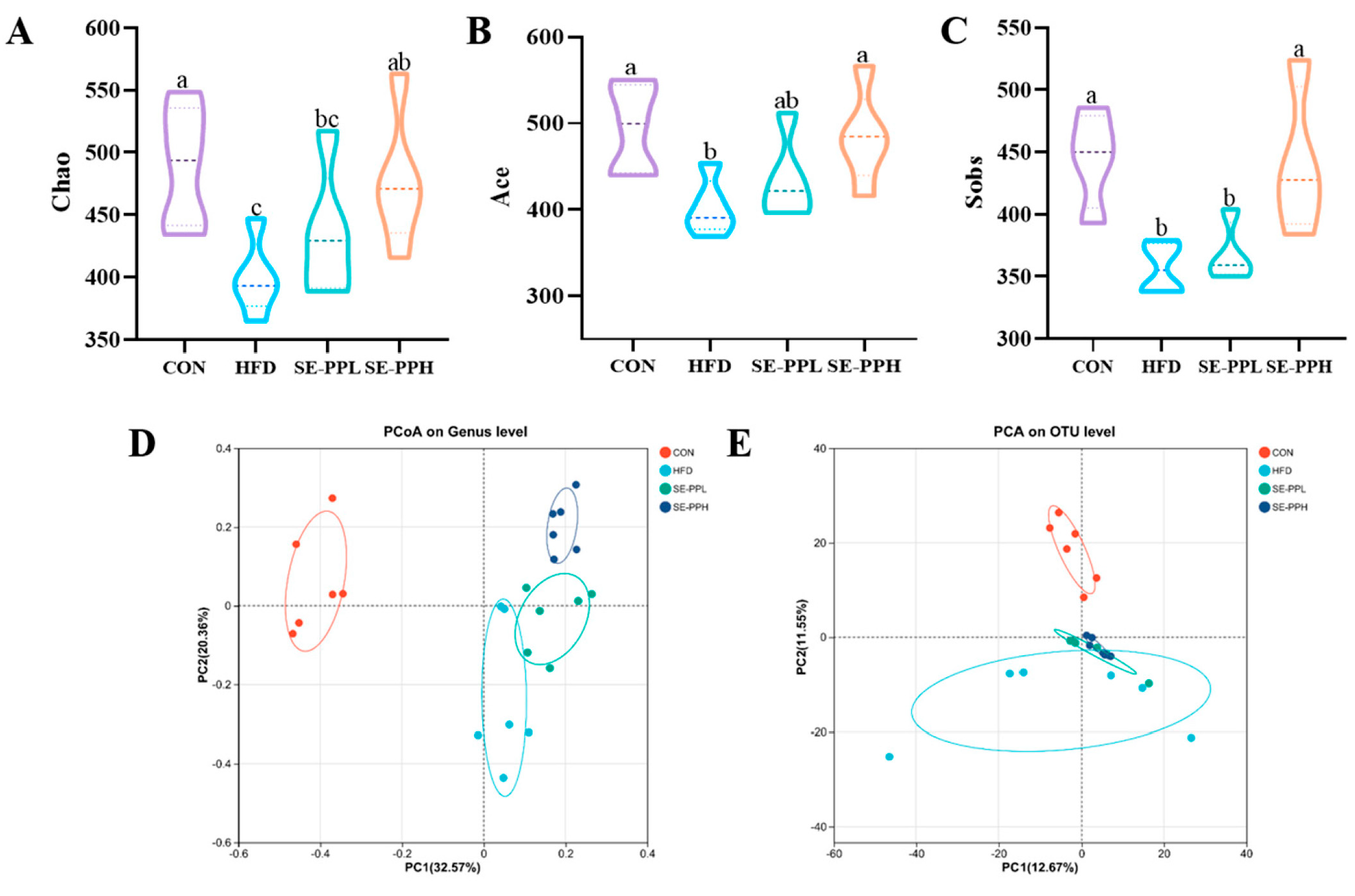
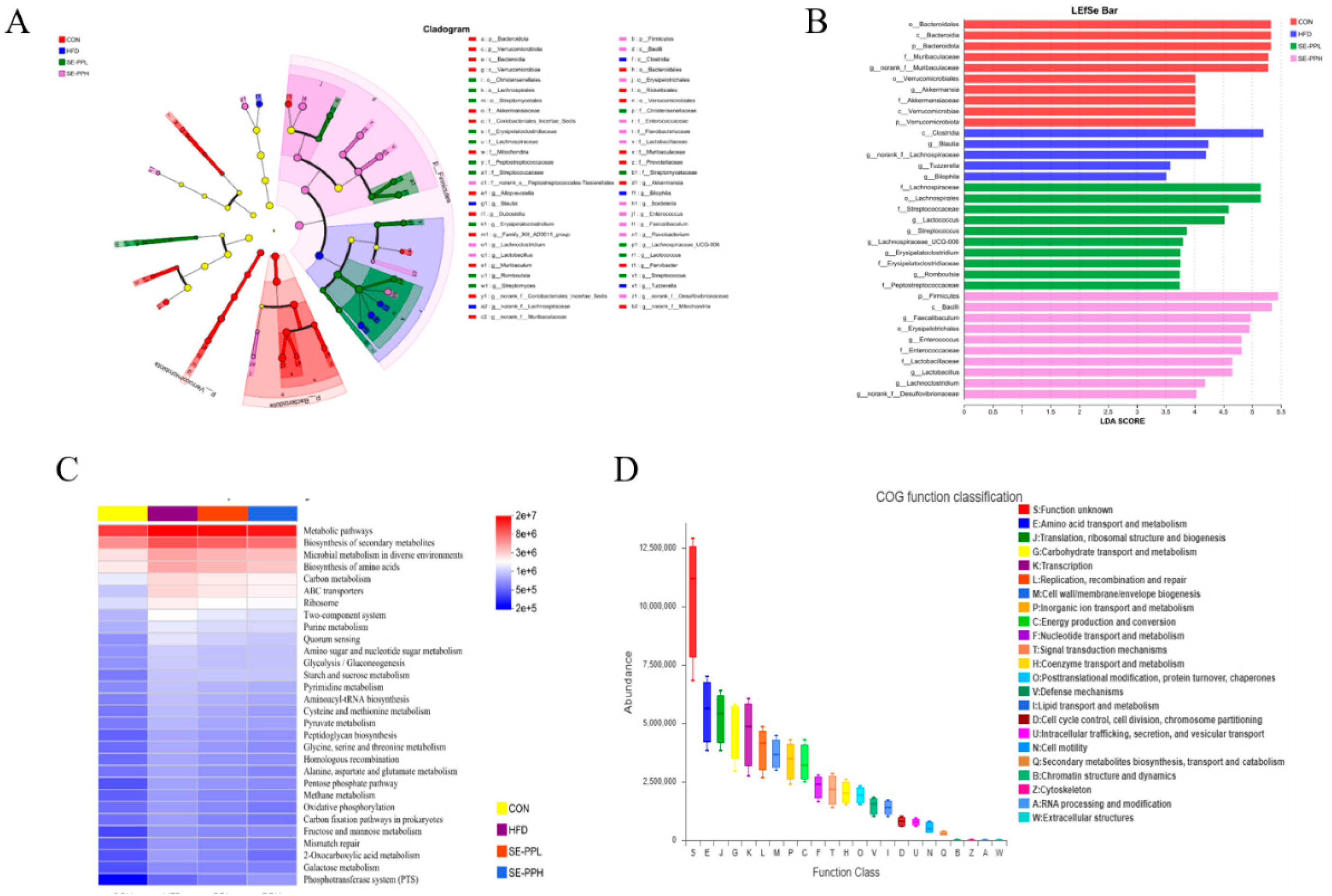
3.3. The Effect of SE-PP on Gut Dysbiosis Induced by an HFD
3.4. The Effect of SE-PP on Gut Microbial Metabolic Functions
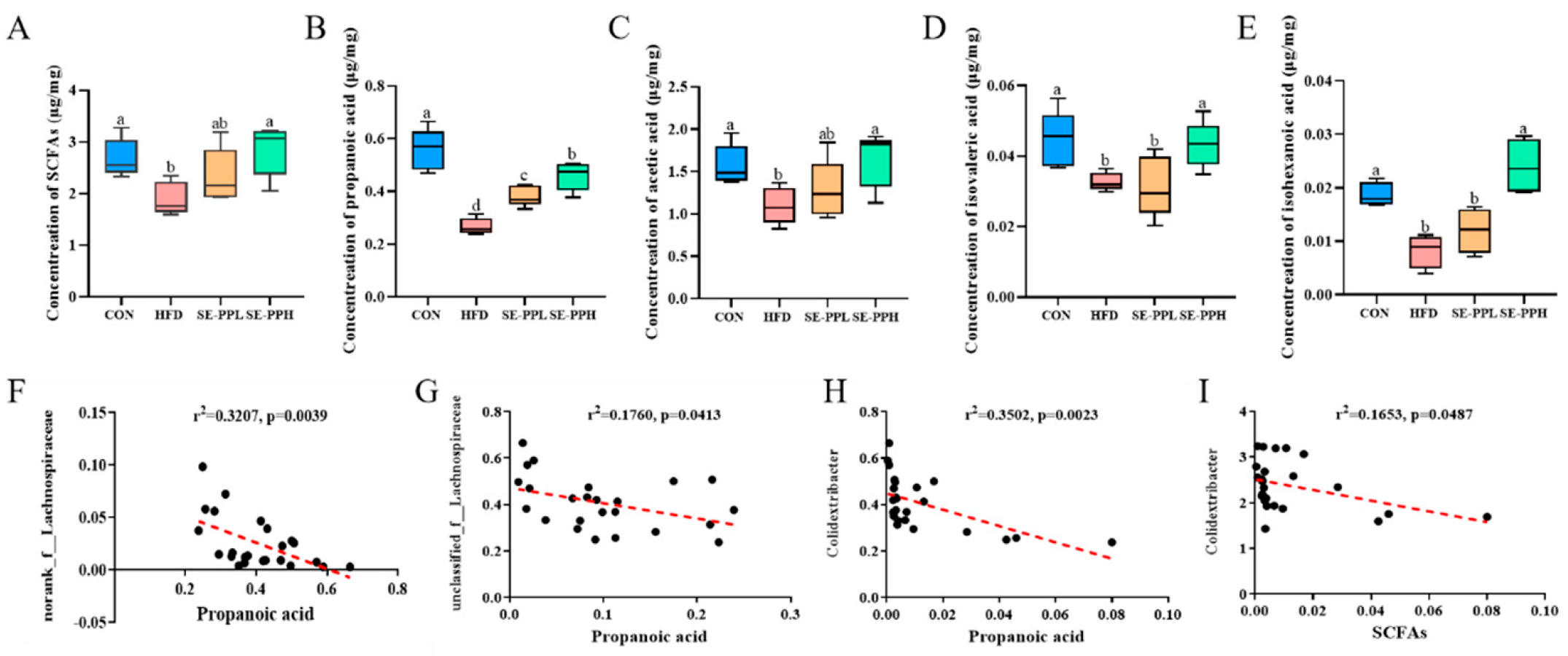
3.5. The Effect of SE-PP on SCFA Profiles in Mice Induced with the HFD
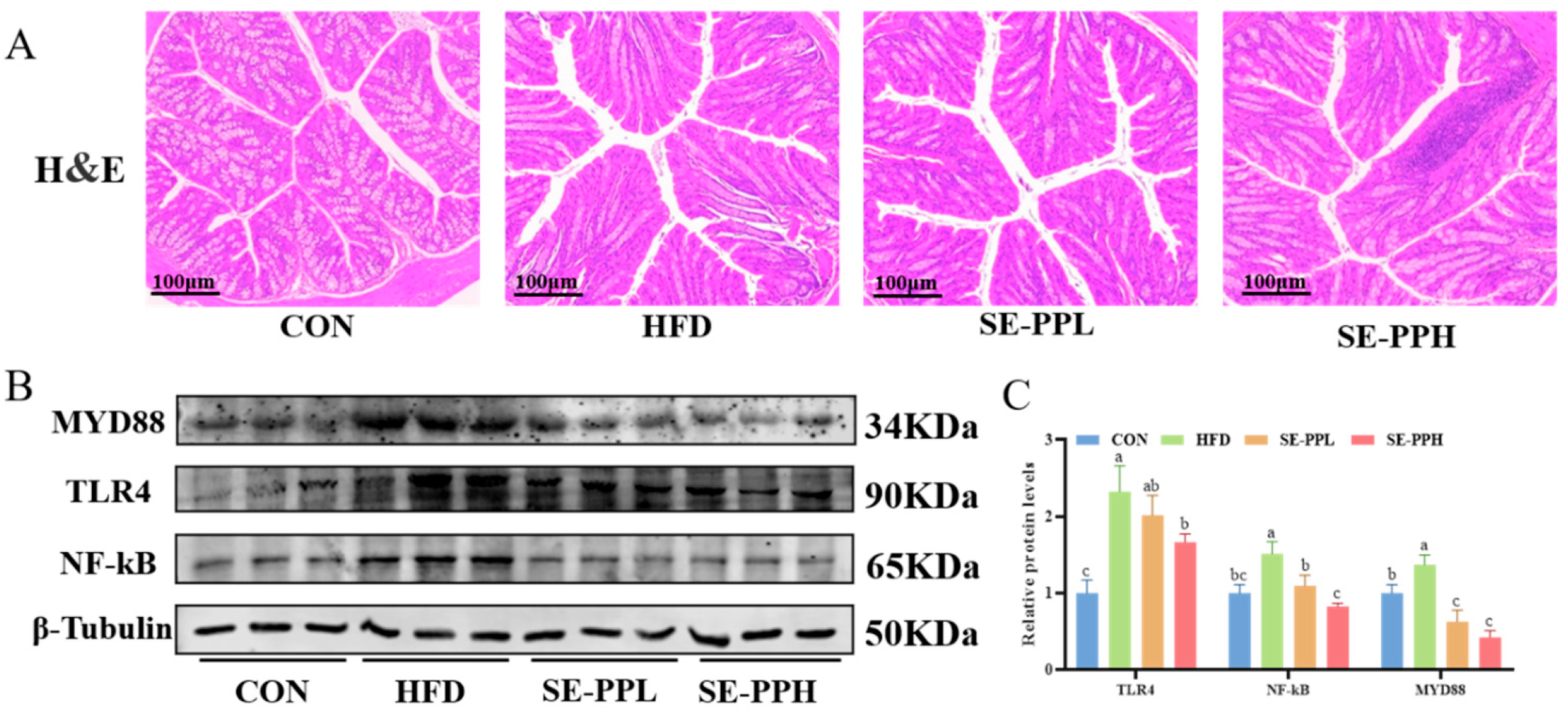
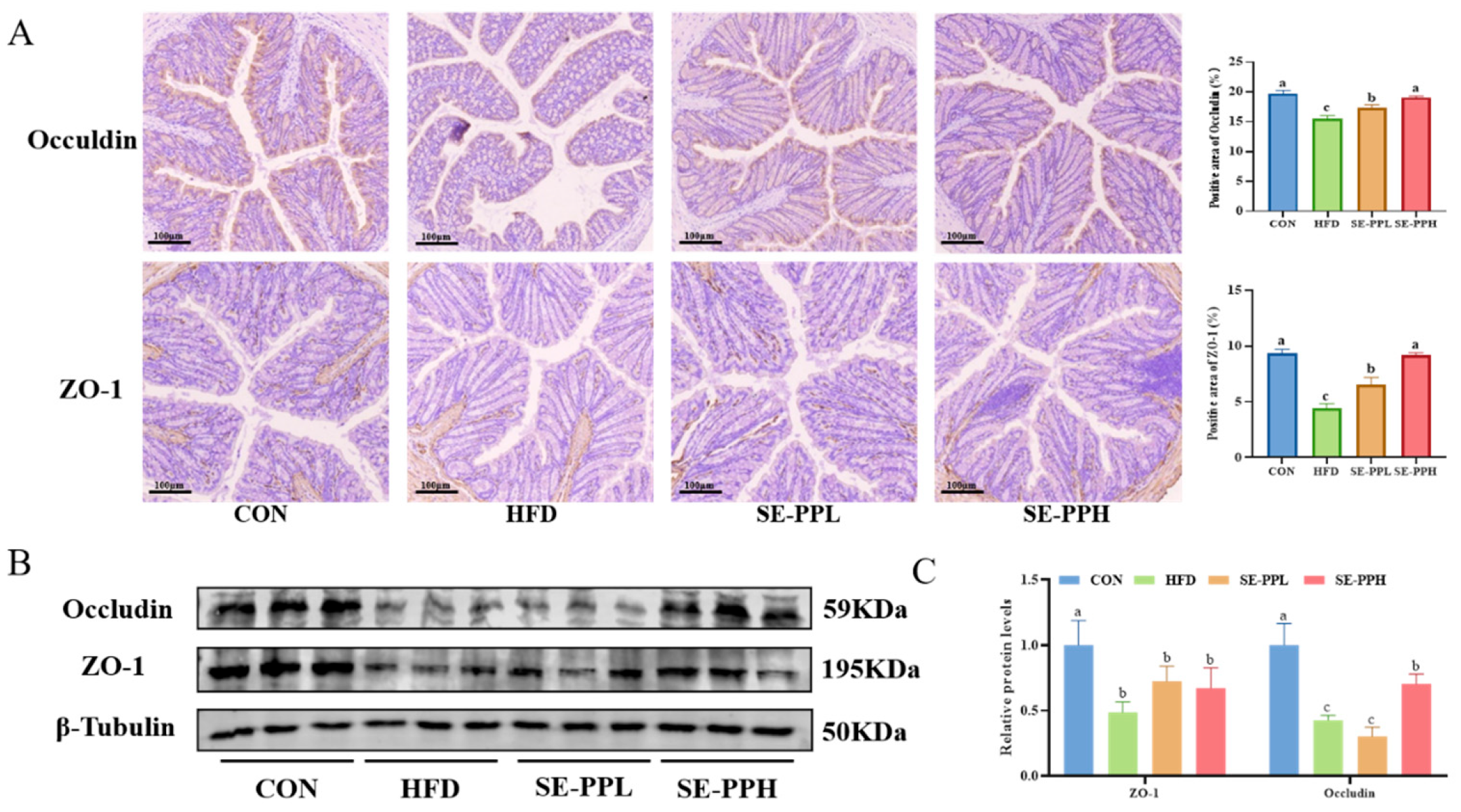
3.6. The Effect of SE-PP on Gut Inflammation in Mice Induced by an HFD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Accili, D.; Deng, Z.; Liu, Q. Insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2025, 21, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, R.F.; Liu, C.J.; Hao, K.X.; Fan, X.D.; Jiang, J.G. Polysaccharides from Flos Sophorae Immaturus ameliorates insulin resistance in IR-HepG2 cells by co-regulating signaling pathways of AMPK and IRS-1/PI3K/AKT. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280, 136088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Ma, L.; Ma, J.; Liu, S.; Fu, J.; Fan, Y.; Liu, Y. Lycium barbarum leaf flavonoids ameliorate high fructose induced insulin resistance in mice by regulating blood glucose and gut microbiota composition. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, T.; Chang, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Lang, J.; Yu, Y.; Ao, Y.; Peng, Y. Hawthorn leaf and its extract alleviate high-fat diet-induced obesity and modulate gut microbiome in mice. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2025, 10, 101025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhao, H.; Xie, J.; Yin, W.; Zheng, M.; Cai, D.; Liu, H.; Liu, J. Effects of zeaxanthin on the insulin resistance and gut microbiota of high-fat-diet-induced obese mice. Foods 2024, 13, 3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Albiñana, P.; Rodrigues-Díez, R.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, P.; Moreno, R.; Muñoz-Valverde, D.; Casani, L.; Villamiel, M.; Blanco-Rivero, J. Structure and properties of citrus pectin as influencing factors of biomarkers of metabolic syndrome in rats fed with a high-fat diet. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2025, 10, 101014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cai, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Z. Psyllium husk powder enhances the management of type 2 diabetes by modulating gut microbiota and their metabolic products. Food Res. Int. 2025, 211, 116393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.S.; Choudhury, A.M.; Gupta, A.; Maiti, P. An injectable cyclodextrin extended polyurethane/carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogel for controlled release of insulin: In-vitro and in-vivo diabetic animal model study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 356, 123396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.I.; Lee, H.M.; Park, J.H.; Lee, Y.G. Improvement of glucose metabolism by Pennogenin 3-O-β-Chacotrioside via activation of IRS/PI3K/Akt signaling and mitochondrial respiration in insulin-resistant hepatocytes. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2025, 69, e70010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Xu, W.; Yuan, T.; Shi, C.; Jin, T.; Chong, Y.; Ji, J.; Lin, L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Platycodon grandiflorus root extract activates hepatic PI3K/PIP3/Akt insulin signaling by enriching gut Akkermansia muciniphila in high fat diet fed mice. Phytomedicine 2023, 109, 154595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, R.Y.; Zhu, J.Y.; Chen, M.; Mu, W.J.; Luo, H.Y.; Li, S.; Yan, L.J.; Yin, M.T.; Li, X.; et al. Maternal exercise prevents metabolic disorders in offspring mice through SERPINA3C. Nat. Metab. 2025, 7, 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, D.; Zhao, T.; Wen, D.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, B.; Huang, X. Enterococcus hirae QT4713 alleviated DSS-induced colitis by modulating gut microbiota and tryptophan metabolism in mice. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Fan, X.; Du, H.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, R.; He, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, J.; et al. Foodborne carbon dot exposure induces insulin resistance through gut microbiota dysbiosis and damaged intestinal mucus layer. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 6081–6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Wen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ai, Z.; Zhao, X.; Dong, N.; Dou, X.; Shan, A. Thymol alleviates colitis by modulating intestinal barrier damage, gut microbiota, and amino acid metabolic pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 7211–7227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Di, L.; Shan, J. A review of saponin intervention in metabolic syndrome suggests further study on intestinal microbiota. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 160, 105088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, G.; Li, M.; Guo, X.; Wang, L.; Yao, Y.; Huang, J.A.; Liu, Z.; Lin, Y. Fu brick tea supplementation ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and associated endotoxemia via maintaining intestinal homeostasis and remodeling hepatic immune microenvironment. Food Res. Int. 2025, 209, 116207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udayappan, S.D.; Hartstra, A.V.; Dallinga-Thie, G.M.; Nieuwdorp, M. Intestinal microbiota and faecal transplantation as treatment modality for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 177, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kadyan, S.; Ukhanov, V.; Cheng, J.; Nagpal, R.; Cui, L. Recent advances in the health benefits of pea protein (Pisum sativum): Bioactive peptides and the interaction with the gut microbiome. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 48, 100944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, R.; Fang, L.; Qin, X.; Cai, M.; Gu, R.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y. Hypoglycemic effects and biochemical mechanisms of pea oligopeptide on high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e13055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wei, Y.; Cai, M.; Gu, R.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, L. Pea-derived peptides, VLP, LLP, VA, and LL, improve insulin resistance in HepG2 cells via activating IRS-1/PI3K/AKT and blocking ROS-mediated p38MAPK signaling. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.; Cao, X.; Xia, H.; Wang, S.; Chen, L.; Sun, G. Pea protein hydrolysate reduces blood glucose in high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1298046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahandideh, F.; Bourque, S.L.; Wu, J.P. A comprehensive review on the glucoregulatory properties of food-derived bioactive peptides. Food Chem. 2022, 13, 100222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakers, A.; De Siqueira, M.K.; Seale, P.; Villanueva, C.J. Adipose-tissue plasticity in health and disease. Cell 2022, 185, 419–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, T.; Tian, T.; Chen, Z.; Ye, T.; Zhu, X.; Song, G.; Wang, D.; Li, L.; Cheng, Y.; Gong, J. Extraction of polyphenols from Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat. leaves. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 231, 121221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tong, J.; Wang, T.; Ma, R.; Elmalki, M.; Li, D.; Li, C.; Xue, Z.; Fang, X.; Nie, G. Combined use of steam explosion, alkali, and microbial methods improving the yield, structure and properties of soluble dietary fiber from bamboo shoot shells. Food Chem. 2025, 471, 142754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Song, L.J.; Li, T.G.; Zhu, L.; Wang, T.L.; Zhao, P.J.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, J.S.; Huang, X.Q. Steam explosion modified pea peptides alleviates hepatosteatosis by regulating lipid metabolism pathways and promoting autophagy. Food Res. Int. 2025, 208, 116182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Zhang, J.; Kang, S.; Shen, X.; Liu, A.; Zheng, Y.; Shao, J.; Yue, X. Effects of a xylitol-casein complex on insulin resistance and gut microbiota composition in high-fat-diet+ streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus mice. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 2741–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retnakaran, R.; Ye, C.; Kramer, C.K. One-hour oral glucose tolerance test for the postpartum reclassification of women with hyperglycemia in pregnancy. Diabetes Care 2025, 48, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retnakaran, R.; Ye, C.; Kramer, C.K.; Hanley, A.J.; Connelly, P.W.; Sermer, M.; Zinman, B. Glycolipid metabolism and metagenomic analysis of the therapeutic effect of a phenolics-rich extract from noni fruit on type 2 diabetic mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 2876–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, J.; Malalgoda, M.; Storsley, J.; Malunga, L.; Netticadan, T.; Thandapilly, S.J. Health benefits of cereal grain-and pulse-derived proteins. Molecules 2022, 27, 3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Lu, H. Iron-Mediated regulation in adipose tissue: A comprehensive review of metabolism and physiological effects. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2025, 14, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Ianiro, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Adolph, T.E. Adipokines: Masterminds of metabolic inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2025, 25, 250–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Yan, T.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, J. Signaling transduction network elucidation of ACE 2 regulating Apostichopus japonicus autolysis by using integrative TMT proteomics and transcriptomics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 2197–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wu, T.; Fang, L.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Shi, J.; Li, M.; Min, W. Anti-diabetic effect by walnut (Juglans mandshurica Maxim.)-derived peptide LPLLR through inhibiting α-glucosidase and α-amylase, and alleviating insulin resistance of hepatic HepG2 cells. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 69, 103944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Yu, Z.; Du, B.; Niu, K.; Yu, X.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y. Non-starch polysaccharides from Castanea mollissima Bl. ameliorate metabolic syndrome by remodeling barrier function, microbial community, and metabolites in high-fat-diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Food Res. Int. 2025, 202, 115638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, K.; Mokkala, K. Overall dietary quality relates to gut microbiota diversity and abundance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fu, X.; Lin, D.; Li, T.; Zhang, N.; Huo, Y.; Zhu, P.; Guo, F.; Huang, F. Conjugated linoleic acid alleviates glycolipid metabolic disorders by modulating intestinal microbiota and short-chain fatty acids in obese rats. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 1685–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Jiang, X.; Ge, Y.; Xu, Q.; Li, Z.; Tang, H.; Cao, D.; Zhang, D. The effects of GABA-rich adzuki beans on glycolipid metabolism, as well as intestinal flora, in type 2 diabetic mice. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 849529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Yi, Y.; Wen, X.; Li, T.; Qin, S. Extract of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis attenuates high-fat diet-induced glycolipid metabolism disorder in rats by targeting gut microbiota and TLR4/Myd88/NF-κB pathway. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Li, N.; Lu, Z.; Li, L.; Hui, S.; Xu, H. Gut microbiota and short chain fatty acids partially mediate the beneficial effects of inulin on metabolic disorders in obese ob/ob mice. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Su, D.; Hu, X.; Yang, G.; Shan, Y. Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone ameliorates high-fat diet-induced glycolipid metabolism disorder in rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 9421–9431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanov, S.; Berlec, A.; Strukelj, B. The influence of probiotics on the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio in the treatment of obesity and inflammatory bowel disease. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, H.; Qi, X.; Cui, H.; Li, Q.; Ma, Y. α-Lactalbumin peptide Asp-Gln-Trp alleviates hepatic insulin resistance and modulates gut microbiota dysbiosis in high-fat diet-induced NAFLD mice. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 9878–9892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Wang, H.; Dai, Z.J.; Yang, X.H.; Ren, X.; Xue, Y.; Shen, Q. Cooked adzuki bean reduces high-fat diet-induced body weight gain, ameliorates inflammation, and modulates intestinal homeostasis in mice. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 918696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Feng, D.; Zuo, Y.; Hu, P. Effect and correlation of Rosa roxburghii tratt fruit vinegar on obesity, dyslipidemia and intestinal microbiota disorder in high-fat diet mice. Foods 2022, 11, 4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Baranova, A.; Cao, H.; Zhang, F. Gut microbiome links obesity to type 2 diabetes: Insights from Mendelian randomization. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant’Ana, C.T.; Verediano, T.A.; Grancieri, M.; Toledo, R.C.L.; Costa, N.M.B.; Martino, H.S.D.; de Barros, F.A.R. Macauba (Acrocomia aculeata) pulp oil has the potential to enhance the intestinal barrier morphology, goblet cell proliferation and gut microbiota composition in mice fed a high-fat diet. Br. J. Nutr. 2024, 131, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, D.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Y.; Lyu, F. Effect and mechanism of insoluble dietary fiber on postprandial blood sugar regulation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 146, 104354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dong, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dai, L.; Wang, S. Active peptide AR-9 from Eupolyphaga sinensis reduces blood lipid and hepatic lipid accumulation by restoring gut flora and its metabolites in a high fat diet–induced hyperlipidemia rat. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 918505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, B.; Zong, G.; Tao, R.; Wei, Z.; Lu, Y. Crosstalk between traditional Chinese medicine-derived polysaccharides and the gut microbiota: A new perspective to understand traditional Chinese medicine. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 4125–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Huang, X.; Zhang, C.; Shao, B.; Li, X.; Li, M. Impact of black soybean peptides on intestinal barrier function and gut microbiota in hypertensive mice. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 123, 106608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Liu, Q.; Du, Q.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Z.; Pan, D.; Tu, M. Multiple roles of food-derived bioactive peptides in the management of T2DM and commercial solutions: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 134993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashaolu, T.J.; Olatunji, O.J.; Karaca, A.C.; Lee, C.C.; Jafari, S.M. Anti-obesity and anti-diabetic bioactive peptides: A comprehensive review of their sources, properties, and techno-functional challenges. Food Res. Int. 2024, 187, 114427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tu, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, T.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Q.; Wu, R.; Wang, T. Anti-Obesity Effects of Pea Peptides Modified by Steam Explosion on Obese Mice: Regulation of Gut Microbiota and Glucose Metabolism. Foods 2025, 14, 3008. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173008
Tu J, Liu C, Zhang J, Li T, Zhu J, Wang Q, Wu R, Wang T. Anti-Obesity Effects of Pea Peptides Modified by Steam Explosion on Obese Mice: Regulation of Gut Microbiota and Glucose Metabolism. Foods. 2025; 14(17):3008. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173008
Chicago/Turabian StyleTu, Jianqiu, Chenggang Liu, Jingjing Zhang, Tiange Li, Jing Zhu, Qing Wang, Rongrong Wu, and Tianlin Wang. 2025. "Anti-Obesity Effects of Pea Peptides Modified by Steam Explosion on Obese Mice: Regulation of Gut Microbiota and Glucose Metabolism" Foods 14, no. 17: 3008. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173008
APA StyleTu, J., Liu, C., Zhang, J., Li, T., Zhu, J., Wang, Q., Wu, R., & Wang, T. (2025). Anti-Obesity Effects of Pea Peptides Modified by Steam Explosion on Obese Mice: Regulation of Gut Microbiota and Glucose Metabolism. Foods, 14(17), 3008. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173008





