Abstract
This paper analyzes the impact of the ongoing war in Ukraine on the productivity and collaboration networks of Ukrainian academics. As a case study, we analyze the publication patterns in open-access MDPI journals using bibliographic analysis methods and compare the research output published in 2022 with research papers published in the three preceding years (2019–2021) with at least one author having an Ukrainian affiliation. A total of 2365 publications were analyzed. The identified publication trends provide an interesting insight into the dynamics of the research network of Ukrainian researchers, which demonstrated a decline in diversity of international collaborations in 2022. The findings of this study emphasize the necessity of international research collaboration in a variety of fields in order to mitigate the detrimental effects of national crises and emergencies.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the world has faced several crises. The COVID-19 dilemma has had a wide-ranging impact on research. The lockdown has considerably interrupted normal communication routes, resulting in the cancellation of meetings and long-planned activities. It has also caused delays in the completion of research initiatives [1]. Complex changes in research publication patterns and collaboration networking have been reported [2]. Several recent studies have examined the influence of the COVID-19 pandemic on research output such as on biomedical publishing patterns noting a significant reduction in international collaboration [3].
The conflict and war in Ukraine, which culminated in direct Russian invasion on 24 February 2022, has impacted the global stock indices [4] and redistribution of national spending towards defence and military sectors [5], contributed towards increased inflation in multiple countries, increased unemployment and decreased purchasing power, caused refugee flows, strained economic relations due to sanctions [6], and influenced the global food supply [7], energy security [8,9], and supply of essential materials [10]. Yet the impact of these crises is disproportionally distributed across countries, leading to a growing divide between states, economic segments and population groups. The most affected actors are usually the countries and population groups with low economic scale and political status [11].
International research cooperation is essential for promoting research performance, strengthening academic networks, and disseminating local challenges and solutions throughout the world. The network of collaboration among several institutions from many nations is an important measure of internationality in research and innovation. Research productivity is critical for any university seeking to improve its global standing. Increased interdisciplinary collaboration has been demonstrated to increase scientific effect but at a higher cost of coordination. Diverse research cooperation is essential for conducting breakthrough science. International research cooperation is also important for addressing global challenges such as climate change, pandemics, and poverty. These challenges require a coordinated effort from researchers across the world to develop effective solutions. International research cooperation can also help to reduce the research divide between countries and promote the development of research capacity in low-income countries. Moreover, international research cooperation can lead to the development of new research ideas and approaches.
Collaboration between researchers from different countries and disciplines can lead to the development of innovative research ideas and approaches that would not have been possible otherwise. This can lead to breakthroughs in research and the development of new technologies and products. The network of collaboration among several institutions from many nations is an important measure of internationality in research and innovation [12]. Research productivity is critical for any university seeking to improve its standing worldwide standing [13]. Increased interdisciplinary collaboration has been demonstrated to increase scientific effect, but at a higher cost of coordination [14]. Diverse research cooperation is essential for conducting breakthrough science. Previous studies have analyzed researcher collaborations and outputs from various viewpoints, including geographical [15], university [16], and research field [17], journal [18], gender [19].
Evaluating international research collaboration is essential to various research assessment tasks [20]; however, the changes in international research collaboration due to national and regional crises have not been explored so far. Investigating cross-country effects is highly relevant and important today because only by recognizing the relevant points that underlie and shape the country’s response to such crises can countries and their relevant policymakers learn and become better prepared for crises. In this paper, we examine how the crisis in Ukraine has affected publishing trends. We investigate changes in the volume of publications in open-access journals, international (co-)authorship of these papers (as measured by diversity and volume), and the possible relationship between journal metrics and these changes. Our research is based on the results of a comparison between the statistical features of the developing networks.
The novelty of this paper lies in its analysis of the impact of a national crisis, specifically the ongoing war in Ukraine, on the productivity and collaboration networks of Ukrainian researchers in open-access journals. We employ bibliometric analysis methods to compare research output published in 2022 with the research papers published in the preceding three years (2019–2021) with at least one author having a Ukrainian affiliation. The paper also discusses the advantages and disadvantages of open-access publishing and the importance of evaluating international research collaboration. Additionally, we analyze co-authorship patterns in research publications from Ukrainian universities and colleges between 2019 and 2022, highlighting the importance of international and inter-institutional cooperation in research and the impact of crises such as the Ukraine–Russia conflict on research. This paper also covers various studies related to open-access publishing, including the impact of collaboration with large publishers on open-access journals, the cost-effectiveness of article-processing charge-funded models, and the prevalence of open-access publications in low-income countries. Overall, the novelty of this research paper lies in its comprehensive analysis of the impact of a national crisis on academic publication output, topics, and research collaboration networks in open-access journals.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows: Section 2 discusses the methods used for bibliometric analysis, Section 3 presents the results of the study, including changes in publication output, topics, and research collaboration networks, Section 4 discusses the implications of the findings, and Section 5 concludes the paper.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
For this study, we have selected OA papers published by MDPI (Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute). By 2021, MDPI was one of the biggest academic publishers in the world in terms of the quantity of papers published. The publisher’s market shares, nevertheless, exhibit an inconsistent pattern across various nations and areas. While MDPI has remained a minor player in scientific superpowers like the United States and China, it has significantly increased its market share in Europe, notably in the Central and Eastern European (CEE) nations. In 2021, scholars from CEE nations (including Ukraine) published 28% of their SCI/SSCI articles in MDPI journals; this percentage was higher than the combined percentage of papers published by the two largest academic publishers in the world, Elsevier and Springer Nature [21]. A majority of journals published by MDPI are listed in the Scopus bibliographic database, which is used for the evaluation of researchers in many countries, including Ukraine [22,23]. Previous bibliographic studies have used the bibliographic data from Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute (MDPI) journals [24,25]. Moreover, the trends in MDPI journal publishing reflect trends in other OA journals, such as the ongoing rise in the number of published papers incorporating international collaboration [24]. Another advantage of collaborative research is the large amount of OA that results from multinational partnerships [26].
2.2. Backgrounds of Scientometric Analysis
Scientometric analysis organizes and examines research output using a multitude of facets such as publication rates, research organization, document type, publication and citation trends by year, most productive countries, organizations, and authors, most frequently used author keywords; co-occurrence network, Conceptual Structure Map of Authors, Trend Topics and Topic Dendrogram, Institutions and Countries.
We have chosen to measure scientific collaboration primarily through the analysis of co-authorship in published research papers. This is a common and widely accepted method for assessing scientific collaboration [17,27,28,29] as follows.
- Total Number of Joint Publications is a straightforward measure of collaboration. A higher number of joint publications indicates a higher level of collaboration between researchers or institutions.
- Share from Publication Output refers to the proportion of a researcher’s or institution’s total publications that are co-authored with others. A higher share would suggest a greater emphasis on collaborative research.
- Number of Publications per Author is used to assess the productivity of individual researchers within a collaborative network. Researchers with a higher number of publications might be seen as key nodes in the network.
The study strategy involved scraping the bibliographic information of articles with at least one author affiliation assigned to an Ukrainian institution and published in MDPI journals using a dedicated Python script, and statistically analyzing the findings to answer the research questions.
According to prior study [30], worldwide cooperation networks are built on international co-authorships. First, the bibliographic data of articles were used to form collaborative linkages. The analysis matrices were then formed to demonstrate which nations or institutions are co-authoring articles with whom. Finally, the closeness centrality, degree centrality, betweenness centrality, and eigenvector centrality metrics were calculated to analyze any changes in the researcher cooperation network.
2.3. Network Characteristics
Network measures have been used for Coauthorship Network Analysis [31]. The degree of the network’s vertices is defined as the number of linkages to a certain author. The strength of the vertices was calculated after converting the multigraph network to a weighted graph with weights equal to the number of authorships between two authors. The entire size of any network is simply measured by the number of authors. Because they are cumulative networks, the number of authors inevitably grows. The number of components, coverage of the gigantic component, and entropy of component distribution are all indices of the network’s large-scale structure. More components imply that the network is separated into non-interactive sub-communities (at least in terms of coauthoring articles); fewer components suggest that the research community has consolidated. The diameter, density, and mean distance can all be read as measurements of the network’s ability to transport information. Lower diameter, greater density, and lower mean distance suggest that information may transfer more easily between any two researchers since there are fewer intermediary coauthors and a higher likelihood of a direct link. As a result, these data point to research community consolidation [32]. Higher density indicates that a greater proportion of the network’s authors collaborated with one another [30]. Longer diameters indicate a slower pace of information dissemination in the network. High centrality values indicate that more authors acted as gatekeepers or regulators of collaboration.
2.4. Collaboration Metrics
Were there any researchers that stood out as exceptionally effective collaborators in the network? The greatest instrument for answering this question is the author betweenness centrality statistic. Authors with high values on this metric are sandwiched between several other authors in the network and act as gatekeepers for the flow of information throughout the network. A ranking of authors based on centrality is a useful measure of the network’s significant cooperating agents.
Betweenness is the number of shortest pathways between alterations that pass through a specific author. It refers to the viewpoint that vertex relevance is related to where a vertex is positioned in relation to the pathways in the network graph. It is defined as follows:
where is the number of shortest routes between s and t that travel through v, and is the total number of shortest paths between s and t irrespective of v.
The number of steps necessary for a certain author to reach every other author in the network is referred to as closeness. It expresses the idea that a vertex is central if it is near numerous other vertices. In the context of a network , where V is the set of vertices and E is the set of edges, the closeness centrality of a vertex v is defined as:
where is the geodesic distance between vertices .
Eigenvectors are the degree to which one author is related to other authors in the network who are also well-connected. It attempts to represent the concept that the more central a vertex’s neighbors are, the more central the vertex itself is. The Eigenvector centrality metric is defined as follows [33]:
where the vector is the solution to the eigenvalue problem = , where A is the adjacency matrix for the network G.
We also calculated edge betweenness centrality, which extends the concept of vertex centrality by assigning a value to each edge based on the number of shortest routes passing that edge. We analyzed edge betweenness to determine whether co-authorship collaborations are significant for information flow. The betweenness centrality of a vertex v in a co-authorship network is defined as:
where is the total number of shortest paths from vertex s to vertex t, and is the number of those paths that pass through v.
2.5. Data Collection and Validation
The data collection process for this study involved two phases. In the first phase, a crawler was programmed in Python to identify the HTML format of MDPI journal home sites and parse them to discover all matching papers for each journal. A total of 2365 articles of bibliographic information were downloaded from MDPI journals in January 2023.
In the second phase, a data validation process was conducted after data extraction to ensure correctness. To maintain openness, the whole analytical method and the underlying information were checked manually. As a result, correct assignment of publishing data, such as nation (based on first author affiliation), authorship, journals, articles, themes, and date, was required. The processed data were utilized to obtain basic information on the associated study article after data verification. Publications were evaluated throughout time, as well as the number of writers and the share of each nation. As a result, trends in many study fields might be depicted.
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Data Analysis
The number of publications published by the Ukrainian researchers has been steadily increasing from 232 in 2019 to 963 in 2022 at an average annual growth rate of 62.7%, although the rate of growth has decreased from 97.4% in 2020/2019 to 35.2% in 2022/2021 (Figure 1). Note however, that many of the studies published in 2022 were likely to be prepared before the war started, so a longer time period would be required to evaluate the influence of war in Ukraine on the research publication productivity of the Ukrainian researchers.
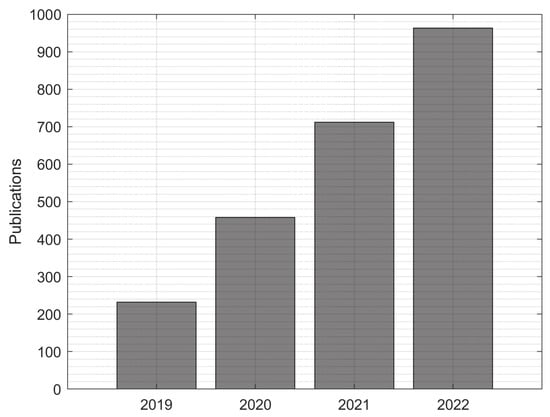
Figure 1.
Count of publications from 2019 to 2022.
Here, the annual growth rate implies the percentage of change in research output over some time. Here, the growth rate () is calculated as the rate of increase (or decrease) of publication output (P) in the year (t) as compared to the preceding year () and calculated by percent (%).
The changes in country-wise collaboration output are summarized in Figure 2. Note as the cooperation with most countries has remained on the same level, the cooperation with Poland’s researchers has been notable increasing from 103 in 2019 to 494 in 2022 with an average annual growth of 73%.
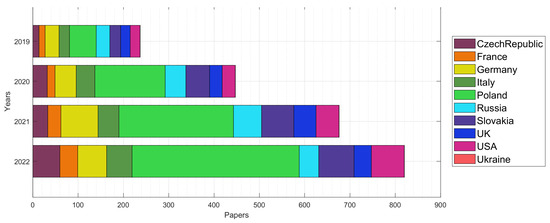
Figure 2.
Changes in country-wise output from 2019 to 2022.
A map illustrating the geographical distribution of European collaborations of authors with Ukrainian affiliations in 2019–2021, and in 2022 is presented in Figure 3. The map show a decrease of the international collaborations with researchers from other countries (except Poland) in 2022 as compared to the period of 2019–2021.
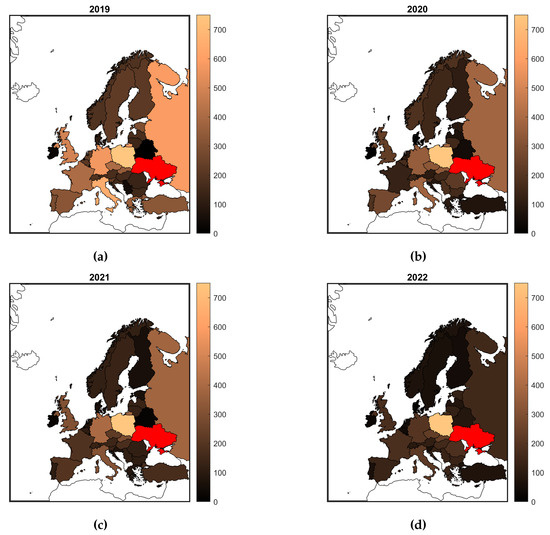
Figure 3.
International collaboration between researchers of Ukraine and other countries in Europe: (a) 2019, (b) 2020, (c) 2021, (d) 2022. Lighter color means more extensive international collaboration. The country of Ukraine is colored in red.
The alluvial flow diagram illustrating institutional research collaborations; width of connection strand between institutions is proportional to extent of cooperation between the respective countries, as presented in Figure 4. It shows both an increase in output and a decrease in diversity of international cooperation in 2022 as compared to 2019. The diversity in cooperation has decreased as a majority of cooperation concentrated on Ukrainian–Polish scientific cooperation (Figure 4).
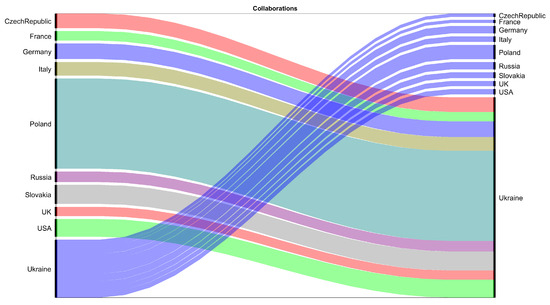
Figure 4.
Changes in collaboration from 2019 (left) to 2022 (right).
Figure 5 shows the most popular publication venues (journals). The venues remain consistent with the most popular publication venue in 2019 being Energies journal, which was surpassed by Applied Sciences and Materials in 2020. In 2021 and 2022, the top two journals remained Materials and Energies, which demonstrated consistency in the research topics of the Ukrainian researchers.
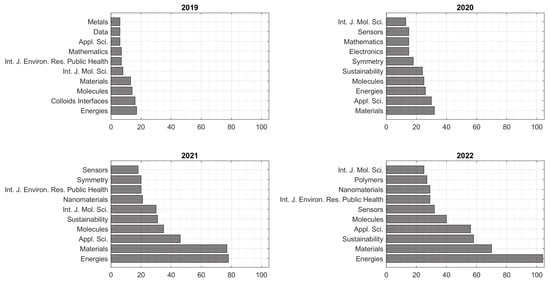
Figure 5.
MDPI journals with publications of Ukrainian researchers from 2019 to 2022.
We found that the majority of publications from Ukrainian researchers in open-access journals were in the health sciences, medical sciences, and natural sciences. This suggests that these fields have been more resilient to the impact of the national crisis than other fields. To interpret these results, it is important to understand the unique collaboration patterns within these fields:
- Health Sciences and Medical Sciences fields often involve large-scale, multi-center studies that require collaboration between researchers in different locations, institutions, and sometimes countries. The nature of health and medical research, which often involves patient populations, clinical trials, and epidemiological studies, necessitates this level of collaboration. Despite the war, Ukrainian researchers in these fields may have been able to maintain their international collaborations through these established networks. Furthermore, the global urgency of health-related research, particularly in the context of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, may have facilitated continued international collaboration and funding opportunities.
- Research in the natural sciences, which includes fields such as physics, chemistry, and biology, often involves collaboration due to the need for diverse expertise and specialized equipment. Ukrainian researchers in these fields may have existing collaborations with international partners that have continued despite the war. Additionally, the fundamental and universal nature of natural sciences research may make it more resilient to geopolitical disruptions.
International collaboration between researchers from different countries, where at least one researcher was affiliated with a Ukrainian research institution or university is presented using chord diagrams in Figure 6. Note that the most intense collaboration was among Ukrainian and Polish researchers, whereas the cooperation between Ukrainian and Russian researchers that was also prominent in 2019, became non-existant in 2022.
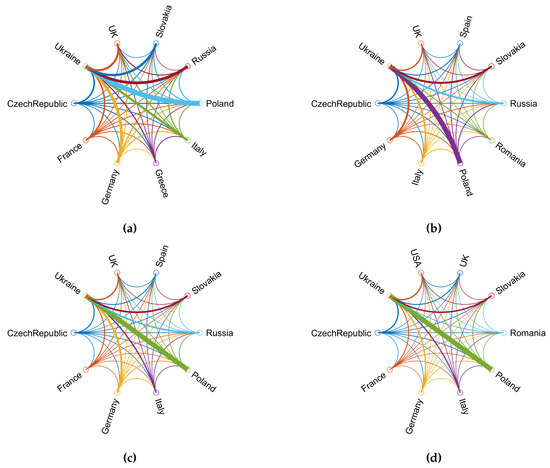
Figure 6.
International collaboration between Ukrainian researchers and researchers from other countries: (a) 2019, (b) 2020, (c) 2021, (d) 2022.
3.2. Collaboration Network Analysis
Collaboration network analysis (Figure 7) disclosed that the change in closeness and closeness frequency (Figure 7a), betweenness and frequency (Figure 7b), degree and frequency (Figure 7c), eigenvector and frequency (Figure 7d).
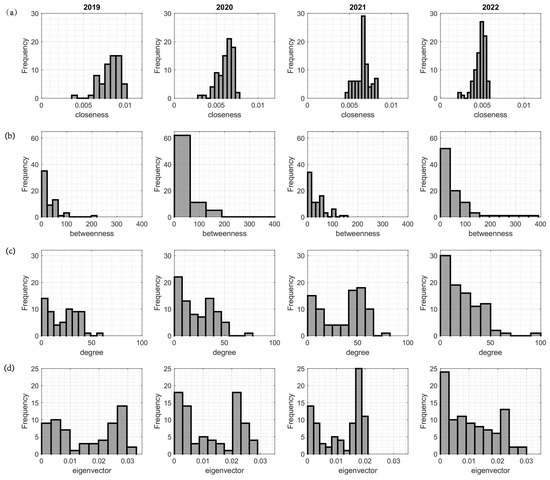
Figure 7.
Changes in distribution of research collaboration network metrics from 2019 to 2022.
- Closeness. The biggest change in closeness was in 2022. The closeness became more concentrated and covered intervals from 0.001 to 0.0056 and the frequency reached 23 points. The results of 2022 disclosed closer and permanent collaboration among Ukrainian and other countries particularly researchers. The tendency of closer collaboration among Ukraine and Poland researchers is shown in Figure 3 and Figure 6, collaboration with other countries decreased.
- Betweenness. In 2022 betweenness covered the interval from 0 to 300. The betweenness remainder was the same, but the frequency was 65 points. The frequency increased by more than 20 points in comparison with the 2019–2021 years.
- Degree. In 2022 the changes in degree are seen as well from 50 to 55 points in 2019–2021 to 75 points in 2022.
- Eigenvector. The eigenvector remained almost the same in 2019–2021. In 2022 the eigenvector increased by 0.004 points, but the frequency increased by about 7.5 points.
Table 1 presents changes in four key network metrics related to the network of publication authorship of Ukrainian researchers from 2019 to 2022: Characteristic Path Length (CPL), Global Efficiency (GE), Local Efficiency (LE), and Clustering Coefficient (CC).

Table 1.
Metrics of research collaboration networks of Ukrainian researchers from 2019 to 2022.
Characteristic Path Length (CPL) is the average shortest path length in the network, i.e., the average number of steps along the shortest paths for all possible pairs of network nodes. It is a measure of the efficiency or speed of information travel in a network. In this data, the CPL increases from 2.0370 in 2019 to 2.3619 in 2022, with a drop in 2021. This might suggest that, on average, the “distance” between researchers in terms of co-authorship is increasing, implying fewer direct collaborations or a more dispersed network. The drop in 2021 suggests a temporary increase in direct collaborations.
Global Efficiency (GE) is the inverse of the harmonic mean of the minimum path length. Higher values indicate a more integrated or efficient network. In the table, GE decreases from 0.5702 in 2019 to 0.4869 in 2022, with a peak in 2021. This indicates that the overall efficiency of the network in terms of information flow is declining, but there was a temporary increase in 2021.
Local Efficiency (LE) is a measure of the efficiency of information transfer in the immediate neighborhood of each node. An increase in local efficiency signifies more closed triads and an increase in the potential for local information transfer. The LE in the table decreases from 0.7064 in 2019 to 0.6098 in 2022, with a peak in 2020. This suggests that the local connectedness or local clustering of the network is generally decreasing.
Clustering Coefficient (CC) measures the degree to which nodes in a network tend to cluster together. It is the fraction of triangles around a node (the fraction of node’s neighbors that are neighbors of each other). In this case, the CC increases dramatically from 3.0880 in 2019 to 10.7246 in 2022. This means that, over time, the authors’ networks have become more tightly knit, with co-authors likely to be co-authors with each other.
From this data, it appears that while the Ukrainian researchers’ network is becoming more clustered with groups of authors frequently working together (increasing CC), the overall connectivity of the network is decreasing (increasing CPL, decreasing GE, and LE). This could indicate the formation of ‘research cliques’ or clusters of authors who frequently work together, leading to increased local interaction but decreased global collaboration.
Table 2 presents the distribution of published papers, the number of nations involved (vertices), and the number of collaborations (edges) among Ukrainian researchers from 2019 to 2022. The number of published papers significantly increased from 2838 in 2019 to 7840 in 2021, representing an almost threefold increase. However, there is a slight decrease in 2022 to 7082 papers. This trend might be due to a number of factors such as an increase in research funding, more active participation of researchers, or increased interest in certain research topics. The slight decrease in 2022 might suggest a negative influence of war in Ukraine on research productivity.

Table 2.
Distribution of published papers, national affiliation of authors and collaborations from 2019 to 2022.
The number of nations involved in the Ukrainian research network expanded from 62 in 2019 to 92 in 2022. This increase signifies that Ukrainian researchers have been collaborating with colleagues from an increasingly diverse range of nations. The continuous rise suggests the internationalization of Ukrainian research ecosystem.
The number of collaborations also shows an upward trend from 662 in 2019 to 1477 in 2021, more than doubling over this period. However, similar to the number of publications, there is a significant reduction in 2022 to 972 collaborations. The increase could be attributed to factors like internationalization and interdisciplinary efforts. The decrease in 2022, despite an increase in the number of participating nations, might indicate less multiple collaborations per nation due to war in Ukraine.
These trends provide an interesting insight into the dynamics of the research network in Ukraine. The steady increase in the number of nations involved highlights the growing international reach and impact of Ukrainian research. However, the decline in publications and collaborations in 2022 shows negative impacts from war in Ukraine.
Table 3 presents the changes in four centrality measures (Closeness, Betweenness, Degree, and Eigenvector) from 2019 to 2022, in the network of publication authorship of Ukrainian researchers. These measures are often used in social network analysis to determine the importance of a node in a network. In this case, the nodes would be the researchers, and the edges would represent co-authorships.

Table 3.
Changes in the average network centrality characteristics of the publication network from 2019 to 2022.
Closeness Centrality is a measure of how close a node is to all other nodes in the network. A higher closeness centrality indicates that a node is relatively close to all other nodes, thus reducing the path lengths to other nodes. From 2019 to 2022, there is a notable decrease in the closeness centrality from 0.083 to 0.048, indicating that the average researcher is becoming less closely connected to all others, perhaps due to the expansion of the research network, with more new researchers entering the field.
Betweenness Centrality represents the degree to which a node stands between other nodes in the network. Nodes with high betweenness centrality can have significant influence within a network by virtue of their control over information passing between others. In this table, we can see an increasing trend in the betweenness centrality from 28.8342 in 2019 to 53.8840 in 2022, suggesting that there is a growing number of researchers who are crucial in connecting others within the network, and maintaining the research contacts and activities.
Degree Centrality is a measure of the number of direct connections a node has. Higher degree centrality indicates more direct connections. In this case, degree centrality increased from 21.3548 in 2019 to 35.5904 in 2021, then fell back to 21.1304 in 2022. This might indicate that there was a surge in collaboration in 2021, possibly due to increased research activities or a specific event, but it dropped in 2022, possibly due to the war.
Eigenvector Centrality considers both the number and the quality of connections. It awards higher scores to nodes connected to other nodes who themselves have many connections. The eigenvector centrality decreased steadily from 0.0161 in 2019 to 0.0109 in 2022. This suggests that over these years, researchers are, on average, less connected to those researchers who themselves are well-connected.
These trends could be due to a variety of factors including changes in funding, research focus, or collaboration practices among Ukrainian researchers. The decrease in closeness and eigenvector centrality coupled with an increase in betweenness might imply that the research network is becoming less cohesive and more reliant on a smaller number of well-positioned researchers to connect different parts of the network.
4. Discussion
4.1. Critical Review
To critically review the literature and justify the results of the study, it is important to consider the broader context of how crises, such as war, can impact academic research and collaboration. The war in Ukraine has led to a significant disruption of the country’s infrastructure, including research facilities. This has been documented in various studies, such as that by Cervantes-Duarte and Fernández-Cano [34], which highlighted the destruction of research facilities and the displacement of researchers as key factors affecting research productivity. This aligns with the findings of the current study, which noted a decrease in the number of publications and a decline in research collaboration networks. The war has also led to financial constraints, which can significantly impact research output. A study by Pastor and Serrano [35] found that financial resources are a significant determinant of research output. In the context of Ukraine, the war has likely led to a reduction in funding for research, which could explain the observed decrease in publication output. The war can also lead to mobility restrictions, which can impact international research collaboration. A study by Wagner and Leydesdorff [36] found that international collaboration is crucial for scientific productivity. The current study found a decrease in international collaboration, which could be due to mobility restrictions caused by the war. The psychological impact of war on researchers should not be overlooked. A study by Charara et al. [37] found that war and conflict can lead to mental health issues, which can negatively impact productivity. This could be another factor contributing to the decrease in research output in Ukraine.
The current study found that the majority of publications from Ukrainian researchers in open-access journals were in the health sciences, medical sciences, and natural sciences. This suggests that these fields are more resilient to the impact of the national crisis than other fields. This aligns with the findings of a study by Arvanitis and Gaillard [38], which found that certain fields, particularly those related to health and natural sciences, tend to be more resilient during times of crisis. While the current study provides valuable insights into the impact of the war in Ukraine on research productivity and collaboration, it is important to consider other potential mediators, such as the psychological impact of war, financial constraints, and the resilience of certain fields. Further research is needed to fully understand the complex interplay of these factors.
4.2. Main Findings
Many Ukrainian scholars’ careers have been essentially interrupted as a result of the war. Many remain in limbo, unable to continue working either abroad or at home. Until the war ends, research in Ukraine will be hampered by a lack of finance, staff, and damage to research facilities.
The results of this study indicate that the ongoing national crisis in Ukraine due to ongoing war with Russia has had a significant negative impact on academic publication output, topics, and research collaboration networks in open-access journals. The decrease in number of publications and the decline in research collaboration networks suggest that the crisis has hampered research productivity in Ukraine. The study also found that international collaboration has decreased, with fewer publications co-authored with researchers from other countries. This is a cause for concern, as international research collaboration is essential for conducting breakthrough science and improving research performance. The decrease in international collaboration may be due to a lack of funding, mobility restrictions, and damage to research facilities caused by the conflict. Despite the challenges posed by the national crisis, Ukrainian researchers have continued to publish in open-access journals. This highlights the importance of open-access publishing in times of crisis, as it allows researchers to disseminate their research findings to a wider audience and maintain their research productivity. The findings of this study also show that the majority of publications from Ukrainian researchers in open-access journals were in the health sciences, medical sciences, and natural sciences. This suggests that these fields are more resilient to the impact of the national crisis than other fields.
4.3. Advantages of the Study
Our research has several advantages. Unlike most works on co-authorship analysis, robust network analysis approaches were employed in this work. To correctly comprehend the structure of our network, we examine the relevance of its attributes. Throughout the pre-processing and analysis processes, we ensured that the obtained data were of high quality. To the best of our knowledge, there are few previous studies [39] on the Ukrainian research partnerships network using co-authorship network analysis. A drawback of co-authorship research analysis is their intrinsic character. In a co-authorship network, collaborators may not always originate from the same scientific discipline or hold the same responsibilities on a given research project. The information we gathered did not allow us to correctly analyze or even guess the disciplines from which each contributor came or their individual contribution to the published paper.
4.4. Study Limitations
This study bears certain drawbacks. First, our study is confined to open-access peer-reviewed academic publications, written by researchers at Ukrainian universities and colleges, and includes all publications with at least one author linked with Ukrainian universities or college libraries throughout the time period under consideration. This means that the study may not provide a complete picture of the impact of the national crisis on academic research in Ukraine. Other types of publications and research institutions should be included in future studies to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the impact of the crisis on academic research in Ukraine.
Second, the study relies on data obtained from the MDPI website (https://www.mdpi.com, accessed on 25 February 2023). While MDPI is a reputable publisher of open-access journals, it is possible that some publications may have been missed or excluded from the analysis. Therefore, the findings of this study may not be entirely representative of the entire population of open-access publications from Ukrainian researchers.
Third, the study spans only four years, from 2019 to 2022. While this time period is sufficient to capture the impact of the ongoing national crisis in Ukraine, it may not be enough to capture the long-term effects of the crisis on academic research in Ukraine.
Finally, the impact of the national crisis on the quality of research publications was not investigated. While this study provides insights into changes in publication output, topics, and research collaboration networks, it does not investigate the impact of the crisis on the quality of research publications.
Future studies should investigate the citation impact of publications from Ukrainian researchers before and after the crisis to provide a more complete picture of the impact of the crisis on academic research in Ukraine.
5. Conclusions
This study aimed to investigate the impact of the ongoing national crisis in Ukraine on academic publication output, topics, and research collaboration networks in open-access journals. The results indicate that the war had a significant negative impact on research productivity in Ukraine, with a decrease in the number of publications and a decline in research collaboration networks. Our findings also show that international collaboration has decreased, with fewer publications co-authored with researchers from other countries. However, our results revealed that Ukrainian researchers have continued to publish in open-access journals, indicating the importance of open-access publishing in times of crisis. The limitations of this study include its focus on open-access peer-reviewed academic publications written by researchers at Ukrainian universities and colleges and the reliance on data obtained from the MDPI website.
Future research could expand the scope of this study to include other types of publications and research institutions. This would provide a more comprehensive understanding of the impact of the national crisis on academic research in Ukraine. First, future research could investigate the impact of the national crisis on the quality of research publications. This could include an analysis of the citation impact of publications from Ukrainian researchers before and after the crisis. Second, future research could explore the impact of the national crisis on the career trajectories of Ukrainian researchers. This could include an analysis of the impact of the crisis on the mobility of researchers, their ability to secure funding, and their career progression.
Finally, future research could investigate the role of open-access publishing in promoting international research collaboration and supporting research in times of crisis. This could include an analysis of the cost-effectiveness of article-processing charge-funded models and the prevalence of open-access publications in low-income countries. Overall, future research in this area could provide valuable insights into the impact of national crises on academic research and the role of open-access publishing in supporting research in times of crisis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.D.; methodology, R.D. and L.Z.-J.; software, R.D.; validation, R.D. and L.Z.-J.; formal analysis, R.D. and L.Z.-J.; investigation, R.D. and L.Z.-J.; resources, R.D. and L.Z.-J.; writing—original draft preparation, R.D. and L.Z.-J.; writing—review and editing, R.D. and L.Z.-J.; visualization, R.D.; supervision, R.D.; funding acquisition, R.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
All data used in this study were obtained from the MDPI website (https://www.mdpi.com) (accessed on 25 February 2023).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Leal Filho, W.; Azul, A.M.; Wall, T.; Vasconcelos, C.R.P.; Salvia, A.L.; do Paço, A.; Shulla, K.; Levesque, V.; Doni, F.; Alvarez-Castañón, L.; et al. COVID-19: The impact of a global crisis on sustainable development research. Sustain. Sci. 2021, 16, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damaševičius, R.; Zailskaitė-Jakštė, L. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on researcher collaboration in business and economics areas on national level: A scientometric analysis. J. Doc. 2022, 79, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviv-Reuven, S.; Rosenfeld, A. Publication patterns’ changes due to the COVID-19 pandemic: A longitudinal and short-term scientometric analysis. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 6761–6784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boungou, W.; Yatié, A. The impact of the Ukraine–Russia war on world stock market returns. Econ. Lett. 2022, 215, 110516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubaker, S.; Goodell, J.W.; Pandey, D.K.; Kumari, V. Heterogeneous impacts of wars on global equity markets: Evidence from the invasion of Ukraine. Financ. Res. Lett. 2022, 48, 102934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.M.; Chin, M.W.C.; Ee, Y.S.; Fung, C.Y.; Giang, C.S.; Heng, K.S.; Kong, M.L.F.; Lim, A.S.S.; Lim, B.C.Y.; Lim, R.T.H.; et al. What is at stake in a war? A prospective evaluation of the Ukraine and Russia conflict for business and society. Glob. Bus. Organ. Excell. 2022, 41, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Li, X.; Jia, N.; Feng, F.; Huang, H.; Huang, J.; Fan, S.; Ciais, P.; Song, X. The impact of Russia-Ukraine conflict on global food security. Glob. Food Secur. 2023, 36, 100661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnassi, M.; El Haiba, M. Implications of the Russia–Ukraine war for global food security. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2022, 6, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lu, G.; Xu, Z.; Yan, X.; Khu, S.; Yang, J.; Zhao, J. Influence of Russia-Ukraine War on the Global Energy and Food Security. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 188, 106657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, U.; Mohammed, K.S.; Tiwari, S.; Nakonieczny, J.; Nesterowicz, R. Connectedness between geopolitical risk, financial instability indices and precious metals markets: Novel findings from Russia Ukraine conflict perspective. Resour. Policy 2023, 80, 103190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Lu, X. Investor attention on the Russia-Ukraine conflict and stock market volatility: Evidence from China. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 52, 103526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, J.K. Visualizing the knowledge outburst in global research on COVID-19. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 4173–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqahtani, M.S.; Abbas, M.; Muqeet, M.A.; Almohiy, H.M. Research Productivity in Terms of Output, Impact, and Collaboration for University Researchers in Saudi Arabia: SciVal Analytics and t-Tests Statistical Based Approach. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, E.; Smyth, B.; Greene, D. Collaboration in the time of COVID: A scientometric analysis of multidisciplinary SARS-CoV-2 research. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2021, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, E.S. International research collaboration in Africa: A bibliometric and thematic analysis. Scientometrics 2022, 127, 2747–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ding, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S. Exploring the Role of International Research Collaboration in Building China’s World-Class Universities. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y. Co-authorship in energy justice studies: Assessing research collaboration through social network analysis and topic modeling. Energy Strategy Rev. 2022, 41, 100859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.L. Topics, author profiles, and collaboration networks in the Journal of Research on Technology in Education: A bibliometric analysis of 20 years of research. J. Res. Technol. Educ. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Cheng, Y.; Ju, X.; Xie, J. Rethinking the effect of inter-gender collaboration on research performance for scholars. J. Inf. 2022, 16, 101352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.X.; Luczak-Roesch, M.; Dinneen, J.D.; Larivière, V. Assessing the quality of bibliographic data sources for measuring international research collaboration. Quant. Sci. Stud. 2022, 3, 529–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csomós, G.; Farkas, J.Z. Understanding the increasing market share of the academic publisher “Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute” in the publication output of Central and Eastern European countries: A case study of Hungary. Scientometrics 2022, 128, 803–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hladchenko, M. Implications of Publication Requirements for the Research Output of Ukrainian Academics in Scopus in 1999–2019. J. Data Inf. Sci. 2022, 7, 71–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarovets, S. Analysis of publications by authors of Ukrainian institutes in Scopus-delisted titles. Learn. Publ. 2022, 35, 499–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cary, M.; Rockwell, T. International collaboration in open access publications: How income shapes international collaboration. Publications 2020, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelwall, M. Journal and disciplinary variations in academic open peer review anonymity, outcomes, and length. J. Librariansh. Inf. Sci. 2023, 55, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyandemye, J.; Thomas, M.P. Low income countries have the highest percentages of open access publication: A systematic computational analysis of the biomedical literature. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Alcaide, G.; Park, J.; Huamanã, C.; BelinchÃn, I.; Ramos, J.M. Evolution of cooperation patterns in psoriasis research: Co-authorship network analysis of papers in medline (1942–2013). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrović, I.; Mišić, M.; Protić, J. Exploring high scientific productivity in international co-authorship of a small developing country based on collaboration patterns. J. Big Data 2023, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedru, H.D.; Zhang, C.; Xie, F.; Yu, S.; Hussain, I. CLARA: Citation and similarity-based author ranking. Scientometrics 2023, 128, 1091–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, H. Digital data-based strategies: A novel form of better understanding COVID-19 pandemic and international scientific collaboration. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, E.; Ding, Y. Applying centrality measures to impact analysis: A coauthorship network analysis. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 2107–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, D.J.; Coil, D.A.; Stahmer, C.G.; Eisen, J.A. Network analysis to evaluate the impact of research funding on research community consolidation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landherr, A.; Friedl, B.; Heidemann, J. A Critical Review of Centrality Measures in Social Networks. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2010, 2, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Duarte, L.; Fernández-Cano, A. Impact of Armed Conflicts on Education and Educational Agents: A Multivocal Review. Rev. ElectróNica Educ. 2016, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, J.M.; Serrano, L. The determinants of the research output of universities: Specialization, quality and inefficiencies. Scientometrics 2016, 109, 1255–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.; Leydesdorff, L. Network Structure, Self-Organization, and the Growth of International Collaboration in Science. Res. Policy 2005, 34, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charara, R.; Forouzanfar, M.; Naghavi, M.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; Afshin, A.; Vos, T.; Daoud, F.; Wang, H.; El Bcheraoui, C.; Khalil, I.; et al. The Burden of Mental Disorders in the Eastern Mediterranean Region, 1990–2015: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease 2015 Study. Int. J. Public Health 2017, 63, 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Arvanitis, R.; Gaillard, J. Science Indicators for Developing Countries; ORSTOM: Paris, France, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Matveeva, N.; Batagelj, V.; Ferligoj, A. Scientific collaboration of post-Soviet countries: The effects of different network normalizations. Scientometrics 2023, 128, 4219–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).