Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Selective Recognition of 17β-Estradiol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of MMIPs
2.3. Characterization of MMIPs
2.4. HPLC Analysis
2.5. Adsorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of MMIPs Preparation Conditions
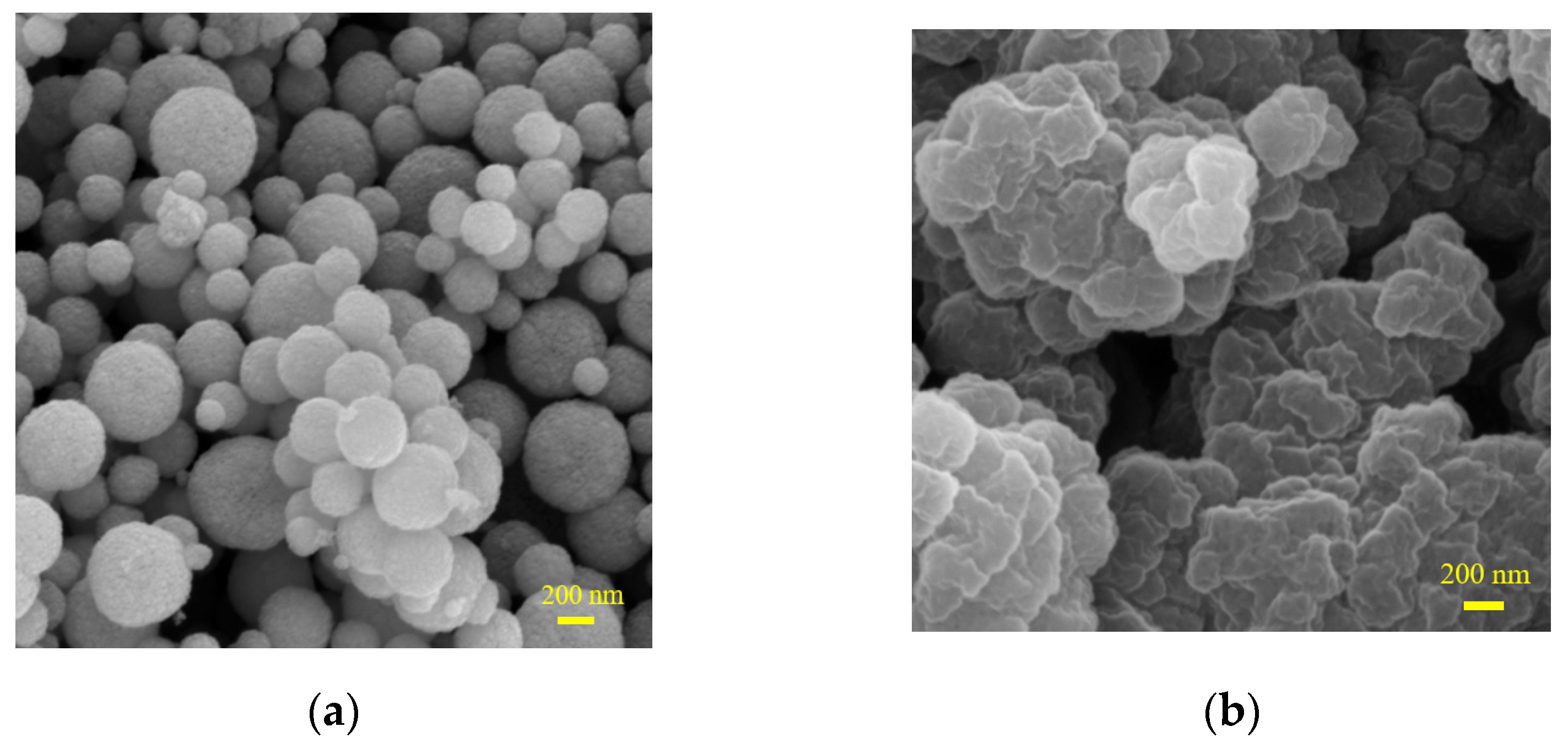
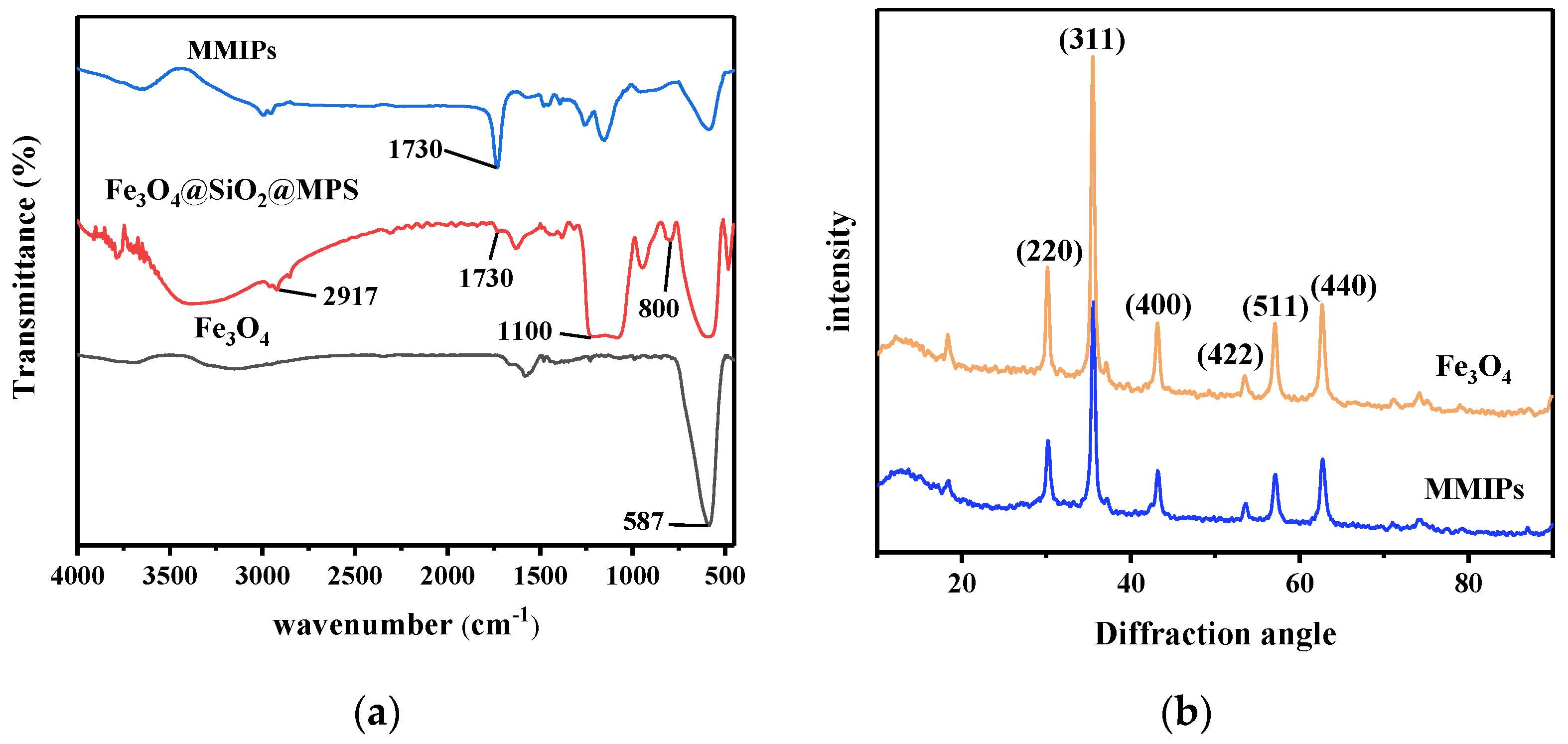
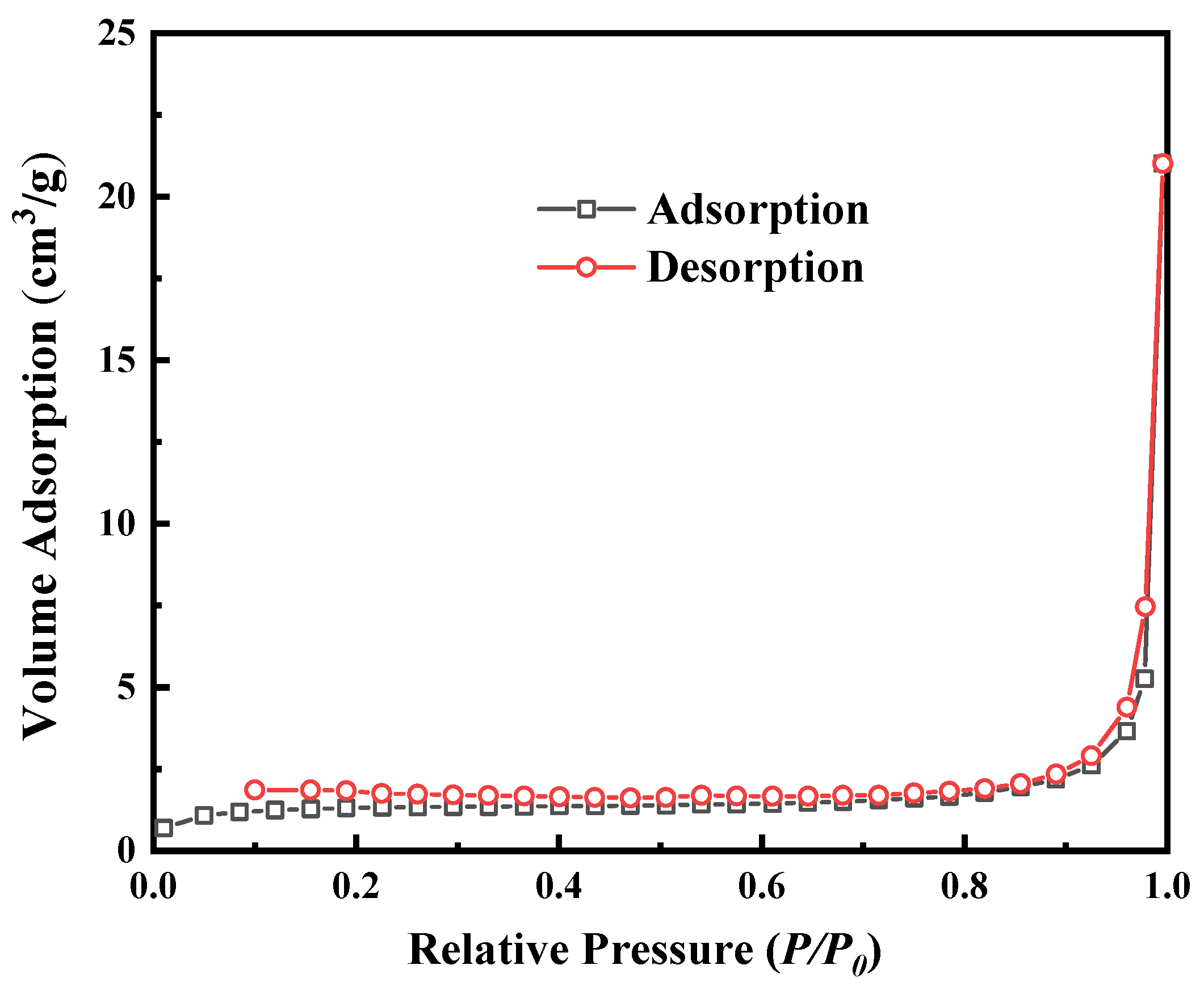
3.2. Characterization of MMIPs
3.3. Adsorption Performance
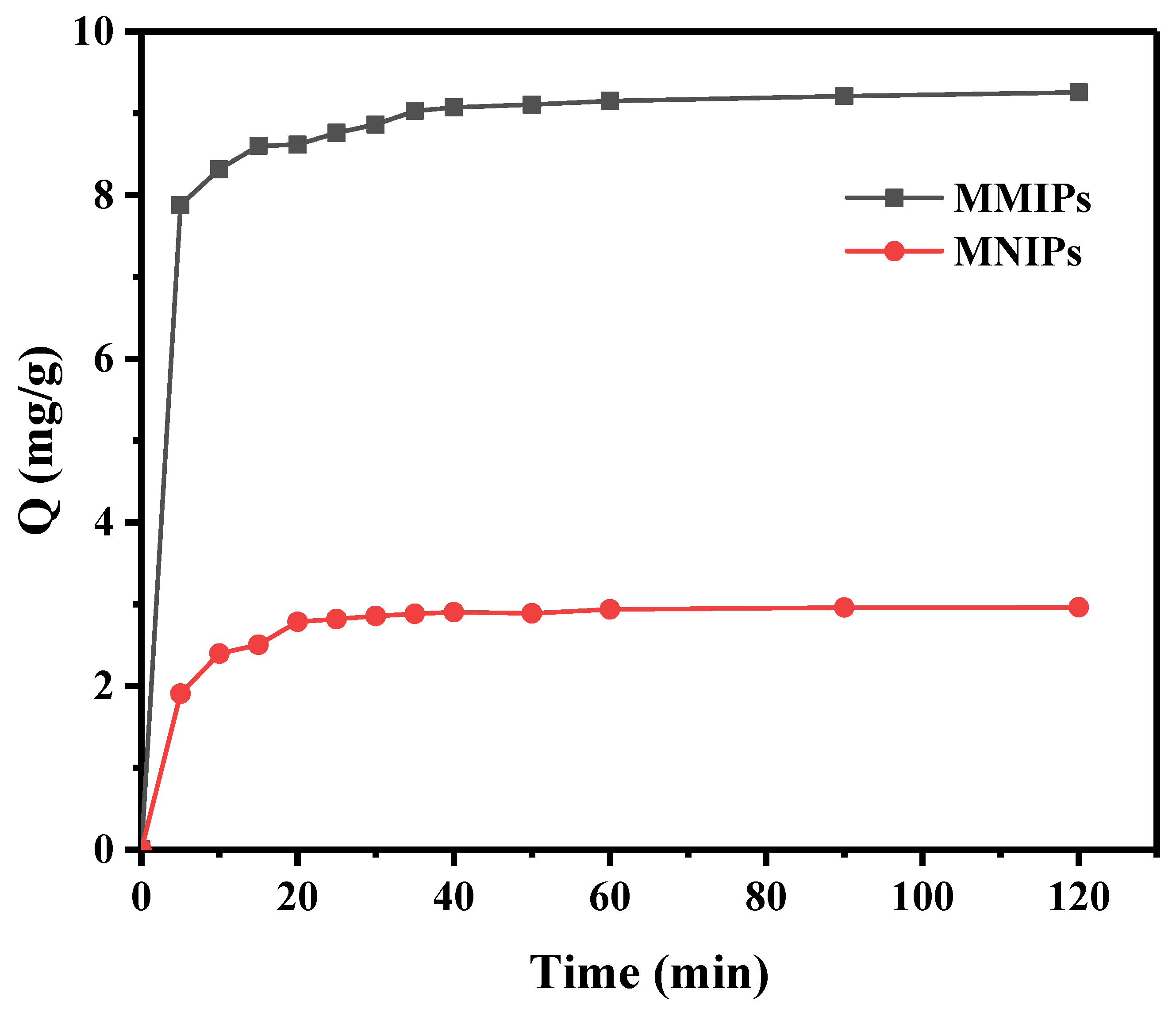
3.3.1. Adsorption Kinetics
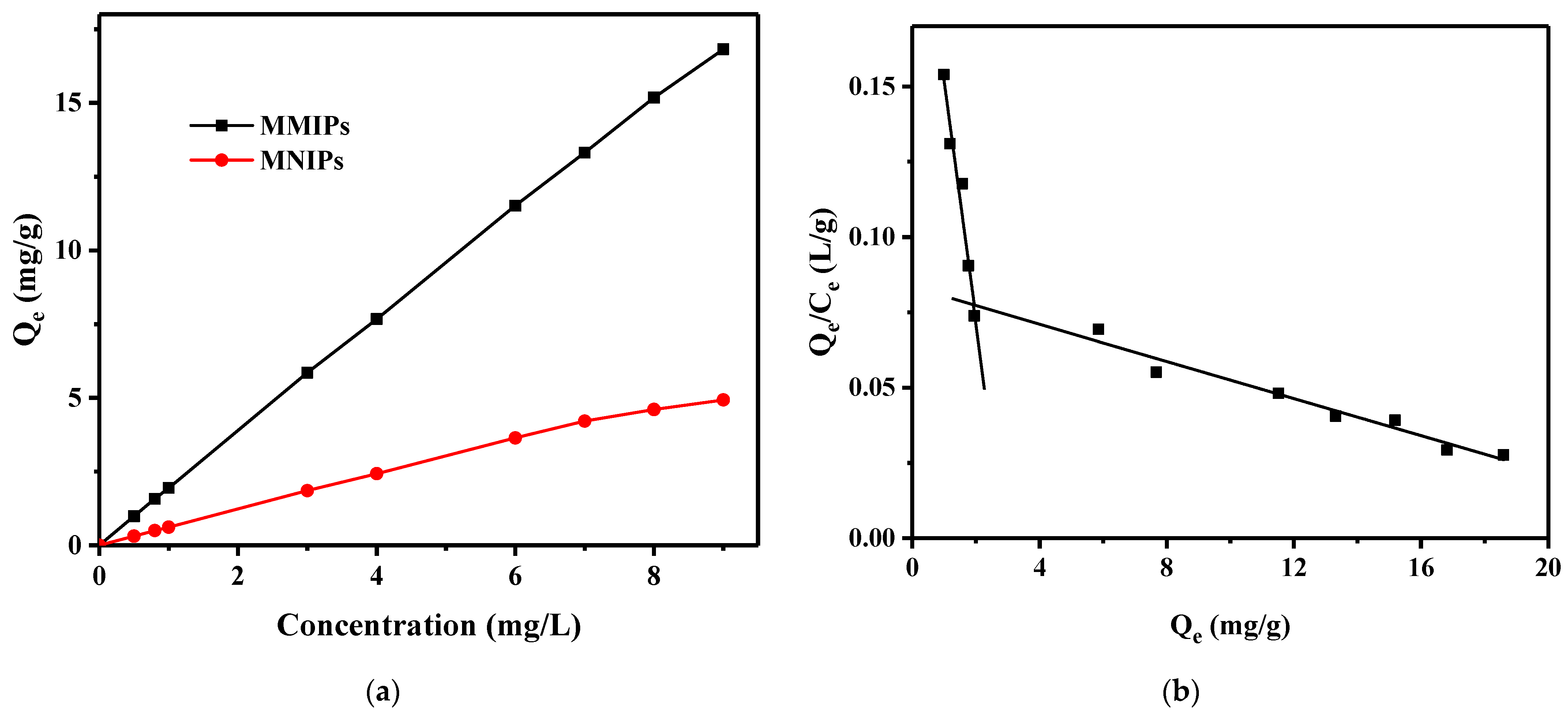
3.3.2. Adsorption Isotherms
3.3.3. Adsorption Selectivity
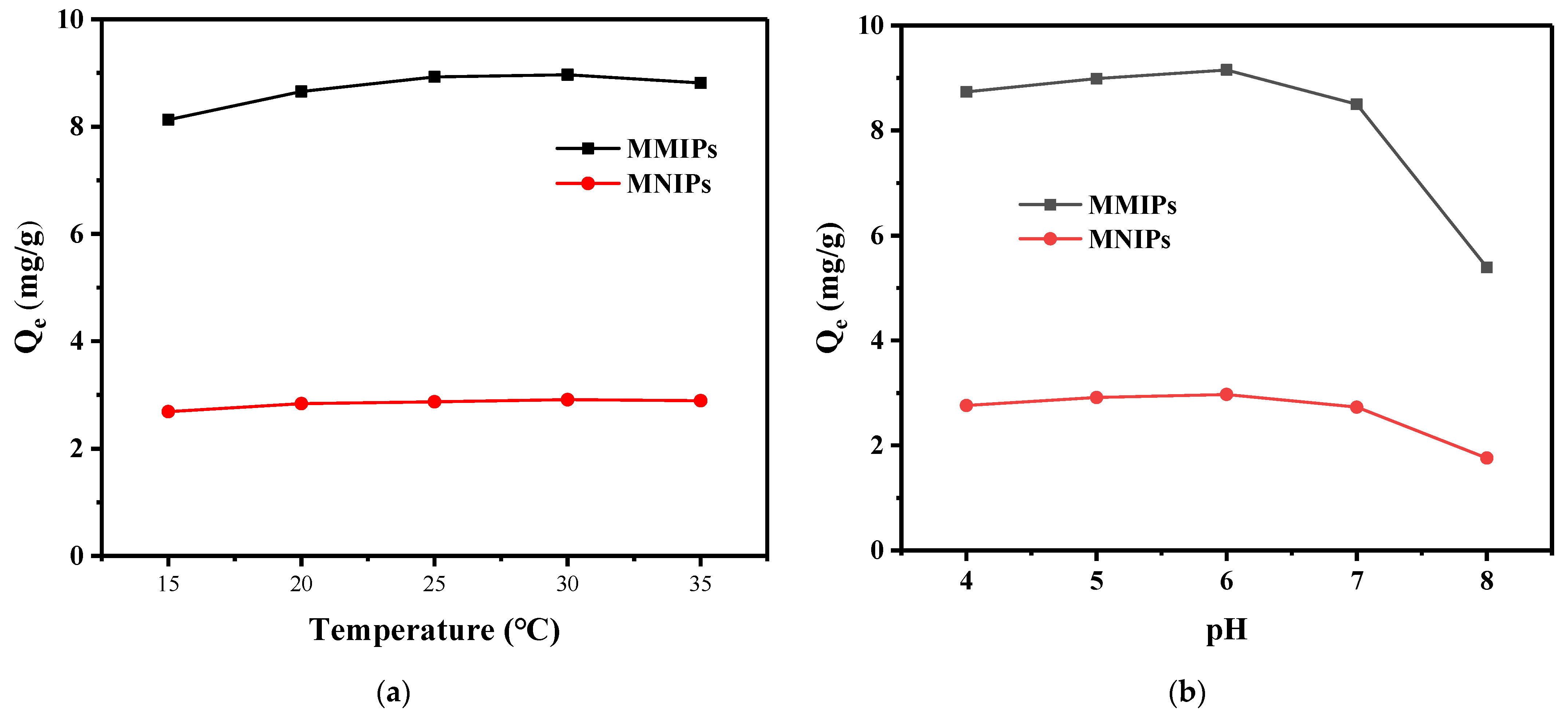
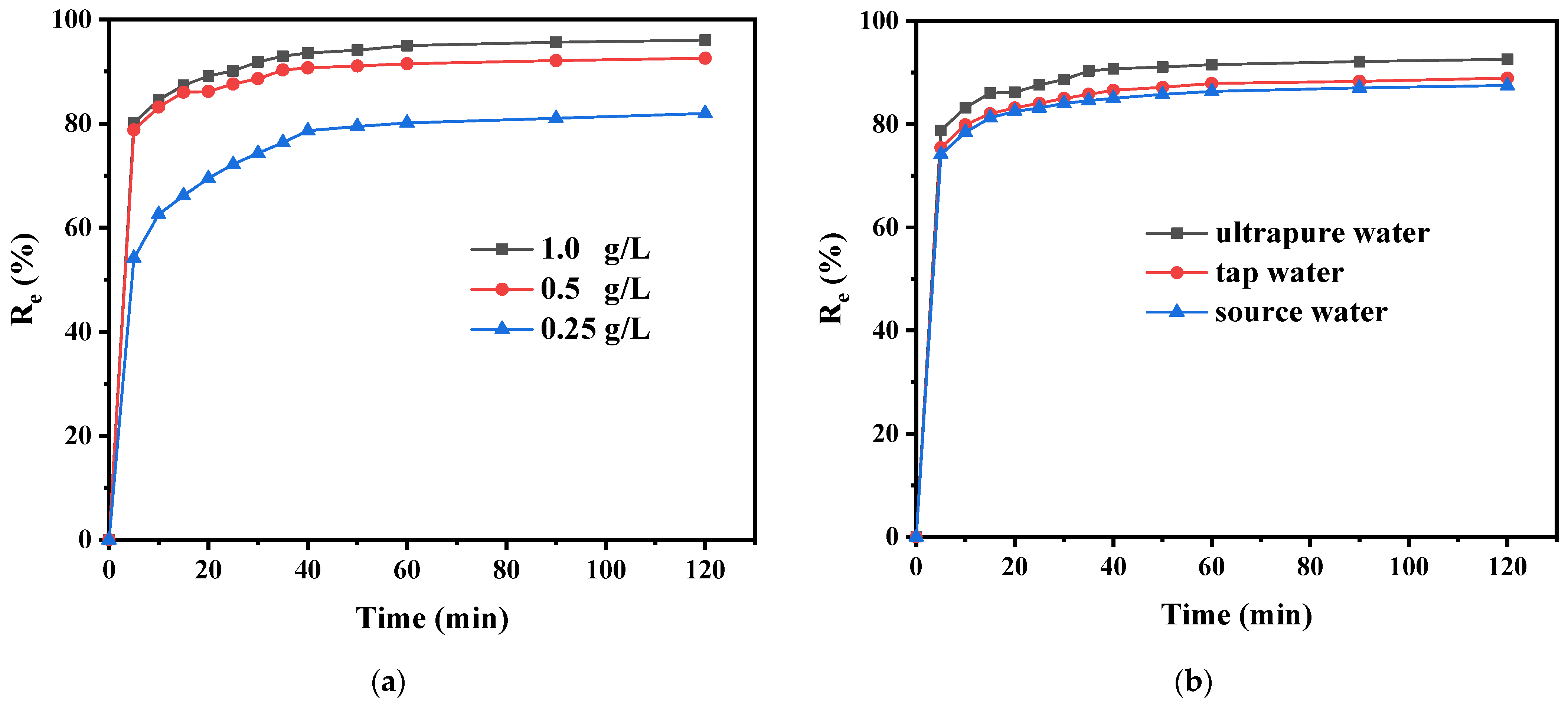
3.4. Effects of Parameters on Adsorption Performance
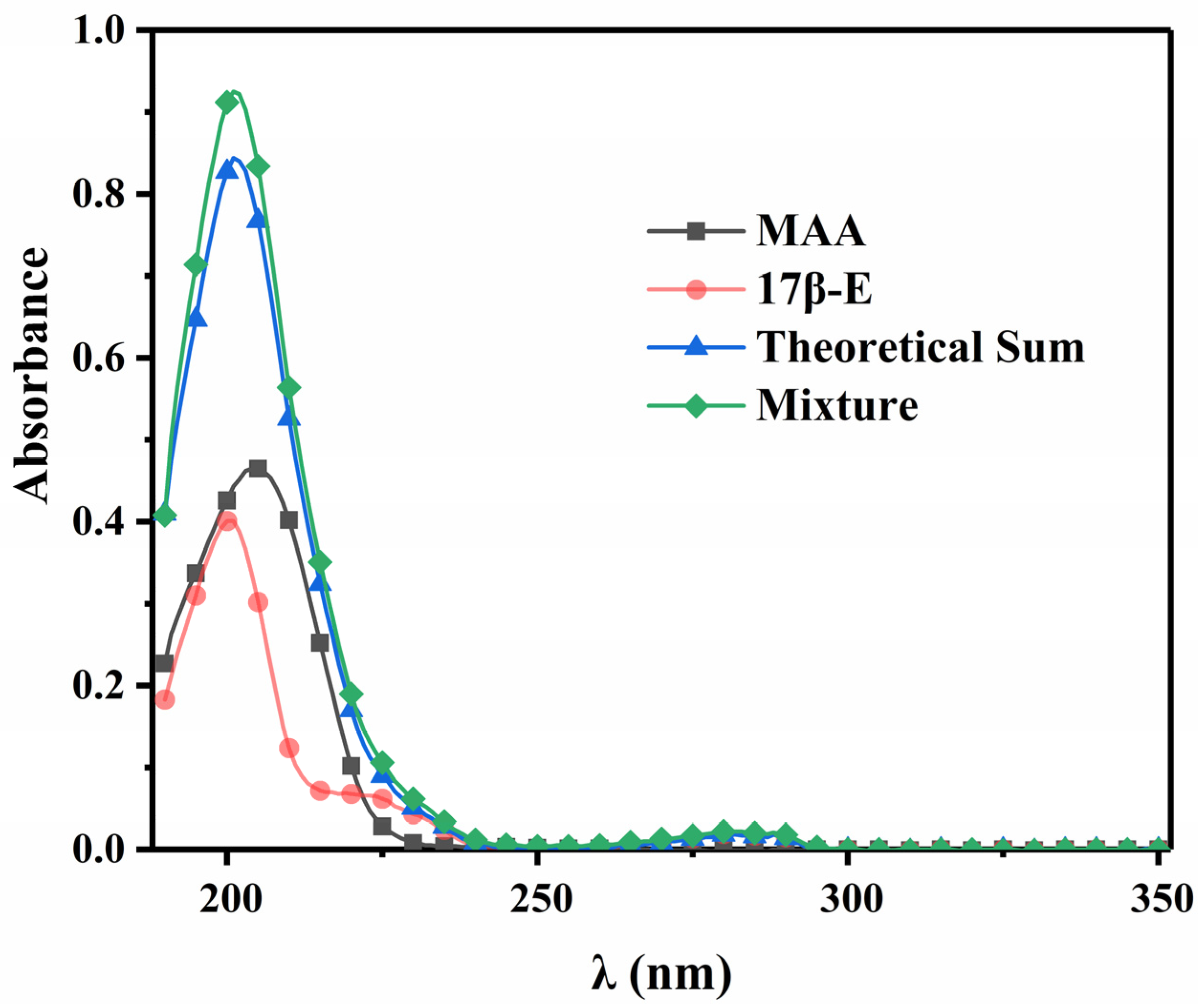
3.5. Possible Mechanism
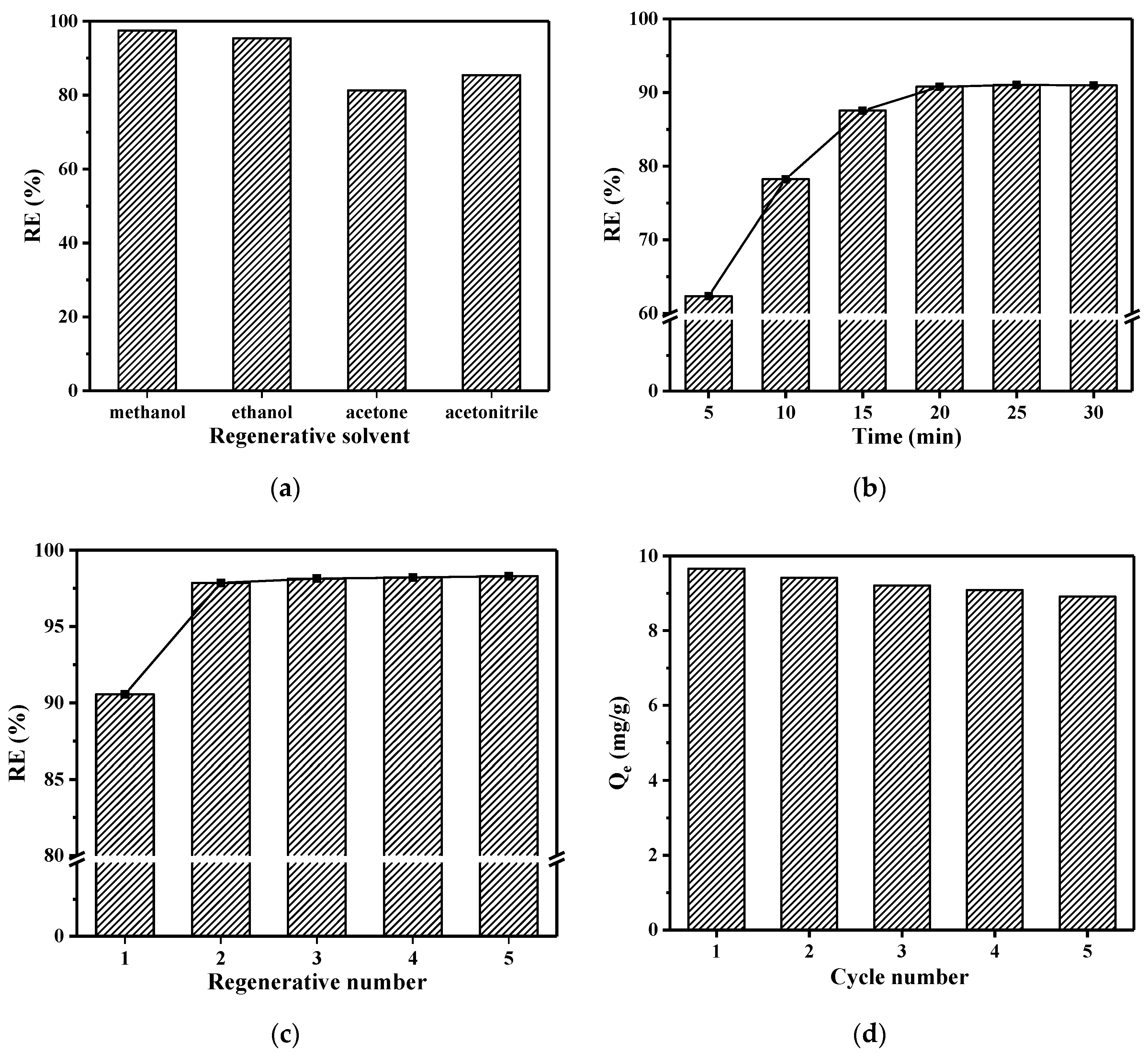
3.6. Regeneration and Reusability of MMIPs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sutherland, D.L.; Ralph, P.J. Microalgal bioremediation of emerging contaminants—Opportunities and challenges. Water Res. 2019, 164, 114921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeel, M.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Francis, D.; Yang, Y. Environmental impact of estrogens on human, animal and plant life: A critical review. Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, M.H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, M.; Yan, C.X.; Shi, H.; Dong, W.B.; Zhou, J.L. Environmental estrogens in a drinking water reservoir area in Shanghai: Occurrence, colloidal contribution and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeel, M.; Zain, M.; Fahad, S.; Rizwan, M.; Ameen, A.; Yi, H.; Baluch, M.A.; Lee, J.Y.; Rui, Y.K. Natural and synthetic estrogens in leafy vegetable and their risk associated to human health. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 36712–36723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Persistence and impact of steroidal estrogens on the environment and their laccase-assisted removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.Q.; Zhang, H.C.; Shen, G.X.; Yuan, Z.J.; Xu, T.; Ji, R. Effects of 17 beta-estradiol and 17 alpha-ethinylestradiol on the embryonic development of the clearhead icefish (Protosalanx hyalocranius). Chemosphere 2017, 176, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Quiroz, C.; Gonzalez, L.; Alvarez, M.S.; Hernandez-Chavez, J.F.; Rodriguez, A.; Deive, F.J.; Ulloa-Mercado, G. Biocompatible amino acid-based ionic liquids for extracting hormones and antibiotics from swine effluents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 117068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ana, K.M.S.; Espino, M.P. Occurrence and distribution of hormones and bisphenol A in Laguna Lake, Philippines. Chemosphere 2020, 256, 127122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, D.J.; Mastrocco, F.; Anderson, P.D.; Lange, R.; Sumpter, J.P. Predicted-no-effect concentrations for the steroid estrogens estrone, 17 beta-estradiol, estriol, and 17 alpha-ethinylestradiol. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1396–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.D.; Johnson, A.C.; Pfeiffer, D.; Caldwell, D.J.; Hannah, R.; Mastrocco, F.; Sumpter, J.P.; Williams, R.J. Endocrine disruption due to estrogens derived from humans predicted to be low in the majority of U.S. surface waters. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirnasab, M.A.; Hashemi, H.; Samaei, M.R.; Azhdarpoor, A. Advanced removal of water NOM by pre-ozonation, enhanced coagulation and bio-augmented granular activated carbon. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 3143–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honorio, J.F.; Veit, M.T.; Suzaki, P.Y.R.; Coldebella, P.F.; Rigobello, E.S.; Tavares, C.R.G. Adsorption of naturals hormones estrone, 17 beta-estradiol, and estriol by rice husk: Monocomponent and multicomponent kinetics and equilibrium. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 1075–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.H.; Liu, Y.G.; Tan, X.F.; Jiang, L.H.; Zeng, G.M.; Liu, S.B.; Tian, S.R.; Liu, S.J.; Liu, N.; Li, M.F. Adsorption of 17 beta-estradiol by a novel attapulgite/biochar nanocomposite: Characteristics and influencing factors. Process Saf. Environ. 2019, 121, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.H.; Liu, Y.G.; Zeng, G.M.; Liu, S.B.; Que, W.; Li, J.; Li, M.F.; Wen, J. Adsorption of 17 beta-estradiol by graphene oxide: Effect of heteroaggregation with inorganic nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 343, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.X.; Zhang, J.; Cong, L.; Meng, L.; Song, J.M.; Zhou, J.; Qiao, X.G. Preparation and characterization of magnetic chitosan microsphere sorbent for separation and determination of environmental estrogens through SPE coupled with HPLC. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.K.; Yan, W.Y.; Guo, C.X.; Zhang, J.H.; Yu, L.G.; Zhang, G.H.; Wang, X.M.; Fang, G.Z.; Sun, D.D. Magnetic molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensors: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1106, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.M.; Chen, W.; Ma, Y.; Pan, G.Q. Molecularly imprinted polymers as receptor mimics for selective cell recognition. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 5574–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagishita, M.; Kubo, T.; Nakano, T.; Shiraishi, F.; Tanigawa, T.; Naito, T.; Sano, T.; Nakayama, S.F.; Nakajima, D.; Otsuka, K. Efficient extraction of estrogen receptor-active compounds from environmental surface water via a receptor-mimic adsorbent, a hydrophilic PEG-based molecularly imprinted polymer. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.X.; Zeng, L.S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, B.M.; Zhou, Y.K.; Jing, T. Structure-Directed Screening and Analysis of Thyroid-Disrupting Chemicals Targeting Transthyretin Based on Molecular Recognition and Chromatographic Separation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 5437–5445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.B.; Zhou, T.; Li, G.K. Recent advances of modern sample preparation techniques for traditional Chinese medicines. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1606, 460377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Zhao, W.H.; Tan, L.J.; Wang, J.F.; Li, H.P.; Wang, J.T. Separation and detection of trace atrazine from seawater using dummy-template molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.G.; Wang, J.J.; Chen, X.; Hu, S.Y.; Gong, T.T.; Xian, Q.M. A novel molecularly imprinted polymer-solid phase extraction method coupled with high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of nitrosamines in water and beverage samples. Food Chem. 2019, 292, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.G.; Zhang, X.P.; Xu, Y.; Du, X.B.; Sun, X.; Sun, L.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, A.M.; Zhang, H.Q.; et al. Determination of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in environmental water samples based on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer extraction followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 662, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.X.; Wang, Y.Z.; Chen, J.; Ni, R.; Meng, J.J.; Liu, Z.W.; Xu, F.T.; Zhou, Y.G. Ionic liquids skeleton typed magnetic core-shell molecularly imprinted polymers for the specific recognition of lysozyme. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1081, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.L.; Wang, H.M.; Wang, H.L.; Wu, C.C.; Li, M.L.; Li, L. Fabrication and evaluation of molecularly imprinted magnetic nanoparticles for selective recognition and magnetic separation of lysozyme in human urine. Analyst 2018, 143, 5849–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, X.G.; Huang, R.F.; Xie, X.W.; Guo, L.H.; Zhang, M.Y. Synthesis of a molecularly imprinted polymer on mSiO2@Fe3O4 for the selective adsorption of atrazine. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 2837–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.Y.; Zhao, H.T.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Dong, A.J.; Wang, J.; Li, B. Selective recognition and fast enrichment of anthocyanins by dummy molecularly imprinted magnetic nanoparticles. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1572, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.L.; Liu, H.; Diao, J.X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.C. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for separating aromatic amines from azo dyes—Synthesis, characterization and application. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 204, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.Y.; Hu, Q.; Ke, R.F.; Zhen, X.Y.; Bu, Y.S.; Wang, S.C. Facile preparation of photonic and magnetic dual responsive protein imprinted nanomaterial for specific recognition of bovine hemoglobin. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvaresh, V.; Hashemi, H.; Khodabakhshi, A.; Sedehi, M. Removal of dye from synthetic textile wastewater using agricultural wastes and determination of adsorption isotherm. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 111, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.X.; Lai, C.; Huang, D.L.; Zeng, G.M.; Chen, L.; Qin, L.; Xu, P.; Cheng, M.; Huang, C.; Zhang, C.; et al. Preparation of water-compatible molecularly imprinted thiol-functionalized activated titanium dioxide: Selective adsorption and efficient photodegradation of 2, 4-dinitrophenol in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 346, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, A.; Bottaro, C.S. A critical review of molecularly imprinted polymers for the analysis of organic pollutants in environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1614, 460603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeola, A.O.; de Lange, J.; Forbes, P.B.C. Adsorption of antiretroviral drugs, efavirenz and nevirapine from aqueous solution by graphene wool: Kinetic, equilibrium, thermodynamic and computational studies. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2021, 6, 100157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Miao, Y.X.; Wei, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.C. Efficient removal of norfloxacin in water using magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, L.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.; Kang, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, B.; Yan, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shen, J. Selective adsorption and enhanced photodegradation of diclofenac in water by molecularly imprinted TiO2. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lai, C.; Zeng, G.M.; Huang, D.L.; Yang, C.P.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Cheng, M. Efficacy of carbonaceous nanocomposites for sorbing ionizable antibiotic sulfamethazine from aqueous solution. Water Res. 2016, 95, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilktac, R.; Gumus, Z.P.; Aksuner, N. Development of rapid, sensitive and selective fluorimetric method for determination of 1-naphthalene acetic acid in cucumber by using magnetite-molecularly imprinted polymer. Spectroc. Acta Part A-Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 218, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Liu, X.T.; Zhang, M.H.; Jiao, J.; Zhang, H.W.; Du, J.; Zhang, B.; Ren, Z.Q. Preparation of highly efficient ion-imprinted polymers with Fe3O4 nanoparticles as carrier for removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dil, E.A.; Doustimotlagh, A.H.; Javadian, H.; Asfaram, A.; Ghaedi, M. Nano-sized Fe3O4@SiO2-molecular imprinted polymer as a sorbent for dispersive solid-phase microextraction of melatonin in the methanolic extract of Portulaca oleracea, biological, and water samples. Talanta 2021, 221, 121620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.J.; Lee, L.T.; Lin, C.C. Adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of polyvinyl alcohol in aqueous solutions using P-25 TiO2. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.M.; Yang, J.; Ma, W.Q.; Ma, J.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.L. The selective binding character of a molecular imprinted particle for Bisphenol A from water. Water Res. 2014, 50, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.N.; Weidler, P.G.; Schwaiger, R.; Schafer, A.I. Interactions between carbon-based nanoparticles and steroid hormone micropollutants in water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 122929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.H.; Han, Y.P.; Wang, G.Z.; Deng, P.Y.; Feng, L.L. Walnut shell biochar based sorptive remediation of estrogens polluted simulated wastewater: Characterization, adsorption mechanism and degradation by persistent free radicals. Environ. Technol. Inno. 2022, 28, 102870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.G.; Hussain, M.Z.; Hammond, N.; Luca, S.V.; Fischer, R.A.; Minceva, M. Synthesis of highly active doped graphitic carbon nitride using acid-functionalized precursors for efficient adsorption and photodegradation of endocrine-disrupting compounds. Chemistryselect 2022, 7, e20220190. [Google Scholar]
- Yasir, M.; Ngwabebhoh, F.A.; Sopik, T.; Lovecka, L.; Kimmer, D.; Sedlarik, V. The adsorptive behaviour of electrospun hydrophobic polymers for optimized uptake of estrogenic sex hormones from aqueous media: Kinetics, thermodynamics, and reusability study. J. Chem. Technol. Biot. 2022, 97, 3317–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, D.S.; Estevam, B.R.; Perez, I.D.; Americo-Pinheiro, J.H.P.; Isique, W.D.; Boina, R.F. Sludge from a water treatment plant as an adsorbent of endocrine disruptors. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honorio, J.F.; Veit, M.T.; Suzaki, P.Y.R.; Tavares, C.R.G.; Barbieri, J.C.Z.; Tavares, F.D.; Lied, E.B. Single and multi-component removal of natural hormones from aqueous solutions using soybean hull. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.Y.; Wang, G.Z.; Li, C.K.; Dou, S.T.; Yuan, W. Removal of estrogen pollutants using biochar-pellet-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 85, 3259–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirec, O.; Alacabey, I.; Erol, K.; Alkan, H. Removal of 17 beta-estradiol from aqueous systems with hydrophobic microspheres. J. Polym. Eng. 2021, 41, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, G.N.; Shu, H.; Cui, X.; Luo, Z.M.; Chang, C.; Zeng, A.G.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Q. Facile covalent preparation of carbon nanotubes/amine-functionalized Fe3O4 nanocomposites for selective extraction of estradiol in pharmaceutical industry wastewater. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1638, 461889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Hu, B.Y.; Gao, S.Y.; Tong, X.; Jiang, L.S.; Chen, X.C.; An, S.Y.; Zhang, F.S. Comparison of 17 beta-estradiol adsorption on soil organic components and soil remediation agent-biochar. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
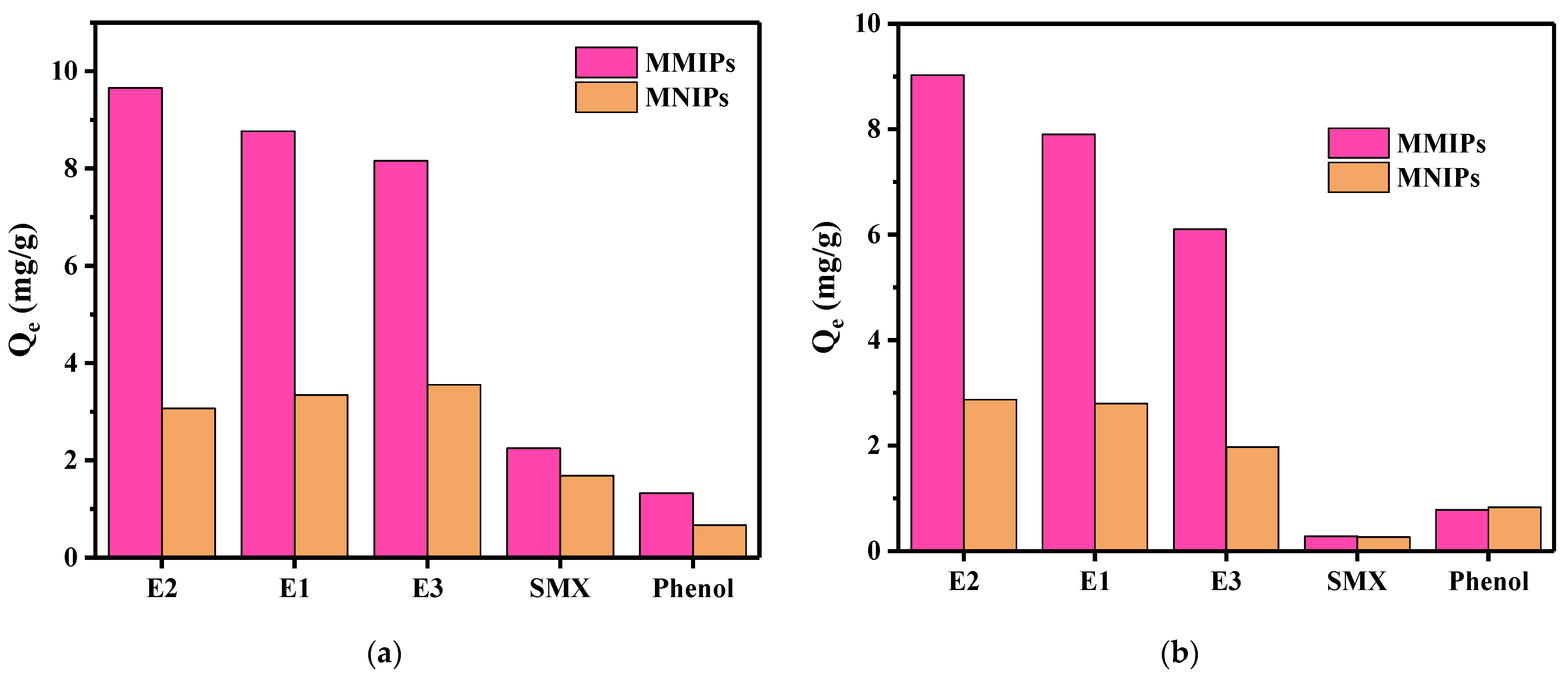
| Analytes | KMMIPs | KMNIPs | IF | α |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E2 | 28.32 | 0.44 | 64.02 | |
| E1 | 7.11 | 0.50 | 14.14 | 4.53 |
| E3 | 4.43 | 0.55 | 8.04 | 7.96 |
| SMX | 0.29 | 0.20 | 1.43 | 44.76 |
| Phenol | 0.15 | 0.07 | 2.13 | 29.99 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bi, L.; Shen, J.; Yao, Z.; Kang, J.; Zhao, S.; Yan, P.; Wang, B.; Chen, Z. Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Selective Recognition of 17β-Estradiol. Separations 2022, 9, 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9110381
Bi L, Shen J, Yao Z, Kang J, Zhao S, Yan P, Wang B, Chen Z. Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Selective Recognition of 17β-Estradiol. Separations. 2022; 9(11):381. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9110381
Chicago/Turabian StyleBi, Lanbo, Jimin Shen, Zhuoran Yao, Jing Kang, Shengxin Zhao, Pengwei Yan, Binyuan Wang, and Zhonglin Chen. 2022. "Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Selective Recognition of 17β-Estradiol" Separations 9, no. 11: 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9110381
APA StyleBi, L., Shen, J., Yao, Z., Kang, J., Zhao, S., Yan, P., Wang, B., & Chen, Z. (2022). Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Selective Recognition of 17β-Estradiol. Separations, 9(11), 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9110381








