Inverse Association Between Helicobacter pylori Infection and Childhood Asthma in Greece: A Case-Control Study
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
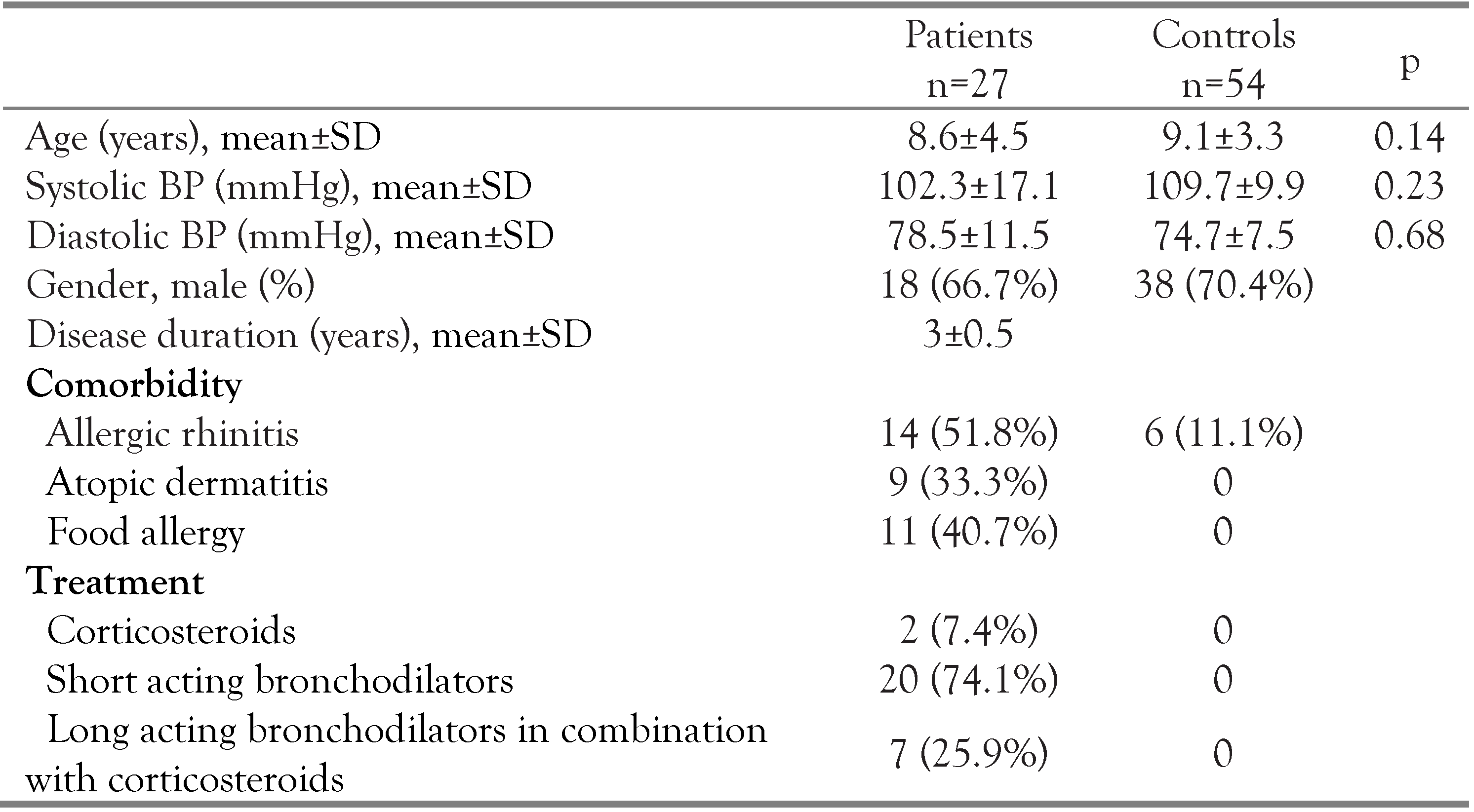
Study population
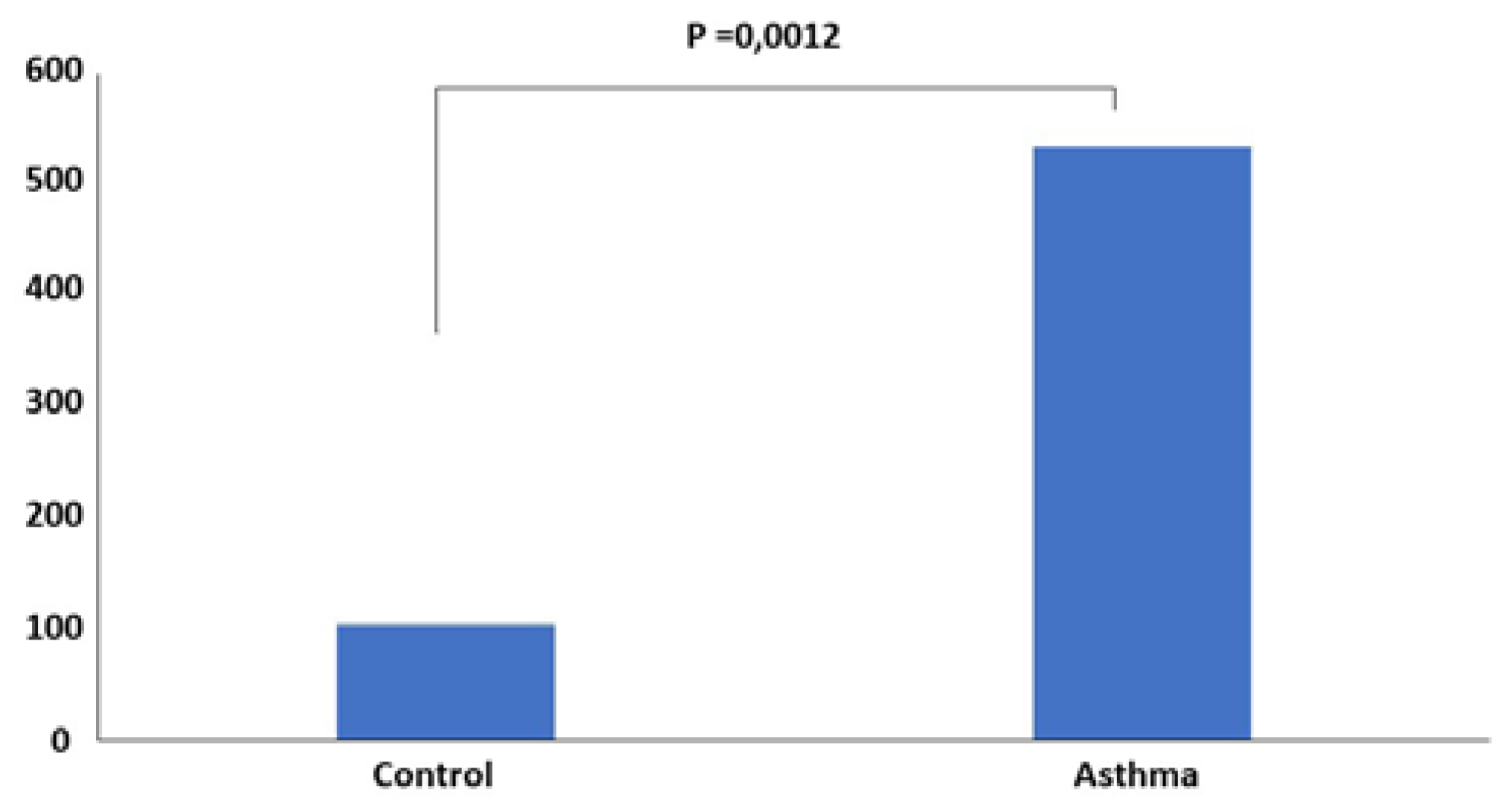
IgE determination
H. pylori infection status
Statistical analysis
Results
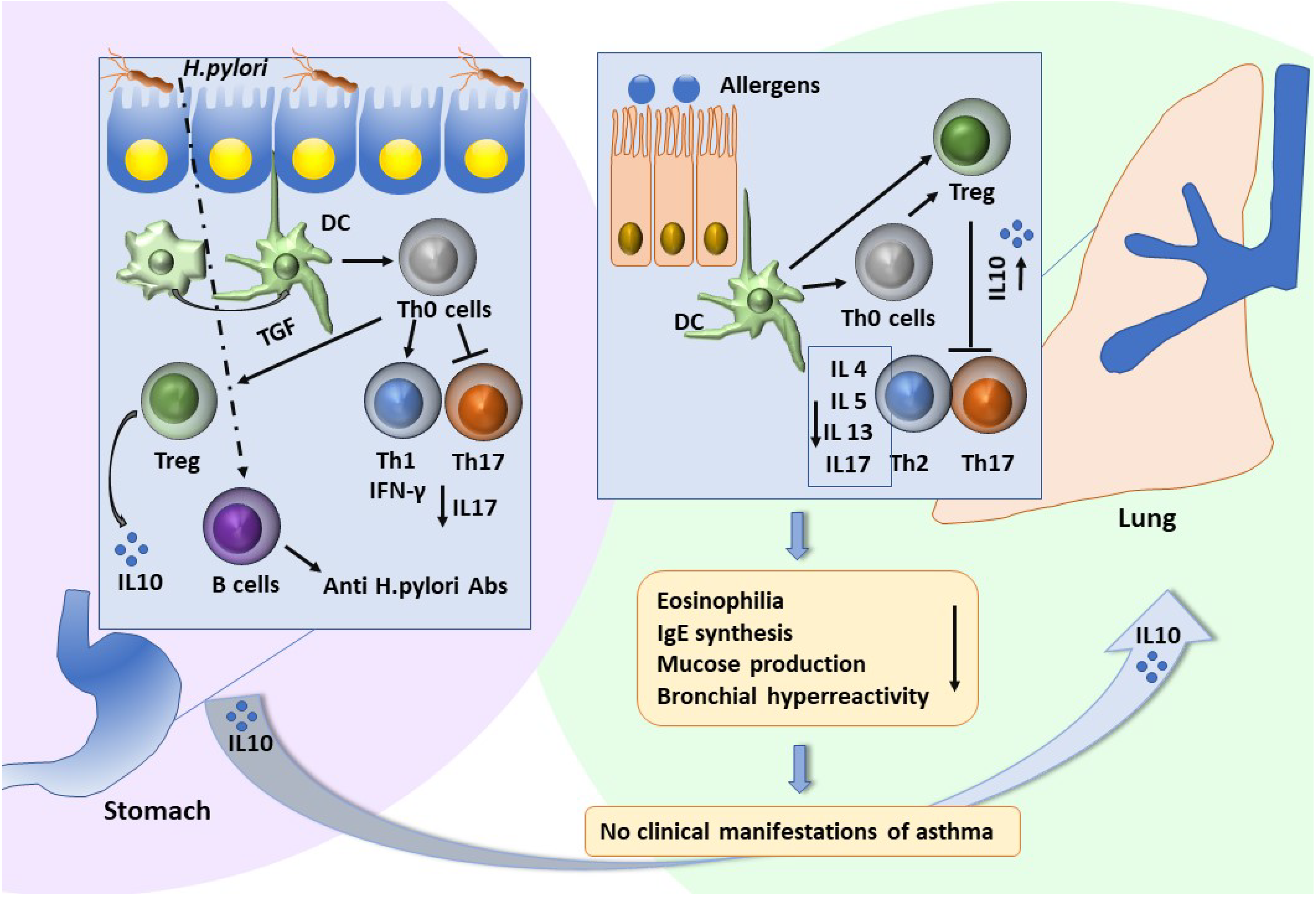
Discussion
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Warren, J.R.; Marshall, B. Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet 1983, 1, 1273–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, P.R. Medical microbiology; Mosby: St Louis, MO, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Møller, H.; Heseltine, E.; Vainio, H. Working group report on schistosomes, liver flukes and Helicobacter pylori. Int J Cancer 1995, 60, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leja, M.; Axon, A.; Brenner, H. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 2016, 21 (Suppl. 1), 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Kim, N.; Lim, S.H.; et al. Inverse relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and asthma among adults younger than 40 years: A cross-sectional study. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016, 95, e2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCaig, L.F.; Besser, R.E.; Hughes, J.M. Trends in antimicrobial prescribing rates for children and adolescents. JAMA 2002, 287, 3096–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, H.R. Prevalence of asthma. BMJ 2005, 330, 1037–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, W.; Ege, M.J.; von Mutius, E. The asthma epidemic. N Engl J Med 2006, 355, 2226–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miftahussurur, M.; Nusi, I.A.; Graham, D.Y.; Yamaoka, Y. Helicobacter, hygiene, atopy, and asthma. Front Microbiol 2017, 8, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amberbir, A.; Medhin, G.; Erku, W.; et al. Effects of Helicobacter pylori, geohelminth infection and selected commensal bacteria on the risk of allergic disease and sensitization in 3-year-old Ethiopian children. Clin Exp Allergy 2011, 41, 1422–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Hollander, W.J.; Sonnenschein-van der Voort, A.M.; Holster, I.L.; et al. Helicobacter pylori in children with asthmatic conditions at school age, and their mothers. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2016, 43, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SPSS, v.23; IBM Corp: Armonk, NY, USA.
- Zevit, N.; Balicer, R.D.; Cohen, H.A.; Karsh, D.; Niv, Y.; Shamir, R. Inverse association between Helicobacter pylori and pediatric asthma in a high-prevalence population. Helicobacter 2012, 17, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strachan, D.P. Hay fever, hygiene, and household size. BMJ 1989, 299, 1259–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, H.; Kuhn, C.; Feillet, H.; Bach, J.F. The ‘hygiene hypothesis’ for autoimmune and allergic diseases: An update. Clin Exp Immunol 2010, 160, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Blaser, M.J. Helicobacter pylori colonization is inversely associated with childhood asthma. J Infect Dis 2008, 198, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLoughlin, R.M.; Mills, K.H. Influence of gastrointestinal commensal bacteria on the immune responses that mediate allergy and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011, 127, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamford, K.B.; Fan, X.; Crowe, S.E.; et al. Lymphocytes in the human gastric mucosa during Helicobacter pylori have a T helper cell 1 phenotype. Gastroenterology 1998, 114, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.G.; Beck, P.; Dangler, C.A.; et al. Concurrent enteric helminth infection modulates inflammation and gastric immune responses and reduces helicobacter-induced gastric atrophy. Nat Med 2000, 6, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, I.C.; Dehzad, N.; Reuter, S.; et al. Helicobacter pylori infection prevents allergic asthma in mouse models through the induction of regulatory T cells. J Clin Invest 2011, 121, 3088–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codolo, G.; Mazzi, P.; Amedei, A.; et al. The neutrophilactivating protein of Helicobacter pylori down-modulates Th2 inflammation in ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma. Cell Microbiol 2008, 10, 2355–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.P.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Correlation between Helicobacter pylori infection, IgE hypersensitivity, and allergic disease in Korean adults. Helicobacter 2015, 20, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalach, N.; Bontems, P.; Raymond, J. Helicobacter pylori infection in children. Helicobacter 2017, 22 (Suppl. 1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.Y.; Uemura, N. Natural history of gastric cancer after Helicobacter pylori eradication in Japan: After endoscopic resection, after treatment of the general population, and naturally. Helicobacter 2006, 11, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noverr, M.C.; Falkowski, N.R.; McDonald, R.A.; McKenzie, A.N.; Huffnagle, G.B. Development of allergic airway disease in mice following antibiotic therapy and fungal microbiota increase: Role of host genetics, antigen, and interleukin-13. Infect Immun 2005, 73, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© GERMS 2025.
Share and Cite
Tsigalou, C.; Konstantinidis, T.G.; Cassimos, D.; Karvelas, A.; Grapsa, A.; Tsalkidis, A.; Panopoulou, M.; Tsakris, A. Inverse Association Between Helicobacter pylori Infection and Childhood Asthma in Greece: A Case-Control Study. Germs 2019, 9, 182-187. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2019.1174
Tsigalou C, Konstantinidis TG, Cassimos D, Karvelas A, Grapsa A, Tsalkidis A, Panopoulou M, Tsakris A. Inverse Association Between Helicobacter pylori Infection and Childhood Asthma in Greece: A Case-Control Study. Germs. 2019; 9(4):182-187. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2019.1174
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsigalou, Christina, Theocharis G. Konstantinidis, Dimitrios Cassimos, Alexandros Karvelas, Anastasia Grapsa, Aggelos Tsalkidis, Maria Panopoulou, and Athanasios Tsakris. 2019. "Inverse Association Between Helicobacter pylori Infection and Childhood Asthma in Greece: A Case-Control Study" Germs 9, no. 4: 182-187. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2019.1174
APA StyleTsigalou, C., Konstantinidis, T. G., Cassimos, D., Karvelas, A., Grapsa, A., Tsalkidis, A., Panopoulou, M., & Tsakris, A. (2019). Inverse Association Between Helicobacter pylori Infection and Childhood Asthma in Greece: A Case-Control Study. Germs, 9(4), 182-187. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2019.1174



