Abstract
Introduction: Transmission of rabies to humans occurs rarely in Europe but in the absence of vaccination, it almost invariably leads to a fatal disease. In 2007, Romania implemented a program for rabies eradication in foxes. Methods: We performed a descriptive study evaluating the trend of rabies disease in Romania, both in animals and in humans, between 2008-2012. Results: In the past years, a large number of adults have presented to the Antirabic Center of the National Institute for Infectious Diseases “Prof.Dr. Matei Balş”, Bucharest, Romania. The major bite-inflicting animals were cats and dogs, particularly stray dogs (more than two thirds of the cases). Most cases of animal rabies were recorded in 2008 (1089 cases), with a subsequent decline in the following years: 516 in 2009, 469 in 2010, and 195 in 2011. Six cases of human rabies have been reported in Romania from 2008 to 2012, two of which were located in the Bacău district. Four of the cases occurred in females, and two in males; half were children and half adults. The animals inflicting the bites were domestic cats and stray dogs in half of the cases. Discussion: Domestic animals, particularly cats, appear to be a major cause of rabies transmission to humans. Therefore, vaccination after cat bites should be taken into account. There is stringent need for specific measures to increase the awareness regarding the problem. People should be educated that cats in rural areas or in the vicinity of forests pose the same level of risk as dogs or wild animals. Conclusions: There is need for a new strategy regarding the prevention of animal rabies and its transmission to humans. Proper surveillance systems and continuous monitoring for the disease in wildlife and cities is of utmost importance and should be continued, together with the programs for vaccination of stray dogs and foxes in order to eliminate rabies infection.
Introduction
Rabies is a zoonosis caused by rabies virus, a Lyssavirus whose main reservoirs are wild and domestic canids (dogs, wolves, foxes, etc.) and bats [1]. Transmission to humans occurs through the contact of infected saliva with open wounds, typically through an animal bite [2]. In the absence of pre- or post-exposure vaccination, rabies is almost invariably a fatal disease [3].
In Bucharest, a large number of people present to the National Institute for Infectious Diseases “Prof.Dr. Matei Balş” rabies center each day to seek prophylaxis after an animal bite or scratch, with an increase in the number of presentations from 2007 to 2012 [4].
Given the small number of rabies cases throughout Europe, Romania has recorded the highest number of human rabies cases in the European Union during 2008-2012.
The prevalence of rabies in Romania’s wild animals has decreased compared to prior years, possibly in direct relation to the decreasing trend in Europe or to the program issued by the Romanian government in 2007 to eradicate rabies in foxes, starting from high risk areas, the forests near the western border [5].
Stray dogs and wild foxes are considered to be the major vectors of transmission for rabies. The large number of stray dogs in Romania and the poor control of the issue represent major threats. In this context, we considered it necessary to perform an analysis of the Romanian data on rabies in order to see what measures are needed for a better control of the situation.
Methods
We performed a descriptive study evaluating the trend of rabies disease in Romania, both in animals and in humans, from 2008 to 2012, the years following the implementation of the program to eliminate rabies through oral vaccination of foxes [6], issued in 2007 by the National Sanitary Veterinary and Food Safety Authority (ANSVSA) in Romania [7,8].
We analyzed the data on rabies from the Antirabic Center, the National Institute for Infectious Diseases “Prof.Dr. Matei Balş”, Bucharest, Romania and we also performed a literature review and gathered epidemiological data from the World Health Organization (WHO) Rabies Bulletin Europe database and from the European Center for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) Epidemiological Reports.
Results
Presentations to the Antirabic Center
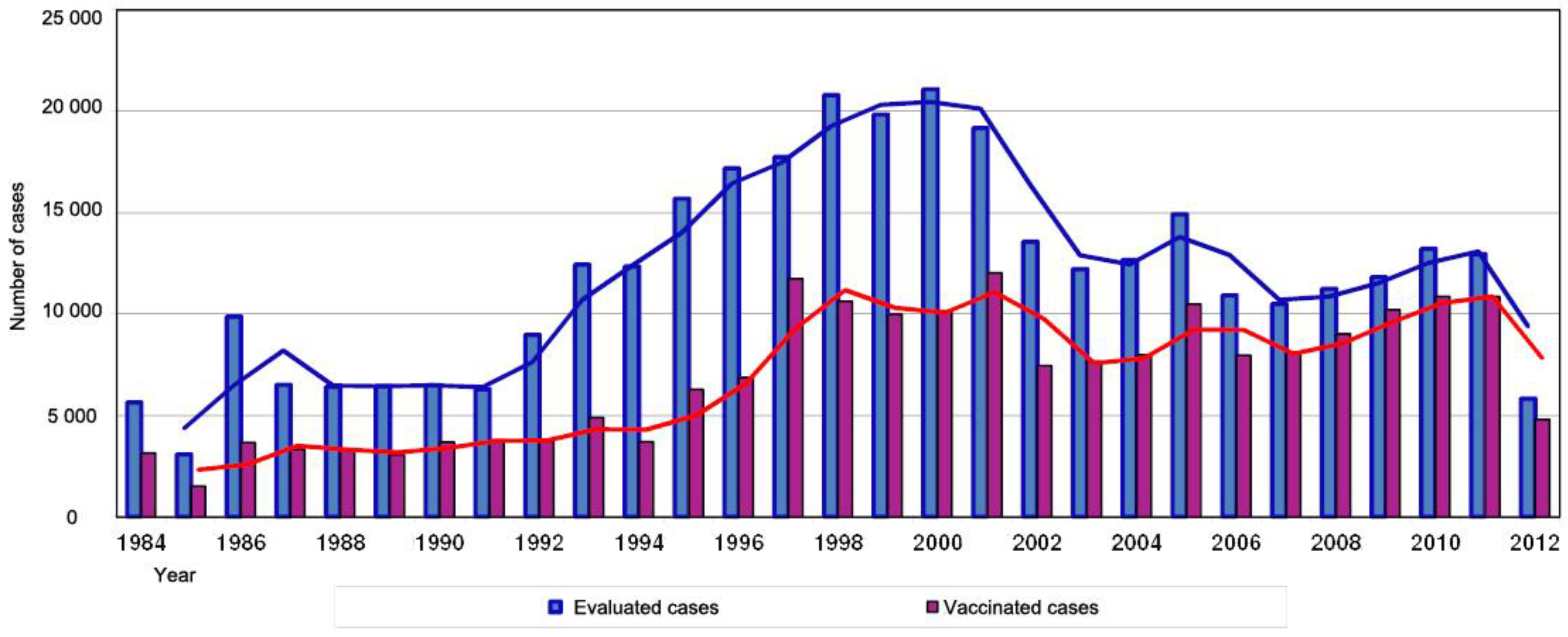
Rabies has been present in Romania in wild animals and it been occasionally transmitted to humans throughout history. During 1987-2000 there was an increasing trend in the number of patients presenting to the Antirabic Center of the National Institute for Infectious Diseases "Prof.Dr. Matei Balş", followed by certain fluctuations (Figure 1).
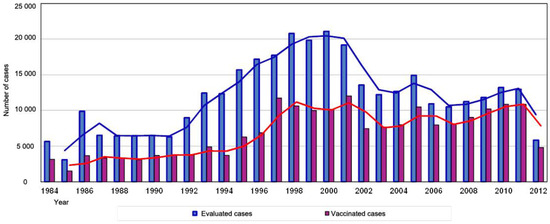
Figure 1.
Number of cases presenting to the Antirabic Center of the National Institute for Infectious Diseases “Prof.Dr. Matei Balş”, between 1984 and April 30, 2012 [9].
Years 1998 and 2000 recorded the largest number of patients (over 20 000) presenting to the Antirabic Center for evaluation, out of which almost half received rabies vaccination based on clinical judgment which analyzed: pre-exposure prophylaxis (yes/no), the type of wound, depth of the wound, area of the body which was wounded, type of animal which induced the wound, location of the animal (rural/urban, areas known for the presence of rabies), type of contact with the animal (scratch, bite, etc.), contact with animal saliva (yes/no, duration), surveillance of the animal (possible/not possible), etc.
Adults presented to the Antirabic Center with animal bites in larger numbers compared to children. Most of the cases presenting to the hospital were citizens of Bucharest rather than from the peripheral regions of the city.
According to the data provided by the patients presenting to the Antirabic Center, the major bite inflicting animals were domestic cats and stray dog (more than two thirds of the cases). Rat bite cases were also a significant presenting complaint.
The highest number of presentations reported bites in sector 2 of Bucharest, followed by the Ilfov area. Cases occurring in adults were due to dog bites (stray and domestic) mostly in the Voluntari area, and to cat bites in Chitila.
For bites occurring in children, domestic dogs were from Voluntari, and stray dogs were from Ştefăneşti and Pantelimon while cases of cat bites occurred in several locations, with a wider distribution.
Rabies in animals
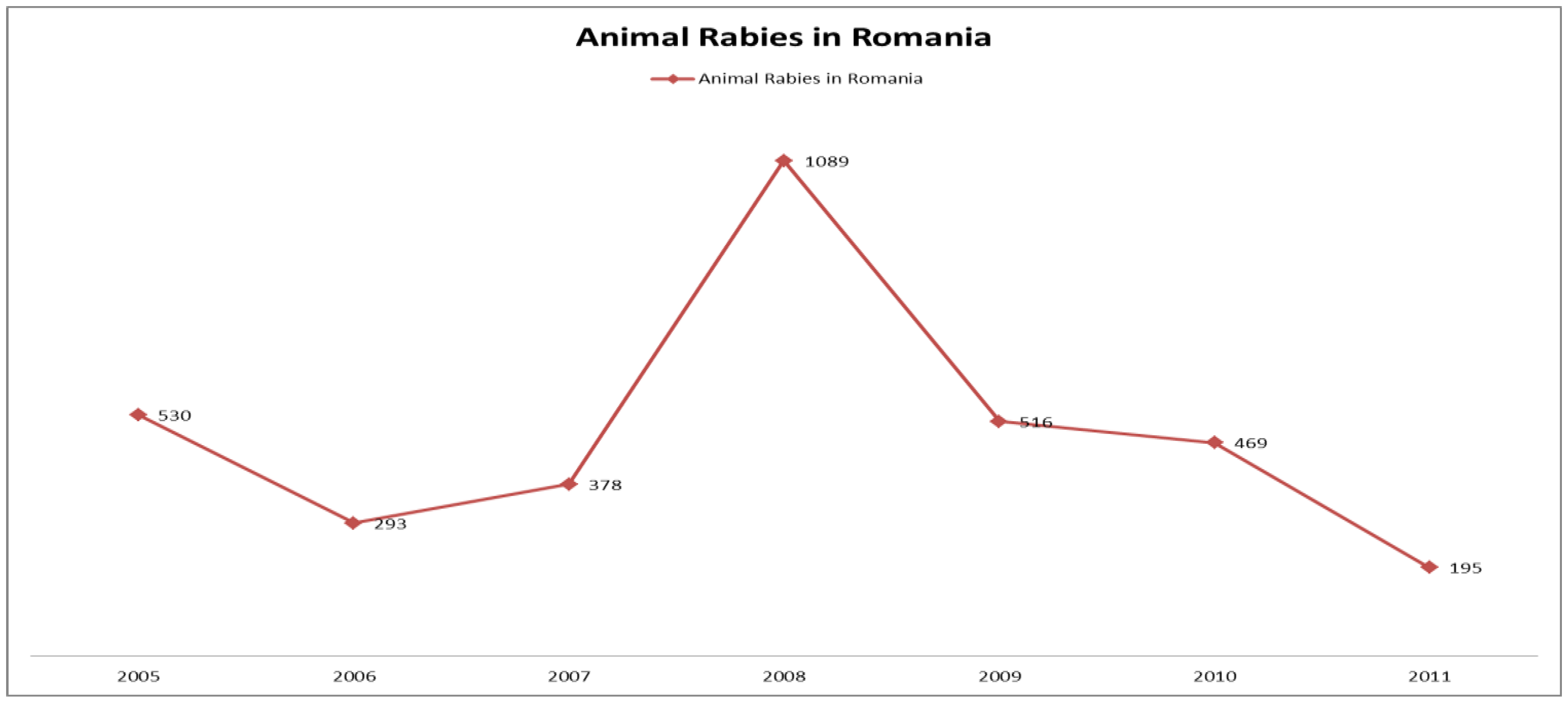
Historical data on animal rabies in Romania show that each year from 2000 to 2007 there were roughly 200-400 cases per year. The beginning of 2008 recorded an extremely high number of cases (266 cases, ten times as many as the numbers recorded for the same period during the previous year) with a total number of 1089 cases by the end of the year.
From 2008 there was a decline in rabies occurrence in domestic and wild animals in Romania, following the general trend in Europe. In 2009 there were 516 cases of rabies, out of which 342 were recorded in foxes. In 2010, there were 469 cases, out of which 256 were recorded in foxes and in 2011 the total number of cases decreased to 195 (Figure 2).
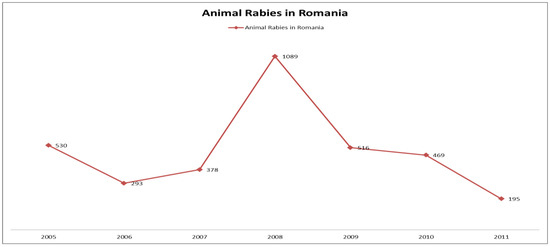
Figure 2.
Number of cases of animal rabies in Romania from 2005 to 2011.
Rabies in humans
From 2008 to 2012, six cases of human rabies were reported, two of which were located in the Bacău district. Four of the cases occurred in females, and two in males; half were children and half were adults. The animals inflicting the bites were domestic cats in two cases, wild animals in two cases and a stray dog in another case. Most bites occurred in the hands and legs but one patient was bitten by the neck and one other patient reported a bite to the face (Table 1).

Table 1.
Characteristics of the cases of rabies reported in Romania from 2008 to 2012.
Discussion
Presentations to the Antirabic Center
Adults rather than children were the main consultation seekers at the Antirabic Center of the National Institute for Infectious Diseases “Prof.Dr. Matei Balş”, Bucharest, Romania [4], data which appears to contradict the available information regarding the high risk of rabies exposure in children under 15 years [10]. This may be due to various reasons: adults may be bitten more often than children; adults may come in contact with animals more than children do; better awareness among adults regarding the risk of rabies after an animal bite (related to adolescents who are bitten but do not seek help, rather than younger children who are in their parents’ supervision, although recent data [11] suggest that not all parents are aware of the correct management of animal bites); severity of the bite; geographic variables; demographic distribution, etc.
Most of the cases of animal bites took place in Bucharest [4]. An assumption based on this data is that other cases which may occur in Romania may be treated in other hospitals across the country, without being reported to the Antirabic center in Bucharest. However, we can also assume that a percentage of cases of bites in Romania are not treated due to the fact that the individual did not seek medical attention.
Animal bites were mostly from dogs and cats, and stray dogs were the major bite-inflicting animals. Unfortunately, stray dogs are still a major problem in Romania, as their number is high, poorly controlled, and they can be considered health hazards [12,13].
Cases of bite accidents by dogs with owners are also high, and suggest poor owner control of the animal. This problem should not be neglected and it should be approached accordingly.
Rabies in animals
The occurrence of rabies in animals in Europe and in Romania is still fluctuating [14]. This can be as a result of several factors involving surveillance system quality and accuracy, heterogeneity of the virus, aggravation of the transmission, total number of wild/domestic animals, habitat quality, climate season and so on.
Between 2005 and 2008 there was a decline in rabies occurrence in Romania in both wild and domestic animals [14], pattern that follows a general decline in Europe rabies incidences and that may be an effect of the program implemented in Romania in 2007, for eradication of rabies through oral vaccination of foxes.
Red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) appear to be the main mediators of the disease among wild animals and we can assume that there is transmission of rabies between wild animals [5]. Among the neighboring countries (Ukraine, Republic of Moldova, Bulgaria, Serbia and Hungary), Ukraine shows the largest number of rabies cases, with group C and group NEE (North East Europe) viruses. Moreover, a recent study based on glycoprotein gene analyses of 78 rabies virus isolates from Ukraine presented evidence for cross-border movements of rabies virus [15].
In European countries fluctuations have been recorded in bats populations [14], with high numbers of cases occurring each year. This is a major threat because bats have the fastest transmission rate and can infect animals as well as humans, particularly since bats carrying the virus can live for longer timespans compared to foxes or dogs which die relatively rapidly from the disease. Bats can also cross borders and transfer the disease to animals or bats in neighboring countries. High numbers indicate a quick solution should be found for eradication of the rabies infection in bats. People should not handle bats or should only do so when wearing gloves; bat workers should receive pre-exposure immunization [16]. However, bats are not considered a major threat in Romania as their current numbers are small [14].
Rabies in humans
Our analysis showed that Romania appears to be the country with the highest number of cases of human rabies in the European Union, with endemic transmission. From 2008 to 2012, there were six notified cases of fatal human rabies in Romania [14].
ECDC reports show that in 2005 there were four cases of rabies in the European Union, all of them in Germany. One patient was infected during a trip to India and consequently infected three more patients who received organs from this donor [17]. In 2006 there were no reports of human rabies while in 2007 there were three cases reported. One case of rabies was infected in the Philippines and hospitalized in Finland [18]; in Germany there was one case imported from Morocco [19], and in Lithuania there was one case of rabies imported from India. In 2008 there were four cases: one in the French Guyana [20], one in the Netherlands (imported from Kenya) [21], one in Romania and one other imported case in the United Kingdom. In 2009, data from the ECDC only reported one case of rabies, in Romania, that of a 69 year-old female bitten by a fox in a rural area; the patient did not seek medical attention [22].
Romanian data prior to 2008 are not recorded by the ECDC since Romania entered the European Union in 2007, and 2008 was the first year when data from Romania was included in ECDC’s infectious diseases annual reports.
Looking at the data available for Romania from 2008 to 2012, we can notice that domestic animals, particularly cats, are a major cause of rabies transmission to humans. Therefore, vaccination after cat bites should be taken into account. There is stringent need for specific measures to increase the awareness regarding the problem. People should be educated that cats in rural areas or in the vicinity of forests pose the same level of risk as dogs or wild animals.
Children should be educated in schools and also by their parents to avoid unknown animals, to be aware of suspicious behavior from a known domestic animal, and to seek medical advice after being in contact with an animal through bite and scratch. Because of the high fatality rate, the prevention of rabies infection is of high importance [23].
Conclusion
Data on rabies available for Romania show that there is need for a new strategy regarding the prevention of animal rabies and its transmission to humans. Proper surveillance systems and continuous monitoring for the disease in wildlife and cities is of utmost importance and should be continued [24], together with the programs for vaccination of stray dogs [25] and foxes in order to eliminate rabies infection [6,26].
Public education of the disease is needed, particularly about the risk of transmission by domestic dogs and especially cats which were not vaccinated and came in contact with the rabies virus. Education programs could be implemented in schools and hospitals, together with media campaigns mentioning the measures which need to be taken before and after coming in contact with an animal.
Author Contributions
All authors had equal contributions.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors – none to declare.
References
- Liu, X.; Feng, X.; Tang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. Characterization and potential diagnostic application of monoclonal antibodies specific to rabies virus. J Biomed Res. 2010, 24, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ECDC. European Center for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Rabies. 2012. Available online: http://ecdc.europa.eu/en/health topics/rabies/Pages/index.aspx (accessed on 19 July 2012).
- Feder, H.M., Jr.; Petersen, B.W.; Robertson, K.L.; Rupprecht, C.E. Rabies: still a uniformly fatal disease? Historical occurrence, epidemiological trends, and paradigm shifts. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2012, 14, 408–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute for Infectious Diseases "Prof.Dr. Matei Balş", Romania. Antirabic Center. 2012. Available online: http://www.mateibals.ro (accessed on 20 August 2012).
- ROMANIA, HOTARÂRE, pentru aprobarea Programului strategic pentru supravegherea, controlul şi eradicarea rabiei la vulpe în România, Ordonanţa Guvernului nr. 42/2004, complătari prin Legea nr. 215/2004.
- Muller, T.; Batza, H.J.; Freuling, C.; Kliemt, A.; Kliemt, J.; Heuser, R.; et al. Elimination of terrestrial rabies in Germany using oral vaccination of foxes. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2012, 125, 178–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- ANSVSA. Notă de fundamentare. Hotărâre privind modificarea şi completarea Hotărârii Guvernului nr. 55/2008 pentru aprobarea Programului strategic privind supravegherea, controlul şi eradicarea turbării la vulpe în România. 2008. Available online: http://www.ansvsa.ro/documente/ admin/Proiect%20HG%20modificare%20si%20compl etare%20HG%20nr.%2055%20din%202008%20Prog ram%20Strategic%20rabie_29149ro.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2012).
- Hotărârea Guvernului, nr. 55/2008 pentru aprobarea Programului strategic privind supravegherea, controlul şi eradicarea turbării la vulpe în România.
- Number of presentations to the National Institute for Infectious Diseases "Prof.Dr. Matei Balş", the Antirabic Center between 1984-2012. 2012. Available online: http://www.mateibals.ro/html/ docBals/antirabic/s5.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2012).
- WHO. Rabies. 2012. Available online: http://www.who.int/rabies/en/ (accessed on 19 July 2012).
- Mehndiratta, S. Animal bites in children: burden in urban Delhi. Trop Doct. 2012, 42, 114–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesterov, V.; Ciofan, I.; Cristescu, P.; et al. Cercetări privind depistarea cazurilor de turbare la carnasierele sălbatice. Analele ICAS. 1973, 29, 87–110. [Google Scholar]
- Vier Pfoten. Fii om cu animalele. Stuaţia câinilor fără stăpân şi soluţia Vier Pfoten România. Available online: http://www.vier-pfoten. ro/website/uploads/Situatia_cainilorcomunitariinRom ania.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2012).
- WHO. Information Surveillance Report. Rabies- Bulletin-Europe 2011, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Picard-Meyer, E.; Robardet, E.; Moroz, D.; Trotsenko, Z.; Drozhzhe, Z.; Biarnais, M.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of rabies in Ukraine. Arch Virol. 2012. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racey, P.A.; Hutson, A.M.; Lina, P.H. Bat Rabies, Public Health and European Bat Conservation. Zoonoses Public Health. 2012. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellenbrand, W.; Meyer, C.; Rasch, G.; Steffens, I. Ammon Cases of rabies in Germany following organ transplantation. Euro Surveill. 2005, 10, E050224–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rimhanen-Finne, R.; Jarvinen, A.; Kuusi, M.; Quiambao, B.P.; Malbas, F.F., Jr.; Huovilainen, A.; et al. Imported human rabies, the Philippines and Finland, 2007. Emerg Infect Dis. 2010, 16, 1318–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmiedel, S.; Panning, M.; Lohse, A.; Kreymann, K.G.; Gerloff, C.; Burchard, G.; et al. Case report on fatal human rabies infection in Hamburg, Germany, March 2007. Euro Surveill. 2007, 12, E070531–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meynard, J.B.; Flamand, C.; Dupuy, C.; Mahamat, A.; Eltges, F.; Queuche, F.; et al. First human rabies case in French Guiana, 2008: epidemiological investigation and control. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012, 6, e1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Thiel, P.P.; van den Hoek, J.A.; Eftimov, F.; Tepaske, R.; Zaaijer, H.J.; Spanjaard, L.; et al. Fatal case of human rabies (Duvenhage virus) from a bat in Kenya: The Netherlands, December 2007. Euro Surveill. 2008, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECDC. Annual surveillance data. Human rabies cases, 2005-2009. Available online: http://ecdc.europa.eu/en/healthtopics/rabies/epidemi ological_data/Pages/surveillance-data.aspx (accessed on 18 August 2012).
- Senior, K. Global rabies elimination: are we stepping up to the challenge? Lancet Infect Dis. 2012, 12, 366–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakkar, M.; Venkataramanan, V.; Krishnan, S.; Chauhan, R.S.; Abbas, S.S. Moving from Rabies Research to Rabies Control: Lessons from India. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012, 6, e1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, M.C.; Hampson, K.; Cleaveland, S.; Meyers, L.A.; Townsend, J.P.; Galvani, A.P. Potential for Rabies Control through Dog Vaccination in Wildlife-Abundant Communities of Tanzania. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012, 6, e1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cliquet, F.; Robardet, E.; Must, K.; Laine, M.; Peik, K.; Picard-Meyer, E.; et al. Eliminating rabies in Estonia. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012, 6, e1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© GERMS 2012.