Abstract
A study on the catalytic oxidation of heavy residual oil (HRO) was carried out. The thermodynamic parameters of components of HRO oxidation products were studied by pulsed nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). A method for the quantitative assessment of thermodynamic parameters of HRO components and oxidized bitumen using pulsed NMR is presented. The relationship between NMR parameters and the viscosity of HRO and its oxidation products is established. The obtained results prove the possibility of using pulsed NMR as a flow-line method for rapid analysis of intermediates and products of the heavy residual oil oxidation.
1. Introduction
Along with the deepening of oil refining, increasing the quality of oil products, for instance, oxidized bitumen for road construction, presents one the most relevant problems in the refining industry [1]. The need for high-quality bitumen increased due to the continuous growth of car parks, an increase in traffic intensity and transport capacity of vehicles, and, as a consequence, a significant increase in dynamic loads on the road surface [2,3].
Bitumen can be obtained from almost any crude oil; nevertheless, the chemical composition of heavy oil feedstock has a significant impact on bitumen properties [4]. One of the widely used processes for bitumen production is the process of oxidation of heavy residual oil (HRO) feedstock consisting of high molecular weight naphthenic-aromatic compounds, resins and asphaltenes. The use of heavy oil residues, consisting of paraffin-naphthenic compounds, as a raw material for oxidation leads to an increase in the energy consumption of the process. The research on obtaining bitumen from the residual oil feedstock of paraffin-naphthenic base will provide the solution for the urgent problem associated with the expansion of the raw material base of the process.
At present, various methods have been developed to increase the efficiency of the oxidation process by reducing the temperature and time of oxidation. The most promising direction for intensifying the oxidation process of HRO is the use of catalysts and initiating additives. Heavy oil residues and bitumen are complex objects for research, as they consist of high molecular weight hydrocarbons, heterogeneous compounds, resins and asphaltenes [5,6]. It should be noted that the study of the composition and structure, as well as the investigation of the structural and dynamic parameters, characterizing the molecular mobility dynamics of such systems, present the topical issue in the development of resource-saving technologies of transportation and deep oil refining. The study of heavy oil residues is associated with great difficulties caused by the complexity of the composition and structure of components, which significantly limits the abilities of conventional chemical and physical methods of analysis [7]. To optimize the transportation processes, as well as the processing of HRO into high-quality products, theoretical and experimental knowledge on the structural and thermodynamic parameters of high-molecular components in their composition is required. However, there are no analytical approaches that correlate the composition and structure of HRO with its structural and thermodynamic parameters, characterizing the mobility of high-molecular-weight components. One of the acceptable and widely used methods of analysis for determining the chemical and structural-group composition of heavy residues of oil refining is adsorption-liquid chromatography; for the structural-thermodynamic analysis of HRO components, the method of pulsed nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) can be used [8,9,10,11].
Measurement of NMR parameters is based on resonant absorption of a high-frequency electromagnetic field by HRO, located in a constant magnetic field [12]. As a result of exposure to a high-frequency electromagnetic field with a frequency equal to the frequency of natural vibrations of hydrogen nuclei, energy transitions occur between the levels of HRO molecules, as a result, the Boltzmann distribution of these levels is violated. After turning off the electromagnetic field, the system spontaneously returns to an equilibrium state due to the nuclear magnetic relaxation process. Meanwhile, the accumulated energy is dissipated due to the interaction of nuclei with each other and the environment—the lattice, which leads to the establishment of energy equilibrium (relaxation). The atomic nuclei of HRO molecules, placed in a constant magnetic field, possess magnetic moments and spins, which respectively form spin systems of phases, the energy states of which differ from the energy state of the molecular environment, called the lattice.
Such relaxation processes are characterized by the constants T1i and T2i, which describe the time required for restoration of the thermodynamic equilibrium between the spin system and the lattice and inside the spin system, where i is the phase of the spin system a, b, c, respectively. The projection value of the magnetization amplitude of the nuclear magnetic resonance signal T2i, proportional to the number of resonating magnetic nuclei, is called the population of P2i phase, and shows the relative fraction of nuclei in the corresponding spin system. In [13] it is shown that the intramolecular contribution to relaxation is due to spin–spin interactions, and based on [14,15], it follows that the intermolecular contribution, associated with the spin-lattice relaxation in heavy oil residues, is much lower compared to the intramolecular contribution from the rotational motion of molecules, and therefore, it is neglected.
The paper shows the correlation between the parameters of pulsed nuclear magnetic resonance with the component composition and properties of the oxidation products of HRO. The possibility of using pulsed NMR as an on-line method for express analysis of catalytic oxidation of heavy oil residues with the production of bitumen is shown.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
As an object of research, heavy oil residue from atmospheric vacuum distillation of the Elkhovsky oil refinery of PJSC TATNEFT was chosen. The heavy oil residue was characterized by a density of 0.9878 g/cm3 at 20 °C, coking capacity of 8.3 wt %, sulfur content of 0.9 wt %, content of solid alkanes of linear structure (with the number of carbon atoms in a molecule more than 16)–15 wt %. The object of research was chosen due to the urgent task associated with the need to involve in the production of bitumen HRO of paraffin-naphthenic base with high content of solid paraffinic hydrocarbons.
As a catalyst for the oxidation process pyrolusite (0.2 wt % to HRO), comprising of manganese dioxide (80 wt %), iron dioxide and silicon oxide, was used. Also, a mixture of oleic, linoleic and linolenic acids with pentaerythritol in a ratio of 10:1, in an amount of 1.8 wt % to HRO, was introduced before oxidation of HRO as initiators of radical-chain reactions of oxypolymerization. The use of the catalyst and initiating additives shortened the oxidation time of HRO to bitumen (with a softening point of 46 °C) by 40% (EN 12591).
2.2. Experiments
The oxidation process of HRO was carried out in a laboratory batch unit. The installation consists of a heated reactor; air supply and flow control systems equipped with a pressure gauge, receiver and compressor; gas purification systems for absorption of hydrogen sulfide and sulfur compounds with an alkaline solution, as well as condensation of water vapor and organic compounds released during oxidation. The reactor is a vertical cylindrical hollow apparatus with a device for uniform air distribution (bubbler flask), equipped with a thermocouple, as well as fittings for supplying air entering the bubbler flask for oxidation, removing gases and the final product.
The optimal thermodynamic conditions for the oxidation of HRO in order to obtain bitumen with acceptable compositions and properties were: temperature 250 °C, air flow rate of 2 l/min per kg of raw material, catalyst content 0.2%.
2.3. Analysis
The analysis of component composition was carried out by preliminarily precipitation of asphaltenes from HRO and oxidation products with a 40-fold volume of hexane, then the hydrocarbon part (HC) and resins were isolated by column adsorption-liquid chromatography on ASK silica gel (fraction 0.25–0.5 mm).
The dynamic viscosity of HRO and oxidation products (bitumen) was measured by a Reotest-2 rotary viscometer with a system of coaxial cylinders at the shear rate from 0.15 to 1310 s−1 at 20 °C. The dynamic viscosity was obtained from the measured shear stresses and shear rates.
Softening point of HRO and oxidation products (bitumen) corresponded to the temperature at which the test sample, within a ring of a certain size, softens with increasing temperature and moves to the bottom plate under the action of a steel ball (EN 1427).
Parameters of pulsed nuclear magnetic resonance—relaxation times and populations of phase protons—in HRO and its oxidation products was measured by an automated NMR 03-08 BK/RS relaxometer (TU 25-4823764.0031-90). Carr–Purcell–Meiboom–Gill sequences of superposition of the electromagnetic field (90-τ-180-2τ-...) for measurements of T2i, and (180-τ-90-τ-180) for measurements of T1i were used, the range of measurements of relaxation times varied for T1i—0.0005–100 s, for T2i—0.0001–10 s, start period from 500 ms to 2 s, interval between 90° and 180° impulses 5–1000, number of accumulations n ≥ 50, analysis time did not exceed 3–5 min. P2i presents the relative fraction of hydrogen nuclei in phases (population), defined as the ratio of the amplitudes of the corresponding phases to the amplitude of the signal equal to 0 at t (t is time).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Component Composition and Properties of HRO Oxidation Products
The data obtained indicates a significant effect of the catalyst and initiating additives on the composition and properties of the HRO oxidation products (Table 1). The viscosity of HRO and oxidation products substantially depends on their component composition, primarily, on the content of the main structure-forming components—asphaltenes and resins. During oxidation of HRO, a decrease in the HC content of products is observed, an increase in the content of resins and asphaltenes occurs, whereby, the general nature of the composition–dynamic viscosity ratio remains the same. Changes in the composition of HRO during oxidation can be represented as follows (1):
HC → Asphaltenes

Table 1.
Component composition and physicochemical properties of the initial heavy residual oil (HRO) and its oxidation products.
It is possible that the formation of asphaltenes from HC occurs through resins (2):
HC → Resins → Asphaltenes
It can be concluded that HC and resins are predominantly converted into asphaltenes during oxidation of HRO, but it is difficult to determine unambiguously how this transition occurs: either oils are directly converted into asphaltenes during oxidation, or their transition to asphaltenes occurs through the formation of resins.
Within the duration of the catalytic oxidation of HRO for 180 min, the concentration of HC in the products decreased from 76.0 wt % up to 52.0 wt %, within 300 min from 76.0 wt % up to 52.2 wt %, while in the control experiment (without catalyst), from 76.0 wt % up to 70.1 wt % and from 76.0 wt % up to 66.4 wt %, respectively. During the catalytic oxidation of HRO, the time required to obtain bitumen with a softening temperature of 46 °C is reduced from 360 to 180 min. The use of a catalyst and an initiator additive made it possible to significantly reduce the oxidation time, and thus to increase the fuel and energy efficiency. There is a sharp increase in the content of resins and asphaltenes in catalytic oxidation products (Table 1). The scheme for the conversion of HRO components during catalytic oxidation can be represented as follows (3):
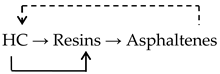

The actual scheme of the catalytic oxidation of HRO may turn out to be more complicated than the one presented; under certain conditions, the reverse process of decomposition of high-molecular to low-molecular compounds is possible, followed by their transformation into heavier components, i.e., during the oxidation of HRO, cyclic processes of interconversion of hydrocarbons occur.
Comparative analysis of the obtained data showed that the softening temperature of the oxidation products changes exponentially, similar to the change in dynamic viscosity. The viscosity of the products of catalytic oxidation of HRO is significantly lower than the viscosity of the products of oxidation of the initial HRO, within equal values of the softening temperature.
3.2. Investigation of the Component Composition of the HRO Oxidation Products Using Pulsed NMR
Investigation of the effect of temperature on changes in the parameters of the spin-spin system makes it possible to quantitatively estimate the molecular mobility of the HRO components and products of its oxidation. Relaxation processes in HRO are largely due to the nature of molecular movements. If these movements are strongly limited, for example, in a viscous state, then the local magnetic fields are weakly averaged, respectively, and the values of the relaxation times T2i are small and amount to several tens of microseconds.
Relaxation processes in such systems depend on the nature of molecular movements, which, in turn, depend on the analysis temperature (abscissa axis on Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4).
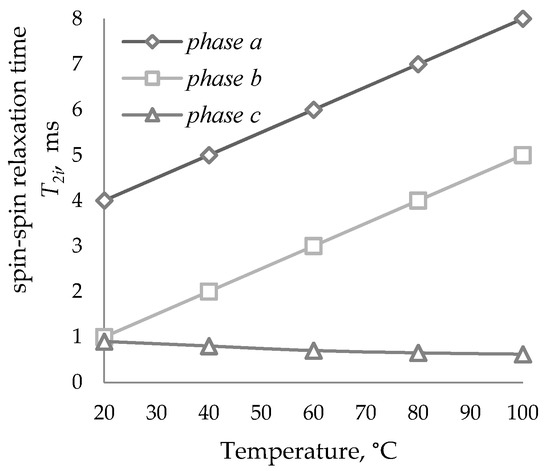
Figure 1.
Spin–spin relaxation time T2i of HRO vs. temperature.
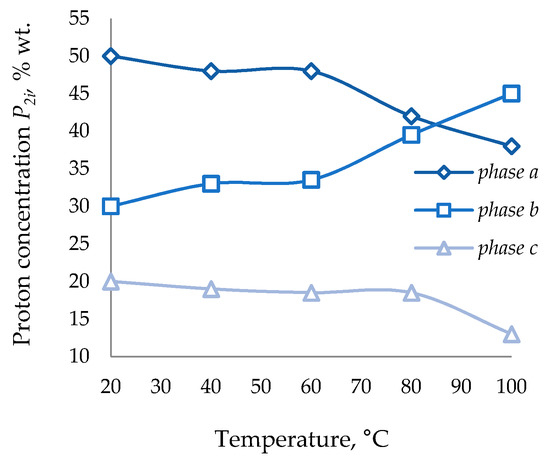
Figure 2.
Proton concentration P2i of HRO vs. temperature.
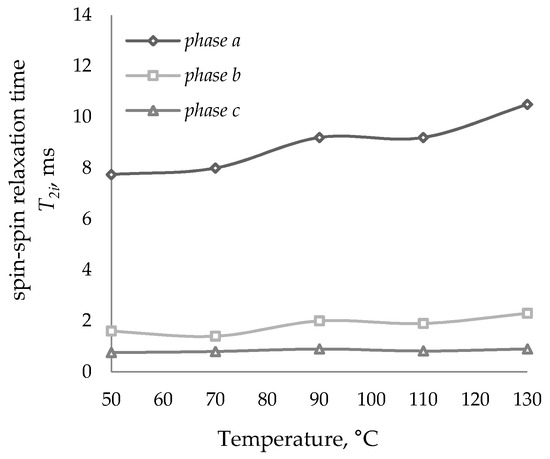
Figure 3.
Spin–spin relaxation time T2i of bitumen vs. temperature.
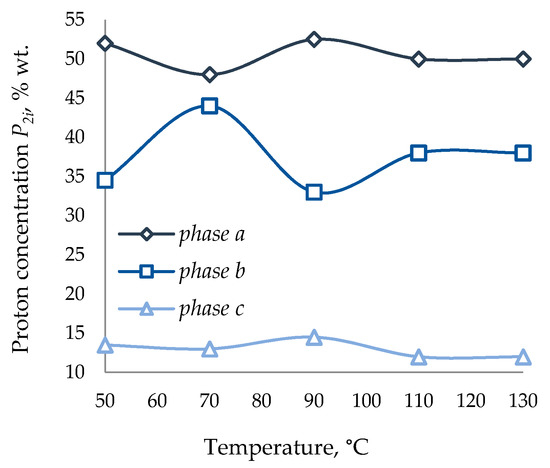
Figure 4.
Proton concentration P2i of bitumen vs. temperature.
The dependence of the echo signal amplitude A(t) on time t is determined by the expression (4). A(t) presents the echo amplitude equal to 0 at t (t is time).
A(t) = A0·e−t/T2i
At temperatures below 20 °C in the bitumen sample, the molecular mobility is so low that the sample is characterized by constant relaxation time. At temperatures above 50 °C for bitumen samples (oxidation products), due to an increase in the intensity of molecular movements and averaging of local magnetic fields, the value of T2i increases, and the dependence of the spin–spin relaxation time on the experimental temperature is observed, whereby three phases are found in the samples.
When three phases are present, the dependence of the echo signal amplitude on time is determined by expression (5):
where A10, A20 and A30 present the amplitudes of the echo signal from individual phases at t = 0.
A(t) = A10·e−t/T2a + A20·e−t/T2b + A30·e−t/T2c
Considering that the signal amplitudes are proportional to the number of magnetic nuclei in phases, we introduce Equation (6):
Pa = A10/(A10 + A20 + A30), Pb = A20/(A10 + A20 + A30), Pc = A30/(A10 + A20 + A30)
Then expression (5) will take the following form (7):
where P2i is the relative fraction of hydrogen nuclei in phases (populations), defined as the ratio of the amplitudes of the corresponding phases to the amplitude value of the signal A0 equal to 0 at t (t is time).
f(t) = P2a·e−t/T2a + P2b·e−t/T2b + P2c·e−t/T2c
The relaxation curves of HRO and the oxidation product (bitumen) with a boiling point of 46 °C are represented by three phases with different values of the proton phase populations, varying in molecular mobility. For each of the phases, the spin–spin relaxation time T2i and the population (concentration) of protons P2i were determined (Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4).
In such systems, three relaxation times are observed and, as a consequence, three phases: T2a—the most mobile molecules (HC); T2b—resins; T2c—asphaltenes. An indispensable condition for the phase correlation is the determination of the true values of the population of protons of phases (there should be a difference in the relaxation times of at least two to three times; the selection of the appropriate temperature at which the molecular mobilities in the phases differ most in intensity; the constancy of the population values in a fairly wide temperature range).
At higher temperatures, due to an increase in the intensity of molecular movements and averaging of local magnetic fields, the values of T2i increase, in addition, a strong dependence of the relaxation time on the temperature is observed.
The temperature vs. relaxation time and proton concentration curves are characterized by a non-monotonous increase in the relaxation time with an increase in the sample heating temperature, but by discrete values. Thus, as the temperature rises, the relaxation time of the initial HRO increases; molecular mobility increases, the ratio of the Pa and Pb phases changes proportionally, the proton concentration of the molecularly least mobile phase with a short relaxation time T2c practically does not change. However, an insignificant decrease in the spin–spin relaxation of the T2c phase coincides with a decrease in the proton concentration Pc, which is associated with the transition of the most mobile molecules to the b phase with a decrease in T2b.
With a temperature increase of pulsed nuclear magnetic resonance, the observed degree of increase in the values of the relaxation time T2i for HRO and bitumen differ several times. This can be explained by changing component composition of HRO during its oxidation to bitumen, namely, an increase in the concentration of high-molecular compounds and an increase in intermolecular interactions, which is reflected in the molecular mobility of spin systems. At the temperatures of analysis, the values of the shortest relaxation times T2c for HRO and bitumen are close, which may indicate the molecular similarity and constancy of this phase in the samples under study.
Phases a, b, and c characterize HRO compounds of high, medium, and low molecular mobility, respectively. Based on the component composition of HRO, phase a, in accordance with large values of relaxation times, characterizes the most mobile oil molecules (HC), phase b describes less mobile resin molecules, phase c, due to the shortest values of spin–spin relaxation times, characterizes asphaltene compounds.
To correlate phases obtained by pulsed NMR spectroscopy with the component composition, the following conditions must be met:
- At least two-times difference of relaxation time T2i of phases,
- No substantial changes in the values of proton concentration P2i of phases in a fairly wide temperature range.
For HRO, the concentration of the P2a and P2b phases are practically constant in the temperature range of 40–60 °C, and the concentration of the P2c phase in the range of 60–80 °C.
However, the constant P2 value, which is responsible for the true content of oil, resin and asphaltenes, as the duration of the oxidation process increases with an increase in the softening point of the obtained bitumen, shifts to the region of higher experimental temperatures. So, for bitumen with a softening point of 46 °C, a constant value of P2 was observed in the temperature range of 110–130 °C. With an increase in the duration of the oxidation process, the reaction products accumulate asphaltenes (phase Pc) with a slight change in the concentration of resins (phase Pb), with a sharp decrease in the content of hydrocarbons in oils (phase Pa). An increase in the oxidation time is accompanied by a decrease in the concentration of phase a protons, and an increase in the concentration of protons in phases b and c (Figure 5). Comparison of the results of the analysis of the quantitative component composition of HRO, determined by adsorption liquid chromatography and by pulsed NMR spectroscopy, allows us to conclude that their convergence is quite good (Table 1).
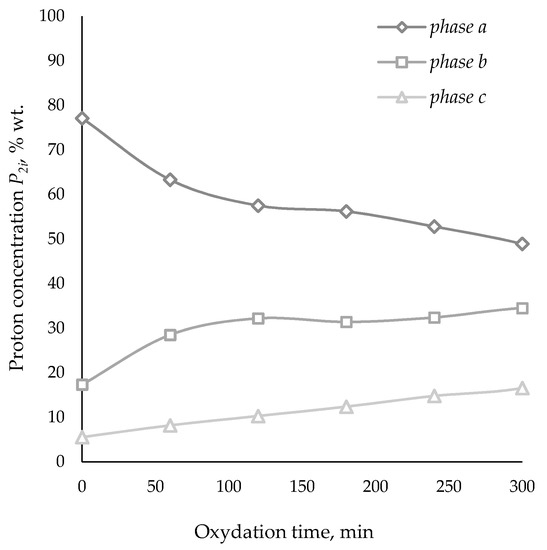
Figure 5.
Proton concentration P2i of catalytic oxidized products of HRO vs. time.
An increase in the viscosity of oxidation products of HRO with an increase in the duration of the process is due to an increase in the content of resins and asphaltenes in them and to a high degree of their association with the formation of a rather strong structure, as evidenced by a decrease in the spin–spin relaxation time of phases. Pulsed NMR parameters (spin–spin relaxation time T2i and proton concentration P2i) reflect thermodynamic properties of components of the HRO oxidation products, and depend on their dynamic viscosity. The viscosity of the HRO oxidation products is defined by the composition and mobility of components: HC, resins and asphaltenes. An inverse dependence of the viscosity and molecular mobility of components of HRO oxidation products is observed (Figure 6).
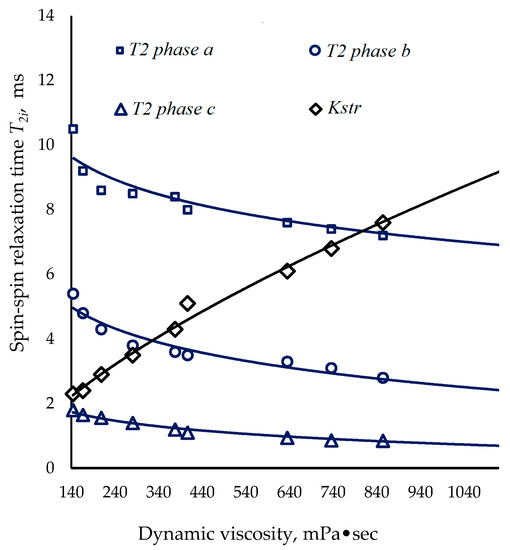
Figure 6.
Spin–spin relaxation time T2i vs. dynamic viscosity of HRO oxidation products.
For a quantitative assessment of the mobility of the components of bitumen and its oxidation products (HC, resins and asphaltenes) based on the obtained NMR parameters, an auxiliary coefficient Kstr (8) was proposed, reflecting the mass ratio of each of the phases (i) with their spin–spin relaxation time T2i. For the oxidation products of HRO, the proton concentrations are associated with spin–spin relaxation by an inverse relationship:
Studies of a large number of bitumen samples and their oxidation products with a known viscosity revealed a direct dependence of the viscosity on the auxiliary coefficient Kstr, described by a function (9):
The resulting regression Equation (9) makes it possible to determine the viscosity of HRO and oxidized bitumen by NMR parameters.
The present research has shown the possibility of using pulsed NMR as an on-line express analyzer of intermediates and products of the oxidation of heavy oil residues.
4. Conclusions
The high value of information capacity of nuclear magnetic resonance on the properties of test samples, the comparative simplicity of the experimental determination of these parameters, as well as the reliability of the theoretical interpretation of the data, make it possible to single it out as an independent informative physical research method.
The study of heavy oil residue and its oxidation products was carried out by pulsed NMR. The pulsed NMR method makes it possible to identify the component composition of HRO and oxidized bitumen by phases differing in the molecular mobility of hydrocarbons and proton concentrations Pi. The relationship between the parameters of pulsed NMR and the component composition and viscosity of HRO and oxidation products has been established.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.I.C., A.V.V.; investigation, G.G.I.; resources, N.Y.B., G.G.I.; writing—original draft preparation, A.G.S., S.M.P.; writing—review and editing, S.M.P., N.Y.B., A.V.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Russian Science Foundation, grant number 18-77-10023.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gridneva, E.S.; Bulychev, N.A. Improving the quality of petroleum products by ultrasonic action. Chem. Pet. Eng. 2012, 48, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauste, R.; Moreno-Navarro, F.; Sol-Sánchez, M.; Rubio-Gámez, M.C. Understanding the bitumen ageing phenomenon: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 192, 593–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Birgisson, B.; Kringos, N. Polymer modification of bitumen: Advances and challenges. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 54, 18–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polacco, G.; Stastna, J.; Biondi, D.; Zanzotto, L. Relation between polymer architecture and nonlinear viscoelastic behavior of modified asphalts. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 11, 230–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokonova, Y.V. Petroleum Bitumen; Sintez: Saint-Petersburgh, Russia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lakhova, A.I.; Petrov, S.M.; Zakieva, R.R.; Ibragimova, D.A.; Baibekova, L.R.; Isakov, D.R. Impact of the Group Content on the Properties of Bitumen of Different Grades. Res. J. Appl. Sci. 2015, 10, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baibekova, L.R.; Petrov, S.; Mukhamatdinov, I.; Burnina, M.A. Polymer Additive Influence on Composition and Properties of Bitumen Polymer Compound. Int. J. Appl. Chem. 2015, 11, 593–599. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, S.L.; Silva, A.M.S.; Ribeiro, J.C.; Martins, F.G.; Da Silva, F.A.; Silva, C.M. Chromatographic and spectroscopic analysis of heavy crude oil mixtures with emphasis in nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 707, 18–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Bai, L.; Chi, Y.; Jia, R.; Fu, X.; Yang, L. Geochemical characterization and quantitative evaluation of shale oil reservoir by two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance and quantitative grain fluorescence on extract: A case study from the Qingshankou Formation in Southern Songliao Basin, northeast China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 109, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, D.; Kowalczyk, R.M.; Collins, C.D. Characterisation of oil sludges from different sources before treatment: High-field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) in the determination of oil and water content. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 174, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, V.G.; Bastos, T.M.; Sad, C.M.S.; Leite, J.S.D.; Castro, E.R.V.; Barbosa, L.L. Application of low-field nuclear magnetic resonance to assess the onset of asphaltene precipitation in petroleum. Fuel 2020, 265, 116955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashman, A.A.; Pronin, I.S. Nuclear Magnetic Relaxation and Its Application in Chemical Physics; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Kashaev, R.S. Science and education development on the base of interdiciplinary approach to use of fundamental and universal method of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Adv. Curr. Nat. Sci. 2011, 2, 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Maklakov, A.I.; Dvoyashkin, N.K.; Tyurin, V.A. Nuclear magnetic resonance: The study of porous media and fluids injected into them. Georesursy 2001, 1, 28–30. [Google Scholar]
- Petrov, S.M. Multifunctional Modifiers for Obtaining Oxidized Road Bitumen with Improved Properties; Kazan State Technological University: Kazan, Russia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).