Abstract
Shale oil, a major unconventional energy source with extensive global reserves, presents significant processing challenges due to the exceptional stability of its emulsions. Characterized by small droplet sizes and high interfacial film strength, these emulsions resist efficient treatment via conventional thermal-chemical or electrostatic dehydration. To address the difficulties in separation, unclear dehydration mechanisms, and inconsistent single-field (electric) performance, this study investigates dehydration using a novel electric–magnetic–ultrasonic coupling field system. Dehydration efficiency under an electric field alone increased with electric field strength, frequency, duration, and temperature. Magnetic or ultrasonic fields alone yielded negligible effects. Coupling an electric field with ultrasound enhanced efficiency, while adding a magnetic field to electricity provided no improvement and decreased efficiency with longer exposure or higher magnetic intensity. The multi-field coupling achieved significant demulsification. Both optimal dehydration performance and minimum energy consumption operating conditions were identified, capable of reducing shale oil water content below 0.5%.
1. Introduction
Shale oil has become an increasingly critical unconventional resource and a critical successor to traditional petroleum resources, diversifying global energy supplies. Its strategic importance and expanding applications solidify its vital role within the world’s evolving energy landscape [1]. However, due to the unique geological storage conditions of shale oil and the specialized fracturing development methods, the produced fluid contains fracturing flowback fluids composed of complex agents such as active water, crosslinking agents, thickeners, and gel breakers [2,3]. Additionally, shale oil itself exhibits characteristics of high pour point, high wax content, and high wax appearance point [4], resulting in shale oil emulsions with fracturing flowback fluids that have small droplet sizes, high oil–water interface strength, and extremely strong stability [2,5]. Currently, the primary dehydration methods for shale oil produced fluids containing fracturing flowback fluids are thermochemical dehydration [6,7] and electric dehydration [8,9]. Given the strong emphasis on national environmental protection policies [10,11] and the implementation of the “green electricity” project in oilfields [12], physical methods that utilize low-cost electrical energy are currently more favorable than chemical demulsification methods, which pose greater risks of environmental pollution in the treatment of shale oil emulsions. Moreover, field applications have revealed that traditional thermochemical dehydration suffers from issues such as high operational energy consumption, large amounts of demulsifier usage, and prolonged dehydration time [13,14]. However, traditional physical methods, such as electric dehydration, face problems of unstable electric fields and fluctuating dehydration efficiency [15,16]. Therefore, achieving efficient and stable dehydration of shale oil-produced fluids with fracturing flowback fluids represents a critical technical challenge urgently requiring resolution in the field of surface engineering for unconventional crude oil development.
High-frequency pulsed electric dehydration technology has emerged as a promising research direction for efficient crude oil demulsification, with several researchers conducting related investigations. Niu et al. [17] developed the HTA series rectangular wave alternating current pulsed power supply with continuously adjustable voltage, frequency, and duty cycle using a secondary inverter transformer boosting method. Combined with offshore crude oil, laboratory static and dynamic dehydration tests were conducted, determining the optimal frequency range to be 4300~4500 Hz. Jin et al. [18] proposed that due to the capacitive load characteristics of oil–water emulsions, lower pulse frequencies result in larger emulsion capacitances and lower voltages across the emulsions, while higher frequencies increase the applied voltage and electric field strength, thereby promoting droplet coalescence. Chen et al. [19] developed a high-frequency pulsed crude oil dehydration power supply based on three-phase full-bridge controlled rectification and IGBT full-bridge inversion, with adjustable frequencies ranging from 1 kHz to 5 kHz. Field tests in a Daqing Oilfield joint station demonstrated its advantages of high dehydration efficiency, energy conservation, and stable operation.
To further enhance dehydration efficiency, researchers have also explored the coupling of electric fields with other physical fields for crude oil dehydration. The excellent performance of ultrasonic fields in enhancing crude oil recovery [20] and preparing nanoemulsions [21] demonstrates their significant impact on the stability of oil–water systems. Moreover, the coupling of ultrasonic fields with electric fields may offer even greater advantages. Bo [22] investigated the dehydration characteristics of crude oil emulsions under the combined action of ultrasonic and electric fields. Under the conditions of an ultrasonic intensity of 0.5 W·cm−2, an ultrasonic frequency of 28 kHz, an electric field strength of 2 kV·cm−1, and a frequency of 1000 Hz, dehydration treatment of a conventional medium-quality crude oil emulsion with a water content of 20% at 60 °C showed that the synergistic effect of acoustic and electric fields outperformed single electric field treatment. Given the unique effect of magnetic fields in reducing crude oil or emulsion viscosity [23,24,25], researchers have been motivated to combine electric and magnetic fields to enhance oil–water separation. Guo et al. [26,27,28] studied the dehydration of water-in-oil emulsions under coupled electric and magnetic fields, finding that the synchronous vertical coupling of electric and magnetic fields exhibited better dehydration performance than sequential application or parallel orientation of the two fields.
Despite the progress in coupled dehydration using electric fields and other physical fields, most current studies focus on conventional crude oils or synthetic model oils, with no reported research on multi-physical field coupled demulsification and dehydration specifically for shale oil. Moreover, the coupling of electric, magnetic, and ultrasonic fields introduces complex and variable oil–water interactions in water-in-oil dispersion systems, and the correlation between multi-field coupling and dehydration efficiency remains inconclusive.
Therefore, this study takes shale oil containing fracturing flowback fluids as the research object and constructs an experimental system for multi-physical field coupling dehydration (electric field-magnetic field-ultrasonic field). The demulsification and dehydration characteristics of shale oil under single-field, dual-field coupling, and multi-field coupling conditions are systematically investigated. By integrating the dehydration performance and mechanisms under different parameters (applied intensity, frequency, and action time) of each physical field, the intrinsic influencing factors of the experimental results are analyzed. Thereby, an optimal combination of multi-physical fields and corresponding operational parameters are proposed, aiming to provide a scientific theoretical foundation for the design and optimization of demulsification and dehydration processes for shale oil.
2. Methodology
2.1. Materials
The shale oil emulsion samples used in this study were collected from a shale oil development block in an oilfield in China. The initial particle size distribution of the shale oil emulsion under 40× magnification is shown in Figure 1. Notably, the shale oil sample exhibits a high water content, with fine and densely distributed water droplets in the oil phase, indicating a high degree of emulsification.

Figure 1.
Micrograph of initial grain size of shale oil samples.
Additionally, the density and viscosity of the shale oil sample were measured using a volumetric flask method and rotational rheometer (RheolabQC, Anton Paar, Graz, Austria), respectively, with the test results shown in Figure 2. Data fitting yielded the density curve formula for the shale oil sample: ρ = −7.88 × 10−4·t + 0.94.
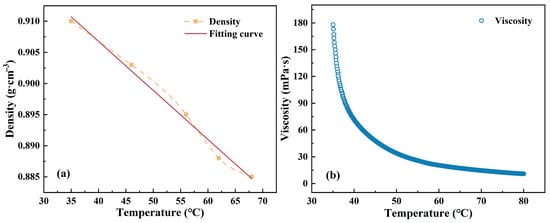
Figure 2.
(a) Density and (b) viscosity of shale oil sample.
To further characterize the emulsification properties of the shale oil sample, the oil–water interfacial tension was measured using a contact angle goniometer (EasyDrop, KrussGmbH, Hamburg, Germany); the zeta potential was determined with a microelectrophoresis instrument (JS94H, Powereach, Shanghai, China); the relative dielectric constant was assessed using a dielectric constant meter (PCM–1A, Nanda Wanhe, Nanjing, China); and the SARA (saturates, aromatics, resins, and asphaltenes) profile and wax content were determined using liquid–solid adsorption chromatography. The results are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Measured values of parameters affecting shale oil emulsification properties.
2.2. Experimental Setup
The electric–magnetic–ultrasonic field coupling dehydration experimental system employed in this study is shown in Figure 3. The AC power supply (HTD Inverter, Sailang Health and Environmental Technology Co., Ltd., Lanzhou, China) is connected to the upper electrode plate of the experimental cell, with the lower plate grounded, thereby generating a high-frequency pulsed electric field along the Z-axis direction within the cell. Meanwhile, voltage and current signals of the AC power supply are tracked and monitored by an oscilloscope (TDS1002 B-BC, Tektronix, OR, USA). The maximum output frequency and voltage of the AC power supply are 5 kHz and 7 kV, respectively. The oscilloscope has a bandwidth of 60 MHz and a real-time sampling rate of up to 1 GS/s. It is connected to the current and voltage monitoring ports of the AC power supply via a coaxial cable to measure the waveform, voltage, frequency, and other parameters of the AC power supply output, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the high-voltage electric field.
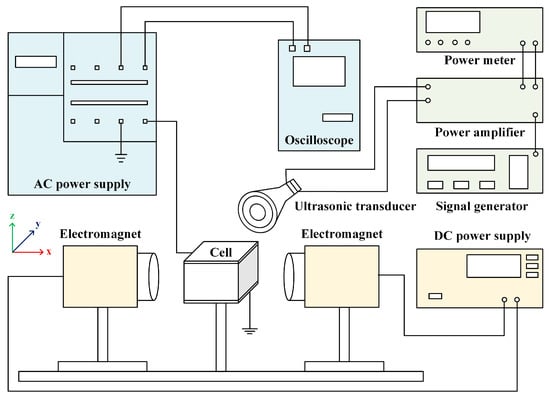
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of electric–magnetic–ultrasonic coupling dehydration experimental system.
The electromagnet (PEM–120AC, Litian Magnetoelectrican Science & Technology Co., Ltd., Mianyang, China) is connected to a DC power supply (JP3067D, ANNAISI, Wuxi, China) to generate a steady magnetic field along the X-axis direction in the sample cell. The electromagnet has a maximum pole face area of 80 mm × 80 mm and a maximum working air gap of 60 mm. Based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, the current source provides current to the electromagnet’s magnetic field coil, generating the magnetic field through the magnetic circuit. By adjusting the size of the pole gap, altering the pole face area, and varying the working current, the magnitude of the magnetic induction strength in the air gap can be modified. Additionally, the electromagnet features a single-clamp C-shaped structure with horizontal water cooling and offers convenient and flexible adjustment of the working air gap. The magnetic poles and pole columns are designed as an integrated structure with sliding connections for easy installation and removal, providing high magnetic induction strength and simplified adjustment of magnetic induction strength levels.
The signal generator (DG2041A, RIGOL, Beijing, China) is linked to the high-voltage amplifier (Model 20/20C, Trek, OR, USA), which supplies voltage to the ultrasonic transducer. The transducer converts electrical signals into ultrasonic waves, producing an acoustic wave field along the Y-axis in the sample cell, with power signals during this process monitored by a power meter (3332, HIOKI, Tokyo, Japan). The signal generator utilizes Direct Digital Synthesis (DDS) technology, with a sampling rate of 100 MSa/s, 14-bit vertical resolution, a storage depth of 512K sampling points, and a maximum output frequency of 40 MHz. It is connected to the signal input terminal of the high-voltage power amplifier via a coaxial cable, delivering basic low-voltage signals in the form of DC, AC, pulse, and square waveforms to the amplifier. The high-voltage power amplifier amplifies the low-voltage signal by a factor of 2000 before output. The output voltage range is from 0 to ±20 kV, with an output current range of 0 to ±20 mA. The output voltage error is less than 0.1%, and the output noise is less than 1.5 V (root mean square value). When the signal frequency exceeds 3.75 kHz, the distortion rate is 1%. The maximum input voltage for the high-voltage power amplifier must not exceed 10 V. This power meter is capable of accurately measuring the active power, reactive power, and total power of high-frequency signals from ultrasonic transducers.
Through the above experimental system, the application of electric–magnetic–ultrasonic coupling fields to the shale oil emulsion in the sample cell is realized.
2.3. Performance Evaluation Indicators
In this study, the water content φ and relative dehydration rate η were adopted to evaluate the dehydration performance of shale oil under external physical fields. The specific calculation formulas are as follows:
where m1 and m2 denote the masses of water and oil in the shale oil emulsion, respectively, in mg; V1 and V2 represent the initial total water volume and the separated water volume after dehydration sedimentation in the shale oil emulsion, respectively, in mL. All error bars in the dehydration experiments are derived from the standard deviation of three replicate experiments.
3. Results
3.1. Dehydration Characteristics of Shale Oil Emulsion Under a Single Physical Field
Electrodehydration is one of the most commonly used physical methods for treating oil-in-water emulsions in oilfields. Among the various factors, electric field strength plays a crucial role in determining the efficiency of electrocoalescence [13,29]. The dehydration performance of shale oil emulsions under a single electric field is shown in Figure 4. As indicated in Figure 4a, the water content of shale oil decreases continuously with increasing electric field strength. Notably, the reduction amplitudes of both water content and relative dehydration rate are relatively low at electric field strengths below 100 kV·m−1 and above 200 kV·m−1, while significant decreases occur in the range of 100~200 kV·m−1. At electric field strengths below 100 kV·m−1, the electrostatic forces between droplets are insufficient to overcome resistance forces such as viscous drag, resulting in low collision–coalescence efficiency. When the electric field strength reaches 100~200 kV·m−1, the enhanced electrostatic forces increase droplet deformation, reduce oil–water interfacial tension, and promote sufficient collision–coalescence of adjacent water droplets, leading to significant improvements in dehydration efficiency. However, little change in relative dehydration rate is observed at electric field strengths above 200 kV·m−1. Therefore, considering both dehydration efficiency and power consumption, the optimal electric field strength is determined to be 200 kV·m−1.
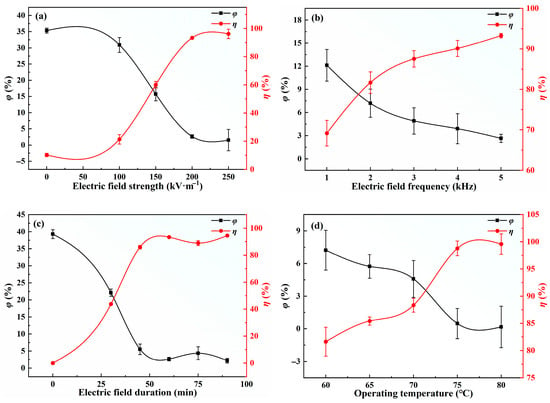
Figure 4.
Shale oil dehydration characteristics under a single electric field: (a) effect of electric field strength, (b) effect of electric field frequency, (c) effect of electric field duration, (d) effect of operating temperature.
In an alternating electric field, the electric field frequency is closely related to the charge induction rate on the droplets, their dynamic response characteristics, and the critical coalescence conditions, all of which can significantly influence the efficiency of droplet electrocoalescence [30,31,32]. Therefore, it is essential to examine the impact of electric field frequency on dehydration performance. Figure 4b demonstrates that the relative dehydration rate increases with increasing electric field frequency, confirming the superiority of high-frequency dehydration. The optimal electric field frequency is identified as 5 kHz.
In practical field applications, processing time and operating temperature often dictate the design parameters of the dehydrator, which are directly linked to energy consumption and economic efficiency [33]. Therefore, examining the impact of electric field duration and operating temperature on dehydration performance provides valuable practical insights for real-world applications. As shown in Figure 4c, within the first 60 min, the relative dehydration rate increases rapidly with prolonged electric field exposure, indicating continuous improvement in dehydration efficiency. However, after 60 min, the relative dehydration rate fluctuates periodically, suggesting an optimal energization duration. This phenomenon may be attributed to the ultra-high-frequency transformer accelerating droplet oscillation-coalescence and dipolar coalescence, enabling rapid formation of large droplets for sedimentation within short timeframes. Prolonged electric field application beyond 60 min may induce “electrodispersion,” where large droplets fragment into micro-droplets, reducing the average droplet size and consequently decreasing the relative dehydration rate [34]. Thus, considering dehydration efficiency and energy consumption (electrical/thermal), the optimal electric field action time is determined to be 60 min. According to Figure 4d, the relative dehydration rate increases with temperature rise due to reduced oil viscosity facilitating droplet coalescence-sedimentation. When the temperature reaches 75 °C, the water content drops below 0.5%, making further temperature elevation unnecessary. Therefore, the optimal operating temperature is established as 75 °C after balancing dehydration performance and thermal energy loss.
The dehydration results of shale oil under a single magnetic field and a single ultrasonic field are presented in Table 2. The intensities of both the magnetic field and ultrasonic field were set to the maximum output intensities of the electromagnet and ultrasonic transducer in the experimental system. According to the results, both single magnetic field and single ultrasonic field exhibited limited dehydration efficiency for the shale oil sample, with performance comparable to that of conventional gravitational sedimentation. Thus, a magnetic field or an ultrasonic field alone cannot be used as a standalone treatment method for shale oil dehydration.

Table 2.
Results of shale oil dehydration under a single magnetic field and a single ultrasonic field.
3.2. Dehydration Characteristics of Shale Oil Emulsion Under Dual Physical Fields
Based on the dehydration results of single physical fields, the electric field exhibited the best demulsification-dehydration performance for shale oil, while single magnetic and ultrasonic fields showed negligible dehydration efficiency. Thus, to further investigate the dehydration characteristics of shale oil under dual physical field coupling, the electric field was adopted as the primary action field, with magnetic and ultrasonic fields serving as auxiliary regulating fields.
Campos-Sofia et al. [35] were the first to apply electric–magnetic coupling fields for treating oil-in-water emulsions. Their research demonstrated that electric–magnetic coupling field effectively promoted the coalescence of water droplets in oil, thereby enhancing the separation efficiency. Building on this, Guo et al. [26,27,28] conducted extensive research and discovered that the magnetic field and magnetic induction strength, as flexible magnetic field parameters, significantly influence the dehydration performance of electric–magnetic coupling field. Therefore, experiments on the dehydration characteristics of shale oil under electric–magnetic coupling fields were conducted. The specific external field settings were as follows: at 70 °C, the electric field parameters were fixed at 150 kV·m−1, 5 kHz, and a duration of 45 min. The magnetic field was applied perpendicularly to the electric field direction, with magnetic field strength and synchronous action time set as research variables. The final water content of the shale oil emulsion after coupled field treatment is shown in Figure 5. Notably, compared with the dehydration performance of the single electric field under the same operating conditions, the coupling of the magnetic field did not significantly enhance dehydration efficiency. Moreover, the dehydration efficiency first increased and then decreased with prolonged magnetic field exposure, while increasing magnetic field strength deteriorated dehydration performance. The mechanism by which electric–magnetic coupling fields enhance droplet coalescence involves altering the structure of the double electric layer in the droplets by influencing ion migration and accumulation, as well as the orientation of surface-active substances [5,36,37,38]. This reduces the steric hindrance to coalescence and increases the electric field strength. However, at the same time, the electric–magnetic coupling field also slows the internal flow field within the droplets by strengthening the ion hydration effect, which in turn reduces the evolution rate of the liquid bridge during droplet coalescence [39,40,41]. This effect is likely to exacerbate the instability of droplet coalescence, thereby diminishing the efficiency of shale oil dehydration in the experiment. It is important to note that the negative impact of the electric–magnetic coupling field on liquid bridge dynamics is typically more pronounced at low electric field strengths. In practical demulsification applications, the coupling field parameters can be adjusted in conjunction with droplet dynamics parameters from the literature [5,36,37,38,39,40,41] to minimize the negative effects of the electric–magnetic coupling field while enhancing its positive influence on droplet coalescence efficiency.
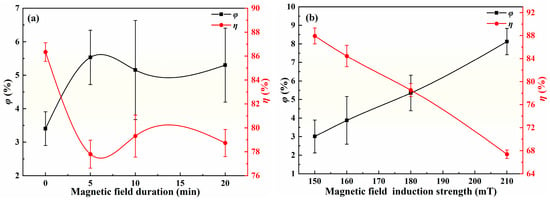
Figure 5.
Shale oil dehydration characteristics under electric–magnetic coupling field (a) effect of magnetic field duration, (b) effect of magnetic induction strength.
Aside from the research by Bo et al. [22], no other studies have explored the use of coupled electric and ultrasonic fields for emulsion breaking. However, the study of Luo et al. [42] on ultrasonic field-based emulsion breaking highlighted the critical influence of ultrasonic duration and intensity on oil–water separation efficiency. Given the potential advantages of the electro-ultrasonic coupled field for demulsification of oil-in-water emulsions, further studies were conducted on the dehydration characteristics of shale oil emulsions under the influence of this coupled field. The specific external field configuration was as follows: at 70 °C, the electric field was fixed at 150 kV·m−1, 5 kHz, and a duration of 45 min. The ultrasonic field was applied perpendicularly to the electric field direction, with experimental results shown in Figure 6. Notably, coupling an ultrasonic field with the electric field significantly enhanced the dehydration efficiency of shale oil. This is attributed to the stripping effect of ultrasonic waves, which causes droplets to accumulate at the wave peaks and troughs of the ultrasonic field [43]. This phenomenon increases the probability of droplet contact and coalescence, thereby effectively improving droplet coalescence–sedimentation efficiency.
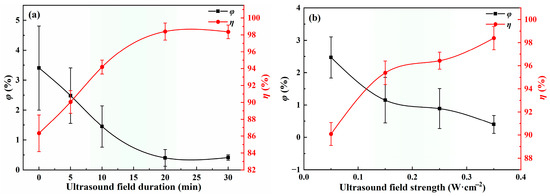
Figure 6.
Shale oil dehydration characteristics under electric-ultrasonic coupling field (a) effect of ultrasonic field duration, (b) effect of ultrasonic field strength.
3.3. Dehydration Characteristics of Shale Oil Emulsion Under Multiple Coupled Fields
Based on the dual-field coupling dehydration experiments, the electric-ultrasonic field coupling exhibited superior performance over electric–magnetic field coupling. To further develop an optimal demulsification-dehydration approach and explore the highest dehydration efficiency, studies on the dehydration characteristics of shale oil under tri-field coupling (electric–magnetic–ultrasonic fields) were conducted. Five operating conditions that met the shale oil export water content standard (φ < 0.5%) were screened out, with results listed in Table 3. As shown in the dehydration results, synchronous coupling of electric, magnetic, and ultrasonic fields significantly reduced the water content of shale oil. As shown in Figure 7, a comparison of the dehydration performance of single electric fields and dual-field systems under identical working conditions reveals that the electric–magnetic–ultrasonic coupling field consistently achieves the highest relative dehydration rate. Notably, for conditions with low processing temperatures (T < 75 °C), the dehydration performance of multi-field coupling is significantly superior to that of other fields. This highlights the potential advantages of multi-field coupling technology in the low-temperature, low-energy consumption dehydration treatment of shale oil.

Table 3.
Qualified electric–magnetic–ultrasonic coupling field processing parameters.
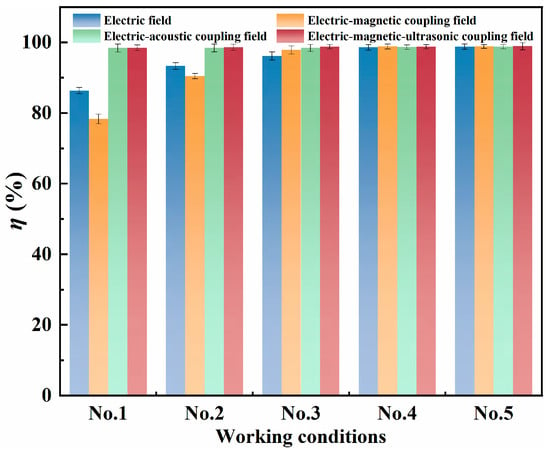
Figure 7.
Comparison of dehydration performance between single-field, dual-field, and multi-field processes.
Additionally, the relative dehydration rates under the five operating conditions were compared, as shown in Figure 8. Condition No. 5 was identified as the optimal dehydration performance case, with detailed parameters: electric field strength of 250 kV·m−1, frequency of 5 kHz, duration of 60 min; magnetic field strength of 210 mT, duration of 10 min; ultrasonic field intensity of 0.35 W·m−2, duration of 20 min; and operating temperature of 80 °C. However, considering operational energy consumption in engineering applications, Condition No. 1 was determined as the optimal energy-efficient case after comprehensive analysis of potential energy consumption under all conditions. Its parameters are as follows: electric field strength of 150 kV·m−1, frequency of 5 kHz, duration of 60 min; magnetic field strength of 210 mT, duration of 10 min; ultrasonic field intensity of 0.35 W·m−2, duration of 20 min; and operating temperature of 70 °C.
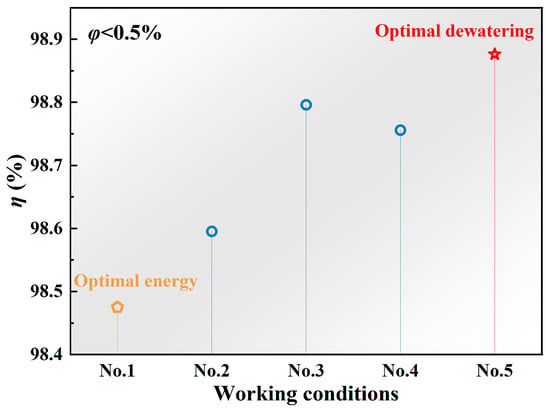
Figure 8.
Comparison of multi-field coupling conditions needed to meet water-content requirements.
3.4. Dehydration Mechanisms Based on the Droplet Force Model Under Multiple Coupled Fields
The optimal dehydration performance of multiple coupled fields is attributed to water droplets in oil being simultaneously subjected to the combined action of electric field force, main sound force, and polarized electromagnetic force under tri-field coupling [26,36,37], which complicates droplet migration trajectories and significantly increases the probability of droplet contact and coalescence, as illustrated in Figure 9.
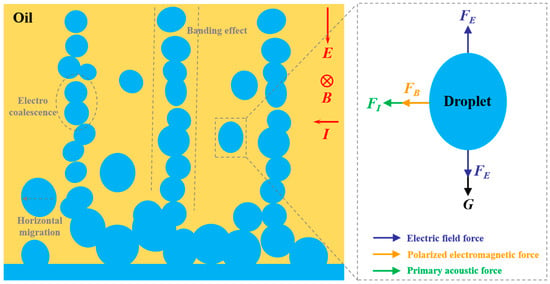
Figure 9.
Dehydration mechanism diagram under electric–magnetic–ultrasonic coupling field.
Specifically, for a single droplet subjected to an alternating electric field, opposite charges are induced at both ends of the droplet along the direction of the electric field. Under the influence of the electric field force FE-de, the droplet’s surface is stretched, causing deformation along the field direction. Additionally, due to the alternating nature of the electric field, the force acting on the droplet’s surface periodically reverses, resulting in oscillatory deformation.
For two or more droplets, the surface charges of adjacent droplets are always opposite, leading to mutual attraction under the influence of dipole forces FE-di. As the droplets move closer together and eventually make contact, they coalesce due to the capillary pressure difference. According to Stokes’ law [44], the larger droplets formed upon coalescence are more likely to settle under gravity, facilitating oil–water separation. The electric field force for droplet deformation FE-de and inter-droplet attraction FE-di are described by Equations (3) and (4), respectively [45,46].
where ε0 and ε represent the vacuum dielectric constant and the relative dielectric constant of the dispersed phase (droplets), respectively; E represents the electric field strength; r is the radius of the droplets; d is the diameter of the droplets; S is the distance between droplets. The expression for the coefficient k is as follows:
When an electric field is applied to an emulsion, the highly polar water molecules in the droplets undergo orientation polarization, generating a polarization current. When a magnetic field is synchronously coupled perpendicular to the electric field, this polarization current interacts with the magnetic field to produce a polarization electromagnetic force perpendicular to the direction of the electric field. Since the electric field is alternating, the polarization current within the droplets periodically reverses direction, causing the resulting polarization electromagnetic force FB to also periodically reverse. This leads to the droplets undergoing continuous lateral displacement perpendicular to the electric field direction.
Compared to a single electric field, the additional lateral displacement of droplets in the electric–magnetic coupling field increases the likelihood of droplets approaching or colliding with each other. This enhanced movement makes it easier for droplets to be attracted by dipole forces or to directly contact and coalesce, thereby effectively promoting droplet sedimentation and oil–water separation. The polarized electromagnetic force FB is presented in Equation (6) [26].
where B is the magnetic induction intensity, ξ is the transient polarization coefficient, e is the element charge, Vi is the volume of a water molecule, and Δt is the steering time of dipoles.
Additionally, due to differences in density and compressibility between the droplets and the continuous phase, the droplets will migrate to the pressure wave nodes or antinode planes under the influence of the primary acoustic force FI in the standing wave field. This causes a significant accumulation of droplets at the wave nodes and antinodes, resulting in the so-called banding effect. In these accumulation zones, the probability of droplet coalescence increases, facilitating droplet aggregation and settling, and thereby promoting oil–water separation. The primary acoustic force FI is as follows [47]:
where λ is the wavelength of the continuous phase (oil phase); Uac is the sound field energy density; κ is the acoustic swimming coefficient; and z is the distance between the droplet and the pressure wave node.
4. Discussion
This study presents an innovative emulsion-breaking process based on the coupling of electric, magnetic, and ultrasonic fields for the first time, which is applied to shale oil emulsion dehydration, demonstrating exceptional oil–water separation performance.
The multi-field coupling enhanced emulsion breaking method proposed in this work builds upon electrodehydration. Electrodehydration, particularly electrostatic coalescence, has been a widely utilized physical dehydration method in major oilfields for many years, owing to its environmental and efficiency advantages [13,29]. Recent advancements in high-frequency and ultra-high-frequency electro-dewatering technologies have further expanded the potential of this approach [31]. However, when applied to high-mineralization emulsions stabilized by displacement agents and natural emulsifiers, the efficiency and depth of electrostatic coalescence often remain suboptimal. This limitation has led to the development of various coupled-field dehydration technologies based on electrodehydration.
Research has demonstrated that electric–magnetic coupling field dehydration, which synchronously applies electric and magnetic fields in a perpendicular configuration, can significantly improve the dehydration efficiency of shale oil [26,27,28,35]. However, this technique often exacerbates instability during droplet coalescence, which constrains the range of feasible operating parameters for electric–magnetic coupling fields [39,40,41]. Electro-acoustic coupled dehydration, another promising method, is also considered a potentially efficient dehydration technique [22]. However, research on the characteristics and underlying mechanisms of electro-acoustic dehydration is still in its infancy, impeding the widespread development and application of this technology.
In summary, the electric–magnetic–ultrasonic coupling field dehydration technology introduced in this study offers an effective solution to the aforementioned challenges. It holds considerable promise for the design and optimization of green, efficient, stable, and highly adaptable demulsification systems.
5. Conclusions
This study constructed a multi-physical field coupling dehydration experimental system to investigate the demulsification-dehydration characteristics of shale oil emulsions under single-field, dual-field coupling, and tri-field coupling conditions. Under single electric field action, the dehydration efficiency of shale oil increased with increasing electric field strength, frequency, action time, and operating temperature. In contrast, single magnetic and ultrasonic fields showed negligible dehydration capacity, comparable to gravitational sedimentation. In electric–magnetic coupling fields, dehydration efficiency decreased with increasing magnetic field strength, attributed to the magnetic field delaying liquid bridge evolution during droplet coalescence. Conversely, electric–ultrasonic coupling significantly enhanced dehydration efficiency due to the stripping effect of ultrasonic waves, which promoted droplet accumulation at acoustic wave peaks/troughs to increase collision–coalescence probability. For electric–magnetic–ultrasonic tri-field coupling, five operating conditions meeting the shale oil export water content standard were screened. The tri-field coupling demonstrated significantly higher dehydration efficiency than single/dual fields. The optimal dehydration performance was achieved at an electric field strength of 250 kV·m−1, a frequency of 5 kHz, and a duration of 60 min; a magnetic field strength of 210 mT and a duration of 10 min; an ultrasonic field intensity of 0.35 W·m−2 and a duration of 20 min; and an operating temperature of 80 °C. Considering practical energy consumption, an optimized low-energy scheme was identified: an electric field strength of 150 kV·m−1, a frequency of 5 kHz, a duration of 60 min; a magnetic field strength of 210 mT, a duration of 10 min; an ultrasonic field intensity of 0.35 W·m−2, a duration of 20 min; and an operating temperature of 70 °C. These results provide critical insights for enhancing shale oil demulsification mechanisms and guiding the design/optimization of multi-field coupling dehydration equipment in unconventional oil development. Future research will focus on conducting a comprehensive techno-economic and environmental impact evaluation of multi-field coupled dehydration processes to further assess their economic feasibility and potential for wider adoption.
Author Contributions
Y.L.: supervision, visualization, funding acquisition, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. Q.H.: investigation, conceptualization, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. Q.L.: formal analysis, validation. Z.L.: project administration, resources. D.Y.: methodology, funding acquisition. M.L.: data curation, investigation. B.L.: conceptualization, supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the [China National Petroleum Corporation Technology Project] grant number [2024DJ26]; the [Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province] grant number [ZR2024ME039]; the [Taishan Scholar Young Expert Program of Shandong Province] grant number [tsqn202312125]; the [Innovation fund project for graduate student of China University of Petroleum (East China) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities] grant number [25CX04013A]. The APC was funded by the [China National Petroleum Corporation Technology Project] grant number [2024DJ26].
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Yuejiu Liang, Qian Huang, Qing Li, Zhibiao Li, Donghai Yang, Mofan Li and Bing Liang were employed by the company China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC). The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Sun, H.; Li, T.; Li, Z.; Fan, D.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhong, J.; Yao, J. Shale oil redistribution-induced flow regime transition in nanopores. Energy 2023, 282, 128553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Lin, F.; Li, X.; Sui, H.; Xu, Z. Interfacial sciences in unconventional petroleum production: From fundamentals to applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5446–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Jiao, X.; Wang, H.; He, W.; Xia, Y. Multiphase fluid-rock interactions and flow behaviors in shale nanopores: A comprehensive review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2024, 257, 104884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, M.; Cheng, X.; Feng, Q.; Yang, F.; He, L. Electrical dehydration performance of shale oil: From emulsification characteristics to dehydration mechanisms. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 676, 132205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Du, L.; Lü, Y.; He, L.; Luo, X.; Bai, Y. Double layer characteristics of droplets dispersed with Na2CO3 in EMSF that is applied to dehydration of Shale oil. Chem. Eng. Process. 2023, 194, 109587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Qi, Y.; Chen, S.; Han, H.; Wang, H.; Gong, X.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Y. Recombination of hydrogen bonds clipping interfacial film effectively for dehydrated tight oil. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 319, 124093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, T.M.; Pottage, M.J.; Tabor, R.F. Graphene Oxide-Stabilized Oil-in-Water Emulsions: pH-Controlled Dispersion and Flocculation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 4529–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Feng, Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, X.; Peng, J.; Feng, M.; Wang, D. An asymmetric AC electric field of triboelectric nanogenerator for efficient water/oil emulsion separation. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Xia, Q.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Pu, L.; Ding, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, E.; Vecitis, D.C.; Gao, G. Electric Demulsification Membrane Technology for Confined Separation of Oil–Water Emulsions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 20277–20288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Weng, S.; Tao, W.; Song, M.; Zhang, L. Measuring carbon neutrality and exploring the threshold effects of its driving factors: Evidence from China. Appl. Energy 2024, 373, 123824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Meng, H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Guo, H. Reversing climate policy stereotypes: Evidence from an energy-dependent region and China’s major economic circles. Appl. Energy 2025, 380, 125026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Hu, L.; Hou, J.; An, T. Green Electricity and Green Hydrogen Demonstration Construction of Yumen Oilfield. China Oil Gas 2024, 31, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Eow, J.S.; Ghadiri, M. Electrostatic enhancement of coalescence of water droplets in oil: A review of the technology. Chem. Eng. J. 2002, 85, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Qi, Y.; Chen, S.; Qiao, Z.; Han, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; et al. Hydrogen bond recombination regulated by strongly electronegative functional groups in demulsifiers for efficient separation of oil–water emulsions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; He, L.; Luo, X.; Xu, K.; Lü, Y.; Yang, D. Charge-Transfer-Induced Noncoalescence and Chain Formation of Free Droplets under a Pulsed DC Electric Field. Langmuir 2020, 36, 14255–14267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ju, M.; Dou, X.; Li, N.; Zhang, W.; Sun, Z.; Yu, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z. Assessing nanoparticle-surfactant-salt synergistic effects on droplet–droplet electrocoalescence by molecular dynamics simulations. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 367, 120570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Wang, J.; Zeng, X.F. A New Type Apparatus Used in Laboratory Aging Oil Electric Dehydration. Dev. Innov. Mach. Electr. Prod. 2013, 26, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Hu, J.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Z. Experimental Study of Factors Acting on the Performance of High-Voltage and High-Frequency Pulse Electrostatic Dewatering Process. J. Chem. Eng. Chin. Univ. 2010, 24, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wei, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, B. Composite Crude Oil Electric Dewatering High-Voltage Power Supply and Its Control Device. CN101550353B, 5 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hamidi, H.; Haddad, A.S.; Otumudia, E.W.; Rafati, R.; Mohammadian, E.; Azdarpour, A.; Pilcher, W.G.; Fuehrmann, P.W.; Sosa, L.R.; Cota, N.; et al. Recent applications of ultrasonic waves in improved oil recovery: A review of techniques and results. Ultrasonics 2021, 110, 106288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, M.; Amirjani, A.; Bagheri, M.; Sharifian, I.; Sabahi, Q. Eco-friendly pesticide based on peppermint oil nanoemulsion: Preparation, physicochemical properties, and its aphicidal activity against cotton aphid. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 6667–6679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, J.X. Study on Dehydration Characteristics and Mechanism of Crude Oil Emulsion Under the Combination of Ultrasonic and Electric Field. Master’s Thesis, Harbin University of Science and Technology, Harbin, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Hou, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, X.; Xiong, Y. Research on Apparent Viscosity Variation of Water-in-Oil Waxy Crude Oil Emulsions Induced by a Magnetic Field. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 17901–17916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Xu, X. Reducing the Viscosity of Crude Oil by Pulsed Electric or Magnetic Field. Energy Fuels 2006, 20, 2046–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homayuni, F.; Hamidi, A.A.; Vatani, A.; Shaygani, A.A.; Dana, R.F. The Viscosity Reduction of Heavy and Extra Heavy Crude Oils by a Pulsed Magnetic Field. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2011, 29, 2407–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Lv, Y.; He, L.; Luo, X.; Yang, D. Experimental study on the dehydration performance of synergistic effect of electric field and magnetic field. Chem. Eng. Process. 2019, 142, 107555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Lv, Y.; He, L.; Luo, X.; Yang, D. Separation characteristics of water-in-oil emulsion under the coupling of electric field and magnetic field. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 2565–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Lv, Y.; He, L.; Luo, X.; Zhao, J. Experimental study on the effect of spatial distribution and action order of electric field and magnetic field on oil-water separation. Chem. Eng. Process. 2019, 145, 107658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eow, J.S.; Ghadiri, M.; Sharif, A.O.; Williams, T.J. Electrostatic enhancement of coalescence of water droplets in oil: A review of the current understanding. Chem. Eng. J. 2001, 84, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; He, L.; Luo, X.; Yin, H. Droplet dynamic response in low-viscosity fluid subjected to a pulsed electric field and an alternating electric field. AIChE J. 2020, 66, e16869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wu, H.; Sun, H.; He, L.; Guo, Y. Ultra-high frequency and Self-adaptive voltage technology for water separation from oil emulsion. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 279, 119732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dou, X.; Yu, K.; Li, N.; Zhang, W.; Xu, H.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J. Molecular dynamics simulations of nanoparticle-laden drop–interface electrocoalescence behaviors under direct and alternating current electric fields. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 344, 117875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryafard, E.; Farsi, M.; Rahimpour, M.R.; Raeissi, S. Modeling electrostatic separation for dehydration and desalination of crude oil in an industrial two-stage desalting plant. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 58, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Yan, H.; Huang, X.; Yang, D.; Wang, J.; He, L. Breakup characteristics of aqueous droplet with surfactant in oil under direct current electric field. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 505, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos-Sofia, M.; Silveira-Font, Y.; Moro-Martínez, A.; Mulet-González, D.; Falcón-Hernández, J. Caracterización microscópica de mezclas de petróleo y agua con tratamiento eléctrico y magnético. Tecnol. Quim. 2016, 36, 210–224. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, K.; Bai, Y.; Yuan, F.; Liu, X.; Ling, X.; Wang, L.; Du, L. Critical coalescence electric intensity of water droplets adsorbing surfactant molecules under electromagnetic synergy field. Chem. Eng. Process. 2023, 191, 109481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Du, L.; Ling, X.; Lü, Y.; He, L.; Luo, X. Microscopic Mechanism for Gradient Diffusion of Salt-Containing Droplets Induced by Electromagnetic Synergy: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Langmuir 2024, 40, 15926–15932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, D.; Lv, S.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Xia, M.; He, L. Understanding the enhancement mechanism of critical electric field strength for salt-laden droplets electric coalescence through synchronous coupled magnetic field. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 703, 135254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Liu, X.; Du, L.; Lü, Y.; Luo, X.; Ling, X. Electrocoalescence Behavior of Droplets Dispersed with Na2CO3 in Oil under the Electromagnetic Synergy Field. J. Phys. Chem. B 2023, 127, 5668–5675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, D.; Chen, C.; Lv, S.; Miao, J.; He, L. Expansion and growth of liquid bridge in saline water-in-oil emulsion under synchronized magnetic field coupled low-intensity electric field. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 072013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Du, L.; Lü, Y.; Bai, Y.; He, L.; Luo, X. Synchronous magnetization to weaken the hindrance of surfactants to droplet coalescence during electric dehydration. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 012104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Cao, J.; Yan, H.; Gong, H.; Yin, H.; He, L. Study on separation characteristics of water in oil (W/O) emulsion under ultrasonic standing wave field. Chem. Eng. Process. 2018, 123, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Cao, J.; Yin, H.; Yan, H.; He, L. Droplets banding characteristics of water-in-oil emulsion under ultrasonic standing waves. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 41, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P.Y.; Schachman, H.K. Studies on the validity of the Einstein viscosity law and Stokes’ law of sedimentation. J. Polym. Sci. 1955, 16, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.-W.; Yang, S. Deformation and breakup of Newtonian and non-Newtonian conducting drops in an electric field. J. Fluid Mech. 2000, 405, 131–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingenberg, D.J.; van Swol, F.; Zukoski, C.F. The small shear rate response of electrorheological suspensions. II. Extension beyond the point–dipole limit. J. Chem. Phys. 1991, 94, 6170–6178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangu, G.D.; Feke, D.L. Droplet transport and coalescence kinetics in emulsions subjected to acoustic fields. Ultrasonics 2007, 46, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).