Abstract
Exploration in the Tarim Craton has established that small-displacement strike–slip faults control carbonate reservoirs’ development and oil and gas accumulation. Oil and gas primarily accumulate within a defined lateral distance from these faults. Material point method (MPM) simulations of such fault systems revealed a functional relationship between the regular spacing of initial oblique Riedel fractures and brittle layer thickness under simple shear. This thickness critically governs the spatial organization of the resultant fault system. Riedel shear zones propagate upwards from the base in a semi-elliptical pattern, producing fewer, but longer, shear zones with increasing brittle layer thickness. Stratum thickness exerts a first-order control on fault configuration during strike-slip deformation, modulating both fault segmentation patterns and interconnectivity. Key quantitative relationships emerged: (1) an inverse proportionality between stratum thickness and Riedel shear zone density and (2) a positive correlation between shear zone length and stratum thickness. This article provides experimental evidence and theoretical guidance for exploring deep-seated strike-slip faults in cratonic basins.
1. Introduction
Exploration has established that small-displacement strike–slip faults within the Tarim Craton exert key control on carbonate reservoirs’ development and oil and gas accumulation. Oil and gas primarily accumulate within a defined lateral distance from these faults [,,]. However, accurately characterizing the complex three-dimensional geometry of these small-displacement strike–slip faults presents significant challenges due to limitations in geophysical and borehole data resolution. The intricate interplay of stresses, the resulting deformation, and variable fault zone architecture further impede predictive efforts []. Addressing these challenges requires detailed investigations to advance the understanding of such fault systems and their role in oil and gas trapping [].
The Manshen 1 Fault Zone, situated in the Aman Transition Zone of the central Tarim Basin (see Figure 1 in Reference []), strikes NNE–SSW. Its evolution comprises six distinct episodes: (1) Nanhua–Sinian normal faulting; (2) Late Ordovician–Early Silurian thrusting; (3) Middle Silurian–Carboniferous normal faulting; (4) Permian normal faulting; (5) Triassic thrusting; and (6) Jurassic normal faulting (ordered oldest to youngest). During the Middle Silurian–Carboniferous phase, a suite of approximately N–S trending normal faults developed. These faults collectively form a NNE–SSW striking, right-stepping, sinistral transtensional fault zone, defining the Manshen 1 Fault Zone (see Figure 2 in Reference []). Based on the deformation characteristics of this phase, we analyzed the relationship between strike–slip fault geometry and Riedel shear development.
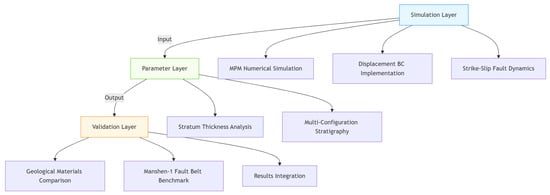
Figure 1.
A numerical simulation flowchart of strike–slip tectonics based on the material point method. By incorporating the dynamic behavior of strike–slip faults with the characteristics of material points method, displacement boundary conditions are imposed in the code. Stratum thicknesses are analyzed as input conditions. The failure patterns of strike–slip faults are then analyzed based on computational results.
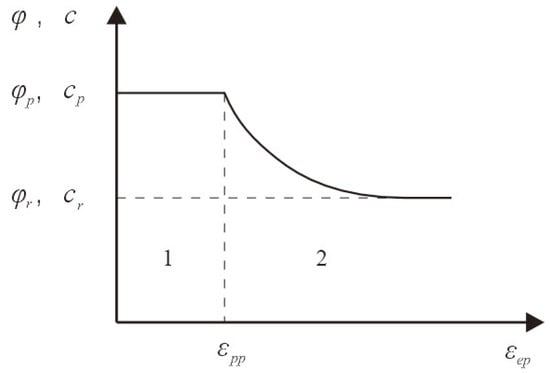
Figure 2.
Softening model. Before reaching the equivalent plastic strain at the limit state, the internal friction angle and cohesion within the peak range (Region 1) remain constant. After reaching the equivalent plastic strain at the limit state, in Region 2, the internal friction angle and cohesion decrease with the increase of the equivalent plastic strain.
Small-displacement strike–slip faults exhibit intricate deformation structures, including a principal fault with plastic deformation and associated secondary structures []. Understanding their evolution requires integrating the analysis of geological data [,], physical simulations [,], and numerical analyses [,,]. Mechanical models (experimental, physical, or numerical) provide critical insights into fault evolution, allowing the comparison of disparate geophysical and drilling data [,,]. These models typically employ simplified, idealized conditions to capture the fundamental characteristics of natural processes. Numerical simulations offer significant advantages by precisely monitoring the 3D evolution of deformation, velocity, and stress fields, revealing details often obscured in experimental approaches []. However, most existing numerical models are predominantly elastic and inadequately address inherent complexities. Strike–slip faults’ evolution involves material damage, fracturing, and pronounced nonlinear irreversible deformation processes [,,]. Mathematically, grid-based methods require solutions for mesh distortion under large deformations, while particle-based methods need enhanced computational efficiency []. Constitutive modeling of failure processes must address inherent nonlinearities, necessitating improved characterization of rock failure mechanisms [,].
Numerical modeling techniques, including the finite element method (FEM) [,], the finite difference method (FDM) [], and the discrete element method (DEM) [,,,,], have been extensively applied to study extreme deformation scenarios, such as those observed in strike–slip faults. For the FEM and FDM, which were designed for continuous media, extreme deformation often results in mesh distortion, leading to interruptions in calculations []. Although artificial discontinuous interfaces can be introduced to facilitate simulations under specific conditions, this approach may hinder the investigation of the spatiotemporal evolution of fault geometry. The significant computational demands of the DEM, stemming from the need to model particle interactions, require the verification of both micro- and macro-parameters and can introduce ambiguities in the underlying principles [,]. Studies using the DEM have explored the Earth’s crust with thicknesses ranging from 3 to 31 km; however, models with thicknesses less than 3 km fail to produce observable en-echelon faults due to resolution limitations []. Consequently, there is a need to explore more effective numerical simulation methods for modeling strike–slip faults.
Recently, the material point method (MPM) [] has gained increased attention in the analysis of large and extreme deformations. This method offers notable advantages when simulating extreme deformation phenomena, such as shear bands []. It operates by tracking the movement of material points to represent object deformation, mapping these points onto a background grid for information transfer, and subsequently solving the equilibrium equations using the grid. The results are then remapped back to the material points for updates. As a result, when applying the material point method to scenarios involving extreme deformation, such as shear bands, mesh distortion is effectively reduced [,]. This method serves as a valuable tool for investigating extreme deformation processes, including strike-slip faults, enabling the analysis of key controlling factors and the mechanisms underlying crustal rupture. In this study, we implemented material point method simulation technology, grounded in an elastoplastic model [], to explore the formation process of strike–slip faults and to evaluate the influence of varying brittle crust thickness on their formation and evolution.
When a brittle rock mass is subjected to shear stress that exceeds its elastic limit, it experiences nonlinear deformation that may ultimately result in fracture failure []. The significant reduction in or loss of strength parameters within a rock mass is indicative of strength parameter softening. In the context of crustal deformation evolution, this phenomenon may lead to the formation of finite deformation fractures that propagate to the surface, as observed in the Riedel shear zone []. Accurately describing these processes necessitates the use of nonlinear models, which become increasingly intricate as our understanding of rock behavior deepens. The advancement of computer technology has facilitated the application of numerical simulation methods to investigate the development of strike–slip faults. Specifically, these simulation tools enable the analysis of shear band spacing and length scales concerning the thickness of the brittle crust, revealing significant geometric correlations.
This study leveraged the material point method’s advantage in calculating large deformations, integrated it with the Manshen 1 failure mode, and simulated translational shear on rock layers with varying thicknesses. The failure patterns of Riedel shear under different thickness conditions were identified.
2. Material Point Method
Numerical simulations were performed using the material point method (MPM), incorporating a code-level enhancement through the implementation of displacement boundary conditions. These displacement boundary conditions enabled the simulation of strike–slip fault rupture dynamics. The primary variable investigated was stratum thickness across different stratigraphic configurations. Finally, geological interpretation materials were used to conduct a comparative analysis with the Manshen 1 Fault Zone, followed by a subsequent analysis of the results (Figure 1).
The material point method (MPM) is a powerful tool for simulating large-deformation problems, making it popular in scientific computing. It combines aspects of both Lagrangian (particle-based) and Eulerian (grid-based) approaches to handle complex material responses efficiently []. Material points represent the material and carry properties such as mass, velocity, and stress. A background grid is used to compute gradients, solve equations, and handle boundary conditions. Particles move freely while the grid remains fixed (Eulerian). At each time step, particle data are projected onto the grid, equations are solved, and updates are transferred back to particles. This avoids mesh distortion issues and is suitable for simulations involving materials such as sand or fracturing strata. To simulate rock behavior (e.g., elasticity, plasticity, and failure), an elastoplastic constitutive model is integrated into the MPM.
The elastoplastic models of the commonly used material point method algorithm for rock and soil masses mainly include the Drucker–Prager model and the Mohr–Coulomb model. The Drucker–Prager model is suitable for simulating most rock and soil materials. Huang [] implemented the calculation of the Drucker–Prager model in the material point method. The Drucker–Prager yield function has two components, shear yield function Fs and tensile yield function Ft.
where is the second invariant of the deviatoric stress tensor; is the first invariant of the stress tensor; is the tensile strength; and and are the model parameters related to the internal friction angle φ and cohesion c.
For the Drucker–Prager model
The potential function includes shear plastic potential function and tensile plastic potential function. The shear plastic potential function Gs is
where qψ is a function of shear dilatation angle.
If the shear dilatation angle is equal to the internal friction angle, then the plastic potential function is equal to the yield function, which is the associated flow rule.
The tensile plastic potential function Gt is expressed as
The softening criterion can reflect the decrease in strength parameters as plastic strain evolves. The back-mapping algorithm was used based on the Drucker–Prager model. We should determine the relationship between the strength parameters and the plastic strain [].
The variation in strength parameters with plastic strain in the softening model is shown in Figure 2. In region 1, cohesion and internal friction angles are constant at the peak cohesion cp and peak internal friction angle φp, respectively. After the peak plastic strain, the model enters region 2, where cohesion and internal friction angles decrease as the plastic strain increases.
where cr and φr are the residual cohesion and the residual internal friction angle; cp and φp are the peak cohesion and peak internal friction angle; η is the influence factor; and εeq is the plastic strain.
Boundary conditions were directly applied at the base, and implemented based on the open-source program MPM3D-F90 []; we enhanced the program code by incorporating displacement boundary conditions.
The calculation model employed an elastoplastic framework grounded in the Drucker–Prager yield criterion, exhibiting a softening behavior post-peak strength. The internal friction angle for the majority of the crust typically ranges from approximately 27° to 45° []. The derived internal friction angle was 30°, with a Poisson’s ratio of 0.25. The shear dilatation angle was recorded as 0°, while the elastic modulus was quantified at 1.6 × 107 kPa. Cohesion was measured at 5 × 106 kPa, and the residual internal friction angle following softening was 20°, accompanied by a residual cohesion of 1 × 104 kPa [].
3. Design of Strike–Slip Fault Simulations
The computational framework for isopachous and non-isopachous strata represents an advanced methodology for analyzing and interpreting thickness variations in sedimentary layers. This model significantly enhances our comprehension of geological formations by offering valuable insights into the spatial distribution and characteristics of these strata, thereby facilitating more precise geological assessments and effective resource management.
3.1. Isopachous Strata
The model dimensions were established within a cubic structure measuring 40 km by 20 km, with varying heights (T) of 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 km (Figure 3a). The gravitational acceleration was quantified at 9.8 m/s2.
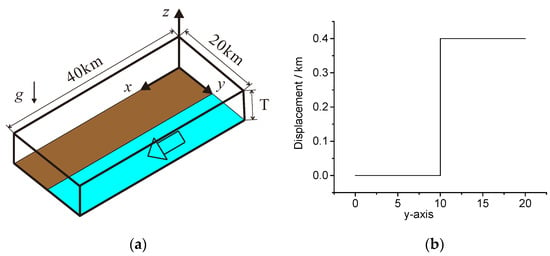
Figure 3.
Computation model for isopachous strata: (a) calculation model and (b) displacement conditions. The computational domain is a rectangular prism. Displacement is applied at the base. The grey region is rigidly fixed at its bottom, while the light blue region undergoes a prescribed displacement of 0.4 km in the direction of the arrow. There is no overlap between the grey and light blue regions. Figure (b) shows the displacement at the base.
In the xy plane, the model’s base was anchored with planes defined by the coordinates (0, 0, 0) and (40, 10, 0), as well as those defined by (0, 10, 0) and (40, 20, 0), which were implemented with translational boundary conditions featuring a displacement of 0.4 m (Figure 3b).
3.2. Non-Isopachous Strata
For non-isopachous strata, we performed an analysis at different angles of inclination. Assuming these strata extended 40 km in length and 20 km in width, the thickness along the length ranged from 1 km to 10 km, as shown in Figure 4a; we set T = 1, 3, 5, and 10 km to calculate. The boundary condition for bottom displacement was set at 0.8 km (Figure 4b).
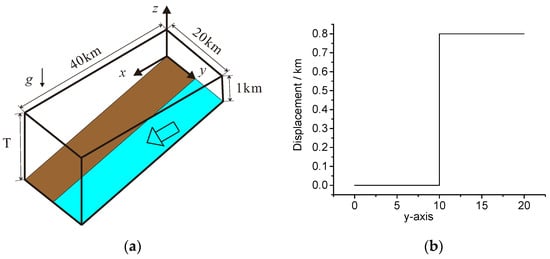
Figure 4.
Computation model for non-isopachous strata: (a) calculation model and (b) displacement conditions. The computational model consists of strata with varying thickness. Boundary conditions are applied at the base: the grey region is fixed, while a displacement boundary condition of 0.8 km is imposed on the light blue region.
The material point method (MPM) employed material points to effectively capture motion information, thereby avoiding mesh distortion. The calculation background utilized a regular hexagonal grid with a grid size of 0.2 and a material point size of 0.1.
4. Analysis of Thickness Control Factors
4.1. Isopachous Stratum
Figure 5 illustrates a schematic diagram of Riedel shear zones, with EF representing the length of the Riedel shear.
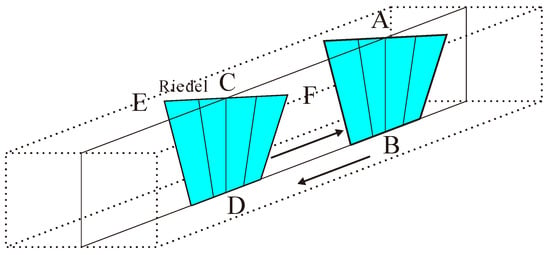
Figure 5.
Riedel schematic diagram. The schematic diagram illustrates the elements of a Riedel shear. Arrows indicate the displacement direction. EF characterizes the Riedel length, AB and CD correspond to the strata thickness, and AC represents the spacing between adjacent Riedel shears.
According to the material point method described in Section 2, the plastic strain distribution diagram was calculated when the displacement was 0.4 km, as shown in Figure 6. The thickness was 1 km, resulting in 18 Riedel shear zones, of which Riedel shear zones on both sides were incomplete, and the lengths of these Riedel shear zones varied. As shown in Figure 6, when the thickness was 1 km, the average value of L was 6.1 km.
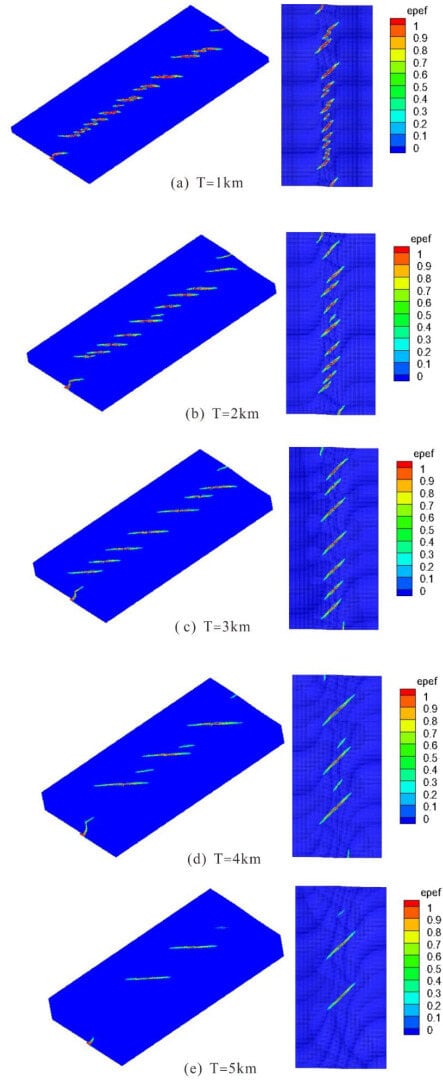
Figure 6.
Shears with thicknesses of 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 km. While the thickness varies, the other strength parameters and displacement conditions remain identical. The number, spacing, and length of Riedel shears exhibit marked variations under different thickness conditions. With increasing thickness, the Riedel shear length increases, the spacing increases, and the number of shears decreases.
When the thickness was 2 km, 12 Riedel shear zones were generated; the lengths of these Riedel shear zones were not equal, but the difference was not significant. The length of the failure area L was 6.8 km. When the thickness was 3 km, nine Riedel shear zones were generated. The length of the failure area L was 7.2 km. When the thickness was 4 km, five Riedel shear zones were generated. There were three long Riedel shear zones and two short Riedel shear zones with staggered distribution. The length of the failure area L was 7.3 km. When the thickness was 5 km, three Riedel shear zones were generated. Among these, two Riedel shear zones were relatively obvious, and one Riedel shear zone was relatively small. The length of the failure area L was 7.6 km.
Under consistent material parameters and boundary conditions, an increase in thickness resulted in a decrease in the number of Riedel shear zones, demonstrating a linear relationship (Figure 7). Concurrently, as thickness increased, Riedel shear length (L) also increased (Figure 8). We conclude that there is a high correlation between the length of the Riedel shear and the thickness of the strata. In isopachous strata, the length of the Riedel shear was directly proportional to the thickness.
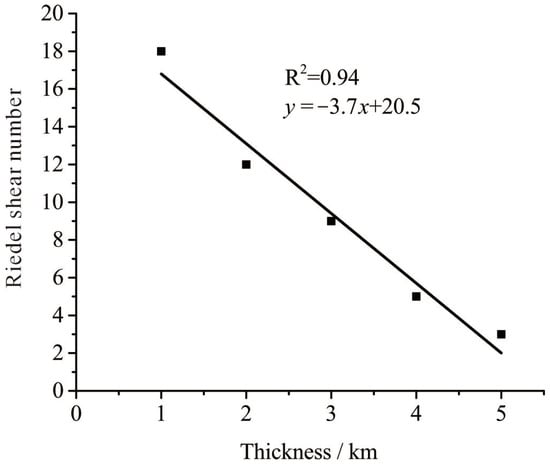
Figure 7.
Relationship between thickness and Riedel shear number. The black squares represent the statistically observed Riedel shear numbers. The correlation between the number of shears and the thickness was obtained by fitting based on five data points.
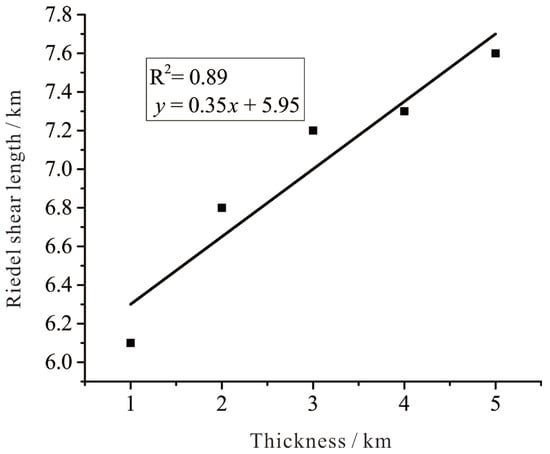
Figure 8.
Relationship between thickness and Riedel shear length. The black squares denote the statistically recorded total length of Riedel shears in the strata, with the fitted relationship based on five data sets.
4.2. Non-Isopachous Stratum
The stratum with non-uniform thickness experienced translational movement, resulting in an increase in shear stress with depth. Figure 9 illustrates the shear band failure process at angles of 0°, 2.9°, 5.7°, and 12.7° (as shown in Figure 10, angle a). When the strata exhibited minor undulations and the thickness variation angle was less than 2.9°, the variation in Riedel shear length was relatively uniform, and the strata can be considered uniform-thickness layers. When the thickness variation angle exceeded 5.7°, the Riedel shear length exhibited non-uniform distribution. As the thickness increased, the exposed Riedel shear length at the surface extended. As depicted in Figure 10, for the non-isopachous stratum, the shear length AD exceeded that of BC, and the extension lines AB, DC, and EF converged at a point where the formation thickness approached zero, signifying the cessation of the shear process. In non-isopachous strata, the length of the Riedel shear was related to the angle of thickening of the strata.
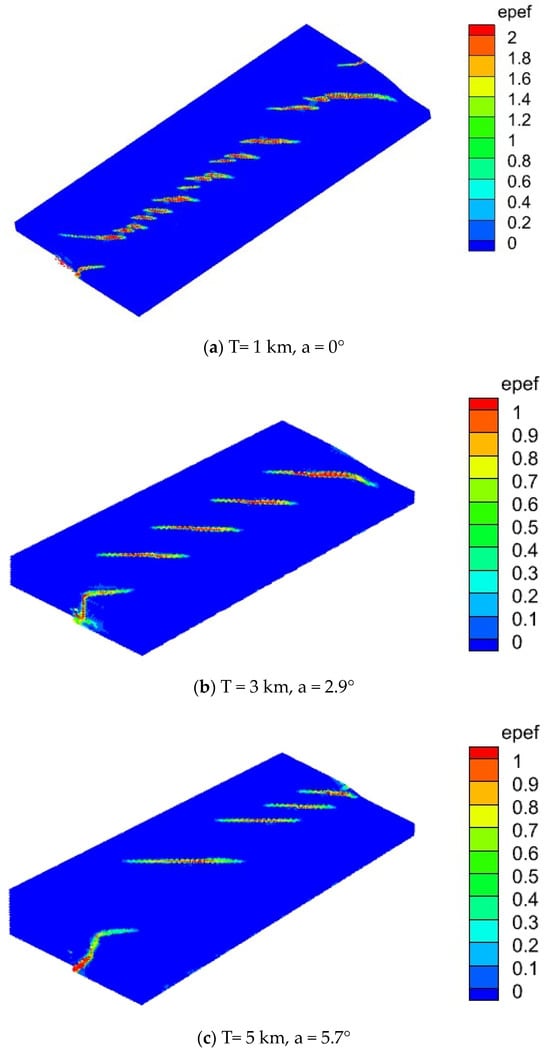
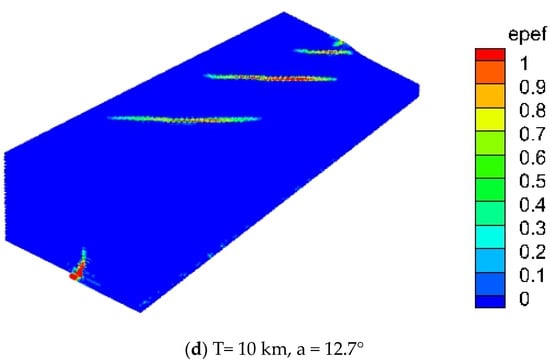
Figure 9.
Riedel shears for non-isopachous strata. Even under varying thickness conditions within the same stratigraphic sequence, the characteristic trend persists: as strata thickness increases, Riedel shear spacing increases, the number of shears decreases, and shear length increases. Basal heterogeneities are manifested by variations in the lengths of surface expressions of Riedel shears.
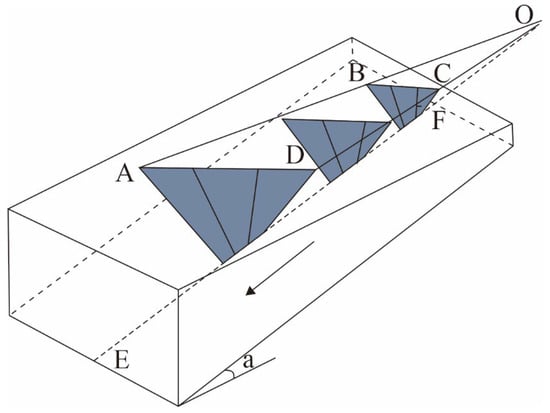
Figure 10.
Schematic diagram for non-isopachous strata. AD and BC represent the lengths of the Riedel shears. EF denotes the midline of the basal plane. Point O is defined by the intersection of the extensions of lines AB and DC. The arrows indicate the displacement direction along the basal plane, while *a* signifies the inclination angle of the strata’s basal plane. The grey surfaces depict the Riedel shears.
In summary, within isopachous stratum, Riedel shear structures demonstrated a linear proportionality to stratum thickness. Enhanced stratigraphic thickness facilitated greater vertical propagation of shear zones toward the surface, governed by strain partitioning mechanisms. However, insufficient basal displacement magnitudes may have impeded the upward development of Riedel shears, resulting in subsurface termination and subsequent invalidation of the linear thickness–shear relationship. These observations underscore a dual regulatory framework, wherein Riedel shear spatial distribution is dictated by the synergistic interplay between basal kinematic constraints and stratigraphic dimensional parameters.
Conversely, in non-isopachous stratum, Riedel shears exhibited progressive elongation parallel to the stratigraphic thickening axis, manifesting distinct kinematic signatures compared to the uniform-scale shear arrays characteristic of isopachous systems. This length disparity exhibited a positive correlation with stratigraphic dip angles, reaching critical thresholds where shear segmentation became geometrically inevitable. Systematic quantification of surface Riedel shear length asymmetries enables inverse modeling of subsurface stratigraphic architecture, resolving both the thickness distribution gradients and basal displacement vector fields. The resulting methodology provides a robust diagnostic tool for paleostress reconstruction and structural compartmentalization analysis through systematic interrogation of surface shear geometries. This approach significantly advances the interpretative paradigm for elucidating concealed structural configurations in fold–thrust zone environments.
5. Deformation Characteristics of Strike–Slip Faults
Using a smooth fault with a thickness of 5 km as a case study, this analysis examined the three-dimensional evolution of the avian structure associated with strike–slip faults, drawing on results obtained from material point simulations (Figure 11).
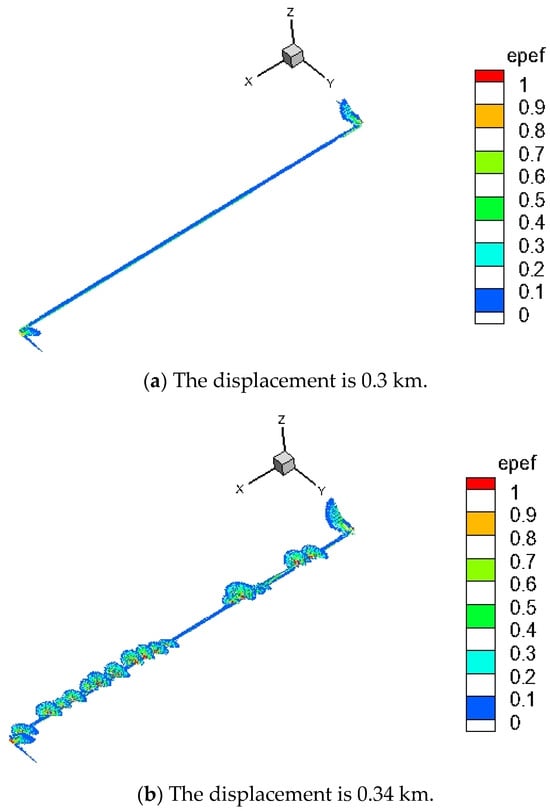
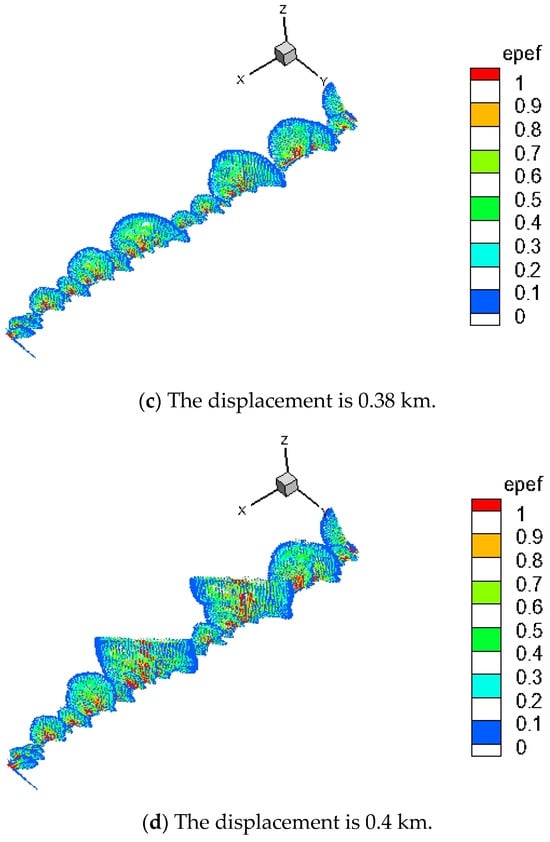
Figure 11.
Riedel shear-forming process. At a model thickness of 5 km, the formation process of Riedel shears with increasing displacement is shown. Shear bands are characterized by plastic strain. As displacement increases, plastic deformation propagates upward from the base.
In the initial phase of model evolution, triggered by an increase in traction force at the lower layer, the response was predominantly elastic. As the displacement at the lower layer reached 0.3 km, non-elastic deformation initiated at the base of the intermediate shear zone, propagating in a linear manner. Riedel shear commenced at the discontinuity of the brittle layer’s base and ascended along a spiral trajectory. Upon reaching a displacement of 0.34 km, multiple mushroom-shaped shear surfaces emerged within the non-elastic region. At this juncture, the original Riedel shear crack began to extend upward from the base shear zone, exhibiting a distinct clustering pattern as opposed to the uniformly distributed cracks along the base shear zone. When the displacement increased to 0.38 km, the mushroom-shaped shear surfaces progressively extended upward along the z-axis, becoming both thicker and wider. At a displacement of 0.4 km, the substantial shear surfaces reached the upper surface, culminating in the formation of a fully developed Riedel shear and the generation of an avian structure.
Under strike–slip loading conditions, the local horizontal stress state at the base of the plane ABCD, situated between two Riedel shear zones, was primarily tensile in nature. The stress state on shear band ABCD was simulated using the material point method. As illustrated, within the shear band plane along the Y-axis, the plane experienced tensile stress, with a peak value of 500,000 kPa (Figure 12). Conversely, within the Riedel shear zone, no tensile stress was observed along the Y-axis.
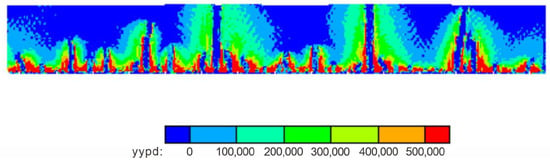
Figure 12.
Shear stress in y direction (kPa). Three fully penetrating shear bands are distinctly visible in the figure. Within the Riedel shear band region, the stress in the y-direction becomes negligible, while significantly higher stresses concentrate around the periphery of the shear bands.
6. Discussion
The integrated numerical modeling and empirical validation presented in this study fundamentally advance our mechanistic understanding of Riedel shear system evolution. Material point method simulations robustly demonstrated that stratum thickness constitutes a primary architectural control on strike–slip fault geometry, reconciling long-standing field observations of variable fault segmentation patterns. The inverse relationship between layer thickness and shear density reflects strain accommodation mechanisms: thinner strata undergo distributed brittle failure to absorb displacement, while thicker units localize strain into fewer through-going structures. This thickness-dependent scaling law provides a quantitative framework for predicting subsurface fault connectivity—a critical parameter in fluid migration studies for hydrocarbon systems. The correlation between shear length and stratum thickness establishes surface fault patterns as kinematic proxies for subsurface stratigraphy. Uniform Riedel dimensions indicate isopachous conditions, whereas progressive shear-length reduction vectors map stratigraphic thinning gradients. This diagnostic capability bridges a key scale gap in tectonic analysis, enabling the reconstruction of concealed basin architecture through surface fault morphology. The Manshen 1 case study confirms this principle: variable fault lengths directly correlated with imaged thickness variations in the Cambrian salt sequence, validating the model’s predictive power for cratonic basement deformation.
Despite these advances, significant limitations remain. Models simplify reality by simulating isotropic elastoplastic materials, thus neglecting natural anisotropies, such as bedding planes and diagenetic heterogeneities, which can substantially influence strain localization. Experiments are confined to small-displacement systems, whereas the influence of stratum thickness on large-offset faults may be masked by subsequent thermal feedback or fluid–rock interactions.
To address these gaps, future work should prioritize implementing stratified media with contrasting rheologies (e.g., shale–sandstone–carbonate sequences) to quantify mechanical stratigraphy effects and develop machine-learning applications by training convolutional neural networks on fault pattern datasets to automate thickness gradient inversion from remote-sensing imagery.
This research establishes stratum thickness as a primary control on strike–slip fault architecture, with significant implications. The direct relationship between surface fault dimensions and subsurface stratigraphy enables quantitative paleo-thickness reconstruction in eroded or buried terrains—a transformative tool for basin analysis. In petroleum systems, thickness-dependent connectivity laws provide a physics-based framework for targeting compartmentalized reservoirs along cratonic fault zones. By quantifying how stratigraphic “blueprints” govern fault evolution, this work has reshaped structural interpretation paradigms in energy geoscience and tectonic hazard assessment.
7. Conclusions
This investigation revealed stratum thickness as the dominant control on Riedel shear system development through material point method simulations validated against the Manshen 1 Fault Zone. Three principal patterns emerged:
- (1)
- Thickness–Density Relationship
Thinner strata developed significantly higher concentrations of Riedel shears compared to thicker layers; 1-m strata typically contained over four times as many shear zones per unit area as 5-m strata.
- (2)
- Thickness–Length Correlation
Shear zone length increased proportionally with stratum thickness. Shear zones in 5-m strata extended more than 1.2 times as long as those developing in 1-m strata.
- (3)
- Surface Expression Diagnostic
Uniform shear dimensions at the surface consistently indicated equally thick subsurface layers. Conversely, progressively shorter shears along a fault’s strike direction reliably mapped thinning stratigraphic sequences—a pattern strongly confirmed in the Manshen 1 Fault Zone, where surface observations matched subsurface imaging.
- (4)
- Formation Mechanism of Riedel Shears
The formation of Riedel shears provided a compelling illustration of multi-scale deformation propagation in brittle materials. At the microscale, intrinsic heterogeneities, such as grain boundaries, micro-cracks, and mineral inclusions, functioned as stress concentrators. These heterogeneities initiated localized failure when local tensile or shear stresses surpassed critical strength thresholds, a process modeled herein using a softening damage constitutive law. These micro-damage locales did not operate independently; rather, during progressive loading, heightened plastic strain and abrupt strength degradation led to the delineation of incipient deformation bands. The instantaneous reduction in cohesion and internal friction angle characterizes comminution-induced damage localization within the rock mass. Ultimately, this interconnected micro-damage network coalesced at the macroscale to generate through-going Y-shears, which subsequently evolved into periodically spaced Riedel shear structures.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.L., S.L., Z.H., J.G. and B.S.; Methodology, B.S.; Software, B.S.; Resources, S.L.; Writing—original draft, B.S.; Writing—review & editing, C.L. and Y.C.; Visualization, B.S.; Supervision, S.L. and Z.H.; Project administration, S.L., Z.H. and J.G.; Funding acquisition, C.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (92255302, 42462025, and 42102270) and the SINOPEC Key Laboratory of Geology and Resources in the Deep Stratum Open Fund Project (33550000-22-ZC0613-0247).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Changsheng Li, Shuangjian Li, Zongquan Hu, Jian Gao, and Butao Shi are employed by the SINOPEC company. The authors declare that this research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Wu, G.; Ma, B.; Han, J.; Guan, B.; Chen, X.; Yang, P.; Zhou, X. Origin and growth mechanisms of strike–slip faults in the central Tarim cratonic basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Zhao, R.; Kong, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, B. Two distinct strike–slip fault networks in the Shunbei area and its surroundings, Tarim Basin: Hydrocarbon accumulation, distribution, and controlling factors. AAPG Bull. 2022, 106, 77–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Lu, X.; Liang, H.; Huang, S.; Su, N. Cratonic strike–slip fault systems in the central Sichuan Basin, China. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2024, 254, 104800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, T.M.; Faulkner, D.R. The nature and origin of off-fault damage surrounding strike–slip fault zones with a wide range of displacements: A field study from the Atacama fault system, northern Chile. J. Struct. Geol. 2009, 31, 802–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemenda, A.I.; Cavalié, O.; Vergnolle, M.; Bouissou, S.; Delouis, B. Numerical model of formation of a 3-strike–slip fault system. Comptes Rendus—Geosci. 2016, 348, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, W.; Luo, C.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhou, H.; Li, C.; Wu, G.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. The faults and faulting phases of the Manshen-1 fault belt, central Tarim Basin. Chin. J. Geol. 2021, 56, 1015–1033, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvester, A.G. Strike–slip faults. Bull. Geol. Soc. Am. 1988, 100, 1666–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogonenkov, G.N.; Timurziev, A.I. Strike–slip faulting in the West Siberian Platform: Insights from 3D seismic imagery. Comptes Rendus—Geosci. 2012, 344, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitman, N.G.; Klinger, Y.; Briggs, R.W.; Gold, R.D. Climatic influence on the expression of strike–slip faulting. Geology 2023, 51, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Konietzky, H. Particle-Based Modeling of Transtensional Pull-Apart Basins. Tectonics 2018, 37, 4700–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Zhou, W.; Han, R. Controlling factors of Riedel shear spacing in the simple shear mode of strike–slip fault: Insights from sandbox models. J. Struct. Geol. 2024, 189, 105261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaoka, A.; Sawada, Y.; Yamada, S. Riedel shear band formation with flower structures that develop at the surface ground on a strike slip fault. Jpn. Geotech. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2016, 2, 751–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Klinger, Y.; Scholtès, L. Fault Segmentation Pattern Controlled by Thickness of Brittle Crust. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL093390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Tapponnier, P.; Mccallum, A.C.-C.; Xu, X. The shape of the Himalayan “Arc”: An ellipse pinned by syntaxial strike–slip fault tips. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2313278121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, T.P.; Schreurs, G. Analogue modelling of intraplate strike–slip tectonics: A review and new experimental results. Tectonophysics 2012, 574–575, 1–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Fan, T.; Shang, Y.; Qi, L.; Yun, L. Structural characterization and hydrocarbon prediction for the SB5M strike–slip fault zone in the Shuntuo Low Uplift, Tarim Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 117, 104418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buiter, S.J.; Schreurs, G.; Albertz, M.; Gerya, T.V.; Kaus, B.; Landry, W.; Beaumont, C. Benchmarking numerical models of brittle thrust wedges. J. Struct. Geol. 2016, 92, 140–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinger, Y. Relation between continental strike–slip earthquake segmentation and thickness of the crust. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2010, 115, B07306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, A.J.; Karma, A. Helical crack-front instability in mixed-mode fracture. Nature 2010, 464, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, L. Fault propagation in pull-apart basins and its implication on depocenter migration: A discontinuum-based numerical study. Geol. J. 2023, 59, 1171–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmelnizkij, A. Improved double-point material point method for dynamic geotechnical problems. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2647, 82013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, D.A.; Divya, P.V. Material point method (mpm) modelling of the impact on debris flow barriers. Int. J. Geosynth. Ground Eng. 2025, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Hua, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, X. Simulation of fluid-structure interaction using the density smoothing b-spline material point method with a contact approach. Comput. Math. Appl. 2024, 176, 525–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.A.; Gomes, I.F.; Miranda, T.S.; Correia Filho, O.J.; Medeiros, C.E.B.; Carvalho, B.R.B.M.; Falcão, T.C. Quantifying damage zones width in strike–slip faults: Insights from a two-dimensional finite-element modeling approach. J. Struct. Geol. 2024, 186, 105201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Liu, Z.; Mao, X.; Wang, C.; Li, L. Ore-forming simulation of the Axi low-sulfidation epithermal gold deposit, Western China: Genetic implications on mineralization pattern. J. Geochem. Explor. 2025, 273, 107740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cundall, P.A.; Strack, O.D.L. A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies. Géotechnique 1979, 29, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donzé, F.V.; Klinger, Y.; Bonilla-Sierra, V.; Duriez, J.; Jiao, L.; Scholtès, L. Assessing the brittle crust thickness from strike–slip fault segments on Earth, Mars and Icy moons. Tectonophysics 2021, 805, 228779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; He, D.; Tian, F.; Huang, C.; Ma, D.; Zhang, W. Control of mechanical stratigraphy on the stratified style of strike–slip faults in the central Tarim Craton, NW China. Tectonophysics 2022, 830, 229307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, C.; Li, J.; Fu, X.; Qian, S.; Zhou, G.; Ma, Y.; Wang, T. Evaluating the response of a tunnel subjected to strike–slip fault rupture in conjunction with model test and hybrid discrete–continuous numerical modeling. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2022, 55, 4743–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yin, H.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; Ren, R. Calibration of the discrete element method and modeling of shortening experiments. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 636512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulsky, D. Application of a particle-indashcell method to solid mechanics. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1996, 96, 105–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreyer, H.L.; Sulsky, D.L.; Zhou, S.J. Modeling delamination as a strong discontinuity with the material point method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2002, 191, 2483–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardenhagen, S.G.; Brackbill, J.U.; Sulsky, D. The material-point method for granular materials. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2000, 187, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardenhagen, S.G.; Guilkey, J.E.; Roessig, K.M.; Brackbill, J.U.; Witzel, W.M.; Foster, J.C. An improved contact algorithm for the material point method and application to stress propagation in granular material. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2001, 2, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Li, S.; Guo, H.; Hao, Z. Large deformation failure analysis of the soil slope based on the material point method. Comput. Geosci. 2015, 19, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlini, M.; Viola, G.; Mattila, J.; Castellucci, L. The role of mechanical stratigraphy on the refraction of strike–slip faults. Solid Earth 2019, 10, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W. Analysis of the Entire Failure Process of the Rotational Slide Using the Material Point Method. Int. J. Geomech. 2018, 18, 4018092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y. The Material Point Method—A Continuum-Based Particle Method for Extreme Loading Cases; Acadademice Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Board of Engineering Geology Manual. Geological Engineering Handbook, 5th ed.; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).