Abstract
Inspired by experiments manifesting unconventional metallic behavior in and superconductivity in , we present -DFT+DMFT results for monoclinic . We unearth the role played by multi-orbital, many-particle physics in understanding the emergence of -orbital selectivity with coexisting pseudogapped, resilient, and Fermi-liquid quasiparticles, which might host unconventional superconductivity in K-doped bulk crystals at low temperatures. Our findings highlight the capability of DFT+DMFT to bridge the gap between electronic structure and electric transport in multi-orbital Hubbard models, providing insights into spin and charge fluctuations, as well as their role in orbital-selective non-Fermi liquid formation.
1. Introduction
The subtleties of correlation-induced bad metallicity and non-Fermi liquid behavior [1] remain a topic of enduring interest [2,3]. Important in this context is the emergence of unconventional (non-BCS) superconductivity [4], which has been observed in some cases at the boundary of electronic localization and itinerancy [2] at different temperatures , chemical compositions, and structural phases [5]. Of particular interest here are systems [6,7,8], which exhibit resistivity curves displaying noticeable departures from the quadratic behavior characteristic of Fermi-liquid (FL) metals [9]. While the FL evolution of has been observed in thin films [10] and high-quality monoclinic bulk crystals [11], among other studies [12,13], superconductivity ( 7 to 18 K) [6,7] in K-Mo-O systems emerges in a non-FL metal with power-law-like T-dependence (). Electrical resistance in the normal state exhibits a value of [6], which is analogous to the characteristics observed in power-law quantum metals [14,15].
Two examples within transition-metal dioxides are and , which undergo to a first-order metal-insulator transition (MIT) around room T [5,16] and above 810 K [17,18,19], respectively. The high-T metallic phase of these dioxides has a tetragonal rutile-type crystal structure, which transforms to a monoclinic structural phase at the MIT [5]. The Mott–Hubbard (many-body correlation) [20] and Peierls (lattice distortion) [21] mechanisms are understood to play essential roles in this transition. These mechanisms may act in concert, since the distortion is assisted [22,23,24,25] by correlation-induced electronic reconstruction [26]. In this study, we demonstrate that a dynamically reconstructed many-particle electronic state induced by multi-orbital (MO) interactions [27] plays a leading role in establishing the orbital-selective nature of monoclinic (distorted-rutile) . By means of density functional dynamical mean-field theory (DFT+DMFT) calculations [28], we show how the electronic structure of monoclinic [29,30,31,32] is reshaped due to the presence of MO electron interactions. Similar to Refs. [22,23,24,25], we reveal how the electronic structure of monoclinic is reconstructed by MO many-particle correlations, showing how a bad-metal, pseudogaped regime with coexisting resilient [33] and FL [9] quasiparticles emerges in bulk crystal as a result of dynamical MO correlations.
The interest in is motivated by its application as a catalyst for isomerization and oxidation, as well as in the petrochemical industry for hydrodesulfurization, as well as hydro- and dehydrogenation reactions [31]. Additionally, is applied in a variety of other fields, ranging from electronics [12], fuel cells [34,35], diffusion barriers [13], and lithium-ion batteries [36,37,38] to dynamic random-access memory capacitors [39]. Similarly to and , is an additional potential material for memristive devices for future neuromorphic computing [40]. is also relevant to understanding its bad metallicity [8,10], its high magnetoresistance [11], and the possibly reduced many-particle correlation effects of electrons in comparison to compounds. As observed in and , electronic structure calculations show a large bonding–antibonding splitting of the orbital sector of monoclinic [29,30,32,41]. DFT calculations [29] indicate that the distorted lattice structure of arises from a Peierls-based instability with band-insulating and metallic states near the Fermi level (). It is noteworthy that these dispersing states give rise to metallicity in monoclinic , in contrast to the bare, one-band insulating state of distorted rutile and [22,42,43,44].
While Refs. [10,11,12,13] report -like dependence for , a review of existing experiments also reveals clear deviations from an FL metal in pure and oxygen-deficient [8,30] and K-doped [6,7], indicating that correlation effects are needed to describe the many-particle electronic state of [27]. Evidence supporting unconventional metallicity includes the absence of Kondo quasiparticles [9] in angle-integrated photoemission spectroscopy (PES) and ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS) data [8,29,30,41,45,46,47], displaying pseudogap-like features close to . Optical data revealed a bump around 0.8 eV and other features near to 4.0 eV [48,49]. Notably, the 0.8 eV bump in optics seems to support the view of an unconventional metallic conduction in . It is also noteworthy that exhibits an upturn with decreasing temperature down to 25 K, followed by T-linear resistivity in samples with [8,50,51]. Indeed, appears to behave as a poor insulator at low temperatures, with a resistivity upturn for 100 K [8,50,51,52], suggesting the presence of substantial correlation effects in [27].
The aim of this study is to gain insight into the electronic state that may potentially host unconventional superconductivity in K-doped samples [6,7]. To this end, we present theoretical results for electronic reconstruction in electron-doped . This is motivated by the fact that potassium ions, when incorporated into bulk crystal, effectively electron dope the Mo band [7]. As previously noted [27], the metallic behavior observed in this system is found to be orbital-selective in nature. This is attributed to electron–electron interactions within the active orbitals in proximity to . Our results contribute to the understanding of the interplay between local MO interactions and electron doping of the parent compound. In particular, pseudogap-like features probed in spectroscopy experiments [8,29,41,45] are shown to result from a dynamical MO reconstruction with coexisting pseudogaped and quasiparticle electronic excitations at low energies. These findings are relevant for understanding the emergence of bad metallicity and, possibly, superconductivity in unconventional metals [53] at low temperatures.
However, before presenting our correlated many-particle results for the -orbital problem of pure and electron-doped , it is important to mention that several developments in understanding the MIT of ( and ) systems have been derived based on DFT+DMFT approximation [28], which accounts for local dynamical interactions hidden in the lattice crystal. Early many-body studies [54,55] have shown that although the metallic-phase could be accounted for by MO single-particle approaches, a description of the interplay between dimerization and MO degrees of freedom would be needed to explore the monoclinic phase. This endeavor was first achieved in Ref. [22], where a DFT approach combined with a cluster DMFT (cDMFT) approach was introduced for . In subsequent studies [56,57], it was shown that consideration of interatomic self-energy corrections between the V atoms in a dimer captures the underlying behavior of the DFT+cDMFT approach. As pointed out in Ref. [58], this perspective was further explored in Ref. [59], which used DFT+V supplemented by a single-site DMFT scheme, yielding similar results as compared to cDMFT. Moreover, a DFT+cDMFT study by Weber et al. [23] showed Mott-localized effects, suggesting that the monoclinic phase of results from of a Peierls-assisted Mott MIT. More recently, a DFT+cDMFT treatment conducted by Brito et al. [25] showed that is also strongly correlated Mott material, as proposed by Laad et al. [54] in earlier days of the DFT+DMFT age. Lastly, a number of studies using other advanced methods [58,60,61] have also highlighted the importance of interaction and dimerization effects in and analogs [26,62], showing qualitative theory–experiment agreement for different physical quantities. In this work, we focus on monoclinic , showing how a description based on single-site DFT+DMFT, in which Mo–Mo dimerization effects are taken into account at the DFT one-particle level correctly simulates the electronic structure in the normal, non-superconducting state of a pure and electron-doped superconductor. Similar to earlier studies on transition-metal oxides, the novelty of our work is that it unearths an orbital-selective electronic reconstruction in crystal, which is intrinsically important for understanding the interplay between many-particle interactions and lattice distortion in Mo-containing oxides [63]. We use our results to argue how an orbital-selective metallic state might generically occur and the relevance of hidden MO electronic correlations for the emergence of a power-law-like [14,15], non-Fermi liquid metal not uncovered in earlier theoretical studies of pure and Mo-containing systems.
It is worth noting here that the importance of local correlations on the electronic structure of molybdenum oxides has been the subject of study within the context of two distinct theoretical frameworks: the DFT+U [63,64,65,66,67] and DFT+DMFT [27] frameworks. However, since DFT+U is a ground-state theory based onconstruction, it only takes into account Hartree-like corrections and, therefore, cannot describe dynamical many-particle effects. Similarly to Ref. [27], here, we extend ab initio-based DFT calculations to describe many-particle correlation effects within the DFT+DMFT method [28]. Notably, this method was used [68], thereby supporting the importance of MO dynamical interactions in Mo-containing materials.
2. Theory
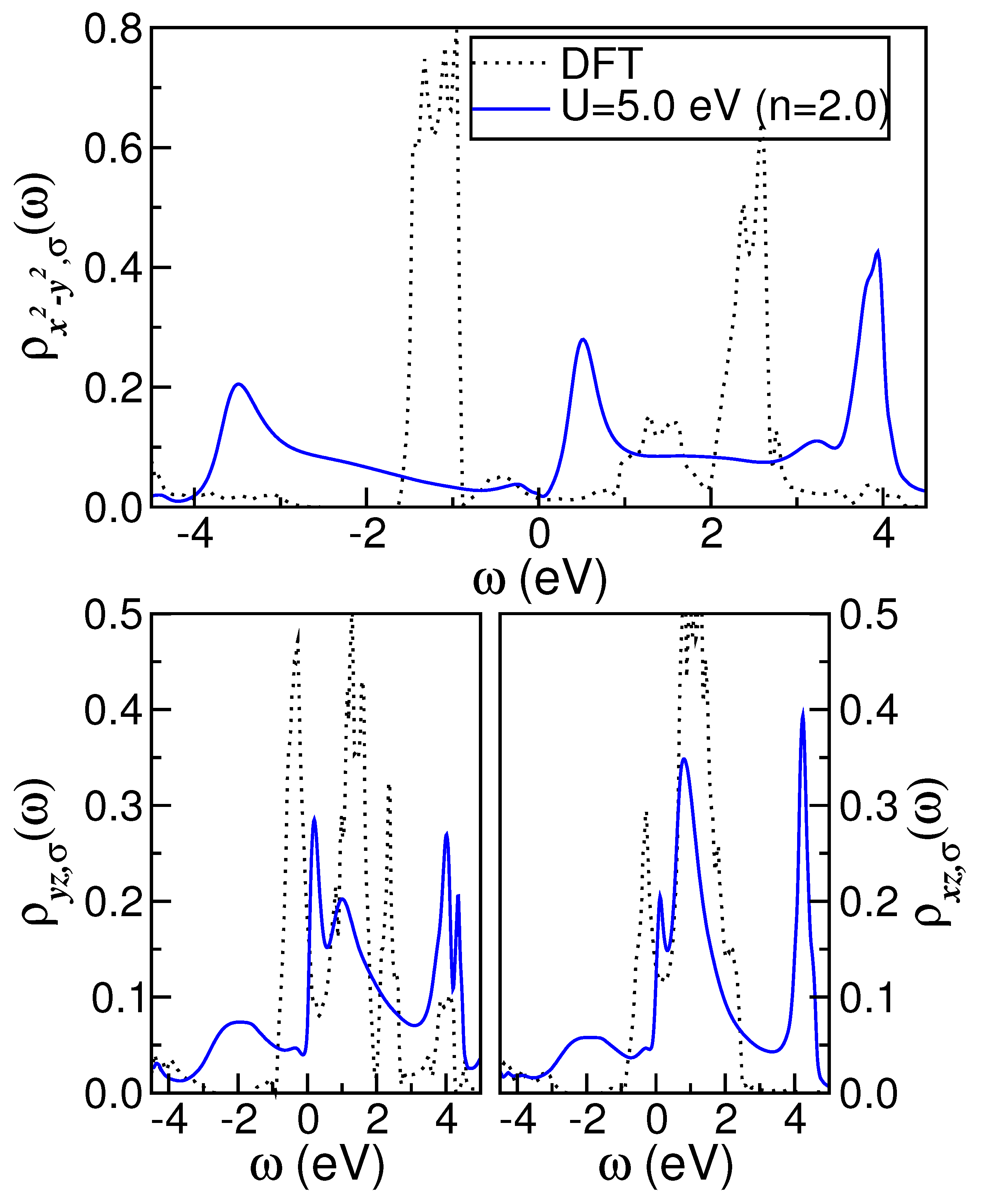
Here, we demonstrate that the pseudogap observed in monoclinic [8,29,41,45] is intrinsic and indicative of its proximity to orbital-selective Mottness. To investigate this further, we utilize the DFT- results for the monoclinic structure (space group ) of that were previously computed in Ref. [27] using lattice parameters reported in Ref. [64]. The band-structure calculations in Ref. [27] were performed within the local density approximation (LDA), using the non-fully relativistic PY-LMTO code [69]. In Ref. [27], self-consistency was obtained by performing calculations on a k-mesh, and the radii of the atoms were chosen as (O) and (Mo) a.u. As illustrated in Figure 1, the DFT density of states (DOS) projected on atomic orbitals reveals that the most relevant states in this distorted rutile compound are the Mo- carriers. This observation is consistent with previous studies that identified all orbitals as having appreciable spectral weight close to the Fermi level (). As with and , due to lattice dimerization resulting from Peierls-like structural effects [21] that promote c-axis dimer pairing [70,71], the orbital splits into bonding/antibonding bands, as shown in Figure 1. However, in contrast to the DFT results derived for monoclinic and [22,43,44], the and orbitals of distorted are metallic, with a non-zero DOS near . As seen in Figure 1, the and DOS of monoclinic exhibit a two-peak structure above and below , albeit with a lesser degree of prominence as compared to that observed in the orbital. The reconstruction of the orbitals with nearly Peierls-localized () and itinerant () spectral functions induced by local dynamical correlations in concert with changes in total electron band filling is crucial for understanding the emergent electronic state of pure and electron-doped . This is the focus of the following discussion.
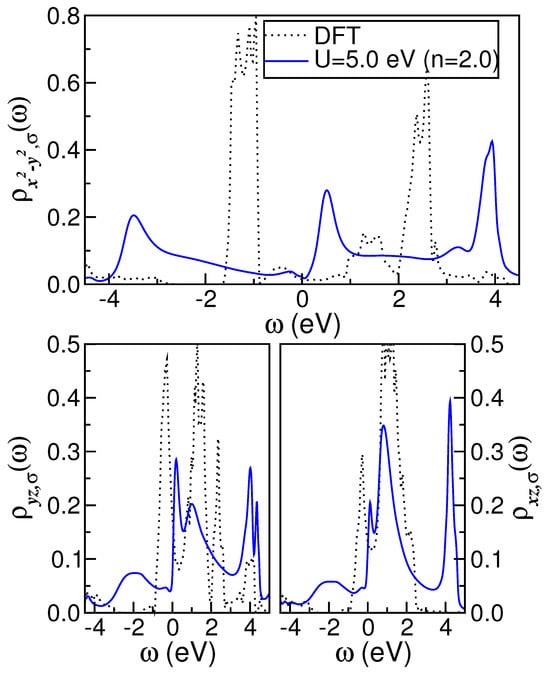
Figure 1.
DFT and DFT+DMFT ( eV) density of states (DOS) of monoclinic taken from Ref. [27]. Notice the splitting of the DFT DOS into bonding/antibonding branches, a characteristic akin to monoclinic materials. Also noteworthy is the metallic behavior of the orbitals with finite DOS at the Fermi level. The DFT+DMFT results shows that the electronic reconstruction induced dynamical correlation effects in the stoichiometric parent compound.
Earlier band-structure calculations [27,29,30,41] for have shown that the electronic states near originate from Mo orbitals. Thus, based on DFT, the bare-band Hamiltonian () of monoclinic [27] is constructed using the orbitals. These three diagonalized orbitals (see Figure 1) are the DFT inputs for DMFT, which dynamically reconstructs the electronic states and generates an orbital-selective metal, as shown below. As in Ref. [27], local two-particle interactions in are included in the many-body Hamiltonian (), which contains the on-site (U) and the inter-orbital () Coulomb interaction, as well as Hund’s exchange interaction . We compute the Green functions of within DFT+DMFT [28] using the iterated perturbation theory for MO systems, i.e., the MO-IPT impurity solver [72]. The full set of DMFT(MO-IPT) equations can be accessed in Ref. [72]. For the sake of brevity, we refrain from repeating the equations here. It should be noted, however, that the IPT self-energy accounts for the correct low- and high-energy reconstruction of the spectral DOS, as well as the correlated FL behavior within the DMFT approximation [9]. The Mott–Hubbard MIT is also ensured by the IPT solver. Both the one-band and MO IPT schemes are computationally very efficient, enabling real frequency output at zero temperature. As shown in the following section, the DFT+DMFT(MO-IPT) solution for monoclinic introduces non-trivial dynamical effects arising from electronic correlations. Specifically, these processes result in a significant spectral weight transfer across a broad energy range in response to minor changes in the electronic parameters. It is also noteworthy that MO-IPT results have been compared with those obtained with a continuous-time QMC approach [73], providing support for this perturbative treatment.
3. Results and Discussion
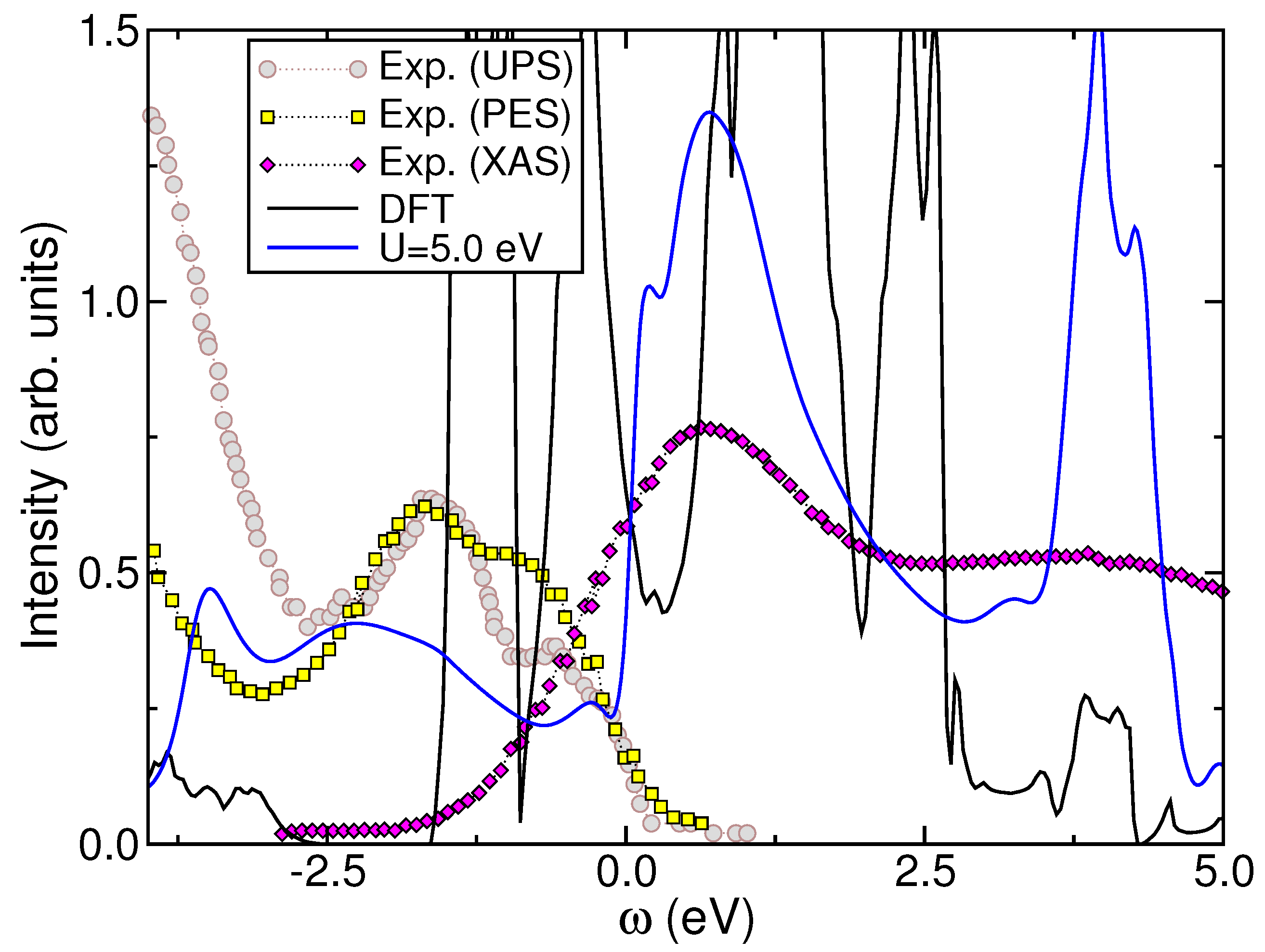
Figure 1 and Figure 2 illustrate the orbital-resolved and total DFT+DMFT results, respectively, computed using eV (and eV) in Ref. [27]. The DFT+DMFT results in these figures demonstrate the significant impact of MO interactions in on the () valence state. Similarly to and [22,25], as well as to - [26], considering , and results in a redistribution of spectral weight over large energies, as visible in Figure 1 and Figure 2. Importantly, the DFT+DMFT result in Figure 2 is in accordance with UPS and PES data presented in Refs. [29] and [41], respectively, which exhibit two principal shoulder features below 1.0 eV binding energy and a pseudogap-like electronic state with a markedly reduced DOS in proximity to in the experimental context. Furthermore, existing PES and angle-resolved PES (ARPES) measurements can be interpreted, to some extent, based on our DFT+DMFT results. An ARPES study [30] reveals a broad maximum centered at approximately 0.2 eV binding energy, which shifts towards as the emission angle and photon energy increase. In light of these observations, we propose that this primary maximum can be identified by the small bump observed in the total DFT+DMFT DOS at eV. As demonstrated in Ref. [27], decreasing the value of U results in the emergence of a significant peak near , which is not observed in experimental data [8,29,41,45]. There is a notable qualitative alignment between our results and the UPS spectra presented in Ref. [29]. Similar to PES, the UPS data at low energies indicate the suppression of FL coherence [8], giving rise to unconventional metallicity in the stoichiometric system. Furthermore, the valence-band spectra obtained from thin films indicate the presence of an energy band with a peak at approximately eV [46], which is consistent with the lower Hubbard band (LHB) centered at energies near to eV, as in Figure 2. Interestingly, this value coincides with a band gap in DFT at which the oxygen p bands begin. The absence of this -band gap in experiments [7,8,45,46,47] may be regarded as an additional fingerprint of hidden dynamical interactions in monoclinic . Finally, to illustrate the influence of many-particle interactions on the system, in Figure 2, we present a comparison between our DFT+DMFT result and the X-ray absorption spectral (XAS) data from Ref. [41]. Although, our result for eV is not perfect, it is nevertheless a valuable contribution to understand the correlated electronic state of the parent compound. The calculated spectra at eV qualitatively reproduce the shoulder feature observed at approximately 0.7 eV above , providing further support for our electronic reconstruction for the bulk crystal shown in Figure 1.
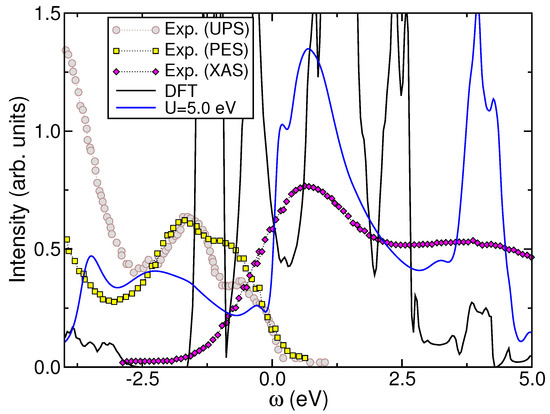
Figure 2.
Comparison between the theoretical DOS for eV ( eV) [27] and the experimental UPS (circles), PES (square), and XAS (diamond) spectra taken from Ref. [29] (UPS) and Ref. [41] (PES and XAS), respectively. (The PES data were shifted downward by 0.3 eV to coincide with UPS data at low energies.) An important feature here is the qualitative theoretical–experimental agreement at 1.0 eV below and the correlation-induced transfer of spectral weight from low to high negative energies. Also note the peak position of the shoulder feature close to 0.7 eV above , which is in agreement with the XAS data. The total DFT DOS is also shown for sake of comparison.
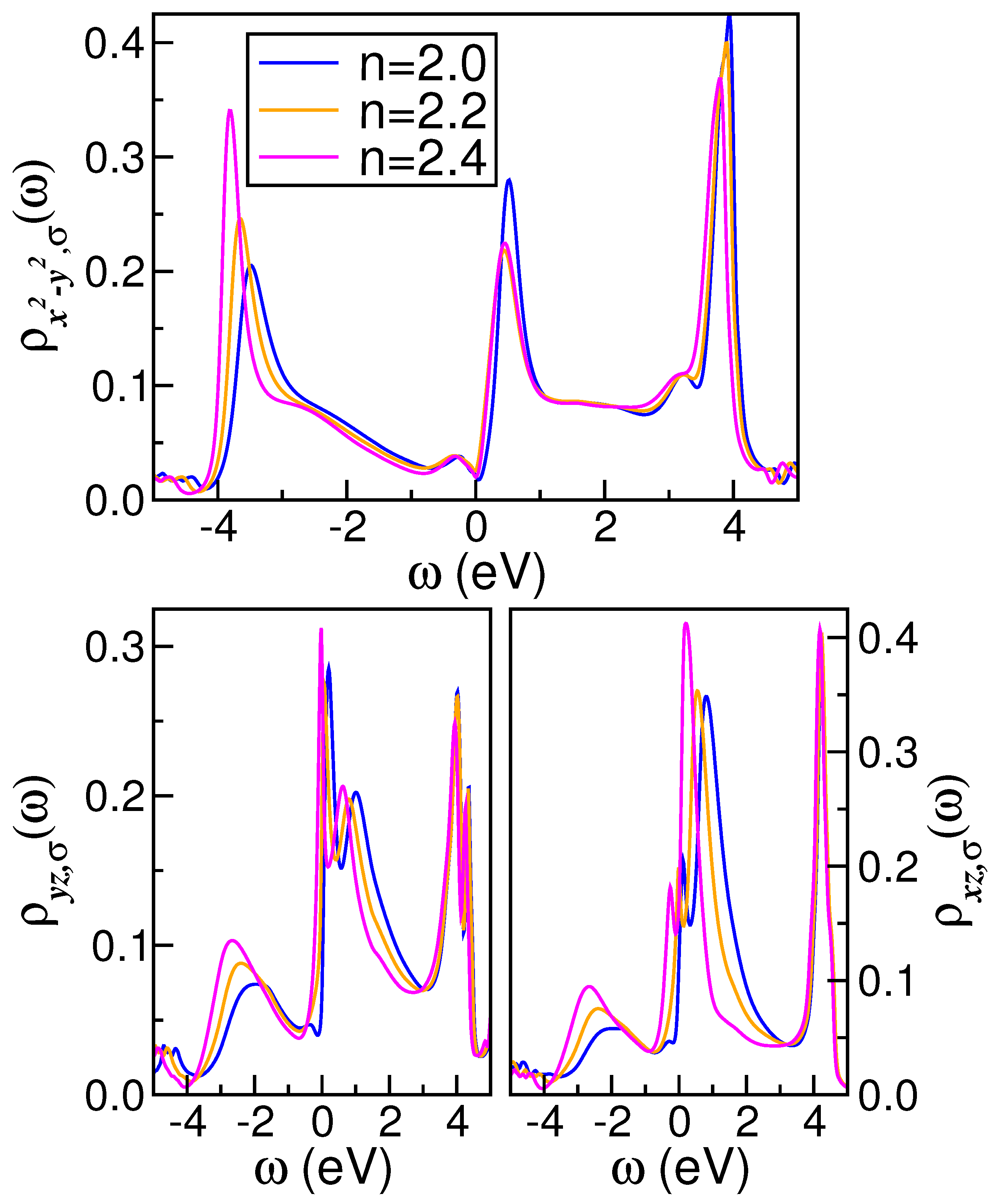
To provide an analysis of the interplay between dynamical MO correlations and electron-doping effects, in Figure 3 and Figure 4, we show how the orbital-resolved spectral functions and real and imaginary self-energy parts change with increases in the total filling (n) of the shell of the parent compound. As revealed in these figures, MO electronic correlations result in orbital-selective modifications of the correlated spectra, demonstrating the resilience of the pseudogapped electronic state [27] against electron doping. Consequently, this orbital exhibits less reshaping than the and orbitals, as evidenced in Figure 3. Moreover, the many-body spectra, which exhibit a reduced bare DOS at in comparison to the orbital, display coherent FL metal characteristics with doping-dependent quasiparticle features at low energies (Figure 3). Finally, it should be noted that the spectral function of the orbital at low energies near deviates from the truly FL coherence [9] of good metals, as discussed below.
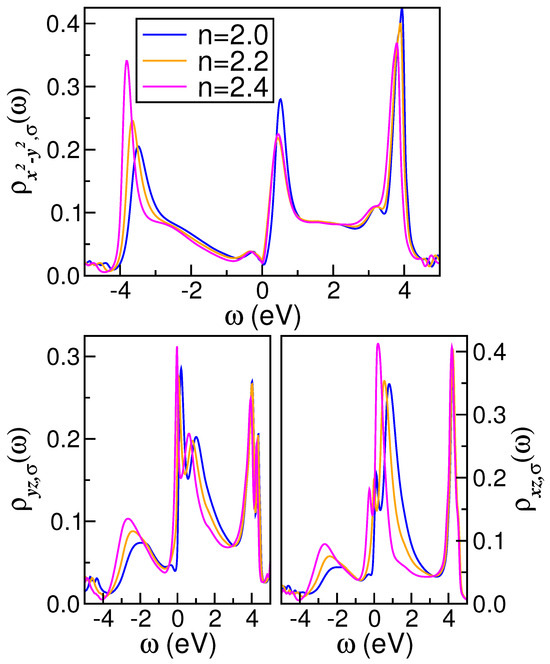
Figure 3.
Effect of electron doping on the orbital-resolved DFT+DMFT spectral functions of monoclinic . Particular features of note are the pseudogap and the shoulder feature above in the orbital, as well as the clearly visible transfer of spectral weight with increases in the total band filling (n).
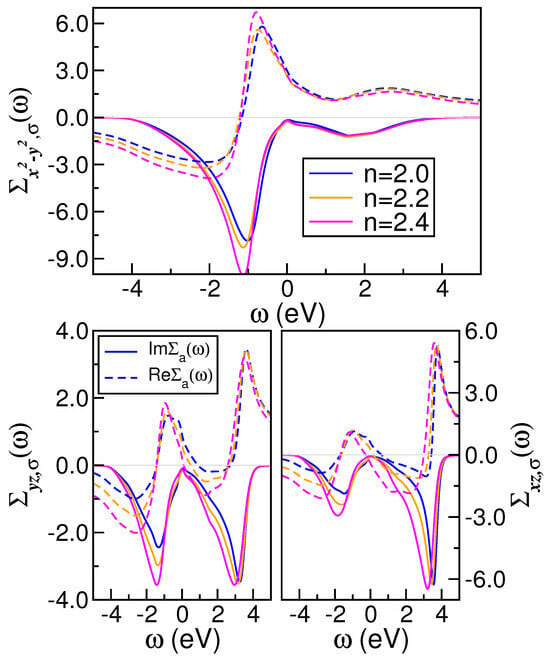
Figure 4.
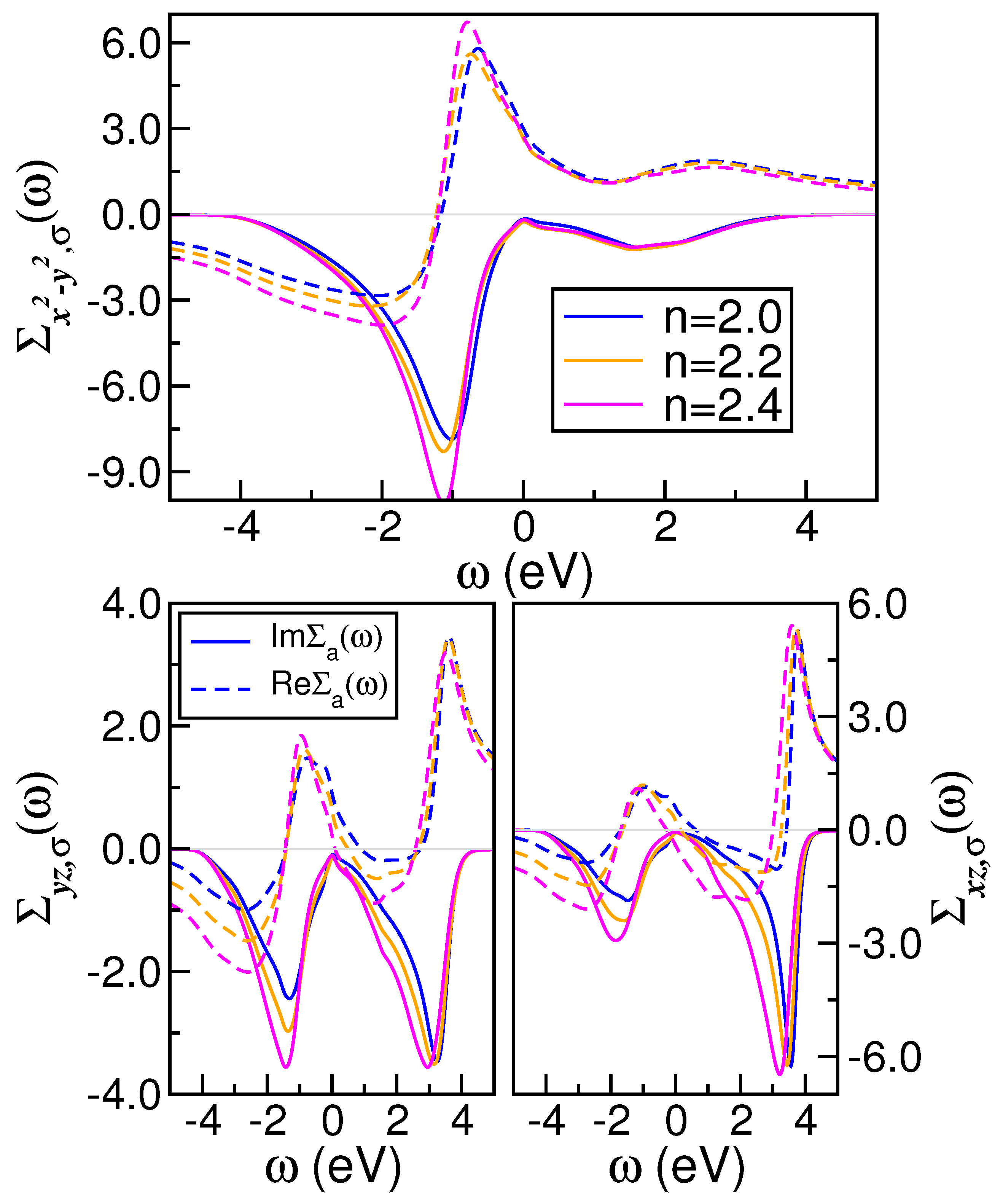
Evolution of the real (dashed lines) and imaginary (solid lines) self-energy parts of bulk crystal with increasing n. Notice the Fermi-liquid-like behavior in the orbital sector and the marginal V-shaped form in the channel. Also interesting are the weak changes of the self-energy to electron doping, as well as the particle-hole asymmetry seen in the and self-energies.
As shown in Figure 3, at eV, a narrow LHB emerges in the orbital, situated close to −3.5 eV, which is dynamically transferred to higher binding energies, becoming slightly more pronounced with increasing total electron filling (n). In contrast to the orbitals, the upper Hubbard band (UHB) is not fully resolved in the orbital sector. Indeed, a sharp antibonding-like peak is observed near to 3.8 eV above , accompanied by a shoulder trace at approximately eV, both exhibiting weak reconstruction with increasing n. Additionally, local correlations between electrons induce a notable dynamical spectral weight transfer in the and orbitals, as seen in Figure 3. Local MO electronic interactions in these orbitals result in the emergence of sharp quasiparticle peaks in close proximity to . These collective many-particle resonances shift towards energies closer to as the number of electrons (n) increases, accompanied by a transfer of spectral weight from the conduction band to the LHBs below 2.0 eV binding energies in the and orbitals. Furthermore, the and orbital proximity effect, which is influenced by sizable and , gives rise to the emergence of UHBs at energies that are in proximity to the renormalized antibonding band in the channels. This phenomenon may explain why, apart from thin films [10], no structural transition has been reported for the compound [29]. It is also noteworthy that incoherent electronic excitations in the valence band induce local moments and, potentially, magnetism [7] related to the development of an LHB [74] with an orbital character in Mo-containing compounds. However, the complex interplay between Fermi surface topology [75] with superconductivity and magnetism [7] in unconventional metals [6,53] is beyond the scope of our present study and is, thus, left for futures studies.
To microscopically elucidate the normal state of pure and electron-doped , in Figure 4, we present evolution of orbital-resolved self-energies (both the real and imaginary parts) associated with the active MO orbitals of monoclinic . A comparison of our results with those of ThFeAsN superconductor [76] reveals the presence of analogous features despite the dissimilar crystal structure, Coulomb interaction parameters, and total band filling in the two systems. This includes a discernible particle–hole asymmetry in Im and an observable orbital selectivity with increasing n. Furthermore, the particle–hole asymmetry is also evident in the real self-energy parts. This frequency and/or energy dependence indicates that the many-particle reconstruction in the effective valence state of is governed simultaneously by the real and imaginary self-energy parts. In the orbital-selective metal at eV, Im shows a nearly quadratic dependence on frequency, while Im exhibits a V-shaped form at low energies. The latter is consistent with the behavior observed in a marginal Fermi-liquid (mFL) metal [77], where the imaginary part of the mFL self-energy is proportional to the frequency, i.e., Im. In contrast, normal FL metals display a quadratic dependence of the imaginary part of the self-energy on frequency [9], i.e., Im. Therefore, our findings for the orbital in Figure 4, which exhibit a sub-linear dependence, indicate the potential for hidden orbital-selective marginal Fermi liquidness in pure and doped , which could contribute to the formation of resilient quasiparticles [33]. When viewed in conjunction with previous studies, our results presented in Figure 4 highlight the interplay between MO electronic correlations and band filling as the system approaches the superconducting state [78].
The DFT+DMFT outcome in Figure 3 demonstrates how MO correlations promotes an orbital-selective self-organization of the -electron DOS of monoclinic . The spectral function reveals FL itinerancy at large U values in both pure and electron-doped and exhibits a shape comparable to that of the -mFL orbital. In contrast, the orbital DOS displays a markedly different line shape, indicative of a more localized character. Furthermore, the transfer of spectral weight (of approximately 8.0 eV) is evident in Figure 3 when the parent compound is subjected to electron doping. In our MO DFT+DMFT calculation, the - and -driven inter-orbital proximity effect results in a redistribution of spectral weight between the active orbitals of . This is a characteristic intrinsic to correlated MO systems and indicates the importance of many-body interactions in pure and doped .
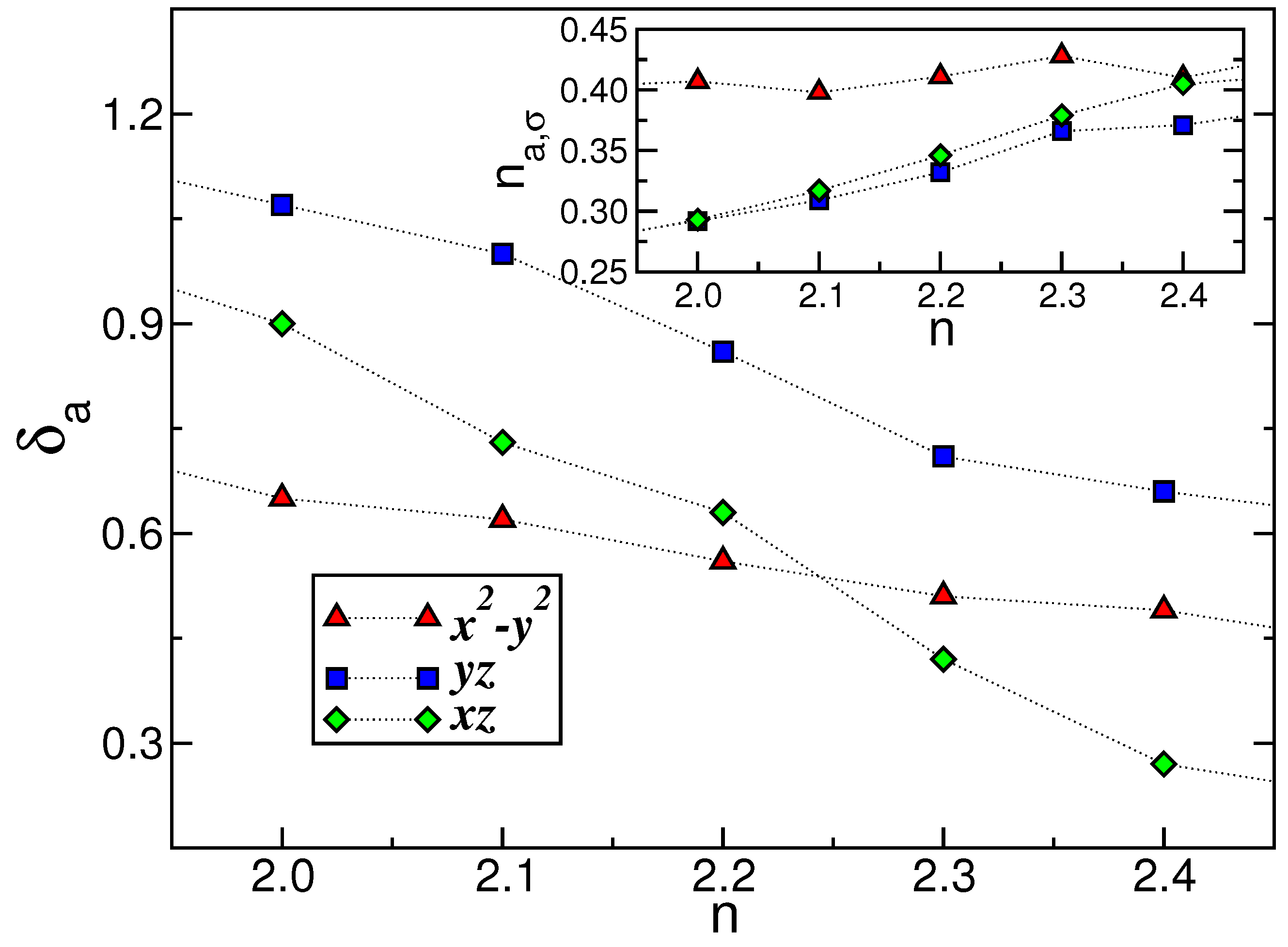
With these caveats, Figure 5 displays the renormalized orbital splitting (; main panel) and the occupation numbers (; inset) predicted using DFT+DMFT for pure and electron-doped . Notice that the orbital polarization is diminished with increasing n, resulting in significant changes in the orbital occupations, as illustrated in the inset of Figure 5. This response to correlated compounds is common; electron band filling is untied to orbital and charge fluctuations in the correlated one-particle electronic state. Moreover, as unveiled in Figure 5, notable modifications in are observed with increasing n. As can be seen, up to , the orbital represents the ground-state (or lowest-energy) orbital, with the orbital occupying this position above total band filling. Here, the gravity center of the orbital is enhanced towards the higher-energy orbital sector. It is noteworthy that the doping-induced twofold () orbital degeneracy observed in the main panel of Figure 5 may have implications for the unconventional superconductivity observed in systems. A review of previous studies on Fe-based superconducting materials indicates that they exhibit orbital degeneracy due to their tetragonal crystal symmetry. Therefore, our theory suggests that Cooper pair formation in doped primarily involves the orbitals. In accordance with our hypothesis, can be conceptualized as a two- electronic fluid, with one taking part in the superconducting state and the other not. Our proposal may be applicable to systems in a bad-metal regime near to twofold orbital degeneracy, wherein part of the normal spectral weight contributes to the superconducting condensate below . In light of these findings, there are promising avenues for two-fluid theories of superconductivity [79] in .
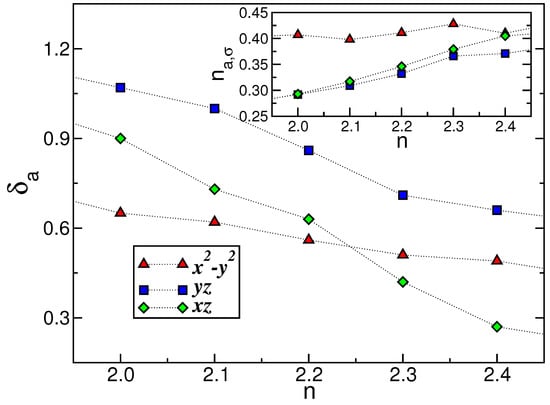
Figure 5.
DFT+DMFT orbital occupations (; inset) and orbital splittings (; main panel) as functions of the total band filling (n). The inset shows the changes in orbital polarization between the and orbitals with increasing n. An additional important aspect is the change in the ground orbital at n close to 2.25 and, thus, the emergence of nearly twofold orbital degeneracy in electron-doped .
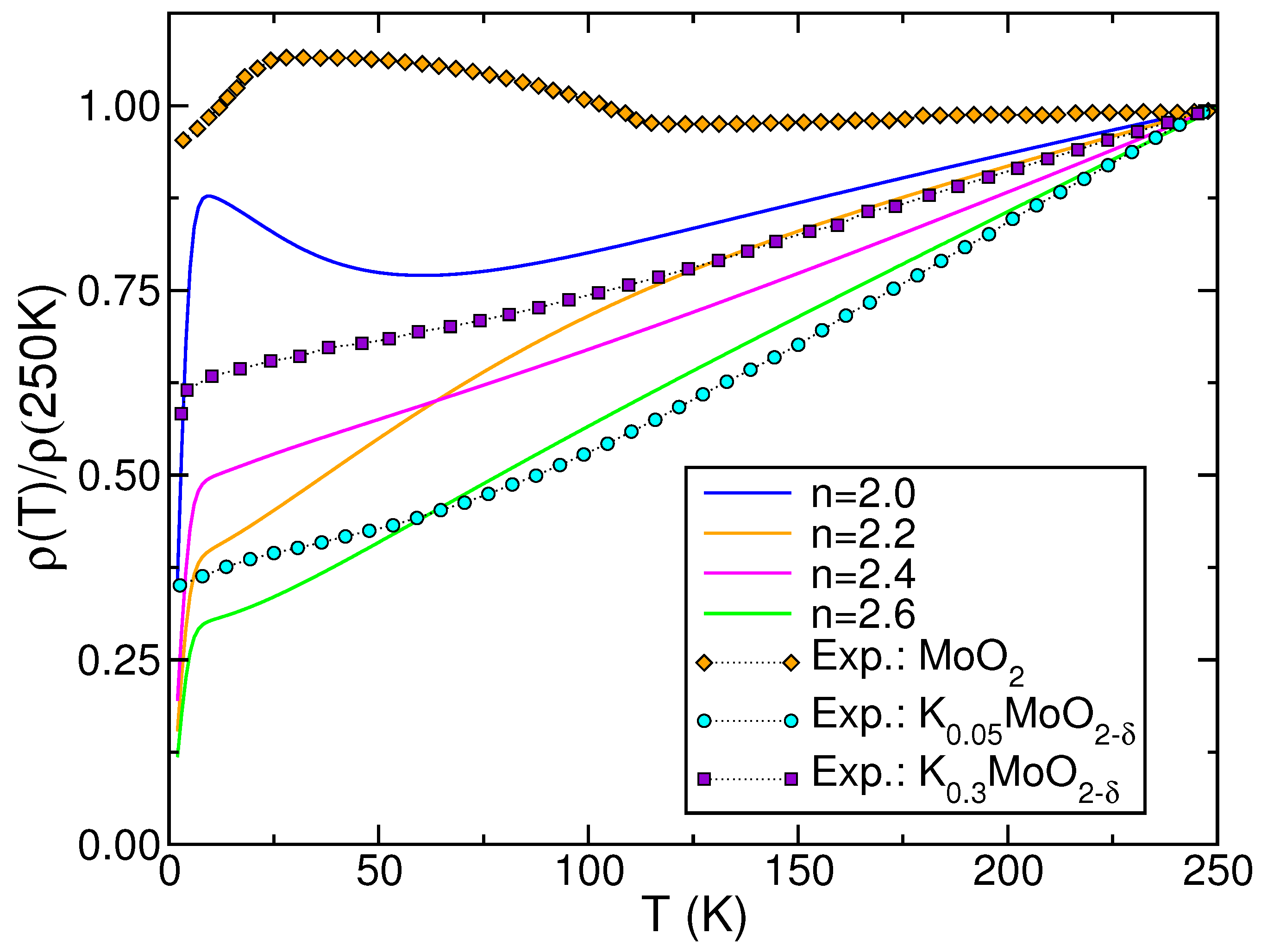
The unusual metallicity evident in pure and oxygen-deficient [8,30], as well as in K-doped , [6,7] and its deviation from the FL dependence of the resistivity in the normal state, lends further support for orbital selectivity in stoichiometric and electron-doped . In particular, here, we describe the T dependence of the resistivity, correlating it with the selective orbital scenario derived above. Given the DMFT spectral functions () the (static) conductivity [80] can be written as . In this expression, is the bare DFT DOS of the a orbitals (Figure 1), is the unit cell volume, and is the Fermi function. As in Refs. [81,82,83], the aim of the approximation made here is to disregard the dependence of the electron’s velocity (). Thus, for simplicity, is thus approximated using a single carrier velocity (v). This approximation has been considered for the evaluations of of heavy-Fermion and transition-metal systems [81,82,83], thereby corroborating our approximation in as previously stated. The aim here is to demonstrate how this approach provides a qualitative description of the experimental resistivity data on Mo-based oxides.
In Figure 6 we display computed using the DFT+DMFT DOS of stoichiometric and electron-doped (see Figure 3). As shown in Figure 6, the DFT+DMFT outcome for the parent compound exhibits a resistivity upturn from 60 down to 10 K. In contrast, experimental findings indicate that the resistivity upturn occurs at a temperature close to 110 K (see the diamond curve). It is notable that upon electron doping, the resistivity upturn disappears, giving rise to resistivity curves that are characteristic of power-law, pseudogaped metals [76]. Furthermore, for , the resistivity is approximately proportional to T from 14 K up to room T, indicating the emergence of strange-metal behavior in electron-doped similar to that observed in , as illustrated in the square curve of Figure 6. Our findings reveal that up to , the FL- response is absent in the electron-doped compound at low T. The reason for this behavior is that in a regime of sizable to strong , the non-FL-like behavior of the orbitals is not destabilized by electron doping, as pointed out in Figure 3 and Figure 4. Therefore, as the total n of the shell increases, becomes less weakly insulating [8], transitioning to a bad-metallic normal state [6,7]. In , a superconducting transition ends up the crossesover to a T-linear metal. However, the T dependence of the computed in the normal state is analogous to that reported in Refs. [6,7], where in the normal state revealed a power-law-like behavior above , subsequently approaching the superconducting transition. However, in view of the conflicting resistivity results for pure and doped [6,7,8,11], it remains to be seen in future studies whether the results derived for electron-doped exhibit characteristics analogous to the power-law liquid realized from Fermionic unparticles [14,15].
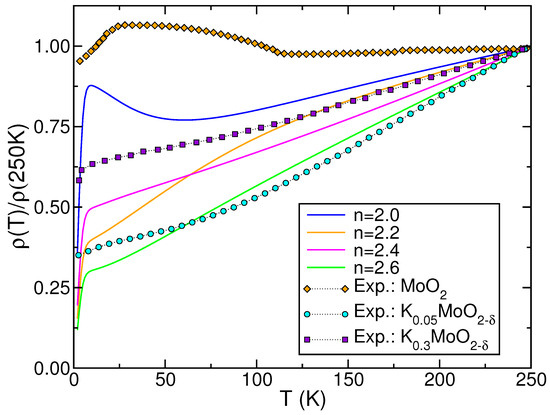
Figure 6.
Theoretical–experimental comparison of the electrical resistivity (normalized at 250 K) of pure and electron-doped . Notice the resistivity upturn for , with similarities akin to those reported for (diamond curve for the experimental data taken from Ref. [8]). Also noteworthy is the evolution of upon electron doping of the parent compound, displaying the similar power-law-like, non-FL T dependence of the data in the normal, non-superconducting state taken from Ref. [7] for (circle curve) and (square curve).
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, we employed combined DFT and DMFT approaches to elucidate the correlated state of superconductors. In particular, for pure and doped , we analyzed the changes in their metallic behavior due to the non-trivial interplay between dynamical correlations and electron doping. Additionally, the orbital-selective electronic behavior is noteworthy, wherein pseudogapped and resilient electronic excitations coexist with coherent, Fermi-liquid electronic states at low energies. This phenomenon is shown to result from the interplay between orbital polarization and electron–electron interactions. To confirm this hypothesis, a combination of theoretical and experimental studies on systems should be conducted. Such studies are required to corroborate our orbital-selective scenario for the normal state of a superconductor [6,7]. It would be of great interest to ascertain whether quantum criticality associated with Mottness is confirmed in . Our work provides a motivation for examining the potential for closer similarities between electron-doped and tetragonal Fe-based superconductors. As in these Fe-based compounds with tetragonal crystal structure, it is anticipated that superconductivity in will manifest as an instability of a correlated bad metal in proximity to twofold orbital degeneracy. In light of our findings, we propose that is an ideal candidate for investigating this hypothesis and the potential realization of infrared power-law liquids [14,15] arising from unparticle interactions. This is compelling motivation to consider Mott materials near to selective orbital localization [26] and suggest a promising route to understanding doped molybdenum dioxide, which exhibits unconventional normal-state quantum metallicity [84]. Our findings are expected to advance the current understanding of the orbital-selective behavior in monoclinic and provide a foundation for future studies of Mo-containing oxides [63].
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request to the author.
Acknowledgments
The author acknowledges CNPq and CAPES, as well as Laurin Craco, for making valuable suggestions to improve the quality of the presentation in the Discussion section based on DeepL Write. The author also acknowledges Stefano Leoni for helpful comments, as well as the Leibniz Institute for Solid State and Materials Research Dresden for hospitality.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction to the reference 35. This change does not affect the scientific content of the article.
References
- Stewart, G.R. Non-Fermi-liquid behavior in d- and f-electron metals. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2001, 73, 797–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Goswami, P.; Si, Q.; Nikolic, P.; Zhu, J.-X. Superconductivity at the border of electron localization and itinerancy. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaramillo, R.; Ha, S.D.; Silevitch, D.M.; Ramanathan, S. Origins of bad-metal conductivity and the insulator–metal transition in the rare-earth nickelates. Nat. Phys. 2014, 10, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, V.J.; Kivelson, S.A. Superconductivity in bad metals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 74, 3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imada, M.; Fujimori, A.; Tokura, Y. Metal-insulator transitions. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1998, 70, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.M.S.; Damasceno, V.I.; dos Santos, C.A.M.; Bortolozo, A.D.; Suzuki, P.A.; Izario Filho, H.J.; Machado, A.J.S.; Fisk, Z. Unconventional metallic behavior and superconductivity in the K-Mo-O system. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 174532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.M.S.; dos Santos, C.A.M.; Benaion, S.S.; Machado, A.J.S.; de Lima, B.S.; Neumeier, J.J.; Marques, M.D.R.; Aguiar, J.A.; Mossanek, R.J.O.; Abbate, M. Superconductivity and magnetism in the KxMoO2−δ. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 073923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.M.S.; Benaion, S.S.; Romanelli, C.M.; dos Santos, C.A.M.; da Luz, M.S.; de Lima, B.S.; Oliveira, F.S.; Machado, A.J.S.; Guedes, E.B.; Abbate, M.; et al. Electrical Resistivity in Non-stoichiometric MoO2. Braz. J. Phys. 2015, 45, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georges, A.; Kotliar, G.; Krauth, W.; Rozenberg, M.J. Dynamical mean-field theory of strongly correlated fermion systems and the limit of infinite dimensions. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1996, 68, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, E.; Seo, Y.-S.; Cho, J.; Lee, I.; Hwangb, J.; Jeen, H. Epitaxial growth and metallicity of rutile MoO2 thin film. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 60704–60708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lou, Z.; Zhang, S.N.; Xu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Du, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; et al. Large magnetoresistance and nonzero Berry phase in the nodal-line semimetal MoO2. Phys. Rev. B 2020, 102, 165133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.-H.; Lin, J.-C.; Liu, H.-J.; Do, T.H.; Zhu, Y.-M.; Ha, T.D.; Zhan, Q.; Juang, J.-Y.; He, Q.; Arenholz, E.; et al. Van der Waals epitaxy of functional MoO2 film on mica for flexible electronics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 253104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosle, V.; Tiwari, A.; Narayan, J. Epitaxial growth and properties of MoOx (2 ≤ x ≤ 2.75) films. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 083539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limtragool, K.; Setty, C.; Leong, Z.; Phillips, P.W. Realizing infrared power-law liquids in the cuprates from unparticle interactions. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 23512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, Z.; Setty, C.; Limtragool, K.; Phillips, P.W. Power-law liquid in cuprate superconductors from fermionic unparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 96, 205101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Cao, X.; Luo, H.; Jin, P. Recent progress in the phase-transition mechanism and modulation of vanadium dioxide materials. NPG Asia Mater. 2018, 10, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, D. Mechanisms for metal-nonmental transitions in transition-metal oxides and sulfides. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1968, 40, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahila, M.J.; Paez, G.; Singh, C.N.; Regoutz, A.; Sallis, S.; Zuba, M.J.; Rana, J.; Tellekamp, R.M.B.; Boschker, J.E.; Markurt, T.; et al. Evidence of a second-order Peierls-driven metal-insulator transition in crystalline NbO2. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2019, 3, 074602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoever, J.; Boschker, J.E.; Anooz, S.B.; Schmidbauer, M.; Petrik, P.; Schwarzkopf, J.; Albrecht, M.; Irmscher, K. Approaching the high intrinsic electrical resistivity of NbO2 in epitaxially grown films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 116, 182103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mott, N.F. Metal-insulator transition. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1968, 40, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodenough, J.B. The two components of the crystallographic transition in VO2. J. Solid State Chem. 1971, 3, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biermann, S.; Poteryaev, A.; Lichtenstein, A.I.; Georges, A. Dynamical singlets and correlation-assisted Peierls transition in VoO2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 026404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.; O’Regan, D.D.; Hine, N.D.M.; Payne, M.C.; Kotliar, G.; Littlewood, P.B. Vanadium dioxide: A Peierls-Mott insulator stable against disorder. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 256402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, W.H.; Aguiar, M.G.O.; Haule, K.; Kotliar, G. Metal-insulator transition in VO2: A DFT+DMFT perspective. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117, 056402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, W.H.; Aguiar, M.G.O.; Haule, K.; Kotliar, G. Dynamic electronic correlation effects in NbO2 as compared to VO2. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 96, 195102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Backes, S.; Yoon, H.; Kim, W.; Sohn, C.; Son, J.; Biermann, S.; Noh, T.W.; Park, S.Y. Orbital-selective Mott and Peierls transition in HxVO2. NPJ Quantum Mater. 2022, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craco, L.; Leoni, S. All-t2g2g electronic orbital reconstruction of monoclinic MoO2 battery material. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotliar, G.; Savrasov, S.Y.; Haule, K.; Oudovenko, V.S.; Parcollet, O.; Marianetti, C.A. Electronic structure calculations with dynamical mean-field theory. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2006, 78, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyert, V.; Horny, R.; Höck, K.-H.; Horn, S. Embedded Peierls instability and the electronic structure of MoO2. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2000, 12, 4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosburger-Will, J.; Kündel, J.; Klemm, M.; Horn, S.; Hofmann, P.; Schwingenschlögl, U.; Eyert, V. Fermi surface of MoO2 studied by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy, de Haas–van Alphen measurements, and electronic structure calculations. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 115113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavoni, E.; Modreanu, M.G.; Mohebbi, E.; Mencarelli, D.; Stipa, P.; Laudadio, E.; Pierantoni, L. First-principles calculation of MoO2 and MoO3 electronic and optical properties compared with experimental data. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, N.; Takeda, H.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yamada, Y.; Iida, K.; Takigawa, M.; Ohta, Y.; Sawa, H. Robust atomic orbital in the cluster magnet LiMoO2. Phys. Rev. B 2020, 102, 081106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Mravlje, J.; Žitko, R.; Ferrero, M.; Kotliar, G.; Georges, A. How bad metals turn good: Spectroscopic signatures of resilient quasiparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 086401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, B.W.; Ellefson, C.; Breit, J.; Kim, J.; Norton, M.G.; Ha, S. Molybdenum dioxide-based anode for solid oxide fuel cell applications. J. Power Sources 2013, 243, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, B.W.; Hu, S.; Marin-Flores, O.; Norton, M.G.; Kim, J.; Scudiero, L.; Breit, J.; Ha, S. High-performance molybdenum dioxide-based anode for dodecane-fueled solid-oxide fuel cells (SOFCs). Energy Technol. 2014, 2, 425–430, Retraction in Energy Technol. 2017, 5, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, J.K.; Lee, H.S.; Park, G.O.; Yoon, J.; Park, E.; Park, G.S.; Kong, S.S.; Jin, M.; Choi, J.-M.; Chang, H.; et al. Discovery of abnormal lithium-storage sites in molybdenum dioxide electrodes. Nat. Comm. 2016, 7, 11049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Hu, X.; Yu, J.C.; Li, Q.; Luo, W.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Y. Morphosynthesis of a hierarchical MoO2 nanoarchitecture as a binder-free anode for lithium-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 2870–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, U.K.; Shaligram, A.; Mitra, S. Intercalation anode material for lithium ion battery based on molybdenum dioxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 14311–14319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.; Cho, C.J.; Lee, W.C.; Hwang, C.S.; Changa, R.P.H.; Kim, S.K. MoO2 as a thermally stable oxide electrode for dynamic random-access memory capacitors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 13250–13256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Poudyal, S.; Rajarapu, R.; Biswal, B.; Barman, P.K.; Kasiviswanathan, S.; Novoselov, K.S.; Misra, A. Low power volatile and nonvolatile memristive devices from 1D MoO2-MoS2 core–shell heterostructures for future bio-inspired computing. Small 2024, 20, 2309163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoeberl, V.; Abbate, M.; Alves, L.M.S.; dos Santos, C.A.M.; Mossanek, R.J.O. X-ray spectroscopy and electronic structure of MoO2. J. Alloys Compds. 2017, 691, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyert, V. The metal-insulator transitions of VO2: A band theoretical approach. Ann. Phys. (Leipzig) 2002, 11, 650–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyert, V. The metal-insulator transition of NbO2: An embedded Peierls instability. Europhys. Lett. 2002, 58, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulmus, K.; Gemming, S.; Schreiber, M.; Pashov, D.; Acharya, A. Theoretical evidence for the Peierls transition in NbO2. Phys. Rev. B 2021, 104, 035128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeberl, V.; Guedes, E.B.; Abbate, M.; Abud, F.; Jardim, R.F.; Mossanek, R.J.O. Charge screening effects in the resonant photoemission of Rh2O3, RuO2, and MoO2. Phys. Rev. B 2020, 102, 155122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, R.; Choudhary, R.J.; Phase, D.M. Electronic structure of Fe (0–5 at.%) doped MoO2 thin films studied by resonant photoemission spectroscopy. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2008, 20, 335225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werfel, F.; Minni, E. Photoemission study of the electronic structure of Mo and Mo oxides. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 1983, 16, 6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, L.L. Optical properties of CrO2 and MoO2 from 0.1 to 6 eV. Phys. Rev. B 1974, 10, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, M.A.K.; Chase, L.L. Optical properties of CrO2, MoO2, and WO2 in the range 0.2–6 eV. Phys. Rev. B 1978, 18, 6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, R.; Phase, D.M.; Choudhary, R.J.; Kumar, R. Structural, electrical, and magnetic properties of Mo1−xFexO2 (x = 0–0.05) thin films grown by pulsed laser ablation. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 043712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Guo, B.; Corr, S.A.; Shi, Y.Q.; Hu, Y.-S.; Heier, K.R.; Chen, L.; Seshadri, R.; Stucky, G.D. Ordered mesoporous metallic MoO2 materials with highly reversible lithium storage capacity. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 4215–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.M.; Hu, X.L.; Luo, W.; Xia, F.F.; Huang, Y.H. Developments in molybdenum oxides as anode materials in lithium-ion batteries. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 3254. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Sheng, H.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Q.; Weng, H.; Fang, Z.; Wang, Z. Superconductivity in unconventional metals. NPJ Comput. Mater. 2024, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laad, M.S.; Craco, L.; Müller-Hartmann, E. Metal-insulator transition in rutile-based VO2. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 195120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebsch, A.; Ishida, H.; Bihlmayer, G. Coulomb correlations and orbital polarization in the metal-insulator transition of VO2. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 085109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, J.M.; Biermann, S. Effective band structure of correlated materials: The case of VO2. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2007, 19, 365206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, J.M.; Aryasetiawan, F.; Biermann, S. Effective bandstructure in the insulating phase versus strong dynamical correlations in metallic VO2. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 115103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlkvik, P.; Merkel, M.E.; Spaldin, N.A.; Ederer, C. Single-site DFT+DMFT for vanadium dioxide using bond-centered orbitals. Phys. Rev. Res. 2024, 6, 033122. [Google Scholar]
- Belozerov, A.S.; Korotin, M.A.; Anisimov, V.I.; Poteryaev, A.I. Monoclinic M1 phase of VO2: Mott-Hubbard versus band insulator. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 85, 045109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, M.; Bruneval, F.; Olevano, V.; Reining, L. Understanding correlations in vanadium dioxide from first principles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 266402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, C.; Acharya, S.; Cunningham, B.; Grüning, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, K.; et al. Role of the lattice in the light-induced insulator-to-metal transition in vanadium dioxide. Phys. Rev. Res. 2020, 2, 023076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craco, L. Orbital-selective electronic localization in dimerized NbO2: From Peierls to Mott. Phys. Rev. B 2024, 109, 235136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-c.; Gaines, D., II; Kim, H.; Salgado-Casanova, A.; Torrisi, S.B.; Chris Wolverton, C. Anomalous reversal of stability in Mo-containing oxides: A difficult case exhibiting sensitivity to DFT+U and distortion. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.04434. [Google Scholar]
- Scanlon, D.O.; Watson, G.W.; Payne, D.J.; Atkinson, G.R.; Egdell, R.G.; Law, D.S.L. Theoretical and experimental study of the electronic structures of MoO3 and MoO2. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyev, I.V. Effects of crystal structure and on-site Coulomb interactions on the electronic and magnetic structure of A2Mo2O7 (A = Y, Gd, and Nd) pyrochlores. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 67, 174406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coquet, D.; Willock, D. The (010) surface of α-MoO3, a DFT+U study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 7, 3819–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Pang, Z.; Lin, L.; Fang, S.; Dai, Y.; Han, S. Origin of magnetism in undoped MoO2 studied by first-principles calculations. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 134407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadati, H.; Yoshimatsu, K.; Kumigashira, H.; Oshima, M.; Sugiyama, T.; Ikenaga, E.; Fujimori, A.; Mravlje, J.; Georges, A.; Radetinac, A.; et al. Photoemission and DMFT study of electronic correlations in SrMoO3: Effects of Hund’s rule coupling and possible plasmonic sideband. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 90, 205131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadov, S.; Qi, X.; Kübler, J.; Fecher, G.H.; Felser, C.; Zhang, S.C. Tunable multifunctional topological insulators in ternary Heusler compounds. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wentzcovich, R.; Schulz, W.; Allen, P.B. VO2: Peierls or Mott-Hubbard? A view from band theory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 72, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentzcovich, R.; Schulz, W.; Allen, P.B. Resistivity of the high-temperature metallic phase of VO2. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 48, 4359. [Google Scholar]
- Craco, L. Quantum orbital entanglement: A view from the extended periodic Anderson model. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 125122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, N.; Mondal, W.R.; Zhang, P.; Moreno, J.; Jarrell, M.; Vidhyadhiraja, N.S. A multi-orbital iterated perturbation theory for model Hamiltonians and real material-specific calculations of correlated systems. Eur. Phys. J. B 2016, 89, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, A.; Si, Q. Quantum criticality in the iron pnictides and chalcogenides. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2011, 23, 223201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Sattar, A.; Bashir, A.I.; Mustafa, H.; Khan, S.N.; Latif, H.; Pang, W.; Qin, S. A potential candidate material for quantum anomalous Hall effect: Heterostructures of ferromagnetic insulator and graphene. Phys. B Condensed Matter 2024, 673, 415439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craco, L.; Leoni, S. Orbital-selective nature of the 3d electronic structure of the ThFeAsN superconductor. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 103, 075110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, C.M.; Littlewood, P.B.; Schmitt-Rink, S.; Abrahams, E.; Ruckenstein, A.E. Phenomenology of the normal state of Cu-O high-temperature superconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1989, 63, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neilson, J.R.; Llobet, A.; Stier, A.V.; Wu, L.; Wen, J.; Tao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Tesanovic, Z.B.; Armitage, N.P.; McQueen, T.M. Mixed-valence-driven heavy-fermion behavior and superconductivity in KNi2Se2. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 054512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeen, J. Two-fluid model of superconductivity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1958, 1, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenzebach, C.; Anders, F.A.; Czycholl, G. Transport properties of heavy-fermion systems. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 195119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urasaki, K.; Saso, T. Correlation effects on optical conductivity of FeSi. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1999, 68, 3477–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saso, T. Calculation of optical Conductivity of YbB12 using realistic tight-binding model. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2004, 73, 2894–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassarre, L.; Perucchi, A.; Nicoletti, D.; Toschi, A.; Sangiovanni, G.; Held, K.; Capone, M.; Ortolani, M.; Malavasi, L.; Marsi, M.; et al. Quasiparticle evolution and pseudogap formation in V2O3: An infrared spectroscopy study. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 113107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, K.L.; McQueen, T.M.; Williams, A.J.; Klimczuk, T.; Stephens, P.W.; Zandbergen, H.W.; Xu, Q.; Ronning, F.; Cava, R.J. Insulator to correlated metal transition in V1−xMoxO2. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 245114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).