The changes below represent the corrections the authors wish to make to the original paper [1].
Errors in Tables
The authors wish to make changes to Tables 2–4. In the original publication, one of the values in Table 2 was not consistent with the text. For Tables 3 and 4, several values were missing a decimal point. The new Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4 are attached below.

Table 2.
Steady-state kinetic parameters of wild-type human GST P1–1 and mutants.

Table 3.
Saturation kinetics in three dimensions.

Table 4.
Catalytic efficiency (kcat/Km) of GST P1–1 variants with alternative thiol substrates.
Changes to Figure and Figure Legend
The authors wish to make changes to Figure 3 and the Figure legend. In the original publication, some values were miscalculated, and a minor typographical error was detected in the Figure legend. The new Figure 3 with the Figure legend has been updated below.
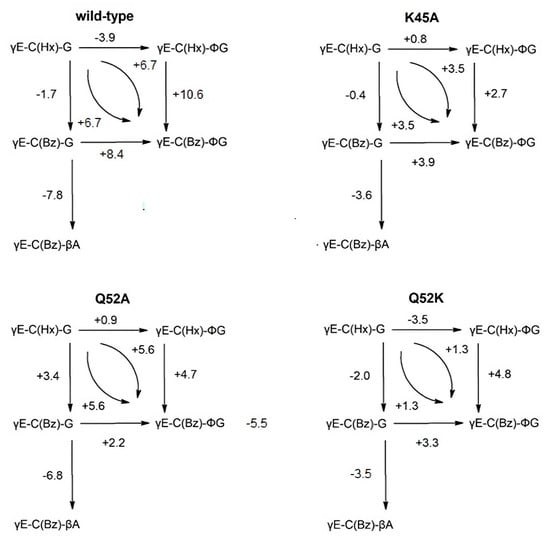
Figure 3.
Schemes of incremental binding energies (kJ mol−1) compared to the binding of five different glutathione derivatives to wild-type GST P1–1 and mutants K45A, Q52A, and Q52K. The complexes with S-hexylglutathione, γE-C(Hx)-G (upper left corners), serve as references. Positive values indicate increased binding affinities.
Correction to Equation
The equation present in the original publication had a typographical error in it. The adjusted equation is attached below.
ΔΔG = −RT ln (Ki/Ki*)
Correction to Text
The authors wish to make changes to errors found in the main text.
3.3. Steady-State Kinetics
Paragraph 1: Original text: Mutant Q52K is most strongly affected with a nine-fold increase of KMCDNB, an eight-fold decrease of kcat, and a resulting 70-fold decrease of kcat/KMGSH (Table 2).
New text: Mutant Q52K is most strongly affected with a nine-fold increase in KMGSH, an eight-fold decrease in kcat, and a resulting seventy-fold decrease in kcat/KMGSH (Table 2).
Paragraph 3: Original text: However, the catalytic efficiency could be determined and showed that mutant Q52K was 50% more efficient than the wild-type enzyme with GSH as the varied thiol substrate.
New text: However, the catalytic efficiency could be determined and showed that the mutant Q52K only displayed a fraction (1.5%) of the efficiency of the wild-type enzyme with GSH as the varied thiol substrate.
3.4. Inhibition Studies
Paragraph 8: Original text: a potent ligand.
New text: a potent inhibitor.
The authors apologize for any inconvenience caused and state that the scientific conclusion of the paper is unaffected. The original publication has also been updated.
Reference
- Shokeer, A.; Ismail, A.; Hegazy, U.M.; Kolm, R.H.; Mannervik, B. Mutational Analysis of the Binding of Alternative Substrates and Inhibitors to the Active Site of Human Glutathione Transferase P1–1. Processes 2020, 8, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).