Optimization of Binary Adsorption of Metronidazole and Sulfamethoxazole in Aqueous Solution Supported with DFT Calculations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Adsorbent
2.3. Concentration Determination of Sulfonamides and Nitroimidazoles
2.4. Obtaining Adsorption Equilibrium Data: Individual and Multicomponent
2.5. Characterization of the Antibiotic-Surface Interaction
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Single and Multicomponent Adsorption Equilibrium
3.1.1. Individual Adsorption Equilibrium
3.1.2. Binary Adsorption Equilibrium
3.2. Characterization of the Antibiotic-Surface Interaction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gondi, R.; Kavitha, S.; Yukesh Kannah, R.; Parthiba Karthikeyan, O.; Kumar, G.; Kumar Tyagi, V.; Rajesh Banu, J. Algal-Based System for Removal of Emerging Pollutants from Wastewater: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moral-Rodríguez, A.I.; Leyva-Ramos, R.; Ocampo-Pérez, R.; Mendoza-Barron, J.; Serratos-Alvarez, I.N.; Salazar-Rabago, J.J. Removal of Ronidazole and Sulfamethoxazole from Water Solutions by Adsorption on Granular Activated Carbon: Equilibrium and Intraparticle Diffusion Mechanisms. Adsorption 2016, 22, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Sun, W.; Xia, L.; Zia, U.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Deng, X. Adsorption of Toxic Tetracycline, Thiamphenicol and Sulfamethoxazole by a Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) under Different Conditions. Molecules 2022, 27, 7980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben, Y.; Fu, C.; Hu, M.; Liu, L.; Wong, M.H.; Zheng, C. Human Health Risk Assessment of Antibiotic Resistance Associated with Antibiotic Residues in the Environment: A Review. Environ. Res. 2019, 169, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, B.D.; Crago, J.P.; Hedman, C.J.; Treguer, R.J.F.; Magruder, C.; Royer, L.S.; Klaper, R.D. Evaluation of a Model for the Removal of Pharmaceuticals, Personal Care Products, and Hormones from Wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 444, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.R.; Belmont, M.A.; Metcalfe, C.D. Pharmaceutical Compounds in Wastewater: Wetland Treatment as a Potential Solution. Sci. World J. 2006, 6, 1731–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Rizwan, K.; Adeel, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Hydrogen-Based Catalyst-Assisted Advanced Oxidation Processes to Mitigate Emerging Pharmaceutical Contaminants. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 19555–19569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzate, S.; Pfister, S.; Oberschelp, C.; Sánchez-Pérez, J.A. Environmental Impacts of an Advanced Oxidation Process as Tertiary Treatment in a Wastewater Treatment Plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahari, S.; Ghahari, S.; Ghahari, S.; Nematzadeh, G.; Sarma, H. Integrated Remediation Approaches for Selected Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products in Urban Soils for a Sustainable Future. Energy Ecol. Environ. 2021, 7, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, I.T.; Santos, L. Antibiotics in the Aquatic Environments: A Review of the European Scenario. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 736–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, M.; Shin, S.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive Removal of Nitroimidazole Antibiotics from Water Using Porous Carbons Derived from Melamine-Loaded MAF-6. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 378, 120761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Cheng, X.; Dionysiou, D.D. Sulfamethoxazole Degradation by Visible Light Assisted Peroxymonosulfate Process Based on Nanohybrid Manganese Dioxide Incorporating Ferric Oxide. Appl. Catal. B 2020, 278, 119297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunath, S.V.; Singh Baghel, R.; Kumar, M. Antagonistic and Synergistic Analysis of Antibiotic Adsorption on Prosopis Juliflora Activated Carbon in Multicomponent Systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasannamedha, G.; Kumar, P.S. A Review on Contamination and Removal of Sulfamethoxazole from Aqueous Solution Using Cleaner Techniques: Present and Future Perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoon, B.L.; Ong, C.C.; Mohamed Saheed, M.S.; Show, P.L.; Chang, J.S.; Ling, T.C.; Lam, S.S.; Juan, J.C. Conventional and Emerging Technologies for Removal of Antibiotics from Wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 122961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, G.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Naushad, M.; Ghfar, A.A.; Stadler, F.J. Quaternary Magnetic BiOCl/g-C3N4/Cu2O/Fe3O4 Nano-Junction for Visible Light and Solar Powered Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole from Aqueous Environment. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 462–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthamarai, C.; Senthil-Kumar, P.; Priyadharshini, M.; Vijayalakshmi, P.; Vinoth, K.; Baskaralingam, P.; Thiruvengararavi, K.V.; Sivanesan, S. Adsorption Behaviour of Methylene Blue Dye onto Surface Modified Strychnos Potatorum Seeds. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2012, 33, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Adhikary, K.K.; Kim, K.; Ahn, W.S. Aqueous Adsorption of Sulfamethoxazole on an N-Doped Zeolite Beta-Templated Carbon. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 582, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyanto, T.; Sarwendah, R.A.G.; Amimmal, Y.M.N.; Laksmana, W.T.; Prasetyo, I. Modifying Nanoporous Carbon through Hydrogen Peroxide Oxidation for Removal of Metronidazole Antibiotics from Simulated Wastewater. Processes 2019, 7, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrales-Alvarado, D.H.; Leyva-Ramos, R.; Martínez-Costa, J.I.; Ocampo-Pérez, R. Competitive Adsorption of Dimetridazole and Metronidazole Antibiotics on Carbon Materials from Aqueous Solution. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauletto, P.S.; Moreno-Pérez, J.; Hernández-Hernández, L.E.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Dotto, G.L.; Salau, N.P.G. Novel Biochar and Hydrochar for the Adsorption of 2-Nitrophenol from Aqueous Solutions: An Approach Using the PVSDM Model. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-Carrizales, J.C.; Collins-Martínez, V.H.; Flórez, E.; Gomez-Duran, C.F.A.; Palestino, G.; Ocampo-Pérez, R. Adsorption of Sulfamethoxazole, Sulfadiazine and Sulfametazine in Single and Ternary Systems on Activated Carbon. Experimental and DFT Computations. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 324, 114740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgionny, A.; Acelas, N.Y.; Ocampo-Pérez, R.; Padilla-Ortega, E.; Pérez, S.; Flórez, E. Mechanism Adsorption Analysis during the Removal of Cd2+ and Cu2+ onto Cedar Sawdust via Experiment Coupled with Theoretical Calculation: Mono- and Multicomponent Systems. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 18, 100715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavand, M.; Eslami, P.; Razeh, L. The Adsorption of Cadmium and Lead Ions from the Synthesis Wastewater with the Activated Carbon: Optimization of the Single and Binary Systems. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 34, 101151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, A.; Retnam, B.G.; Muthukkumaran, A.; Aravamudan, K. Swift, Versatile and a Rigorous Kinetic Model Based Artificial Neural Network Surrogate for Single and Multicomponent Batch Adsorption Processes. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 297, 111888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauletto, P.S.; Lütke, S.F.; Dotto, G.L.; Salau, N.P.G. Forecasting the Multicomponent Adsorption of Nimesulide and Paracetamol through Artificial Neural Network. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 412, 127527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagtash, M.; Zolgharnein, J. Crossed Mixture-Process Design for Optimization of Simultaneous Adsorption of Tartrazine and Indigo Carmine Dyes by Cobalt Hydroxide Nanosorbent. J. Chemom. 2018, 32, e3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, E.; Sheikhmohammadi, A.; Yeganeh, J. Application of the Fe3O4-Chitosan Nano-Adsorbent for the Adsorption of Metronidazole from Wastewater: Optimization, Kinetic, Thermodynamic and Equilibrium Studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 694–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Bian, J.; Zhu, Q. Sulfamethoxazole Removal of Adsorption by Carbon—Doped Boron Nitride in Water. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 349, 118216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathon, B.; Coquery, M.; Liu, Z.; Penru, Y.; Guillon, A.; Esperanza, M.; Miège, C.; Choubert, J.M. Ozonation of 47 Organic Micropollutants in Secondary Treated Municipal Effluents: Direct and Indirect Kinetic Reaction Rates and Modelling. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrales-Alvarado, D.H.; Ocampo-Pérez, R.; Leyva-Ramos, R.; Rivera-Utrilla, J. Removal of the Antibiotic Metronidazole by Adsorption on Various Carbon Materials from Aqueous Phase. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 436, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Padilla, E.S.; Zárate-Guzmán, A.I.; González-Ortega, O.; Padilla-Ortega, E.; Gómez-Durán, A.; Delgado-Sánchez, P.; Aguilar-Aguilar, A.; Cortés, F.B.; Ocampo-Pérez, R. Elucidation of Adsorption Mechanisms and Mass Transfer Controlling Resistances during Single and Binary Adsorption of Caffeic and Chlorogenic Acids. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 26297–26311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
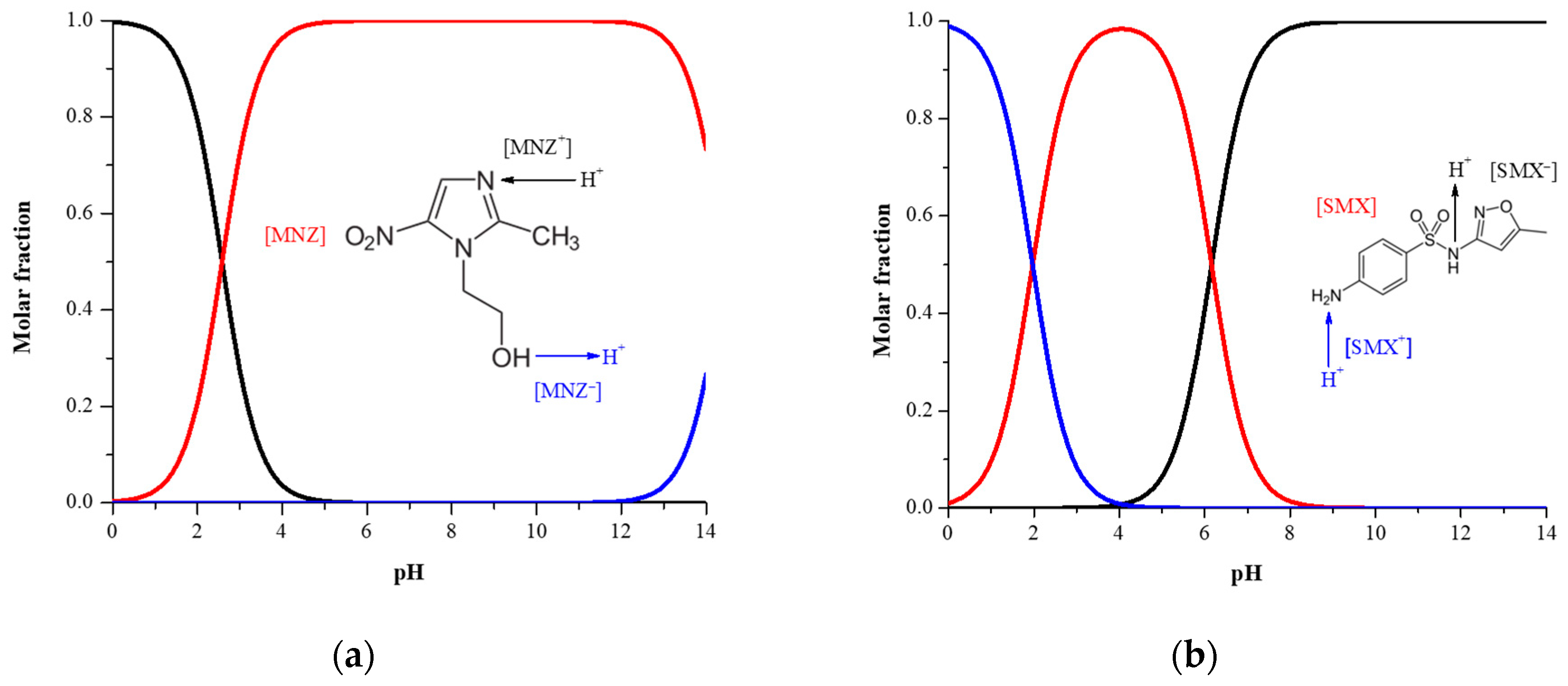
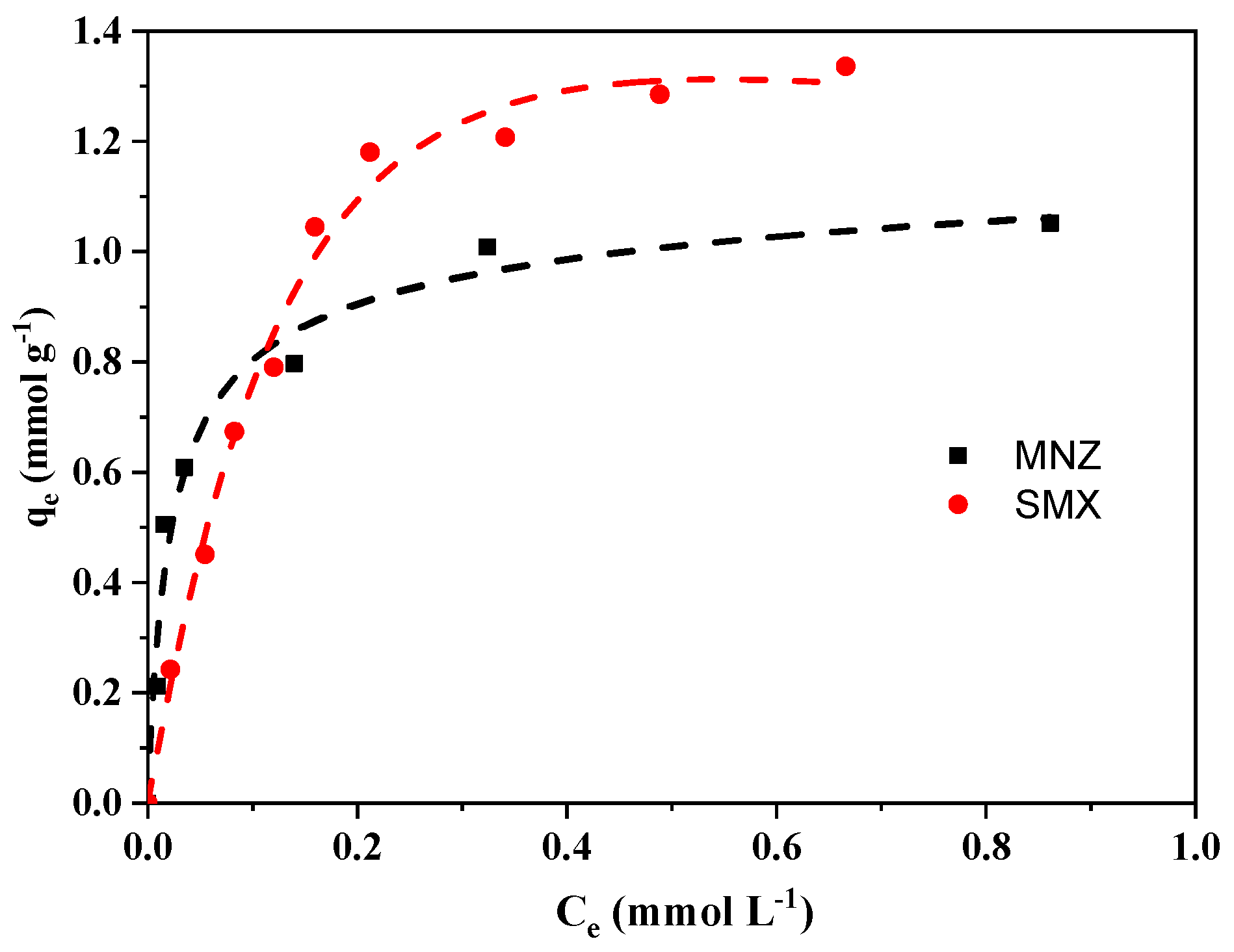

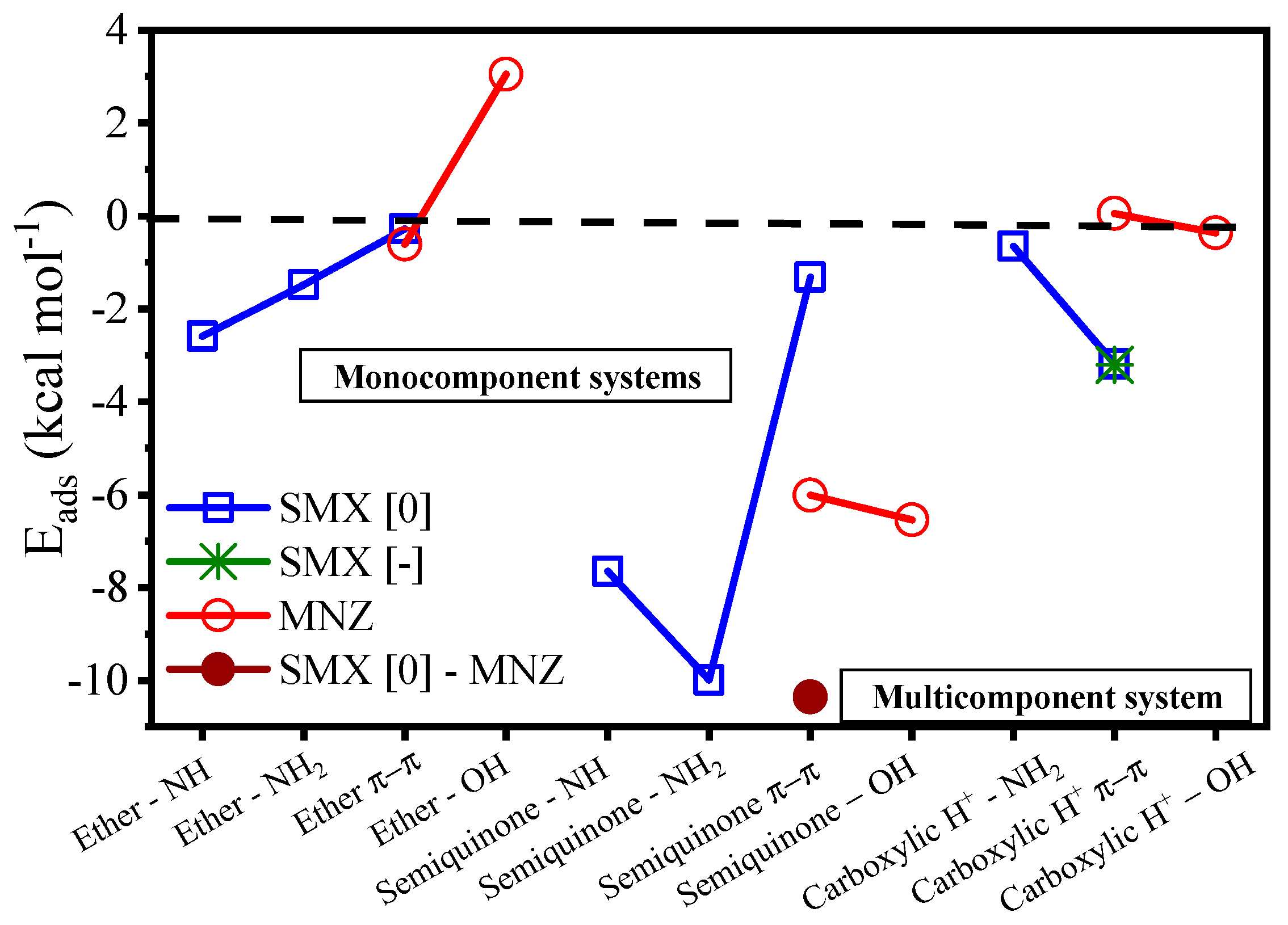

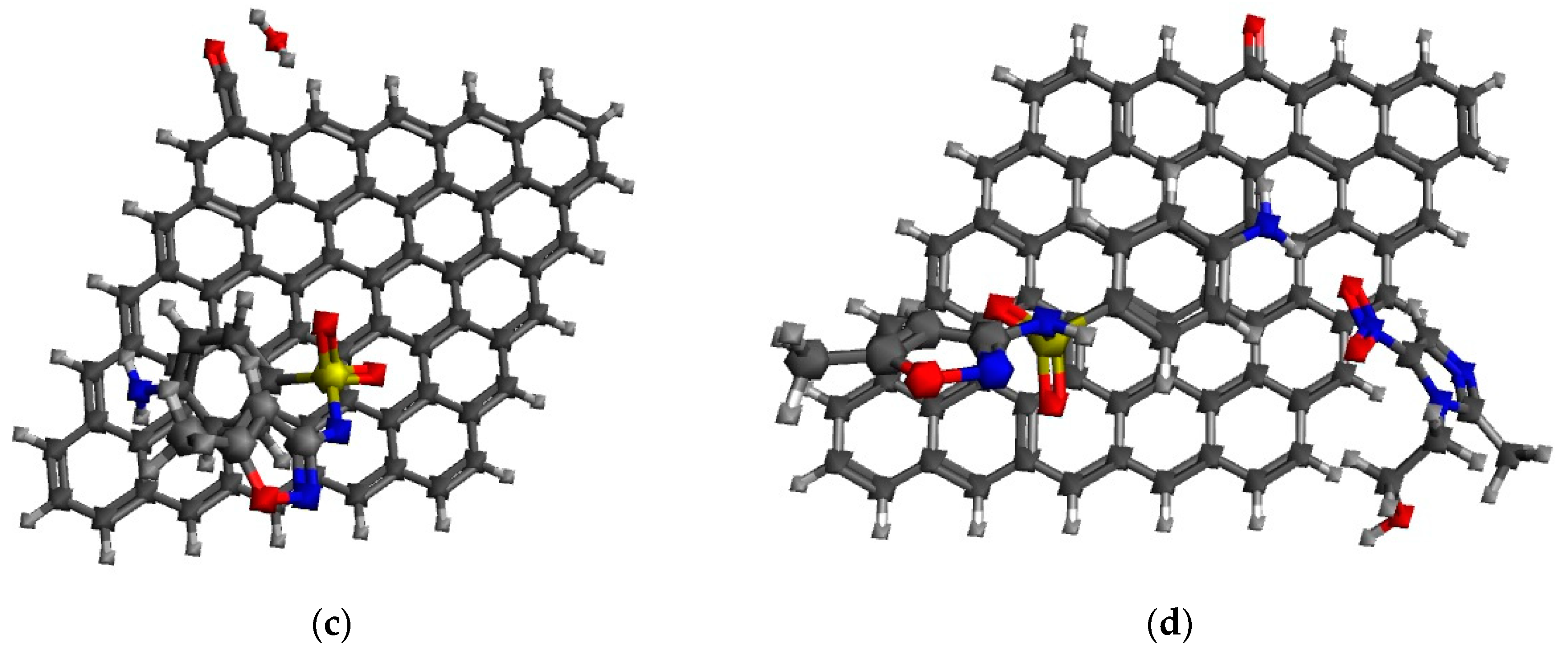
| Physicochemical Property | MNZ | SMX |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | 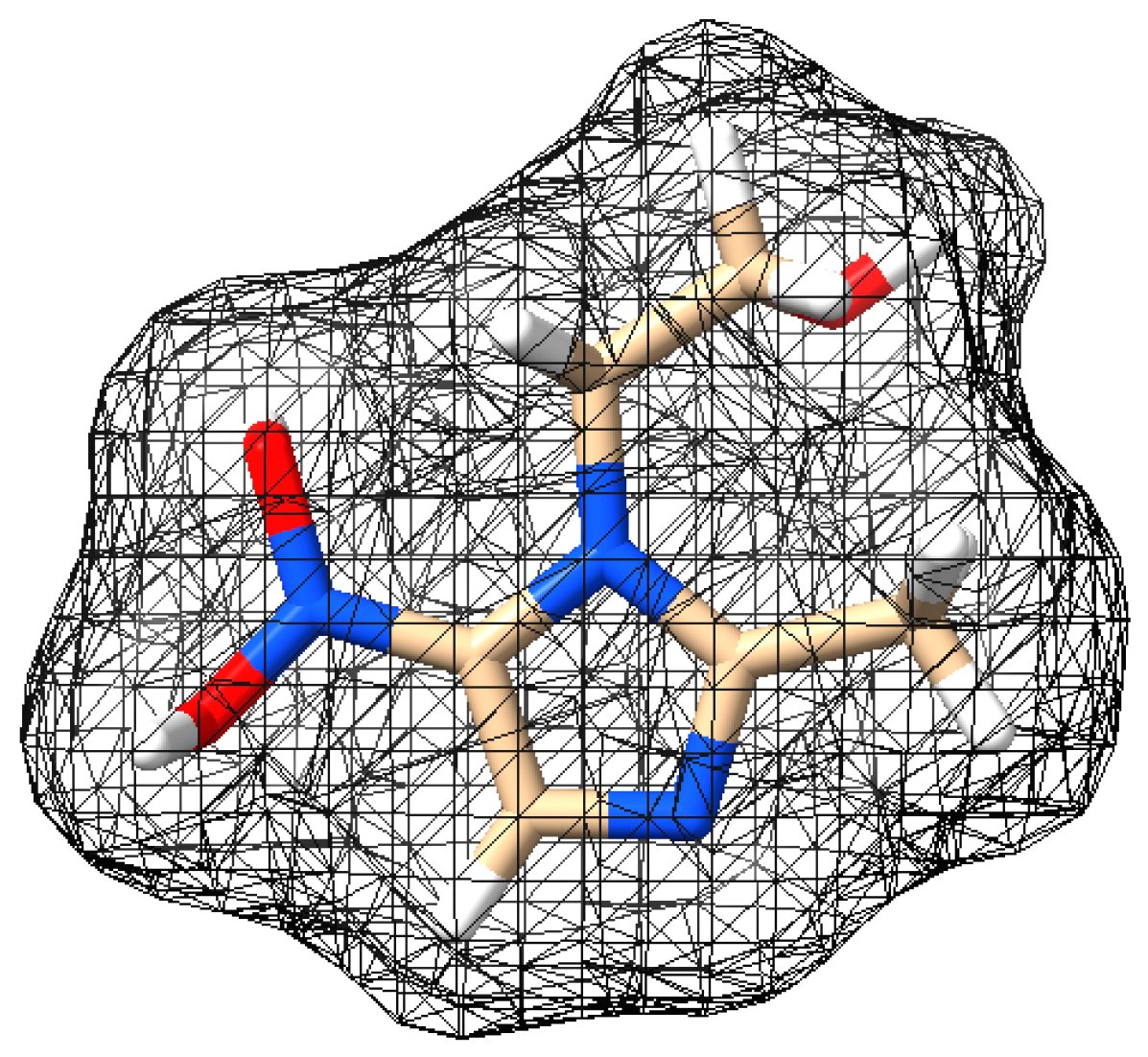 | 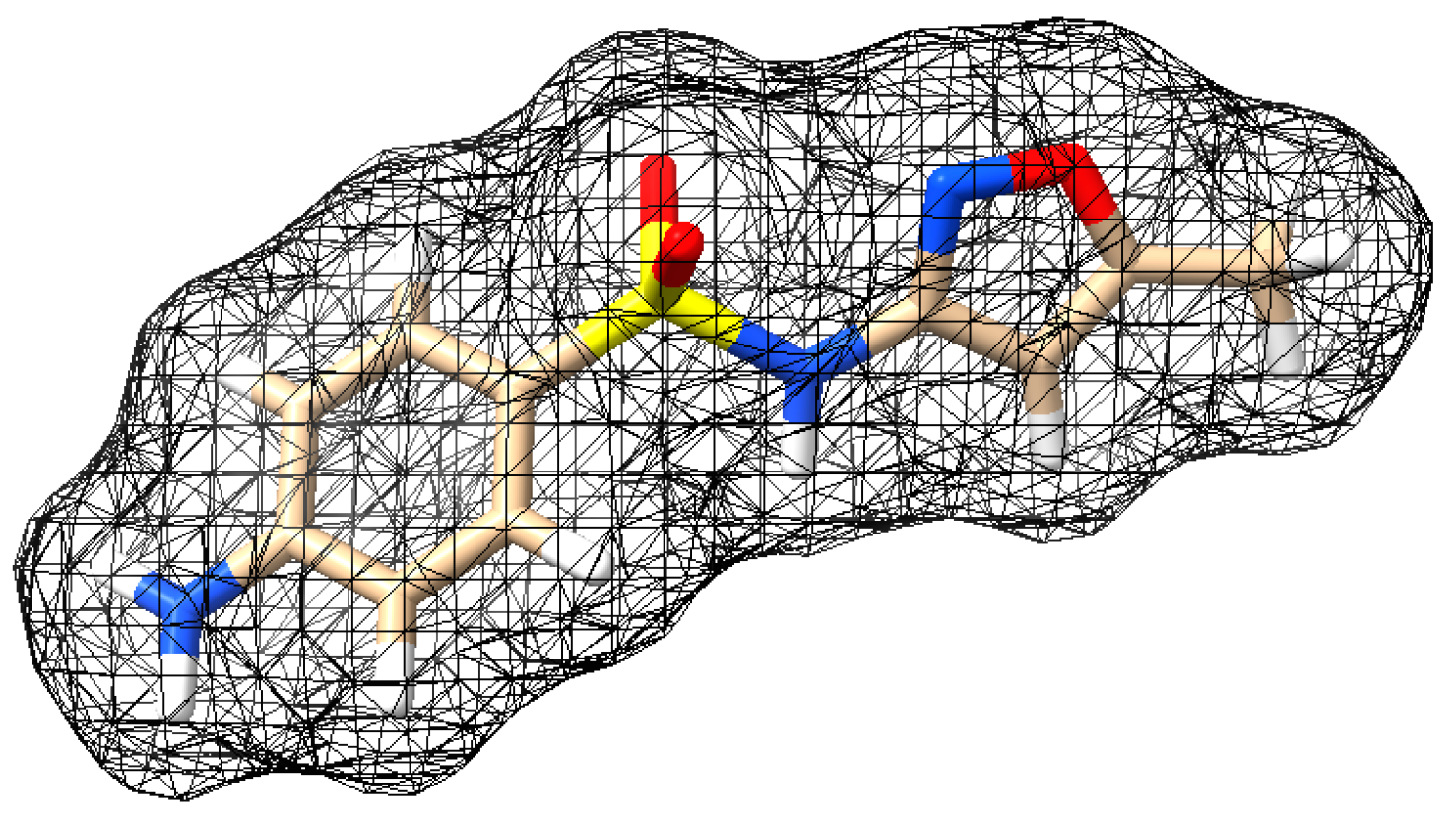 |
| Molecular formula | C6H9N3O3 | C10H11N3O3S |
| Molecular weight (g mol−1) | 171.15 | 253.28 |
| pKa [28,29] | pKa1 = 2.58 pKa2 = 14.44 | pKa1 = 1.97 pKa2 = 6.16 |
| Solubility (mol L−1) [28,29] | 0.041 | 0.001109 |
| Log Kow [30] | −0.02 | 0.9 |
| Molecular size (nm) | x = 0.969 y = 0.736 z = 0.454 | x = 1.517 y = 0.676 z = 0.541 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serna-Carrizales, J.C.; Zárate-Guzmán, A.I.; Aguilar-Aguilar, A.; Forgionny, A.; Bailón-García, E.; Flórez, E.; Gómez-Durán, C.F.A.; Ocampo-Pérez, R. Optimization of Binary Adsorption of Metronidazole and Sulfamethoxazole in Aqueous Solution Supported with DFT Calculations. Processes 2023, 11, 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041009
Serna-Carrizales JC, Zárate-Guzmán AI, Aguilar-Aguilar A, Forgionny A, Bailón-García E, Flórez E, Gómez-Durán CFA, Ocampo-Pérez R. Optimization of Binary Adsorption of Metronidazole and Sulfamethoxazole in Aqueous Solution Supported with DFT Calculations. Processes. 2023; 11(4):1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041009
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerna-Carrizales, Juan Carlos, Ana I. Zárate-Guzmán, Angélica Aguilar-Aguilar, Angélica Forgionny, Esther Bailón-García, Elizabeth Flórez, Cesar F. A. Gómez-Durán, and Raúl Ocampo-Pérez. 2023. "Optimization of Binary Adsorption of Metronidazole and Sulfamethoxazole in Aqueous Solution Supported with DFT Calculations" Processes 11, no. 4: 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041009
APA StyleSerna-Carrizales, J. C., Zárate-Guzmán, A. I., Aguilar-Aguilar, A., Forgionny, A., Bailón-García, E., Flórez, E., Gómez-Durán, C. F. A., & Ocampo-Pérez, R. (2023). Optimization of Binary Adsorption of Metronidazole and Sulfamethoxazole in Aqueous Solution Supported with DFT Calculations. Processes, 11(4), 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041009











