Abstract
The particle size of wheat bran plays an important role in the quality of reconstituted whole-wheat flour and its products. The effects of wheat bran particle size on the quality of reconstituted whole-wheat flour and its cooked noodles were analyzed; the mean particle size (D50) of wheat bran ranged from 26.05 to 46.08 μm. Results show that the decreases in D50 of wheat bran induced the changes in the quality of whole-wheat flour and its noodles. Specifically, the damaged starch content, water absorption, and the solvent retention capacity of sodium carbonate and sucrose of whole-wheat flour increased at various degrees, while pasting viscosity decreased, and the gluten index and SDS-sedimentation volume increased first and then decreased. The cooking yield, cooking loss, and break rate of fresh noodles decreased first and reached a trough at D50 of 26.05 μm, and then increased. The adhesiveness of cooked noodles increased, the score of smoothness, taste, appearance, and color increased to a stable value, but the hardness, springiness, cohesiveness, resilience, firmness score, and elasticity score increased first and then decreased. These turning points of changing trends of indexes mostly occurred when the D50 of wheat bran was 26.51 μm. In conclusion, whole-wheat noodles with wheat bran of D50 of 26.51 μm addition exhibit better cooking, textural, and sensory properties than those with smaller or larger wheat bran. Excessive crushing of wheat bran not only costs highly in terms of energy, but also has a negative impact on the quality of the noodles.
1. Introduction
Wheat (Triticum eastivum L.) is widely cultivated worldwide and ranks second only after maize in terms of production and utilization [1]. It is widely utilized in the production of flour, malt, beer, and a range of bakery products [2]. Whole-wheat flour, a whole grain food that contains higher levels of dietary fiber, vitamins, minerals, and other bioactive compounds, has higher nutritional value than refined wheat flour [3]. Long-term intake of whole-wheat products can promote gut bacteria selectively and reduce the prevalence rate of cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and colon cancer [4,5]. However, inferior palatability and sensory morphology of whole-wheat products have limited the acceptance of consumers [6]. As a result, numerous studies have been conducted to enhance the quality of whole-wheat products [7,8,9,10,11].
Among existing research, particle size of wheat flour has been verified as an important effect on the quality of dough and whole-wheat products. Alzuwaid et al. [7] reported that pasta containing finer bran showed higher phytochemical content and better quality above regular semolina pasta. Protonotariou et al. [8] reported that bread produced with whole-wheat flour of D50 of 17.02 μm had worse physical properties and shorter storage shelf life than those produced with whole-wheat flour of D50 of 53.49 and 29.10 μm. Lin et al. [9] reported that bread made from whole-wheat flour of D50 of 199 μm had a higher specific volume and less compact crumb structure than those made from whole-wheat flour of D50 of 1315 and 450 μm, which resulted in a more appealing texture. In addition, Lin et al. [10] reported that dough containing bran of D50 of 60.4 μm showed better resistance to extension and extensibility than the dough containing bran of D50 of 362.3 μm and 11.3 μm, and Xiong et al. [11] also reported that dough with appropriate particle size wheat bran (D50 = 160 μm) addition had better stability than that with excessively smaller particle size wheat bran. Excessively crushed wheat bran not only has high energy consumption but also adversely affects the quality of whole-wheat dough. Each kind of whole-wheat product has specific needs for dough properties. Therefore, appropriate particle size of wheat bran is necessary for specific whole-wheat products.
Noodles usually made from refined wheat flour occupy a significant position among the daily staple food of Asians, and an average of 20–50% of total wheat flour consumed is made for noodles in many Asian countries [12]. Many nutrients are lost or diminished during the processing of refined wheat flour, which is not beneficial for the consumer’s quest for balanced food nutrition [13]. Whole-wheat noodles with balanced nutrients are expected to develop into one of the daily staple food for Asians. Sim et al. [14] examined the effects of processing methods of wheat bran on the sensory properties, texture, color, and cooking loss of the whole-wheat salted noodles, in which wheat bran was made from the autoclaving, extrusion, jet-cooking, puffing, and roasting. These processes induced the noodles to take up more water during cooking and to exhibit weaker (tensile and compressive strength) and stickier texture properties [14]. Niu et al. [12] have reported the effect of particle size of wheat bran on the quality of whole-wheat flour and its noodles; the D50 of wheat bran ranged from 185 to 319 μm. They found that decreasing the particle size of wheat bran provided beneficial effects on the hardness, springiness, cohesiveness, and resilience of whole-wheat raw noodles [12]. However, the appropriate particle size of wheat bran for producing whole-wheat noodles has not been found. Considering the trend of noodle quality in the study of Niu et al. [12], the effect of smaller particle size wheat bran on the quality of whole-wheat noodles needs to be further explored. In addition, they mainly focused on the polyphenol oxidase activity and pasting properties of whole-wheat flour [12]. Gluten protein and starch are main ingredients in wheat flour, but changes concerning starch composition and gluten quality in whole-wheat flour with decreasing wheat bran particle size have not been elucidated [15].
The quality of cooked noodles determines the acceptance of consumers directly. To explore the effect of wheat bran particle size on the quality of whole-wheat flour and its cooked noodles, the particle size distribution of wheat bran was measured. The starch composition, gluten quality, solvent retention capacity, water absorption, and pasting properties of whole-wheat flour were determined. The cooking, textural, and sensory properties of whole-wheat noodles were also evaluated. Meanwhile, the correlation of the quality between whole-wheat flour and its cooked noodles was analyzed. The obtained results can be applied to guide the production of whole-wheat noodles.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Original wheat bran and refined wheat flour were obtained with the flour extraction rate at around 70% from the local factory (Jinmai 73 cultivar, Yuncheng, China). The composition of original wheat bran was 9.95% moisture, 15.40% protein, 5.65% fat, and 2.55% ash. The composition of refined wheat flour was 10.21% moisture, 12.47% protein, 2.35% fat, and 0.13% ash. The composition was calculated on a dry-weight basis.
2.2. Preparation of Wheat Bran and Whole-Wheat Flour
Wheat bran with different particle sizes was obtained using an Ultra-Micro Pulverizer (ZKY-303, Zhong Ke Hao Yu Technology Development Co. Ltd., Beijing, China) under different frequencies (0, 20, 30, 40, 50 Hz) and constant time (30 min); they were recorded as B1, B2, B3, B4, and B5, respectively. Whole-wheat flour was reconstituted by wheat bran and refined wheat flour in a mass ratio of 3:7 according to the extraction rate [12], and the blends were recorded as F1, F2, F3, F4, F5 corresponding to the contained wheat bran, decreasing in particle size sequentially. Refined wheat flour served as a control.
2.3. Particle Size Distribution of Wheat Bran
Particle size distribution of wheat bran was measured in the wet dispersion mode using ethanol and ultrasonication by a laser particle size analyzer (2600E, Bettersize Instrument Ltd., Dandong, China). A refraction index of 1.53 and absorption parameter of 0.7 were adopted [16].
2.4. Quality of Whole-Wheat Flour
These results were expressed on a 14% moisture content basis according to the AACC approved method 76-21, 54-23 (AACC, 1999).
2.4.1. Starch Composition
The content of total starch, amylose, and damage starch content was determined following the AACC approved method 76-13, 61-03, and 76-30A (AACC, 2000).
2.4.2. Quality of Gluten
Wet gluten content, dry gluten content, and gluten index were determined according to the AACC approved method 38-12A (AACC, 2000). Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) sedimentation volume was determined according to the AACC approved method 56-70 (AACC, 1999).
2.4.3. Solvent Retention Capacity
Solvent retention capacity (SRC) was determined by following the approved method 56-11 (AACC, 2000). The solvents included 5% (m/v) lactic acid (LA), 5% (m/v) sodium carbonate (SC), and 50% (m/v) sucrose solutions (Su).
2.4.4. Water Absorption
Water absorption (WA) was determined using a MicroDoughLAB (Perten2500, PerkinElmer Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China) with a bowl (capacity of 300 g) according to the AACC approved method 54-21 (AACC, 1999).
2.4.5. Pasting Properties
Pasting properties were determined with a Rapid Viscosity Analyzer (Rapid-20, Bosin Industrial Development Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) according to the AACC approved method 76-21 (AACC, 1999). Peak viscosity (PV), minimum trough viscosity (MV), pasting temperature (PT), final viscosity (FV), breakdown value (BV), and setback value (SB) were obtained.
2.5. Preparation of Whole-Wheat Noodles
Raw whole-wheat noodles were prepared according to Pu’s method [17] and the Chinese approved method GB/T 35,875 (GB, 2018) with slight modifications. Whole-wheat flour of 200 g (14 g/100 g mb) and the required amount of water (with 2 g salt) were mixed in a small dough mixer (SC-209, Diamond Kitchen Electric Co., Foshan, China). The required amount of water was 48% of the WA determined by Farinograph. Dough was formed after premixing for 2 min at 90 rpm and mixing for 8 min at 120 rpm. Then the dough was passed through an experimental noodle machine (JMTD168/140, Dongfu Jiuheng Instrument Technology Co., Ltd., Beijng, China) with a gap setting of 3 mm, folded and pressed (repeat it 3 times). After resting in the ziplock bag for 30 min, the dough sheet was calibrated to 1.25 ± 0.03 mm through gaps of 2.50, 2.00, 1.50, 1.25 mm, sequentially. Noodle strands 2 mm wide and 200 mm long were obtained through 2 mm wide cutting blades, and then covered with fresh-keeping film. The noodles were recorded as N1, N2, N3, N4, N5 corresponding to the contained wheat bran, decreasing in particle size sequentially. The noodles made from refined wheat flour served as a control.
Cooked noodles were prepared according to Li’s method, with slight modification [18]. Fresh raw noodles—150 g in amount—in 1800 mL boiling water were cooked to the optimum cooking time, which was defined as the inner core in the noodles not being visible to the naked eyes (AACC 66-50, 1999). The optimum cooking time was 4.5 min based on preliminary trials, and the data between groups did not show a significant difference. After cooking, noodles were immersed in 500 mL water (20 °C) for 30 s, removed with a steel strainer, and then tapped with the edge of the strainer for 10 s to drain the surface running water. Then, cooked noodles were placed on a plate and sealed with preservation film for subsequent determination.
2.6. Quality of Whole-Wheat Noodles
2.6.1. Cooking Properties
Cooking properties of noodles were determined according to Li’s method [18] with slight modification. Raw intact noodles of 20 strands were cooked in 250 mL boiling water for 4.5 min (according to pre-experiment). After cooking, noodles were immersed in 100 mL water (20 °C) for 30 s, removed with a steel strainer, tapped with the edge of the strainer for 10 s to drain the surface running water, and then weighted. The quantity of the intact cooked noodles was recorded. Cooking water and rinsing water were merged into a beaker and placed into an oven at 105 °C until constant weight. The parameters were calculated as:
2.6.2. Textural Properties
The textural properties of cooked noodles were analyzed according to Zhang’s method [19] with slight modifications, with a Texture Analyzer (TA-XT. plus, Stable Micro System company, Godalming, UK). Three 3 cm-long cooked noodles were placed parallel on the test-bed with an interval of 1 cm. The testing parameters of the firmness of the cooked noodles were as follows: the probe was P/50; the strain rate and speed were 70% and 0.8 mm/s; the interval time and trigger force of compression were 2 s and 0.05 N.
2.6.3. Sensory Evaluation
Sensory evaluation was carried out by 12 trained panelists (six men and six women) according to the Chinese approved method GB/T35875, with some modifications. Refined wheat flour served as a control. Sensory evaluation details (palatability, elasticity, smoothness, taste, appearance, and color) are shown in Table S1 (Supplemental Material). The process of evaluation took place within 20 min after the noodles were prepared, and the panelists were seated in separate places to prevent interaction with each other.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
All experiments were conducted at least in triplicate. The results of wheat flour quality were calculated on a 14% moisture basis and presented as means ± standard error. Duncan’s test was used to analyze the variance (ANOVA) and the difference was considered significant at p < 0.05 with the software SAS v8.0 for Windows. Pearson’s correlation analysis was performed with the software Origin v2017 for Windows.
3. Results
3.1. Particle Size Distribution of Wheat Bran
The particle size distribution patterns and statistical results are shown in Figure 1. According to the statistical results, the mean particle sizes (D50) of B1, B2, B3, B4, and B5 decreased significantly; they can be used as samples in this experiment. The decreasing particle size of wheat bran was due to the more intense crushing [20]. As the particle size of the wheat bran decreased, the peak corresponding to larger or smaller disappeared gradually, and only one tall and thin peak could be observed in the end. Similar changes have been observed by Bala et al. [21], who studied the particle size distribution patterns of grass pea flour with different particle sizes. The difference between D90 and D10 decreased with the decrease in particle size of wheat bran, suggesting that the size of the bran was more uniform. Further, previous studies have reported that particle size of wheat bran was related to both dough properties and quality of whole-wheat products [9,10]. The particle size distribution of wheat bran provides a basis for this study.
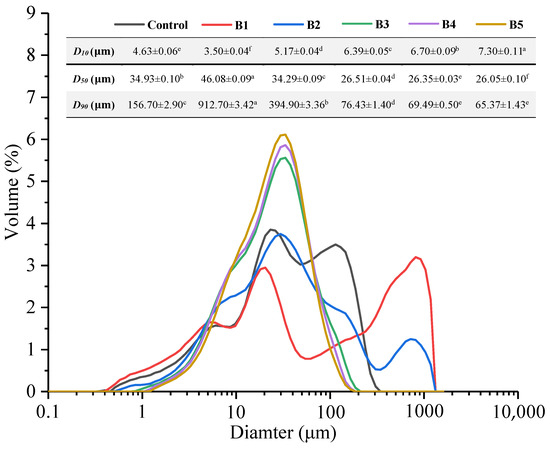
Figure 1.
Particle size distribution of wheat bran. B1, B2, B3, B4, and B5 are the wheat brans with different particle sizes. D10, D50, and D90 are mean particle sizes at 10%, 50%, and 90% of the volume distribution, respectively. Refined wheat flour served as a control group. Different letters on each row indicate significantly different values (p < 0.05).
3.2. Quality of Whole-Wheat Flour
3.2.1. Starch Composition of Whole-Wheat Flour
Starch is a major carbohydrate in cereal grains, and its content and composition affect the quality of starchy food. The starch composition of wheat flour is presented in Table 1. The content of the total starch, amylose starch, and damaged starch in the control group was higher than whole-wheat groups. With the decrease in particle size of wheat bran, the damaged starch content in whole-wheat flour increased significantly from 1.67% to 3.70%, while the content of total starch and amylose starch did not show a difference.

Table 1.
Starch composition and gluten quality of wheat flour.
With the decrease in the particle size of the wheat bran, the increasing damage starch content of whole-wheat flour was attributed to high-intensive rolling during the crushing process. The damaged starch content of rice flour also showed a similar trend when the polished rice was sieved into three different particle sizes [22]. In addition, the damaged starch content in whole-wheat flour increased from 4.68% to 7.22% when the mean particle size of the whole-wheat flour decreased from 1315.6 to 199.1 μm [9]. Based on that, damaged starch has better absorption water capacity than intact starch granules, and excessive damaged flour starch would lead to the formation of a softer and stickier dough that cannot keep the volume of steamed bread [23]. For reconstituted whole-wheat flour, only the wheat bran was crushed further, which can significantly reduce the damaged starch content and avoid forming a soft and sticky dough. The content of total starch and amylose starch did not show a difference with the decrease in particle size of wheat bran. In contrast, previous studies reported that the content of total starch and amylose increased when the D50 of oat flour decreased from 161.33 to 15.66 μm [24]. This different trend may be due to methods of reducing particle size. The particle size of oat flour was controlled by sieves, which induced a change in the distribution of oat nutrients. In this study, the particle size of wheat bran was controlled by crushing intensity. The changes of damaged starch content in wheat flour may induce the difference in noodle quality.
3.2.2. Gluten Quality of Whole-Wheat Flour
Gluten, an important component in wheat flour, confers viscoelasticity on dough, which affects the texture of the products. The gluten quality of wheat flour is shown in Table 1. Compared with the control group, the gluten index and SDS-sedimentation volume were lower in the whole-wheat groups. With the decrease in particle size of wheat bran, the content of wet gluten and dry gluten increased, while the gluten index and SDS-sedimentation volume increased first and then decreased.
The content of wet and dry gluten is usually used to reflect the gluten quality [25]. The content of wet and dry gluten in whole-wheat flour presented a negative correlation with the particle size of wheat bran, which was in accordance with the report by Gulia and Khatkar [25]. Both the gluten index and the SDS-sedimentation volume reflect the relative strength of gluten [25]. In this study, the gluten content and the gluten index or the SDS-sedimentation volume showed different trends with the decrease in particle size of wheat bran. Based on what we found during the experiment, the obtained gluten had residual small wheat bran particles in varying degrees. We speculate that the residual wheat bran in gluten may be due to forming a strong interaction with gluten protein, resulting in the wheat bran note being able to be removed during the preparation process. Chen et al. [26] reported that cellulose and polysaccharides in grape seed powder could crosslink to gluten proteins through non-covalent bonds and hydrophobic interactions. Meanwhile, with the decrease in particle size of wheat bran, the increasing specific surface area exposed more active substances. This promoted the non-covalent and hydrophobic interactions between wheat bran and gluten proteins, resulting in more residual wheat bran particles in the gluten [10]. Thus, the reliability of these indicators in terms of reflecting gluten quality in whole-wheat flour remains to be verified. Next, the correlation between gluten quality and noodle quality is further analyzed.
3.2.3. Solvent Retention Capacity of Whole-Wheat Flour
The test of solvent retention capacity (SRC) is based on the exaggerated swelling behavior of component polymer networks in selected individual diagnostic solvents, and SRC has been recognized as a useful tool for the evaluation of wheat flour quality [27]. The LA SRC value reflects the gluten quality and functionality due to the fact that the 5% LA solution exaggerates the swelling behavior of the gluten network [27]. The SC SRC value reflects the content of damaged starch due to the fact that the 5% SC solution exaggerates the swelling behavior of damaged starch [27]. The Su SRC value reflects the content of arabinoxylan due to the fact that the 50% Su solution exaggerates the swelling behavior of the arabinoxylan network [27]. The solvent retention capacity of wheat flour is shown in Table 2. Compared with the control group, the whole-wheat groups represented higher LA SRC values and lower Su SRC values. With the decrease in particle size of wheat bran, the LA SRC value in whole-wheat flour increased first and reached a stable value, but the SC SRC and Su SRC values decreased.

Table 2.
Solvent retention capacity and water absorption of wheat flour.
The high LA SRC value in the control group suggested the wheat bran disrupted the formation of the gluten network. This was also verified by Han et al. [28], who found that wheat bran dietary fiber caused a reduction of disulfide bond content in gluten, and the gluten exhibited a less compact gluten network. With the decrease in particle size of wheat bran, increasing LA SRC value in the whole-wheat flour suggested that decreasing the wheat bran particle size promoted the aggregation of gluten proteins. This might be due to the smaller steric hindrance of wheat bran having less interference in the aggregation of gluten proteins. When the D50 of wheat bran was less than 26.51 μm, the LA SRC value in the whole-wheat flour tended to a stable value, which may be caused by little steric hindrance of wheat bran no longer affecting the aggregation of gluten proteins. The highly aggregated gluten confers better viscoelasticity on the dough, resulting in the production of firm noodles [9,12]. As expected, the SC SRC value and damaged starch content (Table 1) in whole-wheat flour showed the same trend with the decrease in particle size of wheat bran. The high Su SRC value in the whole-wheat groups was attributed to the high arabinoxylan content in bran [10]. High-intensity crushing resulted in the liberation of arabinoxylan polymers entangled in the cell wall matrix [10]. In addition, the high-intensity crushing might break the covalent bonds inside arabinoxylan molecules, making water-unextractable arabinoxylan water-extractable [29]. These contributed to the higher Su SRC value in whole-wheat flour with the decrease in particle size of wheat bran. This result may provide support for the changes in the quality of whole-wheat products.
3.2.4. Water Absorption of Whole-Wheat Flour
Farinograph is widely used to obtain the water absorption of wheat flour when it reaches the optimum dough consistency. The water absorption of wheat flour is shown in Table 2. Adding wheat bran significantly increased the WA of wheat flour. The WA of whole-wheat flour increased from 60.5% to 70.14% with the decrease in particle size of wheat bran.
The high WA in whole-wheat flour was due to the high dietary fiber content in wheat bran. Dietary fiber is rich in a great number of hydroxyl groups that can interact with more water molecules through hydrogen bonding [28]. The WA of whole-wheat flour increased with the decrease in particle size of wheat bran, and similar trends were observed in the study of Lin et al. [10]. The water absorption capacity of damaged starch is 3–6 times that of native starch [27]. Combining the damaged starch content in Table 1, the increasing WA can be explained. In addition, smaller wheat bran would expose more hydroxyl groups, resulting in more water interaction with wheat bran through hydrogen bonds [30]. Moreover, the high-intensity crushing might make water-unextractable arabinoxylan water-extractable, which might also contribute to the increased WA [27,29]. This result provides basic information on the preparation of noodles for the next experiment.
3.2.5. Pasting Properties of Whole-Wheat Flour
The pasting properties of wheat flour reflect the starch behavior during and after heating, which are related to the quality of its products [31]. The PV, MV, FV, and PT are strongly related to the crystalline structure and swelling properties of starch granules [31]. The BV shows the degree of disintegration of the starch granule structure [32], and the SV reflects the short-term retrogradation tendency of the amylose [33]. The pasting properties of flour are presented in Table 3. Adding wheat bran significantly decreased the PV, MV, FV, BV, and SV of wheat flour, and increased the PT. With the decrease in particle size of wheat bran, the PV, MV, FV, BV, and SV of whole-wheat flour increased, and the PT increased first and then decreased.

Table 3.
Pasting properties of whole-wheat flour.
Owing to its high absorption water, the addition of wheat bran reduces the content of free water in the system. As a result, more energy is required to disrupt the crystal structure of starch, which eventually increases the PT of whole-wheat flour [34]. Meanwhile, the fact that there was less free water contributed to the lower viscosity [10]. In addition, adding wheat bran significantly decreased the total starch content, as shown in Table 1, which also led to the lower viscosity in whole-wheat flour [10]. Grinding treatments would induce the physical conversion of starch granules, in which both the damaged starch content increases and the crystalline region narrows with the increase in particle size of wheat bran. The conversion suggests that starch granules absorbed water molecules and deformed more easily, thus leading to lower viscosity [35]. With the decrease in particle size of wheat bran, the content of highly hydrophilic water-extracted arabinoxylan increased, leading to low retrogradation tendency of the amylose [29]. In addition, high-intensity crushing might interrupt the interaction between starch chains and decompose into the lower degree of cross-linking starch molecules, which also contribute to low SV [36]. Generally, high SV is undesirable, because products made from wheat flour with high SV usually exhibit short shelf life. Based on these results, decreasing the particle size of wheat bran is expected to improve the shelf life of whole-wheat products.
3.3. Quality of Whole-Wheat Noodles
3.3.1. Cooking Properties of Whole-Wheat Noodles
Starch granules and gluten proteins in fresh noodles absorb water molecules and swell during the cooking process. Meanwhile, some solids are released into boil water from the noodle matrix [37]. To evaluate the effect of wheat bran particle size on the quality of whole-wheat noodles, the cooking properties of noodles were compared. Water absorption, cooking loss, and break rate are thought to be major parameters to predict the cooking performance of noodles by both consumers and industry, and these parameters are presented in Figure 2. Compared with the control group, the cooking loss rate and breaking rate of noodles were higher in the whole-wheat groups. The water absorption of W1 was significantly higher than the control and other whole-wheat groups. With the decrease in particle size of wheat bran, the water absorption, cooking loss, and break rate of noodles increased first and then decreased.
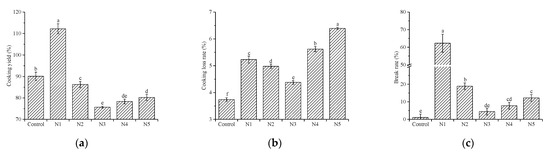
Figure 2.
Cooking properties of whole-wheat noodles. (a) Cooking yield; (b) cooking loss rate; (c) breaking rate. Different lowercase letters on columns indicate significantly different values (p < 0.05). N1, N2, N3, N4, and N5 are noodles corresponding to wheat bran with decrease in particle size sequentially. The noodles made from refined wheat flour served as a control group.
During the cooking process, the absorbed water by fresh noodles is mainly used for starch gelatinization and swelling of the gluten network during cooking [38]. The high water absorption in the control group may be attributed to the high starch content (as shown in Table 1), which required more water molecules for starch gelatinization. However, the starch content is not enough to explain that the water absorption of W1 was higher than the control group. Considering that W1 showed a higher break rate, it could be inferred that more starch is exposed at the cross-section of the noodles, resulting in a significant increase in water absorption [39].
Moreover, with the decrease in the particle size of wheat bran, the changes in the water absorption of noodles may be attributed to the changes in gluten structure. As Xiong et al. [11] reported, decreasing the particle size of the bran facilitated the encapsulation of starch granules by the gluten network, while excessive small bran tended to interfere with the aggregation of gluten proteins. A highly cross-linked gluten network would hinder the water molecular penetration, leading to low water absorption of noodles [40]. In addition, noodles with discontinuous gluten structures are prone to break during the cooking process [17]. Thus, it is reasonable that water absorption and break rate of noodles present the same trend. The cooking loss evaluates the structural integrity of noodles during cooking. A stable protein–gelatinized starch matrix usually presents low cooking loss [17]. Adding wheat bran disrupted the continuous gluten structure in dough, leading to high cooking loss [11]. As the particle size of wheat bran decreased, the trend of cooking loss and break rate suggested that decreasing particle size of wheat bran formed the compact gluten network, but the gluten network became less compact when the D50 was less than 26.51 μm. In contrast, Guan et al. [41] investigated the effect of particle size of refined wheat flour on noodle quality, in which D50 ranged from 108.89 μm to 52.36 μm. They found cooking loss of noodles was not affected by gluten strength, but related to starch properties. The difference may be caused by the properties of study subjects. In whole-wheat flour, wheat bran cannot form gluten by itself, which induces steric hindrance of the gluten-forming network. Decreasing the particle size of wheat bran would significantly decrease the steric hindrance of wheat bran, resulting in forming a more continuous gluten network [10]. In addition, the starch content (25.6–27.7%) of wheat bran is lower than that of refined wheat flour (80.3%), and the damaged starch content shows a small change with the decrease in the particle size of wheat bran [10]. Conversely, concerning refined wheat flour with high starch content, decreasing the particle size of wheat flour resulted in a significant increase in damaged starch [10,41]. These differences in dominant changes between refined wheat flour and whole-wheat flour contribute to the seemingly contradictory conclusions.
3.3.2. Textural Properties of Cooked Whole-Wheat Noodles
The textural properties of cooked noodles are one of the important parameters that determine the eating quality of noodles [12]. Textural profile analysis (TPA) is used widely to estimate the quality of cooked noodles, and the results are presented in Figure 3. Compared with the control group, the hardness of cooked noodles was high, and the springiness, cohesiveness, adhesiveness, and resilience were low in whole-wheat groups. As the decrease in the particle size of wheat bran decreased, the adhesiveness of cooked noodles increased, and the hardness, springiness, cohesiveness, and resilience increased first and then decreased.
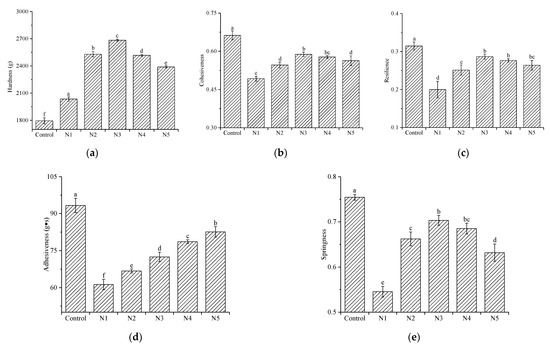
Figure 3.
Textural properties of cooked whole-wheat noodles. (a) Hardness; (b) cohesiveness; (c) resilience; (d) adhesiveness; (e) springiness. Different lowercase letters on columns indicate significantly different values (p < 0.05). N1, N2, N3, N4, and N5 are noodles corresponding to wheat brans with decreases in particle size sequentially. The noodles made from refined wheat flour served as a control group.
The cooked noodles in whole-wheat groups showed higher hardness than that of the control group. This may be due to the fact that wheat bran has a hard texture and acts as a support for the noodle structure, resulting in requiring greater force for a specific deformation. A similar result was observed by Jin et al. [42]. With the decrease in particle size of wheat bran, the hardness of cooked noodles increased first and then decreased, which might be related to the water absorption rate of fresh noodles (Figure 3a) [42]. Further, the high water absorption was mainly caused by the discontinuous gluten network that exposed more starch granules. At the same time, the discontinuous gluten network was also easily deformed upon the press. The springiness, cohesiveness, and resilience of cooked noodles presented similar trends, which was in agreement with Özboy and Köksel [43]. They reported that the springiness, cohesiveness, and resilience were mainly affected by the gluten network, and a strong gluten network usually showed high springiness, adhesiveness, and resilience. Based on the fact that bran itself does not form a gluten network and large wheat bran exhibits strong disruptions to the aggregation of gluten proteins, a looser gluten structure forms [11]. Decreasing the particle size of wheat bran could weaken this disruption, resulting in an increase in springiness, cohesiveness, and resilience of cooked noodles. Meanwhile, the polyphenols released from wheat bran might link to proteins through covalent bonds or non-covalent bonds, altering secondary and tertiary structures of gluten protein [44]. With the decrease in the particle size of wheat bran, more polyphenols are dissolved, leading to more significant damage to the gluten structure. Considering the changes in noodle texture, it can be speculated that the mechanism of decreasing wheat bran particle size on gluten structure is affected by wheat bran particle size. Specifically, when the wheat bran particle size is in a high-level range, reducing particle size induces a decrease in the steric hindrance of wheat bran, promoting the aggregation of gluten proteins. When the particle size of wheat bran is in a low-level range, a large number of polyphenols are released. At this time, the interference of polyphenols exceeds that of steric hindrance and plays a leading role, so further decreasing the particle size of wheat bran shows a stronger interference on the aggregation of gluten proteins. These could explain the changes in springiness, adhesiveness, and resilience of cooked noodles when the particle size of wheat bran decreased. The control group showed a higher adhesiveness than the whole-wheat groups, which may be attributed to higher damaged starch content [41]. Similarly, when the particle size of wheat bran decreased, the increasing damaged starch content supported the increase in adhesiveness of noodles. Considering the results of the textural properties of cooked noodles, it was comprehensively found that whole-wheat noodles with appropriate particle size wheat bran addition exhibit good textural properties.
3.3.3. Sensory Evaluation of Cooked Whole-Wheat Noodles
The sensory evaluation can take the consumer’s subjective evaluation into account, and the overall performance of cooked noodles was evaluated intuitively. In this study, the sensory evaluation mainly focused on the firmness, elasticity, smoothness, taste, appearance, and color of noodles (Figure 4). Compared with the control group, the score of firmness, elasticity, smoothness, appearance, and color of noodles was low in the whole-wheat groups, but the score of taste was high. With the decrease in particle size of wheat bran, the score of smoothness, taste, appearance, and color increased first and then tended to a stable value. The score of firmness and elasticity increased first and then decreased.
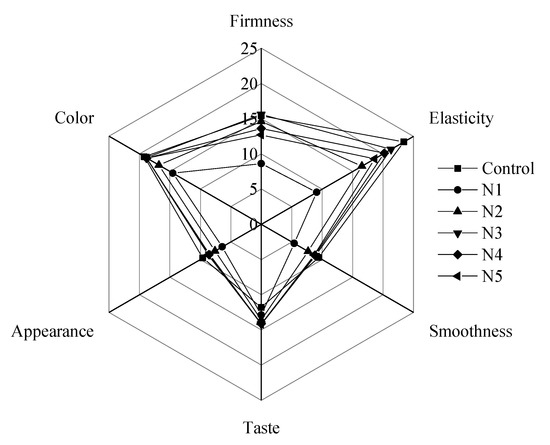
Figure 4.
Sensory evaluation of cooked whole-wheat noodles. N1, N2, N3, N4, and N5 are noodles corresponding to wheat brans with decreases in particle size sequentially. The noodles made from refined wheat flour served as a control group.
While the total score of the control group was 88.8 points and the whole-wheat group ranged from 56.9 points to 83.8 points, the whole-wheat noodles showed a higher flavor score. This result suggested adding wheat bran conferred certain wheat flavor to noodles, but induced an adverse effect on the sensory properties of the noodles. Decreasing the particle size of wheat bran appropriately can effectively improve the sensory score of whole-wheat noodles. Specifically, as the particle size of wheat bran decreased, the scores of firmness and elasticity were consistent with the results of the textural properties (Figure 4). Decreasing the particle size of wheat bran enhanced the score of taste, which might be due to stimulating various reactions resulting in higher level of wheat flavor [45]. In addition, decreasing particle size of wheat bran caused a flatter and smoother surface structure of noodles, which improved the smoothness and appearance of whole-wheat noodles. The score of color also increased with the decrease in particle size of wheat bran, which may be attributed to more even distribution of wheat bran. Similar results were also reported by Chen et al. [46]. Furthermore, decreasing further the particle size of wheat bran had no significant effect on the smoothness, taste, appearance, and color of noodles when the particle size of wheat bran was less than 26.51 μm. Taken together, the total score of whole-wheat noodles with wheat bran of D50 of 26.51 μm is 87.4 points and there is a great potential to be accepted by consumers.
3.4. Correlation Analysis of Quality between the Wheat Flour and Its Cooked Noodles
The flour quality determines the quality of its products to a large extent. Many indicators are used to evaluate the quality of flour and noodles; to clarify the relationship between the indicators, the correlation coefficients of the quality between wheat flour and its cooked noodles are calculated and shown in Figure 5.
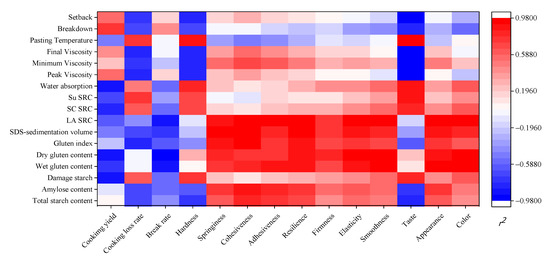
Figure 5.
Heat map of correlation coefficients of the quality between the wheat flour and its cooked noodles. r2 is the correlation coefficient. The LA SRC, SC SRC, and Su SRC represent the retention capacity of the whole-wheat flour to the 5% (m/v) lactic acid, 5% (m/v) sodium carbonate, and 50% (m/v) sucrose solutions, respectively.
The starch composition mainly affected the cooking and textural properties, as well as the taste score of noodles. Damaged starch content of wheat flour had a positive correlation with the hardness (r2 = 0.729) and taste score (r2 = 0.829) of cooked noodles, and a negative correlation with the cooking yield (r2 = −0.854). In this study, the higher damaged starch content is due to that wheat bran suffers more high-intensive rolling. Meanwhile, more high-intensive rolling produces wheat bran with smaller size, which has less disruption on the aggregation of gluten proteins, leading to forming a continuous gluten network [11]. The continuous gluten network is not conducive to the penetration of water molecules during cooking noodles, resulting in the low cooking yield and high hardness of noodles [42]. In addition, the gluten quality played an important role in the quality (except hardness and taste score) of cooked noodles. In particular, SDS-sedimentation volume of flour had a positive correlation with springiness (r2 = 0.922), cohesiveness (r2 = 0.967), resilience (r2 = 0.938), elasticity (r2 = 0.890), smoothness (r2 = 0.812), and appearance (r2 = 0.870) of cooked noodles. LA SRC of flour had a positive correlation with springiness (r2 = 0.887), cohesiveness (r2 = 0.960), adhesiveness (r2 = 0.918), resilience (r2 = 0.967), elasticity (r2 = 0.950), smoothness (r2 = 0.927), appearance (r2 = 0.978), and color (r2 = 0.927) of cooked noodle, while it had a negative correlation with break rate (r2 = −0.875). High SDS-sedimentation volume and LA SRC indicate that gluten proteins form a relatively continuous network which could better wrap starch particles and wheat bran, resulting in better smoothness and appearance of noodles. Similarly, Zhang et al. also suggested that gluten quality was significantly correlated with the macroscopic of the noodle [47]. Further, the pasting properties mainly affected the cooking properties, hardness, and taste score of noodles. Peak viscosity of flour had a negative correlation with both hardness (r2 = −0.803), taste score (r2 = −0.965), and cooking loss (r2 = −0.785). Pasting temperature of flour had a positive correlation with hardness (r2 = 0.869), taste score (r2 = 0.979), and cooking loss (r2 = −0.730). Guan et al. [41] reported that decreasing the particle size of wheat flour reduced the peak viscosity of wheat flour, and the hardness and cooking loss of cooked noodles, which was consistent with our results. Taken together, the texture properties and sensory evaluation of cooked noodles are mainly affected by gluten quality, while the cooking properties of noodles are affected by the combination of starch composition, pasting properties, and gluten quality. Therefore, improving the gluten quality could contribute to producing the noodles that consumers love. It is of great significance to further evaluate the changes of gluten structure in whole-wheat flour with the decreases in particle size of wheat bran.
4. Conclusions
In this study, the effects of wheat bran particle size on the quality of reconstituted whole-wheat flour and its cooked noodles were analyzed to find the appropriate particle size for producing whole-wheat noodles. With the decrease in particle size of wheat bran ranging from 26.05 to 46.08 μm, the LA SRC, Su SRC, water absorption, and pasting viscosity of whole-wheat flour increased, which was mainly caused by increasing the contents of damaged starch and arabinoxylan polymers. Meanwhile, the decrease in the steric hindrance of wheat bran contributed to a more continuous gluten network, resulting in a low cooking yield, cooking loss, and break rate of noodles. In addition, the continuous gluten network conferred high hardness, springiness, cohesiveness, and resilience of noodles. However, when the D50 of wheat bran was less than 26.51 μm, a large number of polyphenols were released. At this time, the interfering effects of polyphenols exceeded the improved effects of steric hindrance and had a stronger interference in the aggregation of gluten proteins, leading to a discontinuous gluten network, ultimately deteriorating the quality of noodles. In conclusion, whole-wheat noodles with wheat bran of D50 of 26.51 μm addition exhibit relatively better cooking, textural, and sensory properties than those with smaller or larger wheat bran. Further studies are essential to evaluate the applicability of these conclusions to other varieties of wheat flour or wheat bran.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pr10051001/s1, Table S1: The sensory evaluation details of cooked whole-wheat noodles.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Data curation, Writing-original draft, Writing-review and editing, S.L.; Methodology, Investigation, Data curation, J.L.; Data curation, Y.Z. and Y.W.; Investigation, G.L.; Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Q.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has been financially supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Projects of China (2016YFD0701801); Financial Support for Agricultural Scientific and Technological Achievements Transformation Projects of Shanxi Province, China (SCZZNCGZH201306); Postgraduate Education Innovation Project of Shanxi Province, China (2021Y308).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank Ronghe Flour Processing Factory (Shanxi, China) for providing the wheat bran and refined wheat flour, as well as thank the Basic Department (Shanxi Agricultural University) for providing the analytical chemistry laboratory.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yang, B.; Yin, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, M. Effect of germination time on the compositional, functional and antioxidant properties of whole wheat malt and its end-use evaluation in cookie-making. Food Chem. 2021, 349, 129125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Mu, M.; Jia, F.; Wang, J.; Liang, Y.; Wang, J. Aggregative and structural properties of wheat gluten induced by pectin. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 100, 103247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, Z.; Guo, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, X. Sourdough improves the quality of whole-wheat flour products: Mechanisms and challenges—A review. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 130038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delannoy-Bruno, O.; Desai, C.; Raman, A.S.; Chen, R.Y.; Gordon, J.I. Evaluating microbiome-directed fibre snacks in gnotobiotic mice and humans. Nature 2021, 595, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, F.; Ding, X.; Wu, G.; Lam, Y.; Wang, X. Gut bacteria selectively promoted by dietary fibers alleviate type 2 diabetes. Science 2018, 359, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heiniö, R.L.; Noort, M.W.J.; Katina, K.; Alam, S.A.; Sozer, N.; de Kock, H.L.; Poutanen, K. Sensory characteristics of wholegrain and bran-rich cereal foods—A review. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2016, 47, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alzuwaid, N.; Fellows, C.; Laddomada, B.; Sissons, M. Impact of wheat bran particle size on the technological and phytochemical properties of durum wheat pasta. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 95, 103033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protonotariou, S.; Stergiou, P.; Christaki, M.; Mandala, I.G. Physical properties and sensory evaluation of bread containing micronized whole wheat flour. Food Chem. 2021, 318, 126497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Gao, J.; Jin, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, W. Whole-wheat flour particle size influences dough properties, bread structure and in vitro starch digestibility. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 3610–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Jin, X.; Gao, J.; Qiu, Z.; Zhou, W. Impact of wheat bran micronization on dough properties and bread quality: Part I—Bran functionality and dough properties. Food Chem. 2021, 353, 129407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Zhang, B.; Meng, N.; Zhao, S. Protein polymerization and water mobility in whole-wheat dough influenced by bran particle size distribution. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 82, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Hou, G.; Lee, B.; Chen, Z. Effects of fine grinding of millfeeds on the quality attributes of reconstituted whole-wheat flour and its raw noodle products. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 57, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.W.; Ma, M.; Zhang, H.H.; Li, M.; Sun, Q.J. Progressive study of the effect of superfine green tea, soluble tea, and tea polyphenols on the physicochemical and structural properties of wheat gluten in noodle system. Food Chem. 2020, 308, 125676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, E.; Park, E.; Ma, F.; Baikd, B.; Fonsecab, J.M. Sensory and physicochemical properties of whole wheat salted noodles under different preparations of bran. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 96, 103112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, T.; Memon, A.A.; Sundquist, K.; Sundquist, J.; Olsson, S.; Nalla, A.; Bauer, M.; Linse, S. Digested wheat gluten inhibits binding between leptin and its receptor. BMC Biochem. 2015, 16, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drakos, A.; Kyriakakis, G.; Evageliou, V.; Protonotariou, S.; Mandala, I.; Ritzoulis, C. Influence of jet milling and particle size on the composition, physicochemical and mechanical properties of barley and rye flours. Food Chem. 2017, 215, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, H.; Wei, J.; Wang, L.; Huang, J.; Chen, X.; Luo, C.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H. Effects of potato/wheat flours ratio on mixing properties of dough and quality of noodles. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 76, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tang, D.; Liu, S.; Qin, S.; Chen, Y. Improvement of noodle quality: The effect of ultrasonic on noodles resting. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 96, 103089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Guan, E.Q.; Yang, Y.L.; Liu, Y.X.; Bian, K. Impact of wheat globulin addition on dough rheological properties and quality of cooked noodles. Food Chem. 2021, 362, 130170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, A.; Guerrini, L.; Parenti, A.; Palladino, G.; Cini, E. Effects of wheat tempering and stone rotational speed on particle size, dough rheology and bread characteristics for a stone-milled weak flour. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 91, 102879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, M.; Handa, S.; Mridula, D.; Singh, R.K. Physicochemical, functional and rheological properties of grass pea (lathyrus sativus l.) flour as influenced by particle size. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Oh, I.; Jeong, S.; Lee, S. Particle size effect of rice flour in a rice-zein noodle system for gluten-free noodles slit from sheeted doughs. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 86, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Li, L.; Hao, C.; Zheng, X.; Bian, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Effects of different milling processes on whole wheat flour quality and performance in steamed bread making. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Qian, X.; Sun, B.; Ma, S.; Tian, X.; Wang, X. Nutritional composition and physicochemical properties of oat flour sieving fractions with different particle size. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 154, 112757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulia, N.; Khatkar, B.S. Quantitative and qualitative assessment of wheat gluten proteins and their contribution to instant noodle quality. Int. J. Food Prop. 2015, 18, 1648–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ni, Z.; Thakur, K.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Shang, Y.; Wei, Z. Effect of grape seed power on the structural and physicochemical properties of wheat gluten in noodle preparation system. Food Chem. 2021, 355, 129500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, M.; Slade, L.; Levine, H. Solvent retention capacity (src) testing of wheat flour: Principles and value in predicting flour functionality in different wheat-based food processes and in wheat breeding—A review. Cereal Chem. 2011, 88, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Ma, S.; Li, L.; Zheng, X.; Wang, X. Gluten aggregation behavior in gluten and gluten-starch doughs after wheat bran dietary fiber addition. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 106, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craeyveld, V.V.; Holopainen, U.; Selinheimo, E.; Poutanen, K.; Delcour, J.A.; Courtin, C.M. Extensive dry ball milling of wheat and rye bran leads to in situ production of arabinoxylan oligosaccharides through nanoscale fragmentation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 8467–8473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudha, M.L.; Vetrimani, R.; Leelavathi, K. Influence of fibre from different cereals on the rheological characteristics of wheat flour dough and on biscuit quality. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 1365–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosbie, G.B.; Ross, A.S. Noodles: Asian wheat flour noodles. Encycl. Grain Sci. 2004, 3, 304–312. [Google Scholar]
- Dufour, D.; Gibert, O.; Giraldo, A.; Sanchez, T.; Reynes, M.; Pain, J.P.; González, A.; Fernández, A.; Díaz, A. Differentiation between cooking bananas and dessert bananas. 2. thermal and functional characterization of cultivated colombian musaceae (Musa sp.). J. Agric. Food chem. 2009, 57, 7870–7876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidul, I.; Yamauchi, H.; Kim, S.J.; Hashimoto, N.; Noda, T. RVA study of mixtures of wheat flour and potato starches with different phosphorus contents. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, M.; Jekle, M.; Becker, T. Starch gelatinization and its complexity for analysis. Starch—Starke 2015, 67, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, E.; Pourmohammadi, K. Chemical modifications and their effects on gluten protein: An extensive review. Food Chem. 2020, 343, 128398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, M.; Zhang, B.; Jia, C.; Zhao, S. Multi-scale structures and pasting characteristics of starch in whole-wheat flour treated by superfine grinding. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Ma, M.; Zhu, K.X.; Guo, X.N.; Zhou, H.M. Delineating the physico-chemical, structural, and water characteristic changes during the deterioration of fresh noodles. Food Chem. 2017, 216, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majzoobi, M.; Ostovan, R.; Farahnaky, A. Effects of gluten powder on the quality of wheat flour spaghetti cooked in distilled or salted water. J. Texture Stud. 2011, 42, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.S.; Baik, B.K. Cooking time of white salted noodles and its relationship with protein and amylose contents of wheat. Cereal Chem. 2004, 81, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Kee, J.I.; Lee, S.; Yoo, S.H. Quality improvement of rice noodle restructured with rice protein isolate and transglutaminase. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 409–416. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, E.; Pang, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, M.; Bian, K. Effects of wheat flour particle size on physicochemical properties and quality of noodles. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 4209–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Lin, S.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, W. How manipulation of wheat bran by superfine-grinding affects a wide spectrum of dough rheological properties. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 96, 103081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özboy, Ö.; Köksel, H. Unexpected strengthening effects of a coarse wheat bran on dough rheological properties and baking quality. J. Cereal Sci. 1997, 25, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Li, Y. Dough properties, bread quality, and associated interactions with added phenolic compounds: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 52, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihlberg, I.; Johansson, L.; Kohler, A.; Risvik, E. Sensory qualities of whole wheat pan bread—Influence of farming system, milling and baking technique. J. Cereal Sci. 2004, 39, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.S.; Fei, M.J.; Shi, C.L.; Tian, J.C.; Sun, C.L.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Z.; Dong, H.X. Effect of particle size and addition level of wheat bran on quality of dry white Chinese noodles. J. Cereal Sci. 2011, 53, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Jia, R.; Yang, T.; Sun, Q.; Li, M. Delineating the dynamic transformation of gluten morphological distribution, structure, and aggregation behavior in noodle dough induced by mixing and resting. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).