Deep Full-Body HPE for Activity Recognition from RGB Frames Only
Abstract
1. Introduction
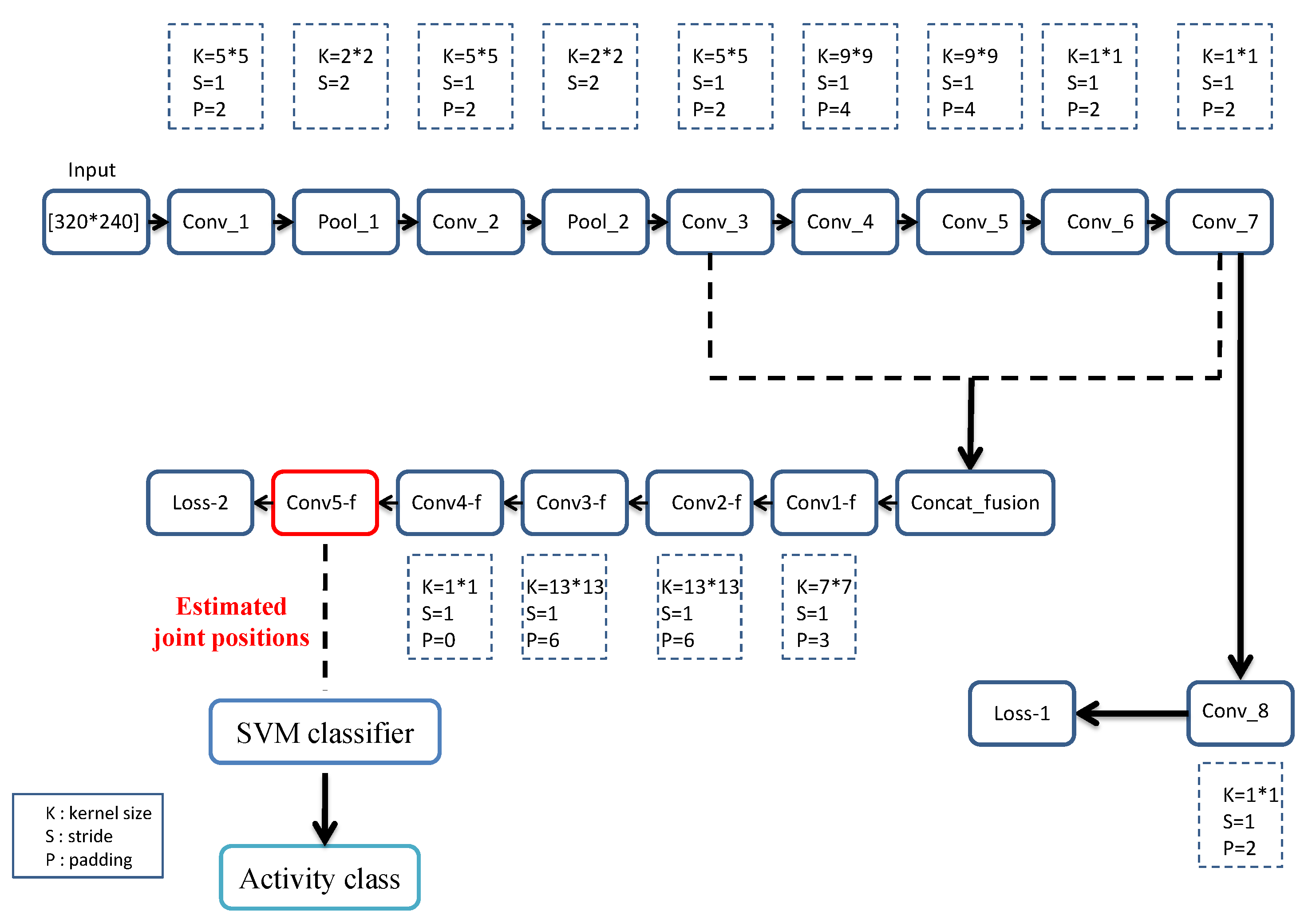
- We present an end-to-end CNN that exploits RGB data only for a full-body pose estimation. The estimated person poses are then considered as discriminative features to recognize different human activities.
- We extensively evaluate various aspects of our HPE architecture: We test different model parameters (including: iteration number, data augmentation techniques, and heat map size). We compare the proposed model with previous approaches on common benchmark datasets (i.e., J-HMDBand CAD-60) for which interesting results for HPE and activity recognition are reported.
- We recognize human activities using human poses rather than RGB information. We conclude that the quality of the estimated poses significantly affects the recognition performance.
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional HPE Approaches
2.2. Deep HPE Approaches
2.3. Deep HAR Approaches
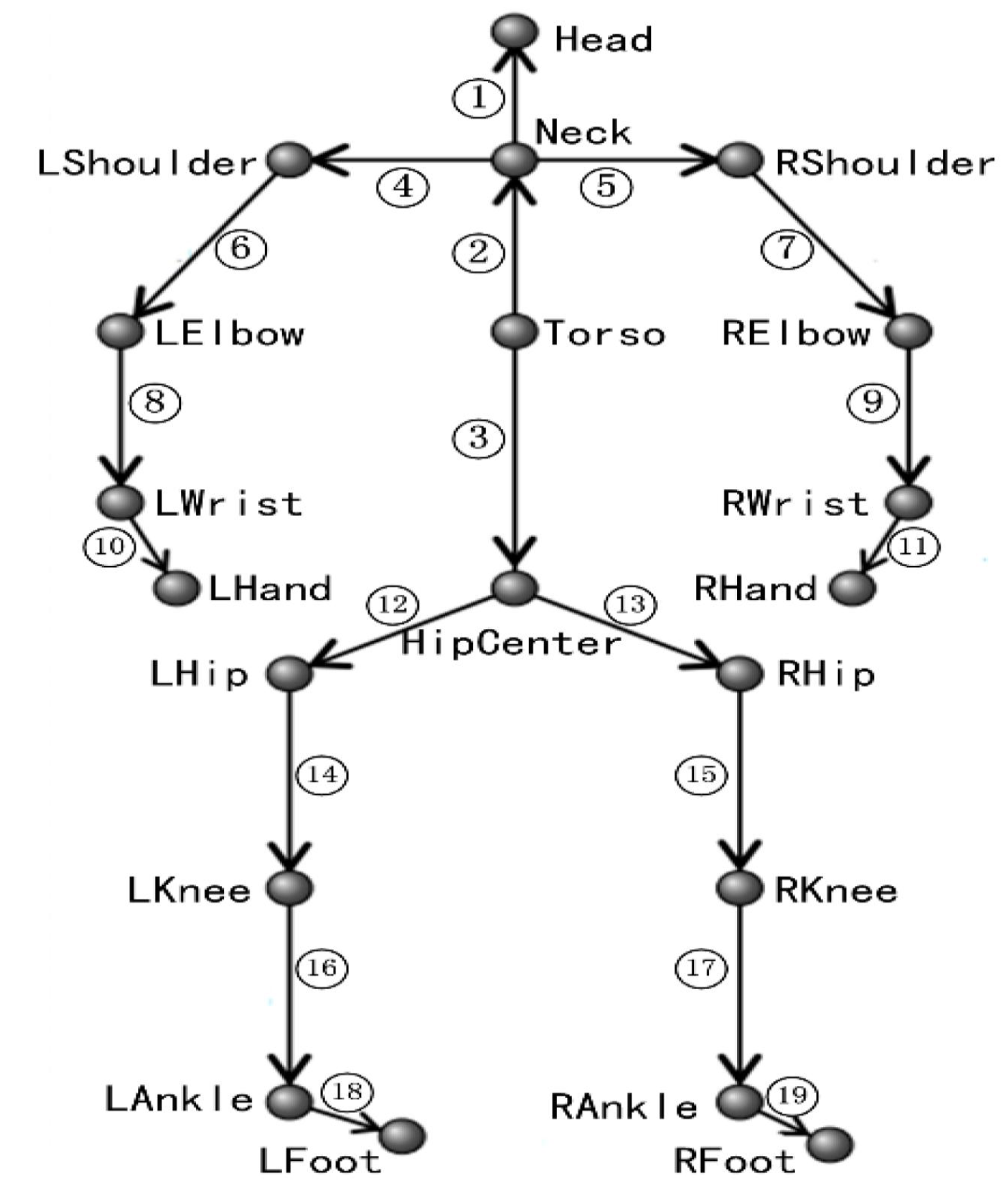
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
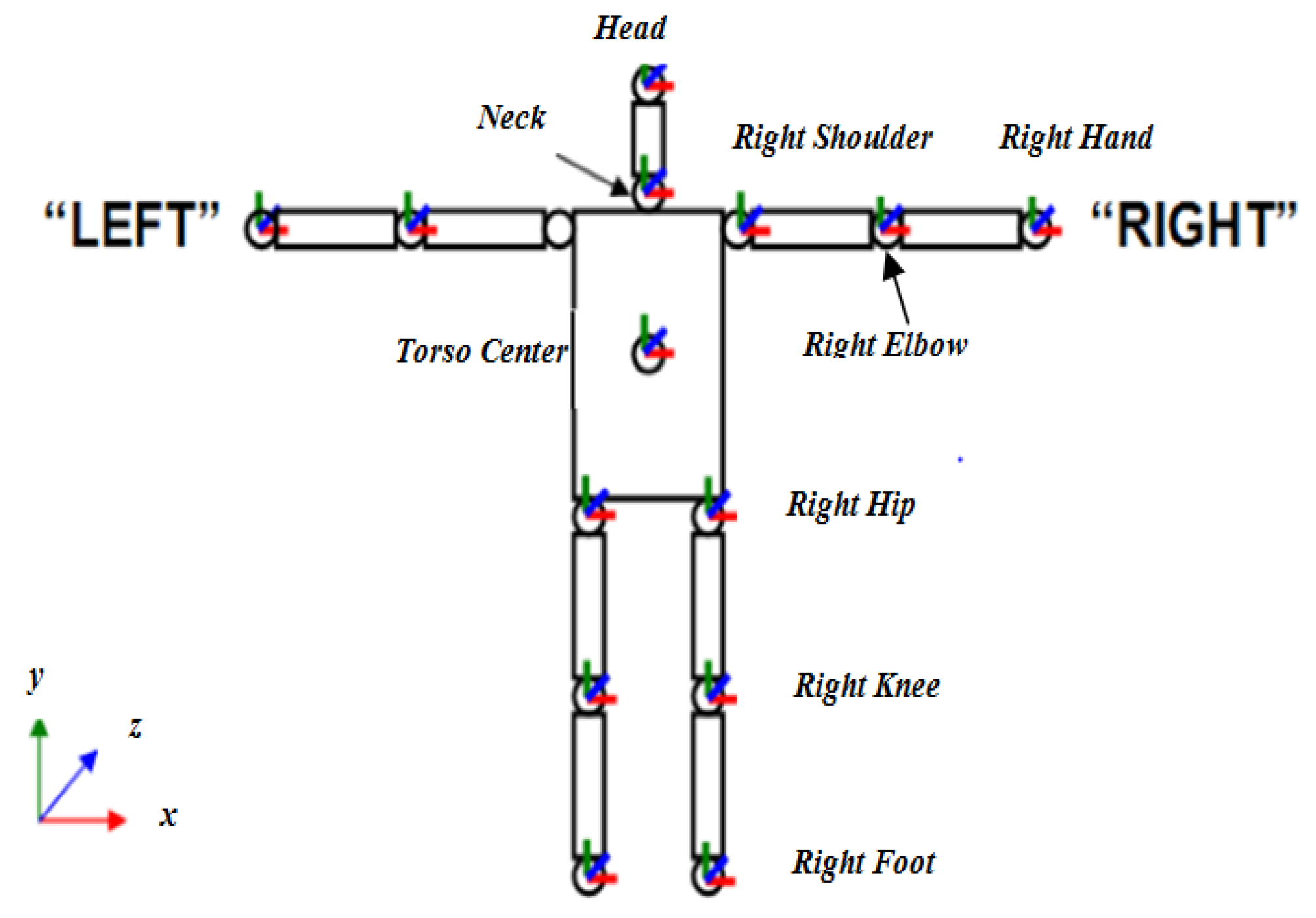
4.1. Datasets
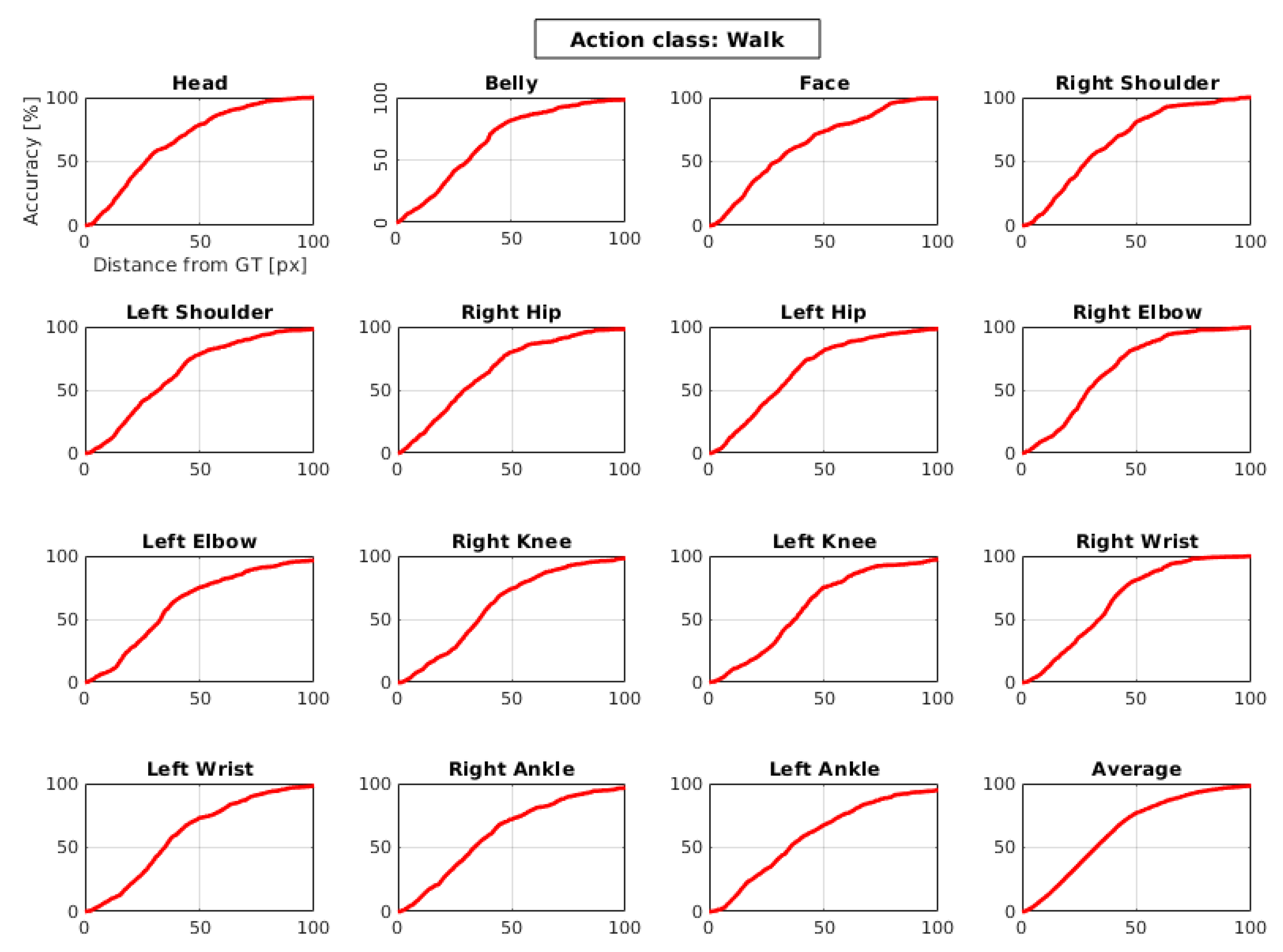
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
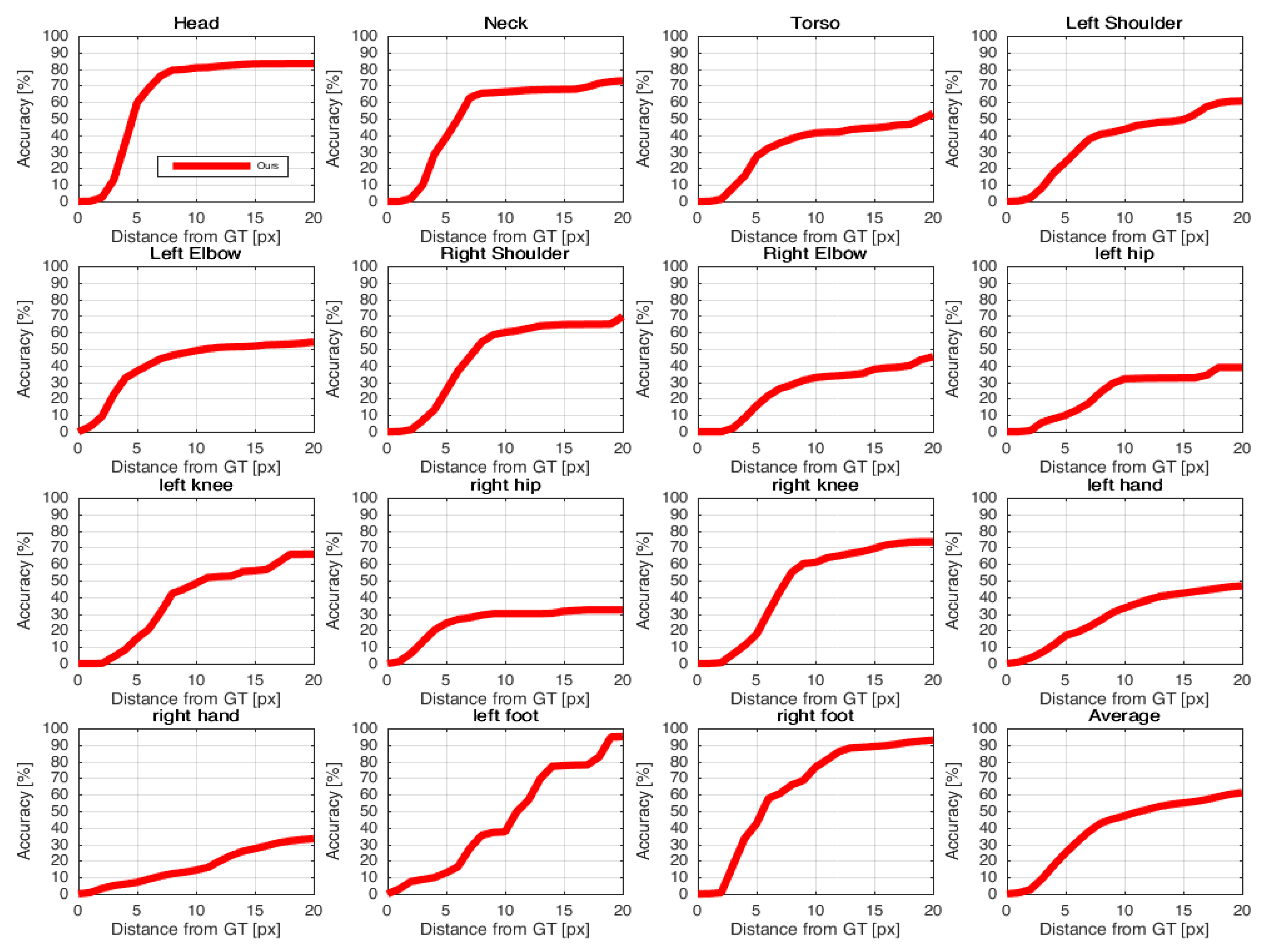
- PCK: It defines a candidate keypoint to be correct if it falls within pixels of the GT keypoint, where h and w are respectively the height and width of the bounding box and is the relative threshold for correctness [16].
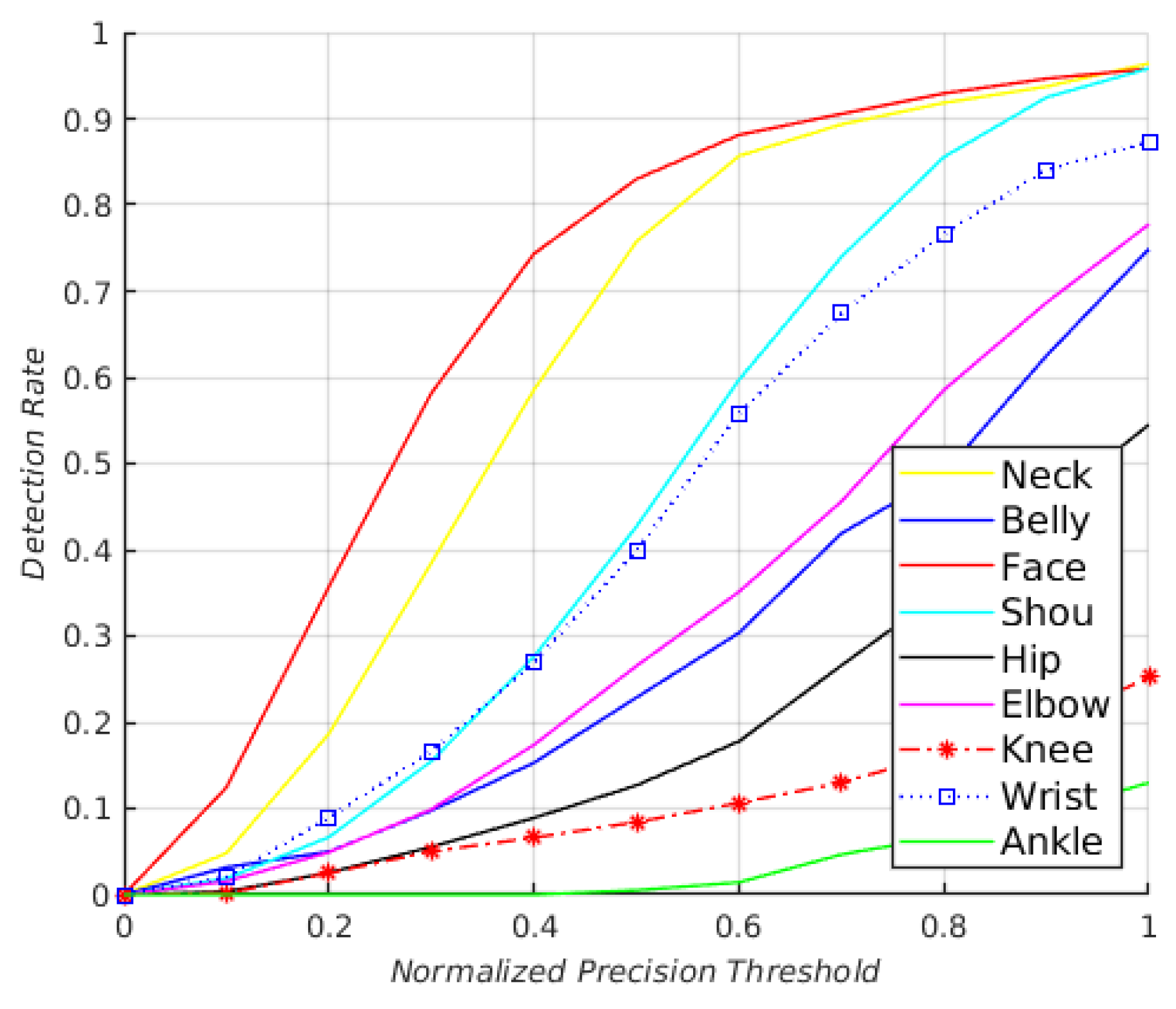
- PDJ: A joint is considered detected if the distance between the predicted joint and the true one is within a certain fraction of the torso diameter. By varying this fraction, detection rates are obtained for varying degrees of localization precision. This metric alleviates the drawback of PCP since the detection criteria for all joints are based on the same distance threshold [20].
4.3. Results of J-HMDB Dataset
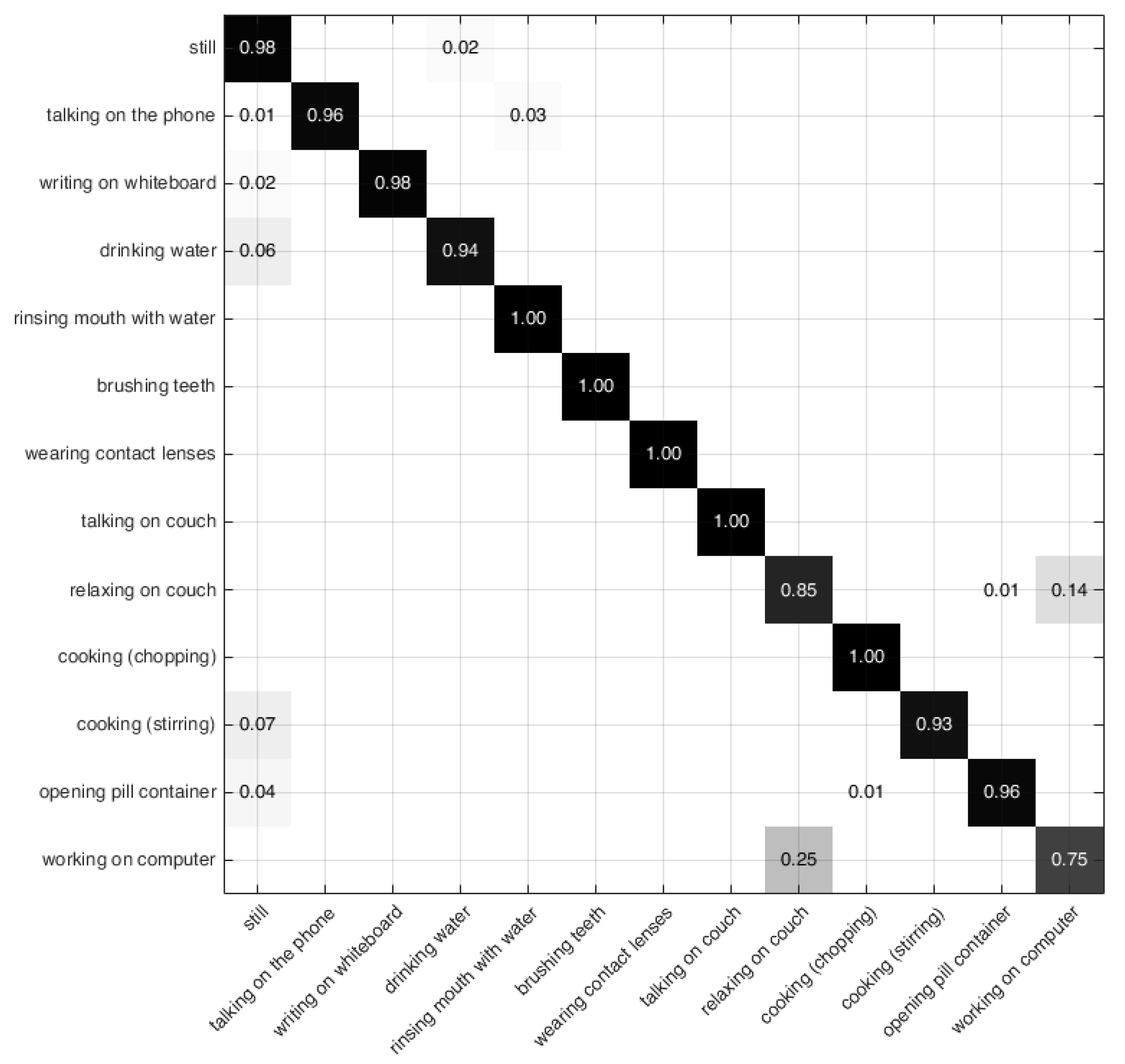
4.4. Results of the CAD-60 Dataset
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiang, L.; Zhang, W.; Hongliang, L.; Ngan, K.N. Hybrid human detection and recognition in surveillance. Neurocomputing 2016, 194, 10–23. [Google Scholar]
- D’Eusanio, A.; Simoni, A.; Pini, S.; Borghi, G.; Vezzani, R.; Cucchiara, R. Multimodal hand gesture classification for the human–car interaction. Informatics 2020, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unzueta, L.; Goenetxea, J.; Rodriguez, M.; Linaza, M.T. Dependent 3D human body posing for sports legacy recovery from images and video. In Proceedings of the 2014 22nd European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Lisbon, Portugal, 1–5 September 2014; pp. 361–365. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Yang, Y.; Nie, F.; Odobez, J.M. 3D human pose recovery from image by efficient visual feature selection. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2011, 115, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.; Alghassi, A.; Ahsan, M.; Haider, J. Deep Learning Model for Industrial Leakage Detection Using Acoustic Emission Signal. Informatics 2020, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantaras, A. Deep Learning and Parallel Processing Spatio-Temporal Clustering Unveil New Ionian Distinct Seismic Zone. Informatics 2020, 4, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yuille, A.L. Articulated pose estimation by a graphical model with image dependent pairwise relations. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 1736–1744. [Google Scholar]
- Zuffi, S.; Romero, J.; Schmid, C.; Black, M.J. Estimating human pose with flowing puppets. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 3312–3319. [Google Scholar]
- Seddik, B.; Gazzah, S.; Essoukri Ben Amara, N. Hybrid Multi-modal Fusion for Human Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference Image Analysis and Recognition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 5–7 July 2017; pp. 201–209. [Google Scholar]
- Seddik, B.; Gazzah, S.; Essoukri Ben Amara, N. Hands, face and joints for multi-modal human-action temporal segmentation and recognition. In Proceedings of the 2015 23rd European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Nice, France, 31 August–4 September 2015; pp. 1143–1147. [Google Scholar]
- Mhalla, A.; Chateau, T.; Maamatou, H.; Gazzah, S.; Essoukri Ben Amara, N. SMC faster R-CNN: Toward a scene-specialized multi-object detector. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2017, 164, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddik, B.; Gazzah, S.; Essoukri Ben Amara, N. Modalities combination for Italian sign language extraction and recognition. In International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing; Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2015; pp. 710–721. [Google Scholar]
- Boualia, S.N.; Essoukri Ben Amara, N. Pose-based Human Activity Recognition: A review. In Proceedings of the 2019 15th International Wireless Communications Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC), Tangier, Morocco, 24–28 June 2019; pp. 1468–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubney, B.; Gibson, D.; Campbell, N. Estimating pose of articulated objects using low-level motion. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2012, 116, 330–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, H.; Xu, W.; Gong, Y.; Huang, T. Discriminative learning of visual words for 3D human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2008 Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition—CVPR 2008, Anchorage, AK, USA, 24–26 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, V.; Marin-Jimenez, M.; Zisserman, A. Progressive search space reduction for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition—CVPR 2008, Anchorage, AK, USA, 24–26 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Shotton, J.; Fitzgibbon, A.; Cook, M.; Sharp, T.; Finocchio, M.; Moore, R.; Kipman, A.; Blake, A. Real-time human pose recognition in parts from single depth images. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Providence, RI, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 1297–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Poppe, R. Evaluating example-based pose estimation: Experiments on the humaneva sets. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2nd Workshop on Evaluation of Articulated Human Motion and Pose Estimation, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 22 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Niyogi, S.; Freeman, W.T. Example-based head tracking. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, Killington, VT, USA, 14–16 October 1996; pp. 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshev, A.; Szegedy, C. Deeppose: Human pose estimation via deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1653–1660. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Paluri, M.; Ranzato, M.; Darrell, T.; Bourdev, L. Panda: Pose aligned networks for deep attribute modeling. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1637–1644. [Google Scholar]
- Pishchulin, L.; Andriluka, M.; Gehler, P.; Schiele, B. Poselet conditioned pictorial structures. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 588–595. [Google Scholar]
- Carreira, J.; Agrawal, P.; Fragkiadaki, K.; Malik, J. Human pose estimation with iterative error feedback. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4733–4742. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, A.; Yang, K.; Deng, J. Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2016; pp. 483–499. [Google Scholar]
- Belagiannis, V.; Zisserman, A. Recurrent human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2017 12th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2017), Washington, DC, USA, 30 May–3 June 2017; pp. 468–475. [Google Scholar]
- Lifshitz, I.; Fetaya, E.; Ullman, S. Human pose estimation using deep consensus voting. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2016; pp. 246–260. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Zhu, M.; Leonardos, S.; Derpanis, K.G.; Daniilidis, K. Sparseness meets deepness: 3D human pose estimation from monocular video. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4966–4975. [Google Scholar]
- Pfister, T.; Charles, J.; Zisserman, A. Flowing convnets for human pose estimation in videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1913–1921. [Google Scholar]
- Nibali, A.; He, Z.; Morgan, S.; Prendergast, L. 3d human pose estimation with 2d marginal heat maps. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa Village, HI, USA, 7–11 January 2019; pp. 1477–1485. [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda, K.; Kono, M.; Rekimoto, J. Post-Data Augmentation to Improve Deep Pose Estimation of Extreme and Wild Motions. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.04250. [Google Scholar]
- Kreiss, S.; Bertoni, L.; Alahi, A. PifPaf: Composite Fields for Human Pose Estimation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.06593. [Google Scholar]
- Gärtner, E.; Pirinen, A.; Sminchisescu, C. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Active Human Pose Estimation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.02024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathis, M.W.; Mathis, A. Deep learning tools for the measurement of animal behavior in neuroscience. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2020, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 568–576. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, Y. Towards good practices for very deep two stream convnets. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1507.02159. [Google Scholar]
- Ijjina, E.P.; Chalavadi, K.M. Human action recognition using genetic algorithms and convolutional neural networks. Pattern Recognit. 2016, 59, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Lin, L.; Wang, M.; Zuo, W. 3D human activity recognition with reconfigurable convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Orlando, FL, USA, 3–7 November 2014; pp. 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, J.; Kang, K.; Change Loy, C.; Wang, X. Deeply learned attributes for crowded scene understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 4657–4666. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Bourdev, L.; Fergus, R.; Torresani, L.; Paluri, M. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 4489–4497. [Google Scholar]
- Varol, G.; Laptev, I.; Schmid, C. Long-term temporal convolutions for action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shou, Z.; Chan, J.; Zareian, A.; Miyazawa, K.; Chang, S.F. CDC: Convolutional-de-convolutional networks for precise temporal action localization in untrimmed videos. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1417–1426. [Google Scholar]
- Neili, S.; Gazzah, S.; El Yacoubi, M.A.; Essoukri Ben Amara, N. Human posture recognition approach based on ConvNets and SVM classifier. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Signal and Image Processing (ATSIP), Fez, Morocco, 22–24 May 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Shelhamer, E.; Donahue, J.; Karayev, S.; Long, J.; Girshick, R.; Guadarrama, S.; Darrell, T. Caffe: Convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Orlando, FL, USA, 3–7 November 2014; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 675–678. [Google Scholar]
- Jhuang, H.; Gall, J.; Zuffi, S.; Schmid, C.; Black, M.J. Towards understanding action recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 3192–3199. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, J.; Ponce, C.; Selman, B.; Saxena, A. Human Activity Detection from RGBD Images. Plan Act. Intent Recognit. 2011, 64, 47–55. [Google Scholar]
- Zuffi, S.; Freifeld, O.; Black, M.J. From pictorial structures to deformable structures. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 3546–3553. [Google Scholar]
- Sapp, B.; Taskar, B. Modec: Multimodal decomposable models for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 3674–3681. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Kläser, A.; Schmid, C.; Liu, C.L. Action recognition by dense trajectories. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 3169–3176. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaohan Nie, B.; Xiong, C.; Zhu, S.C. Joint action recognition and pose estimation from video. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1293–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Chéron, G.; Laptev, I.; Schmid, C. P-cnn: Pose-based cnn features for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 3218–3226. [Google Scholar]
- Gkioxari, G.; Malik, J. Finding action tubes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 759–768. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Wang, L.; Van Gool, L.; Hilliges, O. Two-Stream SR-CNNs for Action Recognition in Videos. In Proceedings of the BMVC, York, UK, 19–22 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Z.; Cao, J.; Li, Y.; Li, B. MSR-CNN: Applying motion salient region based descriptors for action recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Cancun, Mexico, 4–8 December 2016; pp. 3524–3529. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Z.; Xie, W.; Qin, Q.; Poppe, R.; Veltkamp, R.C.; Li, B.; Yuan, J. Multi-stream CNN: Learning representations based on human-related regions for action recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 79, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, I.; Shakhuro, V.; Konushin, A. Deep probabilistic human pose estimation. IET Comput. Vis. 2018, 12, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.J. LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2011, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.; Ponce, C.; Selman, B.; Saxena, A. Unstructured human activity detection from rgbd images. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Saint Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012; pp. 842–849. [Google Scholar]
- Koppula, H.S.; Gupta, R.; Saxena, A. Learning human activities and object affordances from rgb-d videos. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2013, 32, 951–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tian, Y. RGB-D camera-based daily living activity recognition. J. Comput. Vis. Image Process. 2012, 2, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Tian, Y. Effective 3d action recognition using eigenjoints. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2014, 25, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyathilaka, L.; Kodagoda, S. Gaussian mixture based HMM for human daily activity recognition using 3D skeleton features. In Proceedings of the 2013 8th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Melbourne, Australia, 19–21 June 2013; pp. 567–572. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, B.; Pei, Y.; Moulin, P.; Yan, S. Multilevel depth and image fusion for human activity detection. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2013, 43, 1383–1394. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Chia, A.Y.S.; Rajan, D. Human activities recognition using depth images. In Proceedings of the 21st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Barcelona, Spain, 21 October 2013; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 283–292. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Y. Learning actionlet ensemble for 3D human action recognition. In Human Action Recognition with Depth Cameras; Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2014; pp. 11–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, W.; Guo, G. Evaluating spatiotemporal interest point features for depth-based action recognition. Image Vis. Comput. 2014, 32, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, D.R.; Premebida, C.; Nunes, U. A probabilistic approach for human everyday activities recognition using body motion from RGB-D images. In Proceedings of the 2014 RO-MAN: The 23rd IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, Edinburgh, UK, 25–29 August 2014; pp. 732–737. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, J.; Akella, S. 3D human action segmentation and recognition using pose kinetic energy. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Workshop on Advanced Robotics and Its Social Impacts (ARSO), Evanston, IL, USA, 11–13 September 2014; pp. 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Gaglio, S.; Re, G.L.; Morana, M. Human activity recognition process using 3-D posture data. IEEE Trans. Hum. Mach. Syst. 2015, 45, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, G.I.; Weber, C.; Wermter, S. Self-organizing neural integration of pose-motion features for human action recognition. Front. Neurorobotics 2015, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cippitelli, E.; Gasparrini, S.; Gambi, E.; Spinsante, S. A human activity recognition system using skeleton data from RGBD sensors. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2016, 2016, 4351435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddik, B.; Gazzah, S.; Essoukri Ben Amara, N. Human-action recognition using a multi-layered fusion scheme of Kinect modalities. IET Comput. Vis. 2017, 11, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogez, G.; Schmid, C. Mocap-guided data augmentation for 3d pose estimation in the wild. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2016, 29, 3108–3116. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Tang, Z.; Yang, F.; Feris, R.S.; Metaxas, D. Jointly optimize data augmentation and network training: Adversarial data augmentation in human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 2226–2234. [Google Scholar]
| Reference | Method | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Wang 2011 [49] | DTs | 56.6 |
| Nie 2015 [50] | STAOGM | 55.7 |
| Cheron 2015 [51] | P-CNN | 61.1 |
| Gkioxari 2015 [52] | A-tubes | 62.5 |
| Wang 2016 [53] | SR-CNN | 65.51 |
| Tu 2016 [54] | MSR-CNN | 66.02 |
| Tu 2018 [55] | HR-MSCNN | 71.17 |
| Ours | DFB-HPE | 62.07 |
| Iteration | Head | Neck | Torso | Shoulder | Elbow | Hip | Knee | Hand | Foot | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k= 1 | 63.9 | 69.0 | 52.9 | 51.7 | 59.2 | 18.3 | 16.9 | 33.8 | 18.4 | 38.8 |
| k= 2 | 97.2 | 98.5 | 95.5 | 96.0 | 74.7 | 53.1 | 27.8 | 53.3 | 21.4 | 62.9 |
| k= 3 | 82.5 | 67.2 | 44.7 | 57.3 | 44.0 | 32.2 | 63.5 | 35.1 | 83.2 | 55.0 |
| k= 4 | 71.3 | 19.8 | 14.1 | 26.5 | 29.6 | 39.7 | 83.1 | 47.1 | 12.0 | 38.7 |
| Average | 78.7 | 63.6 | 51.8 | 57.8 | 51.8 | 35.8 | 47.8 | 42.3 | 33.7 | 51.5 |
| Algorithm | Precision | Recall | Input Data | Method | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skeleton | RGB | Depth | ||||
| Sung 2012 [59] | 67.9 | 55.5 | * | * | * | DBN |
| Koppula 2012 [60] | 80.8 | 71.4 | * | * | * | MRF |
| Zhang 2012 [61] | 86 | 84 | * | * | * | BOW + SVM |
| Yang 2013 [62] | 71.9 | 66.6 | * | Eigenjoints | ||
| Piyathilaka 2013 [63] | 70 | 78 | * | * | * | GMM+ HMM |
| Ni 2013 [64] | 75.9 | 69.5 | * | * | Latent SVM | |
| Gupta 2013 [65] | 78.1 | 75.4 | * | Codewords + Ensemble | ||
| Wang 2014 [66] | 74.70 | - | * | * | * | Fourier temporal pyramid |
| Zhu 2014 [67] | 93.2 | 84.6 | * | * | * | STIP+ skeleton |
| Faria 2014. [68] | 91.1 | 91.9 | * | Dynamic Bayesian, mixture model | ||
| Shan 2014 [69] | 93.8 | 94.5 | * | Keypose, random forest, HMM | ||
| Gaglio 2015 [70] | 77.3 | 76.7 | * | SVM, HMM | ||
| Parisi 2015 [71] | 91.9 | 90.2 | * | Self-organizing neural | ||
| Cippitelli 2016 [72] | 93.9 | 93.5 | * | Atomic motion, naive Bayes, nearest neighbor | ||
| Seddik 2017 [73] | 92.4 | 93.6 | * | * | * | Bags of visual words, Fisher vectors, and SVM |
| Ours | 95.4 | 95.6 | * | DFB-HPE (ConvNets + SVM) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neili Boualia, S.; Essoukri Ben Amara, N. Deep Full-Body HPE for Activity Recognition from RGB Frames Only. Informatics 2021, 8, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics8010002
Neili Boualia S, Essoukri Ben Amara N. Deep Full-Body HPE for Activity Recognition from RGB Frames Only. Informatics. 2021; 8(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics8010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeili Boualia, Sameh, and Najoua Essoukri Ben Amara. 2021. "Deep Full-Body HPE for Activity Recognition from RGB Frames Only" Informatics 8, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics8010002
APA StyleNeili Boualia, S., & Essoukri Ben Amara, N. (2021). Deep Full-Body HPE for Activity Recognition from RGB Frames Only. Informatics, 8(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics8010002





