Integrative Analysis of Plasma Proteomics and Transcriptomics Reveals Potential Therapeutic Targets for Psoriasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
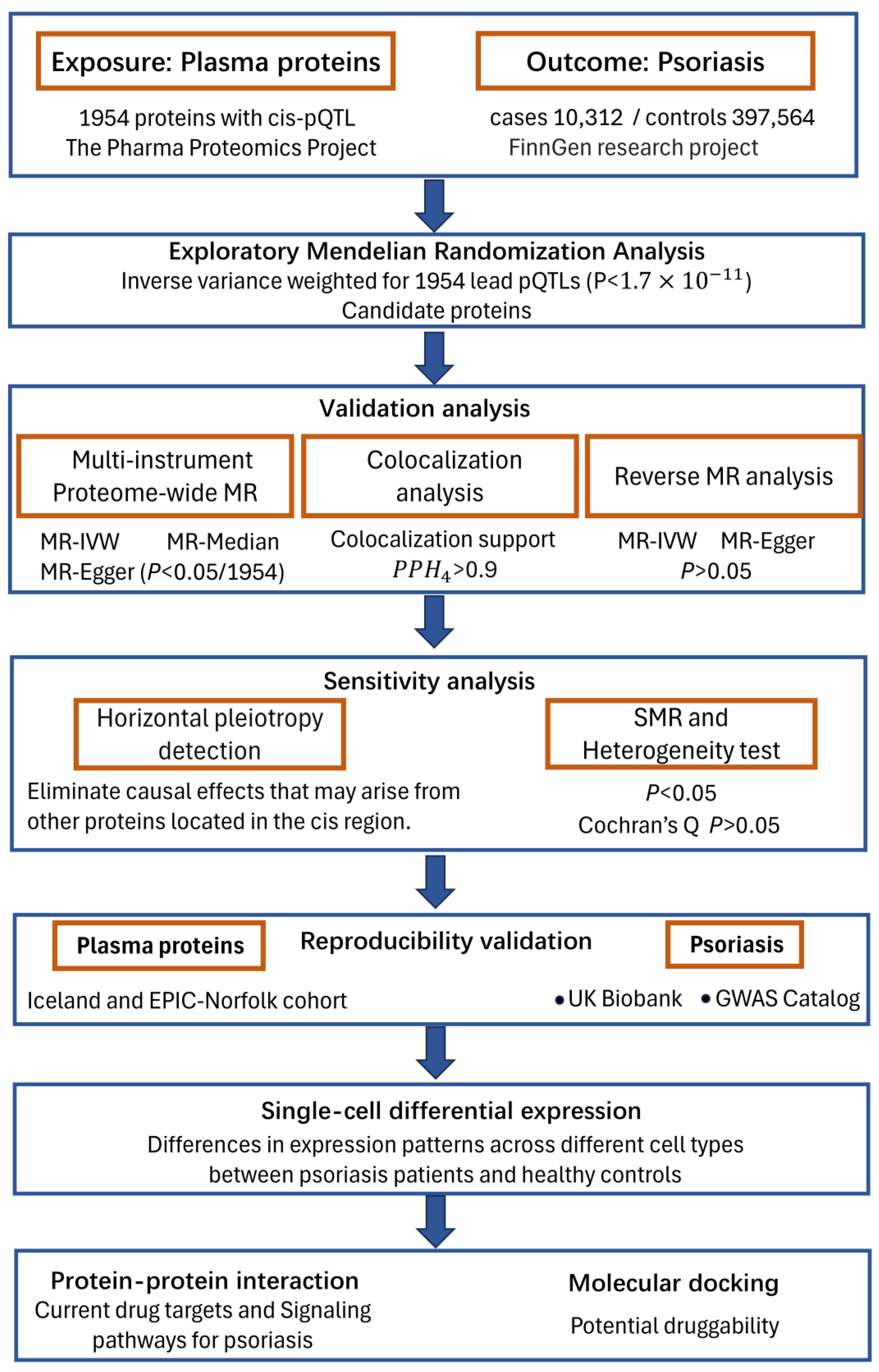
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Plasma Protein Data
2.3. GWAS Summary Association Statistics of PsO
2.4. Mendelian Randomization (MR) Analysis
2.5. Reverse Causality Detection
2.6. Bayesian Colocalization Analysis
2.7. Horizontal Pleiotropy Detection
2.8. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Differential Expression Analysis
2.9. Protein-Protein Interaction Networks and Drug Targets Analysis
2.10. Molecular Docking Analysis of Therapeutic Target Proteins
3. Results
3.1. Proteome Screening for Causal Proteins in PsO
3.2. Reproducibility Validation of Potential Drug Targets for PsO
3.3. Single-Cell Gene Expression Analysis in Psoriatic and Normal Skin
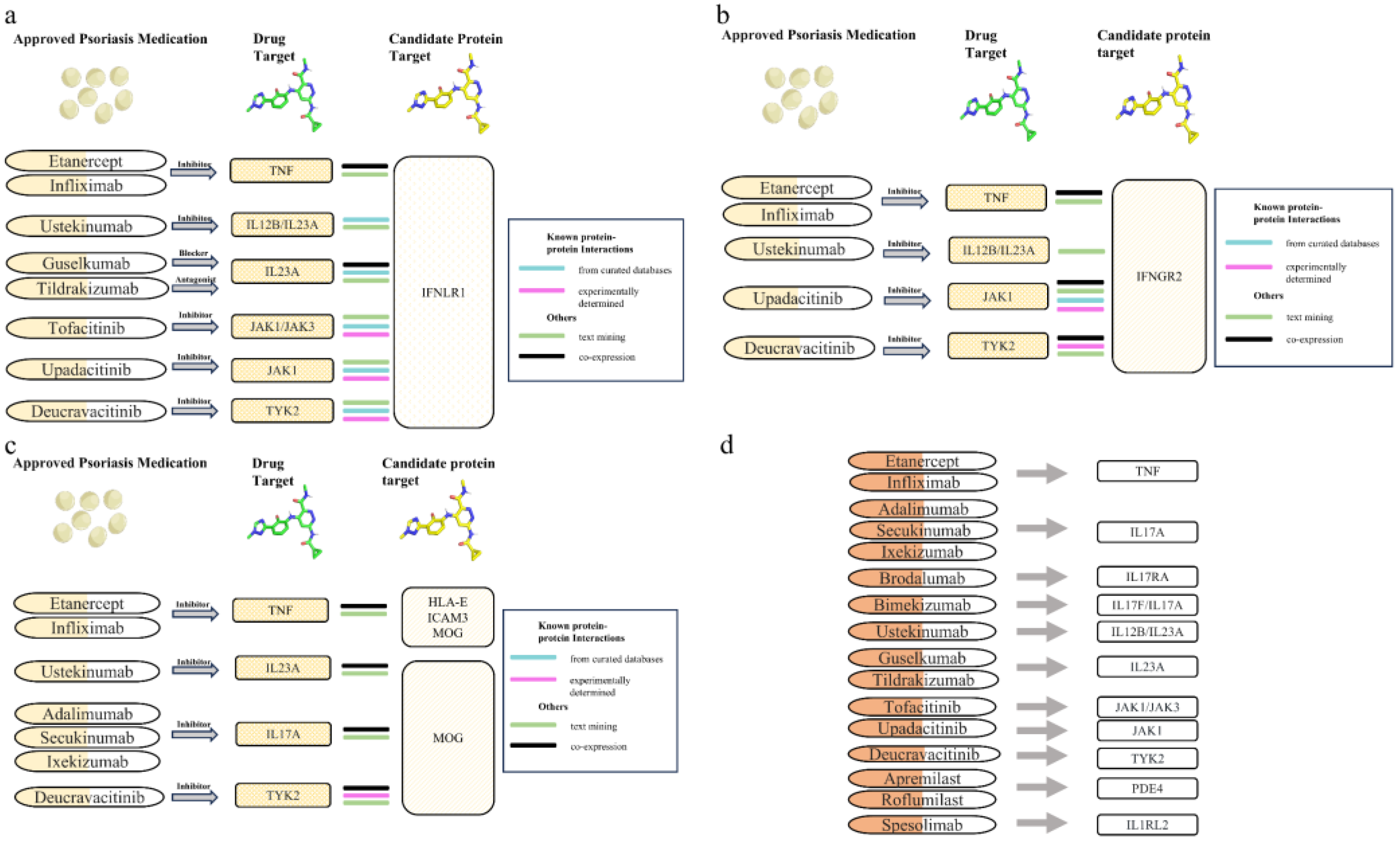
3.4. Protein-Protein Interaction Analysis Between Candidate Therapeutic Targets and Current PsO Medications
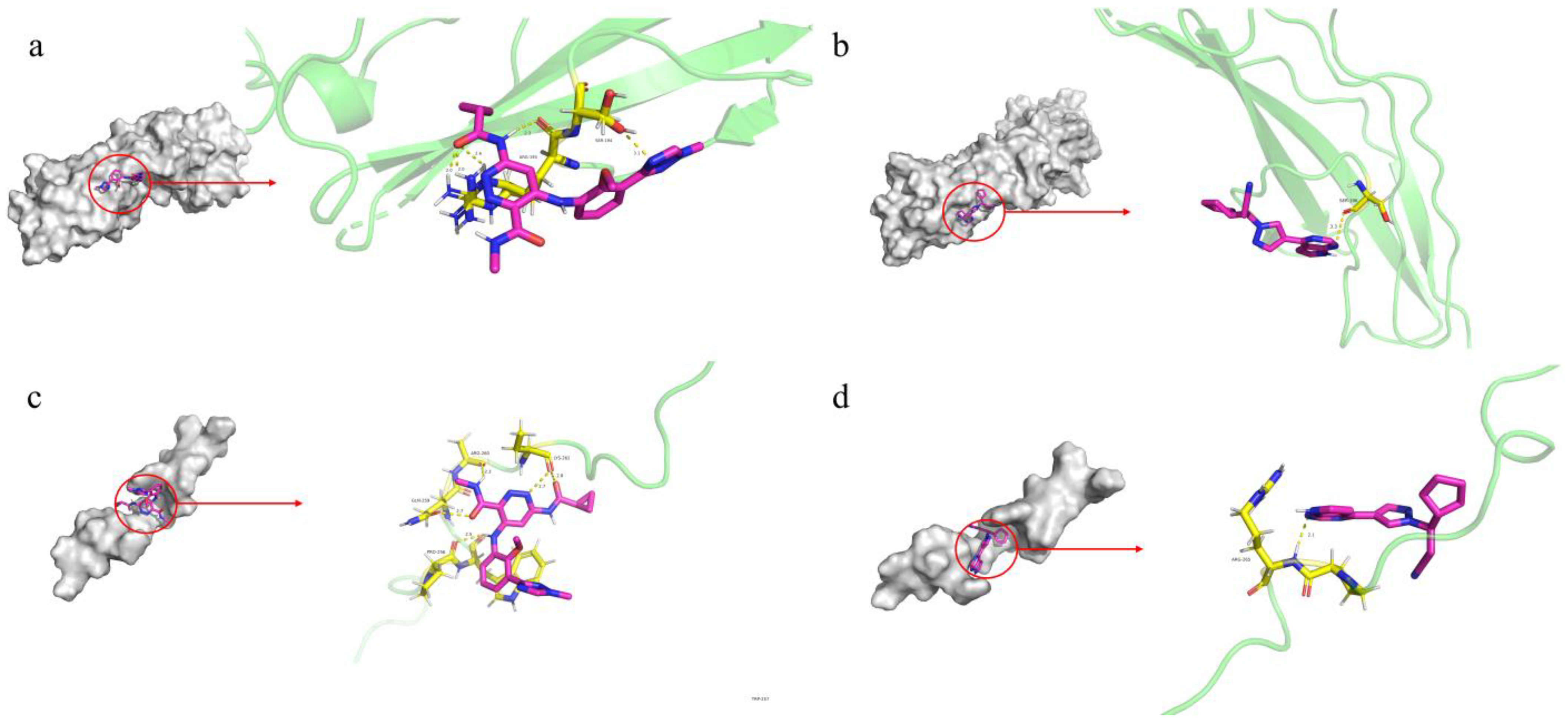
3.5. Molecular Docking Analysis for Druggability Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Griffiths, C.E.; Barker, J.N. Pathogenesis and Clinical Features of Psoriasis. Lancet 2007, 370, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christophers, E. Psoriasis—Epidemiology and Clinical Spectrum. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2001, 26, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, R.; Iskandar, I.Y.K.; Kontopantelis, E.; Augustin, M.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Ashcroft, D.M. National, Regional, and Worldwide Epidemiology of Psoriasis: Systematic Analysis and Modelling Study. BMJ 2020, 369, m1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Han, K.D.; Kim, H.-N.; Park, Y.M.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, Y.-G.; Lee, Y.B. Cancer Risk in 892 089 Patients with Psoriasis in Korea: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Dermatol. 2019, 46, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeberg, A.; Thyssen, J.P.; Gislason, G.H.; Skov, L. Skin Cancer in Patients with Psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 30, 1349–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Li, W.-Q.; Qureshi, A.A.; Han, J. Personal History of Psoriasis and Risk of Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer (NMSC) among Women in the United States: A Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 75, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaengebjerg, S.; Skov, L.; Egeberg, A.; Loft, N.D. Prevalence, Incidence, and Risk of Cancer in Patients with Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. JAMA Dermatol. 2020, 156, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, C.E.M.; Armstrong, A.W.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Barker, J.N.W.N. Psoriasis. Lancet 2021, 397, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoboda, S.A.; Ghamrawi, R.I.; Owusu, D.A.; Feldman, S.R. Treatment Goals in Psoriasis: Which Outcomes Matter Most? Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 21, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, H.; Lin, W.; Lu, L.; Su, J.; Chen, X. Signaling Pathways and Targeted Therapies for Psoriasis. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskandar, I.Y.K.; Warren, R.B.; Lunt, M.; Mason, K.J.; Evans, I.; McElhone, K.; Smith, C.H.; Reynolds, N.J.; Ashcroft, D.M.; Griffiths, C.E.M. Differential Drug Survival of Second-Line Biologic Therapies in Patients with Psoriasis: Observational Cohort Study from the British Association of Dermatologists Biologic Interventions Register (BADBIR). J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, R.B.; Smith, C.H.; Yiu, Z.Z.N.; Ashcroft, D.M.; Barker, J.N.W.N.; Burden, A.D.; Lunt, M.; McElhone, K.; Ormerod, A.D.; Owen, C.M.; et al. Differential Drug Survival of Biologic Therapies for the Treatment of Psoriasis: A Prospective Observational Cohort Study from the British Association of Dermatologists Biologic Interventions Register (BADBIR). J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 2632–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Walker, V.; Haycock, P.C.; Hurle, M.R.; Gutteridge, A.; Erola, P.; Liu, Y.; Luo, S.; et al. Phenome-Wide Mendelian Randomization Mapping the Influence of the Plasma Proteome on Complex Diseases. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, E.; Glymour, M.M.; Holmes, M.V.; Kang, H.; Morrison, J.; Munafò, M.R.; Palmer, T.; Schooling, C.M.; Wallace, C.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Mendelian Randomization. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2022, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reay, W.R.; Cairns, M.J. Advancing the Use of Genome-Wide Association Studies for Drug Repurposing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 658–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, E.A.; Davis, J.W.; Degner, J.F. Are Drug Targets with Genetic Support Twice as Likely to Be Approved? Revised Estimates of the Impact of Genetic Support for Drug Mechanisms on the Probability of Drug Approval. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrivankova, V.W.; Richmond, R.C.; Woolf, B.A.R.; Yarmolinsky, J.; Davies, N.M.; Swanson, S.A.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Timpson, N.J.; Dimou, N.; et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Using Mendelian Randomization: The STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA 2021, 326, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.B.; Chiou, J.; Traylor, M.; Benner, C.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Richardson, T.G.; Surendran, P.; Mahajan, A.; Robins, C.; Vasquez-Grinnell, S.G.; et al. Plasma Proteomic Associations with Genetics and Health in the UK Biobank. Nature 2023, 622, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferkingstad, E.; Sulem, P.; Atlason, B.A.; Sveinbjornsson, G.; Magnusson, M.I.; Styrmisdottir, E.L.; Gunnarsdottir, K.; Helgason, A.; Oddsson, A.; Halldorsson, B.V.; et al. Large-Scale Integration of the Plasma Proteome with Genetics and Disease. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koprulu, M.; Carrasco-Zanini, J.; Wheeler, E.; Lockhart, S.; Kerrison, N.D.; Wareham, N.J.; Pietzner, M.; Langenberg, C. Proteogenomic Links to Human Metabolic Diseases. Nat. Metab. 2023, 5, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurki, M.I.; Karjalainen, J.; Palta, P.; Sipilä, T.P.; Kristiansson, K.; Donner, K.M.; Reeve, M.P.; Laivuori, H.; Aavikko, M.; Kaunisto, M.A.; et al. Author Correction: FinnGen Provides Genetic Insights from a Well-Phenotyped Isolated Population. Nature 2023, 615, E19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karczewski, K.J.; Gupta, R.; Kanai, M.; Lu, W.; Tsuo, K.; Wang, Y.; Walters, R.K.; Turley, P.; Callier, S.; Baya, N.; et al. Pan-UK Biobank GWAS Improves Discovery, Analysis of Genetic Architecture, and Resolution into Ancestry-Enriched Effects. medRxiv 2024, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollis, E.; Mosaku, A.; Abid, A.; Buniello, A.; Cerezo, M.; Gil, L.; Groza, T.; Güneş, O.; Hall, P.; Hayhurst, J.; et al. The NHGRI-EBI GWAS Catalog: Knowledgebase and Deposition Resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D977–D985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glanville, K.P.; Coleman, J.R.I.; O’Reilly, P.F.; Galloway, J.; Lewis, C.M. Investigating Pleiotropy Between Depression and Autoimmune Diseases Using the UK Biobank. Biol. Psychiatry Glob. Open Sci. 2021, 1, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, P.E.; Tsoi, L.C.; Nair, R.P.; Ghosh, M.; Kabra, M.; Shaiq, P.A.; Raja, G.K.; Qamar, R.; Thelma, B.K.; Patrick, M.T.; et al. Transethnic Analysis of Psoriasis Susceptibility in South Asians and Europeans Enhances Fine-Mapping in the MHC and Genomewide. HGG Adv. 2022, 3, 100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey Smith, G.; Hemani, G. Mendelian Randomization: Genetic Anchors for Causal Inference in Epidemiological Studies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, R89–R98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, T.M.; Lawlor, D.A.; Harbord, R.M.; Sheehan, N.A.; Tobias, J.H.; Timpson, N.J.; Smith, G.D.; Sterne, J.A. Using Multiple Genetic Variants as Instrumental Variables for Modifiable Risk Factors. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2012, 21, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, G.; Hung, R.J.; Haycock, P.C.; Aldrich, M.C.; Andrew, A.S.; Arnold, S.M.; Bickeböller, H.; Bojesen, S.E.; Brennan, P.; et al. Causal Relationships between Body Mass Index, Smoking and Lung Cancer: Univariable and Multivariable Mendelian Randomization. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 148, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambartolomei, C.; Vukcevic, D.; Schadt, E.E.; Franke, L.; Hingorani, A.D.; Wallace, C.; Plagnol, V. Bayesian Test for Colocalisation between Pairs of Genetic Association Studies Using Summary Statistics. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Gloudemans, M.J.; Rao, A.S.; Ingelsson, E.; Montgomery, S.B. Abundant Associations with Gene Expression Complicate GWAS Follow-Up. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 768–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovieff, N.; Cotsapas, C.; Lee, P.H.; Purcell, S.M.; Smoller, J.W. Pleiotropy in Complex Traits: Challenges and Strategies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Li, X.; Kunjravia, N.; Rambhia, D.; Cueto, I.; Kim, K.; Chaparala, V.; Ko, Y.; Garcet, S.; et al. Multi-Omics Segregate Different Transcriptomic Impacts of Anti-IL-17A Blockade on Type 17 T-Cells and Regulatory Immune Cells in Psoriasis Skin. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1250504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Stuart, T.; Kowalski, M.H.; Choudhary, S.; Hoffman, P.; Hartman, A.; Srivastava, A.; Molla, G.; Madad, S.; Fernandez-Granda, C.; et al. Dictionary Learning for Integrative, Multimodal and Scalable Single-Cell Analysis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING V11: Protein–Protein Association Networks with Increased Coverage, Supporting Functional Discovery in Genome-Wide Experimental Datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, D.; Gaulton, A.; Bento, A.P.; Chambers, J.; De Veij, M.; Félix, E.; Magariños, M.P.; Mosquera, J.F.; Mutowo, P.; Nowotka, M.; et al. ChEMBL: Towards Direct Deposition of Bioassay Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D930–D940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Guo, A.C.; Lo, E.J.; Marcu, A.; Grant, J.R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Sayeeda, Z.; et al. DrugBank 5.0: A Major Update to the DrugBank Database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1074–D1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Wang, S.; Balius, T.E.; Singh, I.; Levit, A.; Moroz, Y.S.; O’Meara, M.J.; Che, T.; Algaa, E.; Tolmachova, K.; et al. Ultra-Large Library Docking for Discovering New Chemotypes. Nature 2019, 566, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kincaid, V.A.; London, N.; Wangkanont, K.; Wesener, D.A.; Marcus, S.A.; Héroux, A.; Nedyalkova, L.; Talaat, A.M.; Forest, K.T.; Shoichet, B.K.; et al. Virtual Screening for UDP-Galactopyranose Mutase Ligands Identifies a New Class of Antimycobacterial Agents. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 2209–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burley, S.K.; Bhikadiya, C.; Bi, C.; Bittrich, S.; Chao, H.; Chen, L.; Craig, P.A.; Crichlow, G.V.; Dalenberg, K.; Duarte, J.M.; et al. RCSB Protein Data Bank (RCSB.Org): Delivery of Experimentally-Determined PDB Structures alongside One Million Computed Structure Models of Proteins from Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D488–D508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem 2023 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D1373–D1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.R.; Tipney, H.; Painter, J.L.; Shen, J.; Nicoletti, P.; Shen, Y.; Floratos, A.; Sham, P.C.; Li, M.J.; Wang, J.; et al. The Support of Human Genetic Evidence for Approved Drug Indications. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazear, H.M.; Schoggins, J.W.; Diamond, M.S. Shared and Distinct Functions of Type I and Type III Interferons. Immunity 2019, 50, 907–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotenko, S.V.; Gallagher, G.; Baurin, V.V.; Lewis-Antes, A.; Shen, M.; Shah, N.K.; Langer, J.A.; Sheikh, F.; Dickensheets, H.; Donnelly, R.P. IFN-Lambdas Mediate Antiviral Protection through a Distinct Class II Cytokine Receptor Complex. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henden, A.S.; Koyama, M.; Robb, R.J.; Forero, A.; Kuns, R.D.; Chang, K.; Ensbey, K.S.; Varelias, A.; Kazakoff, S.H.; Waddell, N.; et al. IFN-λ Therapy Prevents Severe Gastrointestinal Graft-versus-Host Disease. Blood 2021, 138, 722–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachiotis, S.; Andreakos, E. Lambda Interferons in Immunity and Autoimmunity. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 104, 102319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson Regnault, M.; Shourick, J.; Jendoubi, F.; Tauber, M.; Paul, C. Time to Relapse After Discontinuing Systemic Treatment for Psoriasis: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2022, 23, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotenko, S.V.; Durbin, J.E. Contribution of Type III Interferons to Antiviral Immunity: Location, Location, Location. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 7295–7303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazear, H.M.; Nice, T.J.; Diamond, M.S. Interferon-λ: Immune Functions at Barrier Surfaces and Beyond. Immunity 2015, 43, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, B.; Çakmak Genç, G.; Karakaş Çelik, S.; Solak Tekin, N.; Can, M.; Dursun, A. Association between Psoriasis Disease and IFN-λ Gene Polymorphisms. Immunol. Investig. 2022, 51, 1772–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, S.D.; Schwartz, O.M.; Brown, M.R.; Leto, T.L.; Holland, S.M. Characterization of a Dipeptide Motif Regulating IFN-Gamma Receptor 2 Plasma Membrane Accumulation and IFN-Gamma Responsiveness. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 3991–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcock, D.M. Neuroinflammation in the Aging Down Syndrome Brain; Lessons from Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Gerontol. Geriatr. Res. 2012, 2012, 170276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque-Martin, R.; Angell, D.C.; Kalxdorf, M.; Bernard, S.; Thompson, W.; Eberl, H.C.; Ashby, C.; Freudenberg, J.; Sharp, C.; Van den Bossche, J.; et al. IFN-γ Drives Human Monocyte Differentiation into Highly Proinflammatory Macrophages That Resemble a Phenotype Relevant to Psoriasis. J. Immunol. 2021, 207, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Tao, L.; Peng, K.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, K.; Luan, J.; Pan, J.; Su, X.; Sun, J.; et al. Up-Regulation of BTN3A1 on CD14+ Cells Promotes Vγ9Vδ2 T Cell Activation in Psoriasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2117523119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhao, M.; Ma, X.; Li, D.; Kong, J.; Yang, F. The Role and Application of Three IFN-Related Reactions in Psoriasis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnell, A.; Huang, L.; Singer, M.; Singaraju, A.; Barilla, R.M.; Regan, B.M.L.; Bollhagen, A.; Thakore, P.I.; Dionne, D.; Delorey, T.M.; et al. Stem-like Intestinal Th17 Cells Give Rise to Pathogenic Effector T Cells during Autoimmunity. Cell 2021, 184, 6281–6298.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manivasagam, S.; Klein, R.S. Type III Interferons: Emerging Roles in Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 764062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.-X.; Zheng, D.-S.; Chen, X.-L.; Bai, Z.-P.; Zhang, J.; Deng, W.; Huang, X.-F. An Integrated Multi-Omics Analysis Identifies Protein Biomarkers and Potential Drug Targets for Psoriatic Arthritis. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deprince, A.; Hennuyer, N.; Kooijman, S.; Pronk, A.C.M.; Baugé, E.; Lienard, V.; Verrijken, A.; Dirinck, E.; Vonghia, L.; Woitrain, E.; et al. Apolipoprotein F Is Reduced in Humans with Steatosis and Controls Plasma Triglyceride-rich Lipoprotein Metabolism. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Li, J.; Du, H.; Xia, J. Causal Relationship between PCSK9 Inhibitor and Autoimmune Diseases: A Drug Target Mendelian Randomization Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, M.; Tan, J.; Chen, A.; Guo, J. Plasma Proteins and Inflammatory Dermatoses: Proteome-Wide Mendelian Randomization and Colocalization Analyses. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2024, 316, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxe, J.P.; Chen, M.; Zhao, H.; Lin, H. Tdrkh Is Essential for Spermatogenesis and Participates in Primary piRNA Biogenesis in the Germline. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 1869–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Wu, B.; Chiang, H.-C.; Deng, H.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, W.; Liu, J.; Rozeboom, A.M.; Harris, B.T.; Blommaert, E.; et al. Tumour DDR1 Promotes Collagen Fibre Alignment to Instigate Immune Exclusion. Nature 2021, 599, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynford-Thomas, R.; Jacob, A.; Tomassini, V. Neurological Update: MOG Antibody Disease. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakker, P.; Leach, M.W.; Kuang, W.; Benoit, S.E.; Leonard, J.P.; Marusic, S. IL-23 Is Critical in the Induction but Not in the Effector Phase of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 2589–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Xie, J.; Zhao, S.; Du, R.; Luo, X.; He, H.; Jiang, S.; Hao, N.; Chen, C.; Guo, C.; et al. ICAM3 Mediates Inflammatory Signaling to Promote Cancer Cell Stemness. Cancer Lett. 2018, 422, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, A.T.; Tithof, J.; Izhiman, Y.; Masters, E.A.; McCloskey, M.C.; Gaborski, T.R.; Kelley, D.H.; Pietropaoli, A.P.; Waugh, R.E.; McGrath, J.L. Endothelial Cell Apicobasal Polarity Coordinates Distinct Responses to Luminally versus Abluminally Delivered TNF-α in a Microvascular Mimetic. Integr. Biol. 2020, 12, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kim, J.; Park, A.; Koh, M.; Shin, W.; Park, G.; Lee, T.A.; Kim, H.J.; Han, H.; Kim, Y.; et al. TRIM40 Is a Pathogenic Driver of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Subverting Intestinal Barrier Integrity. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

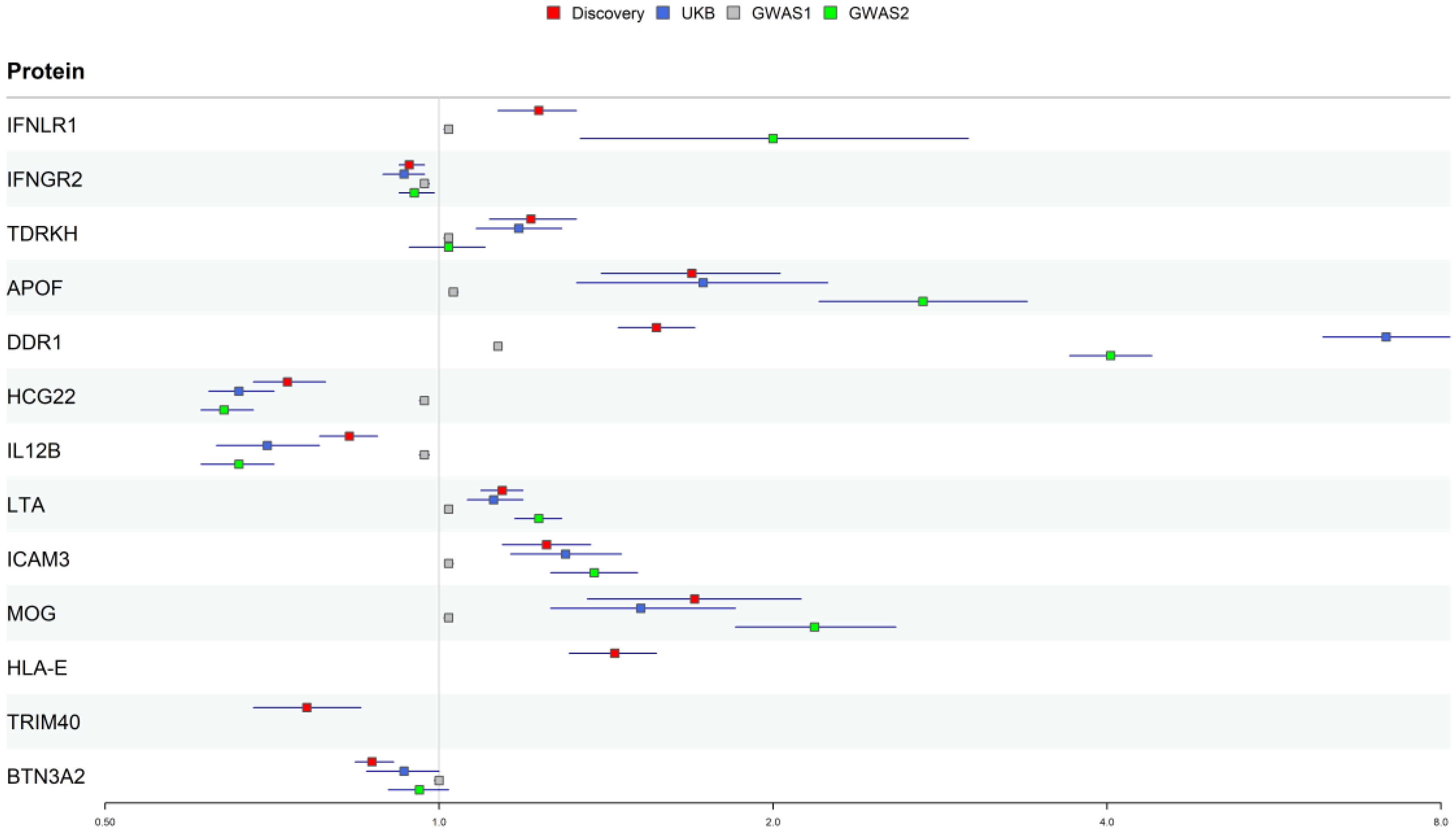

| Protein | UniProt | Pdiscovery | Preplication a | Preverse | Colocalization b | Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IFNLR1 | Q8IU57 | 1.17e−06 | 4.49e−04 | 0.221 | 0.999/0.998 | Tier1 |
| IFNGR2 | P38484 | 7.54e−06 | 4.77e−04 | 0.640 | 0.962/0.929 | Tier1 |
| TDRKH | Q9Y2W6 | 1.94e−05 | 7.11e−06 | 0.349 | 0.915/0.846 | Tier1 |
| APOF | Q13790 | 2.56e−08 | 6.20e−20 | 0.864 | 0.911/0.836 | Tier1 |
| DDR1 | Q08345 | 7.73e−29 | 2.05e−228 | 0.082 | 0.000/0.000 | Tier2 |
| HCG22 | E2RYF7 | 1.19e−16 | 2.51e−56 | 0.117 | 0.000/0.000 | Tier2 |
| IL12B | P29460 | 5.56e−11 | 1.20e−23 | 0.729 | 0.000/0.000 | Tier2 |
| LTA | P01374 | 2.54e−09 | 2.81e−15 | 0.063 | 0.000/0.000 | Tier2 |
| ICAM3 | P32942 | 2.54e−06 | 2.56e−12 | 0.895 | 0.034/0.017 | Tier2 |
| MOG | Q16653 | 3.14e−06 | 2.74e−20 | 0.038 | 0.000/0.000 | Tier2 |
| HLA-E | P13747 | 1.14e−14 | NA | 0.354 | 0.000/0.000 | Tier3 |
| TRIM40 | Q6P9F5 | 1.87e−06 | NA | 0.209 | 0.000/0.000 | Tier3 |
| BTN3A2 | P78410 | 2.46e−09 | 5.09e−02 | 0.044 | 0.000/0.000 | Tier4 |
| Discovery | UKB | GWAS1 | GWAS2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | OR (95%CI) | p | OR (95%CI) | p | OR (95%CI) | p | OR (95%CI) | p |
| IFNLR1 | 1.23 (1.13–1.33) | 1.17e−06 | NA | NA | 1.01 (1.01–1.02) | 4.49e−04 | 2 (1.34–3) | 7.25e−04 |
| IFNGR2 | 0.94 (0.92–0.97) | 7.54e−06 | 0.93 (0.89–0.97) | 4.77e−04 | 1 (0.99–1) | 8.72e−04 | 0.95 (0.92–0.99) | 4.88e−03 |
| TDRKH | 1.21 (1.11–1.33) | 1.94e−05 | 1.18 (1.08–1.29) | 1.51e−04 | 1.02 (1.01–1.02) | 7.11e−06 | 1.02 (0.94–1.1) | 6.86e−01 |
| APOF | 1.69 (1.4–2.03) | 2.56e−08 | 1.73 (1.33–2.24) | 4.19e−05 | 1.03 (1.02–1.04) | 2.80e−06 | 2.73 (2.2–3.39) | 6.20e−20 |
| DDR1 | 1.57 (1.45–1.7) | 7.73e−29 | 7.14 (6.26–8.15) | 3.11e−186 | 1.13 (1.12–1.14) | 2.04e−199 | 4.03 (3.7–4.39) | 2.05e−228 |
| HCG22 | 0.73 (0.68–0.79) | 1.19e−16 | 0.66 (0.62–0.71) | 1.12e−30 | 0.97 (0.96–0.97) | 1.34e−30 | 0.64 (0.61–0.68) | 2.51e−56 |
| IL12B | 0.83 (0.78–0.88) | 5.56e−11 | 0.7 (0.63–0.78) | 3.69e−11 | 0.97 (0.96–0.98) | 1.62e−12 | 0.66 (0.61–0.71) | 1.20e−23 |
| LTA | 1.14 (1.09–1.19) | 2.54e−09 | 1.12 (1.06–1.19) | 1.51e−04 | 1 (1–1.01) | 2.34e−03 | 1.23 (1.17–1.29) | 2.81e−15 |
| ICAM3 | 1.25 (1.14–1.37) | 2.54e−06 | 1.3 (1.16–1.46) | 1.21e−05 | 1.02 (1.02–1.03) | 1.83e−07 | 1.38 (1.26–1.51) | 2.56e−12 |
| MOG | 1.7 (1.36–2.12) | 3.14e−06 | 1.52 (1.26–1.85) | 1.69e−05 | 1.02 (1.01–1.02) | 6.67e−06 | 2.18 (1.85–2.58) | 2.74e−20 |
| HLA-E | 1.44 (1.31–1.57) | 1.14e−14 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| TRIM40 | 0.76 (0.68–0.85) | 1.87e−06 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| BTN3A2 | 0.87 (0.84–0.91) | 2.46e−09 | 0.93 (0.86–1) | 5.09e−02 | 1 (0.99–1) | 5.74e−01 | 0.96 (0.9–1.02) | 2.28e−01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Qin, R.; He, J.; Zhang, X.; Ma, C.; Li, S.; Fan, L.; Wang, L.; Cao, L. Integrative Analysis of Plasma Proteomics and Transcriptomics Reveals Potential Therapeutic Targets for Psoriasis. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061380
Wang H, Wang C, Qin R, He J, Zhang X, Ma C, Li S, Fan L, Wang L, Cao L. Integrative Analysis of Plasma Proteomics and Transcriptomics Reveals Potential Therapeutic Targets for Psoriasis. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(6):1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061380
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hesong, Chenguang Wang, Ruihao Qin, Jia He, Xuan Zhang, Chenjing Ma, Shi Li, Lijun Fan, Liuying Wang, and Lei Cao. 2025. "Integrative Analysis of Plasma Proteomics and Transcriptomics Reveals Potential Therapeutic Targets for Psoriasis" Biomedicines 13, no. 6: 1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061380
APA StyleWang, H., Wang, C., Qin, R., He, J., Zhang, X., Ma, C., Li, S., Fan, L., Wang, L., & Cao, L. (2025). Integrative Analysis of Plasma Proteomics and Transcriptomics Reveals Potential Therapeutic Targets for Psoriasis. Biomedicines, 13(6), 1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061380






