A CECT-Based Radiomics Nomogram Predicts the Overall Survival of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Surgical Resection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Information
2.2. Follow-Up
2.3. Screening of Clinical Variables
2.4. CT Scan
2.5. Radiomics Process
2.5.1. Image Preprocessing, Segmentation, and Radiomic Feature Extraction
2.5.2. Consistency Assessment
2.5.3. Feature Screening and Radscore Construction
2.6. Model Development and Evaluation
2.7. Statistical Tools and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Information
3.2. Screening of Clinical Indicators
3.3. Radiomic Feature Screening and Radscore Construction
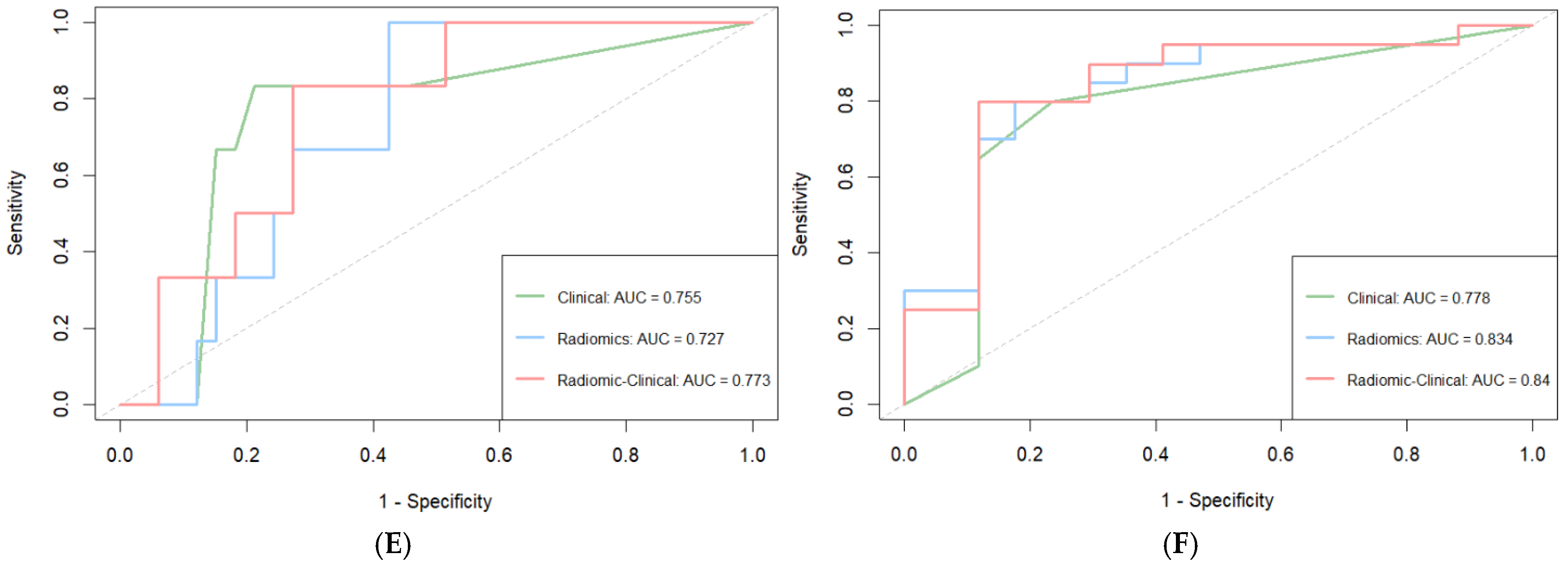
3.4. Model Construction and Evaluation
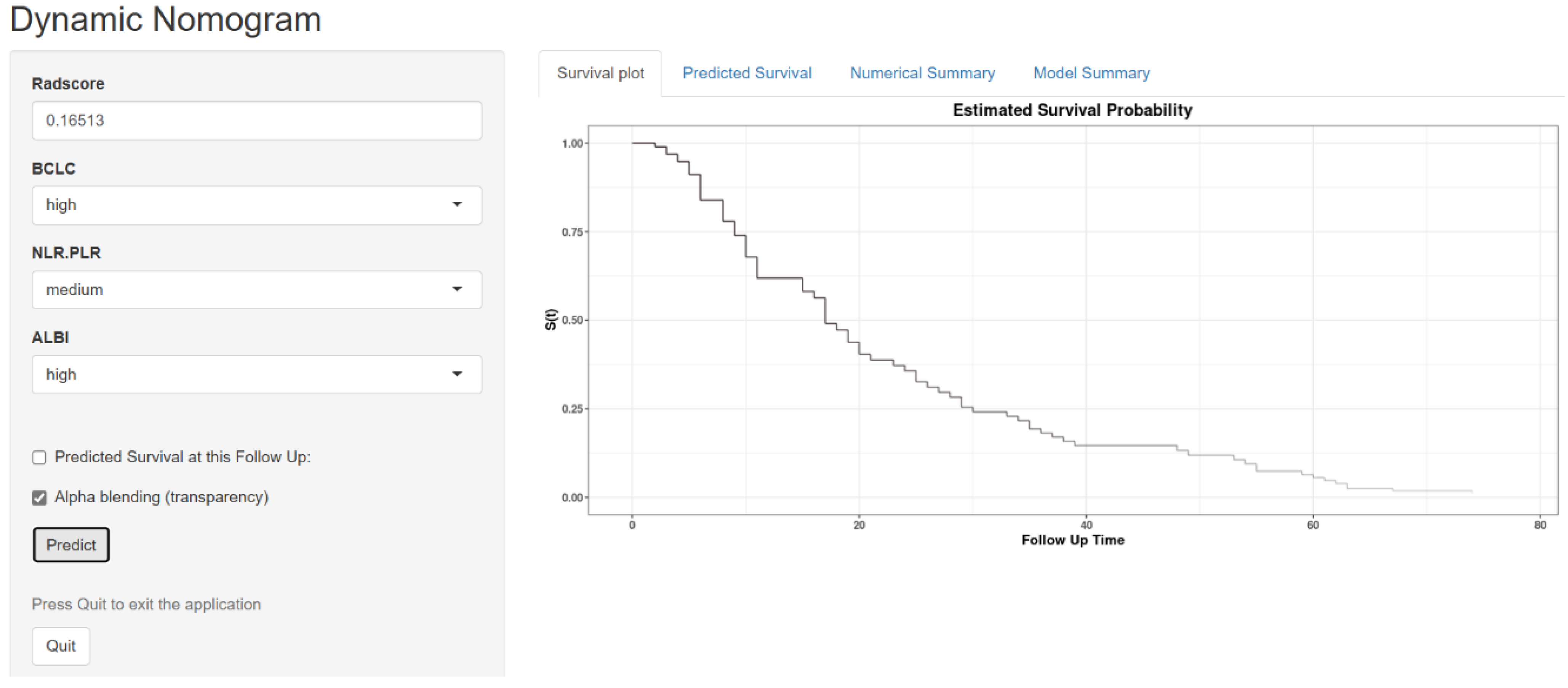
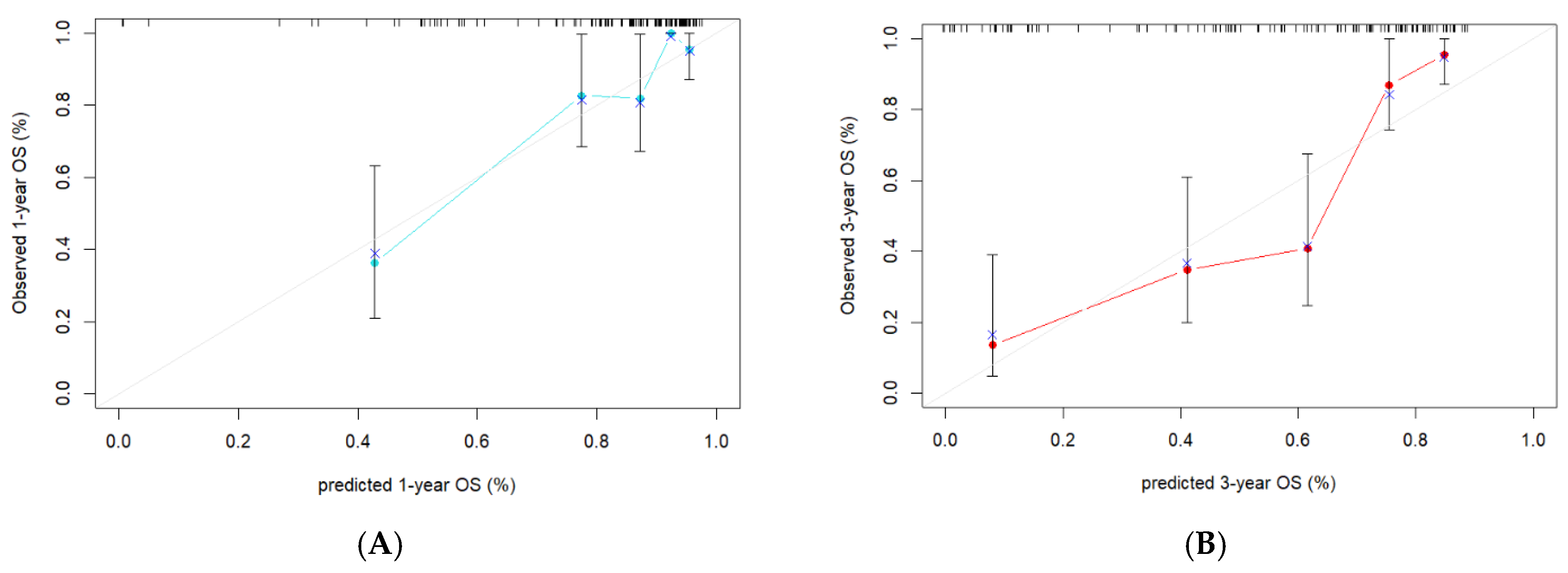
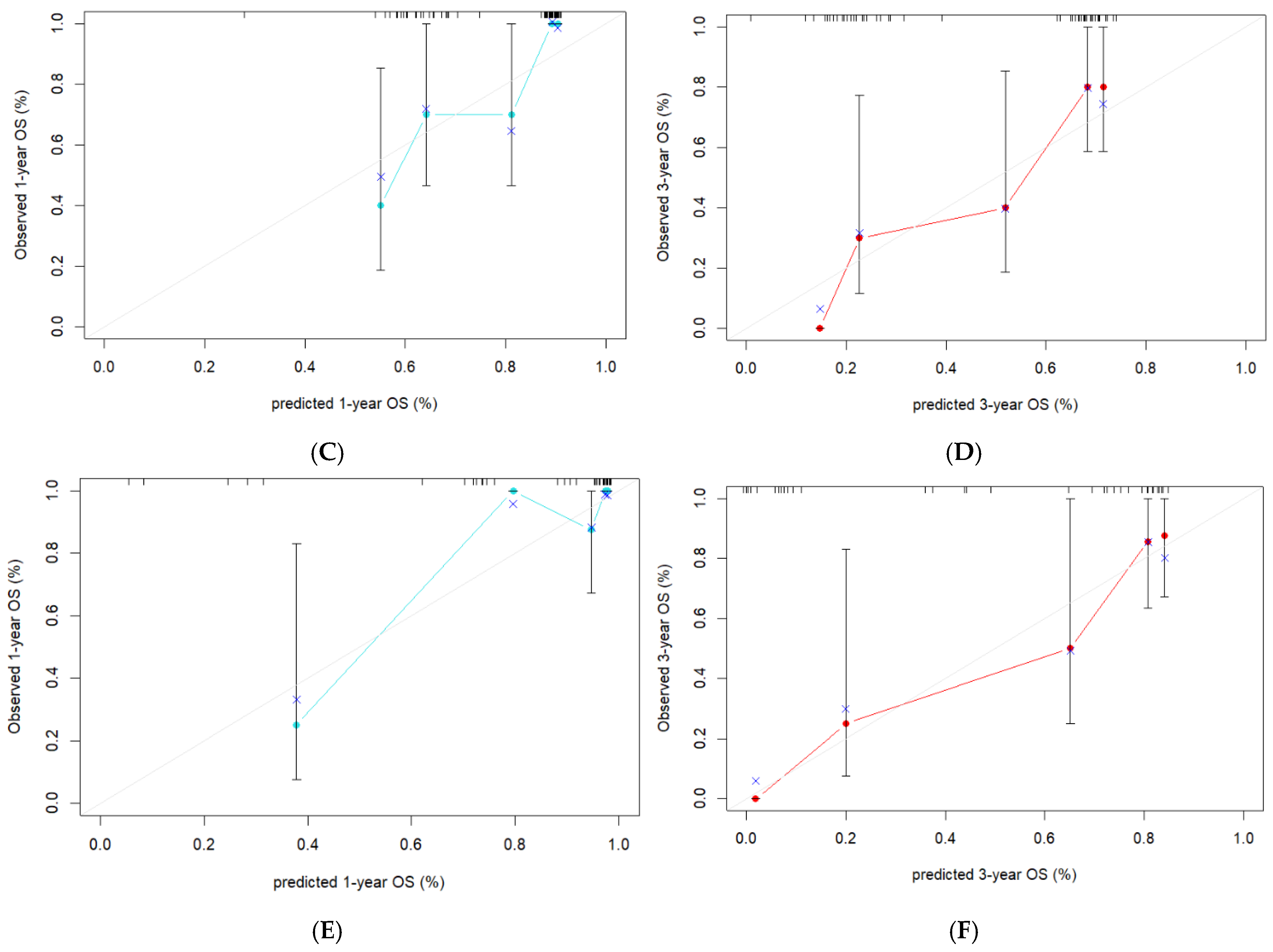
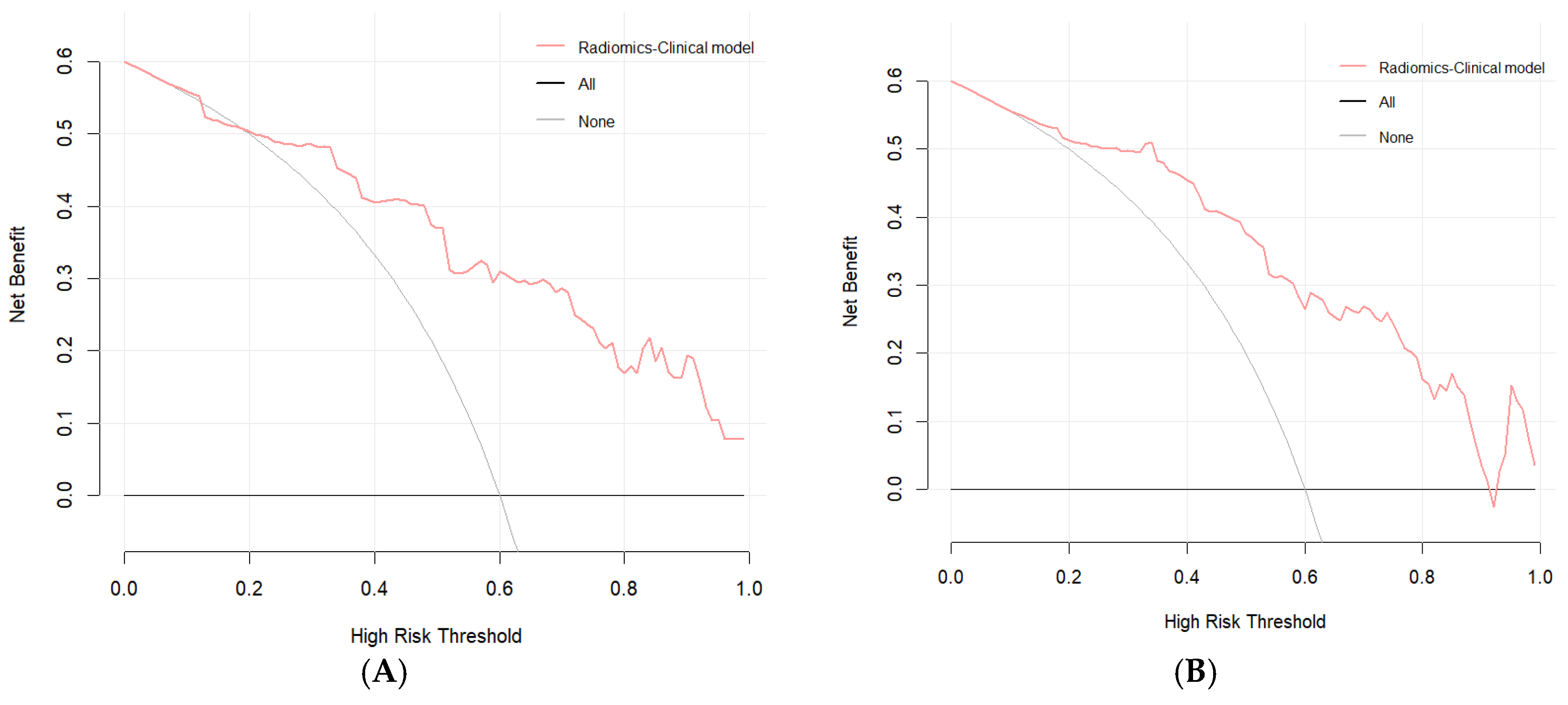
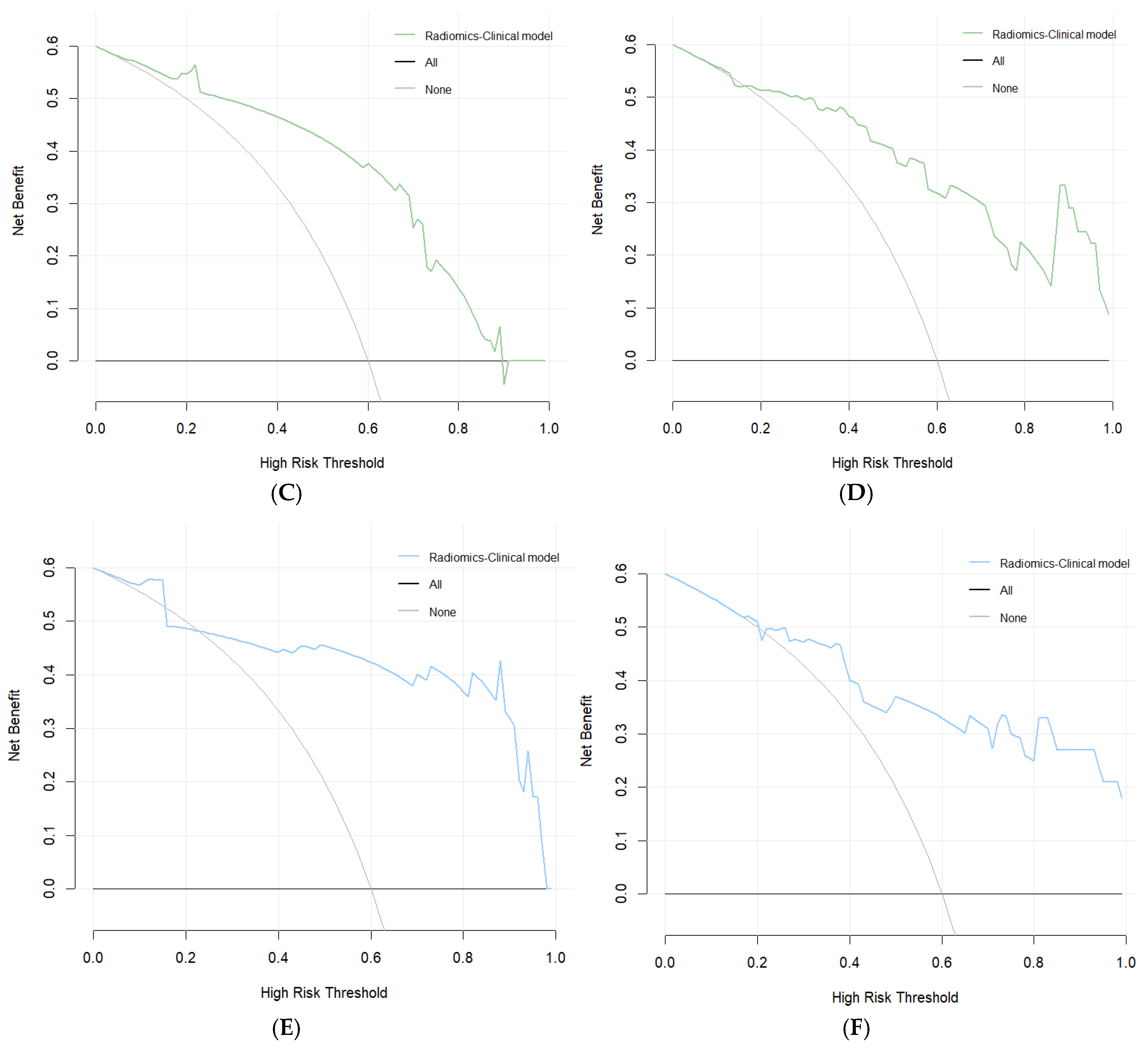
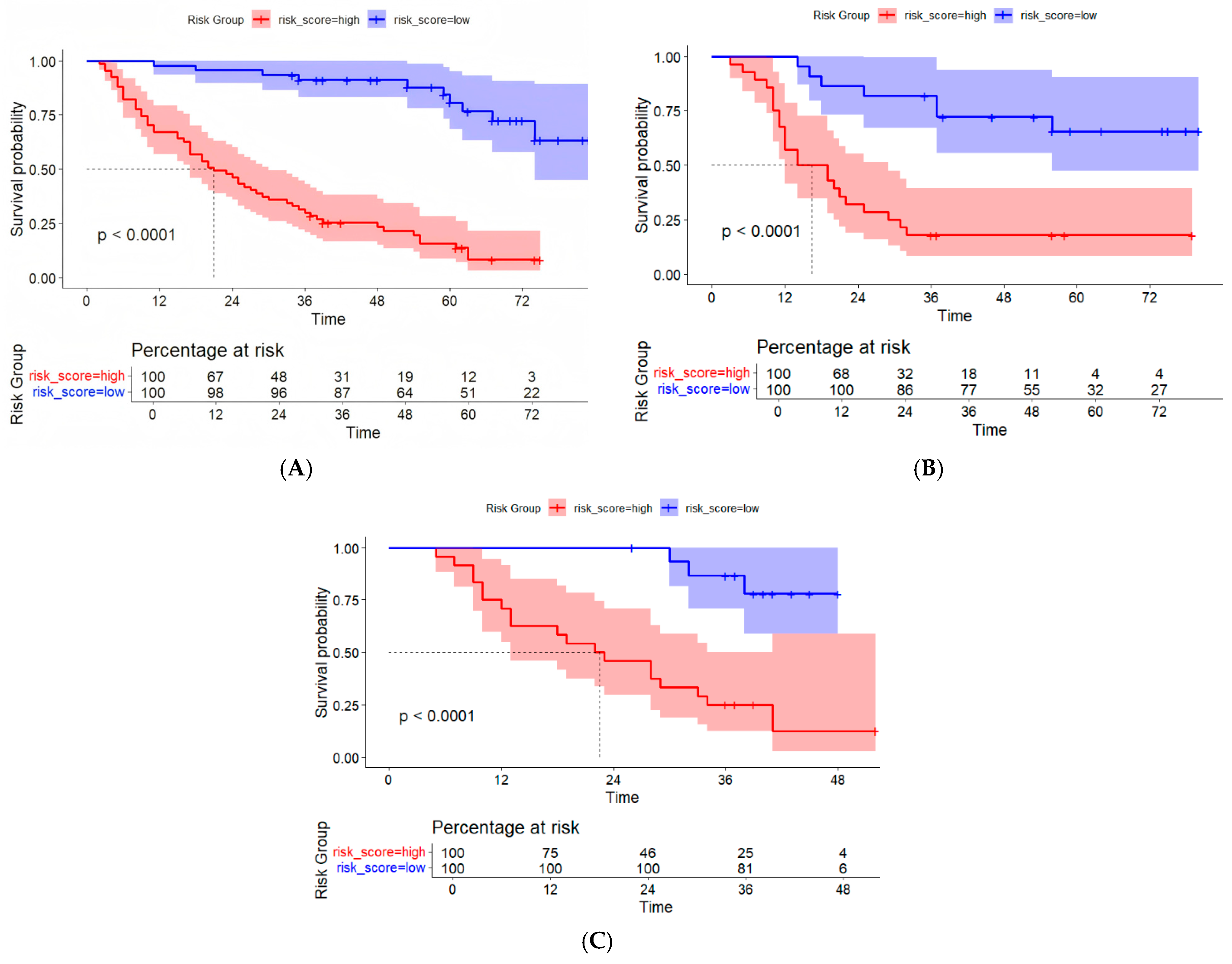
3.5. Evaluation of the Consistency, Clinical Utility, and Risk Stratification of the Combined Model
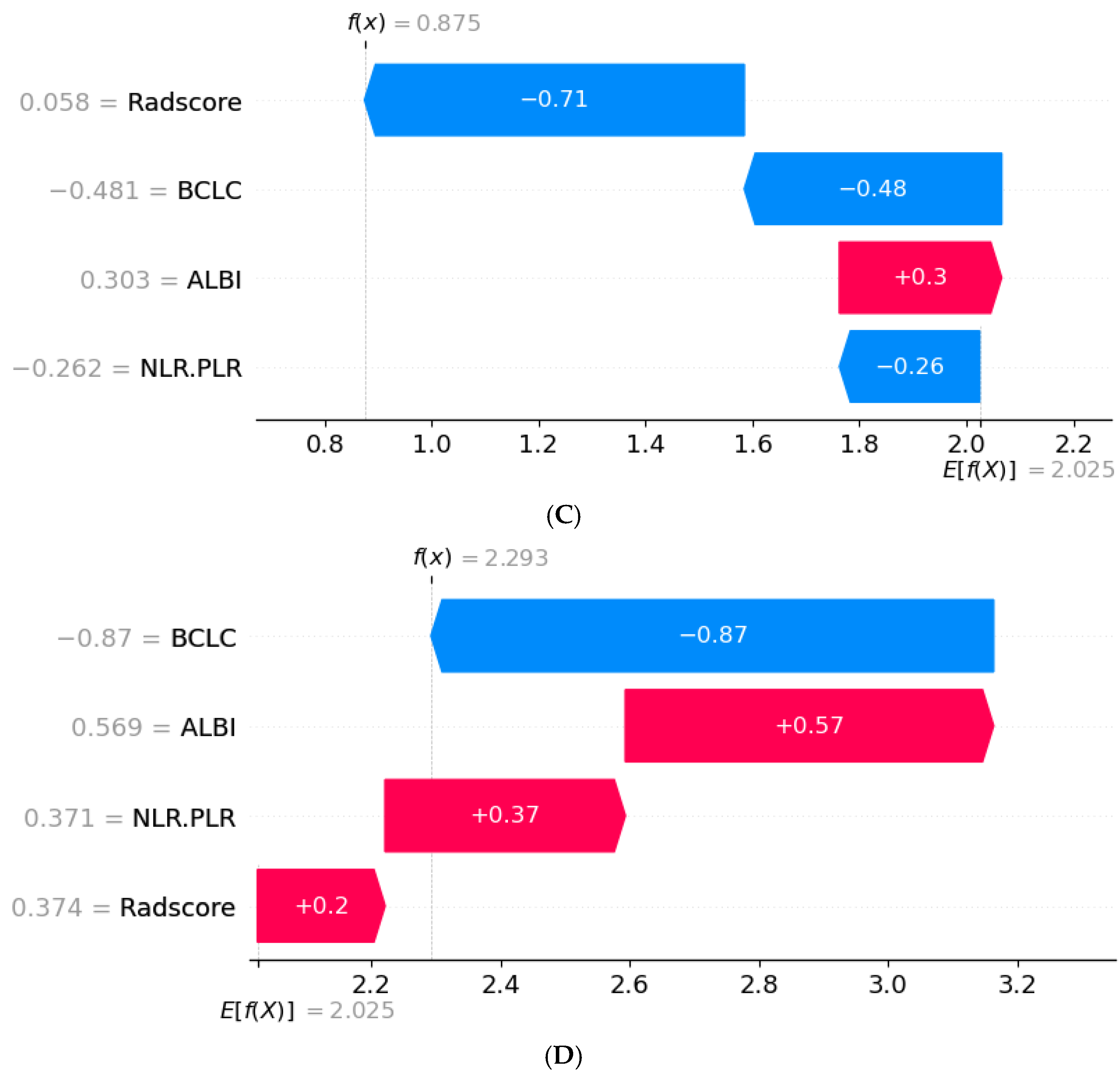
3.6. SHAP Interpretability Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singal, A.G.; Kanwal, F.; Llovet, J.M. Global trends in hepatocellular carcinoma epidemiology: Implications for screening, prevention and therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 864–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Liang, R.; Lu, C.; Lu, L.; Li, S.; Tang, M.; Huang, X.; Huang, S.; Mai, R.; Gao, X.; et al. A Case of Curative Treatment with Apatinib and Camrelizumab Following Liver Resection for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, Z.J.; Tsilimigras, D.I.; Ruff, S.M.; Mohseni, A.; Kamel, I.R.; Cloyd, J.M.; Pawlik, T.M. Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review. JAMA Surg. 2023, 158, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reveron-Thornton, R.F.; Teng, M.; Lee, E.Y.; Tran, A.; Vajanaphanich, S.; Tan, E.X.; Huang, D.Q. Global and regional long-term survival following resection for HCC in the recent decade: A meta-analysis of 110 studies. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 1813–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.W.; Ahn, K.S.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, T.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Kang, K.J. Liver Resection Versus Local Ablation Therapies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Within the Milan Criteria: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Surg. 2021, 273, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.-Q.; Ma, C.; Cao, W.-Z.; Ning, Z.; Tan, G. Prognostic Significance of NLR, PLR, LMR and Tumor Infiltrating T Lymphocytes in Patients Undergoing Surgical Resection for Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 908907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, M.C.; Mihai, R.; Khan, S. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR) as Possible Prognostic Markers for Patients Undergoing Resection of Adrenocortical Carcinoma. World J. Surg. 2021, 45, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Yang, M.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Dai, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J. Prognostic value of inflammation-based indices in patients with resected hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, H.L.; Liu, Q.P.; Sun, S.-W.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, F.-P.; Yang, G.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Liu, X.-S. Radiomic analysis of contrast-enhanced CT predicts microvascular invasion and outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.W.; Zhu, F.P.; Xu, Q.; Wang, K.; Wu, M.-Y.; Tang, W.-W.; Li, X.-C.; Wang, X.-H. Radiomic Features at Contrast-enhanced CT Predict Recurrence in Early Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multi-Institutional Study. Radiology 2020, 294, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, G.X.; Xu, Z.L.; Li, Y.H.; Lu, J.-L.; Bu, X.-Y.; Wei, M.-T.; Jia, W.-D. Computed tomography-based radiomics to predict early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma posthepatectomy in patients background on cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 2128–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahuddin, Z.; Woodruff, H.C.; Chatterjee, A.; Lambin, P. Transparency of deep neural networks for medical image analysis: A review of interpretability methods. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 140, 105111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Fan, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Song, X. Discovering Key Sub-Trajectories to Explain Traffic Prediction. Sensors 2022, 23, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuzinadah, N.; Kumar, P.S.; Alarfaj, A.A.; Alabdulqader, E.A.; Umer, M.; Kim, T.-H.; Alsubai, S.; Ashraf, I. Improved Prediction of Ovarian Cancer Using Ensemble Classifier and Shaply Explainable AI. Cancers 2023, 15, 5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Ding, F.; Chen, K.; Liang, Z.; Han, P.; Wang, L.; Cui, F.; Zhu, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, X.; et al. CT-based radiomics nomogram to predict proliferative hepatocellular carcinoma and explore the tumor microenvironment. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, Q.; Duan, J.; Zhou, W.; Yu, X.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Rong, P. CT Radiomics to Predict Macrotrabecular-Massive Subtype and Immune Status in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Radiology 2023, 307, e221291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Guo, F.; Cao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Dou, J.; Zeng, Q. Correlation Between NLR Combined with PLR Score and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Liver Transplantation. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2024, 17, 2445–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhang, P.; Mao, Q.; Shi, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X. Multisequence MRI-Based Radiomic Features Combined with Inflammatory Indices for Predicting the Overall Survival of HCC Patients After TACE. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2024, 11, 2049–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.Z.; Zhao, B.G.; Huang, X.H.; Xu, T.-F.; Chen, Z.-J.; Wei, Q.-F.; Liu, X.-Y.; Guo, Y.-Q.; Yuan, S.-G.; Liao, W.-J. Preoperative contrast-enhanced computed tomography-based radiomics model for overall survival prediction in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 4376–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, F.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, C.; Lin, Q.; Al Mamun, A.; Pan, J.; Shi, S.; Tu, C.; Shao, C. MRI Radiomics Combined with Clinicopathological Factors for Predicting 3-Year Overall Survival of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Hepatectomy. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2024, 11, 1445–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Hu, B.; Zhu, C.; Xu, W.; Ge, Y.; Hao, X.; Dong, B.; Chen, X.; Dong, Q.; Zhou, X. A Novel Multimodal Radiomics Model for Predicting Prognosis of Resected Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 745258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Y.; Sun, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, X.; Luo, X.; Tan, W.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, C.; et al. Pretreatment CT-based machine learning radiomics model predicts response in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated with lenvatinib plus PD-1 inhibitors and interventional therapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e008953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, H.H.; Yang, L.; Sheng, R.F.; Yu, Y.L.; Wu, D.J.; Rao, S.X.; Zeng, M.S. Multiscale and multiparametric radiomics of gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MRI predicts microvascular invasion and outcome in patients with solitary hepatocellular carcinoma </= 5 cm. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 4824–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiryu, S.; Akai, H.; Nojima, M.; Hasegawa, K.; Shinkawa, H.; Kokudo, N.; Ohtomo, K. Impact of hepatocellular carcinoma heterogeneity on computed tomography as a prognostic indicator. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Lv, Y.; Hu, X.; Luo, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, H.; Hai, Y. Study on the changes of CT texture parameters before and after HCC treatment in the efficacy evaluation and survival predication of patients with HCC. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 957737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Y.; Han, L.; Zhang, L. Radiomics Based on Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Preoperative Differentiation of Combined Hepatocellular-Cholangiocarcinoma from Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multi-Center Study. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2023, 10, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Jiang, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cao, L.; Duan, T.; Ye, Z.; Yao, S.; Pan, X.; et al. Gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI radiomics signature: Prediction of clinical outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical resection. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinato, D.J.; Sharma, R.; Allara, E.; Yen, C.; Arizumi, T.; Kubota, K.; Bettinger, D.; Jang, J.W.; Smirne, C.; Kim, Y.W.; et al. The ALBI grade provides objective hepatic reserve estimation across each BCLC stage of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Wang, Q.; Han, D.; Li, J.; Nie, Y.; Guo, D.; Yang, L.; Tao, K.; Zhang, X.; Dou, K. Prognostic value of preoperative inflammatory markers in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who underwent curative resection. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisani, F.; Vitale, A.; Kudo, M.; Kulik, L.; Park, J.-W.; Pinato, D.J.; Cillo, U. Merits and boundaries of the BCLC staging and treatment algorithm: Learning from the past to improve the future with a novel proposal. J. Hepatol. 2024, 80, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Deng, K.; Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Luo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Geng, Z.; Xie, C. Nomograms for Predicting Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence and Overall Postoperative Patient Survival. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 843589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.J.; Berhane, S.; Kagebayashi, C.; Satomura, S.; Teng, M.; Reeves, H.L.; O’Beirne, J.; Fox, R.; Skowronska, A.; Palmer, D.; et al. Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A new evidence-based approach-the ALBI grade. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, M.; Yang, Z.; Tan, K.; Zheng, D.; Du, X.; Liu, L. Comparison between Child–Pugh score and Albumin-Bilirubin grade in the prognosis of patients with HCC after liver resection using time-dependent ROC. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aida, T.; Haruki, K.; Akaoka, M.; Furukawa, K.; Onda, S.; Shirai, Y.; Shiozaki, H.; Takahashi, K.; Oikawa, T.; Ikegami, T. A novel combined C-reactive protein-albumin ratio and modified albumin-bilirubin score can predict long-term outcomes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatic resection. Ann. Gastroenterol. Surg. 2024, 8, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Yu, X.; Shan, Y.; Fan, R.; Wu, S.; Lu, C. Albumin-Bilirubin (ALBI) and Monocyte to Lymphocyte Ratio (MLR)-Based Nomogram Model to Predict Tumor Recurrence of AFP-Negative Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2021, 8, 1355–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.R.; Hung, C.H.; Chen, C.H.; Lin, C.-C.; Wang, C.-C.; Liu, Y.-W.; Wu, Y.-J.; Yong, C.-C.; Chen, K.-D.; Tsai, Y.-C.; et al. Ability of the postoperative ALBI grade to predict the outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative surgery. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7290. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Wei, S.; Guo, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, Y.; Chen, X.; Lu, M.; Zheng, F.; Zheng, C. Correlation between preoperative peripheral blood NLR, PLR, LMR and prognosis of patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Fu, M.; Yu, L.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Sun, H. Value of markers of systemic inflammation for the prediction of postoperative progression in patients with pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1293842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenpei, G.; Yuan, L.; Liangbo, L.; Jingjun, M.; Bo, W.; Zhiqiang, N.; Yijie, N.; Lixin, L. Predictive value of preoperative inflammatory indices for postoperative early recurrence of hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1142168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Fu, F.; Jiang, H.; Wu, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wei, H.; Yang, T.; Wang, M.; Song, B. Development and validation of the OSASH score to predict overall survival of hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical resection: A dual-institutional study. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 7631–7645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, R.; Zheng, Z.; Deng, M.; Mei, J.; Lin, Y. Assessment of Tumor Burden Score as a Feasible and Reliable Tool for Prognosis Prediction for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Undergoing Hepatectomy: A Multicenter, Retrospective Study. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2025, 12, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polan, D.F.; Brady, S.L.; Kaufman, R.A. Tissue segmentation of computed tomography images using a Random Forest algorithm: A feasibility study. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, 6553–6569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilet-Martos, E.; Vila-Francés, J.; Bagan, J.V.; Vives-Gilabert, Y. Automated classification of oral cancer lesions: Vision transformers vs. radiomics. Comput. Biol. Med. 2025, 189, 109913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
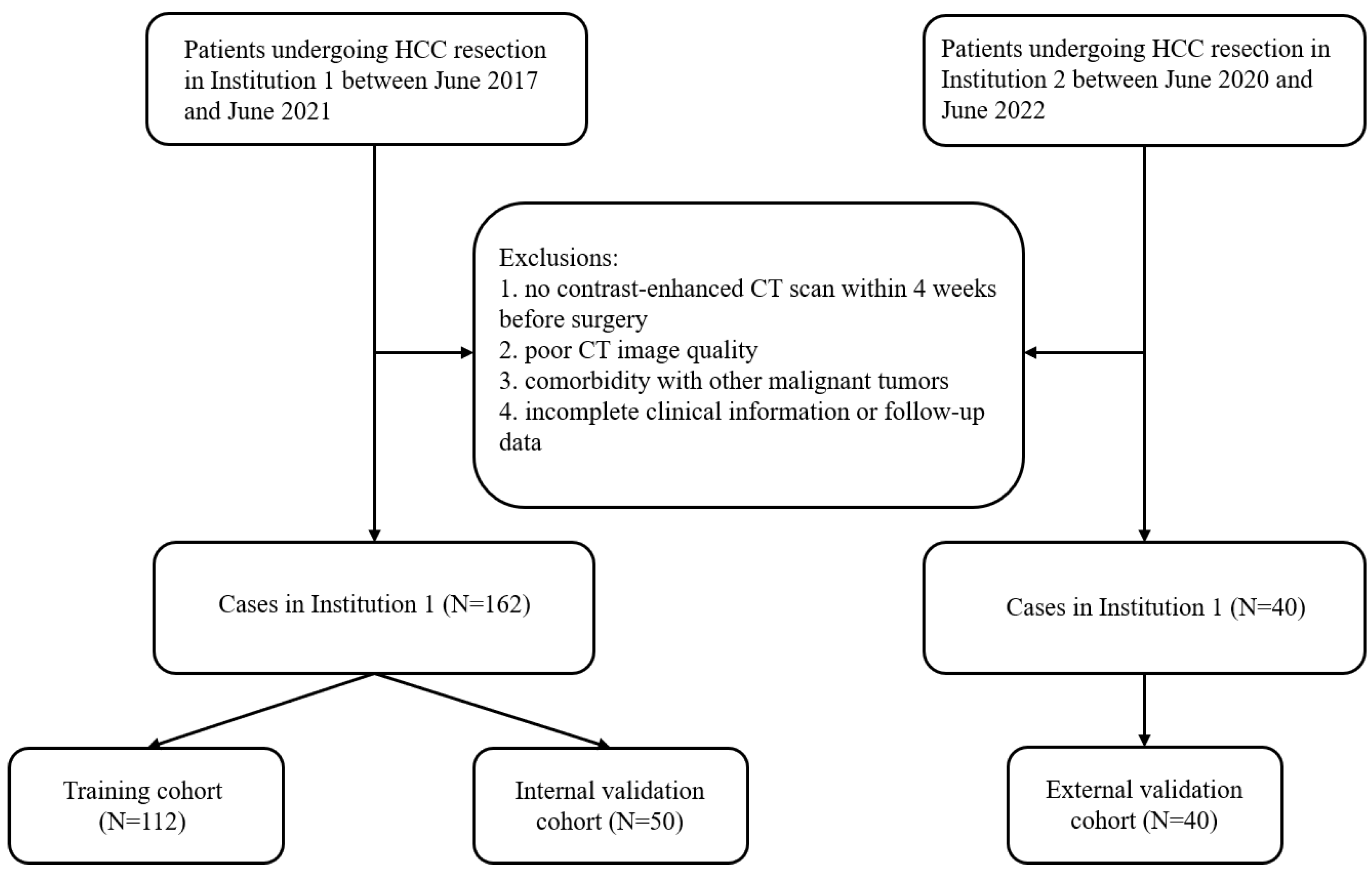
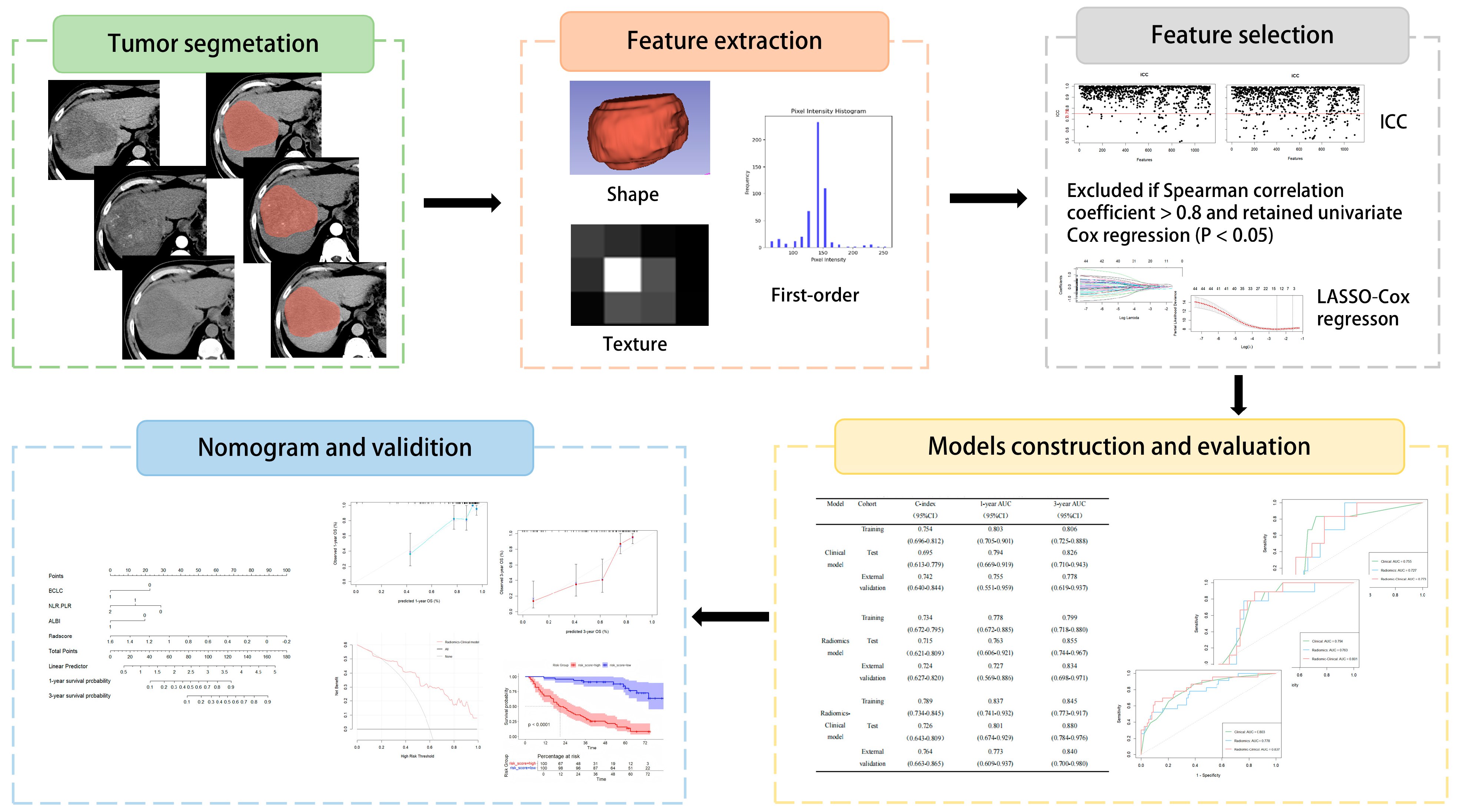

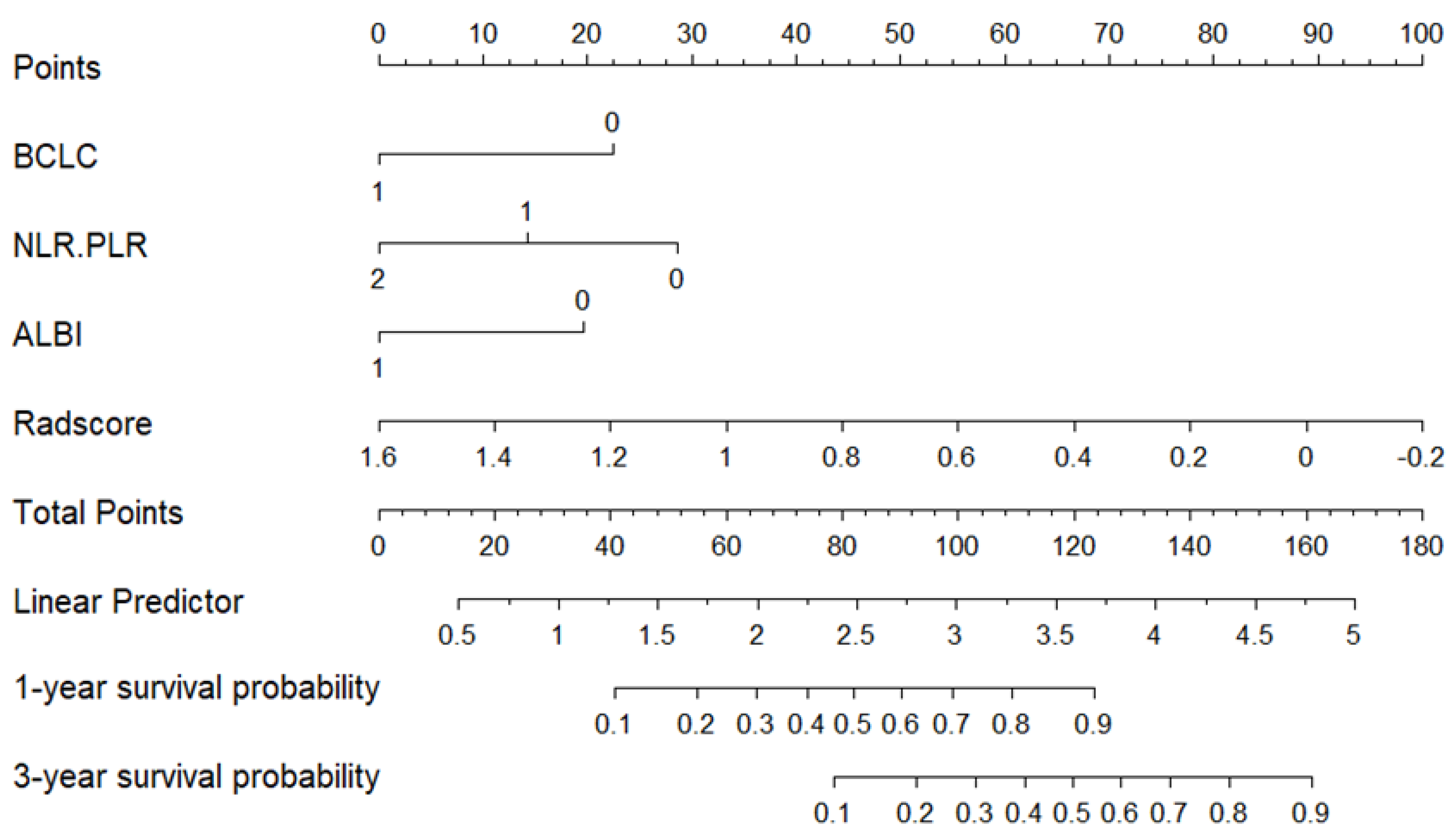

| Variable | Training Cohort (N = 112) | Internal Validation Cohort (N = 50) | External Validation Cohort (N = 40) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 0.242 | |||
| Male | 99 (88.4) | 42 (84.0) | 31 (77.5) | |
| Women | 13 (11.6) | 8 (16.0) | 9 (22.5) | |
| Age (years) | 56.8 ± 11.0 | 58.9 ± 8.9 | 56.45 ± 11.1 | 0.428 |
| Maximum diameter of tumor (cm) | 5.9 ± 2.8 | 6.8 ± 2.9 | 5.47 ± 2.1 | 0.054 |
| Portal vein tumor thrombus | 0.186 | |||
| None | 90 (80.4) | 36 (72.0) | 35 (87.5) | |
| Yes | 22 (19.6) | 14 (28.0) | 5 (12.5) | |
| Satellite lesion | 0.452 | |||
| None | 94 (83.9) | 45 (90.0) | 36 (90.0) | |
| Yes | 18 (16.1) | 5 (10.0) | 4 (10.0) | |
| Cirrhosis of the liver | 0.193 | |||
| None | 29 (25.9) | 19 (38.0) | 15 (37.5) | |
| Yes | 83 (74.1) | 31 (62.0) | 25 (62.5) | |
| HBsAg | 0.346 | |||
| Negative | 38 (34.0) | 21 (42.0) | 11 (27.5) | |
| Positive | 74 (66.0) | 29 (58.0) | 29 (72.5) | |
| AFP (ng/mL) | 0.350 | |||
| ≤400 | 80 (71.4) | 31 (62.0) | 30 (75.0) | |
| >400 | 32 (28.6) | 19 (38.0) | 10 (25.0) | |
| Child–Pugh | 0.928 | |||
| A | 99 (88.4) | 45 (90.0) | 35 (87.5) | |
| B | 13 (11.6) | 5 (10.0) | 5 (12.5) | |
| BCLCs | 0.147 | |||
| 0 + A | 78 (69.6) | 32 (64.0) | 33 (82.5) | |
| B + C | 34 (30.4) | 18 (36.0) | 7 (17.5) | |
| NLR | 2.6 (2.0, 3.8) | 2.9 (2.2, 4.2) | 2.4 (1.8, 3.3) | 0.191 |
| PLR | 104.1 (78.3, 148.9) | 107.6 (84.9, 141.9) | 89.12 (64.5, 133.2) | 0.290 |
| NLR-PLR | 0.275 | |||
| 0 | 52 (46.4) | 20 (40.0) | 25 (62.5) | |
| 1 | 36 (32.2) | 19 (38.0) | 8 (20) | |
| 2 | 24 (21.4) | 11 (22.0) | 7 (17.5) | |
| ALBI | 0.216 | |||
| Grade 1–2 | 60 (53.6) | 34 (68.0) | 22 (55.0) | |
| Grade 3 | 52 (46.4) | 16 (32.0) | 18 (45.0) | |
| AST (U/L) | 0.497 | |||
| ≤40 | 51 (45.5) | 20 (40.0) | 21 (52.5) | |
| >40 | 61 (54.5) | 30 (60.0) | 19 (47.5) | |
| ALT (U/L) | 0.833 | |||
| ≤50 | 80 (71.4) | 38 (76.0) | 29 (72.5) | |
| >50 | 32 (28.6) | 12 (24.0) | 11 (27.5) | |
| PT(s) | 0.154 | |||
| ≤14 | 78 (69.6) | 38 (76.0) | 34 (85.0) | |
| >14 | 34 (30.4) | 12 (24.0) | 6 (15.0) | |
| Status | 0.938 | |||
| Survive | 44 (39.3) | 20 (40.0) | 17 (42.5) | |
| Death | 68 (60.7) | 30 (60.0) | 23 (57.5) |
| Variable | Univariate Cox | Multivariate Cox | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95%CI) | p | HR (95%CI) | p | |
| Sex | 1.14 (0.52–2.48) | 0.750 | ||
| Age | 0.99 (0.97–1.01) | 0.404 | ||
| Maximum tumor diameter | 1.12 (1.05–1.24) | 0.002 | ||
| Portal vein tumor thrombus (PVTT) | 3.55 (2.08–6.04) | <0.001 | ||
| Satellite lesion | 2.26 (1.26–4.04) | 0.006 | ||
| Cirrhosis of the liver | 2.13 (1.16–3.92) | 0.015 | ||
| HBsAg | 0.94 (0.57–1.55) | 0.807 | ||
| AFP | 1.81 (1.09–3.00) | 0.022 | ||
| Child–Pugh | 3.02 (1.56–5.84) | 0.001 | ||
| BCLC | 4.00 (2.44–6.55) | <0.001 | 2.73 (1.62–4.62) | <0.001 |
| NLR | 1.13 (1.06–1.20) | <0.001 | ||
| PLR | 1.01 (1.01–1.01) | <0.001 | ||
| NLR-PLR | <0.001 | 0.006 | ||
| NLR-PLR (1) | 2.45 (1.37–4.37) | 0002 | 2.12 (1.17–3.85) | 0.013 |
| NLR-PLR (2) | 4.39 (2.38–8.09) | <0.001 | 2.74 (1.42–5.26) | 0.003 |
| ALBI | 2.19 (1.35–3.56) | 0.001 | 1.94 (1.19–3.17) | 0.008 |
| AST | 1.84 (1.14–2.96) | 0.012 | ||
| ALT | 2.26 (0.91–5.64) | 0.080 | ||
| PT | 1.86 (1.14–2.96) | 0.014 | ||
| Cohort | Image Type | Feature Class | Feature Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| NCE | Original | Glrlm | LongRunEmphasis |
| Wavelet-HLH | Glrlm | GrayLevelNonUniformityNormalized | |
| Wavelet-HHL | Glszm | SmallAreaEmphasis | |
| Wavelet-HHL | Glszm | SmallAreaHighGrayLevelEmphasis | |
| Wavelet-HHH | Glcm | ClusterProminence | |
| Wavelet-LLL | Firstorder | Maximum | |
| AP | Log-sigma-1–5-mm-3D | Glcm | DifferenceVariance |
| Wavelet-LHH | Glcm | JointAverage | |
| Wavelet-HLL | Glszm | LowGrayLevelZoneEmphasis | |
| Wavelet-HLH | Gldm | DependenceEntropy | |
| Wavelet-HLH | Gldm | DependenceVariance | |
| wavelet-HHL | Glrlm | ShortRunLowGrayLevelEmphasis | |
| PVP | Original | Shape | Sphericity |
| Wavelet-LHL | Glszm | SmallAreaEmphasis |
| Model | Cohort | C-Index (95% CI) | 1-Year AUC (95% CI) | 3-Year AUC (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical model | Training | 0.754 (0.696–0.812) | 0.803 (0.705–0.901) | 0.806 (0.725–0.888) |
| Internal validation | 0.695 (0.613–0.779) | 0.794 (0.669–0.919) | 0.826 (0.710–0.943) | |
| External validation | 0.742 (0.640–0.844) | 0.755 (0.551–0.959) | 0.778 (0.619–0.937) | |
| Radiomic model | Training | 0.734 (0.672–0.795) | 0.778 (0.672–0.885) | 0.799 (0.718–0.880) |
| Internal validation | 0.715 (0.621–0.809) | 0.763 (0.606–0.921) | 0.855 (0.744–0.967) | |
| External validation | 0.724 (0.627–0.820) | 0.727 (0.569–0.886) | 0.834 (0.698–0.971) | |
| Radiomic–clinical model | Training | 0.789 (0.734–0.845) | 0.837 (0.741–0.932) | 0.845 (0.773–0.917) |
| Internal validation | 0.726 (0.643–0.809) | 0.801 (0.674–0.929) | 0.880 (0.784–0.976) | |
| External validation | 0.764 (0.663–0.865) | 0.773 (0.609–0.937) | 0.840 (0.700–0.980) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, P.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, M.; Mao, Q.; Tao, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X. A CECT-Based Radiomics Nomogram Predicts the Overall Survival of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Surgical Resection. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051237
Zhang P, Shi Y, Zhou M, Mao Q, Tao Y, Yang L, Zhang X. A CECT-Based Radiomics Nomogram Predicts the Overall Survival of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Surgical Resection. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(5):1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051237
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Peng, Yue Shi, Maoting Zhou, Qi Mao, Yunyun Tao, Lin Yang, and Xiaoming Zhang. 2025. "A CECT-Based Radiomics Nomogram Predicts the Overall Survival of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Surgical Resection" Biomedicines 13, no. 5: 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051237
APA StyleZhang, P., Shi, Y., Zhou, M., Mao, Q., Tao, Y., Yang, L., & Zhang, X. (2025). A CECT-Based Radiomics Nomogram Predicts the Overall Survival of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Surgical Resection. Biomedicines, 13(5), 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051237





