Neurogenic Inflammation in Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Allergic Contact Dermatitis
3. Neurogenic Inflammation, Allergy, and Skin
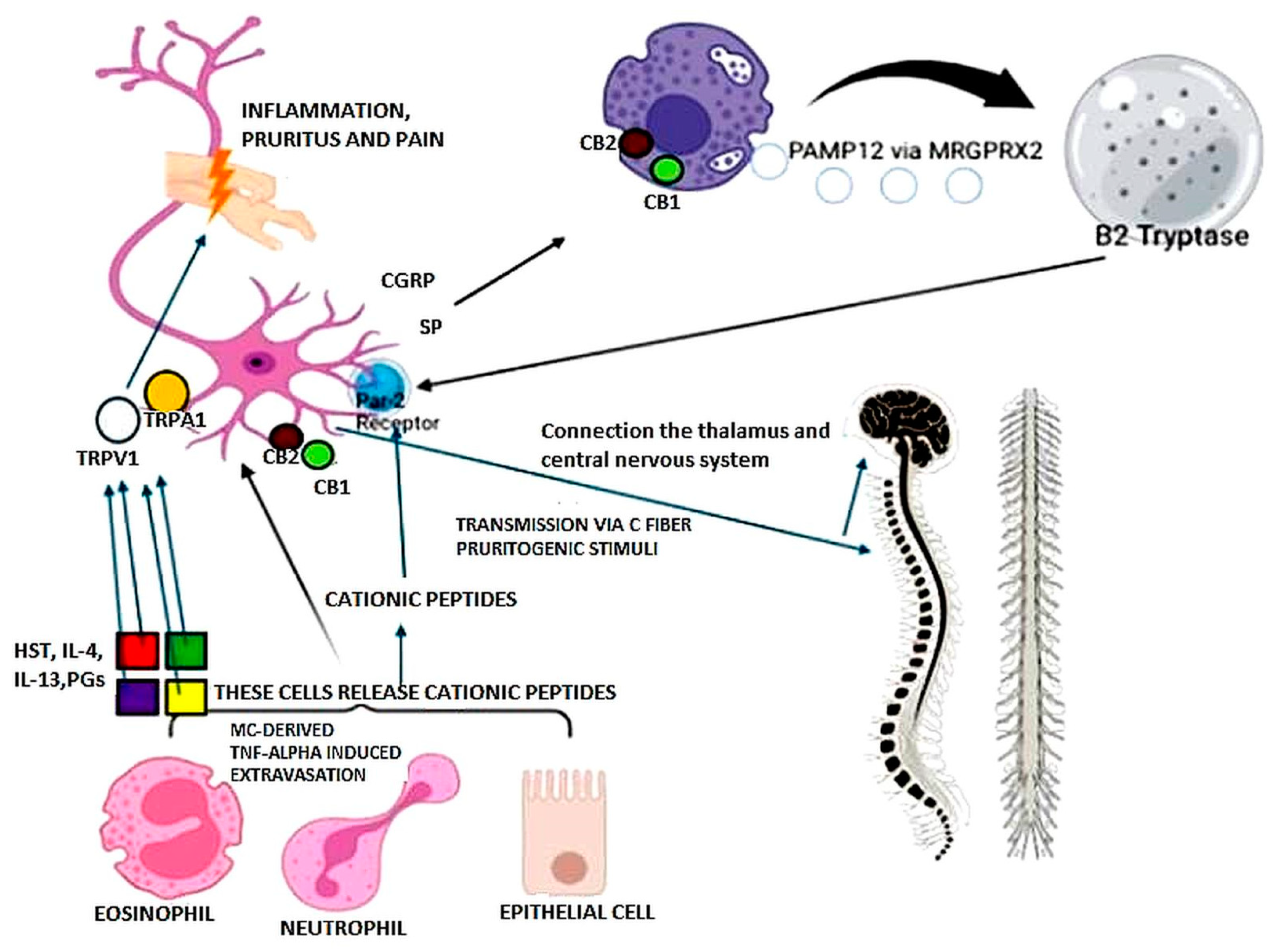
4. Evidence of Neurogenic Inflammation in ACD
5. Mast Cells: Neuroimmune Interactions
6. MRGPRX2: Potential Antagonists?
7. Endocannabinoid System and Topical Pharmacologic Implication
8. Age and Gender Influences on ACD and Neurogenic Inflammation
9. Treatment and Perspectives
| Category | Treatment Options | Perspectives |
|---|---|---|
| Prevention | Primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention Hapten avoidance (not always possible) | |
| Topical | Corticosteroids Calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus, phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors) Barrier creams Emollients Moisturizers | Antioxidants chelators [113] (#) |
| Systemic | Oral corticosteroids Antihistamines Cyclosporine Azathioprine Methotrexate | |
| Photochemotherapy | Psoralen and UVA | |
| Biological therapies | (Literature data, clinical reports) | Omalizumab Dupilumab TNF-α inhibitors Ustekinumab Rituximab |
| Non-histaminergic itch | (#Topical treatments clinical trials) | (non-THC) cannabinoid-based topical treatments CBD, PEA Interaction with CB1, CB2, TRPV1 |
| Neurogenic inflammation | (Experimental models) | Small molecule MRGPRX2 antagonists |
| (Experimental pain models) | Target therapies vs. TRPV1, TRPV2, NK1, CGRP receptors | |
| (No clinical trials) | Genistein Quercetin Isoliquiritigenin Piperine Shikonin Biomarkers, genomic, proteomic |
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nassau, S.; Fonacier, L. Allergic Contact Dermatitis. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 104, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marek-Jozefowicz, L.; Nedoszytko, B.; Grochocka, M.; Żmijewski, M.A.; Czajkowski, R.; Cubała, W.J.; Slominski, A.T. Molecular Mechanisms of Neurogenic Inflammation of the Skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S. Phenotypic and Functional Diversity of Mast Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Scheinman, P.L.; Vocanson, M.; Thyssen, J.P.; Johansen, J.D.; Nixon, R.L.; Dear, K.; Botto, N.C.; Morot, J.; Goldminz, A.M. Contact dermatitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonacier, L.; Noor, I. Contact dermatitis and patch testing for the allergist. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 120, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostner, L.; Anzengruber, F.; Guillod, C.; Recher, M.; Schmid-Grendelmeier, P.; Navarini, A.A. Allergic Contact Dermatitis. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2017, 37, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudeck, A.; Dudeck, J.; Scholten, J.; Petzold, A.; Surianarayanan, S.; Köhler, A.; Peschke, K.; Vöhringer, D.; Waskow, C.; Krieg, T.; et al. Mast cells are key promoters of contact allergy that mediate the adjuvant effects of haptens. Immunity 2011, 34, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, L.E.; Reis, V.M. Immunopathology of allergic contact dermatitis. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2011, 86, 419–433, (In English, Portuguese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tončić, R.J.; Lipozencic, J.; Martinac, I.; Greguric, S. Immunology of allergic contact dermatitis. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. 2011, 19, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brites, G.S.; Ferreira, I.; Sebastião, A.I.; Silva, A.; Carrascal, M.; Neves, B.M.; Cruz, M.T. Allergic contact dermatitis: From pathophysiology to development of new preventive strategies. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 162, 105282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristaudo, A.; Petrucci, F.; Giannarelli, D.; Cercato, M.C.; Orsini, D.; Morrone, A.; Bocca, B. Nickel dermatitis from earrings 15 years after EU directive implementation: A clinical-epidemiological study and a market survey in Rome, Italy. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 12, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordel-Gomez, M.T.; Miranda-Romero, A.; Castrodeza-Sanz, J. Epidemiology of contact dermatitis: Prevalence of sensitization to different allergens and associated factors. Actas Dermo-Sifiliogr. 2010, 101, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonacier, L.S.; Dreskin, S.C.; Leung, D.Y. Allergic skin diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125 (Suppl. S2), S138–S149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chey, W.Y.; Kim, K.L.; Yoo, T.Y.; Lee, A.Y. Allergic contact dermatitis from hair dye and development of lichen simplex chronicus. Contact Dermat. 2004, 51, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmi, C.; Srinivas, C.R.; Pillai, S.B.; Shanthakumari, S. Parthenium dermatitis manifesting clinically as polymorphic light eruption and prurigo nodularis- like lesions with vasculitis-like picture on histopathology. Indian. Dermatol. Online J. 2011, 2, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pesqué, D.; Aerts, O.; Bizjak, M.; Gonçalo, M.; Dugonik, A.; Simon, D.; Ljubojević-Hadzavdić, S.; Malinauskiene, L.; Wilkinson, M.; Czarnecka-Operacz, M.; et al. Differential diagnosis of contact dermatitis: A practical-approach review by the EADV Task Force on contact dermatitis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 38, 1704–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baluk, P. Neurogenic inflammation in skin and airways. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 1997, 2, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. Neurogenic inflammation and asthma. J. Asthma. 1992, 29, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, M.L.; Bacharier, L.B.; Bateman, E.; Boulet, L.-P.; Brightling, C.; Buhl, R.; Brusselle, G.; Cruz, A.A.; Drazen, J.M.; Duijts, L.; et al. Key recommendations for primary care from the 2022 Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) update. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. 2023, 33, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- De Bartolomeis, F.; Savoia, A.; Aitella, E.; Sacerdoti, C.; Parlato, A.; Palmieri, C.; Astarita, C. Urticaria by neurogenic switching of gastroesophageal chemical-infective inflammation: A phenomenon that should always be evaluated in suspected multiple drug hypersensitivity. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2014, 4 (Suppl. S3), P26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martinis, M.; Sirufo, M.M.; Suppa, M.; Ginaldi, L. New Perspectives in Food Allergy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martinis, M.; Sirufo, M.M.; Viscido, A.; Ginaldi, L. Food Allergy Insights: A Changing Landscape. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2020, 68, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitella, E.; De Bartolomeis, F.; Savoia, A.; Fabiani, M.; Romano, M.; Astarita, C. The overlap syndrome of urticaria and gastroesophageal reflux disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Marshall, J.; Waserman, S. Mast Cells and the Nerves—Potential Interactions in the Context of Chronic Disease. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1995, 25, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potenzieri, C.; Meeker, S.; Undem, B.J. Activation of Mouse Bronchopulmonary C-fibres by Serotonin and Allergen-ovalbumin Challenge. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 5449–5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosipovitch, G.; Kim, B.; Luger, T.; Lerner, E.; Metz, M.; Adiri, R.; Canosa, J.M.; Cha, A.; Ständer, S. Similarities and differences in peripheral itch and pain pathways in atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 153, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ständer, S.; Luger, T.; Kim, B.; Lerner, E.; Metz, M.; Adiri, R.; Canosa, J.M.; Cha, A.; Yosipovitch, G. Cutaneous Components Leading to Pruritus, Pain, and Neurosensitivity in Atopic Dermatitis: A Narrative Review. Dermatol. Ther. 2024, 14, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liezmann, C.; Klapp, B.; Peters, E. Stress, Atopy and Allergy. Dermato-Endocrinology 2011, 3, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfrich, Y.L.; Maier, L.E.; Cui, Y.; Fisher, G.H.; Chubb, H.; Fligiel, S.; Sachs, D.; Varani, J.; Voorhees, J. Clinical, Histologic, and Molecular Analysis of Differences Between Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea and Telangiectatic Photoaging. JAMA Dermatol. 2015, 151, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, D.; Kashiwakura, J.; Kita, H.; Kikukawa, Y.; Fujitani, Y.; Sasaki-Sakamoto, T.; Kuroda, K.; Nunomura, S.; Hayama, K.; Terui, T.; et al. Expression of Mas-Related Gene X2 on Mast Cells Is Upregulated in the Skin of Patients with Severe Chronic Urticaria. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 622–633.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilhar, A.; Reich, K.; Keren, A.; Kabashima, K.; Steinhoff, M.; Paus, R. Mouse models of atopic dermatitis: A critical reappraisal. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Nour, H.; Lundeberg, L.; Boman, A.; Theodorsson, E.; Hökfelt, T.; Nordlind, K. Galanin expression in a murine model of allergic contact dermatitis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2004, 84, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidhuber, S.M.; Santic, R.; Tam, C.W.; Bauer, J.W.; Kofler, B.; Brain, S.D. Galanin-like peptides exert potent vasoactive functions in vivo. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arck, P.C.; Handjiski, B.; Kuhlmei, A.; Peters, E.M.; Knackstedt, M.; Peter, A.; Hunt, S.P.; Klapp, B.F.; Paus, R. Mast cell deficient and neurokinin-1 receptor knockout mice are protected from stress-induced hair growth inhibition. J. Mol. Med. 2005, 83, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, A.; Wortsman, J.; Tuckey, R.C.; Paus, R. Differential Expression of HPA Axis Homolog in the Skin. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2007, 265–266, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Zmijewski, M.A.; Zbytek, B.; Tobin, D.J.; Theoharides, T.; Rivier, J. Key Role of CRF in the Skin Stress Response System. Endocr. Rev. 2013, 34, 827–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theoharides, T.; Donelan, J.M.; Papadopoulou, N.; Cao, J.; Kempuraj, D.; Conti, P. Mast Cells as Targets of Corticotropin-Releasing Factor and Related Peptides. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 25, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, R.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Yin, C.; Tai, Y.; Nie, H.; Zeng, D.; Fang, J.; Du, J.; et al. Exploring neuronal mechanisms involved in the scratching behavior of a mouse model of allergic contact dermatitis by transcriptomics. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2022, 27, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Metcalfe, D.; Baram, D.; Mekori, Y.A. Mast Cells. Physiol. Rev. 1997, 77, 1033–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribatti, D. The Staining of Mast Cells: A Historical Overview. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 176, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, E.; Jamur, M.C.; Oliver, C. Mast Cell Function: Mast cell function: A new vision of an old cell. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2014, 62, 698–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyce, J. Eicosanoid Mediators of Mast Cells: Receptors, Regulation of Synthesis, and Pathobiologic Implications. In Mast Cells in Allergic Diseases; KARGER: Basel, Switzerland, 2005; pp. 59–79. [Google Scholar]
- Galli, S.; Nakae, S.; Tsai, M. Mast Cells in the Development of Adaptive Immune Responses. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voisin, T.; Perner, C.; Messou, M.-A.; Shiers, S.; Ualiyeva, S.; Kanaoka, Y.; Price, T.J.; Sokol, C.L.; Bankova, L.G.; Austen, K.F.; et al. The CysLT 2 R Receptor Mediates Leukotriene C 4 -Driven Acute and Chronic Itch. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2022087118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauber, M.; Basso, L.; Martin, J.; Bostan, L.; Pinto, M.M.; Thierry, G.R.; Houmadi, R.; Serhan, N.; Loste, A.; Blériot, C.; et al. Landscape of Mast Cell Populations across Organs in Mice and Humans. J. Exp. Med. 2023, 220, e20230570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frossi, B.; Mion, F.; Sibilano, R.; Danelli Pucillo, C.E.M. Is it time for a new classification of mast cells? What do we know about mast cell heterogeneity? Immunol. Rev. 2018, 282, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Sagi, V.; Gupta, M.; Gupta, K. Mast Cell Neural Interactions in Health and Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, J.; Sobiepanek, A.; Mazurkiewicz-Pisarek, A.; Rogalska, M.; Gryciuk, A.; Kuryk, L.; Abraham, S.N.; Staniszewska, M. Mast Cells as a Target-A Comprehensive Review of Recent Therapeutic Approaches. Cells 2023, 12, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitte, J.; Vibhushan, S.; Bratti, M.; Montero-Hernandez, J.E.; Blank, U. Allergy, Anaphylaxis, and Nonallergic Hypersensitivity: IgE, Mast Cells, and Beyond. Med. Princ. Pract. 2022, 31, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svendsen, S.; Lange, N.G.; Christensen, M.J.; Mørtz, C.G.; Bindslev-Jensen, C. Urticaria. Ugeskr. Laeger 2023, 185, V04230240. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Borges, M.; Aberer, W.; Brockow, K.; Celik, G.E.; Cernadas, J.; Greenberger, P.A.; Masse, M.-S.; Schrijvers, R.; Trautmann, A. Controversies in Drug Allergy: Radiographic Contrast Media. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.J.; Trautmann, A.; Böhm, I.; Scherer, K.; Barbaud, A.; Bavbek, S.; Bonadonna, P.; Cernadas, J.R.; Chiriac, A.M.; Gaeta, F.; et al. Practice Parameters for Diagnosing and Managing Iodinated Contrast Media Hypersensitivity. Allergy 2021, 76, 1325–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falduto, G.; Pfeiffer, A.; Luker, A.; Metcalfe, D.D.; Olivera, A. Emerging Mechanisms Contributing to Mast Cell-Mediated Pathophysiology with Therapeutic Implications. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 220, 107718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, Q.; Lyons, J.J.; Naranjo, A.N.; Olivera, A.; Lazarus, R.A.; Metcalfe, D.D.; Milner, J.D.; Schwartz, L.B. Impact of Naturally Forming Human α/β-Tryptase Heterotetramers in the Pathogenesis of Hereditary α-Tryptasemia. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 2348–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatemoto, K.; Nozaki, Y.; Tsuda, R.; Konno, S.; Tomura, K.; Furuno, M.; Ogasawara, H.; Edamura, K.; Takagi, H.; Iwamura, H.; et al. Immunoglobulin Eindependent activation of mast cell is mediated by Mrg receptors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 349, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Franke, K.; Bal, G.; Li, Z.; Zuberbier, T.; Babina, M. MRGPRX2-Mediated Degranulation of Human Skin Mast Cells Requires the Operation of Gαi, Gαq, Ca++ Channels, ERK1/2 and PI3K—Interconnection between Early and Late Signaling. Cells 2022, 11, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeil, B. MRGPRX2 and Adverse Drug Reactions. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 676354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motakis, E.; Guhl, S.; Ishizu, Y.; Itoh, M.; Kawaji, H.; de Hoon, M.; Lassmann, T.; Carninci, P.; Hayashizaki, Y.; Zuberbier, T.; et al. Redefinition of the human mast cell transcriptome by deep-CAGE sequencing. Blood 2014, 123, e58–e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedi, B.; Gehring, M.; Kapp, A. The pseudoallergen receptor MRGPRX2 on peripheral blood basophils and eosinophils: Expression and function. Allergy 2020, 75, 2229–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Ayudhya CC, N.; Thapaliya, M.; Deepak, V.; Ali, H. Multifaceted MRGPRX2: New insight into the role of mast cells in health and disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babina, M.; Wang, Z.; Franke, K.; Zuberbier, T. Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Promotes MRGPRX2-Triggered Degranulation of Skin Mast Cells in a STAT5-Dependent Manner with Further Support from JNK. Cells 2021, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, Y.; Wang, Z.; Vanderberghe, M.; Two, A.; Gallo, R.L.; Di Nardo, A. Mast Cells Are Key Mediators of Cathelicidin-Initiated Skin Inflammation in Rosacea. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2728–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.-J.; Hao, D.; Wen, X.; Du, D.; He GJiang, X. The Theranostics Role of Mast Cells in the Pathophysiology of Rosacea. Front. Med. 2020, 6, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erjefält, J. Mast Cells in Human Airways: The Culprit? Eur. Respir. Rev. 2014, 23, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruse, G.; Bradding, P. Mast Cells in Airway Diseases and Interstitial Lung Disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 778, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiewak, R. Diseases from the Spectrum of Dermatitis and Eczema: Can “Omics” Sciences Help with Better Systematics and More Accurate Differential Diagnosis? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Oliva, M.; Renert-Yuval, Y.; Guttman-Yassky, E. The ‘omics’ revolution: Redefining the understanding and treatment of allergic skin diseases. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 16, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitella, E.; Romano, C.; Ginaldi, L.; Cozzolino, D. Mast Cells at the Crossroads of Hypersensitivity Reactions and Neurogenic Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stead, R.H.; Dixon, M.F.; Bramwell, N.H.; Riddell, R.H.; Bienenstock, J. Mastcells are closely apposed to nerves in the human gastrointestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology 1989, 97, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stead, R.H.; Tomioka, M.; Quinonez, G.; Simon, G.T.; Felten, S.Y.; Bienenstock, J. Intestinalmucosalmastcells in normal and nematode-infected rat intestines are in intimate contact with peptidergic nerves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 2975–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thapaliya, M.; Chompunud Na Ayudhya, C.; Amponnawarat, A.; Roy, S.; Ali, H. Mast Cell-Specific MRGPRX2: A Key Modulator of Neuro-Immune Interaction in Allergic Diseases. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2021, 21, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, D.P.; Limjunyawong, N.; Gour, N.; Pundir, P.; Dong, X. A Mast-Cell-Specific Receptor Mediates Neurogenic Inflammation and Pain. Neuron 2019, 101, 412–420.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gaudenzio, N.; Sibilano, R.; Marichal, T.; Starkl, P.; Reber, L.L.; Cenac, N.; McNeil, B.D.; Dong, X.; Hernandez, J.D.; Sagi-Eisenberg, R.; et al. Different activation signals induce distinct mast cell degranulation strategies. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 3981–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- McNeil, B.D. Minireview: Mas-related G protein-coupled receptor X2 activation by therapeutic drugs. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 751, 135746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Liu, S.; Ogasawara, T.; Sawasaki, T.; Takasaki, Y.; Yorozuya, T.; Mogi, M. A novel MRGPRX2-targeting antagonistic DNA aptamer inhibits histamine release and prevents mast cell-mediated anaphylaxis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 878, 173104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogasawara, H.; Furuno, M.; Edamura, K.; Noguchi, M. Novel MRGPRX2 antagonists inhibit IgE-independent activation of human umbilical cord blood-derived mast cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 106, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogasawara, H.; Furuno, M.; Edamura, K.; Noguchi, M. Peptides of major basic protein and eosinophil cationic protein activate human mast cells. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2020, 21, 100719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollam, J.; Solomon, M.; Villescaz, C.; Lanier, M.; Evans, S.; Bacon, C.; Freeman, D.; Vasquez, A.; Vest, A.; Napora, J.; et al. Inhibition of mast cell degranulation by novel small molecule MRGPRX2 antagonists. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 154, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila, C.; Massick, S.; Kaffenberger, B.H.; Kwatra, S.G.; Bechtel, M. Cannabinoids for the treatment of chronic pruritus: A review. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ständer, S.; Schmelz, M.; Metze, D.; Luger, T.; Rukwied, R. Distribution of cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and 2 (CB2) on sensory nerve fibers and adnexal structures in human skin. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2005, 38, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.W.; Seo, J.A.; Jang, W.H.; Koh, H.J.; Bae, I.H.; Park, Y.H.; Lim, K.M. Antipruritic effects of TRPV1 antagonist in murine atopic dermatitis and itching models. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 1576–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberlein, B.; Eicke, C.; Reinhardt, H.W.; Ring, J. Adjuvant treatment of atopic eczema: Assessment of an emollient containing N-palmitoylethanolamine (ATOPA study). J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2008, 22, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulvirenti, N.; Nasca, M.R.; Micali, G. Topical adelmidrol 2% emulsion, a novel aliamide, in the treatment of mild atopic dermatitis in pediatric subjects: A pilot study. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. 2007, 15, 80–83. [Google Scholar]
- Szepietowski, J.C.; Reich, A.; Szepietowski, T. Emollients with endocannabinoids in the treatment of uremic pruritus: Discussion of the therapeutic options. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2005, 9, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, G.; Jeong, S.K.; Park, B.M.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Hong, S.P.; Kim, B.; Kim, B.W. Selective Cannabinoid Receptor-1 Agonists Regulate Mast Cell Activation in an Oxazolone-Induced Atopic Dermatitis Model. Ann. Dermatol. 2016, 28, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decuyper, I.I.; Van Gasse, A.L.; Cop, N.; Sabato, V.; Faber, M.A.; Mertens, C.; Bridts, C.H.; Hagendorens, M.M.; De Clerck, L.; Rihs, H.P.; et al. Cannabis sativa allergy: Looking through the fog. Allergy 2017, 72, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, D.; Ponyai, G. Contact Allergy in the Elderly: A Study of 600 Patients. Life 2022, 12, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martinis, M.; Sirufo, M.M.; Viscido, A.; Ginaldi, L. Food Allergies and Ageing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martinis, M.; Sirufo, M.M.; Ginaldi, L. Allergy and Aging: An Old/New Emerging Health Issue. Aging Dis. 2017, 8, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowsky, R.; Sulejmani, P.; Lio, P.A. Atopic Dermatitis: Beyond the Skin and Into the Gut. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.; Meier-Davis, S.R.; Cayme, B.; Shudo, J.; Maibach, H. Allergic contact dermatitis: Effect of age. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2012, 31, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Gao, X.; Xie, W. Research Progress in Skin Aging and Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicka, J.M.; Zmijewski, M.A.; Piotrowska, A.; Nedoszytko, B.; Lange, M.; Tuckey, R.C.; Slominski, A.T. Bioactive forms of vitamin D selectively stimulate the skin analog of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis in human epidermal keratinocytes. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 437, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Martinis, M.; Sirufo, M.M.; Suppa, M.; Di Silvestre, D.; Ginaldi, L. Sex and Gender Aspects for Patient Stratification in Allergy Prevention and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonchai, W.; Likittanasombat, S.; Viriyaskultorn, N.; Kanokrungsee, S. Gender differences in allergic contact dermatitis to common allergens. Contact Dermat. 2024, 90, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.M.; Kang, S.M.; Chung, J.H. The role of TRPV1 channel in aged human skin. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2012, 65, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cetinkaya, A.; Kilinc, E.; Camsari, C.; Muhammed Nur Ogun, M.N. Effects of estrogen and progesterone on the neurogenic infammatory neuropeptides: Implications for gender differences in migraine. Exp. Brain Res. 2020, 238, 2625–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.C.; Wagner, A.F.; Lysle, D.T. Neurokinin 1 receptor signaling mediates sex differences in μ and κ opioid-induced enhancement of contact hypersensitivity. J. Neuroimmunol. 2006, 181, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, N.M.E.; Charlton, M.P.; Dostrovsky, J.O. Sex differences in inflammation evoked by noxious chemical, heat and electrical stimulation. Brain Res. 2009, 1276, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirufo, M.M.; De Martinis, M.; Ginaldi, L. Omalizumab an effective and safe alternative therapy in severe refractory atopic dermatitis: A case report. Medicine 2018, 97, e10897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirufo, M.M.; Bassino, E.M.; De Pietro, F.; Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M. Sex differences in the efficacy of omalizumab in the treatment of chronic spontaneous urticaria. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2021, 35, 20587384211065870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirufo, M.M.; De Pietro, F.; Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M. Sex, Allergic Diseases and Omalizumab. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirillo, N. The local neuropeptide system of keratinocytes. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocheva, G.; Slominski, R.M.; Slominski, A.T. Neuroendocrine aspects of skin aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Martinis, M.; Allegra, A.; Sirufo, M.M.; Tonacci, A.; Pioggia, G.; Raggiunti, M.; Ginaldi, L.; Gangemi, S. Vitamin D Deficiency, Osteoporosis and Effect on Autoimmune Diseases and Hematopoiesis: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, R.M.; Raman, C.; Chen, J.Y.; Athar, M.; Elmets, C. Neuroendocrine signaling in the skin with a special focus on the epidermal neuropeptides. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2022, 323, C1757–C1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, J. Itch in Allergic Contact Dermatitis. Front. Allergy 2021, 2, 702488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bhatia, J.; Sarin, A.; Wollina, U.; Lotti, T.; Navarini, A.A.; Mueller, S.M.; Grabbe, S.; Saloga, J.; Rokni, G.R.; Goldust, M. Review of biologics in allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermat. 2020, 83, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.F.; Rustemeyer, T.; Thyssen, J.P. Recent advances in understanding and managing contact dermatitis. F1000Research 2018, 7, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undem, B.J.; Potenzieri, C. Autonomic neural control of intrathoracic airways. Compr. Physiol. 2012, 2, 1241–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frosch, P.J.; Kurte, A. Efficacy of skin barrier creams (IV). The repetitive irritation test (RIT) with a set of 4 standard irritants. Contact Dermat. 1994, 31, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Khan, S.; Kim, Y.S. Insight into Pain Modulation: Nociceptors Sensitization and Therapeutic Targets. Curr. Drug Targets 2019, 20, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wöhrl, S.; Kriechbaumer, N.; Hemmer, W.; Focke, M.; Brannath, W.; Götz, M.; Jarisch, R. A cream containing the chelator DTPA (diethylenetriaminepenta-acetic acid) can prevent contact allergic reactions to metals. Contact Dermat. 2002, 44, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Main Cells or Pathways | |
|---|---|
| Sensitization phase | ROS/DAMPs→TLR/NLRs KCs: enzymes (pro-hapten→hapten), alarmins, cytokines Dermal DC and LC activation, migration and maturation to draining lymph nodes Effector and memory T-cell expansion and recirculation |
| Elicitation phase | Adhesion molecules, chemokines, cytokines, cells recruitment: DC, KC, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, macrophages, eosinophils T cells, NK cells Mast cell→TNF-α→neutrophil extravasation CD4+ and CD8+ T cells Th1, Th2, Th17, Th22 phenotypes |
| Resolution phase | Regulatory T cells |
| Clearance of hapten | |
| Neurogenic contribution | Cutaneous sensory peptidergic nerves |
| PAMP12 | |
| Mast cells via MRGPRX2 | |
| Tryptase >> histamine, serotonin | |
| PAR-2 | |
| SP, CGRP | |
| Endocannabinoid system |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aitella, E.; De Martinis, M.; Romano, C.; Azzellino, G.; Ginaldi, L. Neurogenic Inflammation in Allergic Contact Dermatitis. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030656
Aitella E, De Martinis M, Romano C, Azzellino G, Ginaldi L. Neurogenic Inflammation in Allergic Contact Dermatitis. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(3):656. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030656
Chicago/Turabian StyleAitella, Ernesto, Massimo De Martinis, Ciro Romano, Gianluca Azzellino, and Lia Ginaldi. 2025. "Neurogenic Inflammation in Allergic Contact Dermatitis" Biomedicines 13, no. 3: 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030656
APA StyleAitella, E., De Martinis, M., Romano, C., Azzellino, G., & Ginaldi, L. (2025). Neurogenic Inflammation in Allergic Contact Dermatitis. Biomedicines, 13(3), 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030656










