CHIVAX 2.1-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles as Intranasal Vaccine Candidates for COVID-19: Development and Murine Safety Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of CVX-Loaded C Nanoparticles
2.3. Average Size and Zeta Potential Determinations
2.4. Morphology
2.5. CHIVAX 2.1 Viability and Encapsulation Efficiency
2.6. Diffuse Reflectance of Infrared by Fourier Transforms (DRIFT)
2.7. Mucin’s Adsorption of CNPs
2.8. In Vitro Release Profiles
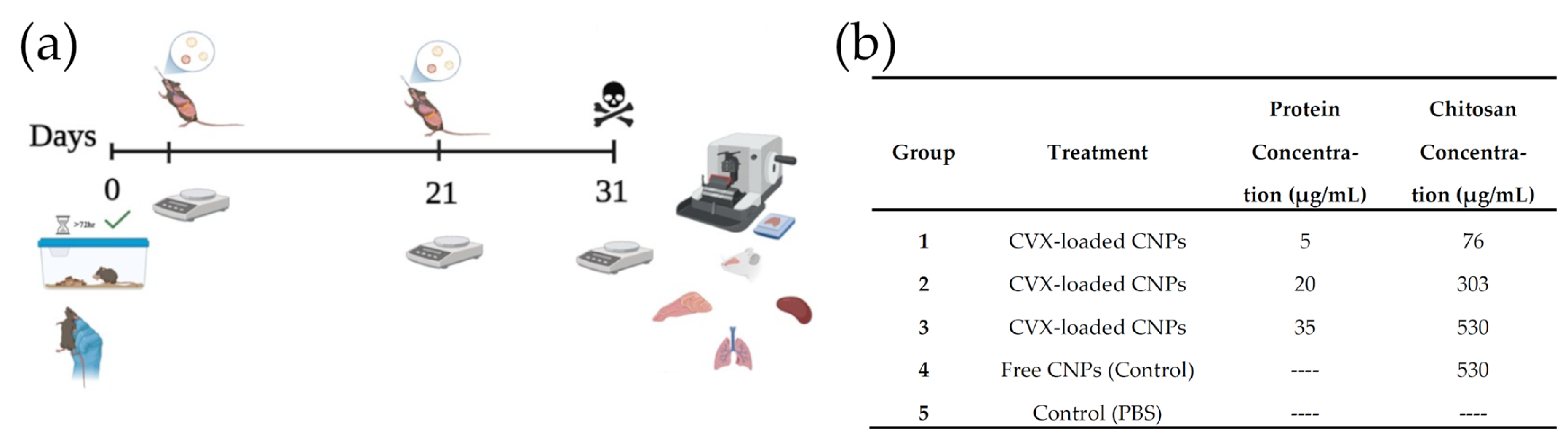
2.9. In Vivo Assays
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of CNPs
3.2. Immune Detection of CVX Recovered from CNPs
3.3. Spectroscopic Properties (FTIR Analyses)
3.4. Mucin Adsorption
3.5. In Vitro Release Kinetics
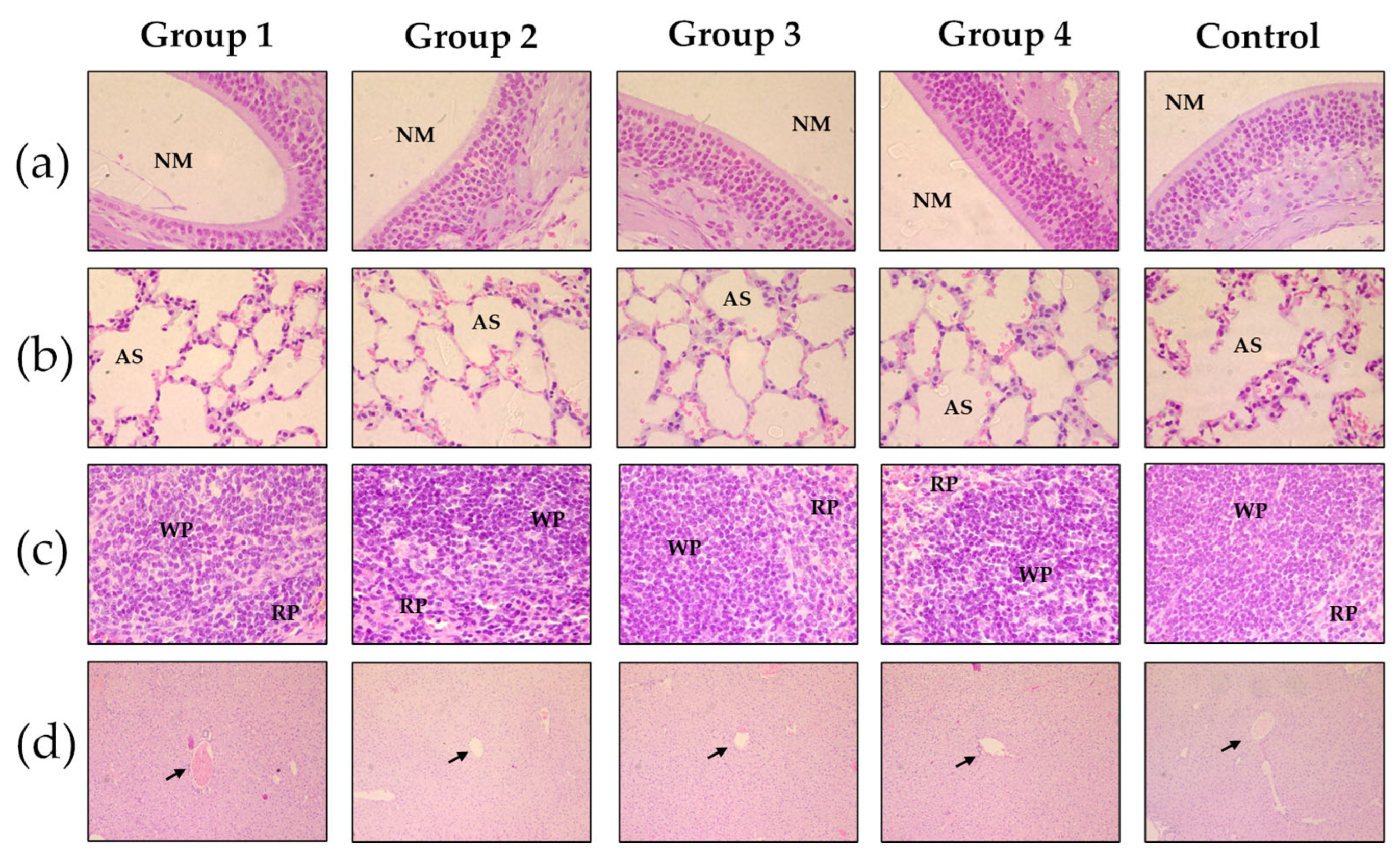
3.6. In Vivo Assays
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Z.-L. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri Sheykhangafshe, F. COVID-19 Vaccination: Challenges and Opportunities. J. Rafsanjan Univ. Med. Sci. 2022, 20, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhama, K.; Dhawan, M.; Tiwari, R.; Emran, T.B.; Mitra, S.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alhumaid, S.; Alawi, Z.A.; Al Mutair, A. COVID-19 Intranasal Vaccines: Current Progress, Advantages, Prospects, and Challenges. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2022, 18, 2045853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marien, A.-G.; Hochart, A.; Lagrée, M.; Diallo, D.; Martinot, A.; Dubos, F. Parental Acceptance of an Intranasal Vaccine: Example of Influenza Vaccine. Arch. Pédiatr. 2019, 26, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gizurarson, S. Anatomical and Histological Factors Affecting Intranasal Drug and Vaccine Delivery. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2012, 9, 566–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, V.A.; Portilho, A.I.; De Gaspari, E. Vaccines, Adjuvants and Key Factors for Mucosal Immune Response. Immunology 2022, 167, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovsky, N. Comparative Safety of Vaccine Adjuvants: A Summary of Current Evidence and Future Needs. Drug Saf. 2015, 38, 1059–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmour, I.; Islam, N. Recent Advances on Chitosan as an Adjuvant for Vaccine Delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 200, 498–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Huang, L.; Yuan, L.; Huang, S.; Zeng, Z.; Cao, Y.; Wei, X.; Wang, X.; Shi, M.; et al. Nanotechnology-Driven Advances in Intranasal Vaccine Delivery Systems against Infectious Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1573037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Gao, Y.; Shu, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, K. Chitosan-Based Nanomaterial as Immune Adjuvant and Delivery Carrier for Vaccines. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlman, S. A Balance between Innovation and Biosafety. In Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Washington, DC, USA, 26–30 April 2024; p. e2410451121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosqueda, J.; Hernández-Silva, D.J.; Vega-López, M.A.; Vega-Rojas, L.J.; Beltrán, R.; Velasco-Elizondo, A.; Ramírez-Estudillo, M.D.C.; Fragoso-Saavedra, M.; Pérez-Almeida, C.; Hernández, J.; et al. Evaluation of the Humoral and Mucosal Immune Response of a Multiepitope Vaccine against COVID-19 in Pigs. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1276950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega Rojas, L.J.; Ruíz-Manzano, R.A.; Velasco-Elizondo, M.A.; Carbajo-Mata, M.A.; Hernández-Silva, D.J.; Rocha-Solache, M.; Hernández, J.; Pérez-Serrano, R.M.; Zaldívar-Lelo De Larrea, G.; García-Gasca, T.; et al. An Evaluation of the Cellular and Humoral Response of a Multi-Epitope Vaccine Candidate Against COVID-19 with Different Alum Adjuvants. Pathogens 2024, 13, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behnaz, N.; Zare Karizi, S.; Nazarian, S.; Kazemi, R.; Motamedi, M.J.; Fasihi-Ramandi, M.; Amani, J. Construction and Structural Assessment of Nanocapsule Containing HER2-MUC1 Chimeric Protein as a Candidate for a Vaccine Against Breast Cancer. Int. J. Cancer Manag. 2019, 12, e66671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akerele, G.; Ramadan, N.; Renu, S.; Renukaradhya, G.J.; Shanmugasundaram, R.; Selvaraj, R.K. In Vitro Characterization and Immunogenicity of Chitosan Nanoparticles Loaded with Native and Inactivated Extracellular Proteins from a Field Strain of Clostridium Perfringens Associated with Necrotic Enteritis. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2020, 224, 110059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.; Davis, S.S.; Illum, L. In Vitro Evaluation of the Mucoadhesive Properties of Chitosan Microspheres. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 166, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, D.; Jaganathan, K.S. Mucoadhesive Glycol Chitosan Nanoparticles for Intranasal Delivery of Hepatitis B Vaccine: Enhancement of Mucosal and Systemic Immune Response. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantle, M.; Allen, A. A Colorimetric Assay for Glycoproteins Based on the Periodic Acid/Schiff Stain. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1978, 6, 607–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, R.G.; Pronk, G.J.; Padmanabhan, V.; Frey, W.H. Delivery of Insulin-like Growth Factor-I to the Rat Brain and Spinal Cord along Olfactory and Trigeminal Pathways Following Intranasal Administration. Neuroscience 2004, 127, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppolu, B.P.; Smith, S.G.; Ravindranathan, S.; Jayanthi, S.; Suresh Kumar, T.K.; Zaharoff, D.A. Controlling Chitosan-Based Encapsulation for Protein and Vaccine Delivery. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4382–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedaghat, M.H.; Behnia, M.; Abouali, O. Nanoparticle Diffusion in Respiratory Mucus Influenced by Mucociliary Clearance: A Review of Mathematical Modeling. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2023, 36, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppolu, B.; Zaharoff, D.A. The Effect of Antigen Encapsulation in Chitosan Particles on Uptake, Activation and Presentation by Antigen Presenting Cells. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2359–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz, S.; Schöttler, S.; Kotman, N.; Baier, G.; Musyanovych, A.; Kuharev, J.; Landfester, K.; Schild, H.; Jahn, O.; Tenzer, S.; et al. Protein Corona of Nanoparticles: Distinct Proteins Regulate the Cellular Uptake. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprifico, A.E.; Foot, P.J.S.; Polycarpou, E.; Calabrese, G. Overcoming the Protein Corona in Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 1825–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopinath, P.M.; Saranya, V.; Vijayakumar, S.; Mythili Meera, M.; Ruprekha, S.; Kunal, R.; Pranay, A.; Thomas, J.; Mukherjee, A.; Chandrasekaran, N. Assessment on Interactive Prospectives of Nanoplastics with Plasma Proteins and the Toxicological Impacts of Virgin, Coronated and Environmentally Released-Nanoplastics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekie, F.S.M.; Hajiramezanali, M.; Geramifar, P.; Raoufi, M.; Dinarvand, R.; Soleimani, M.; Atyabi, F. Controlling Evolution of Protein Corona: A Prosperous Approach to Improve Chitosan-Based Nanoparticle Biodistribution and Half-Life. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Wang, X.; Jing, B.; Li, Z.; Xia, X.; Sun, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, L.; et al. Adjuvants for Coronavirus Vaccines. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 589833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yin, X.-G.; Wen, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, R.-Y.; Zhou, S.-H.; Liao, C.-M.; Wei, H.-W.; Guo, J. MPLA-Adjuvanted Liposomes Encapsulating S-Trimer or RBD or S1, but Not S-ECD, Elicit Robust Neutralization Against SARS-CoV-2 and Variants of Concern. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 3563–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valizadeh, A.; Khaleghi, A.A.; Alipanah, H.; Zarenezhad, E.; Osanloo, M. Anticarcinogenic Effect of Chitosan Nanoparticles Containing Syzygium Aromaticum Essential Oil or Eugenol Toward Breast and Skin Cancer Cell Lines. BioNanoScience 2021, 11, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owczarek, M.; Herczyńska, L.; Sitarek, P.; Kowalczyk, T.; Synowiec, E.; Śliwiński, T.; Krucińska, I. Chitosan Nanoparticles-Preparation, Characterization and Their Combination with Ginkgo Biloba Extract in Preliminary In Vitro Studies. Molecules 2023, 28, 4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.; Syeda, J.; Wasan, K.; Wasan, E. An Overview of Chitosan Nanoparticles and Its Application in Non-Parenteral Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Murthy, P.N.; Nath, L.; Chowdhury, P. Kinetic Modeling on Drug Release from Controlled Drug Delivery Systems. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2010, 67, 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- Wijayawardana, S.; Thambiliyagodage, C.; Jayanetti, M. Kinetic Study of in Vitro Release of Curcumin from Chitosan Biopolymer and the Evaluation of Biological Efficacy. Arab. J. Chem. 2024, 17, 105896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Meng, L.-Y.; Yang, J.-K.; He, Z.; Chen, X.-G.; Liu, Y. Bridging Nanoplatform and Vaccine Delivery, a Landscape of Strategy to Enhance Nasal Immunity. J. Control. Release 2022, 351, 456–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, S.; Shastri, D.H.; Shah, J.; Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. Nasal Delivery to the Brain: Harnessing Nanoparticles for Effective Drug Transport. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehagia, E.; Papakyriakopoulou, P.; Valsami, G. Advances in Intranasal Vaccine Delivery: A Promising Non-Invasive Route of Immunization. Vaccine 2023, 41, 3589–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwoke, M.; Agu, R.; Verbeke, N.; Kinget, R. Nasal Mucoadhesive Drug Delivery: Background, Applications, Trends and Future Perspectives. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1640–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghareeb, S.; Asare-Addo, K.; Conway, B.R.; Adebisi, A.O. PLGA Nanoparticles for Nasal Drug Delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 95, 105564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini, G.; Magrì, D.; Gioria, S.; Medaglini, D.; Calzolai, L. Characterization of Nanoparticles-Based Vaccines for COVID-19. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boivin, G.P.; Bottomley, M.A.; Schiml, P.A.; Goss, L.; Grobe, N. Physiologic, Behavioral, and Histologic Responses to Various Euthanasia Methods in C57BL/6NTac Male Mice. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2017, 56, 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Adler, J.M.; Martin Vidal, R.; Langner, C.; Vladimirova, D.; Abdelgawad, A.; Kunecova, D.; Lin, X.; Nouailles, G.; Voss, A.; Kunder, S.; et al. An Intranasal Live-Attenuated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Limits Virus Transmission. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouailles, G.; Adler, J.M.; Pennitz, P.; Peidli, S.; Teixeira Alves, L.G.; Baumgardt, M.; Bushe, J.; Voss, A.; Langenhagen, A.; Langner, C.; et al. Live-Attenuated Vaccine sCPD9 Elicits Superior Mucosal and Systemic Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 Variants in Hamsters. Nat. Microbiol. 2023, 8, 860–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | Area |
|---|---|
| CVX-loaded CNPs | 5100.25 |
| BSA [0, 5] | 39,663.02 |
| BSA [0, 5] | 39,006.55 |
| BSA [0, 1] | 17,787.853 |
| BSA [0, 1] | 17,413.489 |
| BSA [0, 01] | 3315.82 |
| BSA [0, 01] | 2641.60 |
| BSA [0, 001] | 1558.11 |
| BSA [0, 001] | 1837.70 |
| Component | Concentration |
|---|---|
| NaCl | 7.45 g/L |
| KCl | 1.29 g/L |
| CaCl2 | 0.32 g/L |
| Double distilled water | q.s. |
| System | C Concentration (mg/mL) | Viscosity (mPa·s) | Average Size (nm) | Polydispersity Index (PDI) | ζ-Potential (mV) | Encapsulation Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNPs | 1 | 1.663 ± 0.002 a | 38.5 ± 9.1 a | 0.22 ± 0.05 a | +38.8 ± 1.2 a | --- |
| 2 | 2.967 ± 0. 005 b | 92.3 ± 6.6 b | 0.28 ± 0.04 ab | +40.4 ± 2.5 a | --- | |
| 5 | 6.012 ± 0.003 c | 316.8 ± 8.5 c | 0.30 ± 0.07 ab | +46.5 ± 5.1 a | --- | |
| CVX-CNPs | 1 | 1.671 ± 0.005 a | 87.9 ± 10.6 d | 0.29 ± 0.08 ab | +26.5 ± 2.6 b | 65.4 ± 3.8 a |
| 2 | 2.976 ± 0.008 b | 161.8 ± 11.9 e | 0.36 ± 0.11 ab | +11.7 ± 1.8 c | 84.8 ± 0.9 b | |
| 5 | 6.007 ± 0.004 c | 542.5 ± 40.1 f | 0.41 ± 0.09 b | +4.6 ± 1.2 d | 92.2 ± 1.5 c |
| Higuchi | Korsmeyer–Peppas | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| kH | R2 | n | R2 |
| 0.1197 | 0.9951 | 0.9092 | 0.977 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vega-Rojas, L.J.; Palomino, M.; Corona-Guerrero, I.; Ramos-López, M.Á.; Carbajo-Mata, M.A.; Vázquez-Olguín, D.; Campos-Guillen, J.; Amaro-Reyes, A.; Urbán-Morlán, Z.; Rodríguez-Morales, J.A.; et al. CHIVAX 2.1-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles as Intranasal Vaccine Candidates for COVID-19: Development and Murine Safety Assessment. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102453
Vega-Rojas LJ, Palomino M, Corona-Guerrero I, Ramos-López MÁ, Carbajo-Mata MA, Vázquez-Olguín D, Campos-Guillen J, Amaro-Reyes A, Urbán-Morlán Z, Rodríguez-Morales JA, et al. CHIVAX 2.1-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles as Intranasal Vaccine Candidates for COVID-19: Development and Murine Safety Assessment. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(10):2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102453
Chicago/Turabian StyleVega-Rojas, Lineth Juliana, Monserrat Palomino, Iván Corona-Guerrero, Miguel Ángel Ramos-López, María Antonieta Carbajo-Mata, Diana Vázquez-Olguín, Juan Campos-Guillen, Aldo Amaro-Reyes, Zaida Urbán-Morlán, José Alberto Rodríguez-Morales, and et al. 2025. "CHIVAX 2.1-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles as Intranasal Vaccine Candidates for COVID-19: Development and Murine Safety Assessment" Biomedicines 13, no. 10: 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102453
APA StyleVega-Rojas, L. J., Palomino, M., Corona-Guerrero, I., Ramos-López, M. Á., Carbajo-Mata, M. A., Vázquez-Olguín, D., Campos-Guillen, J., Amaro-Reyes, A., Urbán-Morlán, Z., Rodríguez-Morales, J. A., Mosqueda, J., & Pool, H. (2025). CHIVAX 2.1-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles as Intranasal Vaccine Candidates for COVID-19: Development and Murine Safety Assessment. Biomedicines, 13(10), 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102453











