Rikkosan’s Short-Term Analgesic Effect on Burning Mouth Syndrome: A Single-Arm Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients Selection
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Study Variables
2.4. Statistical Analysis
- Null hypothesis: The reduction in pain intensity is 2 points.
- Alternative hypothesis: The reduction in pain intensity is 2 points or more.
2.5. IRB Approval and Ethics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Russo, M.; Crafa, P.; Guglielmetti, S.; Franzoni, L.; Fiore, W.; Di Mario, F. Burning Mouth Syndrome Etiology: A Narrative Review. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2022, 31, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Classification of Orofacial Pain, 1st edition (ICOP). Cephalalgia 2020, 40, 129–221. [CrossRef]
- Currie, C.C.; Ohrbach, R.; De Leeuw, R.; Forssell, H.; Imamura, Y.; Jääskeläinen, S.K.; Koutris, M.; Nasri-Heir, C.; Huann, T.; Renton, T.; et al. Developing a research diagnostic criteria for burning mouth syndrome: Results from an international Delphi process. J. Oral Rehabil. 2021, 48, 308–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijs, J.; Lahousse, A.; Kapreli, E.; Bilika, P.; Saraçoğlu, İ.; Malfliet, A.; Coppieters, I.; De Baets, L.; Leysen, L.; Roose, E.; et al. Nociplastic Pain Criteria or Recognition of Central Sensitization? Pain Phenotyping in the Past, Present and Future. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, Z.; Renton, T.; Yiangou, Y.; Zakrzewska, J.; Chessell, I.P.; Bountra, C.; Anand, P. Burning mouth syndrome as a trigeminal small fibre neuropathy: Increased heat and capsaicin receptor TRPV1 in nerve fibres correlates with pain score. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2007, 14, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amos, K.; Yeoh, S.C.; Farah, C.S. Combined topical and systemic clonazepam therapy for the management of burning mouth syndrome: A retrospective pilot study. J. Orofac. Pain. 2011, 25, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Imamura, Y.; Okada-Ogawa, A.; Noma, N.; Shinozaki, T.; Watanabe, K.; Kohashi, R.; Shinoda, M.; Wada, A.; Abe, O.; Iwata, K. A perspective from experimental studies of burning mouth syndrome. J. Oral Sci. 2020, 62, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Felipe, C.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; López-Arjona, M.; Pardo-Marin, L.; Pons-Fuster, E.; López-Jornet, P. Response to Treatment with Melatonin and Clonazepam versus Placebo in Patients with Burning Mouth Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Xu, H.; Chen, F.M.; Liu, J.L.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Q.M. Efficacy evaluation of clonazepam for symptom remission in burning mouth syndrome: A meta-analysis. Oral Dis. 2016, 22, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, A.M.; Kuten-Shorrer, M.; Natto, Z.; Ariyawardana, A.; Mejia, L.M.; Albuquerque, R.; Carey, B.; Chmieliauskaite, M.; Miller, C.S.; Ingram, M.; et al. WWOM VII: Effectiveness of systemic pharmacotherapeutic interventions in the management of BMS: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Dis. 2023, 29, 343–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, S.; Carey, B.; Farag, A.M.; Kuten-Shorrer, M.; Natto, Z.S.; Ariyawardana, A.; Mejia, L.M.; Chmieliauskaite, M.; Miller, C.S.; Ingram, M.; et al. WWOM VII: Effectiveness of topical interventions in the management of burning mouth syndrome: A systematic review. Oral Dis. 2023, 29, 3016–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suga, T.; Tu, T.T.H.; Nagamine, T.; Toyofuku, A. Careful use of clonazepam and alpha lipoid acid in burning mouth syndrome treatment. Oral Dis. Den. 2022, 28, 846–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hato, H.; Sakata, K.-i.; Sato, J.; Asaka, T.; Ohga, N.; Yamazaki, Y.; Kitagawa, Y. Efficacy of rikkosan for primary burning mouth syndrome: A retrospective study. BioPsychoSocial Med. 2021, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, S.; Okada, K.; Matsushita, T.; Hegozaki, S.; Sakata, K.-i.; Kitagawa, Y.; Yamazaki, Y. Effectiveness of rikkosan gargling for burning mouth syndrome. Tradit. Kampo Med. 2017, 4, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, K.-i.; Yamazaki, Y.; Ohga, N.; Sato, J.; Asaka, T.; Yoshikawa, K.; Nakazawa, S.; Sato, C.; Nakamura, Y.; Kitagawa, Y. Clinical efficacy of a traditional Japanese (kampo) medicine for burning mouth syndrome. Tradit. Kampo Med. 2016, 3, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veilleux, M.-P.; Moriyama, S.; Yoshioka, M.; Hinode, D.; Grenier, D. A Review of Evidence for a Therapeutic Application of Traditional Japanese Kampo Medicine for Oral Diseases/Disorders. Medicines 2018, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumi-Nakaseko, H.; Chiba, K.; Goto, A.; Kambayashi, R.; Matsumoto, A.; Takei, Y.; Kawai, S.; Sugiyama, A. Electropharmacological Characterization of Licorice Using the Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes Sheets and the Chronic Atrioventricular Block Dogs. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2023, 23, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
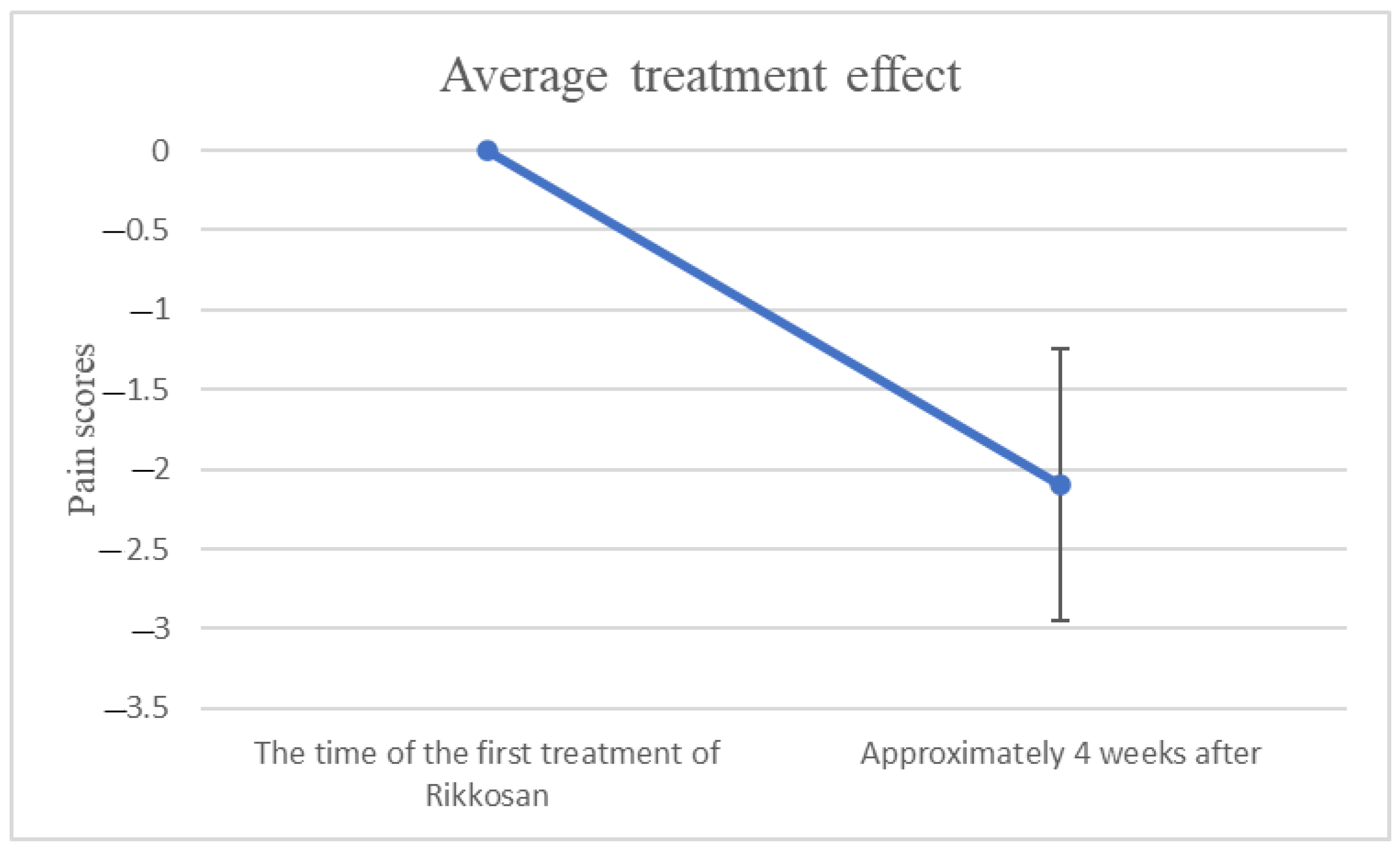
| Pain Scores | Pre | Post |
|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | 5.9 (2.5) | 3.8 (2.2) |
| Variable | Values |
|---|---|
| Paired t test’s p-value | 5.5 × 10−5 |
| The difference | 2.1 |
| Effect size | 1.2 |
| Standard deviation of change | 1.8 |
| Standard error of change | 0.41 |
| Kendall’s coefficient of concordance | 0.85 |
| Friedman’s test’s p-value | 3.7 × 10−5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Itagaki, T.; Nakamura, K.; Tanabe, T.; Shimura, T.; Nakai, Y.; Sakata, K.-i.; Sato, J.; Kitagawa, Y. Rikkosan’s Short-Term Analgesic Effect on Burning Mouth Syndrome: A Single-Arm Cohort Study. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12051013
Itagaki T, Nakamura K, Tanabe T, Shimura T, Nakai Y, Sakata K-i, Sato J, Kitagawa Y. Rikkosan’s Short-Term Analgesic Effect on Burning Mouth Syndrome: A Single-Arm Cohort Study. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(5):1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12051013
Chicago/Turabian StyleItagaki, Tatsuki, Keisuke Nakamura, Tougo Tanabe, Takumi Shimura, Yu Nakai, Ken-ichiro Sakata, Jun Sato, and Yoshimasa Kitagawa. 2024. "Rikkosan’s Short-Term Analgesic Effect on Burning Mouth Syndrome: A Single-Arm Cohort Study" Biomedicines 12, no. 5: 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12051013
APA StyleItagaki, T., Nakamura, K., Tanabe, T., Shimura, T., Nakai, Y., Sakata, K.-i., Sato, J., & Kitagawa, Y. (2024). Rikkosan’s Short-Term Analgesic Effect on Burning Mouth Syndrome: A Single-Arm Cohort Study. Biomedicines, 12(5), 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12051013





