Abstract
The damage caused by outbreaks of fire continues to be enormous despite ongoing improvements in fire detection and fighting. Therefore, the detection of fires at the earliest possible stage is essential. The latest developments in fire detection devices include the addition of carbon monoxide (CO) or temperature sensors into the widespread smoke detectors, but also alternative solutions are searched for. Advantageous is the direct detection of the most relevant fire gases CO and nitrogen dioxide (NO2), because they are produced very early in a developing fire. A sensitive, selective, and low-cost method to detect these gases is the use of colorimetric materials combined with a compact optical readout. In this review, we take account of recent developments in this research field and provide a comprehensive overview on suitable materials for CO and NO2 detection in fire gas sensing and first steps towards novel fire gas detectors.
1. Introduction
In the case of fire, every second counts to prevent the loss of life. In addition, for each additional minute of response time, property damage increases by 2%. Widespread, state of the art sensors are smoke detectors which are often not adequate to alarm inhabitants quickly enough. Also heat detectors measuring the ambient air temperature are too slow to react. With both technologies, nonsmoking fires, e.g., pure ethanol fires, cannot be detected. A viable alternative is the use of systems relying on gas detection rather than particle detection. In particular, gas sensors provide a faster and more accurate fire detecting mechanism since gases are produced prior to aerosols in a developing fire (Figure 1).
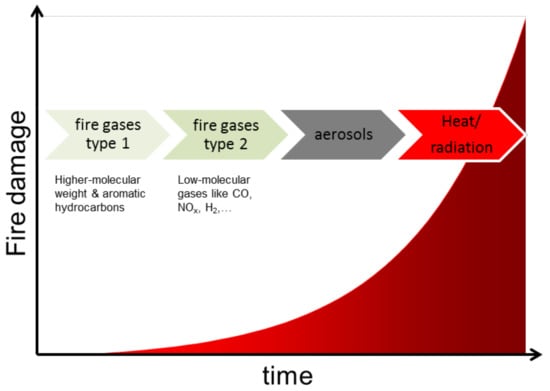
Figure 1.
Scheme of the damage caused by fire outbreak occurring over time related to the fire indicators gas, aerosol, and heat/radiation.
Fire gas detectors, if available, are mainly installed in large automatic fire detection systems, and contain electrochemical cells for carbon monoxide (CO). Often these CO-detecting cells are added to smoke detectors [,]. Research efforts have focused on metal oxide-based (MOX) gas sensors for this application for many years [,,,]. Fire gas detectors containing MOX sensors are commercially available only for some niche applications such as caravanning, motor boats etc., because they suffer from high power consumption and a lack of selectivity. Also suspended gate field effect transistors (SGFETs) were proposed for fire gas detection in literature, but have not been marketed until now [,].
The detection of gases based on chemical reactions developing a visible color change was patented already in 1919 in the USA as a new type of gas detector []. Their main intention was to detect CO in small quantities by making use of the color change of iodine in the presence of CO. With the introduction of the so-called Dräger tubes® in 1937, this principle has begun to find widespread use in fire gas detection. These single-use glass tubes, containing the reactive colorimetric material, are broken at one end upon use and permit a quantitative determination of the target gas. The concentration is read on a scale by the user.
Advances in the control of nanoparticles and synthesis of novel indicator molecules in combination with optical and micro-structuring methods now allow a conceptually new type of low-cost, ultra-low-power consuming fire gas detectors based on a colorimetric read-out. No other gas sensing principle for the specific detection of the two main fire indicator gases CO and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) can achieve energy self-sufficient, battery-supported operation for up to 10 years. In the search for suitable colorimetric materials, further requirements for fire detectors regarding sensitivity and selectivity must be considered: based on the data available for typical test fires (burning wood, ethanol, polyurethane, n-heptane), relative humidities vary between 25% and 40%. In addition to CO2, a significant increase of CO and NO2 concentrations develop in all test fires. For CO, the background concentration (no fire) is 1–3 ppm, this value increases to 5–100 ppm depending on the type of fire. NO2 is present in the environment in a background concentration of about 10 ppb and increases to 40 ppb to 3 ppm in the case of fire. Therefore, suitable colorimetric materials must yield detectable color reactions in the following concentration ranges:
- CO: 5–100 ppm
- NO2: 0.4–3 ppm
Furthermore, the colorimetric materials must be stable for a long period of time (several years) when used for fire gas detectors, especially regarding thermal stresses, i.e., in the case of a fire, the color reaction must still take place. Also, the response time of a sensor based on the colorimetric principle must lie in the range of a few seconds to alarm the inhabitants quickly enough. These factors, i.e., response time, stability and reproducibility of such sensors are crucially influenced by the sensor configuration and the matrix the colorimetric material is embedded in. Especially the matrices are the topic of ongoing research due to their decisive role in a sensor intended to be commercialized. In the following, we review currently known or available colorimetric materials suitable for the detection of CO and NO2 as relevant fire gases.
2. Materials for Carbon Monoxide Detection
The earliest description, dated back to 1928, of the colorimetric determination of CO in air or dissolved in blood can be found in []. The colorimetric material used there was iodine pentoxide (I2O5), which reacts with CO irreversibly as follows:
I2O5 + 5 CO → I2 + 5 CO2
Since the liberated iodine is very easy to detect as a reaction product, this reaction is still used today in the Dräger tubes®. In comparison, Figure 2 shows the extensive technical equipment used for the same purpose scarcely one hundred years ago:
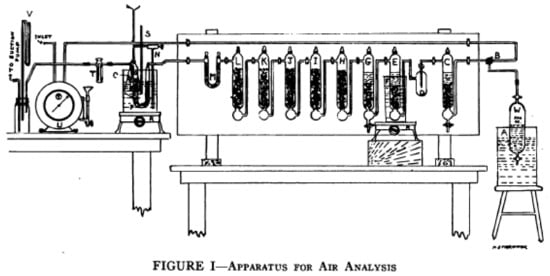
Figure 2.
Experimental setup for the determination of CO in air using I2O5. Reprinted with permission from [].
Martinek and his colleagues already reported a detection limit of 10 ppm in 1928, which roughly corresponds to the detection limit of the Dräger tubes®. About a decade later, the reaction of palladium(II) chloride (PdCl2) with CO was described for the first time []:
CO + PdCl2 + H2O → Pd + CO2 + 2 HCl
In this method, the concentration of unreacted PdCl2 is subsequently determined using potassium iodide and the CO concentration is calculated therefrom.
PdCl2 + 2 KI → PdI2 + 2 KCl
However, the potassium iodide solution is relatively unstable, but can be replaced by other color indicators. Initially, the color reaction was determined using standard solutions of known concentrations. Later, this comparative method was replaced by spectroscopy []. At about the same time, a palladium-ammonium molybdate compound was proposed and patented for the determination of CO [,]. In this case, pure palladium is dissolved in sulfuric acid to produce palladium sulfate as catalyst. Ammonium molybdate hexahydrate ((NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O) is dissolved in water and added in about 30-fold excess to the palladium sulfate. The carrier or matrix used was silica gel. With this method, a yellow solution turns blue in the presence of CO (cf. reaction Scheme 1). A sensor based on this reaction was patented in 1984 by Herskovitz and colleagues []. In 1964, another method was published []: CO reacts in a basic solution with the silver salt of p-sulfaminobenzoic acid. The absorption of the silver colloid solution is determined spectrometrically and is proportional to the CO concentration. With this method it was possible to measure CO concentrations between 5 and 180 ppm with an accuracy of 95 ± 5%.
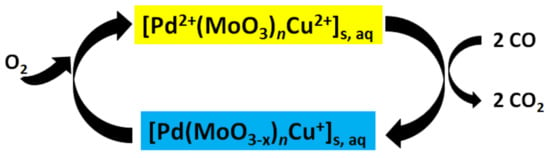
Scheme 1.
Reaction scheme for the reversible detection of CO.
Lambert and colleagues [,] also used palladium chloride to determine CO. The actual colorimetric determination, however, was accomplished by the reduction of the iron complex [Fe(III)EDTA]− to [Fe(II)EDTA]2−. The latter compound triggers ligand exchange with L = 2,2′-dipyridyl or 1,10-phenathroline to form the stable [FeL3]2+ compound, the color of which can be determined spectrophotometrically in the blue/green wavelength range. Sodium molybdate was added as a catalyst. In further experiments they used, in addition to the palladium chloride compound, iodate and Leuco Crystal Violet (4,4′,4′′-methylidynetris(N,N-dimethylaniline) which turns violet in the presence of CO, both as a function of the reaction time the CO concentration. Instead of Leuco Crystal Violet, a promazine hydrochloride complex, also in combination with palladium chloride, was described for colorimetric determination a few years later []. Another publication reports the use of pyronine-G, which is converted to benzene (also with PdCl2 and iodate as base). The absorption of benzene is proportional to the CO concentration in a range of 20–400 ppm with a detection limit of 1 ppm []. Still in 1977, Shuler and Schrauzer patented a method for measuring reducing gases []. Here, a reversible reaction for CO determination was described for the first time: palladium sulfate serves as a catalyst for the intrinsically slow reaction of CO with ammonium molybdate, which changes from yellow to blue, and the reverse reaction with atmospheric oxygen to the ground state (Scheme 1). For the reverse reaction, a metal salt is needed (e.g., copper, iron, nickel chloride, sulfate, etc.).
In a similar fashion, Goswami and colleagues patented in 1994 a specific and reversible CO sensor [] based on molybdenum or tungsten salts with palladium salts as catalyst and metal salts for the reverse reaction. In general, the following redox reaction takes place:
2 Mo6+ + 3 CO + 3 H2O → 2 Mo3+ + 3 CO2 + 6 H+
This reaction proceeds only very slowly, therefore palladium salts are used as catalyst:
Pd2+ + CO + H2O → Pd0 + CO2 + 2 H+
3 Pd0 + 2 Mo6+ → 3 Pd2+ + 2 Mo3+
3 Pd0 + 2 Mo6+ → 3 Pd2+ + 2 Mo3+
For the reverse reaction the metal salts, e.g., iron compounds, are used:
Mo3+ + 3 Fe3+ → Mo6+ + 3 Fe2+
The atmospheric oxygen is sufficient for this reverse reaction, and the molybdenum compound regains its initial state and can react again. Another, relatively simple method was presented by Pal and colleagues in 1987 []. They used silver nitrate (AgNO3) as an indicator in a gelatine solution and were thus able to determine CO in the concentration range of 2–100 ppm, with a standard deviation of 2.6% at 10 ppm CO.
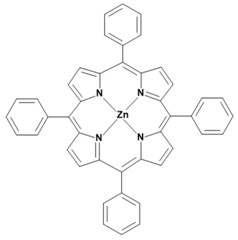
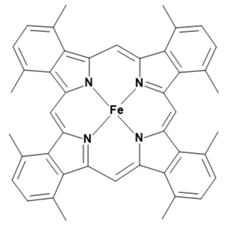
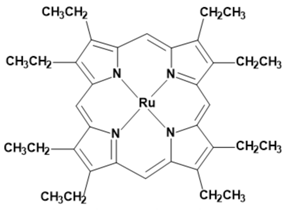
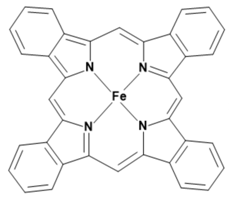
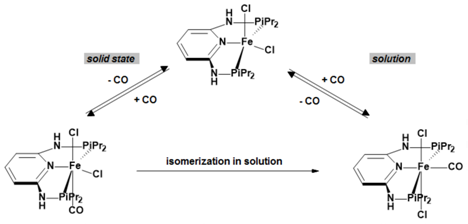
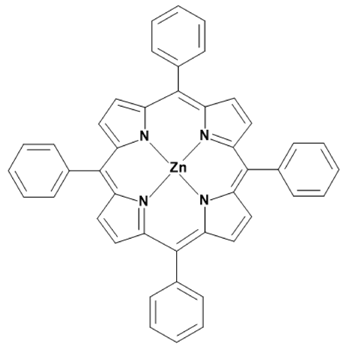
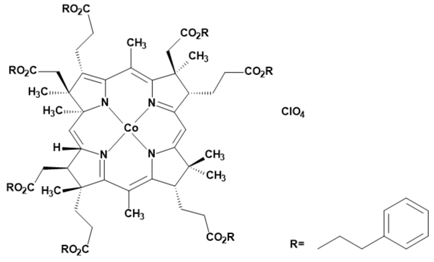
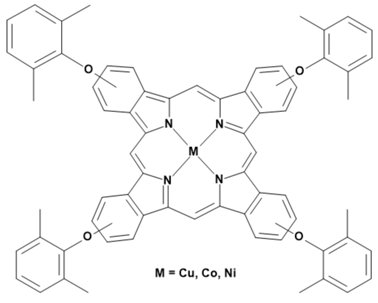
Metalloporphyrins and metallophthalocyanines can also be used for the detection of CO. The reactions of these metal compounds with CO are reversible. Table 1 presents a compilation of currently known complexes:

Table 1.
Metal complexes for the detection of CO.
Another promising material for CO detection is based on binuclear rhodium complexes. They show a fast and selective reaction towards CO and are completely reversible [,,]. The general reaction scheme of the rhodium complexes [Rh2{(XC6H3)P(XC6H4)}n(OCR)2]∙A2 with CO is shown in Figure 3. Table 2 gives the definition of possible ligands. An investigation of different rhodium complexes, obtained by varying the residues of the phosphines, regarding their reaction velocity towards CO exposure is published in [].
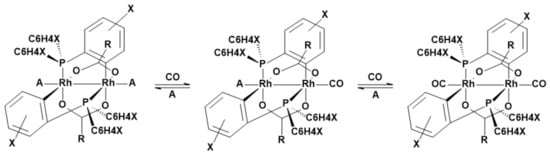
Figure 3.
General two-step reaction scheme of the binuclear rhodium complex with the formula [Rh2{(XC6H3)P(XC6H4)}n(OCR)2]∙A2. The color of the complex turns from violet to orange-yellow. Cf. Table 2 for the definition of the ligands.

Table 2.
Ligands of the rhodium compounds 1∙(A)2–5∙(A)2.
3. Materials for Nitrogen Dioxide Detection
Colorimetric materials for NO2 can roughly be divided into three types: the first is essentially based on the N-(1-naphthyl)-ethylenediamine (NED) proposed by Saltzman in 1954 for the first time for NO2 determination [], the second of Jacobs and Hochheiser 1958 [], and the third, on metal complexes. In the following the three classes are briefly described:
3.1. Saltzman Method
The Saltzman method originally uses a mixture of sulfanilic acid, NED, and acetic acid. Thus, a stable staining could be achieved upon contact of the solution with NO2 with a detection limit of a few ppb. The solution had a low cross-sensitivity to ozone, for other gases it was negligible. The Saltzman method is one of the most sensitive colorimetric determination methods for NO2 and has the advantage that all reagents are mixed in a solution and the color reaction develops over time. However, only a moderate long-term stability of the solution is also reported. However, this does not have to apply to an indicator layer in a suitable matrix, e.g., a polymer.
In detail, the reaction proceeds as follows: sulfanilic acid and NED form nitrite ions in contact with NO2, which are detected by the color reaction. Nitrite reacts in acidic medium (acetic acid) to the nitrosyl cation:
NO2− + 2 H+ → NO+ + H2O.
The nitrosyl cation causes sulfanilic acid and NED to form an azo dye (red-violet). In this case, first a diazotization reaction takes place, in which a diazonium ion is formed; this is followed by azo coupling (in the para-position to the NH2 group of 1-naphthylamine). Figure 4 shows the partial reactions.
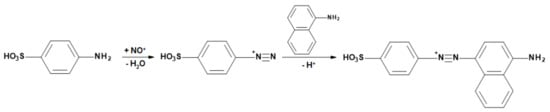
Figure 4.
Partial reactions in the Saltzman method: the nitrosyl cation causes sulfanilic acid and NED to form an azo dye (red-violet). In this case, the first step is the diazotization reaction, in which a diazonium ion is formed; this is followed by the azo coupling.
Thomas and colleagues further developed the method and implemented a calibration because the color change reaction is not linear []. Further modifications of the Saltzman method can be found in [,]. Huygen [] compared various azo dyes, including N,N-(1-naphthyl,acetyl) ethylenediamine-toluene monosulfate (ANEDA), N-(1-naphthyl)ethylenediamine dihydrochloride (NEDA), 1,8-diaminonaphthalene, 1-naphthylamine, and dimethylaniline. The first three yielded the best results. Nash [] additionally added basic guaiacol solution to the reagents and buffered with glycerol. This resulted in a higher stability of the solution.
Smith patented a variation of the Saltzman method in 1972, in which a kind of paste was developed by addition of e.g., MgSO4 and glycerol, and this paste was further processed it into a pellet. As a result, the stability of the reagents could be further improved; moreover, this method allowed the measurement directly in air without the need for any equipment by means of a small sensor [].
About 20 years ago, Tanaka and colleagues intensified the work on colorimetric NO2 sensors [,,,]. Instead of NED, they used N,N-dimethyl-1-naphthylamine (NA) and, through the use of porous glass, also increased the active surface, which further increased the sensitivity of the sensors (<100 ppb). Figure 5 shows the structural formulas of the reagents used, Figure 6 shows an example of the absorption spectra of the reagents when exposed to NO2.
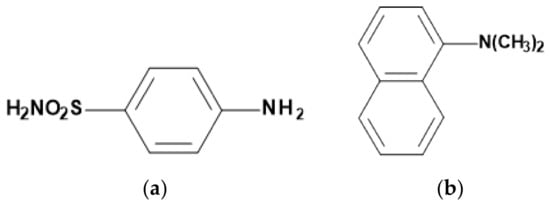
Figure 5.
Structural formulas of (a) sulfanilamide (SA) and (b) N,N-dimethyl-1-naphthylamine (NA).
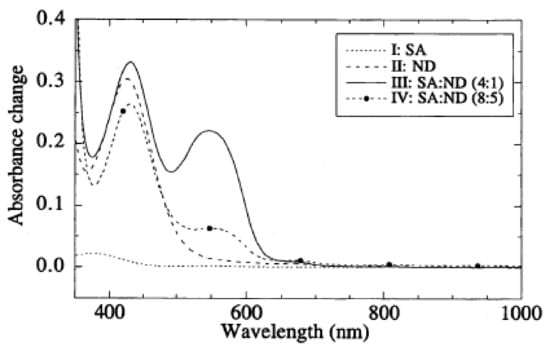
Figure 6.
Absorption spectra of porous glass slides with Saltzman reagents, after exposure to 600 ppb NO2 for 8 h (flow rate 1 L/min): with sulfanilamide (SA) (I), N,N-dimethyl-1-naphthylamine (ND) (II), SA and ND (4:1) (III), and SA and ND (8:5) (IV). Reprinted with permission from [].
The investigation of further redox indicators from the group of aromatic amines is still ongoing: Alexy et al. used N,N′-diphenyl-1,4-phenylenediamine (DPPD), o-dianisidine, N,N′-diphenylbenzidine (DPB) and N,N,N′,N′-tetramethyl-1,4-phenylenediamine (TMPD) immobilized in a gas-permeable polymeric layers for NO2 sensing []. TMPD was found to be highly selective towards NO2 with no cross-sensitivities to other relevant gases [,].
3.2. Jacobs and Hochheiser Method
In the Jacobs and Hochheiser method from 1958, 0.1 m NaOH is used as the absorption medium and the sulfanilamide is dissolved in phosphoric acid. The indicator, as in the Saltzman method, is NED. The colorimetric reaction is readout spectrophotometrically. This reaction was used in an automatic sequence sampler to monitor NO2 emissions in urban areas on a 24 h basis. The reaction is also sensitive to sulfur dioxide, but when oxidized to sulfate by adding hydrogen peroxide, this does not interfere with the reaction. The limit of detection of the Jacobs and Hochheiser method is in the ppb range. Later, sodium arsenite was also used as the absorption medium, this being referred to as a modified Jacobs and Hochheiser method.
3.3. Metal Complexes
Similar to the detection of CO, also NO2 can be measured using different types of metal complexes. Table 3 gives an overview of the metal complexes used for NO2 detection that can be found in literature.

Table 3.
Metal complexes for the detection of NO2.
3.4. Other Methods
In 1984 Bajeva and colleagues presented another simple and sensitive method for the determination of NO2 []: guaiacol is used in basic solution both as an absorption medium and a coupling reagent. With p-nitroaniline, a red dye is formed after the diazotization reaction. Information on the detection limit cannot be found here. Raman used benzidine in 1991 for the diazotization reaction with orcinol after NO2 was absorbed onto sodium arsenite. This reaction causes a yellow color (460 nm), which can be detected spectroscopically []. The absorption according to Lambert-Beer is given as linear in the concentration range of 0.04–0.48 μg/mL nitrite [].
A year later, Kaveeshwar and colleagues [] published a similar procedure to Bajeva’s: o-nitroaniline is used as an absorption and diazotization reagent. The red-violet color reaction results from coupling to 1-amino-2-naphthalene sulfonic acid (ANSA). Kumar and colleagues presented in 1993 a further modification of the above-mentioned methods []: they again used sodium arsenite as an absorption medium and p-nitroaniline and chromotropic acid in acetate solution for the color reaction. The resulting solution has a maximum absorption at 515 nm and is reported as linear in the concentration range of 0–20 μg/mL nitrite. This method was also compared with the Saltzman method, and the detection limit was determined to be 0.5 μg/mL. In Pandurangappa et al. also sodium arsenite as an absorption medium is mentioned []. The color reaction is based on the reaction of nitrite with aminophenyl benzimidazole in an acidic environment and NED as an indicator. The maximum absorption is 555 nm and is described as linear according to Lambert-Beer in the concentration range 0–10 μg in 25 mL solution. Parmar et al. [] used, in addition to sodium arsenite as the absorption medium, aminoacetophenone in acidic solution and phloroglucinol as an indicator with an absorption maximum at 420 nm. The detectable concentration range is given as 0.008–0.12 μg/mL.
4. Conclusions
The present review shows the results of a literature search on currently known or available colorimetric materials for the detection of CO and NO2; the focus was on their suitability for implementation in fire gas detectors. In principle, irreversible compounds are available for single-use sensors for CO such as iodine pentoxide in Dräger tubes®, or reversible indicator molecules for long-term warning sensors, such as different binuclear rhodium complexes, molybdenum compounds with catalysts, or different (metallo-)porphyrins or (metallo-)phthalocyanines. Iron pincer complexes are promising, but their investigation is still basic research. For NO2 detection, sensors based on azo dyes such as NED-based reagents or TMPD, have shown good results, but also metal complexes such as porphyrins or phthalocyanines. Table 4 summarizes the results.

Table 4.
Summary of colorimetric compounds suitable for CO and NO2 detection in fire gases.
Yet for an implementation in fire gas sensors, not only the gas sensing characteristics of the colorimetric compound itself is decisive, but also its long-term stability in changing environments, i.e., temperature and humidity variations. Also, hazardous compounds will probably not come into use (sodium arsenite, azo dyes). Another crucial influence on the sensing characteristics has the matrix in which the colorimetric material is embedded. The matrix must ensure gas permeability and, at the same time, be thermally stable in a fire and insensitive to variations in the relative humidity in the environment. Further challenging is the response time of a sensor based on the colorimetric principle, which is influenced not only by the material itself, but also by the sensor configuration and the matrix. Sensor response times of a few seconds can be already achieved []. Future research should address the development of a matrix with the abovementioned characteristics, in combination with low-cost and compact optical sensors for read-out. This will play a vital role for the implementation of the colorimetric principle in commercial fire gas detectors.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge financial support from the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF—FKZ 13N14076).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gutmacher, D.; Hoefer, U.; Wöllenstein, J. Gas sensor technologies for fire detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 175, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duric, A.; Ebner, H.; Forster, M.; Vinage, I. Development of a multi-sensor detector for fire detection and life safety applications. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Automatic Fire Detection AUBE 2009, Duisburg, Germany, 8–10 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Solorzano, A.; Fonollosa, J.; Fernandez, L.; Eichmann, J.; Marco, S. Fire detection using a gas sensor array with sensor fusion algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2017 ISOCS/IEEE International Symposium on Olfaction and Electronic Nose (ISOEN), Montreal, QC, Canada, 28–31 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Reimann, P.; Schütze, A. Fire detection in coal mines based on semiconductor gas sensors. Sens. Rev. 2012, 32, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, G.F.; Cavanagh, L.M.; Afonja, A.; Binions, R. Metal oxide semi-conductor gas sensors in environmental monitoring. Sensors 2010, 10, 5469–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conrad, T.; Reimann, P.; Schütze, A. A hierarchical strategy for under-ground early fire detection based on a T-cycled semiconductor gas sensor. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors, Atlanta, GA, USA, 28–31 October 2007; pp. 1221–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohle, R.; Simon, E.; Schneider, R.; Fleischer, M.; Sollacher, R.; Gao, H.; Müller, K.; Jauch, P.; Loepfe, M.; Frerichs, H.-P.; Wilbertz, C. Fire detection with low power fet gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 120, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischer, M. Advances in application potential of adsorptive-type solid state gas sensors: High-temperature semiconducting oxides and ambient temperature GasFET devices. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, A.B.; Hoover, C.R. Gas-Detector. U.S. Patent US1,321,062, 4 November 1919. [Google Scholar]
- Martinek, M.J.; Marti, W.C. Modified iodine-pentoxide method for determination of carbon monoxide in air and blood. Am. J. Public Health 1928, 19, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christman, A.A.; Block, W.D.; Schultz, J. Determination of carbon monoxide in air. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1937, 9, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.H.; Root, W.S. Colorimetric determination carbon monox-ide in air by an improved palladium chloride method. J. Biol. Chem. 1955, 216, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, M. Rapid determination of small amounts of carbon monoxide. Anal. Chem. 1947, 19, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, G.M. Colorimetric Gas Detection. U.S. Patent US2,487,077, 8 November 1947. [Google Scholar]
- Herskovitz, T.; Peet, W.G. Composition, Indicator, Process and Device for Detecting Carbon Monoxide. U.S. Patent US4,482,635, 13 November 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Levaggi, D.A.; Feldstein, M. The colorimetric determination of low concentration of carbon monoxide. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1964, 25, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, J.L.; Hamlin, P.A. A New Colorimetric Reagent for Carbon Monoxide. Anal. Lett. 1971, 4, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.L.; Wiens, R.E. Induced colorimetric method for carbon monoxide. Anal. Chem. 1974, 46, 929–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.K. Determination of carbon monoxide by means of a palla-dium-promazine complex. J. Anal. Toxicol. 1977, 1, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvapathy, P.; Pitchai, R.; Ramakrishna, T.V. A rapid spectropho-tometric method for the determination of carbon monoxide in ambient air. Talanta 1990, 37, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuler, K.E.; Schrauzer, G.N. Catalyst and Method for Oxidizing Reducing Gases. U.S. Patent US4,043,934, 23 October 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Goswami, K.; Saini, D.P.S.; Klainer, S.M.; Ejiofor, C.H. Specific and Reversible Carbon Monoxide Sensor. U.S. Patent US5,302,350, 12 April 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, T.; Ganguly, A.; Maity, D.S. Silver-gelatin method for the de-termination of trace amounts of carbon monoxide in air. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1987, 60, 3001–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, D.; Alimelli, A.; Di Natale, C.; Paolesse, R.; D’Amico, A.; Lundström, I. Chemical Sensing with Familiar Devices. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 3800–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, B.R.; Reimer, K.J.; Wong, T.C.T. Reaction of carbon monoxide with ferrous porphyrins. Kinetics and equilibria for the binding of carbon monoxide to octamethyltetrabenzoporphyriniron(II) derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977, 99, 4815–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaton, G.R.; Eaton, S.S. Reversible carbon monoxide binding by ruthenium carbonyl porphyrins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 235–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Sánchez, J.F.; Fernández, I.; Steiger, R.; Beer, R.; Cannas, R.; Spichiger-Keller, U.E. Second generation nanostructured metal oxide matrices to increase the thermal stability of CO and NO2 sensing layers based on iron(II) phthalocyanine. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito-Garagorri, D.; Puchberger, M.; Mereiter, K.; Kirchner, K. Stereospecific and reversible CO binding at iron pincer complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 9142–9145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteban, J.; Ros-Lis, J.V.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Marcos, M.D.; Moragues, M.; Soto, J.; Sancenón, F. Sensitive and selective chromogenic sensing of carbon monoxide by using binuclear rhodium complexes. Angew. Chem. 2010, 49, 4934–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moragues, M.E.; Esteban, J.; Ros-Lis, J.V.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Marcos, M.D.; Martínez, M.; Sancenón, F. Sensitive and selective chromogenic sensing of carbon monoxide via reversible axial CO coordination in binuclear rhodium complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15762–15772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moragues, M.E.; Esteban, J.; Ros-Lis, J.V.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Marcos, M.D.; Martínez, M.; Sancenón, F. An optoelectronic sensing device for CO detection in air based on a binuclear rhodium complex. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 191, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantik, K.; Schmitt, K.; Pannek, C.; Miensopust, L.; Wöllenstein, J. Investigation of Gasochromic Rhodium Complexes Regarding Their Reactivity towards CO. Multidiscip. Dig. Publ. Inst. Proc. 2017, 1, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltzman, B.E. Colorimetric Microdetermination of nitrogen dioxide in atmosphere. Anal. Chem. 1954, 26, 1949–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, M.B.; Hochheiser, S. Continuous sampling and ultramicrodetermination of nitrogen dioxide in air. Anal. Chem. 1958, 30, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.D.; MacLeod, J.A.; Robbins, R.C.; Goettelman, R.C.; Elridge, R.W.; Rodgers, L.H. Automatic apparatus for determination of nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide in the atmosphere. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 1810–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huygen, I.C. Reaction of nitrogen dioxide with Griess type reagents. Anal. Chem. 1970, 42, 407–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nash, T. An efficient absorbing reagent for nitrogen dioxide. Atmos. Environ. 1970, 4, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.B. Colorimetric Indicator for the Detection of Nitrogen Dioxide. U.S. Patent US3,681,027, 1 October 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, T.; Ohyama, T.; Maruo, Y.Y.; Hayashi, T. Coloration reactions between NO2 and organic compounds in porous glass for cumulative gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1998, 47, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruo, Y.Y.; Tanaka, T.; Ohyama, T.; Hayashi, T. System for detecting environmental ppb-level nitrogen dioxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1999, 57, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Guilleux, A.; Ohyama, T.; Maruo, Y.Y.; Hayashi, T. A ppb-level NO2 gas sensor using coloration reactions in porous glass. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1999, 56, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyama, T.; Maruo, Y.Y.; Tanaka, T.; Hayashi, T. A ppb-level NO2 detection system using coloration reactions in porous glass and its humidity dependence. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 64, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexy, M.; Hanko, M.; Rentmeister, S.; Heinze, J. Disposable optochemical sensor chip for nitrogen dioxide detection based on oxidation of N,N′-diphenyl-1,4-phenylenediamine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 114, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannek, C.; Schmitt, K.; Wöllenstein, J. Colorimetric materials for gas selective sensing in low-power applications. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems (TRANSDUCERS), Anchorage, AK, USA, 21–25 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pannek, C. Mikrosystem zur Brandgasdetektion nach dem Farbumschlagsprinzip. PhD Thesis, University of Freiburg, Freiburg, Germany, 2014. (In German). [Google Scholar]
- Nezel, T.; Spichiger-Keller, U.E.; Ludin, C.; Hensel, A. Gas-Selective Optical Sensors for Fire Detectors. CHIMIA Int. J. Chem. 2001, 55, 725–731. [Google Scholar]
- Kudo, T.; Kimura, M.; Hanabusa, K.; Shirai, H.; Sakaguchi, T. Fabrication of gas sensors based on soluble phthalocyanines. J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines 1999, 3, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basova, T.V.; Koltsov, E.K.; Igumenov, I.K. Spectral investigation of interaction of copper phthalocyanine with nitrogen dioxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 105, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baveja, A.K.; Chaube, A.; Gupta, V.K. Extractive spectrophotometric method for the determination of atmospheric nitrogen dioxide. Atmos. Environ. 1984, 18, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, V. Spectrophotometric determination of nitrogen dioxide. Microchem. J. 1991, 44, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaveeshwar, R.; Amlathe, S.; Gupta, V.K. An efficient absorbing system for spectrophotometric determination of nitrogen dioxide. Atmos. Environ. 1992, 26A, 1025–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.S.M.; Srikanth, T.R.; Balasubramanian, N. Spectrophotometric determination of nitrogen dioxide in air. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1993, 345, 592–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandurangappa, M.; Venkataramanappa, Y. Aminophenyl benzimidazole as a new reagent for the estimation of NO2/Nitrite/Nitrate at trace level: Application to environmental samples. Anal. Lett. 2007, 40, 2974–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, P.; Pillai, A.K.; Gupta, V.K. A sensitive spectrophotometric determination of nitrogen dioxide in the working atmosphere. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2009, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).