Abstract
The analysis of wastewater is essential in environmental chemistry, particularly for monitoring emerging contaminants and assessing ecological impacts. In this context, hyphenated chromatographic techniques are widely used, with liquid chromatography being one of the most common. However, gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC-MS) remains a valuable tool in this field due to its sensitivity, selectivity, and widespread availability in most laboratories. This review examines the application of validated methods for wastewater analysis using GC-MS (MS), highlighting its relevance in identifying micropollutants such as pharmaceuticals, drugs of abuse, pesticides, hormones, and industrial by-products. The validation of analytical methods is crucial to ensuring the reliability and reproducibility of data and the accurate monitoring of contaminants. Key parameters, including sample volume, recovery efficiency, and detection and quantification limits, are discussed, evaluating different approaches to optimising the identification of different classes of contaminants. Additionally, this study explores advances in sample preparation techniques, such as solid-phase microextraction (SPME), dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME), and solid-phase extraction (SPE), which enhance efficiency and minimise interferences in the analysis. Finally, future perspectives are discussed, including the integration of emerging technologies such as high-resolution mass spectrometry, the miniaturisation of GC systems, and the development of faster and more sustainable analytical methods.
1. Introduction
Wastewater refers to all effluents resulting from human activities, including domestic sewage, industrial and agricultural discharges, and runoff contaminated with chemical compounds and organic matter [1]. These effluents contain a wide range of pollutants which, if not effectively removed by wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs), can pose risks to public health and cause environmental damage [2]. Urban and industrial expansion has intensified the need for stricter wastewater management and more efficient treatment processes, making this one of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time [3].
Wastewater contaminants originate from diverse sources. Upon reaching WWTPs, influents may contain substances such as pharmaceuticals, pesticides, hormones, preservatives, and plasticisers [3]. The number of identified pollutants varies depending on the origin of the effluents. For instance, Zhang et al. [3] identified 3967 different compounds, whereas broader global inventories estimate the presence of over 350,000 chemical substances [4].
The detection and study of these pollutants have raised increasing concern, particularly with regard to so-called contaminants of emerging concern, such as pharmaceuticals and personal care products. These compounds require ongoing monitoring and continual advancements in identification and treatment technologies [5]. At present, conventional monitoring approaches can detect only a limited number of substances—typically those already regulated by environmental legislation. Nonetheless, recent improvements in the sensitivity and selectivity of analytical instrumentation, combined with the development of more sophisticated purification and sample concentration techniques, have enhanced the effectiveness of WWTPs [6]. Research in this area has progressed significantly in recent years, with numerous studies contributing to the detection and quantification of contaminants, as well as the development of strategies for their removal. Despite these advances, water contamination persists as a challenge, particularly where treatment facilities lack the necessary equipment [6,7].
The European Union (EU) has recently revised the Urban Wastewater Treatment Directive to more effectively address the presence of contaminants in wastewater. The updated directive broadens its scope to include smaller urban agglomerations and introduces specific requirements for the removal of micropollutants, including pharmaceuticals and cosmetics [8]. It also underscores the environmental risks posed by non-domestic wastewaters, as urban WWTPs often receive discharges from industrial facilities, hospitals, and commercial districts. These discharges may contain pollutants not currently covered by legislation, such as heavy metals, microplastics, micropollutants, and other chemicals, including per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAs). Member States are therefore expected to periodically assess such pollution in order to adapt treatment procedures at WWTPs where non-urban pollutants are present. However, it is important to note that this update will only enter into force in August 2027.
One of the most significant changes introduced is the mandatory implementation of quaternary treatment in WWTPs treating loads of 150,000 population equivalents or more by 2045. This additional stage employs advanced technologies—such as ozonation, activated carbon, and innovative membrane systems—with the aim of removing over 80% of the micropollutants present in wastewater [8].
The real-time analysis of pollutants serves not only to alert the public to potential environmental and human health risks but also to strengthen regulatory enforcement. Analytical techniques are also applied in forensic investigations, for example, to detect illicit substances, and in environmental monitoring, assisting authorities in identifying sources of pollution, such as industries discharging untreated effluents into aquatic environments. Simultaneously, these data help WWTP teams to optimise treatment processes, supporting a more effective and sustainable approach to wastewater management [6].
Monitoring wastewater pollutants is equally essential for assessing the environmental impact of human activities. To this end, analytical methods based on chromatography are frequently developed and optimised, as researchers aim to detect contaminants of emerging concern that threaten ecosystems and public health, even at trace levels [9,10]. These emerging pollutants can affect aquatic systems through their toxicity to wildlife—acting as endocrine disruptors, or genotoxic or carcinogenic agents—or by altering growth rates in algae and plants, for instance, by inhibiting microorganisms [11].
In this context, liquid chromatography (LC), often coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), is the predominant technique due to its capacity to identify non-volatile and polar compounds. However, the complex composition of wastewater, which contains high concentrations of organic and inorganic matter, can lead to matrix effects that reduce the sensitivity of LC-MS/MS analyses. To address this, intensive sample pre-treatment is often necessary [9,10].
An alternative technique is gas chromatography (GC), frequently combined with mass spectrometry and/or tandem mass spectrometry. GC is particularly suitable for the analysis of volatile and thermally stable compounds. Limitations related to compound volatility can often be overcome through derivatisation, a process that enhances volatility and, consequently, analytical sensitivity. Although LC has become widely associated with the detection of contaminants of emerging concern, GC remains a valuable and widely employed methodology in environmental pollutant analysis [12,13].
Alongside chromatographic techniques, sample pre-treatment plays a crucial role. Like other environmental matrices, wastewater is highly complex and contains numerous interfering substances. These interferents can lead to co-elution and high background noise, thereby impairing the detection of trace-level analytes. Effective removal of such substances contributes to the preconcentration of target compounds and enhances the overall specificity of the analytical method [14].
To this end, various extraction and clean-up procedures are employed. Among the most commonly used are solid-phase extraction (SPE) and liquid–liquid extraction (LLE), both offering high recovery rates and potential for automation. However, SPE often involves single-use cartridges, increasing operational costs, while LLE typically requires large volumes of organic solvents. In recent years, microextraction techniques such as solid-phase microextraction (SPME) and dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME) have emerged as alternatives. Despite their potential, these methods are not yet routinely adopted due to either lower recovery rates or the complexity of their protocols [15].
This review article highlights the relevance of wastewater analysis from both environmental and public health perspectives, with a particular focus on gas chromatography as a valuable tool for enhancing analytical accuracy and efficiency. Environmental matrices such as wastewater offer critical insights into illegal industrial discharges, WWTP performance, and the improper disposal of pharmaceuticals and illicit substances. By improving the detection and quantification of contaminants of emerging concern, these techniques play a vital role in regulatory enforcement and the protection of environmental and human health.
2. Materials and Methods
This article examines validated analytical methods employing gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and tandem mass spectrometry (GC-MS/MS) for the detection and quantification of micropollutants in wastewater samples, focusing on studies published from 2019 to the present. The data retrieved are critically assessed with regard to their analytical applications.
A comprehensive literature search was conducted using the Web of Science and PubMed databases (accessed on 14 January 2025), employing the search terms detailed in Figure 1.
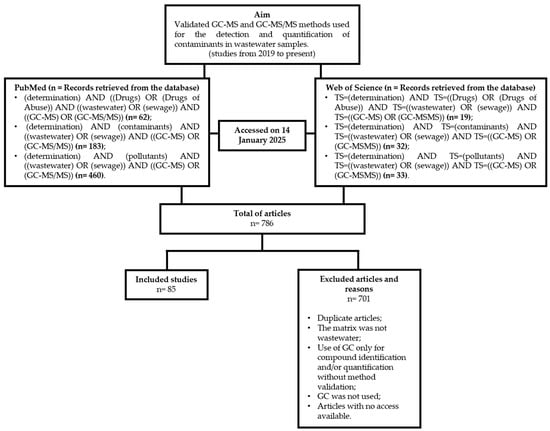
Figure 1.
Flowchart of the article selection process, detailing the research objective, databases consulted, search keywords used, number of records retrieved, studies included and excluded, and the criteria applied for exclusion.
The selection of articles was performed independently by two of the authors, based on their relevance to the objectives of this review. Studies that employed GC-MS or GC-MS/MS solely for compound identification, without method validation, were excluded from consideration.
3. Classification of Contaminants
The selected articles were categorised according to the types of contaminants analysed. In the following subsections, these categories are explored in detail, accompanied by a critical discussion of the findings. The tables in each section summarise the application of validated GC-MS and GC-MS/MS methods in the analysis of wastewater samples.
3.1. Pesticides and Polychlorinated Biphenyls
Pesticides comprise a broad group of chemical compounds used in both agricultural and domestic settings, including herbicides, fungicides, insecticides, and related derivatives. Their primary function is to control pests, weeds, and crop diseases, and their use has increased markedly in response to population growth and the corresponding rise in global food demand [16]. These compounds exhibit diverse chemical properties, particularly with respect to their acid–base character, and may be classified as basic, neutral, or acidic. Such classifications influence their solubility in wastewater. As wastewater generally exhibits an acidic pH, basic pesticides tend to be more soluble, rendering them more persistent in aquatic environments and more difficult to remove through conventional treatment processes [17,18]. The European Union’s water policy establishes specific regulatory thresholds to control and limit the presence of pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in water resources, with the objective of protecting both human health and the environment. Directive (EU) 2020/2184 of the European Parliament and of the Council, concerning the quality of water intended for human consumption, sets parametric values for individual pesticides and for the total pesticide content in drinking water. The combined concentration of all detected pesticides must not exceed 0.50 μg/L [19].
PCBs are organochlorine compounds historically used in dielectric fluids, paints, and plastics. Although banned in many countries, these substances continue to be detected in wastewater due to their high environmental persistence and the improper disposal of outdated equipment [20]. PCBs lack ionisable acidic or basic functional groups and are chemically neutral. They are characterised by very low water solubility and high lipophilicity, contributing to their pronounced chemical stability, low biodegradability, and capacity for widespread environmental dissemination [21,22]. As a result, they are commonly found not only in municipal and domestic wastewater and in WWTPs associated with industrial processes, but also in effluents from medical facilities—posing a significant risk to environmental and public health. These compounds are known to bioaccumulate along the food chain and have been associated with endocrine disruption, neurological effects, and an increased risk of cancer in humans through the ingestion of contaminated water [23]. Table 1 summarises the different methods for detecting pesticides and PCBs in wastewater.

Table 1.
Summary of studies employing validated GC-MS or GC-MS/MS methods for the detection and quantification of pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in wastewater. The table includes information on sample type, sample volume (mL), extraction technique and conditions, limits of detection (LOD) and quantification (LOQ) expressed in ng/mL, recovery rates (%), and details of the instrumentation used, including ionisation mode.
GC-MS or GC-MS/MS is the preferred technique for the determination of PCBs in water. PCBs are semi-volatile and thermally stable, characteristics that make them highly compatible with GC analysis. The technique offers excellent selectivity and sensitivity, enabling accurate identification and quantification of PCB congeners, even at trace levels (ng/L). Moreover, GC provides efficient separation of structurally similar congeners, which is essential for reliable analysis [30].
Alternative techniques, such as LC-MS/MS, are less suitable due to the non-polar and water-insoluble nature of PCBs, which limits their compatibility with reversed-phase LC conditions [43]. Therefore, GC-MS/MS remains the method of choice for PCB analysis in water, offering superior specificity, sensitivity, and congener resolution.
Most validated methods for the analysis of these compounds have focused on wastewater samples collected from urban or municipal treatment plants, reflecting their widespread use and disposal patterns [44]. In our literature review, the majority of studies employed liquid-phase extraction methodologies, with dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME) being the most commonly used technique, followed by switchable solvent liquid-phase microextraction (SS-LPME).
DLLME is favoured due to its simplicity, rapidity, and high efficiency. It involves the rapid dispersion of an extraction solvent into the aqueous sample using a dispersive solvent, forming a temporary emulsion that facilitates analyte transfer into the organic phase. Despite its advantages, a major limitation of DLLME lies in its reliance on toxic organic solvents [45]. Nonetheless, the technique requires only small solvent volumes, making it economically attractive; however, its handling is complex, and it has not yet been widely automated [46]. SS-LPME, on the other hand, is considered a more sustainable and selective alternative. This technique enables the extraction process to be tailored to the physicochemical nature of the target analytes through the use of switchable solvents, whose polarity can be altered—typically via CO2 addition or pH adjustment. Initially miscible with water, the solvent becomes hydrophobic upon stimulation and spontaneously separates, allowing analyte recovery. However, SS-LPME is more time-consuming and requires tighter chemical control [47]. Thus, DLLME is ideal for rapid applications involving hydrophobic compounds, while SS-LPME offers greater environmental compatibility and selectivity, making it well-suited for complex matrices and green chemistry applications.
For instance, Bodur et al. [31] reported limits of detection (LODs) below 3 ng/mL and limits of quantification (LOQs) below 10 ng/mL for four target compounds, using only 8 mL of sample. Their method, which employed DLLME with methanol and chloroform, achieved recoveries exceeding 92% for all analytes. For the same compounds (acibenzolar-S-methyl, chlorpyrifos, β-endosulfan, and propham), Tışlı et al. [35] developed a vortex-assisted SS-LPME method using the same sample volume, yielding LODs ranging from 0.42 to 1.9 ng/mL, LOQs between 1.3 and 6.5 ng/mL, and recoveries between 79.9% and 105%. These results confirm that both techniques are effective for the extraction of such compounds.
In another approach, Chormey et al. [40] employed micro-solid-phase extraction (µ-SPE) using magnetite nanoparticles coated with oleic and stearic acids as sorbents to extract seven analytes from the influent of a wastewater treatment plant. This method achieved recoveries above 95% and high sensitivity, with LODs below 3 ng/mL and LOQs under 9 ng/mL, using only 30 mL of water.
Among the methods reviewed, one study stands out for its novel extraction approach and remarkable sensitivity [30]. The authors used a disposable pipette extraction device filled with graphitic carbon nitride as a sorbent to extract six PCBs from canal water. The method achieved LODs in the ng/L range and LOQs between 12 and 30 ng/L, with approximately 90% recoveries using just 9.5 mL of sample.
3.2. Therapeutic Drugs
Pharmaceuticals are chemical substances used therapeutically in humans, including antibiotics, analgesics, anti-inflammatory agents, antipsychotics, β-blockers, and antidepressants. The growing use and improper disposal of these compounds have led to their widespread occurrence in wastewater. Due to the acidic or basic nature of both the pharmaceuticals and the wastewater matrix, their solubility is affected, which, in turn, influences their environmental persistence and mobility [48]. For example, antidepressants are predominantly weak bases and, as mentioned previously, wastewater typically exhibits an acidic pH. This enhances their solubility, resulting in greater mobility and environmental persistence [49]. These substances can enter the aquatic environment via human excretion, the improper disposal of unused medications, and effluents from hospitals and pharmaceutical industries [50].
The presence of pharmaceuticals in water raises significant environmental and public health concerns, as many of these compounds are not effectively removed by conventional WWTP processes [50]. Consequently, they may affect aquatic organisms, promote antimicrobial resistance, and pose risks to human health through exposure or consumption of contaminated water, potentially leading to hormonal imbalances, neurological effects, and cardiovascular complications [51].
Table 2 compiles various studies that have reported the detection of pharmaceutical compounds in wastewater.

Table 2.
Summary of studies employing validated GC-MS or GC-MS/MS methods for the detection and quantification of therapeutic drugs in wastewater. The table includes information on sample type, sample volume (mL), extraction technique and conditions, limits of detection (LOD) and quantification (LOQ) expressed in ng/mL, recovery rates (%), and details of the instrumentation used, including ionisation mode.
Numerous investigations have focused on assessing contamination levels in hospital and municipal wastewaters. According to our review, the most commonly targeted pharmacotherapeutic groups were antidepressants and anti-inflammatory agents. In terms of extraction methods, SPE was by far the most frequently employed technique, followed by DLLME.
For this group of analytes, the most commonly used SPE cartridge is the OASIS® HLB, a broadly applicable sorbent designed for multiresidue methods due to its high versatility. However, given that many pharmaceutical compounds—particularly antidepressants and β-blockers—exhibit basic properties, cation-exchange cartridges such as the OASIS® MCX are often more effective for targeted applications [69].
For instance, Gonçalves et al. [65] employed OASIS® MCX cartridges to determine 14 antidepressants and β-blockers in 500 mL of wastewater from a treatment plant. The method demonstrated high sensitivity, with all limits of detection (LODs) below 30 ng/L and the highest limit of quantification (LOQ) being 100 ng/L (for paroxetine), alongside recovery rates exceeding 80%.
DLLME has also been applied for the analysis of central nervous system (CNS) drugs. Dalgıç et al. [58], for example, used a binary solvent system comprising isopropyl alcohol (as a dispersant) and a combination of carbon tetrachloride and 1,2-dichloroethane (as extractants). Their method achieved recoveries above 95% from just 8 mL of sample, with LODs as low as 0.28 ng/mL and LOQs below 10 ng/mL.
In addition, SS-LPME has been employed on several occasions, particularly for the determination of antidepressants and antipsychotics [52,54]. When comparing these three techniques, SPE generally achieves the lowest LODs and LOQs, but requires significantly larger sample volumes. In contrast, DLLME and SS-LPME tend to yield slightly higher detection limits but often offer better recovery rates.
Within this category, two less conventional extraction techniques are worth noting. In one study, cellulose fabric coated with Carbowax and a Teflon-coated magnetic stir bar were used for fabric-phase sorptive extraction (FPSE) to analyse municipal and hospital wastewater for lidocaine and prilocaine—local anaesthetics commonly used in topical formulations before surgery. The results were highly competitive in terms of sensitivity and recovery [64]. Another innovative approach was presented by Arismendi et al. [66], who applied rotating-disk sorptive extraction (RDSE) in a multimethod analysis of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, using a Teflon disk and 20 mL of sample. Although the recoveries were somewhat lower compared to other methods, the sensitivity was nevertheless competitive.
Despite the breadth of analytical methods available, the application of GC for the analysis of pharmaceutical compounds in wastewater faces certain limitations. Many pharmaceuticals lack thermal stability (e.g., benzodiazepines and some antibiotics), leading to degradation under the high operating temperatures required for GC analysis. Furthermore, compound polarity can pose additional challenges, as it affects chromatographic retention and elution behaviour, particularly in polar columns. In this context, LC-based methods are often more suitable. Nevertheless, GC continues to offer valid and effective solutions for a broad range of therapeutic compounds, particularly when derivatisation is applied to enhance volatility and thermal stability.
3.3. Personal Care Products
Personal care products (PCPs) encompass a broad range of hygiene and cosmetic items. Among the most frequently detected PCPs in wastewater are antiseptics, UV filters, and fragrances, owing to their widespread use in disinfectants, sunscreens, and perfumes, respectively. This group includes compounds with diverse physicochemical properties, which influence their solubility, biodegradability, and bioaccumulative potential [70].
Compounds such as UV filters are used daily and often exhibit high resistance to degradation by conventional WWTP processes. This resistance is largely attributed to their acidic nature, which, under typical wastewater conditions, results in reduced ionisation and increased environmental persistence. Monitoring PCPs is essential, as many have been shown to exert harmful effects on ecosystems and public health, including DNA damage, endocrine disruption, and the promotion of bacterial resistance in aquatic organisms [71,72]. Table 3 presents selected studies in which antiseptics, UV filters, and fragrances have been detected in the matrices considered in this review.

Table 3.
Summary of studies using validated GC-MS or GC-MS/MS methods for the detection and quantification of PCPs in wastewater, including sample type, volume (mL), extraction technique and conditions, LOD and LOQ (ng/mL), recoveries (%), and details of the instrumentation used, including ionisation mode.
Among these, triclosan (an antiseptic) and various UV filters/stabilisers are the most frequently investigated compounds.
Notably, the FPSE and RDSE methods—previously discussed in the context of pharmaceutical analysis—have also been used to target triclosan. FPSE is based on the sorption of analytes onto a fabric substrate coated with a sorbent. It combines the mechanical robustness of SPE with the equilibrium-driven nature of SPME. Typically, the fabric—made of polyester, cellulose, or similar materials—is coated with sorbents such as C18 (SPE-type) or polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS, typical of SPME). The fabric is immersed in the sample for a fixed period, then retrieved and exposed to an elution solvent prior to GC analysis. The fabric may also be cut into smaller sections to increase surface area and reduce solvent use [83,84].
RDSE, by contrast, relies on mechanical agitation. A Teflon disk coated with sorbent on one side and containing an internal magnet is rotated using a magnetic stirrer. This facilitates contact between the sorbent and the analytes in the sample until equilibrium is reached [85]. Both FPSE and RDSE offer the benefits of SPME and SPE while addressing certain limitations, such as the low sorbent capacity and limited reusability of traditional techniques [83]. FPSE is particularly attractive due to its sorbent versatility and compatibility with low-volume elution. RDSE’s primary limitation lies in the need for specialised rotating disks.
When comparing results for triclosan obtained via these two methods, FPSE demonstrates superior performance. The FPSE technique achieved lower LOD and LOQ values (0.021 and 0.069 ng/mL, respectively) and higher recoveries (96.01–98.35%) compared to RDSE (LOD of 0.07 ng/mL, LOQ of 0.21 ng/mL, and a recovery of 44%), despite using half the sample volume. Both methods employed GC-MS for detection.
In addition to these novel approaches, SPE and DLLME, including their variations, remain the most widely used extraction techniques for PCPs. OASIS® HLB cartridges are particularly common; for example, they were used to extract nine UV filters from 1 L of WWTP samples, achieving LODs and LOQs in the ng/L range [56]. Using the same type of cartridge, another study targeted triclosan in WWTP and urban effluent samples, using half the sample volume. However, that method did not achieve the same performance levels as the one focused on the broader group of analytes [59]. Regarding DLLME, Ebrahimi et al. [73] used methanol and 1,1,1-trichloroethane as solvents to extract triclosan from 5 mL of WWTP influent and effluent samples. The method included derivatisation with N-Methyl-N-trimethylsilyl-trifluoroacetamide and achieved an LOD of 0.04 ng/mL and 100% recovery.
It is also worth highlighting a study in which the authors employed LLE using hexane to analyse 500 mL of WWTP influent and effluent for 11 PCPs. The method yielded excellent performance, with LOQs in the ng/L range and even lower LODs. However, its major limitation was the use of 50 mL of organic solvent per extraction, resulting in a significant environmental burden [79].
3.4. Preservatives
Preservatives are chemical substances used across the food, cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and cleaning industries to extend product shelf life and prevent microbiological degradation. As compounds in this class are predominantly acidic in nature, they tend to exhibit low reactivity, high stability, and increased environmental persistence in wastewater matrices. Among the most frequently detected preservatives in wastewater are parabens, which are commonly found in personal care products, cosmetics, detergents, and pharmaceuticals [86].
The accumulation of these compounds in wastewater is primarily attributed to their widespread use and high production volumes, with domestic, hospital, and industrial effluents representing the main sources. Consequently, parabens are considered contaminants of emerging concern, with potential risks to both the environment and human health [86].
Table 4 summarises the studies in which preservatives were identified in the wastewater matrices considered in this review.

Table 4.
Summary of studies using validated GC-MS or GC-MS/MS methods for the detection and quantification of preservatives in wastewater, including sample type, volume (mL), extraction technique and conditions, LOD and LOQ (ng/mL), recoveries (%), and details of the instrumentation used, including ionisation mode.
The analytes included in this category are methylparaben, ethylparaben, propylparaben, and butylparaben. One noteworthy method employed C18-E SPE cartridges to detect all four parabens in both influent and effluent wastewater from a sewage treatment plant. Vimalkumar et al. [79] reported that the method achieved extremely low limits of detection: 0.0005 ng/mL for methylparaben and propylparaben, and 0.0006 ng/mL for ethylparaben and butylparaben. The LLOQ was 0.0025 ng/mL, with recovery rates ranging from 81% to 98%, using only 100 mL of sample. The only other study in which all four analytes were simultaneously detected employed RDSE. However, this method showed limitations in both detection limits and recovery performance [66].
Gumbi et al. [67] also developed an SPE method using OASIS® HLB cartridges, focusing on the determination of propylparaben. Although the method required a ten times higher sample volume (1000 mL), it achieved a limit of detection of 1.5 ng/mL and demonstrated excellent recovery (102%), indicating good method performance for that specific analyte.
3.5. Illicit Drugs
The detection of illicit drugs—such as cocaine, amphetamines, opioids, and cannabinoids—in wastewater has attracted growing attention, particularly within the framework of wastewater-based epidemiology. This approach enables the monitoring of substance use patterns in urban populations by analysing metabolites excreted into the sewage system, thereby serving as a valuable tool for epidemiological research and the development of public health policies [87]. Beyond their role in monitoring consumption trends, these compounds also represent a significant environmental hazard, as they may adversely affect aquatic organisms by disrupting behaviour, reproduction, and endocrine functions. The majority of compounds within this category are basic in nature, rendering them more readily ionisable and soluble under typical wastewater conditions. As a result, they often persist through conventional WWTP processes and are frequently detected in treated effluents. Although concentrations in environmental waters are generally low, chronic exposure raises concerns regarding potential neurotoxic, hepatotoxic, and endocrine-disrupting effects in humans [88]. Table 5 summarises the studies in which illicit drugs have been detected in wastewater matrices.

Table 5.
Summary of studies employing validated GC-MS or GC-MS/MS methods for the detection and quantification of illicit drugs in wastewater, including sample type, volume (mL), extraction technique and conditions, LOD and LOQ (ng/mL), recoveries (%), and details of the instrumentation used, including ionisation mode.
According to our review, most authors focused on substances of emerging concern—specifically opioids, amphetamines, and new psychoactive substances—reflecting contemporary drug consumption trends.
SPE was the predominant extraction technique employed; however, in contrast to other contaminant categories, the sample volumes were notably smaller. In several studies, sample volumes were reduced to 50 mL, and in one instance, as little as 25 mL was used. That method targeted amphetamine, methamphetamine, and MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine), extracted using OASIS® Prime MCX cartridges and derivatised with (R)-α-methoxy-α-(trifluoromethyl)phenylacetyl chloride [91]. Among the SPE-based studies, one method stands out for its exceptional sensitivity. Liu et al. [95] employed OASIS® MCX cartridges to extract 11 drugs of abuse from WWTP samples. Following derivatisation with bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA) containing 1% trimethylchlorosilane (TMCS), the method achieved LODs and LOQs in the picogram per litre (pg/L) range, with recovery rates exceeding 85%. These results are particularly noteworthy given the small sample volume of just 50 mL.
Other researchers have investigated microextraction techniques. One notable example is the use of thin-film microextraction (TFME) with a divinylbenzene/polydimethylsiloxane (DVB/PDMS) membrane to determine methamphetamine, ketamine, and methaqualone [92]. In another study, Nascimento et al. [90] applied liquid-phase microextraction (LPME) using a solvent mixture of toluene, dichloromethane, and ethyl acetate to analyse nine amphetamines, cathinones, and cocaine derivatives. In LPME, a small volume of an organic, water-immiscible solvent is exposed to the aqueous sample—either by immersion or in the headspace—typically via a syringe. The partitioning of analytes into the organic phase enables rapid and efficient extraction [98]. Despite their miniaturised formats and low sample volumes (less than 20 mL), both the TFME and LPME methods yielded promising detection limits and particularly high recovery rates, demonstrating their potential as efficient, low-impact alternatives for the determination of illicit drugs in environmental waters.
3.6. Endocrine Disruptors, Hormones, and Derivatives
The presence of endocrine-disrupting compounds (EDCs), hormones, and their derivatives in wastewater has become a major concern in environmental and public health contexts. EDCs include substances such as bisphenols, natural and synthetic hormones, and certain surfactants like 4-nonylphenol, which can interfere with the endocrine systems of exposed organisms, causing adverse effects even at extremely low concentrations [99]. Bisphenols, particularly bisphenol A (BPA), are widely used in the manufacture of plastics and epoxy resins and are commonly detected in wastewater due to the improper disposal of plastic products and leaching from packaging materials [100]. Hormones, both natural and synthetic—such as oestrogens and androgens found in contraceptives and hormone therapies—primarily enter aquatic environments through human excretion [101]. 4-Nonylphenol, a degradation by-product of non-ionic surfactants used in detergents and industrial applications, is also classified as an endocrine disruptor due to its ability to mimic oestrogenic activity [102]. Unlike other classes of pollutants, compounds within this category generally exhibit slightly acidic to neutral properties, resulting in low aqueous solubility and a high tendency for bioaccumulation and adsorption onto solids. These features contribute to their persistence, as they are resistant to biodegradation and prone to long-range transport within aquatic systems [103,104]. The environmental effects of EDCs are well documented and include reproductive and developmental abnormalities in aquatic organisms, reduced fertility, and impaired growth [105]. In humans, chronic exposure to EDCs has been linked to hormonal disorders, infertility, obesity, and certain cancers [106].
Table 6 summarises the studies that reported the detection of EDCs and related compounds in wastewater.

Table 6.
Summary of studies employing validated GC-MS or GC-MS/MS methods for the detection and quantification of endocrine disruptors, hormones, and derivatives in wastewater, including sample type, volume (mL), extraction technique and conditions, LOD and LOQ (ng/mL), recoveries (%), and details of the instrumentation used, including ionisation mode.
A wide range of analytical methodologies have been employed for their detection. Due to shared physicochemical characteristics and health impacts, many studies simultaneously address both EDCs and hormone derivatives. For example, the previously discussed method by Chormey et al. [40] included the determination of alkylphenols (4-octylphenol and 4-nonylphenol), BPA, and the hormones estrone and 17-β-estradiol, achieving results comparable to those obtained for other target analytes.
As in other contaminant categories, SPE and DLLME were the most frequently used extraction techniques, with OASIS® HLB cartridges being the most commonly applied due to their versatility. However, several alternative strategies are noteworthy. One study developed a method for detecting PFAs using stir-bar sorptive extraction (SBSE) with a PDMS coating. The authors reported detection limits below 0.02 ng/mL and LOQs from 0.04 ng/mL, although recovery rates were relatively low—an inherent limitation of SBSE techniques [107]. Other sorption-based techniques have also been applied in EDC detection. For instance, headspace solid-phase microextraction (HS-SPME) was used to analyse 4-nonylphenol in industrial wastewater, employing a divinylbenzene/carboxen/polydimethylsiloxane (DVB/CAR/PDMS) fibre. This approach achieved an LOD of 0.1 ng/mL, an LOQ of 0.15 ng/mL, and a recovery rate exceeding 94% [114]. In another innovative approach, Kiejza et al. [109] developed a method for analysing nine bisphenol derivatives in influent and effluent samples using ultrasound-assisted emulsification microextraction (USA-EME). The method involved disodium hydrogen phosphate and chlorobenzene as extraction components and achieved quantification limits from 0.1 ng/mL, with recovery rates above 85%. USA-EME is a rapid and efficient technique that uses ultrasound to emulsify the sample with the organic solvent, improving extraction performance. However, the frequent use of toxic agents in this method raises concerns regarding user safety and environmental sustainability [119].
Despite the diversity of extraction approaches used across targeted and multimethod studies, SPE remains a cornerstone technique due to the robustness and performance of validated methods. Notably, Chafi et al. [110] used OASIS® HLB cartridges to determine 13 steroid hormones in just 100 mL of wastewater. Derivatisation with BSTFA containing 1% TMCS enabled the detection of all analytes with high sensitivity, with the highest LOD and LOQ reported being 0.0003 and 0.001 ng/mL, respectively, for the synthetic oestrogen norethindrone.
While both GC and LC platforms are widely used for screening EDCs and hormones, each presents specific limitations. In GC, compounds with high molecular weights often exhibit extended retention times, sometimes rendering quantification impractical. On the other hand, LC-based analyses are frequently affected by matrix effects, which can compromise quantification accuracy.
3.7. Plasticisers, Polymers, and Siloxanes
Plasticisers, polymers, and siloxanes are classified as emerging contaminants in wastewater, originating from a variety of sources including plastics, cosmetics, industrial products, and packaging materials. These compounds are typically neutral, exhibit low water solubility, and are highly chemically stable and resistant to degradation.
Plasticisers, such as phthalates, have been shown to negatively affect the reproductive systems of both aquatic organisms and humans [120]. Synthetic polymers, including microplastics, are of growing concern due to their environmental persistence and ability to act as carriers for other toxic pollutants. Siloxanes, such as D4 and D5, are commonly used in personal care products and industrial applications; they have been linked to hormonal disruption and may also interfere with the proper functioning of WWTPs [121]. Although concentrations of these compounds in wastewater are generally low, chronic exposure may lead to long-term adverse effects, highlighting the importance of effective monitoring and removal strategies. Advanced technologies—such as chromatography, adsorption, and oxidation processes—are essential for the detection and elimination of these micropollutants, contributing to reduced environmental and public health risks. In parallel, the implementation of stricter regulatory frameworks is necessary to mitigate their widespread occurrence [122].
Table 7 presents the studies that have reported the detection of plasticisers, polymers, and siloxanes in wastewater. As summarised, these micropollutants are primarily derived from domestic effluents, and most of the research has focused on WWTP effluent streams, where their presence has been confirmed. As noted earlier, conventional WWTPs are typically not equipped with adequate systems to detect or remove these compounds effectively.

Table 7.
Summary of studies using validated GC-MS or GC-MS/MS methods for the detection and quantification of plasticisers, polymers, and siloxanes in wastewater, including sample type, volume (mL), extraction technique and conditions, LOD and LOQ (ng/mL), recoveries (%), and details of the instrumentation used, including ionisation mode.
Nevertheless, the studies compiled in Table 7, conducted in recent years, reflect a growing scientific effort to address this gap. These works describe validated analytical methods for detecting plasticisers, polymers, and siloxanes in wastewater, employing various extraction techniques combined with GC-MS and GC-MS/MS, thus contributing valuable tools for improved environmental monitoring.
The data indicate that the most commonly employed extraction techniques are SPE using OASIS® HLB cartridges and its miniaturised counterpart, SPME. Notably, in the study conducted by Wolecki et al. [125], the highest sensitivity was achieved using SPE, with an LOD and an LOQ of 0.001 ng/mL and 0.003 ng/mL, respectively, from a sample volume of 250 mL.
However, a separate study by Kotowska et al. [128], which employed the SPME technique to detect several common analytes—specifically dimethyl phthalate, diethyl phthalate, dibutyl phthalate, and bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate—using a polydimethylsiloxane/divinylbenzene (PDMS/DVB) fibre, also demonstrated high sensitivity and excellent recovery rates. These results were comparable to those obtained with SPE, despite requiring only 10 mL of sample, highlighting the efficiency and reduced solvent/sample demands of SPME.
Other extraction techniques, such as liquid-phase extraction (LPE), have also been applied. For example, Qiao et al. [25] used 700 µL of dichloromethane and n-hexane as extraction solvents, achieving a satisfactory recovery rate. However, the method resulted in higher LOD and LOQ values compared to the previously mentioned SPE and SPME approaches.
In comparison with the study by Kotowska et al. [128], it becomes evident that LPE may not be the most effective strategy for the analysis of this class of micropollutants, particularly when low detection limits and minimal sample volumes are required.
3.8. Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Derivatives
Aromatic hydrocarbons and their derivatives—such as benzene, toluene, xylene, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)—are environmental contaminants characterised by distinct physicochemical properties. Depending on the predominant functional group, these compounds may display either high or low solubility in wastewater. For instance, compounds bearing amine groups tend to exhibit greater solubility due to their higher ionisation potential, whereas those with carboxylic acid groups often have lower solubility and greater persistence in aquatic environments.
The primary sources of these pollutants include industrial effluents and the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels [130]. Once released into the environment, they accumulate in aquatic sediments, contribute to oxygen depletion in water bodies, and pose serious toxic and mutagenic risks to aquatic organisms [131,132,133]. In humans, exposure to these micropollutants may occur through ingestion, inhalation, or dermal absorption, potentially leading to neurotoxicity, hepatic and renal dysfunction, and increased risks of leukaemia and other cancers. As such, effective strategies for the removal and mitigation of these compounds are essential. These include advanced treatment technologies such as adsorption, chemical oxidation, and bioremediation [134].
Table 8 summarises the studies that have reported the detection of aromatic hydrocarbons and their derivatives in wastewater matrices.

Table 8.
Summary of studies using validated GC-MS or GC-MS/MS methods for the detection and quantification of aromatic hydrocarbons and derivatives in wastewater, including sample type, volume (mL), extraction technique and conditions, LOD and LOQ (ng/mL), recoveries (%), and details of the instrumentation used, including ionisation mode.
The analysed studies investigated the presence of emerging contaminants in urban and industrial wastewater, as well as in WWTP effluents, using sample volumes ranging from 10 to 1000 mL. This variation reflects the application of both miniaturised extraction approaches and conventional methodologies.
Among the techniques, HS-SPME emerged as the most frequently employed, owing to its ease of automation and minimal solvent consumption. The selection of different fibre coatings—PDMS, carboxen/PDMS, and polyacrylate—affected both analytical selectivity and compound recovery, with most studies reporting recovery rates exceeding 70%. Notably, the study by Domínguez et al. [141] achieved the highest sensitivity, reporting LOD and LOQ values of 0.00001 and 0.00003 ng/mL, respectively, using only 10 mL of sample.
Other extraction techniques included SPE and LLE, particularly for studies using larger sample volumes (50–1000 mL). For instance, SPE was applied in the study by Xiong et al. [56], achieving an LOD of 0.0003 ng/mL, a result that demonstrates comparable sensitivity to SPME and HS-SPME, despite requiring a 100 times higher sample volume.
In contrast, LLE exhibited significantly higher detection limits, ranging from 1.08 to 13.26 ng/mL, highlighting its lower sensitivity relative to other approaches.
Overall, SPME proved to be more advantageous than traditional liquid-phase extraction techniques, not only for its high sensitivity and efficiency, but also due to its requirement of smaller volumes of both sample and solvent, making it a more sustainable and cost-effective alternative for routine environmental monitoring.
3.9. Alkaloids
Alkaloids, such as caffeine and nicotine, are naturally occurring compounds found in various plants, including coffee and tobacco. With the increasing consumption of products containing these substances, their concentrations in wastewater have also risen [142]. The presence of caffeine and nicotine in wastewater is a matter of growing concern, as these compounds may enter the environment through the improper disposal of items such as coffee filters, cigarettes, and via industrial effluents.
Due to the amine functional groups present in their chemical structures, these alkaloids exhibit a basic character and are consequently highly soluble in aqueous matrices. This property contributes to their persistence in wastewater, potentially requiring more advanced treatment processes at WWTPs to ensure effective removal [143].
When discharged into aquatic environments, alkaloids can exert adverse ecological effects, including the alteration of reproductive behaviour and disruption of biodiversity among aquatic fauna [144,145]. Furthermore, humans may be exposed to these substances through the consumption of contaminated water, raising concerns about potential health risks, such as cardiovascular complications, neurological disorders, and addiction [143].
Table 9 summarises the studies that have reported the detection of alkaloids, specifically caffeine and nicotine, in various types of wastewater matrices.

Table 9.
Summary of studies using validated GC-MS or GC-MS/MS methods for the detection and quantification of alkaloids in wastewater, including sample type, volume (mL), extraction technique and conditions, LOD and LOQ (ng/mL), recoveries (%), and details of the instrumentation used, including ionisation mode.
The comparative analysis of the studies presented in Table 9 highlights the application of SPE using OASIS® HLB cartridges for the detection of caffeine and nicotine in WWTP waters and urban effluents. In the study conducted by Capparelli et al. [59], a 500 mL sample volume was used, and the method demonstrated high sensitivity, yielding low LOD and LOQ values for caffeine (0.02 ng/mL) and nicotine (0.14 ng/mL), with recovery rates of 92% and 85%, respectively.
Conversely, the study by Gumbi et al. [67], which used double the sample volume (1000 mL), implemented an extraction protocol involving larger solvent volumes and an additional derivatisation step. While this approach may have contributed to improved recovery, the method reported significantly higher LOD and LOQ values (0.400 ng/mL and 1.100 ng/mL, respectively), indicating lower sensitivity when compared to the method described by Capparelli et al [59].
3.10. Acids, Fatty Acids, and Derivatives
Acids, fatty acids, and their derivatives are organic compounds commonly found in wastewater, originating from industrial, agricultural, and domestic activities. As their name suggests, these compounds are predominantly acidic in nature and may not fully ionise in aqueous environments, which affects their solubility. Nonetheless, they are often reported to possess good biodegradability. Their sources include the breakdown of lipids, detergents, petrochemicals, and food waste, and they are frequently discharged into effluents without appropriate treatment [146]. The presence of these compounds in wastewater poses a significant risk to aquatic ecosystems, as they can alter the physicochemical properties of water, thereby degrading water quality and affecting the health of aquatic fauna [147]. Carboxylic acids, fatty acids, and their derivatives can lead to the depletion of dissolved oxygen, adversely impacting organisms such as fish and invertebrates and reducing aquatic biodiversity [148]. Table 10 presents studies reporting the detection of acids, fatty acids, and related derivatives in wastewater.

Table 10.
Summary of studies using validated GC-MS or GC-MS/MS methods for the detection and quantification of acids, fatty acids, and derivatives in wastewater, including sample type, volume (mL), extraction technique and conditions, LOD and LOQ (ng/mL), recoveries (%), and details of the instrumentation used, including ionisation mode.
Analysis of the compiled data shows that these compounds predominantly originate from industrial wastewater streams. The most frequently employed extraction techniques were LLE and its miniaturised form, DLLME, using a wide variety of solvents, including ethanol, hexane, acidified methyl tert-butyl ether, and toluene. These techniques demonstrated high extraction efficiency in terms of recovery rates. For example, in the study by Yu et al. [152], DLLME achieved recovery rates above 99%, although the method required a relatively large sample volume (20 mL).
However, these techniques generally exhibited lower sensitivity. In contrast, the study by Liu et al. [149] employed SPME with a hollow polypropylene fibre for biodiesel wastewater analysis. Although the method yielded lower recovery rates (38.8–70.5%), it achieved superior sensitivity, with an LOD of 0.04 ng/mL and an LOQ of 10 ng/mL.
In comparison, the in-syringe magnetic stirring-assisted DLLME technique reported by Vargas-Muños et al. [151] achieved recoveries of up to 102.8%, but with substantially higher LODs, ranging from 20 to 50 ng/mL.
For hospital wastewater, results varied depending on the extraction technique used. In the study by Guérette et al. [150], LLE provided good recovery values (92–119%) but with high LODs (1000 ng/mL). In contrast, derivatisation combined with direct injection significantly improved sensitivity, reducing LOD values to 30–200 ng/mL, though recovery ranged from 31 to 112%.
An important factor in selecting the appropriate extraction technique is sustainability. In this regard, SPME offers clear advantages due to its minimal solvent use, making it a more environmentally friendly alternative compared to LLE and DLLME.
Among the analytes listed in Table 10 are acids [132], fatty acids [131], methyl esters of fatty acids [130,133], and carboxylic acids [132] (second row entry). For the analysis of such compounds by GC, volatility must be ensured. FAMEs are inherently more volatile than their corresponding fatty acids, which explains why transesterification is commonly used in lipid analysis. The remaining acid derivatives often require derivatisation to improve volatility prior to GC analysis [153]. This relative ease in enhancing compound volatility, together with the availability of various derivatisation strategies, makes GC a highly suitable and widely applicable technique for the determination of this group of contaminants.
3.11. Industrial Chemicals
The chemical industry is a major source of contamination in wastewater, particularly due to the improper use and disposal of organic solvents. These compounds, widely employed in manufacturing, cleaning, and extraction processes, are often highly persistent in the environment [154]. When released into aquatic systems without proper treatment, solvents can severely impact ecosystems by altering water quality, reducing biodiversity, and harming aquatic organisms through toxicity and bioaccumulation. Furthermore, many of these compounds are volatile, contributing not only to water contamination but also to atmospheric pollution. In humans, prolonged exposure to these contaminants has been associated with liver, kidney, and nervous system damage, as well as potential carcinogenic effects [155].
Table 11 presents studies in which this class of contaminants has been detected in wastewater.

Table 11.
Summary of studies using validated GC-MS or GC-MS/MS methods for the detection and quantification of industrial chemical in wastewater, including sample type, volume (mL), extraction technique and conditions, LOD and LOQ (ng/mL), recoveries (%), and details of the instrumentation used, including ionisation mode.
As evidenced in Table 11, only two studies reported the detection of chemical manufacturing solvents using validated analytical methods. It is important to emphasise that this review exclusively considered studies in which analytical methodologies were validated or where validated methods were applied. Nevertheless, additional research was identified in which GC-MS or GC-MS/MS was used in SCAN mode for the detection of such compounds, although without method validation, and thus these studies were excluded from the current analysis [156,157,158].
In the study conducted by Majumdar et al. [137], halogenated volatile compounds were extracted from urban wastewater samples using HS-SPME with a PDMS fibre. This technique demonstrated high extraction efficiency, with recovery rates ranging from 95.0% to 100.1%. The fibre selection was a crucial factor in this performance, reflecting its selective affinity for volatile and semi-polar compounds. Moreover, the LOQs achieved (ranging from 0.09 to 0.48 ng/mL) indicate good analytical sensitivity. HS-SPME is particularly well-suited to the analysis of such compounds, as it enables pre-concentration of volatiles, minimises matrix interference, and eliminates the need for organic solvents.
Conversely, the study by Tanimu et al. [138] employed a more recent approach: stir-bar-assisted micro-solid-phase extraction (SB-µ-SPE). This method is an improvement on traditional µ-SPE, involving a device resembling a tea bag composed of a thermally sealed polypropylene membrane filled with a sorbent. SB-µ-SPE addresses common limitations of µ-SPE—such as floating or adherence to container walls, which can compromise extraction efficiency—by incorporating a magnetic stir bar inside the device. This innovation allows the device to sink and rotate during extraction, enhancing contact with the sample and improving efficiency.
In their study, Tanimu et al. validated a method for the quantification of four solvents using SB-µ-SPE, reporting recoveries ranging from 87.9% to 114%. However, when compared with the HS-SPME method described by Majumdar et al. [137], SB-µ-SPE demonstrated lower sensitivity, with higher LOQ values, despite using the same sample volume.
Despite these differences in sensitivity, both techniques showed excellent extraction performance, and each presents distinct advantages. It can thus be concluded that HS-SPME and SB-µ-SPE are both viable and effective methods for the determination of organic solvents in wastewater, with the choice of technique depending on analytical priorities such as sensitivity, simplicity, and solvent use.
4. Comparative Extraction Techniques
This section presents a comparative analysis of the main extraction techniques used in the detection of contaminants in wastewater. The choice of extraction technique constitutes a critical step in the sample preparation process, directly influencing essential parameters such as sensitivity, selectivity, and reproducibility of analytical results. Considering the complexity of the wastewater matrix and the wide diversity of target compounds present in such samples, it is crucial to assess the most commonly used methodologies not only based on their analytical performance but also by taking into account operational aspects such as sample volume and solvent consumption. This analysis is based on data extracted from the studies presented in the previous tables, allowing for the identification of relevant methodological trends in the context of analytical chemistry applied to wastewater monitoring.
Among the various extraction techniques considered, SPE stands out as the most frequently employed in the studies reviewed. This technique, widely used in diverse analytical fields such as environmental, forensic, biological, and food analysis, remains one of the preferred options due to its versatility, speed, and high selectivity. Despite the development of newer and more innovative techniques, SPE continues to be widely applicable, as it allows for multiple simultaneous extractions, isolation of the analytes of interest, and elimination of matrix interferences, thus significantly improving analytical sensitivity. In addition, high recovery rates can be achieved with relatively short extraction times, which is a major advantage in demanding analytical contexts [159]. SPE is particularly well-suited for compounds with low volatility and higher polarity, and it is advantageous when working with dilute analytes in large sample volumes, as it allows efficient concentration and clean-up.
The principle of SPE is based on the retention of analytes on a sorbent material, typically contained within cartridges, whose chemical composition can vary, enabling the user to select the most appropriate cartridge type for the physicochemical properties of the target compounds. Among the studies reviewed, OASIS® HLB cartridges were the most commonly used and applied to the greatest number of contaminant classes. This can be attributed to the neutral chemical properties of the sorbent, making it effective for both acidic and basic compounds and allowing for a broader and more exploratory approach in the analysis of emerging contaminants [159].
Notable examples include the studies by López-Velázquez et al. [108], Chafi et al. [110], and Tang et al. [116], all of which focused on the determination of 17-β-estradiol. In the study by López-Velázquez et al., a 1000 mL sample volume yielded LOD, LOQ, and recovery values of 0.21 ng/mL, 0.71 ng/mL, and 77.5%, respectively. In contrast, Tang et al. [116], using the same volume and instrumentation, achieved LOD and LOQ values approximately 100 times lower, with higher recovery rates, suggesting improved method performance—potentially due to differences in solvent volumes and solvent types used during the extraction procedure. The study by Chafi et al. [110] is particularly noteworthy: using only 100 mL of sample and 600 µL of acetone in the elution step, the method achieved LOD and LOQ values of 0.00001 ng/mL and 0.00004 ng/mL, respectively, with recovery rates between 96% and 102%. These findings clearly demonstrate that adjusting operational parameters, such as reducing the sample volume or optimising solvent use, can significantly enhance the sensitivity and overall efficiency of SPE.
Another noteworthy technique is DLLME, widely used in the analysis of contaminants in complex liquid matrices. This technique is characterised by its speed, high efficiency, low consumption of organic solvents, and simplicity, and is considered a sustainable alternative. Its principle is based on the rapid injection of a mixture of extraction solvent and disperser solvent directly into the sample, forming an emulsion in which the extraction solvent disperses into microdroplets, increasing the contact area and promoting efficient analyte transfer. After centrifugation, the analyte-rich phase is collected for subsequent instrumental analysis. Although DLLME offers clear advantages, its performance heavily depends on the choice and ratio of solvents. It can also be limited in matrices with high particulate loads or viscosity [160]. The physicochemical properties of the target analytes—such as solubility, polarity, and partition coefficient—directly influence the selection of suitable solvents and the efficiency of their extraction. For example, hydrophobic or moderately polar compounds are often better extracted using chlorinated solvents with a high density, whereas more polar analytes may require specific dispersive agents to achieve good distribution.
In the previously reviewed studies, DLLME required significantly smaller sample volumes—approximately 8 mL—and lower amounts of organic solvents compared to SPE. For example, Koçoğlu et al. [42], using only 7.9 mL of sample and 1.2 mL of solvents, achieved recovery rates ranging from 89.7 to 105.9%. However, compared with the study by López-Velázquez et al. [107], which applied SPE to the same compounds (17α-ethynylestradiol, bisphenol A, and 4-nonylphenol), DLLME showed lower sensitivity, with LOD and LOQ values between 4.12 and 4.83 ng/mL and 13.73 and 16.11 ng/mL, respectively. These results demonstrate that despite the advantages of DLLME, SPE still offers superior analytical sensitivity in complex matrices where analyte concentrations are particularly low.
Miniaturised extraction techniques such as SPME, FPSE, and HS-SPME have gained increasing relevance in recent years. These techniques are highly compatible with green analytical chemistry principles, offering advantages such as low solvent usage, minimal sample volume, and shorter processing times. HS-SPME, for instance, is particularly suitable for volatile and semi-volatile compounds (e.g., musk fragrances and solvents), enabling detection in the nanogram per liter range with as little as 10 mL of sample [137]
FPSE, which uses a sorbent-coated fabric, has demonstrated competitive recoveries and low detection limits for a variety of analytes, including personal care products and antiseptics [83,84].
The selection of extraction technique must also consider the physicochemical properties of the target compounds. Table 12 presents a summary of how analyte properties influence method choice.

Table 12.
Comparison of extraction techniques used for wastewater analysis.
It is evident that no single method offers universal applicability; instead, method selection must balance matrix characteristics, target analyte properties, the required sensitivity, and sustainability considerations. While SPE remains the gold standard in terms of sensitivity and recovery, techniques like SPME and FPSE provide green and efficient alternatives, especially when working with small volumes or requiring automation. DLLME continues to offer a good compromise between performance and resource use, though it may fall short in extremely low-concentration scenarios.
In conclusion, the reviewed literature highlights a growing shift towards greener and more sustainable analytical methodologies without compromising detection capabilities. As regulatory frameworks become more stringent and environmental concerns intensify, the integration of such techniques will be essential for efficient and responsible monitoring of contaminants in wastewater systems.
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
The monitoring of micropollutants in wastewater remains a critical component of environmental and public health protection. GC-MS and GC-MS/MS continue to serve as reliable and widely employed analytical techniques, being particularly valued for their high sensitivity, selectivity, and suitability for the detection of volatile and semi-volatile organic compounds. This review has highlighted the diversity of validated GC-based methods applied in recent years and underscored the importance of tailored sample preparation strategies for the accurate detection and quantification of a broad spectrum of contaminants [12,13,30].
Among the various techniques, SPE stands out as the most extensively utilised, particularly in the analysis of pharmaceuticals and personal care products. Its robustness, high recovery rates, and adaptability to complex wastewater matrices have made it the preferred approach in many studies. Sorbents such as OASIS® HLB and MCX have played a pivotal role in achieving high analytical sensitivity, with some methods reaching detection limits in the low nanogram or even picogram per litre range. Nevertheless, SPE frequently requires large sample volumes and extended processing times, which can be limiting for rapid or field-deployable applications [56,65].
To address these constraints, miniaturised and green extraction techniques have gained increasing attention. DLLME offers a fast and efficient alternative with minimal solvent use, although concerns remain regarding the toxicity of common extraction solvents. SS-LPME presents a more environmentally benign option, leveraging pH-responsive solvents, but it is typically more labour-intensive and chemically demanding [35,39].
Other innovative techniques, such as HS-SPME and FPSE, have demonstrated considerable promise. HS-SPME has shown excellent performance for the analysis of volatile and semi-volatile compounds, such as musk fragrances and siloxanes, with detection limits in the ng/L range. FPSE, by contrast, offers advantages including simplicity, reusability, and low solvent consumption, positioning it as a viable green alternative with competitive recovery rates [64,76].
Less conventional methods, such as RDSE and SB-μ-SPE, have also been successfully applied to specific contaminant classes. RDSE is appreciated for its operational simplicity and low cost, while SB-μ-SPE provides high analyte affinity, particularly for volatile or semi-volatile solvents, although it often requires magnetic manipulation and specialised handling [40,66].
A key trend identified across studies is the increasing shift towards sustainable analytical practices, which aim to reduce the use of hazardous reagents, minimise solvent and sample consumption, and lower environmental impact—without compromising performance. This transition aligns with broader regulatory frameworks, such as the forthcoming revisions to the EU Urban Wastewater Treatment Directive, which aim to strengthen micropollutant removal targets by 2045 [8].
Beyond laboratory-based analyses, sensor technologies and real-time monitoring systems are emerging as powerful tools for wastewater-based surveillance. These innovations offer considerable potential for environmental monitoring, forensic analysis, epidemiological assessment, and process optimisation within WWTPs. Such systems enable quicker regulatory responses, improved mapping of pollution dynamics, and more efficient treatment strategies [6,7].
In conclusion, the combination of advanced chromatographic instrumentation and innovative, sustainable extraction techniques is redefining how micropollutants are monitored in wastewater. As environmental pressures grow, these developments will be critical to ensuring the implementation of resilient, effective, and eco-conscious monitoring systems that safeguard both human health and aquatic ecosystems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, E.G., T.R. and A.R.T.S.A.; methodology, G.C. and R.P.; formal analysis, G.C. and R.P.; investigation, G.C. and R.P.; writing—original draft preparation, G.C., R.P., M.F., S.S., E.G., T.R. and A.R.T.S.A.; writing—review and editing, G.C., R.P., M.F., S.S., E.G., T.R. and A.R.T.S.A.; supervision, E.G., T.R., S.S. and A.R.T.S.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
This systematic search was performed via the databases of Web of Science and Pubmed.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| 2F-DCK | 2-Fluorodeschloroketamine |
| 3-MMC | 3-Methylmethcathinone |
| 3,4-DMMC | 3,4-Dimethylmethacathinone |
| BC-MNP-μSPE | Binary-coated magnetic nanoparticle micro-solid-phase extraction |
| B-DLLME | Binary dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction |
| BPA | Bisphenol A |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| BS-DLLME | Binary solvent dispersive liquid–liquid extraction |
| BSTFA | Bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide |
| CAR/PDMS | Carboxen/polydimethylsiloxane |
| CPE | Cloud-point extraction |
| D4 | Octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane |
| D5 | Decamethylcyclopentasiloxane |
| D6 | Dodecamethylcyclohexasiloxane |
| DLLME | Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction |
| DMF | N,N-dimethylformamide |
| D-µ-SPE | Dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction |
| DVB/CAR/PDMS | Divinylbenzene/carboxen/polydimethylsiloxane |
| DVB/PDMS | Divinylbenzene/polydimethylsiloxane |
| EDCs | Endocrine-disrupting compounds |
| EI | Electronic impact |
| EU | European Union |
| FPSE | Fabric-phase sorptive extraction |
| GC | Gas chromatography |
| GC×GC-QTOF-MS | Two-dimensional gas chromatography coupled to quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry |
| GC-MS | Gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry |
| GC-MS/MS | Gas chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry |
| GC-Orbitrap-MS | Gas chromatography coupled to orbitrap mass spectrometry |
| HS-SPME | Headspace solid-phase microextraction |
| L3 | Octamethyltrisiloxane |
| L4 | Decamethyltetrasiloxane |
| L5 | Dodecamethylpentasiloxane |
| LC | Liquid chromatography |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry |
| LLE | Liquid–liquid extraction |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| LPME | Liquid-phase microextraction |
| MBDB | 3,4-Methylenedioxy-methylbutanamine |
| MBTFA | Methyl-bis(trifluoroacetamide) |
| MDEA | 3,4-Methylenedioxy-ethylamphetamine |
| MDMA | 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine |
| µ-SPE | Micro-solid-phase extraction |
| µd-SPE | Micro-dispersive solid-phase extraction |
| MSA-DLLME | Magnetic stirring-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction |
| MSTFA | N-methyl-N-trimethylsilyl-trifluoroacetamide |
| MTBSTFA | N-tert-butyldimethylsilyl-N-methyltrifluoroacetamide |
| MWCNTs | Multi-walled carbon nanotubes |
| n.s. | Not specified |
| OA-MNPs | Oleic acid magnetic nanoparticles |
| PCBs | Polychlorinated biphenyls |
| PCPs | Personal care products |
| PDMS | Polydimethylsiloxane |
| PDMS/DVB | Polydimethylsiloxane/divinylbenzene |
| PFAs | Perfluoroalkyl alcohols |
| PS@MNPs | Polystyrene-coated magnetite nanoparticles |
| Py-GC-MS | Pyrolysis gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry |
| QuEChERS | Quick, Easy, Cheap, Effective, Rugged, and Safe |
| RDSE | Rotating-disk sorptive extraction |
| (R)-MDMA | (R)-3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine |
| (R)-MTPA-Cl | (R)-α-methoxy-α-trifluoromethylphenylacetyl chloride |
| (R)-MTP-CI | (R)-α-methoxy-α-(trifluoromethyl) phenylacetyl chloride |
| (S)-MDMA | (S)-3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine |
| SA-MNPs | Stearic acid magnetic nanoparticles |
| SB-μ-SPE | Stir-bar-assisted micro-solid-phase extraction |
| SBSE | Stir-bar sorptive extraction |
| S-Mg/Al-LDH | Starch-Mg/Al-layered double hydroxide |
| SPE | Solid-phase extraction |
| SPME | Solid-phase microextraction |
| SS-LPME | Switchable solvent liquid-phase microextraction |
| STP | Sewage treatment plant |
| SVEA-LLE | Small-volume ethyl acetate-based liquid–liquid extraction |
| TED-GC-MS | Thermal desorption–gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry |
| TFA | Trifluoroacetic anhydride |
| TF-LPME | Thin-film liquid-phase microextraction |
| TFME | Thin-film microextraction |
| TMCS | Trimethylchlorosilane |
| UAE | Ultrasound-assisted extraction |
| USA-DCC-µ-SPE | Ultrasound-assisted dispersive cyclic conjugation-micro-solid-phase extraction |
| USA-DLLME | Ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction |
| USA-EME | Ultrasound-assisted emulsification microextraction |
| VA-SS-LPME | Vortex-assisted switchable solvent liquid-phase microextraction |
| WWTPs | Wastewater treatment plants |
References
- Hollender, J.; Schymanski, E.L.; Ahrens, L.; Alygizakis, N.; Béen, F.; Bijlsma, L.; Brunner, A.M.; Celma, A.; Fildier, A.; Fu, Q.; et al. NORMAN Guidance on Suspect and Non-Target Screening in Environmental Monitoring. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2023, 35, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wastewater: The Untapped Resource: The United Nations World Water Development Report 2017; United Nations Education, Scientivic and Cultural Organization: London, UK, 2017; ISBN 9789231002014.
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, H.; Song, N.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Ye, F.; Ju, Y.; Jiao, S.; Shi, L. New Insight into Fate and Transport of Organic Compounds from Pollution Sources to Aquatic Environment Using Non-Targeted Screening: A Wastewater Treatment Plant Case Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 161031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Walker, G.W.; Muir, D.C.G.; Nagatani-Yoshida, K. Toward a Global Understanding of Chemical Pollution: A First Comprehensive Analysis of National and Regional Chemical Inventories. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 2575–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapworth, D.J.; Baran, N.; Stuart, M.E.; Ward, R.S. Emerging Organic Contaminants in Groundwater: A Review of Sources, Fate and Occurrence. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 163, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, L.; Malato, S.; Antakyali, D.; Beretsou, V.G.; Đolić, M.B.; Gernjak, W.; Heath, E.; Ivancev-Tumbas, I.; Karaolia, P.; Lado Ribeiro, A.R.; et al. Consolidated vs New Advanced Treatment Methods for the Removal of Contaminants of Emerging Concern from Urban Wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 986–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spina, F.; Gea, M.; Bicchi, C.; Cordero, C.; Schilirò, T.; Varese, G.C. Ecofriendly Laccases Treatment to Challenge Micropollutants Issue in Municipal Wastewaters. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Publications Office of the European Union (OP), Luxembourg. Directive (EU) 2024/3019 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 November 2024 Concerning Urban Wastewater Treatment (Recast) (Text with EEA Relevance). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2024/3019/oj/eng (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Farré, M.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D. Recently Developed GC/MS and LC/MS Methods for Determining NSAIDs in Water Samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglioni, S.; Zuccato, E.; Chiabrando, C.; Fanelli, R.; Bagnatl, R. Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Illicit Drugs in Wastewater and Surface Water. Mass. Spectrom. Rev. 2008, 27, 378–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilachi, I.C.; Asiminicesei, D.M.; Fertu, D.I.; Gavrilescu, M. Occurrence and Fate of Emerging Pollutants in Water Environment and Options for Their Removal. Water 2021, 13, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando, M.D.; Mezcua, M.; Gómez, M.J.; Malato, O.; Agüera, A.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Comparative Study of Analytical Methods Involving Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry after Derivatization and Gas Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry for the Determination of Selected Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in Wastewaters. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1047, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés-Costa, M.J.; Andreu, V.; Picó, Y. Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry as a Tool for Wastewater-Based Epidemiology: Assessing New Psychoactive Substances and Other Human Biomarkers. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 94, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yu, C.; Zhang, J.; Wen, Y. Recent Advances in Biological Sample Preparation Methods Coupled with Chromatography, Spectrometry and Electrochemistry Analysis Techniques. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 102, 123–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelixo, R.; Barroso, M.; Gallardo, E.; Rosado, T. Determination of Arylcyclohexylamines in Biological Specimens: Sensors and Sample Pre-Treatment Approaches. Micromachines 2024, 15, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudi, M.; Ruan, H.D.; Wang, L.; Lyu, J.; Sadler, R.; Connell, D.; Chu, C.; Phung, D.T. Agriculture Development, Pesticide Application and Its Impact on the Environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duro, A.; Goudou, F.; Carmenate-Rodriguez, C.; Melchor-Rodriguez, K.; Minofar, B.; Gaspard, S.; Jauregui-Haza, U. A Computational Study of Adsorption on Activated Carbons Containing Basic Oxygenated Surface Groups of Two Priority Organochlorine Pesticides from Water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 704, 135449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Shi, L.; Xie, F.; Wang, X.; Nie, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, K.; Yu, J.; Wan, L. Flat Membrane–Based Liquid-Phase Microextraction for the Determination of Basic and Acidic Pesticide Residues in Water Samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2025, 1742, 465659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Directive—2020/2184—EN—EUR-Lex. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2020/2184/oj/eng (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- Needham, T.P.; Ghosh, U. Four Decades since the Ban, Old Urban Wastewater Treatment Plant Remains a Dominant Source of PCBs to the Environment. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wei, J.; Wei, X.; Teng, X.; Wang, Z.; Qu, R. Photodegradation of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) on Suspended Particles from the Yellow River under Sunlight Irradiation: QSAR Model and Mechanism Analysis. Water Res. 2024, 267, 122547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elangovan, S.; Pandian, S.B.S.; SJ, G.; Joshi, S.J. Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs): Environmental Fate, Challenges and Bioremediation. Microorg. Sustain. 2019, 10, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, I.A.; Zouari, N.; Al-Ghouti, M.A. Removal of Pesticides from Water and Wastewater: Chemical, Physical and Biological Treatment Approaches. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 101026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Zamora, C.; González-Sálamo, J.; Rivero, D.S.; Carrillo, R.; Hernández-Borges, J. Tetrazine-Based Dynamic Covalent Polymers as Degradable Extraction Materials in Sample Preparation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1318, 342925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Wu, M.; Song, N.; Ge, F.; Yang, T.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G. Automated Pretreatment of Environmental Water Samples and Non-Targeted Intelligent Screening of Organic Compounds Based on Machine Experiments. Environ. Int. 2024, 193, 109072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chormey, D.S. Validation and Green Profile Assessment of a Binary Solvent Liquid Phase Microextraction Method for the Determination of Chlorbenside and Fenobucarb in Lake and Wastewater Samples by GC–MS. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 44697–44705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijangos, L.; Bilbao, D.; Lopez-Herguedas, N.; Ortueta, N.; Olivares, M.; Zuloaga, O.; Etxebarria, N.; Prieto, A. Development of an Analytical Method for the Simultaneous Determination of 50 Semi-Volatile Organic Contaminants in Wastewaters. MethodsX 2023, 11, 102252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlo, F.; Profumo, A.; Fontàs, C.; Anticó, E. Preparation of New Polymeric Phases for Thin-Film Liquid Phase Microextraction (TF-LPME) of Selected Organic Pollutants. Microchem. J. 2022, 175, 107120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalglç Bozyiǧit, G.; Flrat Ayylldlz, M.; Chormey, D.S.; Onkal Engin, G.; Baklrdere, S. Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Based Preconcentration of Selected Pesticides and Escitalopram Oxalate, Haloperidol, and Olanzapine from Wastewater Samples Prior to Determination by GC-MS. J. AOAC Int. 2021, 104, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.C.; Lee, H.K. Fully Automated Graphitic Carbon Nitride-Based Disposable Pipette Extraction-Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Six Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Environmental Waters. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1637, 461824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodur, S.; Özlü, C.; Tışlı, B.; Fırat, M.; Chormey, D.S.; Bakırdere, S. Analytical Protocol for Determination of Endosulfan Beta, Propham, Chlorpyrifos, and Acibenzolar-s-Methyl in Lake Water and Wastewater Samples by Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry after Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budak, T.B.; Ayyıldız, M.F.; Chormey, D.S.; Bakırdere, S. Combination of Vortex Assisted Binary Solvent Microextraction and QuEChERS for the Determination of Prothiofos, Oxadiargyl, and Gamma-Cyhalothrin in Water and Pineapple Samples by Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, R.; Büyükpınar, Ç.; Bakırdere, S. Determination of Fipronil and Bixafen Pesticides Residues Using Gas Chromatography Mass Spectroscopy with Matrix Matching Calibration Strategy after Binary Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2020, 55, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozyiğit, G.D.; Ayyıldız, M.F.; Chormey, D.S.; Engin, G.O.; Bakırdere, S. Development of a Sensitive and Accurate Method for the Simultaneous Determination of Selected Insecticides and Herbicide in Tap Water and Wastewater Samples Using Vortex-Assisted Switchable Solvent-Based Liquid-Phase Microextraction Prior to Determination by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tışlı, B.; Selali Chormey, D.; Fırat Ayyıldız, M.; Bakırdere, S. Experimental Design of Vortex Assisted Switchable Solvent Homogeneous Liquid-Liquid Microextraction for Simultaneous Determination of Four Pesticides in Wastewater. J. AOAC Int. 2020, 103, 1250–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzoniti, M.C.; Rivoira, L.; Castiglioni, M.; El Ghadraoui, A.; Ahmali, A.; El Hakim El Mansour, T.; Mandi, L.; Ouazzani, N.; Del Bubba, M. Extraction of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Polychlorinated Biphenyls from Urban and Olive Mill Wastewaters Intended for Reuse in Agricultural Irrigation. J. AOAC Int. 2020, 103, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durak, B.Y.; Chormey, D.S.; Firat, M.; Bakirdere, S. Validation of Ultrasonic-Assisted Switchable Solvent Liquid Phase Microextraction for Trace Determination of Hormones and Organochlorine Pesticides by GC–MS and Combination with QuEChERS. Food Chem. 2020, 305, 125487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapukıran, F.; Fırat, M.; Chormey, D.S.; Bakırdere, S.; Özdoğan, N. Accurate and Sensitive Determination Method for Procymidone and Chlorflurenol in Municipal Wastewater, Medical Wastewater and Irrigation Canal Water by GC–MS After Vortex Assisted Switchable Solvent Liquid Phase Microextraction. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 102, 848–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari Erkan, H.; Chormey, D.S.; Caglak, A.; Dalgic Bozyigit, G.; Maltepe, E.; Onkal Engin, G.; Bakırdere, S. Binary Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Strategy for Accurate and Precise Determination of Micropollutants in Lake, Well and Wastewater Matrices. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 103, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chormey, D.S.; Akkaya, E.; Erulaş, F.A.; Bakırdere, S. Oleic and Stearic Acid-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles for Sonication-Assisted Binary Micro-Solid Phase Extraction of Endocrine Disrupting Compounds, and Their Quantification by GC-MS. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, A.N.; Zhang, H.; Yang, M. Optimization and Validation of Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction Method Coupled with Gas Chromatography–Triple Quadrupole Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Simultaneous Determination of Volatile and Semi-Volatile Organic Compounds in Coking Wastewater Treatment Plant. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçoğlu, E.S.; Sözüdoğru, O.; Komesli, O.T.; Yılmaz, A.E.; Bakırdere, S. Simultaneous Determination of Drug Active Compound, Hormones, Pesticides, and Endocrine Disruptor Compounds in Wastewater Samples by GC-MS with Direct Calibration and Matrix Matching Strategies after Preconcentration with Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faroon, O.; Olson, J. Toxicological Profile for Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs); Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, Georgia, 2000; p. 443.
- Köck-Schulmeyer, M.; Villagrasa, M.; López de Alda, M.; Céspedes-Sánchez, R.; Ventura, F.; Barceló, D. Occurrence and Behavior of Pesticides in Wastewater Treatment Plants and Their Environmental Impact. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ding, Z.; Lv, L.; Song, D.; Feng, Y.Q. A Novel Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction Based on Solidification of Floating Organic Droplet Method for Determination of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Aqueous Samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 636, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A.; Grześkowiak, T. Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 1382–1399. [Google Scholar]
- Turan, N.B.; Maltepe, E.; Chormey, D.S.; Bakırdere, S. Determination of Fenazaquin in Water and Tomato Matrices by GC-MS after a Combined QuEChERS and Switchable Solvent Liquid Phase Microextraction. Environ Monit Assess 2020, 192, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhuang, T.; Su, Z.; Chi, M.; Wang, H. Antibiotic Residues in Wastewaters from Sewage Treatment Plants and Pharmaceutical Industries: Occurrence, Removal and Environmental Impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Yao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ying, M.; Wu, T.; Jiang, W.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X.X. Transformation Mechanisms of Antidepressants in Biological Wastewater Treatment: Removal Kinetic, Transformation Products and Pathways. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 493, 152557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasawneh, O.F.S.; Palaniandy, P. Occurrence and Removal of Pharmaceuticals in Wastewater Treatment Plants. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 150, 532–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Córcoles, M.T.; Rodríguez-Gómez, R.; de Alarcón-Gómez, B.; Çipa, M.; Martín-Pozo, L.; Kauffmann, J.-M.; Zafra-Gómez, A. Chromatographic Methods for the Determination of Emerging Contaminants in Natural Water and Wastewater Samples: A Review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2019, 49, 160–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozyiğit, G.D.; Zaman, B.T.; Özdemir, O.K.; Kılınç, Y.; Chormey, D.S.; Bakırdere, S.; Engin, G.O. Removal of Two Antidepressant Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients from Hospital Wastewater by Polystyrene-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles–Assisted Batch Adsorption Process. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herghelegiu, M.-C.; Ernault, A.; Beldean-Galea, M.S.; Coman, M.-V. HPLC-PDA versus GC-MS in the Analysis of Paracetamol and Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in Wastewater. Studia Univ. Babes-Bolyai Chemia 2023, 68, 19–35. [Google Scholar]
- Bozyiğit, G.D.; Ayyıldız, M.F.; Chormey, D.S.; Engin, G.O.; Bakırdere, S. Trace Level Determination of Eleven Nervous System–Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients by Switchable Solvent-Based Liquid-Phase Microextraction and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry with Matrix Matching Calibration Strategy. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Hanafiah, Z.; Wan Mohtar, W.H.M.; Abd Manan, T.S.B.; Bachi’, N.A.; Abdullah, N.A.; Abd Hamid, H.H.; Beddu, S.; Mohd Kamal, N.L.; Ahmad, A.; Wan Rasdi, N. The Occurrence of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) in Malaysian Urban Domestic Wastewater. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Q.; Wu, D.; Cheng, Y.X.; Hu, L.X.; Chen, Q.L.; Wu, H.Y.; Sun, Y.H.; Liu, Y.S.; Ying, G.G. Development and Validation of a Simultaneous Method for the Analysis of Benzothiazoles and Organic Ultraviolet Filters in Various Environmental Matrices by GC–MS/MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 6541–6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozyiğit, G.D.; Zaman, B.T.; Özdemir, O.K.; Kılınç, Y.; Chormey, D.S.; Engin, G.O.; Bakırdere, S. Polystyrene—Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles Based Dispersive Micro—Solid Phase Extraction of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients of Antidepressant Drugs and Determination by GC-MS. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202104435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgıç Bozyiğit, G.; Fırat Ayyıldız, M.; Selali Chormey, D.; Onkal Engin, G.; Bakırdere, S. Accurate Quantification of Nervous System Drugs in Aqueous Samples at Trace Levels by Binary Solvent Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction-Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 1570–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capparelli, M.V.; Cipriani-Avila, I.; Jara-Negrete, E.; Acosta-López, S.; Acosta, B.; Pérez-González, A.; Molinero, J.; Pinos-Vélez, V. Emerging Contaminants in the Northeast Andean Foothills of Amazonia: The Case of Study of the City of Tena, Napo, Ecuador. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 107, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiuddin, I.; Grover, A.; Aulakh, J.S.; Malik, A.K.; Lee, S.S.; Brown, R.J.C.; Kim, K.H. Starch-Mg/Al Layered Double Hydroxide Composites as an Efficient Solid Phase Extraction Sorbent for Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs as Environmental Pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, J.; Villén, J.; Aragón, Á.; Vázquez, A. Determination of Diclofenac in Water Samples from Wastewater Treatment Plants by Large Volume Injection-Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. LCGC N. Am. 2019, 37, 194–197. [Google Scholar]
- Caban, M.; Lis, H.; Kobylis, P.; Stepnowski, P. The Triple-Sorbents Solid-Phase Extraction for Pharmaceuticals and Estrogens Determination in Wastewater Samples. Microchem. J. 2019, 149, 103965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Shao, X.T.; Tan, D.Q.; Yan, J.H.; Pei, W.; Wang, Z.; Yang, M.; Wang, D.G. Assessing the Trend of Diabetes Mellitus by Analyzing Metformin as a Biomarker in Wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Kaur, R.; Grover, A.; Rani, S.; Malik, A.K.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Fabric Phase Sorptive Extraction/GC-MS Method for Rapid Determination of Broad Polarity Spectrum Multi-Class Emerging Pollutants in Various Aqueous Samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 2407–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.; Ribeiro, C.; Cravo, S.; Cunha, S.C.; Pereira, J.A.; Fernandes, J.O.; Afonso, C.; Tiritan, M.E. Multi-Residue Method for Enantioseparation of Psychoactive Substances and Beta Blockers by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2019, 1125, 121731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arismendi, D.; Becerra-Herrera, M.; Cerrato, I.; Richter, P. Simultaneous Determination of Multiresidue and Multiclass Emerging Contaminants in Waters by Rotating-Disk Sorptive Extraction-Derivatization-Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Talanta 2019, 201, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumbi, B.P.; Moodley, B.; Birungi, G.; Ndungu, P.G. Target, Suspect and Non-Target Screening of Silylated Derivatives of Polar Compounds Based on Single Ion Monitoring GC-MS. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.H.; Xiao, Y.; Tan, D.Q.; Shao, X.T.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.G. Wastewater Analysis Reveals Spatial Pattern in Consumption of Anti-Diabetes Drug Metformin in China. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yawney, J.; Treacy, S.; Hindmarsh, K.W.; Burczynski, F.J. A General Screening Method for Acidic, Neutral, and Basic Drugs in Whole Blood Using the Oasis MCX Column. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2002, 26, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Biel-Maeso, M.; Corada-Fernández, C.; Lara-Martín, P.A. Removal of Personal Care Products (PCPs) in Wastewater and Sludge Treatment and Their Occurrence in Receiving Soils. Water Res. 2019, 150, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.L.; Lam, N.P.; Martens, D.; Kettrup, A.; Cai, Z. Triclosan Determination in Water Related to Wastewater Treatment. Talanta 2007, 72, 1650–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, M.B.; Christensen, J.H. Can Analyte Protectants Compensate Wastewater Matrix Induced Enhancement Effects in Gas Chromatography—Mass Spectrometry Analysis? J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1676, 463280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Ebrahimpour, K.; Mohammadi, F.; Moazeni, M. Ecotoxicological and Human Health Risk Assessment of Triclosan Antibacterial Agent from Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants. J. Water Health 2024, 22, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajibola, A.S.; Reich, M.; Kümmerer, K. Determination and Risk Assessment of UV Filters and Benzotriazole UV Stabilizers in Wastewater from a Wastewater Treatment Plant in Lüneburg, Germany. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struk-Sokołowska, J.; Kotowska, U.; Gwoździej-Mazur, J.; Polińska, W.; Canales, F.A.; Kaźmierczak, B. Benzotriazoles and Bisphenols in Wastewater from the Food Processing Industry and the Quantitative Changes during Mechanical/Biochemical Treatment Processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yücel, C.; Ertaş, H.; Ertaş, F.N.; Karapinar, I. Development of a Solid Phase Microextraction Gas Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Analysis of UV Filters. Microchem. J. 2024, 200, 110247. [Google Scholar]
- Tüzün, S.C.; Karapinar, I.; Yücel, C.; Nil, F.; Erta¸s, E.; Erta¸s, H.E. Determination of Benzophenone Derivatives in Wastewater by GC–MS/MS Combined with In-port Derivatization. CLEAN–Soil Air Water 2024, 52, 2300145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches Filho, P.J.; Coll, J.P.R.; da Silva, G.M.G.; Amaral, M.A.F.; dos Santos Hackbart, H.C.; Fusinato, M.D.; Arsand, D.R.; da Cunha, M.E. Development of a SPE/GC/MS Method for Simultaneous Determination of UV Filters (Oxybenzone and Octocrylene) and Hormones (Estrone, Beta-Estradiol, and Estriol). Microchem. J. 2024, 198, 110143. [Google Scholar]
- Vimalkumar, K.; Mayilsamy, M.; Arun, E.; Gobinath, B.; Prasanth, S.; Nikhil, P.N.; Krishna-Kumar, S.; Srimurali, S.; Mkandawire, M.; Babu-Rajendran, R. Screening of Antimicrobials, Fragrances, UV Stabilizers, Plasticizers and Preservatives in Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs) and Their Risk Assessment in India. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Hernández, P.; Pacheco-Fernández, I.; Bernardo, F.; Homem, V.; Pasán, J.; Ayala, J.H.; Ratola, N.; Pino, V. Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction Based on the Metal-Organic Framework CIM-80(Al) Coating to Determine Volatile Methylsiloxanes and Musk Fragrances in Water Samples Using Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry. Talanta 2021, 232, 122440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasselli, S.; Guzzella, L. Polycyclic Musk Fragrances (PMFs) in Wastewater and Activated Sludge: Analytical Protocol and Application to a Real Case Study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 30977–30986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, S.; Homem, V.; Santos, L. Simultaneous Determination of Synthetic Musks and UV-Filters in Water Matrices by Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Followed by Gas Chromatography Tandem Mass-Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1590, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, A.; Mesa, R.; Jurmain, J.; Furton, K.G. Fabric Phase Sorptive Extraction Explained. Separations 2017, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, A. Fabric Phase Sorptive Extraction: A New Generation Sample Preparation Strategy. In Green Analytical Methods and Miniaturized Sample Preparation Techniques for Forensic Drug Analysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, P.; Arismendi, D.; Becerra-Herrera, M. The Fundamentals, Chemistries and Applications of Rotating-Disk Sorptive Extraction. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 137, 116209. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak-Lange, M.; Niedziałkowska, K.; Lisowska, K. Cosmetic Preservatives: Hazardous Micropollutants in Need of Greater Attention? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, F.; Castiglioni, S.; Covaci, A.; de Voogt, P.; Emke, E.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Ort, C.; Reid, M.; Sancho, J.V.; Thomas, K.V.; et al. Mass Spectrometric Strategies for the Investigation of Biomarkers of Illicit Drug Use in Wastewater. Mass. Spectrom. Rev. 2016, 37, 258–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Guo, C.; Sun, Z.; Xu, J. Occurrence, Bioaccumulation and Toxicological Effect of Drugs of Abuse in Aquatic Ecosystem: A Review. Environ. Res. 2021, 200, 111362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langa, I.M.; Lado Ribeiro, A.R.; Ratola, N.; Gonçalves, V.M.F.; Tiritan, M.E.; Ribeiro, C. Amphetamine-like Substances and Synthetic Cathinones in Portuguese Wastewater Influents: Enantiomeric Profiling and Role of Suspended Particulate Matter. Forensic Sci. Int. 2024, 361, 112128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, M.M.; Nascimento, M.L.; Pereira dos Anjos, J.; Cunha, R.L.; da Rocha, G.O.; Ferreira dos Santos, I.; Pereira, P.A.d.P.; de Andrade, J.B. A Green Method for the Determination of Illicit Drugs in Wastewater and Surface Waters-Based on a Semi-Automated Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Device. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1710, 464230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verovšek, T.; Heath, D.; Heath, E. Enantiomeric Profiling of Amphetamines in Wastewater Using Chiral Derivatisation with Gas Chromatographic-Tandem Mass Spectrometric Detection. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, S.; Jiang, R.; Luan, T.; Ouyang, G. Rapid Detection and Speciation of Illicit Drugs via a Thin-Film Microextraction Approach for Wastewater-Based Epidemiology Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 842, 156888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langa, I.; Tiritan, M.E.; Silva, D.; Chemosensors, C.R. Gas Chromatography Multiresidue Method for Enantiomeric Fraction Determination of Psychoactive Substances in Effluents and River Surface Waters. Chemosens 2021, 9, 224. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, Z.X.; Shao, X.T.; Liu, S.Y.; Pei, W.; Wang, D.G. Wastewater Analysis Reveals Urban, Suburban, and Rural Spatial Patterns of Illicit Drug Use in Dalian, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 25503–25513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Yu, W.J.; Wang, Y.R.; Shao, X.T.; Wang, D.G. Tracing Consumption Patterns of Stimulants, Opioids, and Ketamine in China by Wastewater-Based Epidemiology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 16754–16766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.T.; Yu, H.; Lin, J.G.; Kong, X.P.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.G. Presence of the Ketamine Analog of 2-Fluorodeschloroketamine Residues in Wastewater. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Shao, X.T.; Tan, D.Q.; Yan, J.H.; Xiao, Y.; Zheng, Q.-D.; Pei, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.G. Reduction in Methamphetamine Consumption Trends from 2015 to 2018 Detected by Wastewater-Based Epidemiology in Dalian, China. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2019, 194, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroso, M.; Moreno, I.; Da Fonseca, B.; Queiroz, J.A.; Gallardo, E. Role of Microextraction Sampling Procedures in Forensic Toxicology. Bioanalysis 2012, 4, 1805–1826. [Google Scholar]
- Čelić, M.; Škrbić, B.D.; Insa, S.; Živančev, J.; Gros, M.; Petrović, M. Occurrence and Assessment of Environmental Risks of Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in Drinking, Surface and Wastewaters in Serbia. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Yasuhara, A.; Shiraishi, H.; Nakasugi, O. Bisphenol A in Hazardous Waste Landfill Leachates. Chemosphere 2001, 42, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.J.; Rocha, E. Synthetic Progestins in Waste and Surface Waters: Concentrations, Impacts and Ecological Risk. Toxics 2022, 10, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasinakis, A.S.; Gatidou, G.; Mamais, D.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Lekkas, T.D. Occurrence and Fate of Endocrine Disrupters in Greek Sewage Treatment Plants. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Jian, Y.; Lu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Deng, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Luo, Z. Distribution, Migration Patterns, and Food Chain Human Health Risks of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals in Water, Sediments, and Fish in the Xiangjiang River. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 930, 172484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacharodi, A.; Hassan, S.; Hegde, T.A.; Thacharodi, D.D.; Brindhadevi, K.; Pugazhendhi, A. Water a Major Source of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals: An Overview on the Occurrence, Implications on Human Health and Bioremediation Strategies. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnevali, O.; Santangeli, S.; Forner-Piquer, I.; Basili, D.; Maradonna, F. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals in Aquatic Environment: What Are the Risks for Fish Gametes? Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 44, 1561–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, C.L.S.; Bassin, J.P.; Peixoto, R.S. Water Contamination by Endocrine Disruptors: Impacts, Microbiological Aspects and Trends for Environmental Protection. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.; Landa, E.N.; Holbrook, K.L.; Walker, W.S.; Lee, W.Y. Rapid, Efficient, and Green Analytical Technique for Determination of Fluorotelomer Alcohol in Water by Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Velázquez, K.; Guzmán-Mar, J.L.; Saldarriaga-Noreña, H.A.; Murillo-Tovar, M.A.; Villanueva-Rodríguez, M. Ecological Risk Assessment Associated with Five Endocrine-Disrupting Compounds in Wastewater Treatment Plants of Northeast Mexico. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 30714–30726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiejza, D.; Kotowska, U.; Polińska, W.; Karpińska, J. USAEME-GC/MS Method for Easy and Sensitive Determination of Nine Bisphenol Analogues in Water and Wastewater. Molecules 2022, 27, 4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafi, S.; Ballesteros, E. A Sensitive, Robust Method for Determining Natural and Synthetic Hormones in Surface and Wastewaters by Continuous Solid-Phase Extraction-Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 53619–53632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Velázquez, K.; Guzmán-Mar, J.L.; Saldarriaga-Noreña, H.A.; Murillo-Tovar, M.A.; Hinojosa-Reyes, L.; Villanueva-Rodríguez, M. Occurrence and Seasonal Distribution of Five Selected Endocrine-Disrupting Compounds in Wastewater Treatment Plants of the Metropolitan Area of Monterrey, Mexico: The Role of Water Quality Parameters. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Dang, Z.; Liu, Y. Possible Overestimation of Bisphenol Analogues in Municipal Wastewater Analyzed with GC-MS. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 273, 116505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Zali, M.; Juahir, H.; Ismail, A.; Retnam, A.; Idris, A.N.; Sefie, A.; Tawnie, I.; Saadudin, S.B.; Ali, M.M. Tracing Sewage Contamination Based on Sterols and Stanols Markers within the Mainland Aquatic Ecosystem: A Case Study of Linggi Catchment, Malaysia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 20717–20736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Berrones, K.; Díaz de León-Martínez, L.; Bernal-Jácome, L.; Rodriguez-Aguilar, M.; Ávila-Galarza, A.; Flores-Ramírez, R. Rapid Analysis of 4-Nonylphenol by Solid Phase Microextraction in Water Samples. Talanta 2020, 209, 120546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caban, M.; Stepnowski, P. The Quantification of Bisphenols and Their Analogues in Wastewaters and Surface Water by an Improved Solid-Phase Extraction Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry Method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 28829–28839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Dang, Z.; Yin, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. Trace Determination of Eleven Natural Estrogens and Insights from Their Occurrence in a Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant and River Water. Water Res. 2020, 182, 115976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzo, V.; Goya-Pacheco, J.; Arismendi, D.; Becerra-Herrera, M.; Castillo-Aguirre, A.; Castillo-Felices, R.; Rosero-Moreano, M.; Carasek, E.; Richter, P. Cork Sheet as a Sorptive Phase to Extract Hormones from Water by Rotating-Disk Sorptive Extraction (RDSE). Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1087, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayaka, S.; Chormey, D.S.; Fırat, M.; Bakırdere, S. Determination of Endocrine Disruptive Phenolic Compounds by Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry after Multivariate Optimization of Switchable Liquid-Liquid Microextraction and Assessment of Green Profile. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hryniewicka, M.; Starczewska, B.; Tkaczuk, N. Simple Approach Based On Ultrasound-Assisted Emulsification Microextraction For Determination Of β-Sitosterol In Dietary Supplements And Selected Food Products. Microchem. J. 2020, 155, 104775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, T.K.; Uddin, M.E.; Jamal, M. Detection and Removal of Microplastics in Wastewater: Evolution and Impact. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 16925–16947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Shi, J.X.; Kang, E.H.; Nelson, T.F.; Sander, M.; McNeill, K.; Hartwig, J.F. Polymers from Plant Oils Linked by Siloxane Bonds for Programmed Depolymerization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 12645–12655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, T.H.; Do, H.T.; Phan Thi, L.A.; Singh, P.; Raizada, P.; Chi-Sheng Wu, J.; Nguyen, V.H. Global Challenges in Microplastics: From Fundamental Understanding to Advanced Degradations toward Sustainable Strategies. Chemosphere 2020, 267, 129275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, C.S.; Cheon, S.J.; Choi, K.I.; Kim, J.; Jung, J.; Yoon, J.K.; Lee, S.H.; Jeong, D.H. Detection of Microplastic Traces in Four Different Types of Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants through FT-IR and TED-GC-MS. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 333, 122017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ou, Q.; Wang, X.; Hou, F.; Li, P.; van der Hoek, J.P.; Liu, G. Assessing the Mass Concentration of Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Wastewater Treatment Plants by Pyrolysis Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 3114–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolecki, D.; Trella, B.; Qi, F.; Stepnowski, P.; Kumirska, J. Evaluation of the Removal of Selected Phthalic Acid Esters (PAEs) in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants Supported by Constructed Wetlands. Molecules 2021, 26, 6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takdastan, A.; Niari, M.H.; Babaei, A.; Dobaradaran, S.; Jorfi, S.; Ahmadi, M. Occurrence and Distribution of Microplastic Particles and the Concentration of Di 2-Ethyl Hexyl Phthalate (DEHP) in Microplastics and Wastewater in the Wastewater Treatment Plant. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.X.; He, S.; Gao, Y.; Li, Z.C.; Chi, H.Y.; Li, C.J.; Wang, D.J.; Yan, B. Protein Corona-Mediated Extraction for Quantitative Analysis of Nanoplastics in Environmental Waters by Pyrolysis Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 6698–6705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotowska, U.; Kapelewska, J.; Sawczuk, R. Occurrence, Removal, and Environmental Risk of Phthalates in Wastewaters, Landfill Leachates, and Groundwater in Poland. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.X.; Hao, L.T.; Wang, H.Y.Z.; Li, Y.J.; Liu, J.F. Cloud-Point Extraction Combined with Thermal Degradation for Nanoplastic Analysis Using Pyrolysis Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 1785–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, X.; Lin, L.; Wang, D. Occurrence, Distribution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Their Derivatives in the Effluents of Wastewater Treatment Plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erick, K.M.; Hudson, N.N.; Mildred, P.N. Physico-Chemical Characteristics and Levels of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Untreated Water from Ngong River, Kenya. J. Pollut. Eff. Control 2016, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liu, B.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J. Spatial Distribution and Sources of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Sediments from Dachan Bay, Shenzhen City. Water 2023, 15, 1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, F.A.; Eid, M.H.; El-Sherbeeny, A.M.; Abdel-Gawad, G.I.; Mohamed, E.A.; Abukhadra, M.R. Environmental and Health Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Toxic Elements in the Red Sea Using Monte Carlo Simulation. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, A.; Zhou, J.L.; Ohashi, A.; Ozaki, N.; Kindaichi, T. Comprehensive Review of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Water Sources, Their Effects and Treatments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 133971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, D.; Murugan, V.; Dhagat, U.; Gupta, P.; Tadala, R.; Karubothula, B.; Golebiewska, I.; Bin Salem, S.; Elamin, W.; Brudecki, G. Introduction of a Small Volume Ethyl Acetate Based Liquid-Liquid Extraction Procedure for Analysis of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Wastewater by Atmospheric Pressure Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry and Evaluation of Method Greenness. J. Chromatogr. A 2025, 1740, 465563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çetintürk, K. A High-Throughput Novel Approach for the Determination of Cresols in Wastewater Based on Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction Along with Thermal Desorption GC-MS/MS. J. Anal. Chem. 2023, 78, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, D.; Majumdar, D. Dissolved Load of Aromatic and Halogenated Non-Methane VOCs in Urban Sewage during Wet and Dry Seasons. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 60289–60301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimu, A.; Jillani, S.M.S.; Ganiyu, S.A.; Chowdhury, S.; Alhooshani, K. Multivariate Optimization of Chlorinated Hydrocarbons’ Micro-Solid-Phase Extraction from Wastewater Using Germania-Decorated Mesoporous Alumina-Silica. Microchem. J. 2021, 160, 105674. [Google Scholar]
- Rakhtshah, J.; Shirkhanloo, H.; Esmaeili, N. A Rapid Extraction of Toxic Styrene from Water and Wastewater Samples Based on Hydroxyethyl Methylimidazolium Tetrafluoroborate Immobilized on MWCNTs. Microchem. J. 2021, 170, 106759. [Google Scholar]
- Behzadi, M. Facile Fabrication and Application of Poly(Ortho-Phenetidine) Nanocomposite Coating for Solid-Phase Microextraction of Carcinogenic Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from Wastewaters. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez, I.; Arrebola, F.J.; Martínez Vidal, J.L.; Garrido Frenich, A. Assessment of Wastewater Pollution by Gas Chromatography and High Resolution Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1619, 460964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senta, I.; Gracia-Lor, E.; Borsotti, A.; Zuccato, E.; Castiglioni, S. Wastewater Analysis to Monitor Use of Caffeine and Nicotine and Evaluation of Their Metabolites as Biomarkers for Population Size Assessment. Water Res. 2015, 74, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Pashalidis, I.; Orfanos, A.G.; Manariotis, I.D.; Tatarchuk, T.; Sellaoui, L.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Mittal, A.; Núñez-Delgado, A. Removal of Caffeine, Nicotine and Amoxicillin from (Waste)Waters by Various Adsorbents. A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego-Soto, G.; Eberhart, J.K. Embryonic Nicotine Exposure Disrupts Adult Social Behavior and Craniofacial Development in Zebrafish. Toxics 2022, 10, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, J.A.; Quadra, G.R.; Almeida, R.M.; Soranço, L.; Lobo, H.; Rocha, V.N.; Bialetzki, A.; Reis, J.L.; Roland, F.; Barros, N. Sublethal Effects of Environmental Concentrations of Caffeine on a Neotropical Freshwater Fish. Ecotoxicology 2022, 31, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quéméneur, M.; Marty, Y. Fatty Acids and Sterols in Domestic Wastewaters. Water Res. 1994, 28, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovičić, K.; Djikanović, V.; Santrač, I.; Živković, S.; Dimitrijević, M.; Vranković, J.S. Effects of Trace Elements on the Fatty Acid Composition in Danubian Fish Species. Animals 2024, 14, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonova, A.A.; Shishlyannikov, S.M.; Volokitina, N.A.; Galachyants, Y.P.; Bukin, Y.S.; Blinov, V.V.; Gnatovsky, R.Y.; Vorobyeva, S.S. Fatty Acid Changes in Nearshore Phytoplankton under Anthropogenic Impact as a Biodiversity Risk Factor for the World’s Deepest Lake Baikal. Diversity 2022, 14, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; He, X.; Hu, X.; Pan, B.; Huang, Z.; Shen, J. Hollow Fiber-Solid Phase Microextraction of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters from Wastewater Coupled with Micro Sample Collector Assisted Injection Technique. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1710, 464415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérette, C.; Lemoine, P.; Ramirez, P.; Segura, P.A. Determination of Short-Chain Carboxylic Acids and Non-Targeted Analysis of Water Samples Treated by Wet Air Oxidation Using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1652, 462352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Muñoz, M.A.; Cerdà, V.; Turnes Palomino, G.; Palacio, E. Determination of Long-Chain Fatty Acids in Anaerobic Digester Supernatant and Olive Mill Wastewater Exploiting an in-Syringe Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction and Derivatization-Free GC-MS Method. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 3833–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.W.; Wang, X.J.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Y.P.; Nie, J.; Li, Z.G.; Fang, X.G.; Lee, M.R. Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Combined with Microwave Demulsification for Determination of FAME Residuals in Biodiesel Wastewater. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2020, 58, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielawska, K.; Dziakowska, I.; Roszkowska-Jakimiec, W. Chromatographic Determination of Fatty Acids in Biological Material. Toxicol Mech Methods 2010, 20, 526–537. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Khalid, T.; Surkatti, R.; El-Naas, M.H. Organic Contaminants in Industrial Wastewater: Prospects of Waste Management by Integrated Approaches. In Combined Application of Physico-Chemical & Microbiological Processes for Industrial Effluent Treatment Plant; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 205–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, N.; Reddy, S. Impact of Solvents Leading to Environmental Pollution. J Chem. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 3, 50–52. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chen, W. Effects of Different Scrap Iron as Anode in Fe-C Micro-Electrolysis System for Textile Wastewater Degradation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 26869–26882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Wan, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Chang, C.; Wang, Y. Enhanced Removal of Nitrate and Refractory Organic Pollutants from Bio-Treated Coking Wastewater Using Corncobs as Carbon Sources and Biofilm Carriers. Chemosphere 2019, 237, 124520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatoon, K.; Malik, A. Cyto-Genotoxic Potential of Petroleum Refinery Wastewater Mixed with Domestic Sewage Used for Irrigation of Food Crops in the Vicinity of an Oil Refinery. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ötles, S.; Kartal, C. Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE): Principles and Applications in Food Samples. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2016, 15, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes Vianna, M.T.; Coutinho da Silva, R.; Marques, M. Optimisation of the Conditions of Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction for Environmentally Friendly Determination of Bisphenols and Benzophenone in Complex Water Matrices by Lc-Ms/Ms. SSRN Electron. J. 2022, 180, 107636. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4034638 (accessed on 31 April 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).