Effectiveness of an Early Intervention in Mild Hyponatremia to Prevent Accidental Falls in Hospitalized Older Adults—A Crossover Ecological Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria and Samples
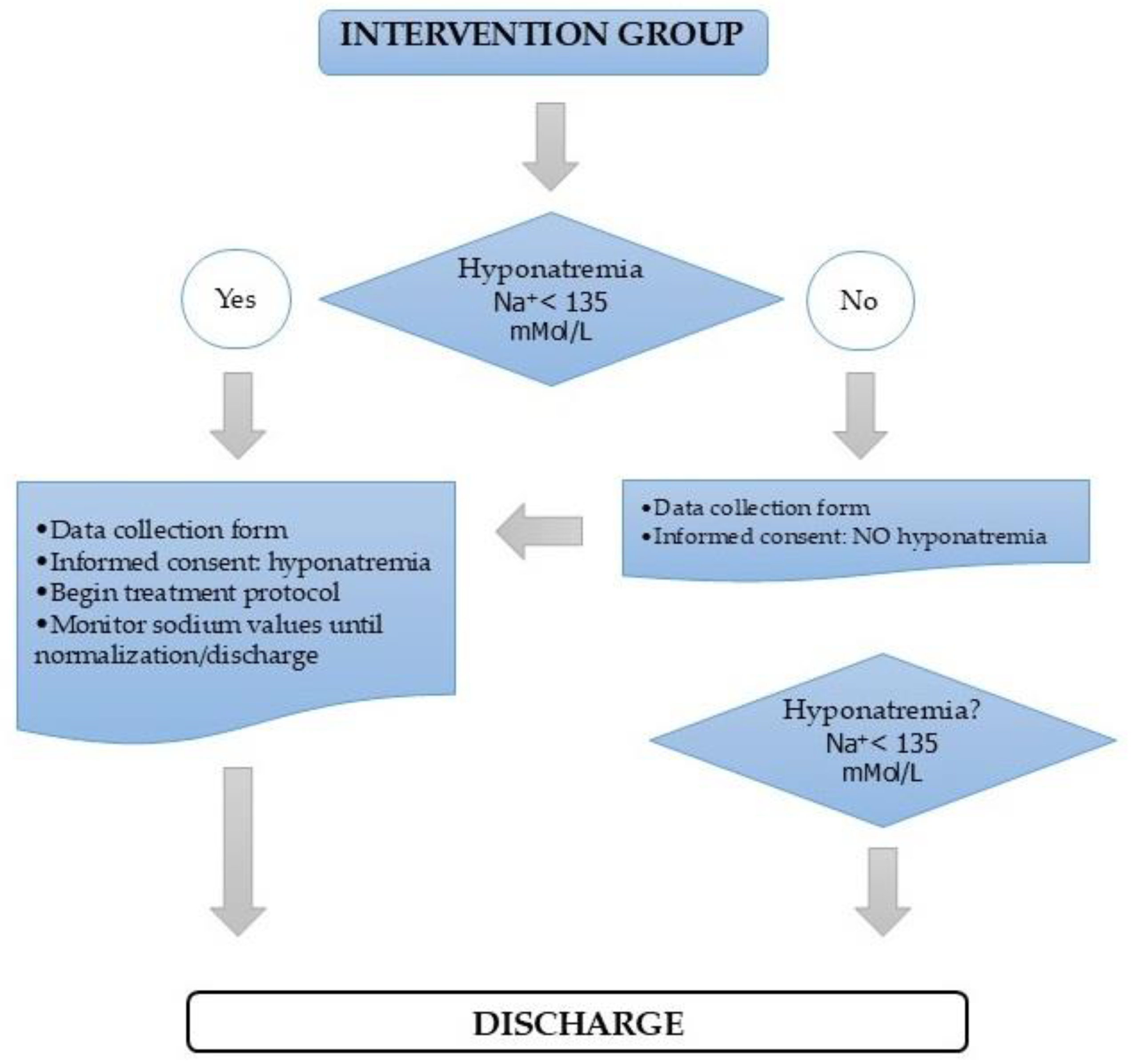
2.3. Intervention Design and Implementation
2.4. Follow-Up and Data Collection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hagino, T.; Hagino, T.; Wako, M.; Ochiai, S.; Taniguchi, N.; Ando, T.; Ichikawa, J.; Haro, H. Assessment of fall risk and adverse events among general ward inpatients at a regional general hospital in Japan. Cureus 2025, 17, e77456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Falls. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/falls (accessed on 30 November 2024).
- Bouldin, E.L.D.; Andresen, E.M.; Dunton, N.E.; Simon, M.; Waters, T.M.; Liu, M.; Daniels, M.; Mion, L.C.; Shorr, R.I. Falls Among Adult Patients Hospitalized in the United States. J. Patient Saf. 2013, 9, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harianto, H.; Anpalahan, M. In-hospital Falls in Older Patients: The Risk Factors and The Role of Hyponatraemia. Curr. Aging Sci. 2017, 10, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzia, M.F.; Prates, C.G.; Bombardelli, C.F.; Adorna, J.B.; Moura, G.M.S.S. Characteristics of falls with damage to hospitalized patients. Rev. Gaúcha Enferm. 2019, 40, e20180307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikos, M.; Trybulska, A.; Czerw, A. Falls—The socio-economic and medical aspects important for developing prevention and treatment strategies. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2021, 28, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. Falls associated with indoor and outdoor environmental hazards among community-dwelling older adults between men and women. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, I.D.; Dyer, S.M.; Panagoda, C.E.; Murray, G.R.; Hill, K.D.; Cumming, R.G.; Kerse, N. Interventions for preventing falls in older people in care facilities and hospitals. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 9, CD005465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, H.; Jazayeri, D.; Shaw, L.; Kiegaldie, D.; Hill, A.M.; Morris, M.E. Hospital falls prevention with patient education: A scoping review. BMC Geriatr. 2020, 20, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukaszyk, C.; Harvey, L.; Sherrington, C.; Keay, L.; Tiedemann, A.; Coombes, J.; Clemson, L.; Ivers, R. Risk factors, incidence, consequences and prevention strategies for falls and fall-injury within older indigenous populations: A systematic review. Aust. N. Z. J. Public. Health. 2016, 40, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.E.; Webster, K.; Jones, C.; Hill, A.M.; Haines, T.; McPhail, S.; Kiegaldie, D.; Slade, S.; Jazayeri, D.; Heng, H.; et al. Interventions to reduce falls in hospitals: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing 2022, 51, afac077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, K.; Staggs, V.; Potter, C.; Cramer, E.; Shorr, R.; Mion, L.C. Fall prevention implementation strategies in use at 60 United States hospitals: A descriptive study. BMJ Qual. Saf. 2020, 29, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannou, P.; Panagiotakis, S.; Tsagkaraki, E.; Tsioutis, C.; Fragkiadakis, K.; Gikas, A.; Filippatos, T.D. Increased mortality in elderly patients admitted with hyponatremia: A prospective cohort study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehlberg, E.A.; Lucero, R.J.; Weaver, M.T.; McDaniel, A.M.; Chandler, A.M.; Richey, P.A.; Mion, L.C.; Shorr, R.I. Associations between hyponatraemia, volume depletion and the risk of falls in US hospitalised patients: A case–control study. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e017045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo-Rodríguez, C.; García-Pozo, A.M.; Gadea-Cedenilla, C.; Moro-Tejedor, M.N.; Pedraz Marcos, A.; Tejedor-Jorge, A. Prevalencia de hiponatremia en pacientes mayores de 65 años que sufren una caída intrahospitalaria. Nefrología 2016, 36, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miller, N.E.; Rushlow, D.; Stacey, S.K. Diagnosis and management of sodium disorders: Hyponatremia and hypernatremia. Am. Fam. Physician 2023, 108, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Biggins, S.W.; Angeli, P.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Ginès, P.; Ling, S.C.; Nadim, M.K.; Wong, F.; Kim, W.R. Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and hepatorenal syndrome: 2021 practice guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1014–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, M.K.; Gill, K.M.; Magliozzi, M.R. Gait Assessment for Neurologically Impaired Patients. Phys. Ther. 1986, 66, 1530–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, F.; Barthel, D. Functional evaluation: The Barthel Index. Md. State Med. J. 1965, 14, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Guralnik, J.M.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Glynn, R.J.; Berkman, L.F.; Blazer, D.G.; Scherr, P.A.; Wallace, R.B. A Short Physical Performance Battery Assessing Lower Extremity Function: Association with Self-Reported Disability and Prediction of Mortality and Nursing Home Admission. J. Gerontol. 1994, 49, M85–M94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—A metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J. Biomed. Inform. 2009, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, T.A.; Lavori, P.W.; Bailar, J.C.; Polansky, M. Crossover and Self-Controlled Designs in Clinical Research. N. Engl. J. Med. 1984, 310, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.D.A.; Silva, A.O.; Rodrigues, R.A.P.; Moreira, M.A.S.P.; Nogueira, J.D.A.; Tura, L.F.R. Assessment of risk of falls in elderly living at home. Rev. Lat. Am. Enferm. 2017, 25, e2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renneboog, B.; Sattar, L.; Decaux, G. Attention and postural balance are much more affected in older than in younger adults with mild or moderate chronic hyponatremia. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 41, e25–e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake-Holland, A.J.; Noble, M.I.M. The Hyponatremia Epidemic: A Frontier Too Far? Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2016, 3, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado Silveira, E.; Muñoz García, M.; Montero Errasquin, B.; Sánchez Castellano, C.; Gallagher, P.F.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J. Prescripción inapropiada de medicamentos en los pacientes mayores: Los criterios STOPP/START. Rev. Esp. Geriatr. Gerontol. 2009, 44, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Norello, D.; Parenti, G.; Sforza, A.; Maggi, M.; Peri, A. Hyponatremia, falls and bone fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Endocrinol. 2018, 89, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Grace, J.; Tomkins, M.; O’Reilly, M.W.; Thompson, C.J.; Sherlock, M. Approach to the Patient: Hyponatremia and the Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuresis (SIAD). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 2362–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, S.; Gayot, C.; Bimou, C.; Mergans, T.; Kajeu, P.; Castelli, M.; Dantoine, T.; Tchalla, A. Prevalence of mild hyponatremia and its association with falls in older adults admitted to an emergency geriatric medicine unit (the MUPA unit). BMC Geriatr. 2019, 19, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, G.H.; Shim, S.R.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, J.H.; Chun, D.I.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, J.H. Risk for Hip Fracture due to Alpha Blocker Treatment in Korean Women: National Health Insurance Database Study. LUTS Lower Urin. Tract. Symptoms 2018, 10, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H. Tools for assessing fall risk in the elderly: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 30, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córcoles-Jiménez, M.P.; Ruiz-García, M.V.; Saiz-Vinuesa, M.D.; Muñoz-Mansilla, E.; Herreros-Sáez, L.; Fernández-Pallarés, P.; Calero-Yáñez, F.; Muñoz-Serrano, M.T. Deterioro funcional asociado a la hospitalización en pacientes mayores de 65 años. Enferm. Clin. 2016, 26, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gettens, S.; Fulbrook, P.; Jessup, M.; Low Choy, N. The patients’ perspective of sustaining a fall in hospital: A qualitative study. J. Clin. Nurs. 2018, 27, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Intervention Group | Hyponatremia n = 25 | Normalized Blood Sodium n = 18 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) Mean (SD) | 83.52 (6.5) | 82.28 (7.4) | 0.417 |
| Length of stay (days) Mean (SD) | 15.56 (15.72) | 11.52 (9.64) | 0.216 |
| Hyponatremia n = 25 (*) | Normalized Blood Sodium n = 18 | ||
| FAC Scale | |||
| Nonfunctional n (%) | 5 (18.5) | 3 (12.5) | 0.135 |
| Dependent n (%) | 18 (66.7) | 15 (62.5) | |
| Independent n (%) | 4 (14.8) | 6 (25.0) | |
| B Scale | |||
| Unable n (%) | 6 (21.4) | 3 (12.2) | 0.607 |
| Needs major help n (%) | 13 (46.4) | 13 (52.0) | |
| Needs some help n (%) | 8 (28.6) | 8 (32.0) | |
| Needs little help n (%) | 1 (3.6) | 1 (4.0) | |
| SPPB Scale | |||
| Frail n (%) | 19 (86.4) | 18 (85.7) | 1 |
| No change n (%) | 3 (13.6) | 3 (14.3) |
| CG n = 1517 | IG n = 408 | p Value | Difference | 95% CI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), Mean (SD) | 81.23 (8.6) | 82.35 (7.4) | 0.009 | −(1.1) | (−1.96 to 0.82) | |
| Downton scale, Mean (SD) | 5.17 (1.9) | 5.2 (1.8) | 0.665 | |||
| Falls, Mean (SD) | 18.56 (7.21) | 17.05 (6.65) | 0.000 | 1.51 | (0.74–2.299) | |
| Incidence of falls, Mean (SD) | 9.80 (4.7) | 6.70 (3.1) | 0.000 | 3.10 | (2.71–3.49) | |
| Sex | Male, No (%) | 692 (45.62) | 192(47.06) | 0.576 | ||
| Female, No (%) | 825 (54.38) | 215 (52.94) | ||||
| Risk of falls on Downton scales | High, No (%) | 1355 (89.32) | 384 (94.12) | 0.237 | ||
| Low, No (%) | 113 (10.68) | 24 (5.88) | ||||
| Second-Phase Group | First-Phase Group | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, No (%) | Male | 56 (56.56) | 136 (44.15) | 0.037 |
| Female | 43 (43.44) | 172 (55.85) | ||
| Treatment started, No (%) | Yes | 5 (100) | 16 (66.66) | 0.283 |
| No | 0 (0) | 8 (33.34) | ||
| Na+ corrected, No (%) | Yes | 1(33.3) | 12 (70.58) | 0.270 |
| No | 2 (66.7) | 5 (29.42) | ||
| Hyponatremia between normalization and discharge, No (%) | Yes | 1 (100) | 3 (20) | 0.250 |
| No | 0 (0) | 12 (80) | ||
| Risk of falls according to Downton scale, No (%) | Low | 9 (9.00) | 15 (4.88) | 0.143 |
| High | 91 (91.00) | 293 (95.12) |
| Second-Phase Group (n = 100) | First-Phase Group (n = 308) | p Value | Mean Difference | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD) | 79.61 (6.1) | 83.24 (7.53) | 0.000 | 3.63 | (2.00–5.27) |
| Downton score, mean (SD) | 4.91 (1.87) | 5.32 (1.87) | 0.059 | ||
| Hyponatremia, mean (SD) | 131.40 (3.20) | 130.20 (3.24) | 0.461 | ||
| FAC Scale Hyponatremia, mean (SD) | 3.40 (0.89) | 1.55 (1.33) | 0.007 | 1.85 | (0.55–3.16) |
| Barthel Hyponatremia, mean (SD) | 68.00 (26.12) | 45.7 (25.8) | 0.093 | ||
| SPPB Hyponatremia, mean (SD) | 3.18 (5.27) | 3.18 (4.14) | 0.141 | ||
| Nº of falls, mean (SD) | 15.18 (8.58) | 17.66 (5.78) | 0.008 | 2.48 | (0.66–4.29) |
| Incidence of falls, mean (SD) | 10.65 (3.90) | 5.41 (1.19) | 0.000 | 5.24 | (4.45/6.02) |
| Blood sodium at discharge, mean (SD) | 139.07 (3.49) | 138.74 (3.57) | 0.428 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lobo-Rodríguez, C.; Pedraz-Marcos, A.; Velarde-García, J.F.; Calderari Fernández, E.; Gadea-Cedenilla, C.; Medina-Torres, M.; Moro-Tejedor, M.N.; Sánchez García, L.; García-Pozo, A.M. Effectiveness of an Early Intervention in Mild Hyponatremia to Prevent Accidental Falls in Hospitalized Older Adults—A Crossover Ecological Clinical Trial. Healthcare 2025, 13, 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13080865
Lobo-Rodríguez C, Pedraz-Marcos A, Velarde-García JF, Calderari Fernández E, Gadea-Cedenilla C, Medina-Torres M, Moro-Tejedor MN, Sánchez García L, García-Pozo AM. Effectiveness of an Early Intervention in Mild Hyponatremia to Prevent Accidental Falls in Hospitalized Older Adults—A Crossover Ecological Clinical Trial. Healthcare. 2025; 13(8):865. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13080865
Chicago/Turabian StyleLobo-Rodríguez, Carmen, Azucena Pedraz-Marcos, Juan Francisco Velarde-García, Elena Calderari Fernández, Carmen Gadea-Cedenilla, Margarita Medina-Torres, Mª Nieves Moro-Tejedor, Leonor Sánchez García, and Ana Mª García-Pozo. 2025. "Effectiveness of an Early Intervention in Mild Hyponatremia to Prevent Accidental Falls in Hospitalized Older Adults—A Crossover Ecological Clinical Trial" Healthcare 13, no. 8: 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13080865
APA StyleLobo-Rodríguez, C., Pedraz-Marcos, A., Velarde-García, J. F., Calderari Fernández, E., Gadea-Cedenilla, C., Medina-Torres, M., Moro-Tejedor, M. N., Sánchez García, L., & García-Pozo, A. M. (2025). Effectiveness of an Early Intervention in Mild Hyponatremia to Prevent Accidental Falls in Hospitalized Older Adults—A Crossover Ecological Clinical Trial. Healthcare, 13(8), 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13080865






