Abstract
Background/Objectives: In this longitudinal study, the relationship between chewing status and steatotic liver disease (SLD) was examined in 3775 people aged ≥50 years who underwent medical checkups at Junpukai Health Maintenance Center in Okayama, Japan. Methods: Participants without SLD at the time of a baseline survey in 2018 were followed until 2022. Chewing status was assessed by a self-administered questionnaire. The presence or absence of SLD was ascertained from the medical records of Junpukai Health Maintenance Center. Results: A total of 541 participants (14%) were diagnosed as having a poor chewing status at baseline. Furthermore, 318 (8%) participants were newly diagnosed with SLD at follow-up. In multivariate logistic regression analyses, the presence or absence of SLD was found to be associated with the following characteristics at baseline: sex (male: odds ratio [ORs] = 1.806; 95% confidence interval [CIs]: 1.399–2.351), age (ORs = 0.969; 95% CIs: 0.948–0.991), body mass index (≥25.0 kg/m2; ORs = 1.934; 95% CIs: 1.467–2.549), diastolic blood pressure (ORs = 1.017; 95% CIs: 1.002–1.032), and chewing status (poor: ORs = 1.472; 95% CIs: 1.087–1.994). Conclusions: The results indicate that a poor chewing status was associated with SLD development after 4 years. Aggressively recommending dental visits to participants with poor chewing status may not only improve their ability to chew well but may also reduce the incidence of SLD.
1. Introduction
Steatotic liver disease (SLD) is the overarching term for conditions in which excess fat accumulates in the liver and lipolysis is impaired, resulting in abnormal lipid metabolism and an unhealthy condition in the liver [1,2]. In recent years, the proportion of Japanese patients with SLD has been increasing, and it is reported that about 10–30% of Japanese people have SLD [3,4,5,6]. Patients with SLD often show few subjective symptoms when the disease is mild [7]. However, as symptoms progress, liver failure, kidney failure, and liver cancer may occur [8,9,10]. Therefore, identifying and controlling factors associated with new-onset SLD will contribute to preventing the development of liver failure, kidney failure, and liver cancer.
Chewing status is one of the health conditions related to eating behavior. In a clinical study, it was shown that chewing probiotics-based gum could improve periodontal health [11]. Another clinical study reported that poor chewing status is a risk factor for dental caries and molar malocclusion [12]. In this way, it is well known that chewing is associated with oral health.
It has also been shown that chewing is implicated in fat accumulation in the body. For example, past epidemiological studies showed that chewing status is associated with abdominal obesity [13,14]. Furthermore, another epidemiological study also reported the association between poor chewing status and SLD [15]. However, these studies showed the cross-sectional association between chewing status and fat accumulation status, and it is not still clear whether poor chewing status could lead to SLD in the future.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare mandates the provision of specific health checkups focusing on lifestyle [16,17]. The questionnaire for these specific health checkups includes items such as eating behavior, including chewing status [18]. Furthermore, in Junpukai Health Maintenance Center in Okayama, Japan, participants who undergo these health checkups can receive medical checkups for SLD if they so desire. Therefore, by combining these data, the association between chewing status and SLD can be investigated.
In addition, it has been reported that chewing status begins to decline around middle age [19], and in Japan, an increase in the “proportion of Japanese people aged ≥50 years with good chewing status” has been set as a health principle in the national health promotion movement “Healthy Japan 21” to promote the health of Japanese people in the 21st century. In other words, there is a high possibility of finding a longitudinal association between masticatory status and SLD in a population aged ≥50 years, in which reduced mastication is more likely to be observed. Given this background, the aim of the present longitudinal study was to clarify the longitudinal relationship between chewing status and SLD in Japanese people aged ≥50 years who had undergone medical checkups at Junpukai Health Maintenance Center over a 4-year period.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
This was a prospective cohort study with a follow-up period of 4 years. The disease of interest was SLD, and the factor considered was good or poor chewing status.
2.2. Participants
Our study comprises an all-participant survey of community residents who underwent medical checkups at Junpukai Health Maintenance Center in Okayama, Japan, and who were not diagnosed with SLD in the 2018 baseline survey. Informed consent was not obtained because this study used anonymized claims data. In total, 10,411 Japanese people aged ≥50 years participated in the baseline survey, which was conducted between April 2018 and March 2019. At baseline, 2458 individuals with SLD and 170 with missing blood test data were excluded from the analysis. Of the remaining 7783 participants, 3775 were followed from April 2022 to March 2023 (follow-up rate: 49%). Therefore, in the present study, data from 3775 community-dwelling residents (1620 male, 2155 female; mean age, 57.6 years) were analyzed. A total of 318 (8%) participants were newly diagnosed with SLD at follow-up (Figure 1).
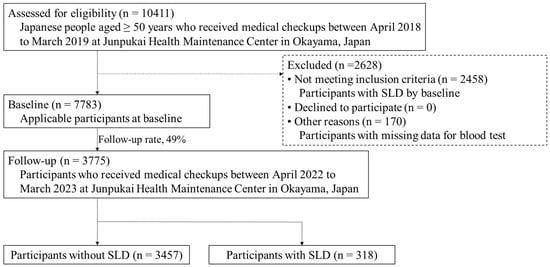
Figure 1.
Flowchart of data selection criteria. Abbreviations: SLD, steatotic liver disease.
2.3. Assessment of SLD
The presence or absence of SLD was diagnosed by abdominal ultrasonography at Junpukai Health Maintenance Center. A skilled technician performed real-time ultrasound examinations to detect blurred vessels, deep attenuation, and increased echotexture of the liver compared with the kidneys to assess the degree of fatty infiltration [20]. An expert physician then confirmed the validity of the findings.
2.4. Assessment of Body Composition
Nurses measured the height and weight of participants. The body mass index (BMI) was calculated as the weight divided by the square of the height (kg/m2) [15]. In general, BMI ≥ 25.0 kg/m2 indicates obesity in Japan [21]. Therefore, the presence or absence of BMI ≥ 25.0 kg/m2 was analyzed as a factor in this study.
2.5. Assessment of the Serum Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) Level, Triglyceride Level, and High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Cholesterol Level
High-performance liquid chromatography was used to measure serum HbA1c levels in venous blood samples collected after overnight fasting [22]. Serum HbA1c levels ≥ 6.5% are generally considered to indicate poor glycemic control [23]. Therefore, the presence or absence of a serum HbA1c level ≥ 6.5% was analyzed as a factor in this study. Therefore, triglyceride level ≥ 150 mg/dL or HDL cholesterol level ≤ 40 mg/dL are generally considered two of the diagnostic indices for dyslipidemia [24]. Therefore, the presence or absence of triglyceride level ≥ 150 mg/dL or HDL cholesterol level ≤ 40 mg/dL was analyzed as a factor in this study.
2.6. Assessment of Blood Pressure Levels
Nurses measured the systolic and diastolic blood pressures of the participants. Blood pressure levels were measured twice for each participant, and the mean value was calculated [25].
2.7. Assessment of Chewing Status and Other Items by a Self-Administered Questionnaire
The self-administered questionnaire was the same one used in specific health checkups in Japan [26]. Regarding current chewing status, participants selected from: “I can eat anything.”; “I sometimes have difficulty chewing due to dental problems such as dental caries or periodontal disease.”; and “I can hardly chew.” Participants who answered “I can eat anything.” were defined as having a good chewing status, whereas those who answered “I sometimes have difficulty chewing due to dental problems such as dental caries or periodontal disease.” and “I can hardly chew.” were defined as having poor chewing status [13]. The questionnaire also included items on the following variables: sex, age, smoking status (the presence or absence of smoking at least one cigarette per day), drinking status (the presence or absence of drinking alcohol at least once per day), exercise habits (the presence or absence of engaging in light exercise for at least 30 min more than twice per week for at least 1 year), physical activity (the presence or absence of going for a walk or the equivalent for at least 1 h per day), sleep status (good or poor), eating speed (slow, medium, or quick), snacking habits (none, sometimes, or daily), skipping breakfast (<3 or ≥3 times/week), and eating dinner within 2 h before bedtime (<3 or ≥3 times/week) [16,26,27,28].
2.8. Statistical Analysis
The normality of the data was checked with the Lilliefors tests. Because the results indicated that the continuous variables were not all normally distributed, the data were expressed as median (first- and third-quartile) values. Fisher’s exact test and the Mann–Whitney U test were used to assess significant differences in the characteristics of each factor by chewing status (good or poor). In addition, univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed using the presence of SLD as the dependent variable. In the multivariate stepwise logistic regression analysis, factors that were significantly different in the univariate logistic regression analysis in addition to sex and age were selected for the third category. The Hosmer–Lemeshow fit test was performed to confirm the suitability of the model using multivariate stepwise logistic regression analysis. All data were analyzed using SPSS (version 27; IBM Japan, Tokyo, Japan), with a p-value < 0.05 considered to indicate statistical significance.
2.9. Research Ethics
The Ethics Committee of Asahi University approved the present study (approval Nos. 27010 and 30018), which was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (as revised in Brazil in 2013).
3. Results
Table 1 shows the characteristics of the participants by chewing status at baseline. A total of 541 participants (14%) were diagnosed as having a poor chewing status at baseline. Participants with a poor chewing status were characterized by a significantly higher proportion of males (p < 0.001), smoking (p < 0.001), drinking (p < 0.001), poor sleep status (p < 0.001), skipping breakfast ≥ 3 times/week (p < 0.001), and dinner within 2 h before bedtime ≥ 3 times/week (p < 0.001). Furthermore, participants with a poor chewing status were characterized by a significantly lower age (p = 0.024), BMI (p < 0.001), triglyceride level (p < 0.001), systolic blood pressure (p < 0.001), and diastolic blood pressure (p < 0.001).

Table 1.
Differences in factors at baseline between good and poor chewing status.
Table 2 shows the relationship between chewing status at baseline and SLD at follow-up. Participants with a poor chewing status at baseline were characterized by a significantly higher proportion with SLD at follow-up (p = 0.002).

Table 2.
Relationship between chewing status at baseline and SLD at follow-up.
The crude odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for SLD at follow-up are shown in Table 3. As shown in the table, the risk of SLD after 4 years was significantly correlated with the following variables at baseline: sex (male: ORs = 2.165; 95% CIs: 1.712–2.738), age (ORs = 0.968; 95% CIs: 0.948–0.988), BMI ≥ 25.0 kg/m2 (ORs = 2.281; 95% CIs: 1.764–2.950), triglyceride level ≥ 150 mg/dL (ORs = 2.499; 95% CIs: 1.118–5.583), HDL cholesterol level ≤ 40 mg/dL (ORs = 2.131; 95% CIs: 1.523–2.983), smoking status (ORs = 1.496; 95% CIs: 1.123–1.993), systolic blood pressure (ORs = 1.007; 95% CIs: 1.001–1.013), diastolic blood pressure (ORs = 1.019; 95% CIs: 1.010–1.029), sleep status (poor: ORs = 1.278; 95% CIs: 1.013–1.613), poor chewing status (ORs = 1.574; 95% CIs: 1.177–2.105), skipping breakfast ≥ 3 times/week (ORs = 1.594; 95% CIs: 1.140–2.229), and having dinner within 2 h before bedtime ≥ 3 times/week (ORs = 1.671; 95% CIs: 1.307–2.136).

Table 3.
Crude ORs and 95% CIs for SLD at follow-up.
The adjusted ORs and 95% CIs for SLD at follow-up are shown in Table 4. After adjusting for sex, age, BMI, triglyceride level, HDL cholesterol level, smoking status, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, sleep status, chewing status, skipping breakfast, and having dinner within 2 h before bedtime, the risk of SLD at 4 years was significantly correlated with the following variables at baseline: sex (male: ORs = 1.806; 95% CIs: 1.399–2.351), age (ORs = 0.969; 95% CIs: 0.948–0.991), BMI ≥ 25.0 kg/m2 (ORs = 1.934; 95% CIs: 1.467–2.549), diastolic blood pressure (ORs = 1.017; 95% CIs: 1.002–1.032), and poor chewing status (ORs = 1.472; 95% CIs: 1.087–1.994).

Table 4.
Adjusted ORs and 95% CIs for SLD at follow-up.
4. Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first longitudinal study to examine the associations between chewing status and SLD in Japanese people aged ≥50 years using data from medical checkups. The results showed that a higher proportion of participants with poor chewing status at baseline had SLD within 4 years than those with good chewing status. The results of the logistic regression analysis showed that after adjusting for sex, age, BMI, triglyceride level, HDL cholesterol level, smoking, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, sleep status, skipping breakfast, and dinner within 2 h before bedtime, the presence or absence of SLD after 4 years was associated with poor chewing status at baseline. These findings indicated that a decrease in chewing status was associated with a higher risk of developing SLD in the future.
There are several possible mechanisms behind the association between chewing status and SLD. First, a lack of systemic caloric expenditure may be involved. It has been noted that poor chewing status causes a decrease in diet-induced heat production and the induction of neurohistamine inactivation [29,30,31]. The lack of calories consumed due to these factors may affect fat accumulation in the liver. Second, eating habits may also be involved. It has been reported that people with poor chewing status tend to consume less vegetables and fruits and more soft high-energy foods than those with good chewing status [32,33,34,35]. Furthermore, it has also been also noted that an increase in the number of chews increases subjective satiety after a meal, which is involved in the prevention of overeating [36]. It has been reported that overeating affects fat accumulation in the liver [37]. These factors contribute to obesity and may affect fat accumulation in the liver. Furthermore, since estrogen has been reported to inhibit fat synthesis in the liver and lower blood fat [38], decreased production of estrogen may also be related to chewing status and SLD. The oral microflora is also known to correlate with the estrobolome of a subset of bacterial species with genes encoding β-glucuronidase and β-galactosidase [39]. Therefore, poor oral hygiene associated with poor mastication status may reduce estrogen production and be associated with the development of SLD. However, the mechanism by which poor chewing status is associated with SLD needs to be clarified in future research.
The relationship between chewing status and fat accumulation has been reported in previous studies. For example, chewing difficulty has been found to affect abdominal obesity [40]. It has also been shown that unbalanced chewing habits due to poor chewing status are associated with overweight and obesity [41]. Previous studies and the present study support the concept that poor chewing status may be involved in unhealthy fat accumulation in the body.
The results of our study suggest that an improvement in chewing status may prevent the future development of SLD and improve fat accumulation in the liver. Actively recommending dental visits to examinees with poor chewing status, treatment by orthodontists [42], and dental health guidance by dental hygienists [43] may not only improve chewing status but also prevent the onset of SLD.
In this study, a self-administered questionnaire was used to assess the participants’ chewing status. Therefore, participants’ subjective symptoms and actual chewing ability may differ. However, the self-reported chewing status is considered valid because it has been reported that it is not only related to the number of existing teeth and molars but also useful as a screening method regarding actual chewing ability using the same questionnaire [44].
In the present study, male sex, younger age (among aged ≥50 years), BMI, and diastolic blood pressure were associated with the presence of SLD in participants aged ≥50 years. These results are consistent with previous studies reporting that SLD is a disease that is more likely to affect men [6,45] and is associated with higher BMI [46,47]. In addition, a previous study reported that the most common age of people with SLD in Japan is about 52 years [48]. Therefore, it is possible that SLD tended to develop at a younger age in the present study, which was limited to participants aged ≥50 years. Furthermore, an elevated diastolic blood pressure is not only a hypertensive state but also suggests the progression of arterial stiffness [49]. SLD is associated with atherosclerosis, as well as hypertension [50,51]. Therefore, though both systolic and diastolic blood pressures were associated with SLD in the univariate analysis, diastolic blood pressure may have been associated with SLD as a stronger factor in the multivariate analysis, in which both factors were analyzed simultaneously.
The proportion of participants with SLD was 8% and that with poor chewing status was 14%. In Japan, it has been reported that the proportion of people with SLD ranges from 10% to 30% [3,4,5,6]. Furthermore, according to data from Health Japan 21 (the third term), the proportion of people aged ≥ 50 years with poor chewing status in 2019 was 29% [52]. This indicates that the proportion of participants with SLD and poor chewing status in this study was lower than that of the average Japanese population. The reason for this is that the participants were people who underwent medical checkups, suggesting that they may have been more health-conscious on a daily basis. Therefore, the results may differ if a different health population were to be targeted.
The multivariate logistic regression analysis model used in the present study utilized the Hosmer–Lemeshow fit test, which is capable of examining the fit of multivariate logistic regression analysis models and testing the compatibility of the event rate observed in a subgroup model and the expected event rate. In the Hosmer–Lemeshow fit test, a p-value > 0.05 is considered to indicate a good fit [53]. In the present study, the p-value was 0.704, thereby indicating a good fit for the multivariate logistic regression analysis model.
However, there are several limitations in the present study. First, the participants included only those who underwent medical checkups at Junpukai Health Maintenance Center. Therefore, external validity should be considered. Second, we did not investigate the amount of alcohol consumption. Since the definition of alcohol intake is important when considering liver disease, we would like to consider future investigations regarding these issues. Third, the dietary intake of the participants was not investigated. A past study reported that SLD is associated with fructose intake and unhealthy eating habits [54]. It is possible that usual eating habits may affect fat accumulation, and we would like to examine this in the future. However, a major strength of the present study is the sample size of over 3700 Japanese people aged ≥50 years. This sample size is sufficient to demonstrate a longitudinal relationship between chewing status and future SLD development, and it may help to find factors associated with unhealthy fat accumulation in the liver in the Japanese population.
5. Conclusions
The results of the present study indicate that Japanese people aged ≥50 years with poor chewing status are at an increased risk of developing SLD after 4 years. Therefore, to prevent unhealthy fat accumulation in the liver, it is important to maintain good chewing status. Aggressively recommending dental visits to participants with poor chewing status may not only improve their ability to chew well but may also reduce the incidence of SLD.
Author Contributions
The present study was carried out with the collaboration of all authors. Methodology, K.I., D.E., T.A. and T.T.; formal analysis, T.A. and T.M.; investigation, T.A., T.Y., K.T., N.T., K.K. and T.M.; writing—original draft preparation, K.I.; writing—review and editing, K.I., D.E. and T.T.; supervision, T.T.; project administration, T.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was self-funded by the authors and their institution. This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Asahi University (No. 27010: approved 21 August 2015; No. 30018: approved 23 February 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was not obtained because this study used anonymized claims data.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to ethical restrictions.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Junpukai Health Maintenance Center for providing the data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Israelsen, M.; Francque, S.; Tsochatzis, E.; Krag, A. Steatotic liver disease. Lancet 2024, 404, 1761–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, P.; Hellerbrand, C. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 28, 637–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, Y.; Hyogo, H.; Ono, M.; Mizuta, T.; Ono, N.; Fujimoto, K.; Chayama, K.; Saibara, T. Prevalence and associated metabolic factors of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the general population from 2009 to 2010 in Japan: A multicenter large retrospective study. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasamori, N. Nationwide results of the 2008 Ningen Dock. Ningen Dokku 2009, 24, 901–948. [Google Scholar]
- Taniai, M. Epidemiology of NAFLD/NASH. Jpn. Soc. Intern. Med. 2020, 109, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Sawada, K.; Tatsuta, M.; Maeshiro, T.; Tobita, H.; Tsutsumi, T.; Akahane, T.; Hasebe, C.; Kawanaka, M.; et al. Prevalence and associated metabolic factors of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the general population from 2014 to 2018 in Japan: A large-scale multicenter retrospective study. Hepatol. Res. 2023, 53, 1059–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusillo, S.; Rudolph, B. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Pediatr. Rev. 2015, 36, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeb, E. NASH (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis): Fatty liver or fatal liver disease? Zentralbl. Chir. 2014, 139, 168–174. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Bu, Y.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.; Sun, D.; Zheng, M. Association of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease with kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2022, 18, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marengo, A.; Rosso, C.; Elisabetta, B. Liver cancer: Connections with obesity, fatty liver, and cirrhosis. Annu. Rev. Med. 2016, 67, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butera, A.; Gallo, S.; Maiorani, C.; Molino, D.; Chiesa, A.; Preda, C.; Esposito, F.; Scribante, A. Probiotic alternative to chlorhexidine in periodontal therapy: Evaluation of clinical and microbiological parameters. Microorganisms 2020, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souto-Souza, D.; Soares, M.; Primo-Miranda, E.; Pereira, L.; Ramos-Jorge, M.; Ramos-Jorge, J. The influence of malocclusion, sucking habits and dental caries in the masticatory function of preschool children. Braz. Oral Res. 2020, 34, e059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, K.; Azuma, T.; Yonenaga, T.; Ekuni, D.; Watanabe, K.; Obora, A.; Deguchi, F.; Kojima, T.; Morita, M.; Tomofuji, T. Association between self-reported chewing status and glycemic control in Japanese adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motokawa, K.; Mikami, Y.; Shirobe, M.; Edahiro, A.; Ohara, Y.; Iwasaki, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Kawai, H.; Kera, T.; Obuchi, S.; et al. Relationship between chewing ability and nutritional status in Japanese older adults: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, K.; Azuma, T.; Yonenaga, T.; Sasai, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Deguchi, F.; Obora, A.; Kojima, T.; Tomofuji, T. Relationship between chewing status and fatty liver diagnosed by liver/spleen attenuation ratio: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 20, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Standard Health Examination and Health Guidance Program for Fiscal Year 2008. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/bunya/shakaihosho/iryouseido01/pdf/info02_66.pdf (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Suzuki, S.; Sano, Y. Guidebook for Specified Health Examination and Specified Health Guidance Leading to Results; Chuohoki: Tokyo, Japan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Miyano, T.; Anada, T.; Furuta, M.; Yamashita, Y. Prefectural differences in chewing ability in questionnaire for specific health checkup and exploring related factors. J. Dent. Health 2023, 73, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Iyota, K.; Mizutani, S.; Oku, S.; Asao, M.; Futatsuki, T.; Inoue, R.; Imai, Y.; Kashiwazaki, H. A cross-sectional study of age-related changes in oral function in healthy Japanese individuals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japan Society of Gastroenterology. Guidelines for NASH/NAFLD in 2020. Available online: https://www.jsge.or.jp/committees/guideline/guideline/pdf/nafldnash2020.pdf#page=58 (accessed on 29 March 2025).
- Japan Society for the Study of Obesity. Obesity Clinical Practice Guidelines in 2016. Available online: https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/naika/107/2/107_262/_pdf/-char/ja (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- Kawahara, T.; Imawatari, R.; Kawahara, C.; Inazu, T.; Suzuki, G. Incidence of type 2 diabetes in pre-diabetic Japanese individuals categorized by HbA1c levels: A historical cohort study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The International Expert Committee. International expert committee report on the role of the A1C assay in the diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Das, S.; Vinayagamoorthy, V.; Malik, A.; Tripathy, S.; Nishi. Dyslipidemia among overweight and obese children in Jharkhand: A hospital-based study. Indian Pediatr. 2023, 60, 641–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Crimmins, E. Blood pressure and mortality: Joint effect of blood pressure measures. J. Clin. Cardiol. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2020, 2, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuma, T.; Irie, K.; Watanabe, K.; Deguchi, F.; Kojima, T.; Obora, A.; Tomofuji, T. Association between chewing problems and sleep among Japanese adults. Int. J. Dent. 2019, 2019, 8196410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, Q.; Shereen, A.; Estabraq, M.; Jood, S.; Abdelfattah, A.T.; Adil, A. Electronic cigarette among health science students in Saudi Arabia. Ann. Thorac. Med. 2019, 14, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Kudo, A.; Asahi, K.; Satoh, H.; Iseki, K.; Moriyama, T.; Yamagata, K.; Tsuruya, K.; Fujimoto, S.; Narita, I.; Konta, T.; et al. Fast eating is a strong risk factor for new-onset diabetes among the Japanese general population. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, Y.; Kashima, H.; Hayashi, N. The number of chews and meal duration affect diet-induced thermogenesis and splanchnic circulation. Obesity 2014, 22, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, J.; Cummings, E.; Baskin, G.; Barsh, S.; Schwartz, W. Central nervous system control of food intake and body weight. Nature 2006, 443, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, T.; Yoshimatsu, H.; Kurokawa, M. Hypothalamic neuronal histamine: Implications of its homeostatic control of energy metabolism. Nutrition 1997, 13, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, A.; Miura, H. Systematic review of the association of mastication with food and nutrient intake in the independent elderly. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2014, 59, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.; Chang, L. Association of dental prosthetic condition with food consumption and the risk of malnutrition and follow-up 4-year mortality risk in elderly Taiwanese. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2011, 15, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Kikutani, T.; Yoshikawa, M.; Tsuga, K.; Kimura, M.; Akagawa, Y. Correlation between dental and nutritional status in community-dwelling elderly Japanese. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2011, 11, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Weyant, J.; Corby, P.; Kritchevsky, B.; Harris, B.; Rooks, R.; Rubin, M.; Newman, B. Edentulism and nutritional status in a biracial sample of well-functioning, community-dwelling elderly: The health, aging, and body composition study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Hsu, W.; Hollis, J. Increasing the number of masticatory cycles is associated with reduced appetite and altered postprandial plasma concentrations of gut hormones, insulin and glucose. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, G.; Schattenberg, J.; Leclercq, I.; Yeh, M.; Goldin, R.; Teoh, N.; Schuppan, D. Mouse models of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Toward optimization of their relevance to human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2241–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Jung, Y. Potential therapeutic application of estrogen in gender disparity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Cells 2019, 8, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatullo, M.; Nor, J.; Orrù, G.; Piattelli, A.; Cascardi, E.; Spagnuolo, G. Oral-Gut-Estrobolome Axis may exert a selective impact on oral cancer. J. Dent. Res. 2024, 103, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Xia, B.; Wu, J.; Zhao, X.; He, X.; Wen, X.; Yuan, C.; Pang, T.; Xu, X. Associations between abdominal obesity, chewing difficulty and cognitive impairment in dementia-free Chinese elderly. Am. J. Alzheimers Dis. Other Demen. 2023, 38, 15333175231167118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.; Araujo, D.; Scudine, K.; Prado, D.; Lima, D.; Castelo, P. Chewing in adolescents with overweight and obesity: An exploratory study with behavioral approach. Appetite 2016, 107, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrikson, T.; Ekberg, E.; Nilner, M. Can orthodontic treatment improve mastication? A controlled, prospective and longitudinal study. Swed. Dent. J. 2009, 33, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, A.; Hosaka, Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Akamatsu, M.; Fukaya, C.; Matsumoto, S.; Ueshima, F.; Hayakawa, H.; Fujinami, K.; Nakagawa, T. Effect of initial periodontal therapy on oral health-related quality of life in patients with periodontitis in Japan. J. Periodontol. 2010, 81, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, T.; Ueno, M.; Shinada, K.; Ohara, S.; Kawaguchi, Y. Validity of self-reported masticatory function in a Japanese population. J. Dent. Health 2010, 60, 214–223. [Google Scholar]
- Lonardo, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Ballestri, S.; Fairweather, D.; Win, S.; Than, T.; Abdelmalek, M.; Suzuki, A. Sex differences in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: State of the art and identification of research gaps. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamura, S.; Kawaguchi, T.; Nakano, D.; Tomiyasu, Y.; Yoshinaga, S.; Doi, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Anzai, K.; Eguchi, Y.; Torimura, T. Prevalence and independent factors for fatty liver and significant hepatic fibrosis using B-mode ultrasound imaging and two dimensional-shear wave elastography in health check-up examinees. Kurume Med. J. 2021, 66, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zhu, Z.; Mao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Du, J.; Tang, X.; Cao, H. HbA1c may contribute to the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease even at normal-range levels. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20193996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Dohi, M.; Watanabe, M.; Goromaru, N.; Kanasaki, M.; Shirakashi, M.; Inagawa, M.; Masuda, T.; Takeda, T. Fatty liver has the same background characteristics in those under their ideal weight and the general population. J. Ningen Dock Prev. Med. Care 2024, 39, 440–446. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, M.; Alfaddagh, A.; Elajami, T.; Ashfaque, H.; Haj, I.H.; Welty, F. Diastolic blood pressure predicts coronary plaque volume in patients with coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 2018, 277, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, G.; Chen, Z.; She, Z.; Cai, J.; Li, H. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: An emerging driver of hypertension. Hypertension 2020, 75, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and Atherosclerosis at a crossroad: The overlap of a theory of change and bioinformatics. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2020, 11, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. The National Health and Nutrition Survey Japan 2019. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/content/001066903.pdf (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S. Applied Logistic Regression, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Faienza, M.; Baima, J.; Cecere, V.; Monteduro, M.; Farella, I.; Vitale, R.; Antoniotti, V.; Urbano, F.; Tini, S.; Lenzi, F.; et al. Fructose intake and unhealthy eating habits are associated with MASLD in pediatric obesity: A cross-sectional pilot study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).