Abstract
The purpose of this study was to explore the effect of playability in secondary physical education classes in Korea on academic grit and attitudes toward physical education. A total of 296 middle school students located in Seoul and Gyeonggi-do, Korea were surveyed via simple random sampling. Data were analyzed via descriptive statistical analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, reliability analysis, correlation analysis, and standard multiple regression analysis. Three primary results were obtained. First, playfulness was found to have a significant positive effect on academic grit. Specifically, mental spontaneity positively and significantly affected academic passion (β = 0.400), academic perseverance (β = 0.298), and consistency of academic interest (β = 0.297). Additionally, among the sub-variables of playfulness, humorous perspective was found to have a positive significant effect on maintaining consistency of academic interest (β = 0.255). The second primary finding was that playfulness had a significant positive effect on classroom attitudes to physical education. Specifically, physical animation and emotional fluidity were found to positively and significantly affect basic attitudes (β = 0.290 and 0.330, respectively) and social attitudes (β = 0.398 and 0.297, respectively). Third, academic grit was found to have a significant positive effect on PE classroom attitudes. Specifically, academic passion was found to have a positive and significant effect on basic attitudes (β = 0.427) and social attitude (β = 0.358). The results imply that attitude toward school life can be improved through physical activity in secondary physical education classes.
1. Introduction
On average, students who engage in intense or appropriate physical activities for more than three days a week are found to have a higher satisfaction with life than those who do not engage in physical activities at all [1]. In addition, it has been reported that students who actively engage in sports activities are less likely to engage in deviant behavior such as school violence, delinquency, and gaming addiction, and are less likely to develop depression [2,3,4].
However, in Korean society, physical education (PE) continues to attract less attention compared to other classes [5]. In Korean society, education is linked to college admissions. This education involves the effective application of cognitive skills related to subjects including Korean language, English, and mathematics. The community has neglected PE, in turn leading to social problems such as the poor physical strength of Korean teenagers, excessive competition for entrance exams, school violence, and suicide [5].
In particular, in 2011, a 13-year-old middle-school student was bullied by another student and eventually committed suicide in an apartment. This incident shocked the Korean public [6]. The Korean government then recognized the importance of PE, announced the “Seven Practical Tasks for Eradicating School Violence”, and instigated “Middle School Sports Club Activities” [7]. This policy has received positive reviews from students, stating that it contributes to interpersonal relationships, self-esteem, and physical development [8,9]. However, education in Korean society continues to ignore school playgrounds and focuses on cognitive skills rather than PE [10].
Above all, adolescence is a stage wherein individuals transition from childhood to adulthood. It directly affects physical, mental, and social development; if children grow up in a negative way, their societal lives will be characterized by negative thoughts and behaviors after they reach adulthood [11]. From this perspective, PE in adolescence can have a positive effect on physical, mental, and social growth; thus, adolescents should be encouraged to maintain continuous and diverse participation in PE [12].
Physical activity involves performing activities with pleasure [13]. Play is an important part of physical activity. Humans enjoy play from childhood onwards [14]. Since sports comprise elements of play, humans continue to participate in sports. From this perspective, elements of PE also include playability [15]. With continued participation in PE, individuals can develop patience and passion to achieve their goals [16]. During this process, individuals’ attitudes towards PE are also positively affected [17].
The concept of grit is important in physical activity. Grit is defined as exerting one’s potential through patience and passion for achievement of long-term goals [17], including continued long-term efforts despite the accompanying difficulties such as failure, frustration, and so on, that arise when achieving an objective [18]. High grit means that individuals are passionate about participating in PE and do not give up on difficult tasks, overcoming them with persistence and sincerity. In other words, if one feels pleasure toward PE through a positive experiences, academic grit is indicated, which positively affects PE-related attitudes, resulting in positive effects on life throughout adolescence.
Accordingly, studies on playability, academic grit, and classroom attitude have been conducted for psychological variables such as passion, positive thinking, and happiness [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26], alongside studies related to sociality including academic results, school-life satisfaction, and interpersonal relationships [27,28,29,30,31,32]. However, there has been no study to date on how playability as an independent variable influences PE-related attitudes, with grit serving as a mediator.
Therefore, this study aimed to assess how playability in secondary PE classes affects middle-school students’ academic grit and PE-related attitudes. The research hypotheses are as follows: First, playability in secondary PE classes will affect academic grit. Second, playability in secondary PE classes will affect the attitudes of students. Third, academic grit will affect students’ attitudes toward PE.
1.1. Relationships between Playfulness, Academic Grit, and PE-Related Attitude
Playfulness positively affects adolescents’ academic achievement and life satisfaction through aspects such as positive emotions and pleasant experiences, motivation to laugh and act, promotion of creativity and human relationships, and relaxation of tension [19,20]. In particular, school sports are based on playability in order to develop pleasurable physical activities for participating individuals [15]. In other words, when playability expands, emotions such as passion develop, and positive activities can be achieved.
The concept of grit was introduced by Duckworth (2016), implying a strong will or motivation to pursue to a conclusion the goals one has set [18,23]. Previous studies showed that cognitive factors such as intelligence have direct effects on academic excellence [33]. However, in recent years, psychological factors including non-cognitive attitudes, values, and motives have been emphasized, and their effects on academic excellence have become apparent. Among them, grit forms an important factor. Grit is one of the representative non-cognitive abilities that stimulate an individual’s level of motivation, achievement, patience, self-efficacy, and clear sense of a goal [34,35]. Therefore, grit predicts success and is expressed as tenacity, persistence, determination, passion, persistence, sincerity, consistency of effort, and a sense of long-term purpose necessary for achieving an individual’s potential.
Furthermore, attitude includes a tendency to respond continuously and consistently to a specific object and is an important preceding variable that predicts behavior [36]. Within attitude, classroom attitude is a tendency to think positively or negatively about one’s education, through which students’ level of class participation can be predicted [37]. PE-related classroom attitude reflects the mindset or stature of a student in relation to PE classes. In other words, it involves individuals’ values or thoughts about PE classes. According to the theory of planned behavior, behavior and attitude are closely related [36].
Each of the variables described above has a close influence on the others. Previous studies have focused on playfulness, academic grit, and PE-related attitude. Specifically, studies on playfulness have investigated its relationship with psychological variables such as passion, positive thinking, and happiness [19,20,21], as well as how playfulness affects social behavior [27,28]. It was found that studies related to adolescents and playability have been conducted concerning sports, exercise, and study [38,39,40]. Since a human’s basic desire is to pursue pleasure, behavior that lacks playability cannot be continuously performed; thus, elements of pleasure are essential to enable continuous and positive results. Consequently, it was shown that adolescents with static playability could derive positive results in their studies.
In addition, research on adolescents and grit has been conducted assessing psychological variables, such as positive thinking, efficacy, resilience, and depression [22,41,42], social variables [29,30], and career variables [43,44]. Among these, studies on academic grit have attempted to explain the relationship between various variables relating to learning, such as classroom attitude, school life satisfaction, and class satisfaction [43,44]. In addition, studies related to sports have been conducted [45,46,47], showing that passionate athletes are more positive in terms of behavior, more active, and perform at their best in the process. Students with positive academic grit can produce excellent results in all subject-related studies, as well as positive results in PE classes. It has been stated that students with strong emotional variables, including grit, can excel in PE classes even if they do not possess outstanding physical skills.
Moreover, most of the research on adolescents and classroom attitude has been related to academic studies. Previous studies were conducted on students’ educational attitudes [31,32], academic achievement [48], persistence, passion, sincerity, and instructional attitudes [25,26] in relation to teacher behavior. Likewise, there have been many studies on academic attitudes in PE classes, alongside studies on the effect of psychological variables on PE classroom attitude and how the latter affects academic studies [49,50]. Students with a positive attitude toward PE have demonstrated positive results in school life, studies, and interpersonal relationships; they do not give up on tasks and they produce positive results with passion because they possess positive thoughts in general.
The abovementioned variables thus form the basis for supporting theoretical explanations in our study.
1.2. Study Hypotheses and Model
The hypotheses of this study were based on the effects of the playfulness of middle-school PE on academic grit and PE attitudes in the Republic of Korea. The hypothetical model is illustrated in Figure 1.
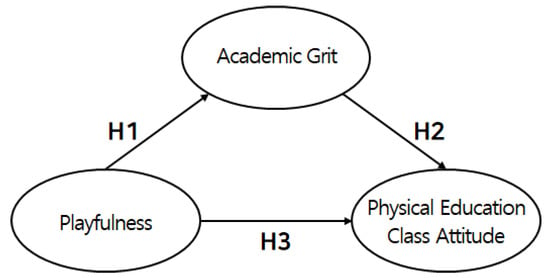
Figure 1.
Study model.
Figure 1 shows each hypothetical path of the conceptual model. This includes H1, which is the playfulness of middle-school PE, positively affecting academic grit. Next, H2 is academic grit, which positively affects attitudes toward middle-school PE. Lastly, H3 is the playfulness of middle-school PE, positively affecting PE attitudes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
Middle-school students in Seoul and Gyeonggi Province, representing major population centres in the Republic of Korea, were selected as the study population. A sample of 350 students was selected using simple random sampling. Specifically, considering the characteristics of each region, Seoul was divided into four regions, and one school was selected from each of 28 cities in Gyeonggi-do. After excluding 54 questionnaires with incomplete or missing responses, the data from 296 participants were included in the analysis. According to the G-Power program, the appropriate number of samples was found to be greater than 118 (actual power: 0.80). The general characteristics of the study participants are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Participants’ general characteristics.
2.2. Instruments
Based on previous studies and theory, a structured questionnaire was employed to achieve the study’s objectives. The questionnaire comprised 53 items, including 2 for demographic characteristics, 20 for playfulness, 23 for academic grit, and 8 for PE attitude.
Playfulness was assessed using the questionnaire developed by Staempfli (2007), after modifying and adapting the items for this study [21]. The playfulness scale consisted of five factors: four items for physical animation, four for social engagement, four for mental spontaneity, four for emotional fluidity, and four for humorous perspective. Each item was rated on a five-point Likert scale.
Academic grit was assessed using items developed by Duckworth and Quinn (2009) modified and adapted for use in this study [23]. The scale consisted of three factors: ten items for academic passion, five for academic perseverance, and seven for academic consistency of interest. Each item was rated on a five-point Likert scale.
PE attitude was assessed using the scale developed by Kenyon (1968) modified and adapted for use in this study [50]. The scale consists of two factors: four items for basic attitude and four for social attitude. Each item was rated on a five-point Likert scale. Questionnaire questions for variables were added to Appendix Table A1.
2.3. Validity and Reliability of the Instruments
The content validity of the structured questionnaire was evaluated by two Sociology of Sports professors and one Ph.D. researcher. In addition, confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was performed using maximum likelihood and Cronbach’s α to evaluate the validity and internal consistency of the instrument.
CFA for playfulness showed fit indices of χ2 = 300, df = 155, TLI = 0.907, CFI = 0.912, SRMR = 0.064, and RMSEA = 0.079. CFA for academic grit showed fit indices of χ2 = 373, df = 185, TLI = 0.933, CFI = 0.946, SRMR = 0.056, and RMSEA = 0.083. CFA for PE attitude showed fit indices of χ2 = 73.1, df = 19, TLI = 0.911, CFI = 0.940, SRMR = 0.039, and RMSEA = 0.079. Reliability, as tested with Cronbach’s α, ranged from 0.746 to 0.954 for the parameters, indicating good reliability, see Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4.

Table 2.
CFA and reliability of school happiness.

Table 3.
CFA and reliability of academic grit.

Table 4.
CFA and reliability of attitude toward PE.
2.4. Investigative Procedure
To achieve the objectives of this study, we visited the selected schools and requested their cooperation. Data were collected from May to June 2022, until 350 samples had been extracted. The survey took 25 min to complete. We explained to the participants the purpose and method of completing the questionnaire and asked them to complete it via self-reporting. We conducted in-person interviews based on the questionnaire for participants who had difficulty responding.
2.5. Data Processing
The collected data were processed. First, a frequency analysis was performed using SPSS 24.0. Then, the validity and reliability of the instruments were tested via CFA and Cronbach’s α, respectively, using Jamovi 1.6.23 [51,52,53]. Finally, correlation analysis and standard multiple regression analysis were performed using SPSS 24.0, to achieve the study’s objectives. Statistical significance was set at 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Playfulness in Middle-School PE on Academic Grit
3.1.1. Correlations among Study Variables
Table 5 shows the correlations between the factors with unidimensionality, in order to examine their satisfaction with discriminant validity. The correlation coefficients (r) among the associated variables ranged from 0.177 to.798, and there were partially significant correlations among the variables. However, the correlation coefficients did not exceed 0.80. Therefore, discriminant validity was deemed to be established according to the Kline (2011) criteria [54]. Moreover, the multicollinearity criterion was met (<0.80), confirming the absence of multicollinearity among the independent variables [55].

Table 5.
Correlations among playfulness, academic grit, and attitude toward PE.
3.1.2. Effects of Playfulness in Middle School PE on Academic Grit
Table 6 shows the results of the standard multiple regression performed to examine the effects of the playfulness of middle-school PE on the components of academic grit: academic passion, academic perseverance, and consistency of academic interest.

Table 6.
Standard multiple regression for the effects of playfulness on academic grit.
The playfulness of middle-school PE explained 17.3% (R2adj = 0.173) of the academic passion component of grit. Moreover, the mental spontaneity component of playfulness (β = 0.400) significantly affected academic passion (p = 0.000).
The playfulness of middle-school PE explained 11.7% (R2adj = 0.117) of the academic perseverance component of academic grit. Moreover, the mental spontaneity component of playfulness (β = 0.298) significantly affected academic performance (p = 0.003).
The playfulness of middle-school PE explained 13.0% (R2adj = 0.130) of the consistency of academic interest component of academic grit. Moreover, the mental spontaneity (β = 0.297) and humorous perspective (β = 0.255) components of playfulness significantly affected consistency of academic interest (p = 0.003 and 0.050, respectively).
3.2. Effects of Playfulness in Middle-School PE on PE Attitude
Table 7 shows the results of the standard multiple regression examining the effects of playfulness in middle-school PE on the basic and social components of PE attitude.

Table 7.
Standard multiple regression for the effects of playfulness on attitude toward PE.
The playfulness of middle-school PE explained 29.8% (R2adj = 0.298) of the basic component of PE attitude. Moreover, the physical animation (β = 0.290) and emotional fluidity (β = 0.330) components of playfulness had significant effects on basic attitude (p = 0.003 and 0.000, respectively).
The playfulness of middle-school PE explained 29.9% (R2adj = 0.299) of the social component of PE attitude. Moreover, the physical animation (β = 0.398) and emotional fluidity (β = 0.297) components of playfulness had significant effects on social attitude (p = 0.000 and 0.001, respectively).
3.3. Effects of Academic Grit on PE Attitude
Table 8 shows the results of the standard multiple regression analysis examining the effects of academic grit on the basic and social components of PE attitudes in middle school.

Table 8.
Standard multiple regression for the effects of academic grit on attitude toward PE.
Academic grit explained 18.3% (R2adj = 0.183) of the basic component of PE attitudes. Moreover, the academic passion component (β = 0.427) of academic grit significantly affected basic attitudes (p = 0.019).
Academic grit explained 13.7% (R2adj = 0.137) of the social component of PE attitudes. Moreover, the academic passion component (β = 0.358) of academic grit significantly affected social attitudes (p = 0.050).
4. Discussion
This study aimed to investigate the effects of playfulness in middle-school PE on academic grit and PE attitudes. The study sample was drawn from middle-school students in Seoul and Gyeonggi Province, South Korea, and data from 296 participants were analyzed.
First, we examined the effects of playfulness in middle-school PE on academic grit. Playfulness positively affected academic passion, perseverance, and consistency of interest, associated with academic grit. Other studies have also reported similar results regarding the playfulness of PE classes and academic grit [47,55,56,57,58].
Barnett (1990) stated that playfulness is a personality trait of humans and represents the degree to which a person freely expresses pleasure or joy [59]. In other words, playfulness is an internal pleasure and happiness that one expresses. Playfulness is essential for humans who cannot persistently engage in a behavior where play is lacking [60]. Therefore, playfulness is essential to humans. Playfulness may be displayed in all patterns of behavior, in addition to leisure activities. All activities, including studying, music, art, and exercise, encompass playfulness, and only people who enjoy these activities perform well in them [19]. Some people achieve good academic performance, while others excel at sports; the difference is attributable to the different areas that people enjoy as play. The discrepancy of outcome is due more to how one enjoys that particular activity than to one’s in-born competency [20].
Playfulness and academic grit are believed to have similar properties [61]. Several studies have argued that these two factors are strongly associated [38,39,40], with people who strongly exhibit playfulness also showing high academic grit [39]. Similarly, students who demonstrated a high degree of playfulness in middle-school PE showed higher academic grit. In other words, students who perceive playful features in PE classes more frequently and strongly display an unwavering passion for academic pursuits. Furthermore, these students can be expected to acheive positive outcomes in academic study and also PE.
Based on our findings, instructors should research ways to engage in PE classes so that male and female students can enjoy PE. In addition, teachers must strive to help students feel they can enjoy their studies. If students can enjoy class, they will be more engaged and achieve better academic outcomes. Moreover, these students will be able to produce consistent results based on their high confidence levels. This will positively affect academic grit, leading to positive outcomes in their overall lives.
Secondly, we analyzed the effects of academic grit on PE attitudes among middle-school students. The results showed that academic grit positively affected the basic and social components of PE attitudes. More specifically, academic grit has a similar property to passion, so people with strong academic grit are passionate during PE classes, as indicated by many studies [25,48,62]. In addition, people with academic grit show positive attitudes in other academic areas besides PE, and engage in positive school lives, interpersonal relationships, and social behaviors [45,46].
Grit is the display of perseverance and passion to overcome adversity and failure to achieve a long-term goal [63]. Similarly, academic grit refers to the passion, perseverance, and effort to achieve academic goals. In other words, it focuses on non-cognitive attitudes and behaviors, as opposed to cognitive features, required to attain good grades in school [63]. Even if students have poor cognitive abilities, students with strong academic grit attain good grades more often than students with good cognitive abilities that do not strive to achieve their goals of good academic performance. Students with strong academic grit do not fear failure and continue to advance toward their ultimate goals.
This attitude is also displayed in PE, where students with better physical abilities ultimately attain better outcomes and enjoy class more than their less capable counterparts [64,65]. Those students with poorer physical abilities fear PE classes and may want to remain passive. Such an attitude leads to their experiencing physical activities unpleasantly, which ultimately discourages them from exercise for the rest of their lives. However, students with strong academic grit do not give up during PE and continue to work hard until they accomplish the given task and eventually succeed [25,32,44,45,46,48]. An accumulation of positive experiences like this instills good memories of exercise and motivates individuals to engage in sports throughout their lives. Moreover, they are better able to seize other opportunities in life, perpetuating a virtuous cycle.
In other words, fostering grit in more students may help nurture those who are not merely focused on competing and winning against others—a mindset rampant in public schools in Korea—and can instead positively influence society [66,67]. Thus, diverse types of education, social systems, and educational programs that foster emotional abilities such as passion, hard work, perseverance, and grit, should be developed instead of focusing only on improving cognitive abilities. Continued advances based on positive processes and results will transform our society and help to resolve, at least partially, societal problems that are prevalent worldwide.
Third, we investigated the effects of playfulness in middle-school PE on PE attitudes. The results showed that playfulness positively affected the basic and social components of PE attitudes. Specifically, students who perceived more playfulness and enjoyment in PE displayed more active attitudes during PE, as observed in many studies [31,32,68].
Playfulness is an internal tendency that enables high-quality playful interactions in various environments and contexts [11]. Students who lack playfulness fail to perceive the playful features of the activities and tasks presented by teachers or other students and consider them as assignments. This increases their vulnerability to psychological pressures and stress. On the other hand, students with a high level of playfulness easily detect playful components in various aspects of their lives and readily discover fun things in life [38]. Hence, they reflect on their desires or thoughts through play and gain a happy experience. Previous studies on playfulness and academic activity support our findings that students’ playfulness positively influences their classroom attitudes [39]. That is, students with a high level of playfulness discover playful features in various situations at school, can effectively cope with academic stress or psychological pressure, and are more likely to enjoy happy and fun lives at school.
The playfulness of school PE and PE attitudes among adolescents were found to be significantly interrelated. Playfulness positively influences PE attitude and academic grit, and this result sheds light on the desired direction on which school PE should focus. Being playful is associated with high energy and being physically and socially active. Playful individuals can actively respond to a threatening or critical situation without perceiving it negatively [60,68,69,70]. Our findings showed that adolescents who enjoy PE could enhance their physical fitness and be motivated to participate in all activities, maintaining a positive attitude. As such, perceived pleasure manifests as voluntary involvement in class. Here, activity level is a positive factor that improves mental health through physical development [71]. Students’ attitudes toward PE are crucial because they focus on the process (participating or not in physical activity during PE) and the consequent outcomes, as opposed to being results-oriented and making students overly competitive while focusing primarily on their grades.
Therefore, instructors must advance their PE classes by experimenting with various approaches instead of simply adopting and following the prevailing trend. Moreover, they should not divide students based on “good“ or “bad“ performances in PE. Instead, they should implement physical activity education that stresses playfulness, so that all students can enjoy PE and feel motivated to seek challenges. Adolescents who learn physical activity while enjoying it will acquire passion, a challenge-seeking mindset, and a persistent attitude that encourages them never to give up. If such practices are established as habits in daily life, they will be able to paint a more promising future for themselves.
5. Conclusions
This study aimed to investigate the effects of playfulness in middle-school PE on academic grit and PE attitude. We drew the following conclusions based on our results: the playfulness of middle-school PE significantly affected academic grit, academic grit significantly affected PE attitudes, and the playfulness of middle-school PE significantly affected PE attitudes. Finally, these results show that engaging in physical activity through middle-school PE can enhance students’ attitudes toward their education.
There were a few limitations to this study. First, the research was conducted focusing on the relationship between variables, analyzed through regression analysis; therefore, there was limited analysis of differences between genders and school grades, among demographic characteristics. If the study had focused on the relationship between variables in terms of differences between genders or grade levels, the results would be interpreted differently. Second, this study is limited in terms of its investigation of the effect of individual psychology on variables such as playfulness, academic grit, and attitude toward PE. Future studies should focus on how PE in school affects our society, looking at the relationships between macroscopic variables. Third, in the regression analysis, there were no controls for gender, race, family characteristics, teacher characteristics, or school characteristics; however, it is possible that these variables may affect attitudes toward PE and academic grit in students.
Future research should focus on examining PE attitudes based on a fundamental scale for games and sports, as this will shed light on the practical effects of physical activity. Moreover, although we examined attitudes toward PE, students’ attitudes in other academic areas should also be examined. Thus, student participation in school sports clubs should also be investigated to explore measures that promote values and positive attitudes toward sports.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.G. and J.S.; methodology, H.G.; investigation, J.S.; data analysis, H.G.; writing—original draft preparation, H.G. and J.S.; writing—review and editing, J.S.; supervision, H.G. and J.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Gachon University Institutional Review Board (NO. 1044396-202206-HR-131-01; date of approval: 21 August 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Questionnaire.
Table A1.
Questionnaire.
| Variable | Sub-Variable | No. | Contents of Article |
|---|---|---|---|
| Playfulness | Physical animation | 1 | I like extreme physical play with my friends. |
| 2 | I like to go around with my friends. | ||
| 3 | I like being physically active. | ||
| 4 | I am motivated and motivated to be physically active. | ||
| Social engagement | 5 | I think people who play well get along easily with others. | |
| 6 | I like to play, frolic and hang out with people. | ||
| 7 | I like to make others laugh. | ||
| 8 | I joke easily with others. | ||
| Mental spontaneity | 9 | I imagine myself or someone else in a “fun situation.” | |
| 10 | I like play or games that require a lot of thought. | ||
| 11 | I have a lot of imagination. | ||
| 12 | I imagine being a person with a different personality or ability than I am now. | ||
| Emotional fluidity | 13 | When I’m happy, I like to sing or hum. | |
| 14 | I often smile or laugh. | ||
| 15 | Others (family, friends, etc.) easily notice that I am in a good mood or happy. | ||
| 16 | I tend to freely express my feelings to others. | ||
| Humorous perspective | 17 | I like to do funny things. | |
| 18 | I tend to find something funny or funny even in difficult situations. | ||
| 19 | I tend to look for humorous or comical things better than other people. | ||
| 20 | I like to tell funny stories. | ||
| Academic grit | Academic passion | 1 | I am very motivated to study. |
| 2 | I have a strong will to study. | ||
| 3 | I am a student with a high passion for study. | ||
| 4 | I have clear goals for my studies. | ||
| 5 | Even if I face setbacks, I have a strong will to study. | ||
| 6 | When I study, I am full of enthusiasm. | ||
| 7 | I study with enthusiasm. | ||
| 8 | Even though my studies are difficult, my enthusiasm does not diminish. | ||
| 9 | I set goals and study. | ||
| 10 | I keep studying | ||
| Academic perseverance | 11 | I study steadily. | |
| 12 | I study steadily for several months or longer. | ||
| 13 | I persevere in my studies. | ||
| 14 | I finish my studies well to the end. | ||
| 15 | I study patiently and meticulously. | ||
| Consistency of academic interest | 16 | When I study, I am interested and curious. | |
| 17 | My studies are not interrupted by other things or thoughts. | ||
| 18 | I don’t know how time flies when I’m studying. | ||
| 19 | I am interested in studying | ||
| 20 | I am interested and immersed in my studies. | ||
| 21 | Studying is fun so I can give up other activities I enjoy. | ||
| 22 | I maintain a steady interest in studying. | ||
| Physical education-related attitude | Basic attitude | 1 | PE class is fun regardless of athletic ability |
| 2 | Actively participates in physical education class. | ||
| 3 | Physical education classes help life. | ||
| 4 | I think physical education class is more important than other subjects. | ||
| Social attitude | 5 | Physical education class develops the habit of following the rules in social life. | |
| 6 | Physical education classes develop understanding and improve relationships with friends. | ||
| 7 | PE classes foster personal and social responsibility. | ||
| 8 | Through physical education class, you can learn order in a group. |
References
- OECD. Education at a Glance 2021. OECD Indicators. 2021. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/education/education-at-a-glance/ (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- Hoge, R. Advances in the assessment and treatment of juvenile offenders. Kriminol. Soc. Integr. 2009, 17, 49–70. [Google Scholar]
- Hood, J.C. Parenting a youthful offender. Stud. Symb. Interact. 2011, 37, 79–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofler, I.R. Bullying, hazing, and workplace harassment: The nexus in professional sports as exemplified by the first NFL Wells report. Int. Rev. Psychiatry 2016, 28, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, W.J.; Ahn, C.W.; Gwon, H.S. Causal Model of Participation, Perceived Enjoyment, and Learning Attitudes in “the 0th Period Physical Education Class” of Middle Schools in South Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.I. A study on the analysis of policy-making process of school sports club activity in a middle school: With focus on policy streams framework. Korean J. Sport Pedagog. 2014, 21, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Ministry of Education. Comprehensive Measures the Elimination of Violence in Schools; Korea Ministry of Education: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2012.
- Lim, S.W.; Lee, K.M.; Kim, I.H.; Lee, H.G. The operation system and implications of “the 0 period physical education class”: The case study about “blue” elementary school. Korean J. Phys. Educ. 2014, 53, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, A.J.; Dyment, J.E. Where do children choose to play on the school ground? The influence of green design. Int. J. Prim. Elem. Early Years Educ. 2009, 38, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallis, J.F.; Prochaska, J.J.; Taylor, W.C. A review of correlates of physical activity of children and adolescents. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J. Relationships: Are they bridges or barriers to physical activity in physical education class for South Korean female secondary school students? Quest 2022, 74, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, B.A.; Etnier, J.L. The relationship between physical activity and cognition in children: A meta analysis. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2003, 15, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, H.A. Explorations in Personality; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1938. [Google Scholar]
- Proyer, R.T. Playfulness over the lifespan and its relation to happiness: Results from an online survey. Z. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2014, 47, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnuson, C.D.; Barnett, L.A. The playful advantage: How playfulness enhances coping with stress. Leis. Sci. 2013, 35, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markland, D.; Hall, C.R.; Duncan, L.R.; Simatovic, J. The effects of an imagery intervention on implicit and explicit exercise attitudes. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2015, 17, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orvidas, K.; Burnette, J.L.; Russell, V.M. Mindsets applied to fitness: Growth beliefs predict exercise efficacy, value and frequency. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2018, 36, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, A.; Arslan, S. The relationships between achievement goal orientations and grit. Educ. Sci. 2014, 39, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proyer, R.T.; Gander, F.; Brauer, K.; Chick, G. Can playfulness be stimulated? A randomised placebo-controlled online playfulness intervention study on effects on trait playfulness, well-being, and depression. Appl. Psychol. Health Well-Being 2021, 13, 129–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proyer, R.T.; Tandler, N. An update on the study of playfulness in adolescents: Its relationship with academic performance, well-being, anxiety, and roles in bullying-type-situations. Soc. Psychol. Educ. 2020, 23, 73–99. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11218-019-09526-1 (accessed on 5 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Staempfli, M.B. Adolescent playfulness, stress perception, coping and well being. J. Leis. Res. 2007, 39, 393–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Credé, M.; Tynan, M.C.; Harms, P.D. Much ado about grit: A meta-analytic synthesis of the grit literature. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2017, 113, 492–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckworth, A.L.; Quinn, P.D. Development and validation of the Short Grit Scale (GRIT–S). J. Pers. Assess. 2009, 91, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivcevic, Z.; Brackett, M. Predicting school success: Comparing Conscientiousness, Grit, and Emotion Regulation Ability. J. Res. Pers. 2014, 52, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurbavliyev, O.; Kaymak, S.; Sydykov, B. The effect of active learning method on students’ academic success, motivation and attitude towards mathematics. J. Lang. Linguist. Stud. 2022, 18, 701–713. [Google Scholar]
- Viciana, J.; Cervelló, E.M.; Ramírez-Lechuga, J. Effect of manipulating positive and negative feedback on goal orientations, perceived motivational climate, satisfaction, task choice, perception of ability, and attitude toward physical education lessons. Percept. Mot. Skills 2007, 105, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; He, Y.; Wang, H. Influence mechanism of employee playfulness personality on employee creative deviance. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 821285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, E.; Jenvey, V. Play and theory of mind: Associations with social competence in young children. Early Child Dev. Care 2011, 181, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fang, M.; Wang, W.; Sun, G.; Cheng, Z. The influence of grit on life satisfaction: Self-esteem as a mediator. J. Belg. Assoc. Psychol. Sci. Psychol. Belg. 2018, 58, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Sohn, Y.W.; Lee, S.R. The effect of corporate social responsibility on employees’ organizational citizenship behavior: A moderated mediation model of grit and meaning orientation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trolian, T.L.; Parker, E.T. Shaping students’ attitudes toward diversity: Do faculty practices and interactions with students matter? Res. High Educ. 2022, 63, 849–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.H.; Nguyen, T.T.; Uyen, B.P.; Ngan, L.K.; Khanh, L.T.; Tinh, P.T. Realistic mathematics education’s effect on students’ performance and attitudes: A case of ellipse topics learning. Eur. J. Educ. Res. 2021, 11, 403–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegmark, M.; Alatalo, T.; Vinterek, M.; Winberg, M. What motivates students to read at school? Student views on reading practices in middle and lower-secondary school. J. Res. Read. 2022, 45, 100–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, A.E. Teaching the Character Competencies of Growth Mindset and Grit to Increase Student Motivation in the Classroom. Ph.D. Thesis, New England College, Henniker, NH, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, C.A.; Wang, C.; Black, J.M.; Bugescu, N.; Hoeft, F. The matter of motivation: Striatal resting-state connectivity is dissociable between grit and growth mindset. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2016, 11, 1521–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishbein, M.; Ajzen, I. Belief, Attitude, Intention and Behavior: An Introduction to Theory and Research; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Ruzimbaev, M.A. Methodological methods of teaching children for movement activities in the process of physical education classes. Web Sci. Int. Sci. Res. J. 2021, 2, 313–322. [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood, R.; O’Connor, S. Playfulness in adults: An examination of play and playfulness and their implications for coaching. Coach. Int. J. Theor. Res. Pract. 2017, 10, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proyer, R.T.; Gander, F.; Bertenshaw, E.J.; Brauer, K. The positive relationships of playfulness with indicators of health, activity, and physical fitness. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Güllich, A. Childhood practice and play as determinants of adolescent intrinsic and extrinsic motivation among elite youth athletes. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2019, 19, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usher, E.L.; Li, C.R.; Butz, A.R.; Rojas, J.P. Perseverant grit and self-efficacy: Are both essential for children’s academic success? J. Educ. Psychol. 2019, 111, 877–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K. Students’ well-being: The mediating roles of grit and school connectedness. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 787861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinley, S.; Mattila, A.S. Overcoming job insecurity: Examining grit as a predictor. Cornaell Hosp. Q. 2019, 61, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadabi, A.; Karpinski, A.C. Grit, self-efficacy, achievement orientation goals, and academic performance in University students. Int. J. Adolesc. Youth 2020, 25, 519–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.N.; Malecki, C.K. Academic Grit Scale: Psychometric properties and associations with achievement and life satisfaction. J. Sch. Psychol. 2019, 72, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Wang, M.T.; Guo, J.; Salmela-Aro, K. Building grit: The longitudinal pathways between mindset, commitment, grit, and academic outcomes. J. Youth Adolesc. 2019, 48, 850–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutberg, S.; Nyberg, L.; Castelli, D.; Lindqvist, A.K. Grit as perseverance in physical activity participation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anghelache, V. Determinant factors of students’ attitudes toward learning. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 93, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moral-Garcia, J.E.; Jiménez, A.; Cabaco, A.S.; Jiménez-Eguizabal, A. The role of physical activity and school physical education in enhancing school satisfaction and life satisfaction. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 18, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenyon, G.S. Six scales for assessing attitude toward physical activity. Res. Q. 1968, 39, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Jamovi Project. Jamovi. (Version 2.2) [Computer Software]. 2021. Available online: https://www.jamovi.org (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- R Core Team. R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. (Version 4.0) [Computer Software]. 2021. (R Packages Retrieved from MRAN Snapshot, 2021-04-01). Available online: https://cran.r-project.org (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- Rosseel, Y.; Jorgensen, T.D.; Rockwood, N.; Oberski, D.; Byrnes, J.; Vanbrabant, L.; Savalei, V.; Merkle, E.; Hallquist, M.; Rhemtulla, M.; et al. Lavaan: Latent Variable Analysis. [R Package]. 2018. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=lavaan (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- Kim, G.S. Structural Equation Model; Suk Jeong: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Moreno, A.; Cavas-García, F.; López-Gullón, J.M.; Díaz-Suárez, A. Effects of fatigue and grit on club sports coaches. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesqui, R.A.B.; Young, B.W. Investigating grit variables and their relations with practice and skill groups in developing sport experts. High Ability Stud. 2017, 28, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guelmami, N.; Chalghaf, N.; Tannoubi, A.; Puce, L.; Azaiez, F.; Bragazzi, N.L. Initial development and psychometric evidence of physical education grit scale (PE-grit). Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 818749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, V.; Kalajas-Tilga, H.; Koka, A.; Raudsepp, L.; Tilga, H. How grit is related to objectively measured moderate-to-vigorous physical activity in school student. Monten. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2019, 8, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, L.A. Developmental benefits of play for children. J. Leis. Res. 1990, 22, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, L.A. The nature of playfulness in young adults. Pers. Individ. Differ. 2007, 43, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.J.; Kim, E.B.; Lee, I.S. Influence of self-esteem of middle school students for mental care on academic achievement: Based on the mediation effect of GRIT and academic enthusiasm. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.N.; Dorio, N.B.; Eldridge, M.A.; Malecki, C.K.; Demaray, M.K. Adolescent academic achievement: A model of social support and grit. Psychol. Sch. 2020, 57, 204–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckworth, A.L. The Power of Passion and Perseverance; Scribner: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Granero-Gallegos, A. New developments in physical education and sport. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, S. Attitude research in physical education: A review. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 2017, 36, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, J.; Kumari, P. Examining the relationship between grit and quality of life: The mediating role of social support among nurses. Asia Pac. J. Acad. Res. Soc. Sci. 2021, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, L.; Perkins, V.; Zuraik, A.; Luse, W. Social impact: The role of authentic leadership, compassion and grit in social entrepreneurship. J. Entrep. 2022, 31, 298–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, L.A. The playful child: Measurement of a disposition to play. Play Cult. 1991, 4, 51–74. [Google Scholar]
- Schnohr, P.P.; Kristensen, T.S.; Prescott, E.E.; Scharling, H.H. Stress and life dissatisfaction are inversely associated with jogging and other types of physical activity in leisure time-the Copenhagen City Heart Study. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2005, 15, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkweather, A.R. The effects of exercise on perceived stress and IL-6 levels among older adults. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2007, 8, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, W.B.; Malina, R.M.; Blimkie, C.J.; Daniels, S.R.; Dishman, R.K.; Gutin, B.; Hergenroeder, A.C.; Must, A.; Nixon, P.A.; Pivarnik, J.M.; et al. Evidence based physical activity for school-age youth. J. Pediatr. 2005, 146, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).