Abstract
The generalized time fractional Kolmogorov-Petrovsky-Piskunov equation (FKPP), , which plays an important role in engineering, chemical reaction problem is proposed by Caputo fractional order derivative sense. In this paper, we develop a framework wavelet, including shift Chebyshev polynomial of the first kind as a mother wavelet, and also construct some operational matrices that represent Caputo fractional derivative to obtain analytical solutions for FKPP equation with three different types of Initial Boundary conditions (Dirichlet, Dirichlet-Neumann, and Neumann-Robin). Our results shown that the Chebyshev wavelet is a powerful method, due to its simplicity, efficiency in analytical approximations, and its fast convergence. The comparison of the Chebyshev wavelet results indicates that the proposed method not only gives satisfactory results but also do not need large amount of CPU times.
1. Introduction
A generalization of differentiation and integration with arbitrary (non-integer) order which is called fractional calculus has gained considerable popularity and during the past almost three decades, mainly due to its attractive applications in numerous diverse and widespread fields of sciences and engineering [1,2,3]. The concepts of fractional derivatives are to incorporate nonlocal and systematic memory effects through fractional order space and time derivatives, which are powerful features that allow modeling of phenomena across multiple time and space scales without having to partition the problem into smaller compartment [4]. Operators of fractional differentiation and integration have been used in the hydraulics of dam, diffusion problems, and waves in liquids and gasses. Many systems can be described more accurately and more conveniently by fractional differential equations. The main advantage of the fractional calculus is that the fractional derivative provides an excellent instrument for the description of memory and hereditary properties of various materials and processes.
Fractional derivatives have been widely used in mathematical modeling of reaction-diffusion systems, which explain how the concentration of one or more substances distributed in space changes under the influence of two processes: local chemical reactions in which the substances are transformed into each other and diffusion which causes the substances to spread out over a surface in space.
Analytical and approximate series solutions for the nonlinear fractional differential equations are fundamental importance for seeking solutions of the most complex phenomena that are modeled. There are many methods that have also been proposing for solving analytical and approximate series solutions: the transform methods, including Laplace, Fourier, and Mellin transforms [5]; the Tau method [6]; the Adomian decomposition method [7]; the variational iteration method [7,8]; the Sumudu decomposition method [9]; the blockpulse functions [10]; shifted Chebyshev polynomials [11]; shifted Legendre polynomials [12]; Chebyshev wavelets [13,14]; and Legendre wavelets [15].
The Chebyshev wavelet method is one powerful tool by employing the fundamental concept of wavelets and shifted Chebyshev polynomials. Approximations through Chebyshev wavelet effectively handle singularities in the problem. It is fast convergence and not undergo from the instability problems related to other numerical methods. Y. Chen et al. proposed The Chebyshev wavelet method by solving fractional integral and differential equations of Bratu-type [13]. A.K. Gupta and S.S. Ray studied the solution of fractional fifth-order Sawada-Kotera equation using second kind Chebyshev wavelet method [14] and many others [16,17,18,19].
In this paper an efficient mathematical tool the Chebyshev wavelet collocation method, introduced by some operational matrices for fractional derivative and integration is successfully applied to obtain the analytical solution of the generalize time fractional Kolmogorov-Petrovsky-Piskunov equation (FKPP) of a volume chemical reaction:
subjected to the initial condition
and three types of boundary conditions:
where represents the concentration of one substance, is diffusion coefficients and several types of a rate, , of a volume chemical reactions such as power–law nonlinearities, ; exponential nonlinearities, ; or logarithmic nonlinearities, [20].
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Fractional Calculus
In this section we introduce some necessary definitions, notations, and mathematical preliminaries of fractional calculus [21].
Definition 1.
The Riemann-Liouville fractional integral operator of a function and of order is defined as
where some properties of the operator are provided as follows:
Definition 2.
The Caputo fractional derivative operator of a function and of order is defined as
Some properties of Caputo fractional derivatives:
where , denotes the largest integer less than or equal to and is the smallest integer greater than or equal to and
2.2. Chebyshev Wavelet Method
By a definition, Chebyshev wavelets consist of a family of functions that are coming from dilation and translation of a Chebyshev function named a mother wavelet, which n as a dilation parameter and m as translation parameter vary continuously. The following family of continuous Chebyshev wavelets may be obtained [22] and defined on the interval by
where k can be determined as any positive integer and , are the first kind Chebyshev polynomials of degree m defined on the interval and satisfy the following recursive formula.
which are orthogonal with respect to the weight function .
2.3. The Kronecker Product
The matrices A and B are given by
The Kronecker product is the matrix and defined as [23,24]
where some Kronecker product properties are provided by
- where is a scalar.
- .
- .
- .
- .
- .
- ,( denotes conjugate transpose).
2.4. Hadamard Product
Definition 3.
For two matrices A and B,
The Hadamard product [25] is a matrix of the same dimension as the operands, with elements given by
where some important properties are given by
- 1.
- .
- 2.
- .
- 3.
- .
- 4.
- .
- 5.
- .
3. Chebyshev Wavelets Approximation
An arbitrary function of two variables defined over , can be approximated by Chebyshev wavelets basis as
where the Chebyshev wavelet in (13). In the other hand, the function in (14) can be rewritten a finite sum of entries of the spatial matrix as
where are entries of the Hadamard-Kronecker product matrix and
where
The h-times integration of in (13) can be expressed as follows
, where h-times integration of Chebyshev wavelets matrix is obtained by
Riemann-Liouville fractional integration order of in (13) can be expressed as follows
so fractional integration with order of Chebyshev wavelets matrix becomes
The h-times differentiation of Chebyshev wavelets matrix is obtained by
and the fractional differentiation with order of Chebyshev wavelets matrix is given by
4. Description of the Proposed Method
In this section, we applied a fundamental solution of the Chebyshev wavelet method for generalized time fractional Kolmogorov-Petrovsky-Piskunov equation (FKPP) with the initial condition and three types of boundary conditions.
Case 1: the time fractional KPP equation with Dirichlet boundary conditions:
subjected to the initial and boundary conditions
where denotes the Caputo fractional derivative of the function . The function , and are continuous on . Now, by performing Chebyshev wavelets method on (25).
Let be a solution of (25), where are entries of the the Hadamard-Kronecker product matrix . To determine the Hadamard-Kronecker product matrix , we first assume that
where the unknown coefficient matrix can be determined and the matrix is defined by (18). By Caputo fractional integration (12), integrating of (29) with respect to t from 0 to t and using condition (26), we obtain
where the matrix is
Evaluating in (31), we have:
so
then substituting (32) into (31), we have
substituting boundary conditions (27) and (28), then we get
Taking Riemann-Liouville fractional integrating of (34), so the Hadamard-Kronecker product matrix is given by
The collocation points of time and space are defined by
Substituting (30), (34), (35), and (36) into (25), we have the system that can be solved the coefficient matrix :
where and in (20) and (22), respectively, is a zero matrix, and then substituting the coefficient matrix into (35), therefore the solution
of FKPP (25) with Dirichlet boundary conditions, where are entries of the matrix in (35).
Remark 1.
For fractional order , from (35) the matrix is replaced by the matrix so the Hadamard-Kronecker product matrix is given by
Case 2: The time fractional KPP equation with Dirichlet-Neumann boundary conditions:
subjected to the initial and boundary conditions
From (33) and the Dirichlet-Neumann boundary conditions in (41) and (42), we have
Finally, substituting the known coefficient matrix into (44), so the solution of FKPP is given by
where are entries of the Hadamard-Kronecker product matrix .
Case 3: the time fractional KPP equation with Neumann-Robin boundary conditions:
subjected to the initial and boundary conditions
Now, substituting (30), (50), and (36) into (25), the coefficient matrix A can solve from the system
Finally, substituting the known coefficient matrix into (50), so the solution of FKPP is given by
where are entries of the Hadamard-Kronecker product matrix .
5. Convergence and Error Analysis of the Chebyshev Wavelet
We next investigate convergence and error analysis for Chebyshev wavelets approximation
Theorem 1.
If the Chebyshav wavelets solution where
of the fractional KPP equation in (25) has a bounded second-order of partial derivatives , , then the Chebyshev wavelet solution converges uniformly with
Our proof is similar to the proof in the work by the authors of [26].
Theorem 2.
If the Chebyshav wavelets solution where
of the fractional KPP equation in (25) has a bounded second-order of partial derivatives , , and the Chebyshev wavelet approximate solution of the fractional KPP equation in (25) given by
where are entries of the Hadamard-Kronecker product matrix , in (16) and in (17) then the absolute error is defined by
This proof is similar to the proof in the work by the authors of [27].
6. Chebyshev Wavelet Solutions for the Time Fractional Kpp Equations
In this section, the efficiency and reliability of Chebyshev wavelet method are shown in some examples.
Example 1.
Consider the KPP equation (Fisher equation) with power–law nonlinearities chemical reaction:
subject to the initial condition
Case 1: Dirichlet boundary conditions
The exact solution of this problem is
In Chebyshev wavelets process, given and the collocation points in (36) are given by
Using the system from (37) and the Maple program (Maple 17) for solving the coefficient matrix as
which gives the matrix as
Therefore, the Chebyshev wavelet solution of KPP equation () is given by
We show the accuracy of this method by comparing between the Chebyshev wavelet solutions ( and ) and the exact solution with absolute errors, that numerical results have shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Numerical results and absolute error.
Case 2: Dirichlet-Neumann boundary conditions
By using Equation (45), the Chebyshev wavelet solution of KPP with Dirichlet-Neumann boundary condition () is given by
The graph of Chebyshev wavelet solution is shown in Figure 1 and the graph of the absolute errors is shown in Figure 2.
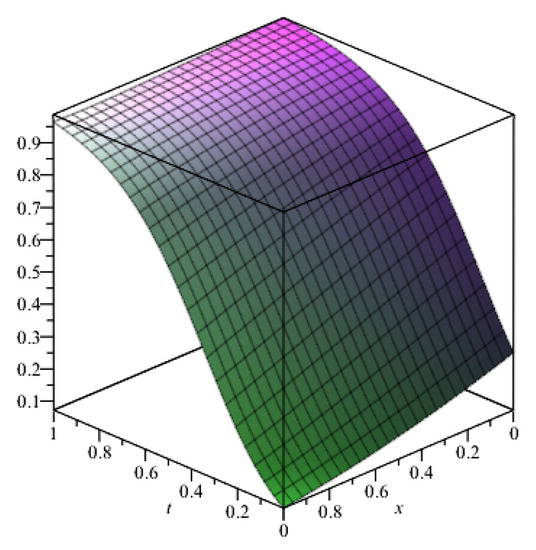
Figure 1.
Graph of Chebyshev wavelet solutions with .
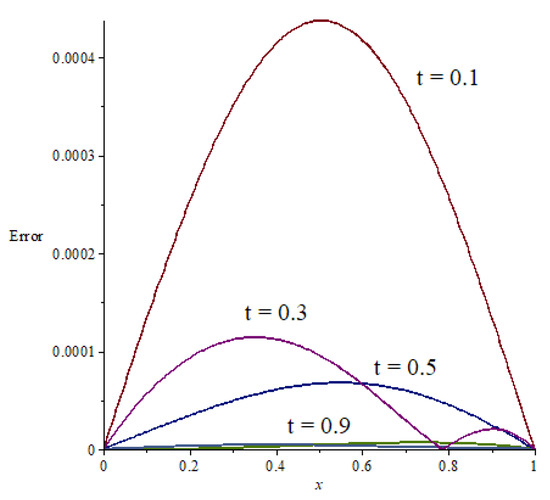
Figure 2.
Graph of absolute errors with .
Case 3: Neumann-Robin boundary conditions
By using Equation (51) the analytical Chebyshev wavelet solution of KPP with Neumann-Robin boundary conditions (, , 4, 5, and 7) is given by
and graphs of absolute errors for when and 7 are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
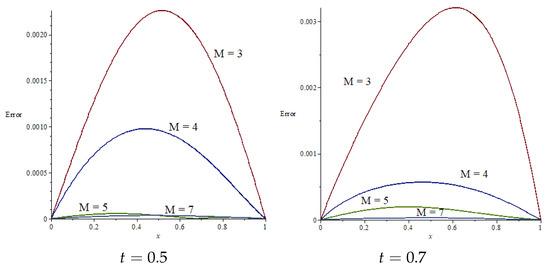
Figure 3.
Graphs of absolute errors for Fisher equation at and .
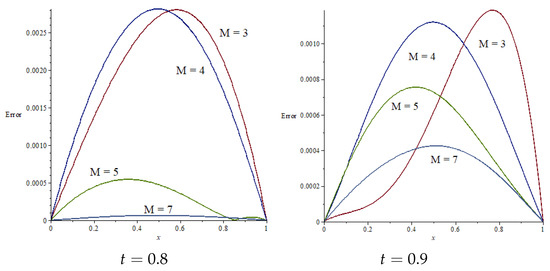
Figure 4.
Graphs of absolute errors for Fisher equation at and .
Example 2.
Consider the Fractional Kolmogorov-Petrovsky-Piskunov equation with exponential nonlinearities chemical reaction:
subject to the initial condition
Case 1: Dirichlet boundary conditions
Computing by Chebyshev method (37) the solution with is given by
We compare the Chebyshev wavelet solution with numerical solution of finite difference method in Table 2.

Table 2.
Numerical results for and compare with finite difference method from the MAPLE program.
Case 2: Dirichlet-Neumann boundary conditions
In this case, the Chebyshev wavelet solutions for and 1 can be computed using the Chebyshev wavelet method in (45):
Numerical solutions for , and 1 are reported in Table 3.

Table 3.
Numerical results of the fractional Kolmogorov-Petrovsky-Piskunov (FKPP) equation with difference values of .
Case 3: Neumann-Robin boundary conditions
The graphs of Chebyshev wavelet solutions for and 1 from Chebyshev wavelet method (51) which satisfy Neumann-Robin boundary conditions can be shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6.
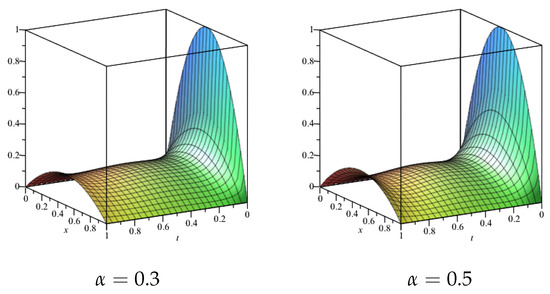
Figure 5.
Graphs of solutions for order and .
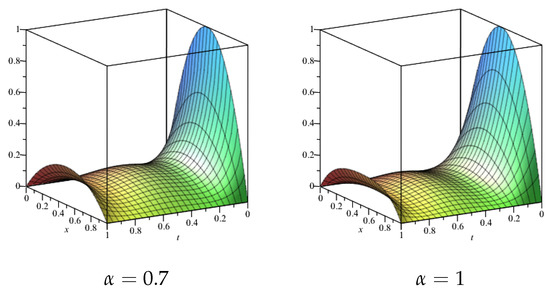
Figure 6.
Graphs of solutions for order and 1.
Example 3.
Consider the fractional Kolmogorov-Petrovsky-Piskunov equation with logarithmic nonlinearities chemical reaction:
subject to the initial condition
Case 1: Dirichlet boundary condition
Case 2: Dirichlet-Neumann boundary condition
Case 3: Neumann-Robin boundary condition
The Chebyshev wavelet solution for with Dirichlet boundary condition (Case 1), is given by
The Chebyshev wavelet solution for with Dirichlet-Neumann boundary condition (Case 2), is given by
The Chebyshev wavelet solution for with Neumann-Robin boundary condition (Case 3), is given by
The graphs of Chebyshev wavelet solutions for , and are shown in Figure 7.
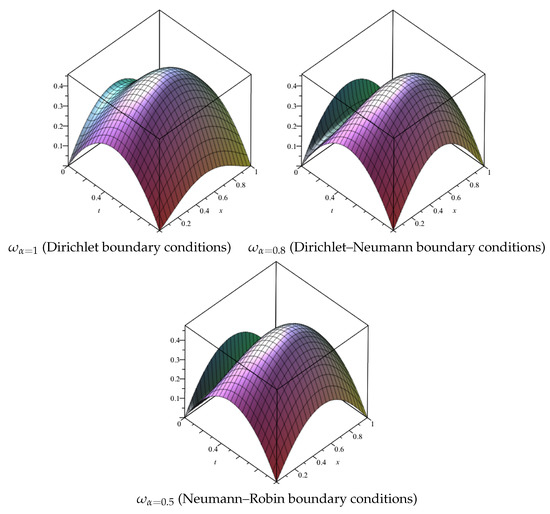
Figure 7.
Graphs of solutions for order , and .
7. Conclusions
The proposed method uses a technique for computation of Caputo fractional differential equation by constructing their operational matrices that represent Caputo fractional integration and differentiation. This approach provide the suitable analytical solutions of FKKP equation in Caputo fractional derivative sense, which is able to determine for initial condition, Dirichlet boundary, Dirichlet-Neumann boundary, and Neumann-Robin boundary conditions, respectively. The validity, accuracy and applicability of Chebyshev wavelet method have been illustrated through several examples by comparing with analytical results and exact solutions in Table 1, numerical solutions of finite difference method in Table 2. The execution of Chebyshev wavelet method shows that it is very simple and very efficient as an analytical result; the comparisons show that the Chebyshev wavelet method gives good accuracy and more rapidly convergent when increasing dilation () and translation (M) parameters. The Chebyshev wavelet method can solve some analytical solutions of FKPP Dirichlet boundary problem with various fractional orders . Furthermore, useful applications form the proposed method can be applied to solve solutions for various fractional order derivatives or other fractional partial equations.
Author Contributions
T.K. conceived of the study, conducted application of the Chebyshev Wavelet Method to solve the FKPP equation, developed numerical solutions and drafted the manuscript. K.N. reviewed the procedures, algorithms and numerical results for accuracy and efficiency. S.K. participated in the study’s design and coordination, provided guidance, and helped to draft and revise the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Applied Science and Graduate College, King Mongkut’s University of Technology North Bangkok for supporting this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Podlubny, I.; Chechkin, A.; Skovranek, T.; Chen, Y.; Jara, B.M.V. Matrix approach to discrete fractional calculus II: Partial fractional differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 2009, 228, 3137–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, G.; Kannan, K.; Sharma, K. Haar wavelet method for solving Fisher’s equation. Appl. Math. Comput. 2009, 211, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandraker, V.; Awasthi, A.; Jayaraj, S. A numerical treatment of Fisher equation. Procedia Eng. 2015, 127, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeresha, P.; Prakasha, D.G.; Baleanu, D. An efficient numerical technique for the nonlinear fractional Kolmogorov-Petrovskii-Piskunov equation. Mathematics 2019, 7, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazem, S. Exact solution of some linear fractional differential equations by laplace transform. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2013, 16, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Allahviranloo, T.; Gouyandeh, Z.; Armand, A. Numerical solutions for fractional differential equations by Tau-Collocation method. Appl. Math. Comput. 2015, 271, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İbiş, B.; Bayram, M. Numerical comparison of methods for solving fractional differential-algebraic equations (FDAEs). Comput. Math. Appl. 2011, 62, 3270–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turut, V.; Guzel, N. On solving partial differential equations of fractional order by using the variational iteration method and multivariate Pade approximations. Eur. J. Pure Appl. Math. 2013, 6, 147–171. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Khaled, K. Numerical solution of time-fractional partial differential equations using Sumudu decomposition method. Rom. J. Phys. 2015, 60, 99–110. [Google Scholar]
- Mashayekhi, S.; Razzaghi, M. Numerical solution of nonlinear fractional integro-differential equations by hybrid functions. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2015, 56, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, S.; Sedaghat, S.; Mohammadi, I. A fast numerical algorithm based on the second kind Chebyshev polynomials for fractional integro-differential equations with weakly singular kernels. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2016, 308, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakdaman, M.; Ahmadian, A.; Effati, S.; Salahshour, S.; Baleanu, D. Solving differential equations of fractional order using an optimization technique based on training artificial neural network. Appl. Math. Comput. 2017, 293, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, L.; Liu, L.; Xie, J. The Chebyshev wavelet method for solving fractional integral and differential equations of Bratu-type. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2013, 9, 5601–5609. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Ray, S.S. Numerical treatment for the solution of fractional fifth-order Sawada-Kotera equation using second kind Chebyshev wavelet method. Appl. Math. Model. 2015, 39, 5121–5130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Wang, L.; Huang, J. Legendre wavelets method for the numerical solution of fractional integro-differential equations with weakly singular kernel. Appl. Math. Model. 2016, 40, 3422–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, M.; Hooshmandasl, M.; Ghaini, F.M. A new approach of the Chebyshev wavelets method for partial differential equations with boundary conditions of the telegraph type. Appl. Math. Model. 2014, 38, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.S.; Gupta, A.K. Wavelet Methods for Solving Partial Differential Equations and Fractional Differential Equations; Chapman and Hall/CRC: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Awashie, G.E.; Amoako-Yirenkyi, P.; Dontwi, I.K. Chebyshev wavelets collocation method for simulating a two-phase flow of immiscible fluids in a reservoir with different capillary effects. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2019, 9, 2039–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oruç, Ö.; Bulut, F.; Esen, A. Chebyshev Wavelet Method for Numerical Solutions of Coupled Burgers’ Equation. Hacet. J. Math. Stat. 2019, 48, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyanin, A.D.; Zaitsev, V.F. Handbook of Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations; CRC Press: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Podlubny, I. Fractional Differential Equations: An Introduction to Fractional Derivatives, Fractional Differential Equations, to Methods of Their Solution and Some of Their Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 198. [Google Scholar]
- Babolian, E.; Fattahzadeh, F. Numerical solution of differential equations by using Chebyshev wavelet operational matrix of integration. Appl. Math. Comput. 2007, 188, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schacke, K. On the Kronecker Product. Master’s Thesis, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dayar, T.; Orhan, M.C. On vector-Kronecker product multiplication with rectangular factors. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2015, 37, S526–S543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, R.A. The hadamard product. Proc. Symp. Appl. Math. 1990, 40, 87–169. [Google Scholar]
- Adibi, H.; Assari, P. Chebyshev wavelet method for numerical solution of Fredholm integral equations of the first kind. Math. Probl. Eng. 2010, 2010, 138408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Lin, E.B. Legendre wavelet method for numerical solutions of partial differential equations. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. Int. J. 2010, 26, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).