Abstract
Coastal vulnerability describes the susceptibility of a system to adverse effects from natural hazards. It is typically evaluated using spatial data on geographical attributes and is often synthesized using tools such as a Coastal Vulnerability Index (CVI). However, the literature highlights that there is no universal method for assessing vulnerability, emphasizing the importance of site-specific adaptations. A key challenge in coastal risk management is dealing with the inherent uncertainty of environmental variables and their future dynamics. Incorporating this uncertainty is essential for producing reliable assessments and informed decision-making. In this paper, we present an R package that facilitates the implementation of probabilistic graphical models explicitly incorporating epistemic uncertainty. This approach allows for vulnerability assessments even in situations where data availability is limited. The proposed methodology aims to deliver a more flexible and transparent framework for vulnerability analysis under uncertainty, providing valuable support to local policymakers, in particular during the early phases of intervention planning and technology selection for coastal mitigation strategies.
Keywords:
Bayesian models; epistemic uncertainty; graphical models; coastal vulnerability; coastal protection intervention; CVI MSC:
62C10
1. Introduction
Coastal vulnerability, as defined in Pantusa et al. [1], represents the degree to which coastal zones are exposed and susceptible to damage resulting from both natural processes and human-induced changes. This concept encompasses not only the physical sensitivity of coastal systems to hazards such as sea-level rise, erosion, and extreme events, but also the socioeconomic exposure of people, assets, and activities concentrated in these dynamic areas. Vulnerability therefore results from the interplay among physical processes, environmental characteristics, and societal factors, which collectively determine the potential impacts of coastal hazards.
The scientific community has long recognized that vulnerability assessment must integrate these multiple dimensions.
Physical drivers (forcing factors) include wave energy, tidal range, storm surges, sea-level rise, and shoreline morphology [2]. Geological features deal with morphology and earth material, such as sediment types, coastal slope, and elevation. Natural buffers like dunes, wetlands, and vegetation constitute the so called ecological factors, among which the “dune variable” specifically captures both the width and the morphological type of the dune. Dune width plays a key role in coastal zone preservation, since wider dunes enhance shoreline resilience. Given that wave collision is often the prevailing regime, leading to dune retreat and volume loss without overtopping, dune width emerges as a crucial component of coastal defence [3,4]. The socio-economic dimension often plays a crucial role, reflecting land use, urban expansion, protective infrastructure (e.g., seawalls), and population density. Exposure and sensitivity of the ecosystem and of the built environment to coastal hazards must be evaluated to quantitatively assess the potential severity of impact on vulnerable areas.
The combination of these perspectives underpins recent efforts toward more comprehensive risk frameworks, where the traditional Coastal Vulnerability Index (CVI) can be complemented by probabilistic graphical models to describe not only exposure and sensitivity but also the uncertainty of underlying processes. In this context, our work introduces an innovative framework for assessing coastal vulnerability and impact, combining expert elicitation with a Bayesian Probabilistic Graphical Model (PGM) with the aim of taking into account the inherent uncertainty of the considered environmental context. In the literature, specialized classes of PGM have already been proposed. Guidelines for developing and evaluating Bayesian network models of environmental systems are provided in [5], in which a case study on the habitat of the Tasmanian giant freshwater crayfish is also considered. Life-cycle reliability assessment of reinforced concrete structures under marine atmospheric environments is discussed in [6], where a comprehensive Bayesian Network (BN) framework is developed based on several physical models, also addressing time dependence. In [7], the challenges of assessing sea-level rise (SLR) risks are addressed to overcome limitations of traditional mechanistic models in representing the complexity of coastal systems. An integrated methodological framework built upon Bayesian decision networks is proposed to combine participatory approaches, probabilistic modeling, and decision analysis. In their earlier work, Castelletti and Soncini-Sessa [8] recognized the high potential of Bayesian networks in water resource management and formulated a proposal on how to integrate BNs with other methodologies, e.g., Markov chains and mechanistic models. In [9], BNs are recognized as the proper tool-to-model complex coastal processes after comparing predictive and descriptive BNs using a 10-year dataset of 137 storm events at Narrabeen-Collaroy Beach. In [10], a BN approach is applied to assess multi-risk scenarios for the Venice coast using 2015–2019 data to support local authorities in coastal risk management and adaptation planning; results show that sea level, wave height, and direction strongly affect shoreline erosion, accretion, and water quality. It is worth noting that all contributions cited above, except for [7], do not handle epistemic uncertainty through the adoption of subjective probability.
A remarkable contribution to the field of BNs is a paper by Durap [11]. It develops a GIS-based Bayesian Network model to assess coastal vulnerability along Queensland’s shoreline. From a statistical perspective, it integrates BNs into the traditional Coastal Vulnerability Index (CVI) framework, using conditional probability tables and a directed acyclic graph (DAG) to model dependencies among geomorphological, oceanic, and climatic variables. The model quantifies exposure, sensitivity, and vulnerability probabilistically and achieves over predictive accuracy compared to traditional CVI methods. However, no expert elicitation is explicitly conducted, as parameterization relies on empirical and spatial data rather than subjective priors. Therefore, the capability of making optimal decisions under limited or unavailable data is not addressed.
In [12], a Bayesian Network for Coastal Risk Assessment Framework is developed, that is a probabilistic model for large-scale coastal hazard assessment. Conditional probabilities are derived from empirical data and numerical modeling (wave, surge, and morphodynamic simulations) with the aim of estimating coastal flooding likelihood. Model parameters are data-driven, not elicited from experts; thus, no subjective priors or expert elicitation are required. The BN structure enables scenario analysis and quantification of uncertainty propagation across hazard variables.
Our approach is applied to the low-lying coasts of Calabria, a region highly exposed to climate change impacts and subject to intense anthropogenic pressures. Building on the Coastal Vulnerability Index (CVI) developed in [1] for the same area, the model retains the three-sub-index structure: geological, hydro-physical, and vegetation.
Structured expert judgments are elicited in terms of both intervals and plausible point values. These inputs allow the model to generate probability distributions for each vulnerability and impact class in order to quantify uncertainty and to update predictions under different scenarios of human intervention.
The proposed R package 4.5.1 supports the calculations needed to achieve the above mentioned goals in the context of the Calabrian coast (Italy), and it constitutes a useful template for similar calculations in other contexts. The model results indicate that, in the absence of intervention, the most likely levels of vulnerability and impact are in the highest classes. Simulating interventions targeting geological and vegetation vulnerabilities reduces uncertainty and clearly distinguishes the “High” and “Very High” classes. We reconsider the data from Pantusa et al. [1] to assess the PGM’s performance. Applying the model to 39 transects with empirical data yields results consistent with those obtained from expert-elicited data alone, under both intervention and non-intervention scenarios.
The structure of the paper reflects the foundational elements of our proposal. The following Section 2 starts with a short description of the class of PGMs in Section 2.1, then the main features of the Calabrian case study are summarized in Section 2.2, where a specific PGM is detailed. The structure of the elicitation is described in Section 2.3. The R package is introduced in Section 2.4 together with explanations of its main functions. Finally, the discussion in Section 3 puts this work in perspective, emphasizing its flexibility, limitations, and some directions for future research.
2. Materials and Methods
We start by introducing the class of models considered in this package, then the Calabrian coastal case study in [1] is described through 22 variables encompassing attributes, vulnerability sub-indexes, risk factors, and impacts. We note in passing that observational data are available only for a subset of these variables (specifically, the attributes) in the Calabrian case study [1], while no data are available for the remaining ones.
2.1. Probabilistic Graphical Models
Probabilistic Graphical Models (PGMs, [13]) are suited to represent multivariate contexts where the decomposition of the joint probability density function (PDF) into the product of conditional probability density functions is characterized by a small number of conditioning variables within each factor. In the context , a set of variables is considered, and the joint distribution is written as follows:
where is the set of variables required in the conditional PDF of .
A directed acyclic graph (DAG), , is a qualitative representation of conditional independence (C.I.) relationships where V is the set of vertices, also called nodes, and E is the set of directed edges joining distinct nodes. The qualitative representation of Equation (1) is obtained by setting and by introducing a directed edge into E for each conditioning variable (parent) in joining (child), with . An equivalent explicit notation for parents is , with a total of parent nodes for in the DAG. In Figure 1, is a variable with parent nodes equal to , and . Although 22 variables are considered, this DAG is sparse, i.e., the number of directed edges is low: the resulting models are often less cognitively demanding to humans, helping to avoid a premature detachment of human intuition from the context [13]. A color-enhanced version of the DAG shown in Figure 1 is available in the Supplementary Materials (file “DAG drawing v4 color.png”).
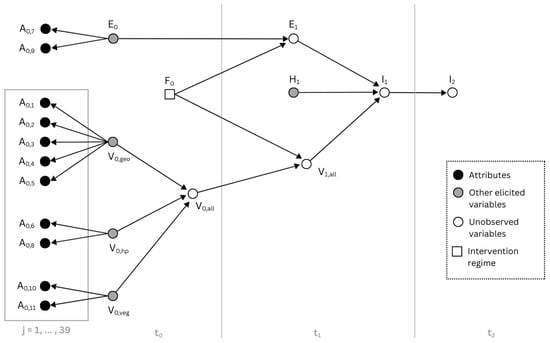
Figure 1.
Graph is the complete PGM of the system. From left to right the temporal evolution of the system from to is shown. The attributes are displayed in their configuration as children of their respective vulnerability sub-index and the overall vulnerability index depends in on the sub-indices ; in time interval vulnerability may change, , and with two other factors they contribute to risk evaluation as parents of the impact node ; an indirect impact in time interval is quantified by .
DAGs are also useful to describe causal relationships, and in this setup, a directed edge from to indicates a direct causal relationship from a variable representing hazard to a variable representing impact (see [14], for an introduction). In the class of structural causal models (SCM), each causal relationship is a deterministic function as follows:
where parents of node , , are endogenous variables representing direct causes of ; the implicit function also depends on the exogenous variable , which accounts for all other causal factors not explicitly considered in the current model. The Markovian assumption on the joint distribution of characterizes many useful models as follows:
thus, exogenous variables are marginally independent. It is worth noting that some inferential tasks may be equally performed after integrating out all the exogenous variables to obtain a causal Bayesian network (BN), where each variable (but ) has a PDF.
Most of the vertices defined in this study are discrete ordinal random variables, thus they take 2, 3, or 5 ordered values; for example, a five-level sample space may be defined as = {“Very Low”, “Low”, “Medium”, “High”, “Very High”}, and it is often represented by integers [15]. The conditional PDFs are also discrete, and the vector (or matrix) of the parameters refers to the conditional pdfs for the random variable . The collection of all model parameters is indicated as .
Parameter learning in the graphical model considered here is performed according to Bayes’ theorem. The likelihood function of model parameters is, with just one observation, as follows:
A special class of prior PDFs for parameters of categorical variables deserves to be mentioned—the Dirichlet family. We simplify the notation a bit by omitting the index j, while describing the Dirichlet prior distribution , where the sample space of is . For vectors and we say that pi follows the Dirichlet distribution if
and where .
The final (posterior) distribution after conditioning to n exchangeable vectors is as follows:
thus, the initial PDF of is made by marginally independent vectors, ; the omitted normalizing factor is . If all variables are categorical and for each pair vectors for the configuration of parents are independent with pdf in the Dirichlet family, then the posterior distributions are also Dirichlet (with complete data): the final hyperparameters lambda are obtained adding to the observed counts in class k of , e.g., with no parents .
2.2. The Calabrian Coastal Case Study
The R package vulneraR deals with a minimal but not-trivial context located in the Calabrian coast. Figure 1 illustrates the main features through an annotated DAG, in which each vertex-variable is assigned to one of the subsequent time intervals (, , and ), delimited by vertical gray lines. The length of the intervals is context-specific: the period must be sufficiently long to allow the occurrence of the event of interest (the hazard), yet not so long that the assessments or assumptions regarding the attributes and variables measured in , , and lose validity or temporal relevance. When working with the hazard variable, we refer to the definition by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC, https://www.ipcc.ch/srocc/chapter/glossary/, accessed on 4 August 2025): “The potential occurrence of a natural or human-induced physical event or trend that may cause loss of life, injury, or other health impacts, as well as damage and loss to property, infrastructure, livelihoods, service provision, ecosystems, and environmental resources. See also Disaster, Exposure, Loss and Damage, and losses and damages, Risk and Vulnerability.” In our context, dealing with the Calabrian coasts, the expert stated that the three time intervals could each be two years long. It is worth noting that the scale is expressed in months rather than days or hours, since a higher level of detail is not required at the considered model granularity.
The plate [16] on the left, in general, contexts may contain eleven variables [1], because sampled transects each contribute the same set of eleven variables. However, during the elicitation of distributions with our expert (see Section 2.3), the DAG was refined by making attributes (“Relative Sea Level Change”) and (“Mean Tide Range”) children of the Exposure node, . Since these two hydro-physical attributes are not site-specific and remain spatially uniform across the study area, they are more informative for assessing exposure than vulnerability.
We note in passing that if then in Figure 1 the PGM corresponds to a discrete Bayesian network, see [17]. Last, our context is characterized by unobserved variables, that is, and all variables located in time intervals greater than : future global vulnerability, exposure, hazard, and impacts.
The eleven attributes in Figure 1 are detailed in [1], and they are grouped according to different types of vulnerability, as summarized in Table 1. The overall vulnerability depends on sub-vulnerability indices , and it may change in the next time interval into , as described in the next section. Similarly, in Figure 1, the exposure may change into in time interval, . Here, exposure and vulnerability variables determine, together with hazard variable , the value of the direct impact variable . Nevertheless, an indirect impact may occur at time , as a consequence of the impact at time . Lastly, the node represents two possible regimes [18] in which the model can work and the vulneraR package can be used: with intervention and without intervention.

Table 1.
Description: and grouping by vulnerability sub-index of the 11 attributes considered in this work and initially identified in [1].
Different types of human intervention (manipulation) in the area can involve hard solutions such as building coastal structures, soft solutions, hybrid solutions, or even doing nothing (idle intervention). A causal arrow is therefore introduced in the DAG (Figure 1), from the manipulation node to exposure and vulnerability . Variable is not associated with a PDF, but it always conditions and , but not . This is the reason why a square vertex is plotted: it is set to “no intervention” by default and changed only if an actual manipulation-intervention is performed and the relative data are available. A detailed definition of exposure is provided in Pantusa et al. [1] and in [2], where the authors state:
thus variable is also part of our context.Exposure includes the whole inventory of elements that can be adversely affected by an impact. Although reducing exposure to physical assets such as buildings and infrastructures is common practice, information associated with indirect effects (e.g., sectoral GPD, income) cannot be ignored. For instance, when an industrial plant becomes flooded, consequences are not limited to damages to structure and contents but can include loss of profits due to business interruption or delay.
In accordance with our expert, we define the sample space of attributes and vulnerability variables across five distinct levels. Furthermore, the sample space for the exposure, hazard, and impact variables was specified using three levels.
Some further remarks are in order about the structure of our DAG (Figure 1). Firstly, while in the original article by Pantusa et al. [1] the distinction among geological, hydro-physical, and vegetation attributes is merely formal, as it does not affect the calculation of the final vulnerability index, in our model this distinction is reflected in their contributions to three separate vulnerability sub-indices: , , and . In the proposed model, the three sub-indexes are later combined into one vulnerability index, , that will indirectly contribute, through temporal evolution with , to the evaluation of the direct impact (next section for details). Secondly, an experienced reader might be surprised by the decomposition of the joint conditional PDF of the attributes given the vulnerability sub-index into conditional distributions of single attributes given the sub-vulnerability alone as follows:
but this “Naïve Bayes” configuration, despite being successful in many contexts, should be only considered a starting point before introducing more structure where appropriate, as in the Tree Augmented Naïve Bayes (TAN) by Friedman et al. [19].
2.3. Elicitation
The sparse nature of our PGM facilitates human interpretation and makes elicitation less cognitively demanding. Elicitation is the process of representing expert knowledge and beliefs about uncertain quantities in a quantitative form by means of a (joint) probability distribution [20,21]. The person whose knowledge is elicited is called an “expert”. For this study, the expert selection criteria were a good understanding of geological, hydrological, and physical processes and an intimate knowledge of the case study area. The second key figure of an elicitation process is the facilitator, whose main task is to gather the expert’s knowledge—for example, by conducting the interview—and to carefully translate such knowledge into probabilistic form [20].
A single expert elicitation is here considered by implementing an R package in order to reduce efforts and costs commonly associated with vulnerability assessments. Using elicited data, the goal is to define the conditional distributions of all vulnerability attributes and the marginal distributions of the vulnerability sub-indexes, the exposure at time , and hazard at time . The distributions of interest are as follows:
with a, v, e, and h the index for the class of the corresponding variable; index refers to the considered attribute, and to the type of vulnerability sub-index.
The decision to adopt either a direct or an indirect elicitation approach is determined by the nature of the quantities to be elicited. For the conditional probabilities of the attributes, , and for the distributions of , values were elicited indirectly. Indirect elicitation consists of using virtual transects, formulating questions such as: “Assume that you know for sure that you have 1000 transects belonging to context that have been given Geological Vulnerability score of 1 (very-low), then what is the lowest number of transects you believe would have a vulnerability score of 3 in the Geomorphology attribute? What would be the highest plausible number? What is the most plausible number of transects with a moderate vulnerability score (v.s. = 3) in Geomorphology?”. For and , a direct elicitation was performed by asking for probability estimates directly, without relying on virtual transects. For both the direct and indirect elicitation, the elicited answer is a triplet consisting of the minimum, median, and maximum values for an interval. A single triplet, for example, describes the degree of belief and the confidence of the expert about attribute taking score , given that the vulnerability sub-index (parent of attribute ) takes value , in other terms it gives information on .
A complete protocol for elicitation is provided within the vulneraR package, together with an Excel worksheet developed for the facilitator to collect the data. The protocol contains precise instructions, including scripts and descriptions that the facilitator can read aloud or provide to the expert. The worksheet explicitly includes written questions and spaces for recording the expert’s answers. These answers are then processed, converted into the format required by the package functions, and graphically elaborated to provide both the facilitator and the expert with immediate visual feedback on the progress of the interview, all within the same worksheet.
The literature supports the need for such a protocol (see [21,22,23]). We found that a transparent record of the elicitation procedure, accompanied by step-by-step instructions, mitigates biases and misunderstandings while improving the interpretation and analysis of results. In the vulneraR package, the function get_elicita_files is provided to copy templates of the “.xlsx” file and of the elicitation protocol (“.pdf” file) in a selected folder.
The distributions for variables , , , , and are not elicited because they are defined through deterministic relationships among hyperparameters (see the next section). This choice reflects the expert’s degree of belief and also reduces the cognitive burden due to the large number of questions that would otherwise result.
Detailed guidelines on how to collect data on coastal vulnerability through a structured single-expert elicitation round are available as Supplementary Materials (file “Elicitation_protocol.pdf”).
2.4. The vulneraR Package
The vulneraR package (link available in the Supplementary Materials) is designed to analyze the data collected during an elicitation process, as described in the previous section, and to obtain PDFs for all the variables included in the model. Several functions have been implemented to support this task, guiding the user through the entire workflow: from data import to the definition of the PDFs, including the temporal evolution of some variables (nodes) in the model. The core functions of the package work at the hyperparameter level, so their outputs are vectors whose elements are lambda values, for example:
thus, for example, element refers to the hyperparameter of the Dirichlet distribution when variable takes value 1 given that the conditioning variable is equal to 4.
The initial data expected by the package consist of a .csv file containing the Conditional Probability Tables (CPTs) of the attributes and one containing the triplets elicited for the vulnerability sub-indexes (, ), of the exposure node () and of the hazard node (). These files can be easily obtained if the elicitation was performed using the provided worksheet by exporting the dedicated self-filling sheets. These CPT sheets contain the elicited triplets and are read and loaded as dataframes by dedicated functions in the package.
The package follows a structured approach with respect to the model, finding each node’s distribution from left to right in the DAG. Attributes, sub-indexes, exposure, and hazard all have corresponding elicited data entering as arguments into the getLambdaAttr and getLambdaVEH functions. These functions work identically, but with different input dataframes. The reason for introducing two functions lies in the nature and structuring of the input data: while for the attributes the data are CPTs, in the case of the vulnerabilities, exposure, and hazard, there was not a conditioning variable, and therefore they are simple probability tables. Nevertheless, the functions follow the same implementation scheme and yield analogous results for the different elicited nodes.
Applying these two functions, the resulting 2 dataframes will contain the hyperparameters of the distributions of all the variables for which elicited data are available, which means the following:
- -
- Geological attributes: ;
- -
- Hydro-physical attributes: ;
- -
- Vegetation attributes: ;
- -
- Vulnerability sub-indexes: ;
- -
- Exposure: ;
- -
- Hazard: .
To exemplify these functions, a walk-through of the implementation and use of getLambdaVEH() will now be provided. The arguments of the function are as follows:
- mydata—Dataframe containing the conditional probability tables for , , , and . It must have the same structure and format as the object returned by the loadDataVEH() function;
- choice_quant—An array of three doubles specifying the quantiles to be associated with the (min, mean, max) triplet in the Beta fit of each variable class. The default is ;
- manip—Matrix containing the probability shifts for each variable class. It must have the same structure and format as the object returned by the makeManip function. The default is the idle intervention represented by a identity matrix;
- tr_number—One of two strings to define whether the values obtained through indirect elicitation were obtained setting a 1000 virtual transects scenario (“1000 tr”) or a 100 virtual transects scenario (“100 tr”). Defaults to “1000 tr”;
- graph—Boolean variable, indicating whether the graphs should be produced (TRUE) or not (FALSE); the default is TRUE;
- out_path—The folder where files are saved; if NA then the parent of the working directory is selected.
The function uses the provided dataframe and quantiles and initially relies on the SHELF package to perform an initial step where each class is fitted to a beta distribution such that the elicited triplet corresponds to the specified quantiles (argument) of the distribution. The five (or three, in the case of and ) beta distributions are then fitted to a five-dimensional (or three-dimensional) Dirichlet distribution. The beta and Dirichlet fits are performed using the fitdist and fitDirichlet functions of the SHELF package, respectively. As output, the function returns a dataframe containing the hyperparameters of the final fitted distribution (one row per variable, one column per class). If the graph argument is left to the default or set to TRUE, the function also produces plots of the marginal probability distributions of each class for the final Dirichlet distribution. These plots are saved in subfolders specified by the user or in the parent folder of the working directory. The files are organized hierarchically, according to whether an intervention was introduced or not.
The elicitation of the remaining nodes in the model is carried out through deterministic relationships at the hyperparameter level. Both and use linear combinations with similarly calculated weights, but in R they are implemented via different functions. Firstly, this choice was primarily due to two peculiarities of the nodes themselves. The linear combination is constructed to represent a perturbation of two terms (weights less than 1) around one dominant term (weight equal to 1). A separate implementation allows the dominant term for the total vulnerability to vary depending on the context of application, meaning that the user can select which of the three sub-indexes will serve as the dominant one. In agreement with the results of the analysis performed by [1] and with statements made by the expert during the elicitation, geological vulnerability was chosen as the most informative of the three sub-indexes for this study and is set as the default dominant term in the function implementation. The dominant term for , on the other hand, is the total vulnerability, without the possibility of selecting another component as dominant. The second reason for a separate implementation involves the impact variable, because its parents have different dimension.
The hazard node has a sample space of size three; thus, , while variable , which is also of size three, has two parent nodes, thus a vector is required for each element in the Cartesian product made by the sample spaces of the parents nodes, variable and . As regards , the two lower classes and two higher classes were merged into a single class each to reduce the dimensionality of . Several points were considered while merging classes: (i) it is important to maintain the main features of the central class, because it is extremely informative, especially in the behavior of a variable; (ii) the two lower classes and the two higher classes show significant overlap in the distribution of ; and (iii) the merging procedure should carry an increase in uncertainty without introducing artifacts.
The selected transformations are:
therefore, the new three-dimensional vector of hyperparameters for has the same lambda value in the central class as its five-dimensional counterpart and has a lower total sum, a feature that implies a wider dispersion in each class has, i.e., higher associated uncertainty.
A more in-depth description of the getLambdaV0 function follows, detailing its structure and weight selection. The arguments for the function are as follows:
- lambdas—Dataframe containing all fitted hyperparameters for the vulnerability, exposure and hazard nodes. Must have the same structure and format as the object returned by the getLambdaVEH function.
- first_term An integer number either 1, 2 or 3 to indicate which sub-index to use as a main component for the linear combination: 1 for V0geo, 2 for V0hp and 3 for V0veg. Defaults to 1, geological vulnerability as first component.
- graph—Boolean variable, indicating whether the graphs should be produced (TRUE) or not (FALSE); the default is TRUE.
- out_path—The folder where files are saved; if NA then the parent of the working directory is selected.
The function takes the output of the initial getLambdaVEH function as argument: it contains the vector of hyperparameters for the three vulnerability sub-indexes required to calculate the scalar weights as in Equations (11) and (12). The choice of scalar weights calculated using the sum of all elements of the hyperparameter vectors of the sub-indexes ensures that all the classes of the variables’ distributions contribute equally. This implementation guarantees that changes brought on by the dominant term are greater as the perturbation term becomes more and more informative (larger ) with respect to the dominant class.
where for the dominant term and analogously for the first perturbation term, , and for the second one, . The object returned is a dataframe containing the hyperparameters for the total vulnerability at time , . If the first_term argument defaults (i.e., as per the Calabrian case study), the resulting hyperparameter vector is built as in Equation (13)
where the dominant term is the geological one, the first perturbation term is hydro-physical, giving and the second one is vegetation, giving .
Lastly, the package includes a function to implement temporal evolution of a variable, tempEvol. This function takes as argument a vector of hyperparameters of a node and returns the vector of hyperparameters of the same node but at the subsequent time interval. The core principle that guides the deterministic relationship implemented for distributions at a future moment in time, is that temporal evolution does not change the expected value of a variable, but it does change the uncertainty associated with its distribution. So the child variable at would preserve the same expected value as that at time , but its distribution would be wider. This function also works at the hyperparameter level and increases the uncertainty of a temporally evolved distribution by increasing by 10% the distance between the 20% and 80% quantiles of the distribution in . The distribution the function acts on is the marginalized distribution of the central class of the variable of interest, selected as the most informative.
In an effort to reproduce its mitigating nature, intervention is implemented through a transfer of probability from a higher class of vulnerability (or exposure) to the adjacent lower class. Such implementation allows keeping control of the reaction of a single class to intervention, since even performing the same manipulation, “Moderate” vulnerability conditions might cause an area to respond very differently than “Very High” vulnerability conditions. Working within the intervention regime requires deep knowledge of both the technique in use and the area of interest. Indeed, this critical step is better solved if an extensive study of the selected context, here the Calabrian coast, is performed, taking into consideration the type of intervention, its expected performance, and the site response in order to properly quantify the probability shifts required by the package.
Within the package, the possibility to work under different regimes, intervention or no intervention, is selected by the user when invoking the getLambdaVEH function. The function itself calls for the manipulation matrix as an argument. If the regime is that of no intervention, then no action is required and manipulation defaults to the identity matrix to implement an idle regime. The non-identity matrix required by an intervention regime may be produced using the makeManip function. The function calls for the following arguments:
- probshift_Vgeo—Probability shifts for Geological vulnerability: 5-element numerical array containing 5 values between 0 and 1; default is rep(0,5).
- probshift_Vhp—Probability shifts for Hydro-physical vulnerability: 5-element numerical array containing 5 values between 0 and 1; default is rep(0,5).
- probshift_Vveg—Probability shifts for Vegetation vulnerability: 5-element numerical array containing 5 values between 0 and 1; default is rep(0,5).
- probshift_E—Probability shifts for Exposure: 5-element numerical array containing 5 values between 0 and 1, the first 3 regarding the exposure classes and the last two as fillers; default is rep(0,5).
A numerical example helps sharpen intuition. If the expected effect of the intervention is to shift of probability from class 4 to class 3 of the geological vulnerability, the 4th element of the geological argument should be . The first element of each vector should be 0 since there is no lower adjacent class, and other values will be ignored.
The probability shift is performed at the hyperparameter level by the getLambdaVEH function. It checks whether the matrix argument is the identity matrix and behaves accordingly. Intervention shifts the expected value for a parameter of the vulnerability class (), but does not change the associated uncertainty (). In the case of a hypothetical intervention that requires the transfer of of probability from Class 5 to Class 4 and then another transfer from Class 4 to Class 3, then the expected value of Class 4 after intervention, , is calculated as in Equation (14) as follows:
where the hyperparameter for Class 4 after manipulation is .
We conclude this section by emphasizing that providing an explicit definition of probability shifts for each affected variable is essential. Such a definition enables a rigorous characterization of the intervention regime, through a user-defined manipulation matrix.
3. Results
In this section, we present a use case of the package vulneraR with examples of both numerical and graphical outputs relative to the Calabrian case study as presented in Section 2.2. In Figure 2, a schematic representation of the main workflow for the package is shown.

Figure 2.
A schematic summary of the main workflow when using the vulneraR package to assess coastal vulnerability and impacts on a coastal area. Boxes with dotted outlines are optional steps that can be skipped if data are not to be exported from the provided elicitation protocol or intervention is not implemented.
This worked example shows the use of the package in case of an elicitation performed following the provided protocol and worksheet, using 1000 virtual transects for the attribute nodes elicitation and implementing a hypothetical intervention.
To use the vulneraR package, the first step is to load the elicited data for all the attributes and the vulnerability, exposure, and hazard nodes. This is done by calling the loadData1000 (Table 2) and the loadDataVEH functions to load the .csv files the user has previously exported from the worksheet. The attributes dataframe contains an indication of the attribute’s parent sub-index in column V_type, the attribute and its score, and the elicited triplets for each vulnerability score.

Table 2.
Output from function loadData1000().
For the vulnerability, exposure, and hazard nodes, the imported dataframe contains the elicited triplets for each score of each variable.
After loading the data into the global environment, it is possible to obtain the first dataframe of hyperparameters for the attributes. In this example, attributes and were considered as children of the exposure node (see Section 2.2) and so the corresponding argument for getLambdaAttr function, del_A7A9 is left to default and they are not present in the final output.
Since intervention is implemented, the makeManip function is called before getLambdaVEH to produce the desired manipulation matrix, providing as argument the array of probability shifts for each class of all affected variables. In this example, only geological vulnerability is affected by intervention, shifting probabilities as follows:
- from class 5 to class 4;
- from class 4 to class 3;
- from class 3 to class 2;
- from class 2 to class 1.
- As shown in Table 3, calling the makeManip function. The matrix produced by this call contains a row with the user-defined probability shifts for the variable where intervention is implemented (in this case, the first row for ), while all other rows remain unchanged from the default idle intervention matrix (identity matrix).
 Table 3. Output of the makeManip function, when implementing an intervention that only affects the first variable, .
Table 3. Output of the makeManip function, when implementing an intervention that only affects the first variable, .
After the manipulation matrix is created, calling getLambdaVEH with the matrix as argument will produce the dataframe of hyperparameters for the distributions of , , , , and . Both the getLambdaAttr and getLambdaVEH functions are called, leaving the graph argument to default, meaning the function will call on plot_marginal and produce the graphs of the fitted marginal distributions for each score of each variable. All the graphical output is saved in a dedicated folder that is created in the parent folder of the working directory, unless specified differently by the user.
With the hyperparameters for the distributions of the elicited variables, the call for getLambdaV0 will provide the hyperparameters for . In this case, the dominant term was chosen as , in accordance with statements elicited from the expert and with the results from [1]. Furthermore, in this case a graph of the marginal distributions for each score was produced by setting the argument graph = TRUE.
Temporal evolution is now applied to the nodes and , and the arrays obtained from these two calls to tempEvol are then given to the getImpact function to obtain the vector of hyperparameters for .
Finally, calling tempEvol with the hyperparameter vector for the initial impact returns the hyperparameters of the secondary-impact distribution, , as shown in Figure 3.
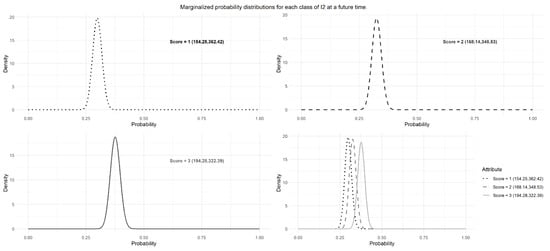
Figure 3.
Graphical output of the tempEvol function called to temporally evolve the hyperparameters for the distribution of the initial impact as returned by the function getImpact. This output is produced by a call to plot_marginal, which is also called by any function in the package that produces graphs. As seen in the figure, the graph contains individual plots for the marginal distribution of each class and one comprehensive plot that shows all classes together.
4. Discussion
This work proposes an explicit quantification of the uncertainty inherent in vulnerability studies, rather than relying solely on sensitivity analysis [1] and numerical robustness. We propose a PGM, and the accompanying R code, that supports the translation of statements elicited from an expert into a quantitative representation based on probability distributions.
Alternative approaches exist in the literature, e.g., [24], where authors claim that the Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process (FAHP) reduces subjective evaluations and the uncertainty inherent in human judgment. However, FAHP does not eliminate subjectivity; judgments remain human, nor does it guarantee a quantitative reduction of uncertainty; rather it is based on fuzzy sets whose specification depends on human choices (e.g., fuzzy scale, membership function, defuzzification rule). In our view, the critical issue is to work with a well-informed and calibrated expert within the subjective Bayesian perspective [20]. When such an expert is not available, uncertainty may be quantified by eliciting judgments from multiple experts in order to mitigate the influence of individual thought processes. In this case, a greater effort is required from the facilitator to integrate the different judgments into final probability distributions [21,23]. The implications of these methodological issues for vulnerability studies deserve space in future work.
Formal statements based on the d-separation theorem [17] are beyond the scope of this work, as we concentrate on the R code and the motivations behind it. Nevertheless, we note in passing that such a theorem can be exploited by defining as the collection of separating variables, as the collection of measured variables, and as the collection of unobserved variables. Then it follows that Y is conditionally independent of A given Z, formally , thus the application of this theorem provides a further motivation for our updating procedure based on the observed data.
The R package vulneraR should be considered a starting effort to support the elicitation in relatively simple, but not trivial, contexts for several reasons. Firstly, we implicitly assumed that the expert is able to answer questions about the degree of vulnerability and exposure while reasoning with five ordered classes in the selected time scale. In such a situation, only training for elicitation is needed; otherwise, the training step should also include elements of environmental science and coastal engineering, including field inspections of similar transects and footage of previous extreme events in similar areas (exchangeable statistical units). Secondly, the level of achievement attained through this endeavor also depends on the considered spatial scale, in our context restricted to only a few dozen kilometers. Larger areas are expected to require extensions of the PGM to account for further structured heterogeneity. Lastly, the proposed model granularity is also well suited to contexts in which the available information relies solely on expert judgment, pending the collection of field data. Nevertheless, our PGM could be extended to include nodes for field sensors, once an appropriate hierarchical structure is defined, and to integrate a down-scaled climatological model supporting the elicitation of the future hazard.
Future work could focus on strengthening decision-making support in a quantitative manner. The proposed PGM could be extended by introducing additional intervention nodes and by quantifying potential side effects resulting from the performed manipulations. For instance, a utility node could be employed to evaluate the trade-off between the achievement of mitigation and the tolerance of side effects.
The availability of this R package as an open-source project makes possible the broad collaboration that characterizes the R user community.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/math13223603/s1. The PDF file “Elicitation_protocol.pdf” contains detailed guidelines on how to collect data on coastal vulnerability through a structured single-expert elicitation round. The file “DAG drawing v4 color.png” presents a color-enhanced version of the DAG depicted in Figure 1. The R package vulneraRcan be downloaded from the GitHub repository https://github.com/federico-m-stefanini/vulneraR.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.M.S., S.A. and F.D.; methodology, F.M.S., S.A. and F.D.; software, S.A. and F.M.S.; validation, S.A. and F.D.; formal analysis, F.M.S. and S.A.; investigation, F.M.S., S.A. and F.D.; resources, F.D.; data curation, S.A.; visualization, S.A.; writing—original draft preparation, F.M.S. and S.A.; writing—review and editing, F.M.S., S.A. and F.D.; supervision, F.D. and F.M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Italian Ministry of University and Research (MUR) under the “Dipartimenti di Eccellenza” program (Law 232/2016, Article 1, Commas 314-337), through funding from ESP-UNIMI.
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in the study are openly available in the R package vulneraR at https://github.com/federico-m-stefanini/vulneraR.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BN | Bayesian network |
| CPT | Conditional Probability Table |
| CVI | Coastal Vulnerability Index |
| DAG | Directed Acyclic Graph |
| Probability density function | |
| PGM | Probabilistic Graphical Models |
| TAN | Tree Augmented Naive Bayes |
References
- Pantusa, D.; D’Alessandro, F.; Frega, F.; Francone, A.; Tomasicchio, G.R. Improvement of a coastal vulnerability index and its application along the Calabria Coastline, Italy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toimil, A.; Losada, I.J.; Nicholls, R.J.; Dalrymple, R.A.; Stive, M.J.F. Addressing the challenges of climate change risks and adaptation in coastal areas: A review. Coast. Eng. 2020, 156, 103611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gent, M.R.A.; van Thiel de Vries, J.S.M.; Coeveld, E.M.; de Vroeg, J.H.; van de Graaff, J. Large-scale dune erosion tests to study the influence of wave periods. Coast. Eng. 2008, 55, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho, F.; Abreu, T.; D’Alessandro, F.; Tomasicchio, G.R.; Silva, P.A. Surf hydrodynamics under collapsing coastal dunes. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 64, 144–148. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.H.; Pollino, C.A. Good practice in Bayesian network modelling. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 37, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Dong, Y.; Bastidas-Arteaga, E. Mixed Bayesian Network for reliability assessment of RC structures subjected to environmental actions. Struct. Saf. 2024, 106, 102392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catenacci, M.; Giupponi, C. Integrated assessment of sea-level rise adaptation strategies using a Bayesian decision network approach. Environ. Model. Softw. 2013, 44, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelletti, A.; Soncini-Sessa, R. Bayesian Networks and participatory modeling in water resource management. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 1075–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuzen, T.; Splinter, K.D.; Marshall, L.A.; Turner, I.L.; Harley, M.D.; Palmsten, M.L. Bayesian Networks in coastal engineering: Distinguishing descriptive and predictive applications. Coast. Eng. 2018, 135, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.V.; Dal Barco, M.K.; Pourmohammad Shahvar, M.; Furlan, E.; Critto, A.; Torresan, S. Bayesian Network Analysis for Shoreline Dynamics, Coastal Water Quality, and Their Related Risks in the Venice Littoral Zone, Italy. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durap, A. Mapping coastal resilience: A GIS-based Bayesian network approach to coastal hazard identification for Queensland’s dynamic shorelines. Anthr. Coasts 2024, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanuy, M.; Jiménez, J.A.; Plant, N. A Bayesian Network methodology for coastal hazard assessments on a regional scale: The BN-CRAF. Coast. Eng. 2020, 157, 103627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, D.; Friedman, N. Probabilistic Graphical Models: Principles and Techniques; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pearl, J.; Glymour, M.; Jewell, N.P. Causal Inference in Statistics: A Primer; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Chichester, West Sussex, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Laitila, P.; Virtanen, K. Advancing construction of conditional probability tables of Bayesian networks with ranked nodes method. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 2022, 51, 758–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buntine, W.L. Operations for Learning with Graphical Models. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 1994, 2, 159–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearl, J. Probabilistic Reasoning in Intelligent Systems: Networks of Plausible Inference; Morgan Kaufmann: San Mateo, CA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Dawid, P. What Is a Causal Graph? Algorithms 2024, 17, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Webb, G. Tree Augmented Naive Bayes. In Encyclopedia of Machine Learning and Data Mining; Springer Science + Business Media: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 1283–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garthwaite, P.H.; Kadane, J.B.; O’Hagan, A. Statistical Methods for Eliciting Probability Distributions. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2005, 100, 680–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mary, A. Meyer, J.M.B. Eliciting and Analyzing Expert Judgment: A Practical Guide; ASA-SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, M.G. Use (and abuse) of expert elicitation in support of decision making for public policy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7176–7184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemming, V.; Burgman, M.A.; Hanea, A.M.; McBride, M.F.; Wintle, B.C. A practical guide to structured expert elicitation using the IDEA protocol. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantusa, D.; Saponieri, A.; Tomasicchio, G.R. Assessment of coastal vulnerability to land-based sources of pollution and its application in Apulia, Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 886, 163754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).