Abstract
Achieving consensus in group decision-making is both essential and challenging, especially in which non-cooperative behaviors can significantly hinder the process under uncertainty. These behaviors may distort consensus outcomes, leading to increased costs and reduced efficiency. To address this issue, this study proposes a data-driven robust minimum-cost consensus model (MCCM) that accounts for non-cooperative behaviors by leveraging individual adjustment willingness. The model introduces an adjustment willingness function to identify non-cooperative participants during the consensus-reached process (CRP). To handle uncertainty in unit consensus costs, Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Kernel Density Estimation (KDE) are employed to construct data-driven uncertainty sets. A robust optimization framework is then used to minimize the worst-case consensus cost within these sets, improving the model’s adaptability and reducing the risk of suboptimal decisions. To enhance computational tractability, the model is reformulated into a linear equivalent using the duality theory. Experimental results from a case study on house demolition compensation negotiations in Guiyang demonstrate the model’s effectiveness in identifying and mitigating non-cooperative behaviors. The proposed approach significantly improves consensus efficiency and consistency, while the data-driven robust strategy offers greater flexibility than traditional robust optimization methods. These findings suggest that the model is well-suited for complex real-world group decision-making scenarios under uncertainty.
MSC:
93D50
1. Introduction
In group decision-making, diverging opinions among decision-makers often lead to disagreements or conflicts. Designing an effective consensus-reached process (CRP) is critical for ensuring robust outcomes [,]. Non-cooperative behaviors during the CRP constitutes a major impediment, potentially causing deviations in group decisions or hindering the decision-making process altogether. This issue has garnered significant scholarly attention. Yang et al. [] classified non-cooperative behaviors based on confidence levels and trust relationships, emphasizing that minority opinions should not be prematurely labeled as non-cooperative. Zhou et al. [] developed a dynamic consensus model using probabilistic linguistic term sets and Tanimoto coefficients to reconcile minority opinions and non-cooperative behaviors in large-scale group decision-making. Xu et al. [] examined management strategies for addressing minority opinions and non-cooperative behaviors in large-scale groups. Regarding the management and detection of non-cooperative behaviors, scholars have proposed various methods, such as innovative behavior monitoring [], multi-attribute evaluation matrices [], and cooperation intention indices [], to minimize the impact of non-cooperative behaviors on group consensus formation. Additionally, Yuan et al. [] proposed a budget-constrained consensus framework designed to minimize group conflicts and address non-cooperative behaviors. Existing research on non-cooperative behaviors has broadly addressed elements such as trust relationships [,,,] and conflict dynamics. However, studies focusing on decision-makers’ willingness to adjust their own behavior remain insufficiently explored.
In the process of multi-stage negotiation for group decisions, cost-effectiveness is a key consideration in the CRP. Ben-Arieh et al. [] first introduced the concept of minimum-cost consensus (MCC) and developed solution frameworks for achieving MCC under both linear and quadratic cost functions. Wang et al. [] leveraged cooperative game theory to construct a holistic consensus optimization model that incorporates individual adjustment preferences. Subsequently, to strike a balance between cost minimization and benefit maximization, Ma et al. [] integrated a dual social network framework into a consensus optimization model. Subsequent research has witnessed continuous innovation in consensus-related methodologies, with scholars actively integrating cross-disciplinary theories to advance the field [,,,,,]. In order to address the impact of unit cost changes, researchers have incorporated robust optimization techniques into consensus model construction, enhancing the resilience of decision frameworks []. Traditional robust optimization methodologies encompass box, ellipsoidal, and polyhedral uncertainty sets. By incorporating diverse uncertainty sets, researchers can construct distinct consensus models that account for data uncertainty [,,]. Advancing this line of research, Li et al. [] integrated stochastic programming with robust optimization techniques to develop a robust two-stage optimization consensus model. While also adopting a two-stage framework, Ma et al. [] proposed a two-stage distributed robust maximum expert consensus model, and Zhu et al. [] introduced a novel distributed robust opportunity-constrained maximum expert consensus model, further addressing cost asymmetry and distributed fuzziness in group decision-making to enhance decision efficiency under uncertainty. Furthermore, Han et al. [] incorporated confidence levels to formulate a chance-constrained robust minimum-cost consensus model (MCCM). Li et al. [] proposed a CRP framework for uncertain large-scale group decision-making based on robust discrete optimization, controlling the conservatism of optimal consensus opinions, and computing optimal corrective opinions for decision-makers. Through a comparative analysis with conventional robust optimization techniques, their approach demonstrated significant reductions in solution conservatism.
Complementing such chance-constrained frameworks, data-driven robust optimization methodologies offer an alternative approach to mitigate the inherent over-conservatism of traditional models []. Han et al. [] specifically addressed weight uncertainty in group decision aggregation by devising a data-driven robust MCCM framework, establishing a critical linkage between distributional robustness and consensus efficiency. Wei et al. [] pioneered a quadratic cost function to quantify complex resistance dynamics in expert opinion adjustment, subsequently developing a data-driven robust maximum expert consensus model. Their empirical analysis substantiates that such data-driven robust methodologies simultaneously elevate consensus achievement levels and mitigate solution conservatism. Robust optimization has been substantially applied to group decision-making, with significant advances. However, research on leveraging data-driven uncertainty sets for consensus model optimization remains relatively underexplored. This research gap presents a key point for future methodological innovation.
In light of the information above, this study develops a data-driven robust MCCM that incorporates non-cooperative behaviors characterized by individual adjustment willingness. The model is validated through a real-world case of house demolition compensation negotiations in a community in Guiyang, thus demonstrating its feasibility and effectiveness in practice. The main contributions of this paper are as follows: (1) An individual adjustment willingness function is proposed. It explicitly identifies and quantifies non-cooperative behaviors within the group decision-making process and captures the influence of participants’ adjustment willingness on both individual behavior and consensus dynamics. This function overcomes the limitation of traditional methods that lack a mechanistic representation of non-cooperation. (2) Data-driven uncertainty sets are constructed using Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Kernel Density Estimation (KDE). They not only address uncertainty in unit consensus costs but also reduce the conservatism inherent in traditional robust optimization approaches. (3) A robust MCCM is developed that explicitly considers non-cooperative behaviors and the unit cost uncertainty. This model provides a quantitative framework for behavioral deviations and enhances decision robustness under uncertainty. It addresses a critical gap in existing research where the coupling effect of behavior and uncertainty is often neglected.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 provides the basic knowledge of MCCM and non-cooperative behaviors. Section 3 describes the construction process of the data-driven robust MCCM. Section 4 offers a case study to prove the applicability of the proposed model. Conclusions are presented in Section 5.
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Minimum-Cost Consensus Model
Consensus cost refers to the total cost required for all decision-makers to adjust their individual opinions. In practice, it can also be extended to the money, time, and labor required to reach consensus. Suppose there are n decision-makers in the group decision-making process and is the set of decision-makers, where di denotes the i-th decision-maker. Let oi be the initial opinion given by di, oc be the consensus opinion, and ci be the unit cost of adjusting di’ s opinion. Based on the above notation, Ben-Arieh and Easton [] designed a linear MCCM in which the consensus reached is a hard consensus, meaning that the consensus level must be a specific value, as shown in model (M1). Although this model results in highly unified final opinions, it also leads to difficulties in achieving optimal consensus and excessively high consensus costs.
The consensus cost in model (M1) refers to the optimal value of the objective function, which represents the total cost required for all decision-makers to adjust their individual opinions. In practice, this cost can be extended to include other factors. Therefore, soft consensus is more effective in most real-world group decision-making scenarios. To this end, Ben-Arieh et al. [] proposed a threshold-based MCCM, as shown in model (M2), which replaces the hard consensus with a soft consensus; that is, the acceptable deviation between consensus opinion oc and the decision-maker’s adjusted opinion is controlled within a certain threshold .
The objective function of model (M2) represents the minimization of the total consensus cost. Constraint (2a) indicates that the acceptable deviation between the consensus opinion and the decision-maker’s adjusted opinion is within a certain threshold. It is designed to reflect the varying importance of different individuals, ensure the uniqueness of the consensus solution, and avoid the multiple optimal solutions present in model (M2). On this basis, Zhang et al. [] further considered the weight of decision-makers, constructed a weighted MCCM, and aggregated the adjusted opinions of decision-makers into consensus opinions by using the weighted average operator, as shown in model (M3), where wi represents the weight of the decision-maker di, and . Constraints (3b) indicate that the consensus opinions are weighted by the adjusted opinions of the decision-makers. The other formula symbols are consistent with those in model (M2).
2.2. Individual Adjustment Willingness Function
To reduce conflicts in the group decision-making process, decision-makers modify their original opinions with the help of a moderator. This is called the willingness to adjust behavior. To operationalize this concept, Zhang et al. [] defined an individual adjustment willingness function (4), quantifying the degree of approximation between a decision-maker’s initial opinion oi and adjusted opinion . Larger values of the function represent that the decision-maker can accept a larger range of adjustment and a higher degree of cooperation. Conversely, lower values indicate restricted adjustment tolerance and heightened non-cooperative tendencies.
3. Model Building
3.1. Consensus Model Considering Non-Cooperative Behaviors
Combined with the above-mentioned individual willingness adjustment function, parameter δi is defined as the upper tolerance bound for decision-maker di. A higher δi value signifies a greater disposition toward opinion modification, a wider acceptable adjustment range, and a stronger inclination to cooperate. Conversely, the closer the value of δi is to 0, the more the decision-makers will adhere to their original viewpoints, manifesting a heightened non-cooperative resistance. Consequently, this paper firstly quantifies and defines non-cooperative behaviors by individual adjustment willingness value δi and then develops an MCCM that explicitly incorporates non-cooperative dynamics, thereby bridging the gap between behavioral disposition and optimization frameworks. The model can be expressed as (M4):
where the adjusted opinion is the decision-making variable. Constraint (5a) identifies non-cooperative behaviors, where denotes the upper tolerance limit of decision-maker di’s willingness to adjust. Constraints (5b) ensure that the acceptable deviation between the consensus opinion oc and the decision-maker di’s adjusted opinion is within a certain threshold . It takes the different thresholds of each decision-maker into account, and it is thus more precise than constraint (3a). Other formula symbols are consistent with those in model (M3).
Model (M4) is a nonlinear programming problem. To facilitate its solution, let and transform it into the linear programming model (M5), where constraints (6a) to (6c) are equivalent to constraint (5a), and constraints (6d) and (6e) are equivalent to constraint (5b).
3.2. Data-Driven Uncertainty Sets
Robust optimization is a sophisticated decision-making methodology designed to reconcile system security imperatives with economic efficiency objectives in uncertain operational environments. As a worst-case optimization paradigm, this approach has been widely applied in diverse domains involving uncertain decision-making processes. Distinct from stochastic programming or fuzzy optimization techniques, robust optimization characterizes uncertainties exclusively via bounded uncertainty sets, thereby eliminating dependencies on probabilistic distribution models or fuzzy membership functions. However, classical robust optimization methods derive uncertainty sets based on empirical experience, which often leads to overly conservative results. To tackle this problem, some researchers construct uncertainty sets based on historical data, which are also referred to as data-driven uncertainty sets. Data-driven uncertainty sets are constructed by using confidence intervals from statistical hypothesis testing to accurately characterize the distribution of uncertain parameters. This paper constructs data-driven uncertainty sets using PCA and KDE.
Through linear combination, PCA can map high-dimensional data to a lower-dimensional space while retaining as much key information of the original data as possible. On the other hand, KDE, as a non-parametric estimation technique, does not require data to conform to a specific function form. Instead, it estimates the probability density distribution based on actual data. Therefore, combining the advantages of both approaches, this paper first uses PCA to identify and extract the irrelevant principal components in the data and maps the sample data onto these principal components. Then, KDE is applied to deeply analyze the potential distribution characteristics of the projected data for each principal component. Finally, the combined effect values of each principal component are integrated to construct a set of uncertainty-related features.
Suppose that m × n sample data points for the unit consensus cost c of a decision problem are constructed to form a matrix U = [uik]m×n. Each sample point uik represents the uncertain data for the unit consensus cost c. The average vector is expressed as , and is calculated as follows:
The sample matrix is scaled to a matrix U0, with a mean of zero by normalization, as shown in Equation (8):
where e is a row vector with all elements equal to 1, and the covariance matrix S can be obtained from U0, as shown in Equation (9).
The principal components are obtained by eigenvalue decomposition of the covariance matrix S, as shown in Equation (10). The matrix p = [pik]m×n consists of eigenvectors corresponding to n eigenvalues, and v = diag{λ1, λ2, …, λn} is a diagonal matrix with eigenvalues arranged in decreasing order, i.e., λ1 ≥ λ2… ≥ λn.
Projecting the uncertain data onto the principal components, as shown in Equation (11), denotes the projection of the uncertain data point uik onto the k-th principal component.
Let ξi be the potential uncertainty variable along the i-th principal component, and α be the predefined confidence level. denotes the probability density function estimated via the KDE method, as shown in Equation (12):
where Kh denotes a kernel function with bandwidth h. This paper adopts the Gaussian kernel function, which is widely used in the kernel smoothing method. The quantile function represents the inverse function of the cumulative probability function , as shown in Equation (13).
Let and be the lower and upper bound vectors of the principal components, respectively, and denote them as Equations (14) and (15):
The uncertainty set constructed based on PCA and KDE is shown in Equation (16), which reduces the conservatism of traditional uncertainty sets:
where μ0 is the mean vector of the sample matrix, and p is the eigenvector matrix of the sample data obtained by PCA. and denote the negative and positive deviation vectors, respectively. The operator “°” represents the Hadamard product, and e represents the all-one vector. The parameter φ serves as the uncertainty scaling factor that controls model robustness.
3.3. Robust Minimum-Cost Consensus Model
The uncertainty set can be constructed by Equation (16) and substituted into model (M4) to obtain model (M6).
The objective function of model (M6) contains a nested min-sup composition, and due to its non-convex and combinatorial nature, direct computational solutions are infeasible. In robust optimization, the problem is usually transformed into an easy-to-handle linear optimization problem with the help of the duality theory. Therefore, the uncertain parameter can be explicitly represented by the uncertainty set of Equation (16), and the auxiliary variable is introduced to replace the absolute term and linearize the objective. Thus, the objective function can be preliminarily transformed into . The most critical step is to apply the strong duality theorem to transform the inner sup-maximization problem into its dual counterpart: a minimization problem of dual variables subject to additional constraints. This transformation equivalently reformulates the original nonconvex min–max problem into a fully linear problem and ultimately converts model (M6) into the linear form shown in (M7).
In model (M7), constraints (18a) to (18e) are linear transformations of constraints (17a) and (17b), and constraints (18g) to (18j) embed the data-driven uncertainty sets constructed via the integrated PCA-KDE methodology introduced in Section 3.2. Since the objective functions and constraints (18g) to (18j) involve positive and negative deviation variables and uncertain parameters φ that control the robustness of the model, it is difficult to solve directly. To resolve this, dual variables , and Ω are introduced to transform model (M7) into its dual problem, as shown in model (M8). Constraints (19g) and (19h) are dual transformations of constraints (18g) to (18j).
4. Case Study
4.1. Case Background
With the rapid acceleration of global urbanization, urban renewal has emerged as a vital strategy for optimizing city structures and stimulating economic growth. As an essential component of this transformation, demolition and relocation of aging residential districts have become socioeconomically inevitable. Homeowners affected by such initiatives, however, exhibit complex and diversified attitudes toward demolition. Certain groups actively endorse governmental policies and willingly cooperate. Others strategically view demolition as an economic opportunity to secure financial compensation. A distinct segment, meanwhile, staunchly resists displacement from their established communities due to deep-rooted place attachment. Hence, to ensure the smooth implementation of urban renewal projects, governments must establish a harmonious negotiation mechanism with homeowners to minimize aggregate social costs and maintain socio-spatial justice.
In this context, a residential community named “Harmony Home” in Guiyang was designated for demolition and relocation according to urban planning requirements. The local government intended to construct a new commercial center in this area to further promote Guiyang’s economic development. Regarding compensation, ten homeowner representatives were selected to engage in negotiations with the local government. The compensation package covered several components, including land compensation, property compensation, decoration reimbursement, resettlement allowances, and relocation fees. Each representative proposed an initial expected total compensation amount, represented by the vector o = (251, 220, 322, 305, 272, 283, 332, 292, 288, 208) (in CNY 10,000). Considering various factors such as individual influence and the size and number of properties owned by individuals, corresponding weights for each homeowner were assigned as ω = (0.10, 0.08, 0.05, 0.16, 0.12, 0.06, 0.13, 0.07, 0.14, 0.09). To ensure fairness and limit individual deviations from the group consensus, a consensus threshold was introduced, denoted as ε = (0.85, 0.70, 0.80, 0.85, 0.76, 0.88, 0.79, 0.85, 0.76, 0.86). This threshold defines the maximum acceptable difference between each individual opinion and the group consensus. Furthermore, to quantify non-cooperative negotiation behaviors, this study introduces an individual adjustment willingness parameter δ. A homeowner is considered non-cooperative if their δ value is below 0.5. Reckoned with factors such as acceptance of the new environment and personal financial capability, the adjustment willingness values were determined as δ = (0.1, 0.8, 0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 0.5, 0.6, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8).
4.2. Numerical Results
As the total compensation amount consists of multiple payment categories, 100 sample data points regarding the compensation amount were collected by visiting homeowners, assessing the current condition of their houses, and understanding their family situations, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Sample data of the case (Unit: CNY 10,000).
The average vector μ0 corresponding to the sample data in Table 1 can be obtained by Equation (7), and the covariance matrix S can be obtained by preliminary normalization of the sample data by Equations (8) and (9), as shown below.
μ0 = [306.48, 314.90, 280.05, 316.21, 298.02, 350.72, 304.0, 308.24, 292.48, 282.63]
By eigenvalue decomposition of the covariance matrix S, the matrix p can be obtained, consisting of 10 eigenvectors. According to Equation (10), v is a diagonal matrix of all eigenvalues in descending order: v = diag{10,965.93, 7816.47, 6382.80, 4610.96, 3165.41, 1311.51, 592.33, 138.02, 39.95, −0.01}. The matrix p is as follows:
According to Equations (11)–(15), the lower bound vector = (0.00, −0.10, −0.29, −0.56, −0.12, −0.22, −0.01, −0.04, −0.02, −0.87) of the principal component and the upper bound vector = (0.00, 0.20, 0.07, 0.04, 0.13, 0.10, 0.15, 1.21, 0.32, 0.01) are obtained by projecting uncertainty data onto principal components. Then, the above data were used as inputs to the model (M8) and calculated using the LINGO software, and finally, the adjustment opinions of each homeowner were obtained as = 276.10, = 276.25, = 277.75, = 276.63, = 276.19, = 277.83, = 277.74, = 277.80, = 277.71, and = 276.09, the consensus opinion = 276.95, and the total consensus cost was CNY 929,656,200. That is, the local government ultimately requires a total of CNY 929,656,200 to reach consensus with homeowners. Beyond direct compensation payments, this total consensus cost also encompasses ancillary expenditures, including construction delays caused by prolonged negotiations, additional property appraisal fees, and stakeholder engagement costs such as public relations and media communications. As a result, government authorities involved in demolition negotiations must proactively incorporate these hidden cost contingencies into their decision-making frameworks. To minimize overall costs, targeted strategies must be implemented, such as enhancing policy transparency by improving the dissemination of demolition regulations to raise homeowner awareness and introducing calibrated compensation adjustments to raise relocation standards and better safeguard residents’ interests. These measures can significantly lower conflict-related costs. Ultimately, promoting smooth and effective negotiations with homeowners, mitigating or preventing demolition disputes, and reducing the incidence of non-cooperative behaviors during the demolition process are crucial to advancing government-led demolition and resettlement initiatives at minimal cost.
4.3. Sensitivity Analysis
4.3.1. Consensus Threshold Analysis
Based on empirical case study data and calculated results, we examine the influence of consensus thresholds in the decision model and reveal changes in the adjustment opinions of individual decision-makers under different consensus thresholds. As shown in Figure 1, we analyzed opinion adjustments of ten homeowners involved in decision-making under different consensus thresholds. We summarized their behavior patterns into three categories.
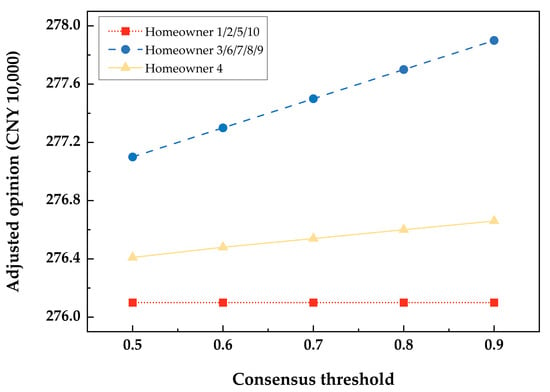
Figure 1.
Impact of consensus thresholds on the adjusted opinion of each decision-maker.
Category 1: Homeowners 1, 2, 5, and 10. Their adjusted opinions remained unchanged (consistently at CNY 2.761 million) as the consensus threshold changed. This suggests these homeowners may have a high-risk appetite, making them susceptible to external influences during decision-making.
Category 2: Homeowner 4. While adjustments were insignificant, Homeowner 4 showed a willingness to adjust opinions to a certain extent based on changes in consensus. Such decision-makers exhibit flexibility in decision-making: their risk appetite drives them to accept changes within a limited range. With proper guidance from coordinators, they may adjust further to benefit the group.
Category 3: Homeowners 3, 6, 7, 8, and 9. Their adjusted opinion values had a significant positive correlation with the consensus threshold. These decision-makers demonstrate high cooperation in the group: they willingly adjust opinions based on changes in collective views to enhance group decision consistency and effectiveness. However, they may be more vulnerable to social influence and group pressure.
4.3.2. Individual Adjustment Willingness and Robustness Analysis
For the convenience of analysis, assuming that all individuals have the same adjustment willingness value, we explore the impact of individual adjustment willingness value δ on the consensus cost. The relationship between the individual adjustment willingness value and the total consensus cost is shown in Figure 2. When the individual adjustment willingness value is 0.25, it can be regarded as a situation where all decision-makers are non-cooperators, and the consensus cost reaches more than CNY 110 million. This phenomenon highlights the negative influence of non-cooperative behaviors on the cost of the consensus in group decision-making. As the value of individual adjustment willingness increases, the consensus cost shows a decreasing trend, indicating that cooperative behaviors help to reduce the cost of reaching consensus. When the willingness value exceeds 0.45, the consensus cost is no longer affected and remains constant. This suggests that in group decision-making, once decision-makers hold a neutral attitude toward adjustment willingness or are willing to cooperate, further increasing their adjustment willingness will no longer significantly reduce the consensus cost. In addition, it is evident in Figure 2 that when individual adjustment willingness is greater than 0.45, the consensus cost is much lower than the cost when individual adjustment willingness is 0.25, further confirming the importance of cooperative behaviors in reducing the consensus cost. Therefore, the influence of non-cooperative behaviors in group decision-making cannot be ignored.
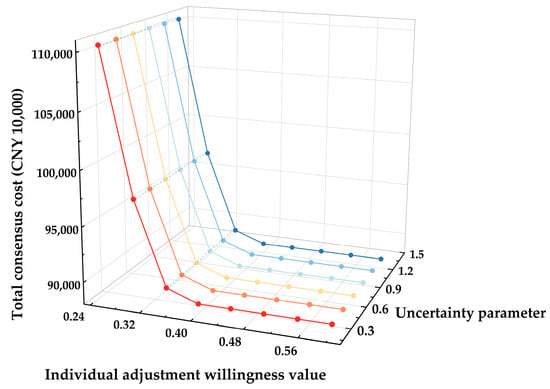
Figure 2.
Impact of individual adjustment willingness and uncertain parameters on consensus cost.
In the model proposed in this paper, the uncertainty parameter φ is introduced to control and represent the robustness of the method. The adjustment of this parameter directly affects the robustness of the model and thus impacts the final value of the objective function. By setting different values of φ, its effect on the total consensus cost is analyzed, and the results are shown in Figure 2. With the increase in φ, the consensus cost shows a steady upward trend. Specifically, when the φ increases from 0 to 1.4, the consensus cost increases by only CNY 7000. This small increase highlights the model’s ability to adapt to uncertain changes, thus demonstrating the robustness of the model. In order to strike a balance between robustness and cost-effectiveness, this paper chooses φ = 0.8 as the optimal parameter value, considering the adaptability of the model to uncertainty and the need for cost control.
4.3.3. Individual Adjustment Willingness and Model Analysis
To explore how individual adjustment willingness δ influences decision-makers’ opinion adjustments across different consensus models, this study systematically scaled δ to 0.8–1.2 times its original value. Figure 3 illustrates the resulting opinion changes in models (M3), (M4), and (M8). It can be seen from Figure 3 that with the increase in δ, both the consensus model (M4), considering only individual willingness, and the data-driven robust model (M8), considering non-cooperative behaviors proposed in this paper, show a significant positive correlation growth trend. In contrast, the traditional consensus model (M3), without considering individual willingness, remains unchanged and is unaffected by δ variations. In addition, under the five zoom levels of δ, the fluctuation amplitude of the adjusted opinion value in model (M8) is always lower than that of model (M3). This phenomenon indicates that model (M8) is more robust to the fluctuation of individual adjustment willingness δ because it is integrated with a data-driven uncertainty set, and its adjustment results are more stable. In summary, the analysis results effectively verify the superiority of the proposed data-driven robust consensus model (M8). Unlike the traditional models (M3 and M4), (M8) accounts for non-cooperative behaviors. Notably, it balances responsiveness to individual willingness and maintenance of system stability.
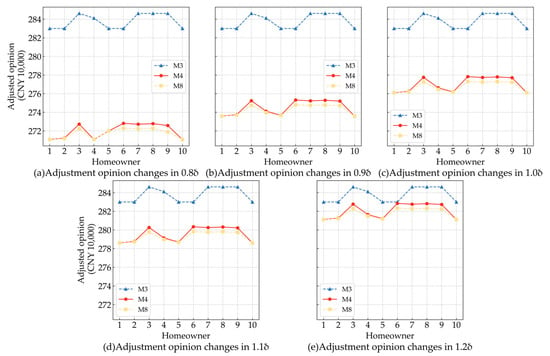
Figure 3.
Impact of individual adjustment willingness on different models.
4.4. Comparative Analysis
4.4.1. Comparison of Methods
The model proposed in this paper is compared and analyzed with existing studies, as shown in Table 2. It can be seen that only this paper has considered all four aspects: non-cooperative behaviors, individual willingness, and data-driven and robust optimization. Xu et al. [], Yuan et al. [], and Shang et al. [] have considered non-cooperative behaviors in group decision-making, but have not explored the causes of non-cooperative behaviors in depth from the perspective of the decision-maker’s individual willingness, and have not assessed the problem of uncertainty that exists in group decision-making in general. Zhang et al. [] and Zhong et al. [] both consider the individual willingness of the decision-maker, and Zhang et al. [] only adopt the data-driven robust optimization method for the uncertainty of unit adjustment cost in the decision-making process, but do not involve the non-cooperative behaviors that may arise in the decision-making process. Zhong et al. [] consider non-cooperative behaviors and individual willingness, but do not incorporate data-driven robust optimization, and thus fail to fully consider the uncertainty in the decision-making process.

Table 2.
Comparison of methods for consensus problems.
Robust optimization has significant advantages in dealing with parameter uncertainty in the decision-making process, and data-driven uncertainty sets can effectively alleviate the problem of over-conservative classical robust optimization. While considering the behavior of decision-makers, Zhang et al. [] constructed a consensus model based on three classical robust optimization uncertainties. However, among the reviewed literature, only this paper, Zhang et al. [], and Wei et al. [] considered the data-driven robust optimization method. In contrast, the data-driven robust MCCM, considering non-cooperative behaviors proposed in this paper, not only analyzes the non-cooperative behaviors of decision-makers from the perspective of individual willingness but also uses the data-driven robust optimization method to deal with the uncertainty of unit adjustment cost in the process of consensus-reaching. In addition, the proposed model also solves the problem of over-conservatism of the solution that may be caused by traditional robust optimization.
4.4.2. Model Comparison
The data-driven robust MCCM (M8) proposed in this paper, which considers non-cooperative behaviors, is compared with the classical MCCM (M3) and the MCCM (M4) that considers only non-cooperative behaviors. The case data were substituted into models (M3), (M4), and (M8) for calculation, and the corresponding consensus opinion and the total consensus cost c were obtained, as shown in Table 3. It can be seen that the model (M3), as the MCCM in the ideal state, achieves consensus at the highest opinion value and incurs the lowest total consensus cost. However, this model assumes all decision-makers are fully cooperative, a scenario that does not align well with most real-world group decision-making contexts. Compared with model (M3), model (M4) accounts for the non-cooperative behaviors of decision-makers. Although this results in a lower consensus opinion and an increased total consensus cost, it is more representative of actual decision-making scenarios. Furthermore, the comparison demonstrates that non-cooperative behaviors significantly impact both consensus-reaching and cost. Building upon model (M4), model (M8) further incorporates the uncertainty of the decision-making environment. It employs a data-driven robust optimization method to address uncertainty while mitigating the excessive conservatism associated with traditional robust optimization. Compared to model (M4), model (M8) achieves the same consensus opinion, but incurs a higher total consensus cost. This increase stems from the data-driven robust optimization approach, which focuses not only on the cost of current decisions but also accounts for potential future uncertainties and their implications. The comparison of these models highlights that we should not rely solely on decisions derived from an ideal state in increasingly complex decision-making contexts. Instead, it is crucial to consider realistic decision-maker behaviors, various uncertainties, and minimize their impacts.

Table 3.
Comparison of models for consensus problem (Unit: CNY 10,000).
5. Conclusions
This paper proposes a data-driven robust MCCM that accounts for non-cooperative behaviors. This is achieved by introducing an individual adjustment willingness function and constructing data-driven uncertainty sets. Compared with traditional MCCMs, the proposed approach not only captures the influence of non-cooperative behaviors but also incorporates robust optimization techniques to address uncertainty in unit adjustment costs. This dual approach effectively mitigates the over-conservatism which is typical of traditional robust models, and improves practical applicability in uncertain environments.
The results of the case analysis reveal the following key findings: (1) The effect of consensus threshold variation on opinion adjustment is individual-specific. By guiding different types of decision-makers with tailored interventions, the decision-making process can be made more efficient. (2) Higher adjustment willingness leads to improved cooperation and reduced consensus cost. However, when the willingness reaches a certain level, its marginal effect on cost reduction diminishes. (3) The model exhibits strong robustness, maintaining performance in the presence of uncertainty and variability, confirming its suitability for real-world decision scenarios. These findings directly address the core research problem of achieving a cost-efficient consensus amid behavioral uncertainty and cost fluctuations. They provide a theoretical and practical foundation for designing more adaptive and behavior-aware consensus mechanisms, with implications for policy-making and facilitation practices in participatory decision environments such as medical care, supply chain management, multi-stakeholder management, and collaborative governance. For example, in multidisciplinary consultations within healthcare, quantitative expert adjustment willingness can be used to identify and mitigate non-cooperative behaviors, thereby promoting more efficient multidisciplinary consensus.
Despite these demonstrated strengths, the model is not without limitations. Specifically, this study identifies non-cooperative behaviors solely through the adjustment willingness function. However, analyzing such behaviors from the perspective of observable decision-maker behavior patterns may offer additional insights. Future research could therefore expand the behavioral analysis framework by incorporating measurable decision actions and dynamic behavioral cues—such as communication frequency, or inconsistency in preference elicitation. In addition, developing dynamic consensus mechanisms that account for evolving environmental contexts and the temporal shifts in decision-makers’ preferences enhances the model’s practical relevance and robustness in real-time applications.
Author Contributions
J.F.: Supervision, Validation, Methodology, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing; X.G.: Writing—original draft, Investigation, Software, Resources; X.H.: Conceptualization, Writing—review and editing; G.C.: Formal analysis, Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Guizhou Provincial Philosophy and Social Sciences Planning Project of China (24GZYB134), the Intelligent Policing Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province Project of China (ZNJW2025KFQN011), the Guizhou Provincial Basic Research Program (Natural Science) (MS〔2025〕629), and the Guizhou Provincial University Philosophy and Social Science Laboratory Pilot Construction Foundation of China (GDJD202409).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Guo, W.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, W.G.; Xu, Y. Minimum cost consensus modeling under dynamic feedback regulation mechanism considering consensus principle and tolerance level. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2023, 306, 1279–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Labella, Á.; Meng, M.-J.; Wang, Y.-M.; Rodríguez, R.M. Hesitant Fuzzy Consensus Reaching Process for Large-Scale Group Decision-Making Methods. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.R.; Wang, X.; Ding, R.X.; Lin, S.P.; Lou, Q.H.; Herrera-Viedma, E. Managing non-cooperative behaviors in large-scale group decision making based on trust relationships and confidence levels of decision makers. Inf. Fusion 2023, 97, 101820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.L.; Chen, J.A. A consensus model to manage minority opinions and noncooperative behaviors in large group decision making with probabilistic linguistic term sets. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 29, 1667–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.H.; Du, Z.J.; Chen, X.H. Consensus model for multi-criteria large-group emergency decision making considering non-cooperative behaviors and minority opinions. Decis. Support Syst. 2015, 79, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhan, J. Group Decision-Making in Heterogeneous Multi-Scale Information Fusion: Integrating Overconfident and Non-Cooperative Behaviors. Inf. Fusion 2026, 125, 103401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wu, S.; Dong, Y. Managing Non-Cooperative Behaviors and Ordinal Consensus through a Self-Organized Mechanism in Multi-Attribute Group Decision Making. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 240, 122571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wang, S.; Ji, F.; Gai, T.; Wu, J. The Reconciliation Mechanism by Cooperative Intention Index for Managing Non-Cooperative Behaviors in Social Network Group Decision Making. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 126, 107066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, C.; Cheng, D.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, Z.; Cheng, F. Minimum conflict consensus models for group decision-making based on social network analysis considering non-cooperative behaviors. Inf. Fusion 2023, 99, 101855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, P. A dynamic dual-trust network-based consensus model for individual non-cooperative behaviour management in group decision-making. Inf. Sci. 2024, 674, 120750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huan, J.; Shen, J.; Chen, L.; Cao, J.; Cheng, Y. Social network large-scale group decision-making considering dynamic trust relationships and historical preferences of decision makers in opinion evolution. Inf. Fusion 2025, 117, 102837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, T.; Chiclana, F.; Jin, W.; Zhou, M.; Wu, J. A Transformation Method of Noncooperative to Cooperative Behavior by Trust Propagation in Social Network Group Decision Making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2025, 33, 2238–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Arieh, D.; Easton, T.; Evans, B. Minimum cost consensus with quadratic cost functions. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2008, 39, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yu, X.; Mao, Y. Social network-based consensus reaching model with rational adjustment allocation for large-scale group decision making. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 281, 127724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, X.; Gong, Z.; Liu, F. The bi-level consensus model with dual social networks for group decision making. Inf. Fusion 2025, 114, 102714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Pedrycz, W.; Qin, J. Optimizing-information-granule-based consensus reaching model in large-scale group decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 32, 2413–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Kou, G.; Ye, C. A consensus model under framework of prospect theory with acceptable adjustment and endo-confidence. Inf. Fusion 2023, 97, 101808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.G.; Gong, Z.; Xu, Y.; Słowiński, R. Multi-dimensional multi-round minimum cost consensus models with iterative mechanisms involving reward and punishment measures. Knowl. Based Syst. 2024, 293, 111710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yan, S.; Li, Y. A multi-attribute quantum group consensus model considering psychological preference. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 144, 110086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liang, H.; Qu, S. Robust Consensus Modeling: Concerning Consensus Fairness and Efficiency with Uncertain Costs. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Dutta, B.; García-Zamora, D.; Ji, Y.; Qu, S.; Martínez, L. ELICIT Information-Based Robust Large-Scale Minimum Cost Consensus Model under Social Networks. Appl. Soft Comput. 2025, 170, 112647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Han, Y. Consensus of large-scale group decision making in social network: The minimum cost model based on robust optimization. Inf. Sci. 2021, 547, 910–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, S.; Li, Y.; Ji, Y. The mixed integer robust maximum expert consensus models for large-scale GDM under uncertainty circumstances. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 107, 107369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ji, Y.; Wijekoon, C. Robust maximum expert consensus model with adjustment path under uncertain environment. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 155, 111430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qu, S.; Peng, Z.; Dai, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Ji, Y. A robust minimum cost consensus model based on social networks considering conflict constraints. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 191, 110158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ji, Y.; Ding, J.; Qu, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Robust two-stage optimization consensus models with uncertain costs. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2024, 317, 977–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ji, Y.; Qu, S.; Li, Y. A two-stage distributionally robust maximum expert consensus model with asymmetric costs and risk aversion. Inf. Sci. 2025, 689, 121518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Qu, S.; Ji, Y.; Ma, Y. Distributionally Robust Chance Constrained Maximum Expert Consensus Model with Incomplete Information on Uncertain Cost. Group Decis. Negot. 2025, 34, 135–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; García-Zamora, D.; Dutta, B.; Ji, Y.; Qu, S.; Martínez, L. Large-scale group decision consensus under social network: A chance-constrained robust optimization-based minimum cost consensus model. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 231, 120728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ji, Y.; Qu, S. Consensus Building for Uncertain Large-Scale Group Decision-Making Based on the Clustering Algorithm and Robust Discrete Optimization. Group Decis. Negot. 2022, 31, 453–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ji, Y.; Yu, R.; Qu, S.; Dai, Z. The robust cost consensus model with interval-valued opinion and uncertain cost in group decision-making. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 24, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Ji, Y.; Qu, S. A robust minimum-cost consensus model with uncertain aggregation weights based on data-driven method. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2021, 9, 1167–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Xu, X.; Qu, S.; Wang, Q. Consensus modeling for maximum expert with quadratic cost under various uncertain contexts: A data-driven robust approach. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2025, 323, 192–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Arieh, D.; Easton, T. Multi-criteria group consensus under linear cost opinion elasticity. Decis. Support Syst. 2007, 43, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X. Machine learning-based data-driven robust optimization approach under uncertainty. J. Process Control 2022, 115, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ji, Y.; Qu, S.; Li, H.; Li, Y. Data-driven robust cost consensus model with individual adjustment willingness in group decision-making. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 183, 109455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, C.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, X. An adaptive consensus model in large-scale group decision making with noncooperative and compromising behaviors. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 149, 110944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Xu, X.; Pan, B. A non-threshold consensus model based on the minimum cost and maximum consensus-increasing for multi-attribute large group decision-making. Inf. Fusion 2022, 77, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhu, Y.; Zhan, M. Robust maximum expert consensus model with uncertain cooperative behavior in group decision making. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2025, 204, 111098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Qu, S.; Wang, Q.; Luan, D.; Zhao, X. The novel data-driven robust maximum expert mixed integer consensus models under multirole’ s opinions uncertainty by considering noncooperators. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2022, 10, 3454–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).