Evolution and Simulation Analysis of Digital Transformation in Rural Elderly Care Services from a Multi-Agent Perspective in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model Assumptions and Construction
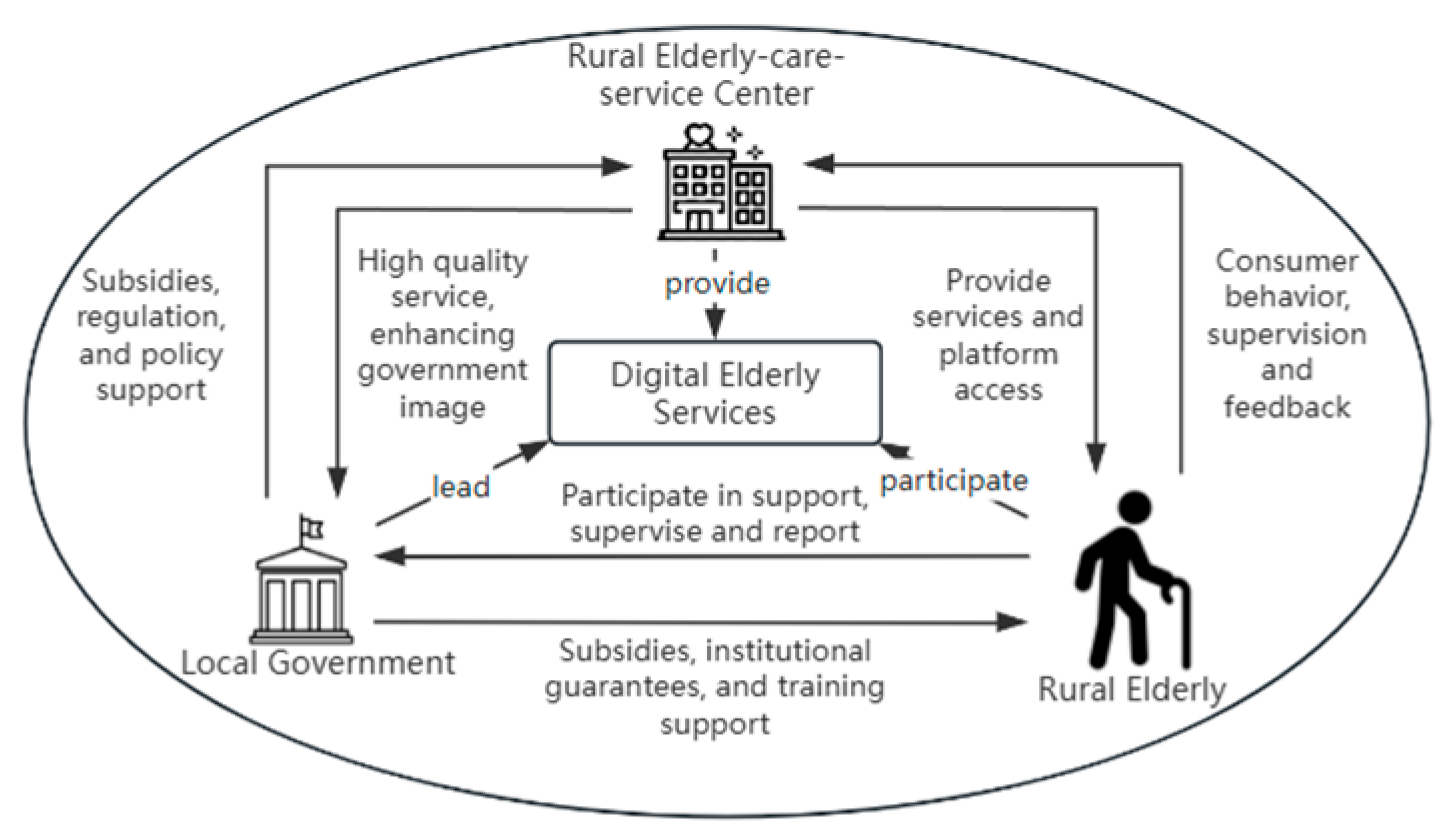
2.1. Analysis of the Subject of the Game
2.2. Model Assumptions
2.3. Model Construction
2.3.1. Parameter Setting
2.3.2. Payment Matrix
3. Model Analysis
3.1. Calculation of Dynamic Replication Equations
3.2. Asymptotic Stability Analysis of Game Subjects
3.2.1. Asymptotic Stability Analysis of Local Governments
3.2.2. Analysis of the Progressive Stability of RECS Centers for the Elderly
3.2.3. Analysis of the Progressive Stability of the Rural Elderly
3.3. Equilibrium Points and Evolutionarily Stable Strategies in Tripartite Evolutionary Games
3.3.1. Evolutionary Game Equilibrium
3.3.2. Evolutionary Stabilization Strategies
4. Simulation Analysis
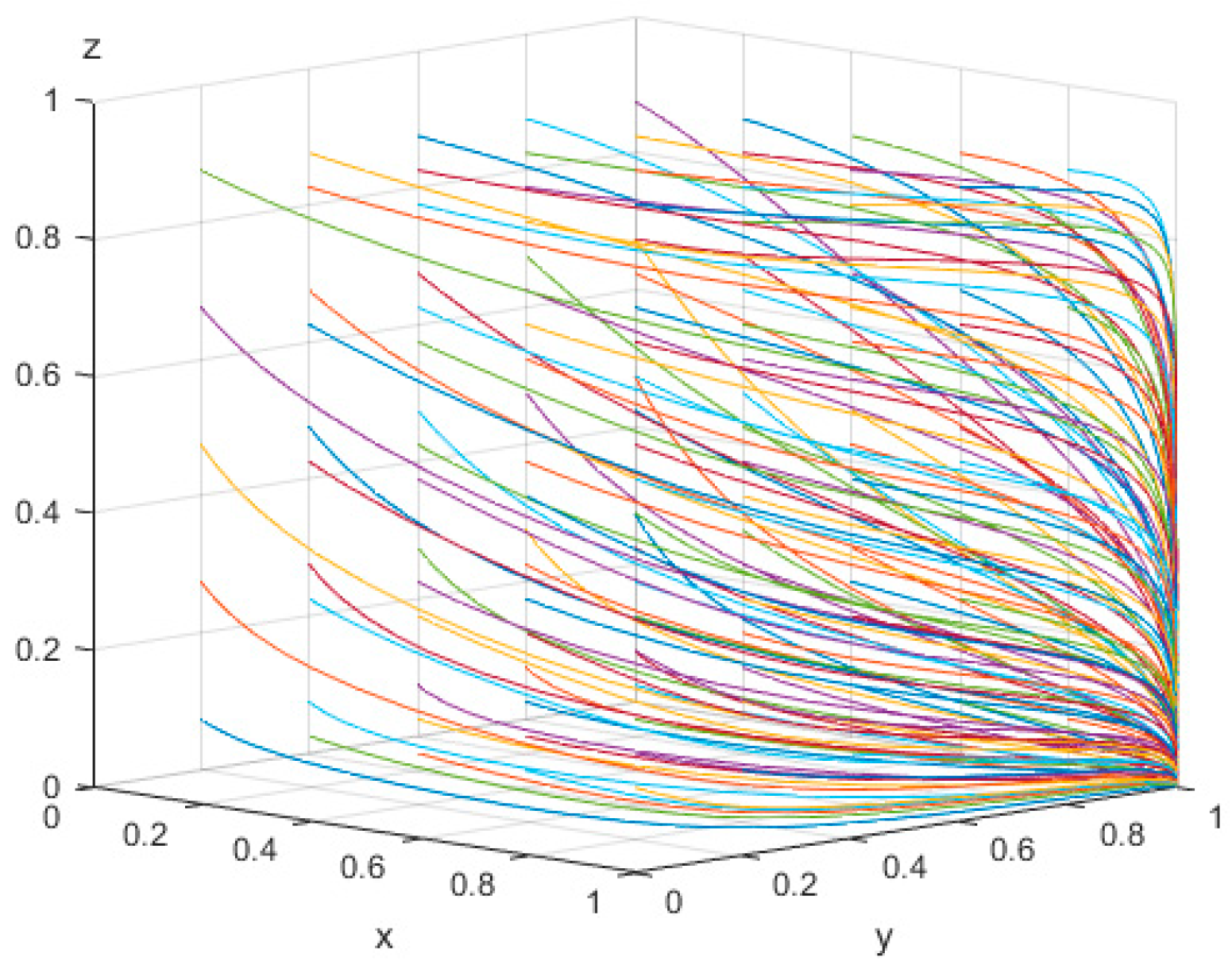
4.1. Impact of Changes on Evolutionary Stability of Initial Strategy
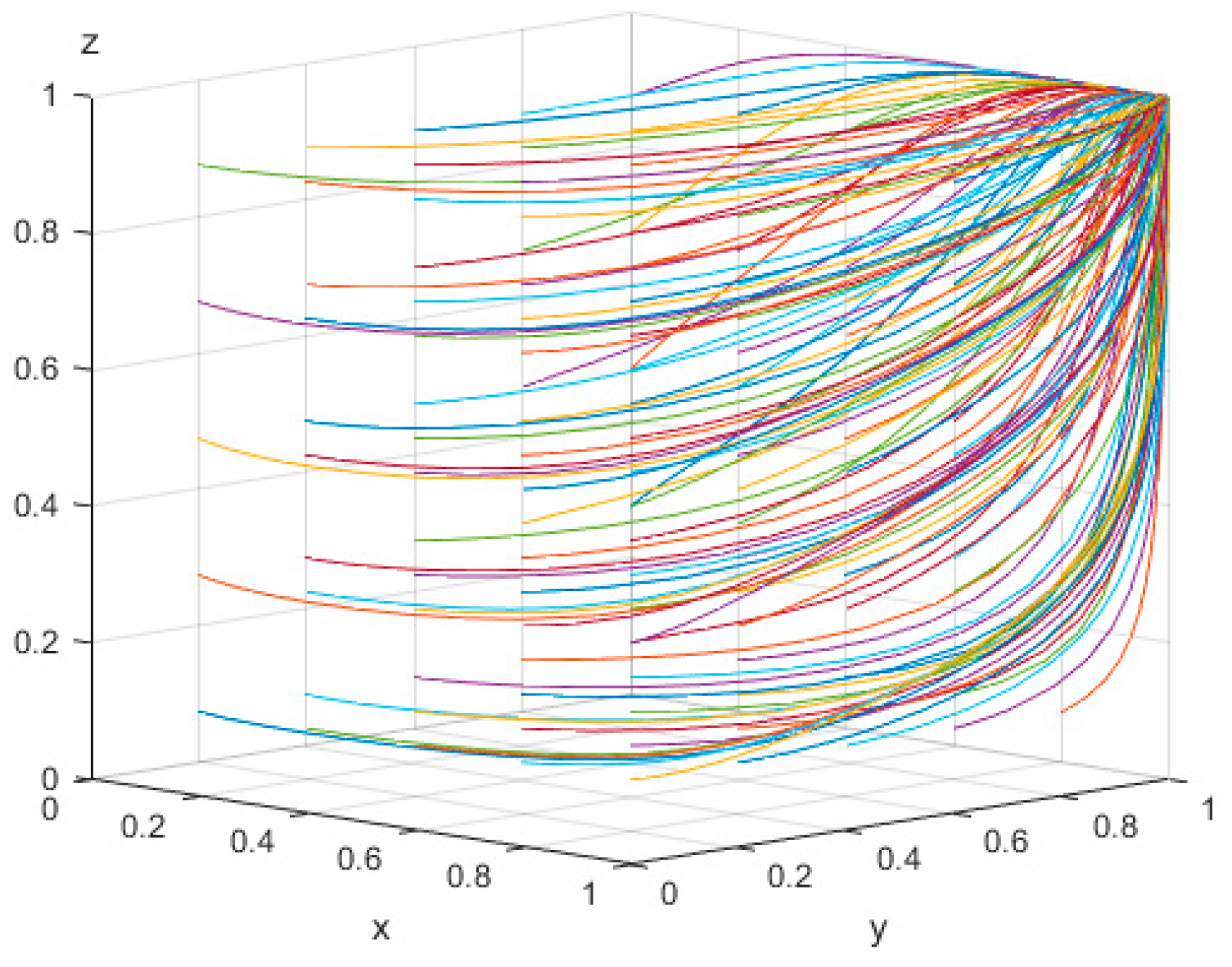
4.1.1. Scenario 1: Numerical Simulation
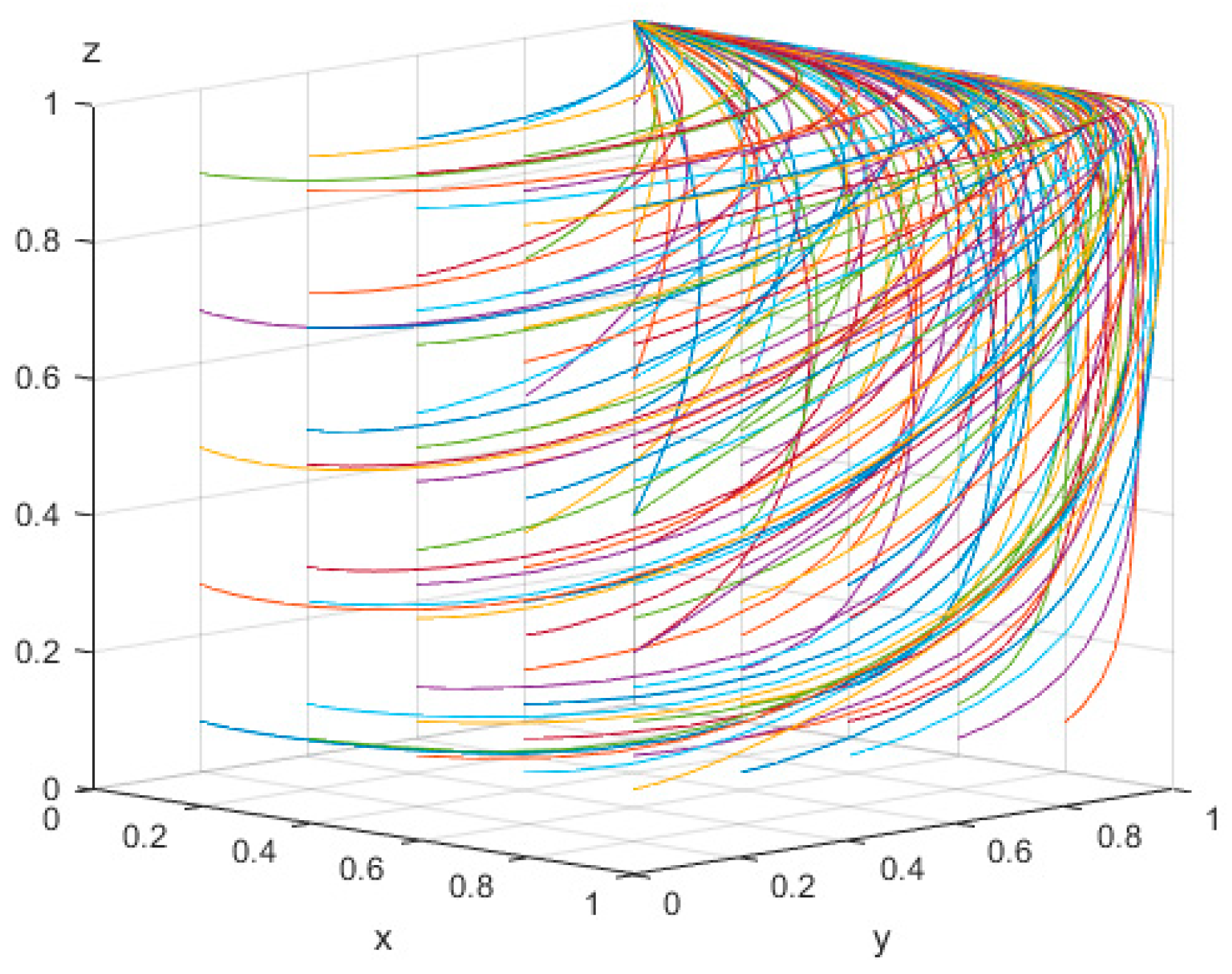
4.1.2. Scenario 2: Numerical Simulation
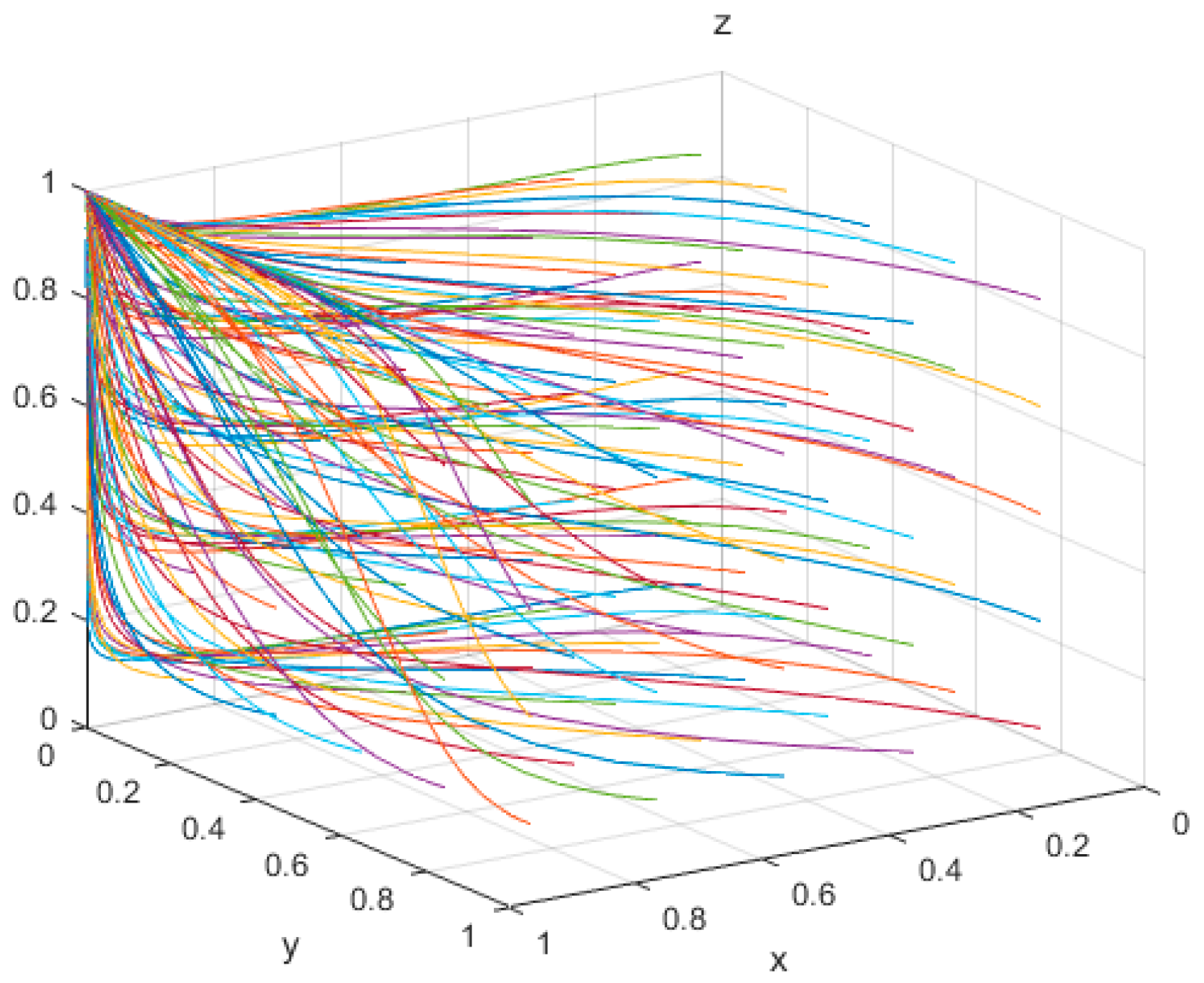
4.1.3. Scenario 3: Numerical Simulation
4.1.4. Scenario 4: Numerical Simulation
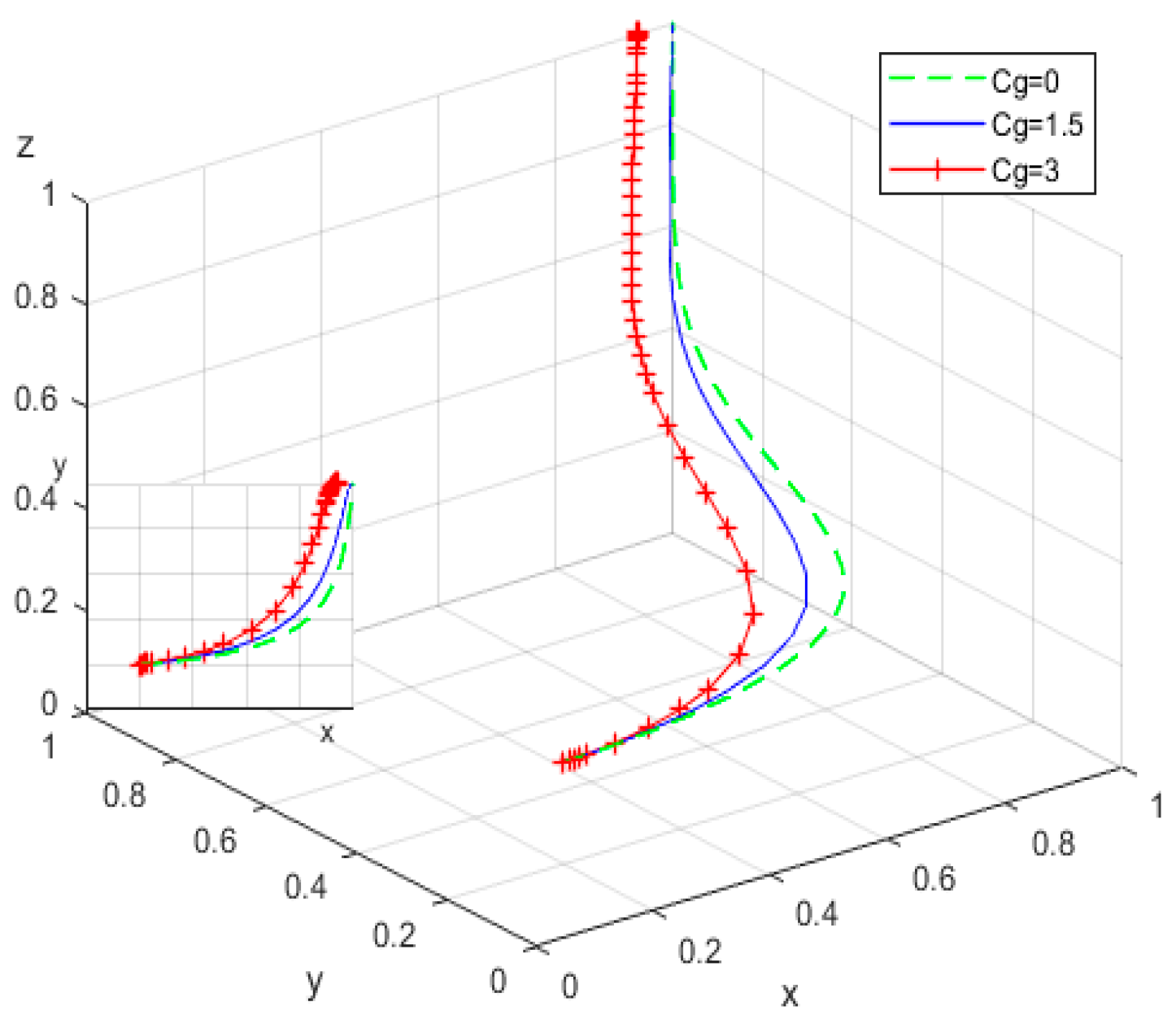
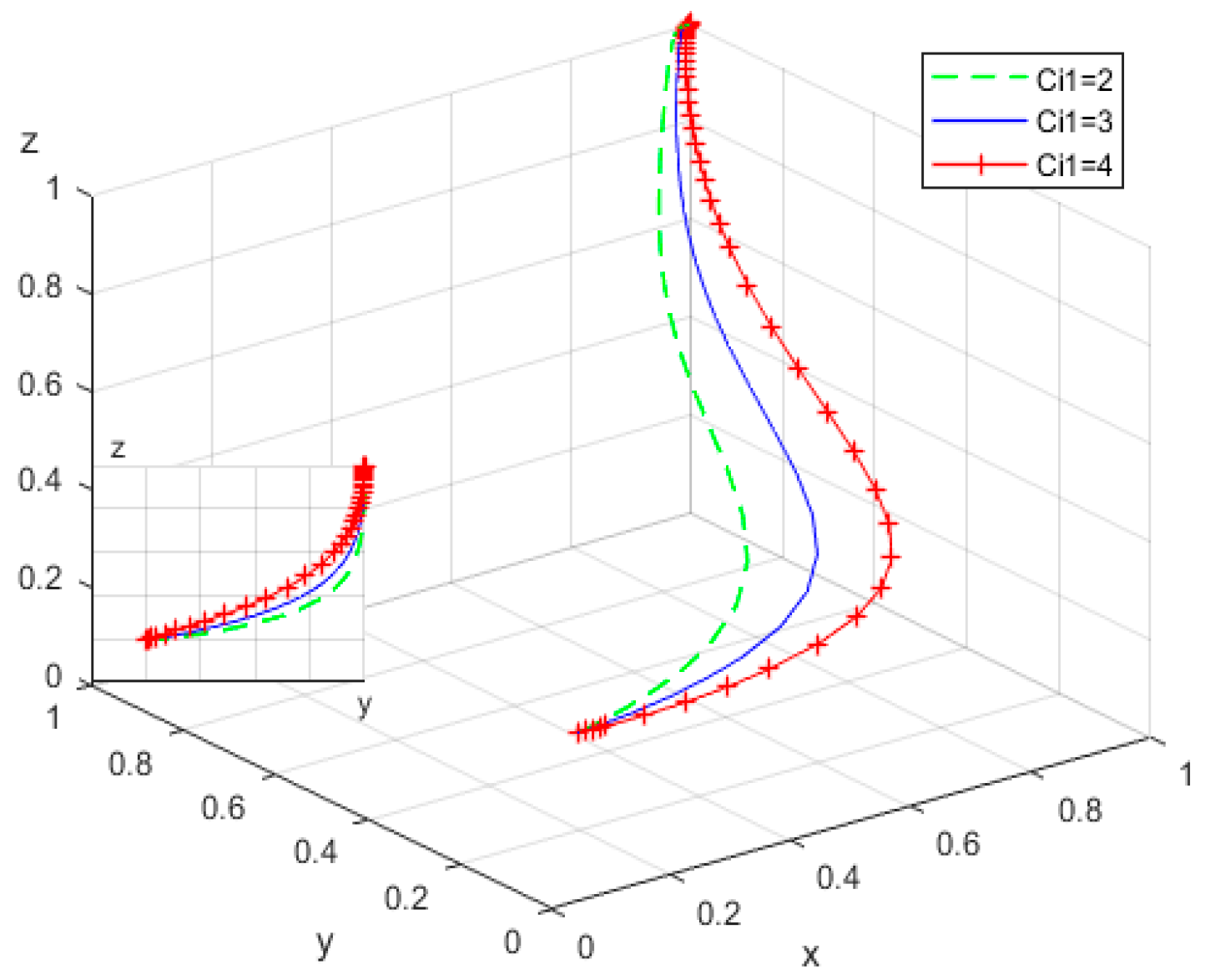
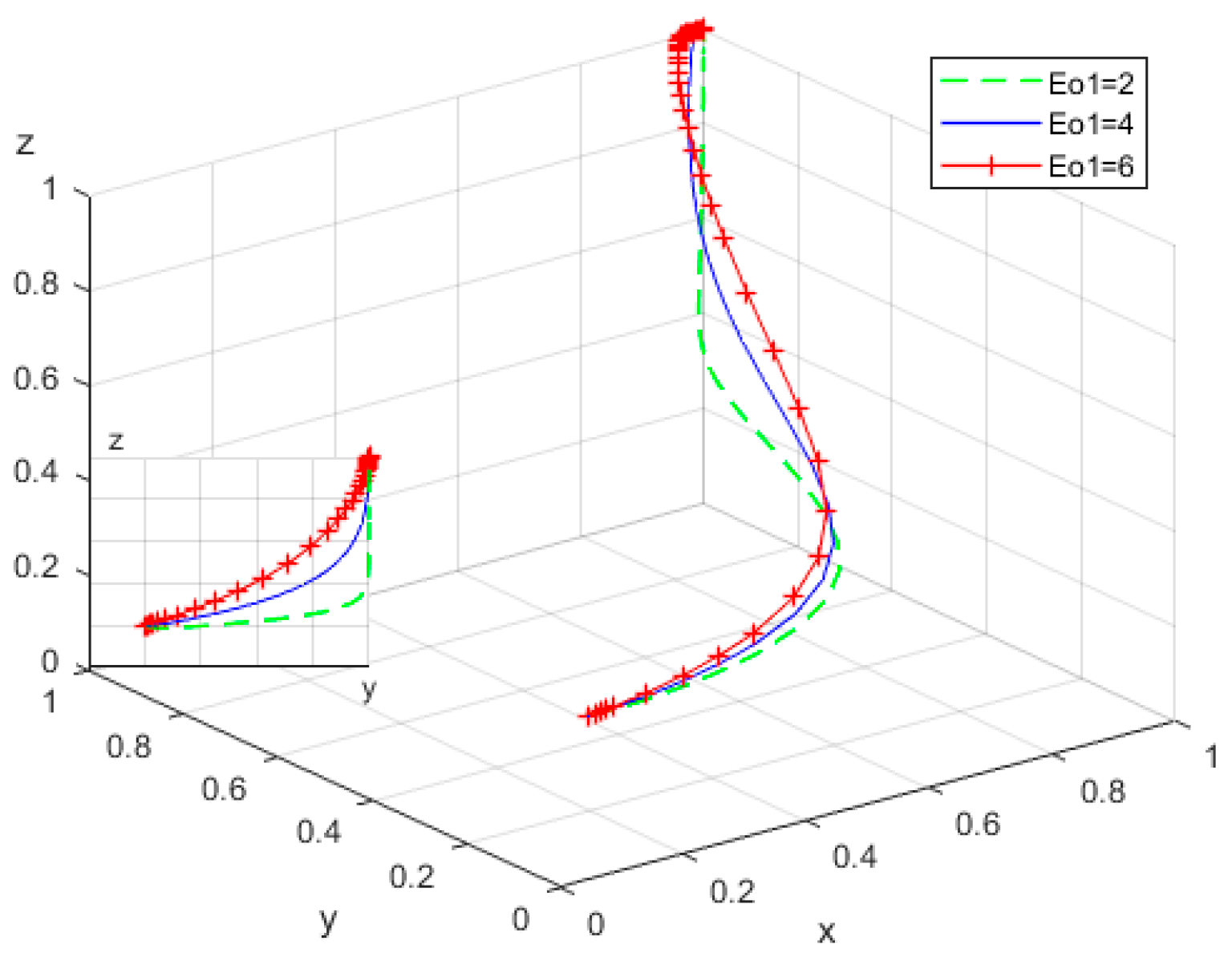
4.2. Influence of the Values of the Main Parameters on the Evolution of Subjects’ Behavior
5. Conclusions and Recommendation
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RECS | rural elderly care service |
References
- Guillemot, J.R.; Zhang, X.; Warner, M.E. Population Aging and Decline Will Happen Sooner than We Think. Soc. Sci. 2024, 13, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. World Population Prospects 2024. Available online: https://www.un.org/development/desa/pd/world-population-prospects-2024 (accessed on 11 March 2024).
- Wang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Lv, F.; Wang, J. Analysis of Demand and Influencing Factors for Smart Senior Care among Older Adults in Underdeveloped Regions of Western China: A Case Study of Lanzhou. Front. Public. Health 2024, 12, 1337584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Hao, Y.; Ma, J. Family Income Level, Income Structure, and Dietary Imbalance of Elderly Households in Rural China. Foods 2024, 13, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais Campos, H.L.; De Leon, E.B.; Merllin Batista De Souza, I.; Quialheiro, A.; Araújo de Oliveira, E.R. Cognition, Physical Function, and Life Purpose in the Rural Elderly Population: A Systematic Review Protocol. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0291699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, K.J.; Jones, R.B.; Shenton, D.; Page, T.; Maramba, I.; Warren, A.; Fraser, F.; Križaj, T.; Coombe, T.; Cowls, H.; et al. The Use of Smart Speakers in Care Home Residents: Implementation Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e26767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.N.; Chang, S.J.; Kim, S. Associations with Smartphone Usage and Life Satisfaction among Older Adults: Mediating Roles of Depressive Symptoms and Cognitive Function. Geriatr. Nurs. 2024, 55, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Ge, S.; Qu, Z.; Wang, A.; Tang, X. The Willingness and Influencing Factors to Choose Smart Senior Care among Old Adults in China. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Liu, S.; Hong, Y.; Chen, K.; Luo, Y. Perspectives on the Popularization of Smart Senior Care to Meet the Demands of Older Adults Living Alone in Communities of Southwest China: A Qualitative Study. Front. Public. Health 2023, 11, 1094745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Mao, Y.; Sun, Q.; Xu, L. Smart Transition Pathways and Development Incentive Mechanism of China’s Smart Community Elderly Care Industry under Market Dominance: Considering a Multi-Subjective Behavior Game. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0297696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hagedorn, A.; An, N. The Development of Smart Eldercare in China. Lancet Reg. Health—West. Pac. 2023, 35, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.A.; Greaney, M.L. Aging in Rural Communities. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2022, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boobalan, J.; Malleswaran, M. A Novel and Customizable Framework for IoT Based Smart Home Nursing for Elderly Care. In Emerging Trends in Computing and Expert Technology; Hemanth, D.J., Kumar, V.D.A., Malathi, S., Castillo, O., Patrut, B., Eds.; Lecture Notes on Data Engineering and Communications Technologies; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 35, pp. 27–38. ISBN 978-3-030-32149-9. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.; Linner, T.; Trummer, J.; Güttler, J.; Kabouteh, A.; Langosch, K.; Bock, T. Developing a Smart Home Solution Based on Personalized Intelligent Interior Units to Promote Activity and Customized Healthcare for Aging Society. Popul. Ageing 2020, 13, 257–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Jang, E.; Cho, J.; Lee, J.; Rhee, J.H.; Lee, H.; Lee, M.; Cha, S.H.; Koo, C.; Baik, O.M. A Living Lab to Develop Smart Home Services for the Residential Welfare of Older Adults. Technol. Soc. 2024, 77, 102577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, T.H.; Ma, J.H.; Cha, S.H. Elderly Perception on the Internet of Things-Based Integrated Smart-Home System. Sensors 2021, 21, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creaney, R.; Reid, L.; Currie, M. The Contribution of Healthcare Smart Homes to Older Peoples’ Wellbeing: A New Conceptual Framework. Wellbeing. Space Soc. 2021, 2, 100031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Shi, K.; Yang, C.; Niu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, N.; Liu, T.; Chu, C.H. Ethical Issues of Smart Home-Based Elderly Care: A Scoping Review. J. Nurs. Manag. 2022, 30, 3686–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirzada, P.; Wilde, A.; Doherty, G.H.; Harris-Birtill, D. Ethics and Acceptance of Smart Homes for Older Adults. Inform. Health Soc. Care 2022, 47, 10–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalotia, N.; Kumar, M.; Alameen, A.; Mohapatra, H.; Kolhar, M. A Helping Hand to the Elderly: Securing Their Freedom through the HAIE Framework. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y. Research on the Optimization Path of Smart Endowment Industry Based on Industry Chain Integration Theory. China Soft Sci. 2019, 4, 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, D.; Liu, X. The Problem and Paths of Home Pension Based on Artificial Intelligence Technology. J. Xi’an Univ. Financ. Econ. 2020, 33, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Y. Research on the Growth Path of the Elderly Care Industry Enabled by Digital Economy. Popul. Econ. 2024, 4, 45–58. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R. Path exploration for solving rural elderly care problems in the new era. People’s Trib. 2022, 5, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Q. Investigation and Research on Media Literacy of Rural Elderly Groups under the Background of Intelligent Pension. Health Vocat. Educ. 2023, 41, 118–121. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Meng, R. The intrinsic mechanism and micro-evidence of digital backfeeding driving the participation of rural elderly in smart home-based elderly care. Electron. Gov. 2024, 3, 105–116. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, C.; Zhou, X.; Wang, C.; Guo, Y.; Diao, Y.; Shen, S.; Reis, S.; Li, W.; Xu, J.; Gu, B. Ageing Threatens Sustainability of Smallholder Farming in China. Nature 2023, 616, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Li, S.; Wang, J. Research on the Long-term Mechanism of Responsible Innovation from the Perspective of Multi-agent Behavior Evolution. Manag. Rev. 2024, 36, 155–167. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Wen, Z.; Yi, D. Research on Elderly Care Service Supervision based on System Dynamics from the Perspective of Multi-agent. Northwest Popul. J. 2020, 41, 88–101. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, C.; Luo, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ping, Y. Analysis on the Evolution Game of Rural Pension Mechanism in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. J. Syst. Sci. 2020, 28, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, X.; Lin, Y. The Effectiveness of the Feedback from Elderly Users in Elderly Care Services: An Evolutionary Game Analysis. J. Jiangxi Univ. Financ. Econ. 2022, 04, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Huang, M.; Lü, Q. Evolutionary Game Analysis of Smart Elderly Service Ecosystems in a Digital Context. Complex Systems and Complexity Science. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/37.1402.N.20240130.1756.004.html (accessed on 30 January 2024).
- He, J.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, Y. Strategic Analysis of Participants in the Provision of Elderly Care Services-an Evolutionary Game Perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 8595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Liu, H. The Impact Mechanism of Government Regulation on the Operation of Smart Health Senior Care Service Platform: A Perspective from Evolutionary Game Theory. Int. J. Health Policy Manag. 2025, 14, 8646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapunov, A.M. The general problem of the stability of motion. Int. J. Control. 1992, 55, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameters | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Regulatory cost incurred by the local government under positive construction to supervise RECS centers | |
| Rewards from higher-level governments and social reputation incentives received by the local government when the RECS centers positively transform under positive construction | |
| Penalties from higher-level governments and social reputation losses borne by the local government when RECS centers negatively transform under negative construction | |
| Economic benefits obtained by RECS centers under positive transformation | |
| Economic benefits obtained by RECS centers under negative transformation | |
| Digital operation and construction cost incurred by RECS centers when positively transforming | |
| Digital operation and construction costs incurred by RECS centers when negatively transforming | |
| Subsidies received by RECS centers for positively transforming under positive government construction | |
| Penalties borne by RECS centers for negatively transforming under positive government construction | |
| Costs incurred by the elderly when positively participating in smart home-based elderly care services | |
| Subsidies received by the elderly for positively participating in smart home-based elderly care services under positive government construction | |
| Utility gained by the elderly when positively participating in smart home-based elderly care services under the positive transformation of RECS centers | |
| Utility gained by the elderly when positively participating in smart home-based elderly care services under the negative transformation of RECS centers |
| RECS Centers | Rural Elderly | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local governments | Positive construction | Positive transformation | ||
| Negative transformation | ||||
| Negative construction | Positive transformation | |||
| Negative transformation | ||||
| Balance Point | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Balance Point | Scenario 1 | Stability | Scenario 2 | Stability | Scenario 3 | Stability | Scenario 4 | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| instability | instability | instability | instability | |||||
| instability | instability | instability | instability | |||||
| instability | instability | instability | instability | |||||
| instability | instability | instability | instability | |||||
| instability | ESS | instability | instability | |||||
| instability | instability | ESS | instability | |||||
| instability | instability | instability | ESS | |||||
| ESS | instability | instability | instability |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, Z.; Mo, M.; Xu, J. Evolution and Simulation Analysis of Digital Transformation in Rural Elderly Care Services from a Multi-Agent Perspective in China. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111756
Wen Z, Mo M, Xu J. Evolution and Simulation Analysis of Digital Transformation in Rural Elderly Care Services from a Multi-Agent Perspective in China. Mathematics. 2025; 13(11):1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111756
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Zheng, Ming Mo, and Jin Xu. 2025. "Evolution and Simulation Analysis of Digital Transformation in Rural Elderly Care Services from a Multi-Agent Perspective in China" Mathematics 13, no. 11: 1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111756
APA StyleWen, Z., Mo, M., & Xu, J. (2025). Evolution and Simulation Analysis of Digital Transformation in Rural Elderly Care Services from a Multi-Agent Perspective in China. Mathematics, 13(11), 1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111756





