Abstract
Effective berth allocation in container terminals is crucial for optimizing port operations, given the limited space and the increasing volume of container traffic. This study addresses the discrete dynamic berth allocation problem (DDBAP) under uncertain ship arrival times and varying load capacities. A novel deep Q-network (DQN)-based model is proposed, leveraging a custom state space, rule-based actions, and an optimized reward function to dynamically allocate berths and schedule vessel arrivals. Comparative experiments were conducted with traditional algorithms, including ant colony optimization (ACO), parallel ant colony optimization (PACO), and ant colony optimization combined with genetic algorithm (ACOGA). The results show that DQN outperforms these methods significantly, achieving superior efficiency and effectiveness, particularly under high variability in ship arrivals and load conditions. Specifically, the DQN model reduced the total waiting time of vessels by 58.3% compared to ACO (262.85 h), by 57.9% compared to PACO (259.5 h), and by 57.4% compared to ACOGA (257.4 h), with a total waiting time of 109.45 h. Despite its impressive performance, DQN requires substantial computational power during the training phase and is sensitive to data quality. These findings underscore the potential of reinforcement learning to optimize berth allocation under dynamic conditions. Future work will explore multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) and real-time adaptive mechanisms to further enhance the robustness and scalability of the model.
Keywords:
berth allocation; parallel ant colony algorithm; DQN; container terminal; dynamic scheduling MSC:
68T20
1. Introduction
As economic globalization progresses, port cargo demand has surged, intensifying the need for higher operational efficiency and productivity in container terminals [1,2]. Consequently, the primary challenge in terminal operations is how to optimally allocate limited berth resources to vessels arriving within various service time windows [3,4]. This challenge, known as the berth allocation problem (BAP) [5], is critical for the sustainable development of ports. The main objective of the BAP is to optimize berth allocation in order to minimize vessel waiting times and alleviate terminal congestion. Effective berth allocation not only boosts terminal operational efficiency but also reduces fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions from waiting vessels, contributing positively to environmental sustainability [6]. Therefore, developing efficient methods to address the BAP within the planning cycle is essential for improving the overall operational capacity of container terminals.
The BAP is typically categorized into two types: the static berth allocation problem (SBAP) and the dynamic berth allocation problem (DBAP) [7]. The static model assumes that all vessels arrive before the planning period starts, while the dynamic model accounts for vessels arriving throughout the planning period based on given arrival data [8]. Additionally, the BAP can be categorized into discrete and continuous forms [9]. In the discrete model, each berth is treated as a fixed position, where only one vessel can be berthed at a time, regardless of its length [10]. The service time of a vessel includes waiting for a berth, the berthing time, and the time required for loading and unloading operations. As a typical NP-hard scheduling problem, the goal of the BAP is to improve terminal efficiency. To this end, researchers have continuously sought more effective solutions. A notable variant, the discrete dynamic berth allocation problem (DDBAP), adds complexity by requiring the consideration of dynamic vessel arrivals, uncertainties, and physical port constraints. Although previous studies have proposed solutions to the DDBAP, many methods rely on static or simplified assumptions. While these approaches are important for theoretical analysis, they are insufficient for addressing the highly variable conditions encountered in real port operations. For example, mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) and heuristic algorithms perform well for small-scale problems but exhibit significant computational complexity when applied to dynamic and large-scale scenarios. Furthermore, existing research incorporates uncertainty into berth allocation but often simplifies key operational constraints, such as quay crane scheduling or vessel-specific loading/unloading requirements. Reinforcement learning (RL), especially deep Q-network (DQN), has demonstrated immense potential in solving dynamic and uncertain optimization problems [11]. However, the application of DQN to DDBAP is still in its exploratory phase. This study aims to fill this gap by proposing an innovative DQN model that combines real-time decision-making capabilities with port-specific constraints to provide a more robust solution for berth allocation. Using DQN, the algorithm enables optimal decision-making in uncertain environments, thereby enhancing throughput and operational efficiency. Comparative experiments with ant colony optimization (ACO), parallel search structure-enhanced ant colony optimization (PACO), and ant colony optimization combined with genetic algorithm (ACOGA) show that the proposed algorithm significantly improves the operational efficiency of container terminals. The contributions of this study include the following:
- (1)
- Identifying and addressing key limitations of traditional berth allocation methods, particularly their shortcomings in handling large-scale dynamic scenarios;
- (2)
- Developing a DQN-based framework that incorporates vessel-specific constraints, real-time decision-making, and adaptive learning capabilities into the solution of the DDBAP;
- (3)
- Conducting comparative experiments with traditional algorithms, including ACO, PACO, and ACOGA, to validate the proposed DQN model’s advantages in terms of efficiency and scalability.
The structure of this paper is as follows: Section 2 reviews and summarizes the relevant literature; Section 3 defines the DDBAP problem and its mathematical model; Section 4 presents the reinforcement learning algorithm used to solve the DDBAP model; Section 5 compares the performance of several heuristic algorithms with the proposed algorithm through case studies, providing a detailed analysis of the experimental results; and finally, Section 6 summarizes the main contributions and findings of this work.
2. Literature Review
The focus of this study is the berth allocation problem in container terminals. This section will systematically analyze the contributions of existing research on berth allocation, multi-port resource allocation, and discrete dynamic scenarios and highlight the necessity of introducing reinforcement learning to address such issues.
In berth scheduling, Kim et al. [12] formulated the scheduling of terminal berths and cranes in two phases using a mixed-integer linear programming model, taking into account a variety of constraints. Lai et al. [13] improved the traditional berth allocation strategy by changing the criteria for berth allocation and proposed three different berth allocation strategies, using heuristics and computer simulation to measure the different allocation strategies. Yang et al. [14] investigated the continuous berth allocation problem (BAPC) under the dynamic arrival scenario of ships and established an integer linear programming model with the objective of minimizing the total dwell time of the ship in the port. Lin et al. [15] considered both the dwell time and the associated penalty cost and established a mixed-integer planning model. Sheikholeslami et al. [16] used a mixed-integer linear programming model, considering tidal effects with the objective of minimizing the delay time of ship departure. However, the MILP models used in the above-mentioned studies are efficient for solving smaller-scale problems, but when faced with large-scale dynamic environments in real-world container terminals, they become unsuitable due to the increased computational complexity. Park et al. [17] investigated the robust berth allocation problem for container terminals, which incorporates an adaptive search process of time buffers into a particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm. Song Y et al. [18] systematically investigated the berth allocation problem under different water depth conditions with the objective of seeking to minimize the weighted service time, using a weighting strategy to adjust the priority of each vessel. Iris Ç et al. [19] proposed a mixed-integer linear programming model to solve the problem of integrated operational planning and energy management for ports with smart grids, taking into account renewable energy generation uncertainties. Xiang et al. [20] proposed a berth allocation model that minimizes the ship operation cost by considering both the uncertainty of ship arrival time and the operation time of the shore bridge to minimize the total cost of deviation between the ship’s planned and expected berthing times. However, even in existing research on berth scheduling involving uncertain scenarios, assumptions are still made, limiting their adaptability and making it difficult to meet the practical demands of dynamic environments. Traditional optimization and heuristic methods often struggle to scale effectively when handling large-scale, highly variable port operations, leading to inefficient computations and suboptimal solutions.
In terms of multi-port resource allocation, Zhang et al. [21] established a cooperative optimization model for berth allocation in dual ports to provide theoretical support for the construction of green ports, and Xu et al. [22] converted a multi-terminal berth scheduling problem into a special single-terminal berth scheduling problem through the introduction of a virtual terminal in order to cope with the demand for multi-port resource integration and low-carbon operation; Venturini et al. [23] established a berth optimization scheduling model in the context of multiple ports, with the minimum total cost of all ships in port as the objective function; Bi et al. [24] established a multi-objective nonlinear decision model for the joint scheduling of multiple berths in multiple ports under container port clustering and designed an improved genetic algorithm; and Lujan et al. [25] introduced a fuzzy optimization model for the BAP and the quay crane allocation problem (QCAP) to deal with the problem of berth allocation. A fuzzy optimization model was introduced to handle imprecise arrival times and optimize terminal utilization. AbouKasm et al. [26] proposed a mathematical formulation integrating berth allocation, quay crane allocation, and scheduling, considering different operating policies and highlighting the impact of the choice of policy on the service time. Al Samrout M [27] considered a dynamic with the ship-to-ship transshipment container terminal berth allocation problem and proposed a new mixed-integer linear programming for optimizing berthing schedules and establishing transit connection planning between the feeder and mother ship. Although there have been studies on multi-port resource coordination and optimization in the existing literature, such studies often assume high flexibility in the cooperation and resource allocation between ports, neglecting management constraints and other factors that arise in actual operations. This makes multi-port integration research difficult to implement in practice.
Ting C J et al. [28] investigated the discrete dynamic berth allocation problem with the objective of minimizing the total waiting time and loading–unloading time of all ships and established a mixed-integer programming model for the BAP. A particle swarm optimization (PSO) approach was proposed to solve the BAP. Golias M et al. [29] proposed a berth scheduling strategy to minimize delayed ship departures and indirectly reduce fuel consumption and emissions in ship idling mode. Dai J et al. [30] used a local search algorithm, which defines the neighborhood structure using the concept of sequence pairs, to solve the static berth allocation planning problem into a rectangular layout problem with release time constraints. Yıldırım M S et al. [31] used the first-come-first-served (FCFS) prioritization principle for accepting berths of arriving ships. A decision support system based on a population-based artificial bee colony optimization algorithm was proposed. Legato P et al. [32] integrated two independent models into a simulation-optimization framework to support decision-making for the BAP. Imai A et al. [33] investigated the problem of determining dynamic berth assignments to ships in a public berthing system and developed a heuristic procedure based on the Lagrangian relaxation of the original problem. Zhen L et al. [34] proposed a robust planning formulation for the case of limited information about probability distribution from a stochastic point of view. These results are often based on idealized assumptions regarding inter-terminal resource coordination, overlooking constraints such as berth demand and management policies in real operations. When faced with large-scale, highly dynamic, and uncertain real-world production environments, optimization efficiency and accuracy often encounter significant challenges. These limitations highlight the urgent need for an adaptive, scalable, and context-aware optimization method.
In the face of uncertain discrete dynamic berth allocation problems, the introduction of reinforcement learning will allow for better adaptive learning in uncertain environments. Reinforcement learning does not rely on problem-specific rules or predefined objective functions. Instead, it adaptively learns decision strategies to obtain optimal or near-optimal solutions through continuous interaction with the environment. The most commonly used DRL algorithms are DQN and its variants, and the most frequently considered dynamic event is the arrival of a new job [35]. Li C et al. [36] considered terminal information and vessel demand information, integrating useful features of bulk terminal working hours into a state set. Based on double DQN, they proposed an improved deep reinforcement learning method that discretizes the scheduling process into actions, simplifying the scheduling problem into simple inputs and outputs. Dai Y et al. [37] proposed a mixed-integer model to allocate quay cranes, terminals, and berths, considering not only the type of cargo but also the time required for setting up the gantry cranes. The proposed model uses an offline algorithm based on greedy insertion to optimize berth allocation when vessel information is available. In uncertain vessel information scenarios, the model employs an online optimization strategy based on reinforcement learning algorithms, demonstrating that the proposed algorithm can learn from feedback and adapt quickly in real time. Li B et al. [38] designed a reinforcement learning algorithm based on dueling double DQN for the multi-terminal dynamic continuous berth allocation problem. A series of computational experiments verified the effectiveness of the algorithm and its capability in multi-terminal joint operations. Turgut Y et al. [39] applied a DQN model to train agents to dynamically schedule jobs by minimizing job delay time. The trained DQN model was compared with two popular scheduling rules (shortest processing time and earliest due date) to test the proposed model, showing that the DQN model outperformed these scheduling rules. Zhao Y et al. [40] addressed the scheduling problem in manufacturing workshops, aiming to reduce production costs and improve processing efficiency. They transformed the job shop scheduling problem into a reinforcement learning problem based on a Markov decision process. The adaptive scheduling algorithm in the paper designed five continuous value range state features as inputs to a deep neural network (DNN) and selected ten well-known heuristic scheduling rules as the action set for DQN. Experiments verified that the proposed algorithm has better performance and generality than single scheduling rules or traditional Q-learning algorithms. Ai T et al. [41] analyzed the scheduling process and unloading operations in bulk port import businesses, establishing a Markov decision process model. They proposed an enhanced reinforcement learning algorithm that combines the advantages of double DQN and dueling DQN, based on prioritized experience replay and Softmax strategy. The algorithm was evaluated using real port data and benchmarked against other algorithms. Numerical experiments and comparative analysis confirmed that the proposed algorithm significantly improved the efficiency of berth and yard scheduling at bulk terminals, reducing port operation costs. Cervellera C et al. [42] trained a learning model to solve complex Markov decision problems as a tool for addressing intermodal terminal berth allocation issues. Simulation tests demonstrated the good performance of the strategy under various conditions. While RL has shown potential in scheduling problems, its application in berth allocation remains in the early stages of exploration. Existing studies have not fully leveraged RL’s capacity to learn adaptive strategies in large and complex scenarios in real time. Existing models often fail to consider key constraints such as berth characteristics, tidal effects, or vessel handling differences, which limits their practical feasibility. As the uncertainty and complexity of real port environments grow, training more effective learning methods will further enhance port operational efficiency.
By analyzing the existing literature, we gain insights into current research on resilient scheduling in ports under uncertainty. To address the deficiencies mentioned above, we have designed a more innovative and effective reinforcement learning model to dynamically respond to uncontrollable changes in vessel arrival times and unloading times, ensuring that the system becomes more robust and effective in handling the variability of port operations.
3. Problem Statement and Model Formulation
Due to the varying transportation times for each container from its initial storage area to the designated berth, the loading and unloading times for each vessel differ across different berths. However, most published berth allocation problem (BAP) models typically assume that vessel handling times are deterministic. This assumption is generally based on the following considerations:
- (a)
- The handling time is known in advance and remains fixed;
- (b)
- The handling time depends on the vessel’s berthing location;
- (c)
- It depends on the number of cranes assigned to service the vessel;
- (d)
- The crane’s work schedule plays a crucial role in the efficiency of loading and unloading;
- (e)
- All the mentioned conditions (b,c) need to be considered simultaneously.
In this study, the handling time is determined by the number of cranes, the volume of containers to be transshipped, and the operational efficiency of the assigned cranes. Let there be m vessels (i.e., vessels 1, 2, …, m) and mb berths (i.e., berths 1b, 2b, …, mb). It is assumed that each vessel can only dock at one berth at a time, and each berth can accommodate only one vessel at any given moment. If a vessel gg begins docking at a berth, it will remain at that berth for the next time unit.
The dynamic berth allocation problem (DDBAP) studied in this paper can be viewed as a parallel machine scheduling problem, where vessels correspond to tasks and berths correspond to machines [43]. Each task j has a processing time pj, an arrival time aj, and a weight wj and can be processed by a specific set of machines (berths). The processing time pj is determined by the number of cranes assigned to the vessel and their operational efficiency. To mathematically define the problem, we first model the scheduling of vessels at a single berth and then extend this to the berth allocation and scheduling problem for multiple berths.
3.1. Notation
The symbols used in this section are listed in alphabetical order as follows.
| Sets |
| B: Set of berths, B = {1, 2, …, nb}; |
| C: Set of QCs, C = {1, 2, …, nc}; |
| J: Inbound vessels during the planning period, J = {1, 2, …, n}; |
| Model-Related Notations |
| n: Number of vessels entering the port during the planning period, positive integers; |
| nb: Number of berths available at the port; |
| nc: Number of quay cranes; |
| njcap: Container capacity of vessel j; |
| njl: Number of containers loaded and unloaded on board j; |
| Oi: An ordered subset of vessels to be loaded/unloaded at berth i; |
| tijb: The moment when vessel j starts berthing at berth i; |
| tjw: Vessel j’s moment of arrival at the waiting area, tjw ≥ 0; |
| Tjb: The length of time a vessel is at anchor and away is assumed to be fixed and the same for different vessels, Tjb > 0; |
| tijfl: Completion time of loading and unloading of vessel j at berth i, tijfl = tijl + Tijl; |
| tijl: Start time of the loading and unloading of vessel j at berth i; |
| Tijl: Duration of loading and unloading vessel j at berth i; a function of njl, njcap and njc; |
3.2. Mathematic Model
In most container terminals, multiple berths are available, so the multi-berth allocation problem involves not only the sequencing of vessel loading and unloading operations but also the optimization of berth assignments. The berth allocation model is based on the following assumptions:
- (1)
- The arrival time of vessels is a random variable;
- (2)
- The handling time is determined by the number of containers, the number of quay cranes (QCs), QC productivity, and other relevant factors;
- (3)
- The berth conditions must meet the vessel’s actual requirements regarding draft depth and berth length;
- (4)
- Each vessel can be assigned to only one berth, and the possibility of moving a vessel from one berth to another is not considered.
Berth allocation plays a crucial role in minimizing vessel turnaround time, which is a key performance indicator for port operations. The objective of berth allocation can be expressed in Equation (1).
The conditions for the equations have been defined in Section 3.1. The objective function (1) aims to minimize the total time, which includes both total waiting time and total processing time. Constraint (2) ensures that each vessel has the opportunity to berth. Constraint (3) limits the number of vessels berthed at a single berth to one at any given time. Constraint (4) is used to estimate the handling time of the vessels.
3.3. MDP Model
- (1)
- State
As the input to the agent, selecting an appropriate state to represent environmental information is crucial. Considering the dynamic characteristics of the scenarios in this study, the state set is composed of the completion times for each berth, which reflects the real-time loading and unloading progress of vessels at the port.
The state set consists of the completion time of each berth, where represents the completion time of the last loading and unloading task of berth j at the current time step. Using the min-max normalization method to normalize the state, the formula is as follows: .
- (2)
- Action
The action set consists of the number of each berth, where j represents the berth number.
- (3)
- Reward
In reinforcement learning, the reward function is the direct feedback from the environment to the agent for taking a specific action in a given state. This directly impacts the calculation of Q-values. Considering that the goal of this study is to minimize the total waiting time of vessels, we have used the negative value of the total waiting time as the reward function for the agent’s learning, where M is the total number of ships, and represents the waiting time of ship i.
4. Solution Algorithm
4.1. Preliminary on Reinforcement Learning
The core objective of reinforcement learning is to determine the optimal policy through the interaction between an agent and its environment (see Figure 1). Its theoretical framework is based on the Markov decision process (MDP), which can be defined by a tuple . The agent selects actions based on accumulated experience and enhances future decision-making by randomly exploring new action paths.
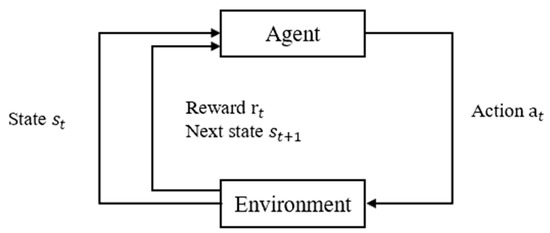
Figure 1.
Framework of reinforcement learning.
During the training process of reinforcement learning, the agent observes the current state at each decision point and selects and executes an action, transitioning the system to the next state while receiving a corresponding reward (as shown in Figure 1). The reward serves to evaluate the effectiveness of the current decision. When the agent follows a policy (i.e., a probability distribution over actions in different states), it generates a sequence of states , actions , and rewards , known as a trajectory . The agent learns and updates its policy autonomously based on these trajectories, ultimately finding the optimal policy .
4.2. DQN Algorithm
Q-learning is a value-based reinforcement learning method. Compared to traditional Q-learning and other machine learning methods, DQN is capable of handling high-dimensional state and action spaces with greater efficiency and adaptability. By using deep neural networks to approximate the Q-table, DQN can effectively learn in complex state spaces, which improves the algorithm’s applicability and solution efficiency in large-scale problems. However, it is important to note that, as a data-driven model, DQN is highly dependent on the quality and quantity of data, making it sensitive to data quality and potentially limited by the representativeness of the training data. Its core idea is to update the value function through the interaction between the agent and the environment by applying the Q-learning update rule (Equation (8)) based on the current policy. A new policy is then generated from the updated value function, with an expected return higher than that of the original policy. Through this iterative process, the algorithm gradually converges to the optimal value function, selecting actions that maximize the value function and ultimately deriving the optimal policy.
Due to the limited capacity of Q-tables, Q-learning is only suitable for small-scale problems. When the number of states grows exponentially, the performance of traditional methods declines significantly. Deep learning, with its ability to handle large-scale data and extract complex patterns, enhances Q-learning by introducing deep Q-network (DQN). DQN approximates Q-tables using deep learning techniques, addressing the limitations of traditional Q-learning.
The DQN algorithm learns the action-value function corresponding to the optimal policy by minimizing the loss function (Equation (9)), where the loss function is used to adjust the parameters of the neural network.
As shown in Figure 2, the Q-network in the DQN framework is used to predict Q-values, with its input being the latest state parameters from the current environment. The Q-network’s weights are updated with each iteration, denoted as θ. The output of the Q-network is represented as . To enhance stability, the algorithm introduces a target Q-network, which is periodically updated with input parameters. The weights of the target Q-network are denoted as , and its output is represented as . The training objective of the neural network is to optimize the model by minimizing the loss function constructed from the predicted Q-values and target Q-values. Subsequently, stochastic gradient descent is employed to update the Q-network’s parameters through backpropagation.
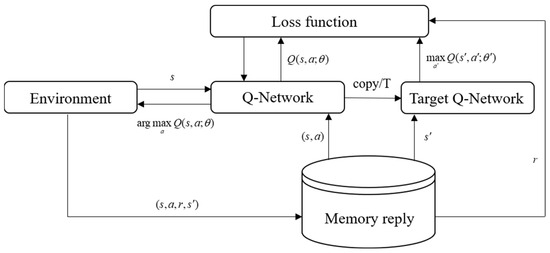
Figure 2.
Algorithm framework of deep Q-network.
In Figure 2, Copy/T indicates that every T time steps, the parameters of the Q-network are copied to the target Q-network, reducing the correlation between the predicted and target Q-values. This helps mitigate divergence or oscillation, thereby improving the stability of the algorithm. Additionally, the algorithm incorporates an experience replay buffer that stores the data samples generated by the agent’s interactions with the environment at each time step. During training, a random subset of data is sampled from the replay buffer to train the network, further enhancing the stability of the training process.
5. Experimental Study
To conduct the numerical analysis, it is essential to first define the values for several key parameters. The parameter settings for the proposed method are as follows:
Based on a survey conducted at a four-berth container terminal at the Port of Shanghai (including time, reference numbers, and/or other relevant survey details), a random time period was selected during which a fleet of 20 vessels arrived simultaneously at the port. Table 1 presents the inter-arrival times of the vessels (for simplicity, the arrival time of the first vessel is taken as the reference point, with time set to 0) as well as the corresponding loading and unloading processing times.

Table 1.
Parameters for DQN.
Note: The arrival time in the tables refers to the time interval between the arrival of the respective vessel and the arrival of the first vessel. For example, if vessel 1 arrives at 01:00, then the arrival times of vessel 2 and vessel 3 are 14:30 and 22:30, respectively (see Table 2).

Table 2.
Ships Arrival Intervals and Loading/Unloading Schedules.
5.1. Based on ACO
Based on the known arrival times and handling times of 20 vessels, the ACO algorithm, a type of metaheuristic algorithm, was used to calculate the total stay time of all vessels in the port, including both berthing waiting time and handling time. According to Dorigo’s research, when the heuristic factor α is set to values within {0.5, 1} and β is set to values within {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, the ACO algorithm can reliably converge to the optimal solution. Additionally, when the number of ants m approaches the number of nodes n, the algorithm demonstrates superior performance. Based on this, the parameters for the ACO algorithm in this experiment were set as follows: pheromone evaporation factor Q = 100, heuristic factor α = 1, β = 5, evaporation rate ρ = 0.5, maximum iterations of 200, and ant population size c = 5. Python 3.9 was used to perform 10 repeated experiments, yielding a best total stay time of 262.85 h and a worst result of 280.95 h.
According to the first-come-first-serve (FCFS) rule, the vessel-berth allocation under the best-case scenario (262.85 h) is as follows:
- Berth 1:4-5-13-17-19
- Berth 2:2-7-10-12-15-20
- Berth 3:1-3-8-11-18
- Berth 4:6-9-14-16
The change in the objective value as the number of iterations increases is shown in Figure 3:
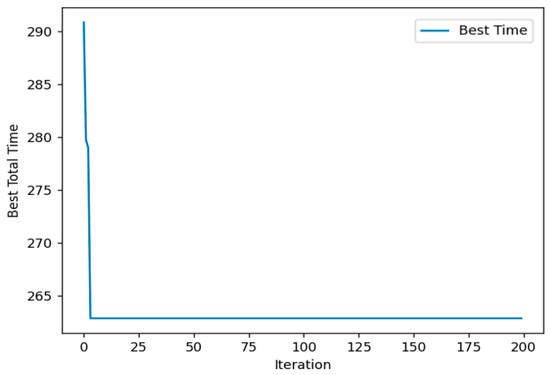
Figure 3.
Results of multi-berth allocation based on ACO.
The y-axis in Figure 3 represents the total port stay time for the 20 vessels. From the data presented in the figure, it can be observed that the use of the ACO algorithm enables the model to converge to the optimal solution in a relatively short amount of time. This demonstrates that the ACO algorithm exhibits strong efficiency and stability when applied to the optimization of vessel scheduling in ports.
5.2. Based on PACO
Building on the experiments described in Section 5.1, this paper further optimizes the standard ACO algorithm and designs a parallel ACO algorithm to address the vessel scheduling problem. During the implementation of the parallel ACO algorithm, the parameter settings remain consistent with the traditional ACO algorithm to ensure the comparability and consistency of the experimental results, thereby providing a reliable basis for subsequent comparative analyses. After running the experiment 10 times, the results indicate that the system achieved optimal performance when the total scheduling time was 259.5 h. The specific vessel berthing plans and corresponding berth allocations are shown in the figure below.
- Berth1: 1-2-7-9-13-20
- Berth2: 6-10-12-18
- Berth3: 3-8-11-15-17
- Berth4: 4-5-14-16-19
The curve showing the change in the objective value with the increase in the number of iterations using the PACO algorithm is presented in Figure 4:
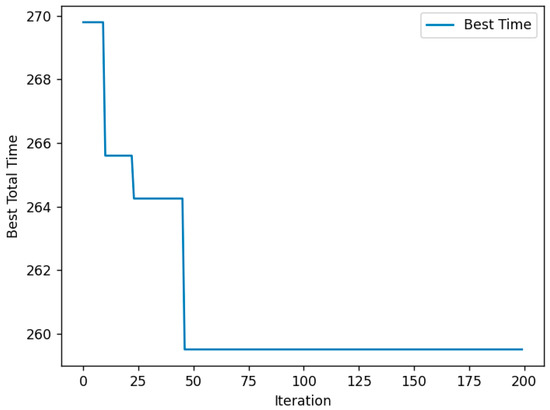
Figure 4.
Results of multi-berth allocation based on PACO.
From the results shown above, it is evident that the PACO algorithm achieves the target value in a relatively short time, and it significantly outperforms the traditional ACO algorithm in reducing ship waiting times at the port, further validating PACO’s superiority in solving complex scheduling problems.
5.3. Based on ACOGA
In addition to the parallelization of the ACO algorithm, this paper incorporates crossover and mutation operations from the genetic algorithm (GA) to improve the standard ACO for optimizing berth allocation. In the improved ACO algorithm, the parameter settings remain consistent with the traditional ACO algorithm to ensure the comparability and consistency of the experimental results, providing a solid basis for subsequent comparative analysis. After 10 consecutive optimization runs, the best scheduling result was 257.4 h, while the worst result was 260.4 h. Based on the first-come, first-served rule, the specific berth allocation for 20 vessels under the optimal condition, with a total stay time of 257.4 h, is presented below.
- Berth1: 1-2-4-8-12-14-17
- Berth2: 6-9-15-19
- Berth3: 3-7-10-11-13-16-20
- Berth4: 5-18
The curve showing the change in the objective value with the increase in the number of iterations under the ACOGA algorithm is presented in Figure 5:
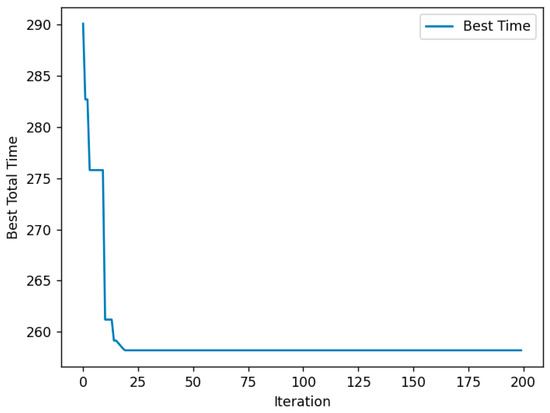
Figure 5.
Results of multi-berth allocation based on ACOGA.
The experimental results indicate that, compared to the standard ACO algorithm, the ACOGA algorithm demonstrates greater robustness, with a smaller difference between the best and worst results. Additionally, as shown in the figure, the ACOGA algorithm converges within a relatively short time, although its convergence speed is slightly slower than that of the PACO algorithm. However, it is significantly faster than the standard ACO algorithm. At the same time, the optimization results obtained by the ACOGA algorithm are considerably better than those of the standard ACO, further validating its effectiveness in solving complex scheduling problems.
5.4. Based on DQN
Building on this foundation, this paper further applies the DQN algorithm from deep reinforcement learning to solve the experimental problem. Under identical conditions, the algorithm was run 10 times, and the curve showing how the objective value changes with the number of iterations, when the optimal objective value is obtained, is presented in the following figures (Figure 6 and Figure 7):
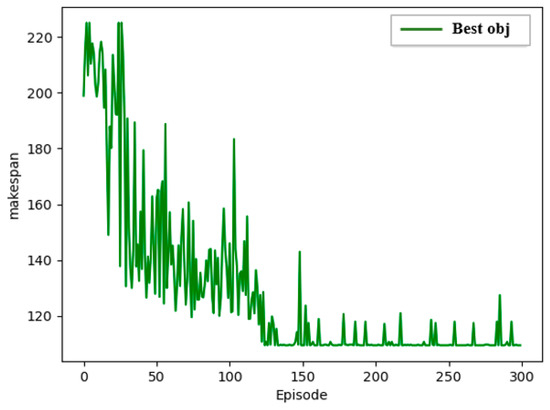
Figure 6.
Total completion time of berth loading and unloading operations.
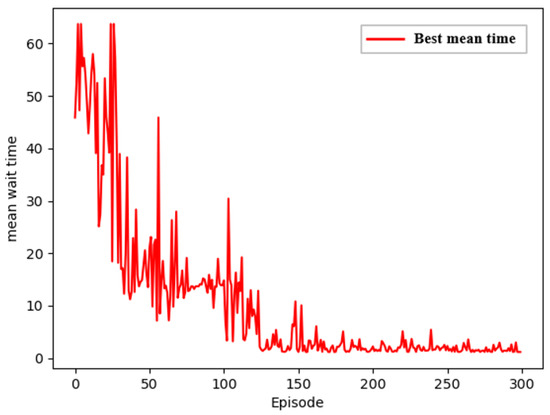
Figure 7.
Average waiting time of ships.
The specific arrival time, loading and unloading start time, completion time, and detailed berth information for each vessel are shown in the table below. The arrival time was explained earlier, and the waiting time corresponds to the specific waiting time for each vessel. The start and completion times for loading and unloading are processed intervals relative to the arrival time of the first vessel, simplifying the calculations (see Table 3).

Table 3.
Ship loading and unloading schedule at port.
The time distribution of berth utilization and the corresponding vessel information are detailed in Figure 8. In Figure 8, each solid rectangle represents a ship, with the left end indicating the ship’s actual arrival time and the right end indicating its actual departure time. Rectangles with the same color signify that the corresponding ships docked at the same berth.
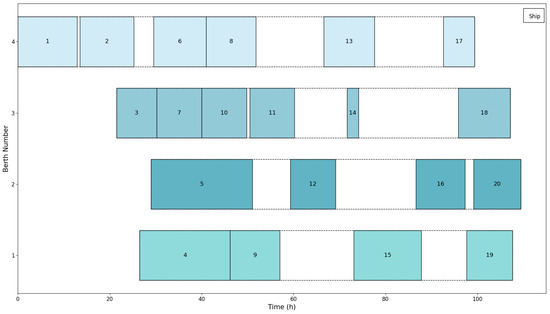
Figure 8.
Ship docking schedule.
Based on the results above, the total waiting time for ships after optimization using the DQN algorithm is 109.45 h, indicating that the algorithm is capable of converging to the desired value within a relatively short computation time, with an average waiting time per ship of 1.145 h. Compared to ACO, PACO, and ACOGA, DQN demonstrates significant advantages in efficiency and effectiveness due to its powerful self-learning capabilities, better generalization, and higher adaptability. DQN can learn strategies directly from raw input data without relying on manually designed features or complex state representations. Through deep neural networks, DQN can automatically extract important features from the input data, effectively avoiding the dependency on feature engineering found in traditional reinforcement learning methods. Additionally, DQN introduces an experience replay mechanism, which randomly samples batches of historical experience data during the learning process, breaking the correlations between data points. This enhances sample utilization efficiency and reduces potential variance in the training process. The comparative experiments further validate the superiority of this algorithm in solving vessel scheduling problems, suggesting that it can be effectively applied in real-world port scenarios. In extremely congested or unpredictable traffic patterns, although there are certain requirements for computational performance and training data, and the convergence speed may be slightly slower, DQN still manages to more effectively and quickly alleviate congestion compared to other methods.
In this experiment, we randomly selected vessel data from specific operational periods of the terminal for initial training. Due to limitations in computational resources, such as the processing power of personal computers, the training process consumed a significant amount of time. However, it is noteworthy that although the training phase requires substantial computational effort, the trained model demonstrated strong performance in large-scale scenarios, providing rapid and accurate responses. This suggests that while the training process is computationally demanding, the model can effectively scale during deployment and perform well in high-demand real-world environments, underscoring its potential for widespread application in large terminal operations. Overall, compared to ACO, PACO, and ACOGA, the DQN model provides a better balance between computational costs and scheduling performance. It not only optimizes computational efficiency and effectively reduces vessel waiting times but also exhibits highly adaptive performance, seamlessly adapting to changing operational constraints, demonstrating its practical applicability.
6. Conclusions
In this study, we propose a dynamic berth allocation model based on DQN to address the challenges posed by the high uncertainty in vessel arrival times and processing times in container terminal operations. This model advances the application of deep reinforcement learning (DRL) in dynamic scheduling problems under uncertain environments, bridging the gap between intelligent optimization technologies and the practical needs of logistics operations. The experimental results show that the DQN model excels in improving port throughput and reducing vessel waiting times, especially under high congestion and complex data environments, where its advantages are particularly pronounced. This not only demonstrates the practical value of the model in enhancing port efficiency but also further expands its theoretical significance in the field of logistics optimization.
However, despite the positive results achieved by DQN in solving the berth allocation problem, its limitations warrant further exploration. The model’s dependency on training data may lead to inadequate adaptability when facing new or unknown operational conditions, potentially impacting its scalability across diverse scenarios. Additionally, the computational complexity during the training phase could present barriers to large-scale deployment, particularly when dealing with high-demand port environments. To address these limitations, future research should focus on improving the model’s adaptability and robustness. Proposed future research directions include the following: first, exploring multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) to simulate the interactions of multiple stakeholders in complex logistics systems, thereby enhancing the scalability and robustness of the algorithm, and second, integrating real-time adaptive mechanisms and dynamic data flows into the model to improve the system’s response capability to sudden traffic surges and operational disruptions. Moreover, further investigation into distributed learning techniques and parallel computing strategies should be conducted to optimize computational efficiency and ensure the model’s operational feasibility in large-scale applications. These improvements will not only enhance the theoretical and practical contributions of the DQN model but also open new prospects for its widespread application in dynamic logistics and port management.
Author Contributions
Methodology, P.W.; Validation, J.L.; Resources, X.C.; Writing—original draft, P.W.; Writing—review & editing, J.L.; Supervision, X.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was sponsored by Hubei Province’s key research and development project number: 2023BAB013.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest in the manuscript.
References
- Lu, B.; Hua, G. Optimizing berth operation system in container terminal by simulation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Logistics, Informatics and Service Sciences (LISS), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 24–27 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zou, M.; Lv, Y.; Sun, D. AGV scheduling for optimizing irregular air cargo containers handling at airport transshipment centers. Mathematics 2024, 12, 3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; de Koster, R. Stochastic modeling of unloading and loading operations at a container terminal using automated lifting vehicles. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 266, 895–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierwirth, C.; Meisel, F. A follow-up survey of berth allocation and quay crane scheduling problems in container terminals. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 244, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierwirth, C.; Meisel, F. A survey of berth allocation and quay crane scheduling problems in container terminals. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 202, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frojan, P.; Francisco, C.J.; Alvarez, V.R.; Koulouris, G.; Manuel, T.J. The continuous berth allocation problem in a container terminal with multiple quays. Expert Syst. Appl. Int. J. 2015, 42, 7356–7366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakub, W.; Maciej, D. Selecting algorithms for large berth allocation problems. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2020, 283, 844–862. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.W.; Ting, C.J. Solving the dynamic berth allocation problem by simulated annealing. Eng. Optim. 2014, 46, 308–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, G.R.; Lorena, L.A.N.; Lorena, L.A.N.; Laporte, G. An adaptive large neighborhood search for the discrete and continuous berth allocation problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2016, 70, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Molins, M.; Salido, M.A.; Barber, F. Robust scheduling for berth allocation and quay crane assignment problem. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 2014, 834927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Lv, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ji, X. Enhanced Ant Colony Algorithm for Discrete Dynamic Berth Allocation in a Case Container Terminal. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Park, T.K. A note on a dynamic space-allocation method for outbound containers. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2003, 148, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.K.; Shih, K. A study of container berth allocation. J. Adv. Transp. 1992, 26, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.M.; Hu, Z.H.; Ding, X.Q.; Luo, J.X. An integer linear programming model for continuous berth allocation problem. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Management, Innovation Management and Industrial Engineering, Xian, China, 26–27 December 2009; Volume 4, pp. 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.W.; Ting, C.J.; Wu, K.C. Simulated annealing with different vessel assignment strategies for the continuous berth allocation problem. Flex. Serv. Manuf. J. 2018, 30, 740–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, A.; Mardani, M.; Ayazi, E.; Arefkhani, H. A dynamic and discrete berth allocation problem in container terminals considering tide effects. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2020, 44, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Cho, S.W.; Lee, C. Particle swarm optimization algorithm with time buffer insertion for robust berth scheduling. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 160, 107585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Chu, C. The berth allocation optimisation with the consideration of time-varying water depths. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 57, 488–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iris, Ç.; Lam, J.S.L. Optimal energy management and operations planning in seaports with smart grid while harnessing renewable energy under uncertainty. Omega 2021, 103, 102445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Liu, C. An expanded robust optimisation approach for the berth allocation problem considering uncertain operation time. Omega 2021, 103, 102444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, Z.; Qiu-shuang, C. Coordinated Berth Allocation for Port Group Considering Vessel Emissions. J. Transp. Syst. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2014, 14, 99. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Du, Y.; Long, L. Berth scheduling model and algorithm for coordinated operation of multiple container terminals in a port. Syst. Eng. 2015, 33, 128–138. [Google Scholar]
- Venturini, G.; Iris, Ç.; Kontovas, C.A.; Larsen, A. The multi-port berth allocation problem with speed optimization and emission considerations. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 54, 142–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y. Multi-port and multi-berth integrated scheduling based on container port cluster. J. Comput. Appl. 2012, 32, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lujan, E.; Vergara, E.; Rodriguez-Melquiades, J.; Jiménez-Carrión, M.; Sabino-Escobar, C.; Gutierrez, F. A fuzzy optimization model for the berth allocation problem and quay crane allocation problem (BAP + QCAP) with n quays. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Kasm, O.; Diabat, A.; Cheng, T.C.E. The integrated berth allocation, quay crane assignment and scheduling problem: Mathematical formulations and a case study. Ann. Oper. Res. 2020, 291, 435–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Samrout, M.; Sbihi, A.; Yassine, A. An improved genetic algorithm for the berth scheduling with ship-to-ship transshipment operations integrated model. Comput. Oper. Res. 2024, 161, 106409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, C.J.; Wu, K.C.; Chou, H. Particle swarm optimization algorithm for the berth allocation problem. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golias, M.M.; Saharidis, G.K.; Boile, M.; Theofanis, S.; Ierapetritou, M.G. The berth allocation problem: Optimizing vessel arrival time. Marit. Econ. Logist. 2009, 11, 358–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Lin, W.; Moorthy, R.; Teo, C.P. Berth allocation planning optimization in container terminals. In Supply Chain Analysis: A Handbook on the Interaction of Information, System and Optimization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 69–104. [Google Scholar]
- Yıldırım, M.S.; Aydın, M.M.; Gökkuş, Ü. Simulation optimization of the berth allocation in a container terminal with flexible vessel priority management. Marit. Policy Manag. 2020, 47, 833–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legato, P.; Mazza, R.M.; Gullì, D. Integrating tactical and operational berth allocation decisions via simulation–optimization. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2014, 78, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, A.; Nishimura, E.; Papadimitriou, S. The dynamic berth allocation problem for a container port. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2001, 35, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, L. Tactical berth allocation under uncertainty. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 247, 928–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Xu, Z. Real-time scheduling for distributed permutation flowshops with dynamic job arrivals using deep reinforcement learning. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2022, 54, 101776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gomes, L. Intelligent scheduling method for bulk cargo terminal loading process based on deep reinforcement learning. Electronics 2022, 11, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, B. Optimizing berth allocation in maritime transportation with quay crane setup times using reinforcement learning. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yang, C.; Yang, Z. Multiple Container Terminal Berth Allocation and Joint Operation Based on Dueling Double Deep Q-Network. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, Y.; Bozdag, C.E. Deep Q-network model for dynamic job shop scheduling problem based on discrete event simulation. In Proceedings of the 2020 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), Orlando, FL, USA, 14–18 December 2020; pp. 1551–1559. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H. Dynamic jobshop scheduling algorithm based on deep Q network. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 122995–123011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, T.; Huang, L.; Song, R.J.; Huang, H.F.; Jiao, F.; Ma, W.G. An improved deep reinforcement learning approach: A case study for optimisation of berth and yard scheduling for bulk cargo terminal. Adv. Prod. Eng. Manag. 2023, 18, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervellera, C.; Gaggero, M.; Macciò, D. Policy optimization for berth allocation problems. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Shenzhen, China, 18–22 July 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.; Zou, M.; Li, J.; Liu, J. Dynamic berth allocation under uncertainties based on deep reinforcement learning towards resilient ports. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2024, 252, 107113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).