Abstract
In this paper, we study a Yosida variational inclusion problem with its corresponding Yosida resolvent equation problem. We mention some schemes to solve both the problems, but we focus our study on discussing convergence criteria for the Yosida variational inclusion problem in real Banach space and for the Yosida resolvent equation problem in q-uniformly smooth Banach space. For faster convergence, we apply an inertial extrapolation scheme for both the problems. An example is provided.
MSC:
65J15; 47J25; 65K15
1. Introduction
Variational inclusions are the generalized forms of variational inequalties introduced by Hassouni and Moudafi [1]. Many interrelated and unrelated problems of basic and applied sciences can be easily studied via variational inclusions, such as the problems arising in elasticity, structural analysis, oceanography, image processing, physics and engineering sciences, etc., see for example [2,3,4,5,6,7,8].
The concept of resolvent equations was introduced by Noor [9,10]. Resolvent equations are generalized forms of Wiener–Hopf equations. The equivalence between the variational inclusions and resolvent equations was shown by many authors. The resolvent operator technique is useful to solve variational inclusion problems, as projection methods fail to solve them. Various generalized resolvent operators involving different monotone operators are available in the literature.
It is a fact that maximal monotone operators are fundamental objects in modern optimization. In addition, set-valued monotone operators can be regularized into a single-valued monotone operator by a process called Yosida approximation. Applications of Yosida approximation operator can be found in a heat equation that describes the distribution of heat over time in a fixed region of space, an initial value problem for the linearized equations of coupled sound and heat flow, and a wave equation in the form of second-order partial differential equation used for the description of waves, see for example [11,12,13,14,15].
Many iterative algorithms were developed using generalized resolvent operators, but it is always beneficial to use an algorithm which accelerates the fast convergence for the sequence generated by the algorithm. Inertial extrapolation schemes are developed by using the inertial extrapolation term by several authors, where is an extrapolating factor that speeds up the convergence rate of the method. Polyak [16] first introduced the inertial-type iterative algorithm to deal with the heavy ball method. The inertial-type iterative algorithm has two steps in which the consecutive iterations are gained by using the former two terms, see for example [17,18,19,20].
In view of the above important discussion, in this paper, we consider a Yosida variational inclusion problem with its corresponding Yosida resolvent equation problem. We mention some schemes for solving Yosida variational inclusion as well as the Yosida resolvent equation problem. We concentrate our study on convergence analysis of both the problems through inertial extrapolation schemes. An example is provided through MATLAB 2015a with a computation table and a convergence graph.
2. Fundamental Tools and Concepts
Suppose that is a real Banach space and is its topological dual equipped with norm and duality pairing between and . By , we denote the set of all non-empty subsets of .
For , the generalized duality mapping is defined by
For , becomes normalized duality mapping. Particularly, is called normalized duality mapping on . It is well known that for and is the subdifferential of functional at e, see [21]. The mapping is single-valued if is uniformly smooth.
The definition of uniformly smooth Banach space, modulus of smoothness and the following important Lemma can be found in Xu [21].
Lemma 1.
A real uniformly smooth Banach space is q-uniformly smooth if and only if there exists a constant such that for all , the following inequality holds:
Before providing essential definitions for the presentation of this paper and for the convenience of readers, we mention the following well-known definitions. For this purpose, we take , a real Hilbert space.
Definition 1.
A single-valued mapping is called
- (i)
- Monotone if
- (ii)
- Strongly monotone if there exists a constant such that
Definition 2.
A set-valued mapping is called monotone, if
Definition 3.
Let be a mapping. A set-valued mapping is called -monotone if M is monotone and
The generalizations of above Definitions 1–3 in q-uniformly smooth Banach space are as follows, which are needed for the presentation of this paper.
Definition 4.
A single-valued mapping is called
- (i)
- Accretive if
- (ii)
- Strongly accretive if there exists a constant such that
- (iii)
- Lipschitz continuous if there exists a constant such that
Definition 5.
A set-valued mapping is called accretive if
Definition 6.
Let be a mapping. The set-valued mapping is called -accretive if M is accretive and
It is well known that all the splitting methods are based on the resolvent operator of the form , where M is a set-valued monotone mapping, is a positive constant and I is the identity mapping.
Definition 7.
The resolvent operator , where H is a Hilbert space, is defined as
Definition 8.
The Yosida approximation operator , where H is a Hilbert space, is defined as
The generalized forms of Definitions 7 and 8 are mentioned below.
Definition 9.
Let be a mapping and be a set-valued mapping. The generalized resolvent operator associated with and M is defined as:
Definition 10.
The generalized Yosida approximation operator is defined as:
Note that if , the identity mapping, then from Definitions 9 and 10, one can obtain Definitions 7 and 8, respectively.
Proposition 1.
[22] Let be strongly accretive mapping with constant r and be an -accretive set-valued mapping. Then, the generalized resolvent operator is Lipschitz continuous with constant , that is
Lemma 2.
[23] Let be a sequence of non-negative real numbers such that
where
- (i)
- (ii)
- (iii)
Then,, as .
Proposition 2.
(i) If is r-strongly accretive, -expansive, -Lipschitz continuous and generalized resolvent operator is -Lipschitz continuous, then the generalized Yosida approximation operator is -strongly accretive with respect to , that is
where and all the constants are positive.
(ii) If is -Lipschitz continuous, r-strongly accretive and is -Lipschitz continuous, then the generalized Yosida approximation operator is -Lipschitz continuous, that is
where .
Proof.
(i) Using the definition of generalized duality mapping, expansiveness and Lipschitz continuity of and Lipschitz continuity of , we evaluate
That is,
Thus, the generalized Yosida approximation operator is -strongly accretive with respect to .
(ii) Using Lipschitz continuity of and , we evaluate
That is,
Thus, the genearlized Yosida approximation operator is -Lipschitz continuous. □
3. Yosida Variational Inclusion Problem and Yosida Resolvent Equation Problem
Let be single-valued mapping and be set-valued mapping. Let be a generalized Yosida approximation operator. We consider the following Yosida variational inclusion problem.
Find such that
If , then problem (1) reduces to the problem of finding such that
which is a fundamental problem of analysis that has been considered by Rockafellar [24].
Lemma 3.
The Yosida variational inclusion problem (1) has a solution if and only if the following equation is satisfied:
Proof.
One can prove it easily by using the definition of generalized resolvent operator . □
Based on Lemma 3, we mention an iterative scheme as well as an inertial extrapolation scheme for solving Yosida variational inclusion problem (1).
Iterative Scheme 1.
For any , compute the sequence by the following scheme:
and is a constant.
Equation (2) can also be written as
Based on (4), we suggest the following iterative scheme.
Iterative Scheme 2.
For any , compute by the recurrance relation,
and is a constant.
We mention the following inertial extrapolation scheme using the predictor–corrector approach.
Iterative Scheme 3.
For any , compute by the recurrance relation,
where , is the extrapolating term for all and is a constant.
Note that one can use the above-mentioned schemes 1 and 2 to obtain the existence and convergence result for Yosida variational inclusion problem (1). Using inertial extrapolation scheme 3, we prove a convergence result for Yosida variational inclusion problem (1) in the sequel.
In connection with Yosida variational inclusion problem (1), we state the following Yosida resolvent equation problem.
Find , such that
where and .
The following Lemma ensures that Yosida variational inclusion problem (1) is equivalent to Yosida resolvent equation problem (8).
Lemma 4.
Proof.
Let be a solution of Yosida variational inclusion problem (1). Then, by Lemma 3, it satisfies the equation:
Thus, we have
which is required for Yosida resolvent equation problem (8).
Conversely, let be the solution of Yosida resolvent equation problem (8). Then, we have
Since is one–one, we have
By Lemma 3, it follows that is the solution of Yosida variational inclusion problem (1). □
Alternative Proof.
Let
Based on Lemma 4, we state the following scheme for solving Yosida resolvent equation problem (8).
Iterative Scheme 4.
For any , compute the sequences and by the following scheme:
where and is a constant. □
The Yosida resolvent equation problem (8) can be restated as:
Using fixed point formulation (13), we suggest the following iterative scheme.
Iterative Scheme 5.
For given , compute the sequences and by the following scheme:
where and is a constant. □
For positive step size , the Yosida resolvent equation problem (8) can also be written as:
Verification.
which gives
□
The fixed point formulation (14) enables us to suggest the following iterative scheme.
Iterative Scheme 6.
For , compute the sequences and by the following scheme:
where are constants and .
One can apply schemes 4–6 to obtain existence and convergence results for Yosida resolvent equation problem (8).
In order to accelerate the convergence rate, we suggest the following inertial extrapolation scheme for solving Yosida resolvent equation problem (8).
Equation (10) can also be written as
Based on (15), we establish the following implicit scheme for solving Yosida resolvent equation problem (8).
Iterative Scheme 7.
For , compute the sequences and by the recurrance relation
where and .
We design the following inertial extrapolation scheme for solving Yosida resolvent equation problem (8) applying the predictor–corrector technique.
Iterative Scheme 8.
For , compute sequences and by the recurrance relation:
where is a constant, such that and is an extrapolating term for all .
4. Convergence Analysis
First, we discuss the convergence of scheme 3 for Yosida variational inclusion problem (1) in real Banach space. Thenceforth, we demonstrate convergence of scheme 8 for Yosida resolvent equation problem (8) in real q-uniformly smooth Banach space.
Theorem 1.
Let be real Banach space and be single-valued mapping such that is r-strongly accretive and -Lipschitz continuous. Let be -accretive set-valued mapping. Suppose that is a generalized resolvent operator such that is -Lipschitz continuous and is a generalized Yosida approximation operator such that is -Lipschitz continuous. Suppose that the following conditions are satisfied:
where .
Let , for all such that
where all contants are positive and is an extrapolating term.
Then, sequence generated by the scheme 3 strongly converges to the unique solution of Yosida variational inclusion problem (1).
Proof.
Let be the solution of Yosida variational inclusion problem (1). Using (4), we have
where , for all . Using (7) and (22), we evaluate
Applying the Lipschitz continuity of generalized resolvent operator and generalized Yosida approximation operator , from (23), we obtain
From (6), we have
Thus, we have
Letting , from condition (19). By condition (21), we have and . Setting and . Then, by Lemma 2 and (26), we have , as . Thus, the sequence generated by scheme 3 strongly converges to the unique solution of Yosida variational inclusion problem (1). Furthermore, we show that the solution of Yosida variational inclusion problem (1) is unique.
Let be the two solutions of Yosida variational inclusion problem (1). Then, by Lemma 3, we have
Now, we study the convergence analysis of scheme 8 for Yosida resolvent equation problem (8) in the setting of q-uniformly smooth Banach space. Note that by Lemma 4, Yosida variational inclusion problem (1) is equivalent to Yosida resolvent equation problem (8). As Yosida variational inclusion problem (1) admits a unique solution, Yosida resolvent equation problem (8) also admits a unique solution.
Theorem 2.
Let be q-uniformly smooth Banach space and be single-valued mapping such that is one–one, -Lipschitz continuous, -expansive and r-strongly accretive.
Let be -accretive set-valued mapping and be a generalized resolvent operator such that is -Lipschitz continuous. Let be a generalized Yosida approximation operator such that is -strongly accretive with respect to and -Lipschitzcontinuous. Let , where . Suppose that the following conditions are satisfied.
Let , for all such that
where is a constant, is the same as in Lemma 1, and , and all the constants are positive.
Then, sequences and generated by scheme 8 strongly converge to the unique solution and of Yosida resolvent equation problem (8).
5. Numerical Experiment
In support of Theorem 1, construct the following numerical example using MATLAB 2015a with a computation table and convergence graph.
Example 1.

Let with usual inner product and norm, be single-valued mapping and be set-valued mapping such that
(i) is r-strongly accretive and -Lipschtiz continuous.
Thus, is -strongly accretive mapping.
In addition,
Thus, is -Lipschitz continuous mapping.
(ii) M is -accretive.
That is, M is accretive and also for , it is easy to verify that
Thus, M is -accretive mapping.
(iii) For , we define a generalized resolvent operator
In addition,
Thus, the generalized resolvent operator is -Lipschitz continuous.
(iv) Based on step (iii), we calculate the generalized Yosida approximation operator
In addition,
Thus, the generalized Yosida approximation operator is -Lipschitz continuous.
(vi) For and , inertial extrapolation scheme 8 has the following model:
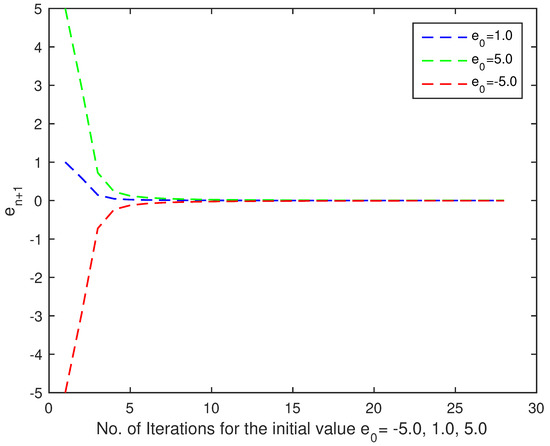
It is shown through a computation table (Table 1) and convergence graph (Figure 1) that for different initial values , the sequence converges to , which is the solution of Yosida variational inclusion problem (1). For the composition of a computation table and convergence graph, we use the tools of MATLAB 2015a.

Table 1.
Computation outputs for different initial values and .

Figure 1.
Graphical representation of convergence of sequence with different initial values and .
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we have considered and studied a Yosida variational inclusion problem with its corresponding Yosida resolvent equation problem. Using the resolvent operator technique, it is shown that both the problems are equivalent under appropriate conditions. We mention the number of iterative schemes for solving both the problems. We concentrate our study on the convergence analysis of both the problems applying an inertial extrapolation scheme. For illustration, an example is constructed.
One can extend our results in higher-dimensional spaces. Engineers, physicists and other scientists may use our result for their practical purposes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.K.R. and R.A.; methodology, Y.W.; software, A.K.R.; validation, M.I. and Y.W.; formal analysis, M.I.; investigation, R.A.; resources, Y.W.; data curation, M.I.; writing—original draft preparation, A.K.R.; writing—review and editing, R.A. and J.-C.Y.; visualization, M.I.; supervision, R.A. and J.-C.Y.; project administration, J.-C.Y.; funding acquisition, Y.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 12171435).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
All authors are thankful to all referees for their valuable suggestions which improve this paper a lot.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hassouni, A.; Moudafi, A. A perturbed algorithm for variational inclusions. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 1994, 185, 706–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Ansari, Q.H. An iterative algorithm for generalized nonlinear variational inclusions. Appl. Math. Lett. 2000, 13, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, Q.H.; Yao, J.C. A fixed point theorem and its applications to a system of variational inequalities. Bull. Aust. Math. Soc. 1995, 159, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.P.; Luo, C.L. Perturbed proximal point algorithms for general quasi-variational like inclusions. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2000, 113, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannessi, F.; Maugeri, A. Variational Inequalities and Network Equilibrium Problems; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Yao, J.C. Iterative methods for solving variational inequality problems with a double-hierarchical structure in Hilbert spaces. Optimization 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Postolache, M.; Yao, J.C. An Iterative Algorithm for Solving Generalized Variational Inequalities and Fixed Points Problems. Mathematics 2019, 7, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.J. A new class of generalized set-valued implicit variational inclusions in Banach spaces with an application. Comput. Math. Appl. 2001, 41, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, M.A. Generalized mixed variational inequalities and resolvent equations. Positivity 1997, 1, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, M.A. Generalized set-valued variational inclusions and resolvent equations. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 1998, 228, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaka, M.; Tomomi, Y. Applications of the Hille-Yosida theorem to the linearized equations of coupled sound and heat flow. AIMS Math. 2016, 1, 165–177. [Google Scholar]
- De, A. Hille-Yosida Theorem and Some Applications. Ph.D Thesis, Central European University, Budapest, Hungary, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sinestrari, E. On the Hille-Yosida Operators; Dekker Lecture Notes; Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1994; Volume 155, pp. 537–543. [Google Scholar]
- Sinestrari, E. Hille-Yosida Operators and Cauchy Problems. Semigroup Forum 2011, 82, 10–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosida, K. Functional Analysis; Grundlehren der Mathematischen Wissenschaften; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1971; Volume 123. [Google Scholar]
- Polyak, B.T. Some methods of speeding up the convergence of iteration methods. USSR Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 1964, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, S.; Noor, M.A.; Noor, K.I. Inertial inerative methods for general quasi-variational inequalities and dynamical systems. J. Math. Anal. 2020, 11, 14–29. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, B.; Cho, S.Y. An inertial Mann-like algorithm for fixed points of nonexpansive mappings in Hilbert spaces. J. Appl. Numer. Optim. 2020, 2, 335–351. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, B.; Li, S. Strong Convergence of inertial Mann algorithms for solving hierarchical fixed point problems. J. Nonlinear Var. Anal. 2020, 4, 337–355. [Google Scholar]
- Maingé, P.E. Convergence theorem for inertial KM-type algorithms. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2008, 219, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.K. Inequalities in Banach spaces with applications. Nonlinear Anal. Theory Methods Appl. 1991, 16, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Ali, I.; Rahaman, M.; Ishtyak, M.; Yao, J.C. Cayley inclusion problem with its corresponding generalized resolvent equation problem in uniformly smooth Banach spaces. Appl. Anal. 2020, 101, 1354–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.K. Iterative algorithms for nonlinear operators. J. Lond. Math. Soc. 2002, 66, 240–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockafellar, R.T. Monotone operators and the proximal point algorithms. SIAM J. Control Optim. 1976, 14, 877–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).