Abstract
In this paper, we introduce the property on Banach lattices and present its characterization in terms of disjoint sequences. Then, an example is given to show that an order-to-norm continuous operator may not be -order continuous. Suppose is an order-bounded operator from Dedekind -complete Banach lattice E into Dedekind complete Banach lattice F. We prove that T is -order-to-norm continuous if and only if T is both order weakly compact and -order continuous. In addition, if E can be represented as an ideal of , where is a -finite measure space, then T is -order-to-norm continuous if and only if T is order-to-norm continuous. As applications, we extend Wickstead’s results on the order continuity of norms on E and .
Keywords:
Banach lattices; property (h); order weakly compact operators; order-to-norm continuous operators; σ-order continuous operators MSC:
46A40; 46B42; 47B65
1. Introduction
Throughout this paper, E and F will denote Banach lattices, whereas X and Y will denote Archimedean Riesz spaces. The set of all positive vectors of X is called the positive cone of X, and is denoted by . Similarly, . A net in X is said to be order convergent to x, written as , if there exists another net in X satisfying , such that for all . Put . The net in X converges e-uniformly to x if there exists a positive real number net with , such that for all . In this case, we write (e-ru). And the net in X converges relatively uniformly to x, denoted by , if there exists e in such that converges e-uniformly to x. Every relatively uniformly convergent sequence is also order convergent.
Recall that E is said to
- Have an order-continuous norm if whenever in E.
- Have a -order continuous norm if whenever in E.
- Be a space if every increasing norm-bounded sequence in has a norm limit.
The concepts of order convergence and relative uniform convergence are identical on E if and only if E has an order-continuous norm; see [1] (Proposition 3). If H is a closed sublattice of E and , then in H if and only if in E; see [2] (Proposition 2.12).
Niculescu [3] extended Lozanovskii’s results on Banach lattices with -order continuous norms to type A operators defined on Banach lattices. In 2021, Jalili et al. continued the study of operator versions of order-continuous norm and introduced order-to-norm continuous operators (see [4]). An operator is said to be
- Type A if is norm convergent whenever in E.
- Order weakly compact if for every , is weakly compact in F.
- M weakly compact if for every norm-bounded disjoint sequence in E.
- Order-to-norm continuous if whenever in E.
- -order-to-norm continuous if whenever in E.
- order continuous if whenever in E.
- -order continuous if whenever in E.
In Theorem 2, we also present that every order-bounded -order-to-norm continuous operator into a Banach lattice with property (see Definition 1) can be defined in order relation. It is proved in [3] (Lemma 3.1) that type A operators and order weakly compact operators are equivalent. Moreover, is order weakly compact if and only if for every order bounded disjoint sequence in E. Meyer-Nieberg shows that every order weakly compact operator admits a factorization through a Banach lattice with an order continuous norm. These details can be found in [5] (Theorem 3.4.6) and [6] (Theorem 5.58). Now, we are in position to list some necessary notes. The natural factorization of occurs through a quotient space. We define lattice seminorm on E as for every . Let be the null ideal of . And let denote the canonical projection. Suppose that is the norm completion of normed Riesz space under the quotient norm . The formula gives rise to a well-defined continuous operator with . Hence, S extends to all of , satisfying . We have the factorization of T,
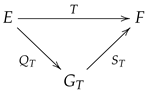
Moreover, if is order bounded and F is Dedekind complete, then the modulus of T exists. Given any , , hence
To see , put . Since for every , by [6] (Theorem 1.18), we have . It follows that
In this paper, we mainly study the relative uniform order convergence of sequence on Banach lattices. At the same time, the main results of the article relate to the properties of -order-to-norm continuous and order-to-norm continuous operators. We refer the reader to [5,6,7,8] for unexplained terminology on Banach lattices.
2. Banach Lattices with Property ()
Every relatively uniformly convergent sequence converges in norm. However, the opposite may be not true. denotes the sequence of real numbers whose term is one and the rest are zero. in but not relatively uniformly convergent. Recall that E is said to be an -space if for . In [9] (Proposition 2), Wirth proved that E is isomorphic to an -space if and only if every norm convergent sequence in E is relatively uniformly convergent and if and only if every norm convergent sequence in E is order convergent. If E is a -space or -order continuous Banach lattice, then for every sequence in E, if and only if and .
Definition 1.
The Banach lattice E has property (h), provided that if and only if and in E.
Example 1.
Let E be the -sum of the space sequence i.e.,
E is a Dedekind complete Banach lattice without order continuous norm under the pointwise ordering. In fact, E lacks property .
Proof.
Define a sequence in E by
Evidently, is an order-bounded disjoint norm null sequence and for all m. We claim that is not true. Otherwise, there exists and a real number sequence satisfying , such that for all . It follows that for every ,
This implies that
for every m. We obtain a contradiction. □
Recall that in a discrete Banach lattice E, for every order bounded norm null sequence in E.
Proposition 1.
Let E be a discrete Dedekind σ-complete Banach lattice. The following assertions are equivalent.
- (1)
- E has property (h).
- (2)
- if and only if is order bounded and .
Recall that Riesz space X has principal projection property if and only if every principal band is a projection band i.e., for every , exists for each . In this case, for , the band projection from E onto by is defined by for every , where is the principal band generated by u in E. By [6] (Theorem 1.47), every Dedekind -complete Riesz space has principal projection property. The following lemmas will be useful in the sequel discussions of property .
Lemma 1
([5], Proposition 2.8.2). If Riesz space X has principal projection property, then the following statements are hold.
- (1)
- For any in , there exist disjoint elements in X, such that and .
- (2)
- For any in with , there exist disjoint elements in X, such that and .
Lemma 2
([6], Theorem 4.12). Let X be a Riesz space and in X. For every , there exist disjoint sequences of , such that for each n,
Lemma 3
([10], Theorem 105.15). If and in E, then in E.
Next, we characterize Banach lattices with property in terms of disjoint sequences.
Theorem 1.
Let E be a Dedekind σ-complete Banach lattice. The following assertions are equivalent.
- (1)
- E has property (h).
- (2)
- for every order-bounded disjoint norm null sequence in E.
Proof.
is evident. Let and . Since E is a Dedekind -complete Banach lattice, according to [5] (Proposition 1.1.10), implies . We assert that . Next, we prove the assertion by contradiction. Assume that is not true. According to [11] (Theorem 15.4), is not a Cauchy sequence since . Thus, we can find and a subsequence of , such that
for every . Note that . According to Lemma 2, there are disjoint sequences , such that for every n,
It follows from that for every and . By Lemma 1, for every and there exist pairwise disjoint elements , such that and for each . It follows that the order-bounded disjoint sequence is for every . Therefore, according to the assumption of , . We can find and , such that for every j and for every i and j. Therefore,
Letting , we determine that for every k. This is a contradiction. Hence, . According to Lemma 3, . This implies . □
Remark 1.
Let and be two sequences in Riesz space X. is said to be dominated by , written as , if for every . According to the proof of Theorem 1, for every sequence in Dedekind σ-complete Banach lattice, if and only if the following statements hold:
- (1)
- .
- (2)
- If , then .
In general, the property cannot imply or order-continuous property.
Example 2.
Let E be the -sum of the space sequence i.e.,
E is a Dedekind complete Banach lattice. Evidently, E is neither -space nor an order-continuous Banach lattice. However, E has property .
Proof.
Suppose that and is a disjoint norm null sequence in , where . For every , define the projection by for every . Now, fixed m, is a disjoint norm null sequence in . Note that is an -space. It follows that in for every m. For fixed , there exists , such that . Therefore,
For every , . Given any , since . It follows that
Therefore, . According to Lemma 3, we obtain . □
In general, every Dedekind -complete Banach lattice contains a norm closed ideal which has property (h).
Definition 2.
Let E be a Banach lattice. An element is said to have property (h) if every disjoint sequence with is uniformly convergent. The collection of all elements that have property (h) is denoted by .
In Example 1, it is easy to verify that .
Theorem 2.
Let E be a Dedekind σ-complete Banach lattice. is a norm-closed ideal of E.
Proof.
- (1)
- is an ideal of E. Given any and , if is a disjoint sequence such that and , then due to the Riesz decomposition property of [6] (Theorem 1.13), there exist two positive disjoint sequences, and , such that and for every n. Then, for . This implies that . We obtain that for every and . It is easy to see that if and only . And the condition and can imply that . We have proved that is an ideal of E.
- (2)
- Assume that in E with . Let be a disjoint sequence in . For every , there exists , such that . It follows from that . Thus, we can find and a real number sequence with , such that for every n. For every , we have
It follows that is a disjoint sequence. According to Birkhoff’s inequalities (see [6], Theorem 1.9), for every ,
This implies that the series converges in its norm. Therefore, . According to Lemma 3, . This implies that . Based on the proceeding deduction, we conclude that . Hence, is a closed subspace of E. □
3. Order-to-Norm Continuous Operators on Banach Lattices
Evidently, every -order-to-norm continuous operator from a Dedekind -complete Banach lattice to another Banach lattice is order weakly compact. The identity operator on Banach lattice without -order continuous norm is neither order-to-norm continuous nor order weakly compact.
Example 3.
Let and . Then, there is an operator which is order-to-norm continuous and order weakly compact but not σ-order continuous.
Proof.
According to Dvoretzky–Rogers’ theorem (see [12], Theorem 2), there is an unconditionally convergent series in , such that for every n. Define by
for all . When using [13] (Corollary 2.5), T is not order bounded. Therefore, there exists , such that is not order bounded, i.e., is not order bounded. Note that is a space. is not norm bounded. Therefore, there exists an increasing sequence and a subsequence of , such that for every k. Define a sequence in by for every and . Clearly, . We claim that T is not -order continuous. Otherwise, T is -order continuous. This implies that . It follows that there is , such that for every i. Hence,
This is a contradiction. □
Every order-bounded -order-to-norm continuous operator in a Banach lattice with property can be defined in order.
Proposition 2.
Let be Banach lattices with F Dedekind complete. is an order-bounded operator. The following statements hold.
- (1)
- If T is σ-order-to-norm continuous, then T is σ-order continuous.
- (2)
- If F has property , then the following assertions are equivalent.
- ()
- for every in E.
- ()
- T is σ-order-to-norm continuous.
Proof.
- (1)
- Let in E. We have . It follows that . According to [6] (Theorem 1.56), T is -order continuous.
- (2)
- is evident. Note that and for every in E. Since F has property , we have .
□
Recall that a net in E is said to be laterally decreasing if for all . If E is Dedekind -complete, then is laterally decreasing to zero if and only if there is a disjoint sequence in , such that for every n.
Lemma 4
([14], Proposition 0.3.5). Let E be a Dedekind σ-complete Banach lattice. The following statements hold.
- (1)
- If in E, then for every and index , there exists a net satisfying , such that for all α and for . Therefore, there exists a laterally decreasing net such that for all α and for .
- (2)
- If in E, then for every , there exists an order-bounded disjoint sequence , such that and for all n.
Lemma 5
([5], Lemma 3.4.3). Let be a norm-bounded operator between two Banach lattices. Then, for every .
The -order-to-norm continuous operators have a number of nice characterizations.
Theorem 3.
Let E be a Dedekind σ-complete Banach lattice and F Dedekind complete. If is an order-bounded operator, then the following statements are equivalent.
- (1)
- T is σ-order-to-norm continuous.
- (2)
- admits a factorization through an order-continuous Banach lattice ,
 where the factor is a σ-order-to-norm continuous lattice homomorphism and is a norm-bounded operator.
where the factor is a σ-order-to-norm continuous lattice homomorphism and is a norm-bounded operator. - (3)
- for every order-bounded disjoint sequence in .
- (4)
- for every in E i.e., is a σ-order continuous functional for every .
- (5)
- for every in E.
- (6)
- for every in E.
- (7)
- T is order weakly compact and T is σ-order continuous.
Proof.
The derivation of the proof of this theorem is shown as follows
is obtained by [6] (Theorem 1.56). and are evident.
follows directly from Proposition 2.
Let in E. If , then passing to a subsequence, we assume that there exists , such that for every n. According to Lemma 5,
Therefore, for all n, we can find some satisfying . According to [6] (Theorem 1.18), . It follows that there exists , such that . Hence, and for every . This is a contradiction. We find that for every in E.
Suppose that is an order-bounded disjoint sequence in E. Since E is Dedekind -complete, exists in E. Therefore,
Note that has an order-continuous norm. . This implies that
Let be an order-bounded disjoint sequence in E. Evidently,
for any . To see , put . In view of [6] (Theorem 1.18), , there exists , such that . By our assumption in ,
It follows that
This implies that . Similarly,
So . The order continuity of norm on implies the series converges in norm. Therefore, in view of Lemma 5,
Let in E. Suppose that . According to Lemma 4, for every , there exists a positive disjoint sequence , such that and for every n. Therefore,
This implies that for every . Therefore, , hence .
By this assumption, T is an order weakly compact operator and is a -order continuous operator for every . Therefore, according to [5] (Theorem 3.4.4), is order weakly compact and is a -order continuous operator for every . We obtain that the series converges in norm for every order-bounded disjoint sequence in E. Given any an order-bounded disjoint sequence in , we also have . This implies that
The rest of the verification is contained in .
Suppose that T is order weakly compact and -order continuous. Let in E. Then, , according to [5] (Theorem 3.4.4), there exists , such that . Then, the -order continuity of T implies . Therefore, . We obtain that . □
Remark 2.
In the above theorem, since has an order continuous norm, T is σ-order-to-norm continuous. It is also equivalent to is σ-order continuous.
Let be the collection of all order-bounded -order-to-norm continuous operators from E to F. We are interested in when is an ideal in . Evidently, if F has an order-continuous norm, then, as demonstrated by Proposition 2 and [1] (Proposition 3), . Recall that a Banach lattice E is said to be order-bounded if the series converges in E for every unconditional convergent series in E with order bounded. And E has a weakly Fatou property if there exists such that for every net in E, it follows that .
Corollary 1.
Let Banach lattice be Dedekind complete and be an order-bounded operator. If one of the following statements holds
- (1)
- F is an -space with an order unit.
- (2)
- F is order bounded and F has a weakly Fatou property.
Thus, T is σ-order-to-norm continuous if and only if is σ-order-to-norm continuous.
In this case, is an ideal in .
Proof.
- (1)
- Suppose that F is an -space with an order unit and is a -order-to-norm continuous operator. According to Theorem 3, admits a factorization through an order-continuous Banach lattice ,
 where the factor is a -order continuous lattice homomorphism and is a norm-bounded operator. Since F has an order unit, is order bounded. Let in . We have . Therefore,
where the factor is a -order continuous lattice homomorphism and is a norm-bounded operator. Since F has an order unit, is order bounded. Let in . We have . Therefore, - (2)
- For every , we write the restriction of T to as , where is the ideal generated by x in E. Evidently, T is order weakly compact if and only if is weakly compact for every . According to S. Kakutani’ theorem (see [6], Theorem 4.29), for every , there is Hausdorff compact topological space K, such that is isomorphic to . In view of [15] (Theorem 3.3), is weakly compact for every . Therefore, is order weakly compact. It follows from the order continuity of T that is order continuous; see [6] (Theorem 1.56). By Theorem 3, is -order-to-norm continuous.
□
In general, may not be a band in . For example, let be the band projection from onto . Then, and is contained in . However, , the identity operator on , is not -order-to-norm continuous.
Theorem 4.
Let Banach lattice E be Dedekind complete. The followings are equivalent.
- (1)
- E has order continuous norm.
- (2)
- Every order-bounded operator from E to is σ-order-to-norm continuous.
- (3)
- Every order-bounded σ-order continuous operator from E to is σ-order-to-norm continuous.
Proof.
and are trivial.
If E is not order continuous, then there exists an order bounded sequence of disjoint elements such that . As shown by [14] (Proposition 0.5.5), the sublattice
is norm closed regular and order isomorphic to , where is the order limit of sequence . There exists an interval preserving projection P from E onto F; see [14] (Proposition 0.5.5). We can find satisfying and . Let be the band projection onto the band generated by in E. Set , then for , and , where and . The operator is defined by
for every . Clearly, P is a projection from E onto F. Now, define the lattice isomorphism by for every . Suppose that . Clearly, T is -order continuous. Note that
hence, does not converge to 0 in norm. This proves that the operator T is -order continuous but -order-to-norm continuous. □
Suppose that is a measure space and is the Riesz space of all real valued -measurable functions f on . Now, our aim comes down to studying the relationship between -order-to-norm continuous operators and order-to-norm continuous operators on the subspaces of . Recall that a Riesz subspace Z of X is called a regular sublattice of X if in Z implies in X.
Lemma 6.
Let E be a Dedekind σ-complete Banach lattice which is lattice isomorphic to a regular sublattice of . If is a finite measure space i.e., , then for every and every satisfying and , there exists a subsequence of , such that .
Proof.
Let . Suppose is a net in satisfying and . Identifying E with its copy in , put . Evidently, , where is the characteristic function of A. Fixed , it follows that in E and in , where . Since E is a regular sublattice of , for every , we have . Therefore, in E. Then, in ; hence, in , where represents real absolutely integrable functions on a measure space . By the continuity of norm on , . Therefore, there exists an increasing subsequence of , such that . It follows that in . This implies that in . We obtain that in E. □
Theorem 5.
Let E be a Dedekind σ-complete Banach lattice and F a Dedekind complete Banach lattice. is an order-bounded operator. If one of the following conditions holds:
- ()
- is a finite measure space and E is lattice isomorphic to a regular sublattice of ;
- ()
- is a σ-finite measure space and E is lattice isomorphic to an ideal of ;
then the following statements hold.
- (1)
- If T is a σ-order-to-norm continuous operator, then the following assertions hold.
- ()
- is an ideal in .
- ()
- is order continuous and is a band in E.
- ()
- T is order continuous.
- (2)
- T is σ-order-to-norm continuous if and only if T is order weakly compact and order continuous.
- (3)
- T is σ-order-to-norm continuous if and only if T is order-to-norm continuous.
- (4)
- Every σ-order continuous functional on E is order continuous.
Proof.
(1a) If , then . Put and (where ). Note that for some sequence in . Passing to a subsequence, we can assume that in . It follows that in . According to Remark 2, is -order continuous. We have
At the same time,
This implies that .
(1b) Firstly, in two cases, we will prove that is order continuous. To see this, it is sufficient to prove that for every in E. Let in E. For a fixed and given any , by Lemma 4, there exists a decreasing net , such that and for every .
- Case 1.
- The assertion is true.
According to Lemma 6, there exists a subsequence of , such that . Therefore, based on the statements and of Theorem 3, . For every ,
It follows that . Hence,
We have . This implies that for every in E. According to [6] (Theorem 1.56), is order continuous.
- Case 2.
- The assertion is true.
Since is a -finite measure space, there is a disjoint sequence of subsets of , such that and for all m. Identifying E with its copy in , since E is an ideal in , we have for every m. Then, . For every , put . Hence,
for every . Fixed , in since in for every m. Note that the band generated by in E is contained in . Then, in . In the view of Case 1, . Let . Without loss of generality, assume that for every .
We have for all m hence i.e., . Note that is -order continuous. We obtain
By the order continuity of norm on , . For every ,
Hence, . And implies that . We also obtain for every in E. According to [6] (Theorem 1.56), is order continuous.
Next, we prove that is a band in E. Since is a Riesz seminorm on E, is an ideal in E. If in E with , then . Note that has an order continuous norm. . We have hence . This implies taht is a band in E.
(1c) According to the proof of (1b), is order continuous; hence, it is also order-to-norm continuous. If in E, then in . We have . Hence, According to [6] (Theorem 1.56), T is order continuous.
and are obtained by and Theorem 3. is a simple indirect argument of . □
Recall that a net in E is said to be unbounded order convergent to 0 (or -converges to 0), written as , if for every . The details on unbounded order convergence can be found in [16,17]. As an application of -order-to-norm continuous operators, we give a characterization of -order continuous M-weakly compact operators.
Theorem 6.
Let E be Dedekind σ-complete Banach lattice and F Dedekind complete. If is an order-bounded operator, then the following statements are equivalent.
(1) for every norm-bounded in E.
(2) T is M-weakly compact and T is σ-order continuous.
Proof.
is obvious in Proposition 2.
This is similar to the proof of in Theorem 3 (replace “ in E” with “disjoint in ”) in which is M-weakly compact. Note that every M-weakly compact operator is order weakly compact. In view of Theorem 3 and Theorem 5, is order-to-norm continuous. According to [6] (Theorem 5.60), for every , there exists such that for every . Given any with , we have ; hence,
for every . This implies that . We obtain that . The proof is complete. □
Recall that is said to be L-weakly compact if every disjoint sequence in the solid hull of converges to zero. Meyer-Nieberg prove in [6] (Theorem 5.64) that the notions of L- and M-weakly compact operators are in duality to each other. By [6] (Theorem 1.73), every order-bounded operator has an order-continuous adjoint. Note that the norm dual of a Banach lattice is a Dedekind complete Banach lattice. We are now in the position to give a new characterization of L-weakly compact operators.
Corollary 2.
Let be Banach lattices and be an order-bounded operator. The following statements are equivalent.
for every norm-bounded in .
T is L-weakly compact.
In [17] (Theorem 5), A.W. Wickstead gave a characterization of the order continuity of norms on E and in terms of unbounded order convergent nets. To be precise, E and have order continuous norms if and only if every norm-bounded net in E which -converges to zero must converge weakly to zero. It does not suffice to consider only sequences in this equivalence, as is shown by the space of all continuous real-valued functions on the one point compactification of an uncountable discrete space. A norm-bounded -convergent sequence there must converge in norm, so certainly weakly ([18], Example 33.1).
Theorem 7.
Let E be a Banach lattice. The following statements are equivalent.
E is Dedekind σ-complete and for every norm-bounded in E.
E and have order-continuous norms.
Proof.
is by [17] (Theorem 5). Based on the assumption of , for every , for every norm-bounded . According to Theorem 6, for every , is M-weakly compact and -order continuous. In the view of [11] (Theorem 39.5), E has a -order continuous norm if and only if for each , whenever in E. We find that E has a -order continuous norm. Note that E is Dedekind -complete. According to [14] (Theorem 1.1), E has an order-continuous norm. It is proved in [10] (Theorem 116.1) that has an order-continuous norm if and only if for every norm-bounded disjoint sequence in E. Note that every disjoint sequence must -converge to zero. Again, based on the assumption of , has an order-continuous norm. □
4. Conclusions and Recommendation
This paper under review aims to further explore -order-to-norm continuous and order-to-norm continuous operators. To prove that the -order-to-norm continuous operator can be defined using the order relation, we introduce a basic property of Banach lattices, namely the property (h). Theorem 3 plays an important role in this paper, in which we present a number of nice characterizations for a -order-to-norm continuous operator. This result is also the basis for our extension on Wickstead’s results on the order continuity of norms on E and .
This research can be categorized under the topic “Operators Acting on Banach Lattices and Related Applications”. Our future work is to extend these results to more general spaces (e.g., topological Riesz spaces) as well as applying them to the field of non-linear analysis. In [19], Çevik and Altun introduce and investigate a class of spaces equipped with vetor metrics, mainly vector metric spaces. One of the research components could be the application of relative uniform convergence to the fixed point theory on vector metric spaces. Based on [20,21,22], we could consider replacing order convergence, in the definition of vectorial convergence (see [19], Definition 2.4), with relative uniform convergence to obtain more of the properties of vectorially continuous functions (see [20], Definition 3).
Author Contributions
Methodology, F.Z. and Z.C.; validation, F.Z. and H.S.; investigation, F.Z. and H.S.; data curation, F.Z. and H.S.; project administration, H.S. and Z.C.; writing—original draft, F.Z. and Z.C.; writing—review and editing, Z.C. and H.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bedingfield, S.E.; Wirth, A. Norm and order properties of Banach lattices. J. Aust. Math. Soc. 1980, 29, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.A.; Troitsky, V.G. Bibasic sequences in Banach lattices. J. Funct. Anal. 2020, 278, 108448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, C. Order σ-continuous operators on Banach lattices. Banach Space Theory and its Applications. In Proceedings of the First Romanian-GDR Seminar, Bucharest, Romania, 31 August–6 September 1981; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 188–201. [Google Scholar]
- Jalili, S.A.R.; Azar, K.H.; Moghimi, M.B.F. Order-to-topology continuous operators. Positivity 2021, 25, 1313–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Nieberg, P. Banach Lattices; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; NewYork, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Aliprantis, C.D.; Burkinshaw, O. Positive Operators, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Aliprantis, C.D.; Burkinshaw, O. Locally Solid Riesz Spaces with Applications to Economics; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Luxemburg, W.A.J. Riesz Spaces; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wirth, A. Relatively uniform Banach lattices. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 1975, 52, 178–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaanen, A.C. Riesz Spaces II; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Zaanen, A.C. Introduction to Operator Theory in Riesz Spaces; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretzky, A.; Rogers, C.A. Absolute and unconditional convergence in normed linear spaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1950, 36, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, H.Y. On whether or not L(E,F)=Lr(E,F) for some classical Banach lattices E and F. Indag. Math. 1984, 87, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wnuk, W. Banach Lattices with Order Continuous Norms; Polish Scientific Publishers PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Groenewegen, G.; van Rooij, A. The modulus of a weakly compact operator. Math. Z. 1987, 195, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Troitsky, V.G.; Xanthos, F. Uo-convergence and its applications to Cesro means in Banach lattices. Isr. J. Math. 2017, 220, 649–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickstead, A.W. Weak and unbounded order convergence in Banach lattices. J. Aust. Math. Soc. 1977, 24, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luxemburg, W.A.J.; Zaanen, A.C. Notes on Banach function spaces. XI. Indag. Math. 1964, 26, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çevik, C.; Altun, I. Vector metric space and some properties. Topol. Met. Nonlinear Anal. 2009, 34, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çevik, C. On continuity functions between vector metric spaces. J. Funct. Spaces 2014, 2014, 753969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, H.; Abbas, M.; Soleimani Rad, G. Common fixed point results for four mappings on ordered vector metric spaces. Filomat 2015, 29, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, H. Best proximity point theory on vetor metric spaces. Commun. Fac. Sci. Univ. Ank. Ser. A1 Math. Stat. 2021, 70, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).