The Role of Second Language Reading Proficiency in Moderating Second Language Word Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Comparing Chinese and English Word Recognition
1.2. The Changing Patterns of L1 Influences on L2 Word Recognition
2. Materials and Methods
- (1)
- Do the Chinese EFL learners with higher and lower English reading proficiency differ in their sensitivity to phonological and orthographic information in English word meaning retrieval?
- (2)
- Do the Chinese EFL learners with higher and lower English reading proficiency differ in their processing skills of phonological and orthographic information in English word meaning retrieval?
2.1. Participants
2.2. Tasks
2.2.1. Reading Proficiency Test
2.2.2. Semantic Category Judgment Task
2.2.3. Phonological Processing Task
2.2.4. Orthographic Processing Task
2.2.5. Word Meaning Retrieval Task
2.2.6. Working Memory Test
2.3. Procedure
3. Results
3.1. RQ1: Do the Chinese EFL Learners with Higher and Lower English Reading Proficiency Differ in Their Sensitivity to Phonological and Orthographic Information in English Word Meaning Retrieval?
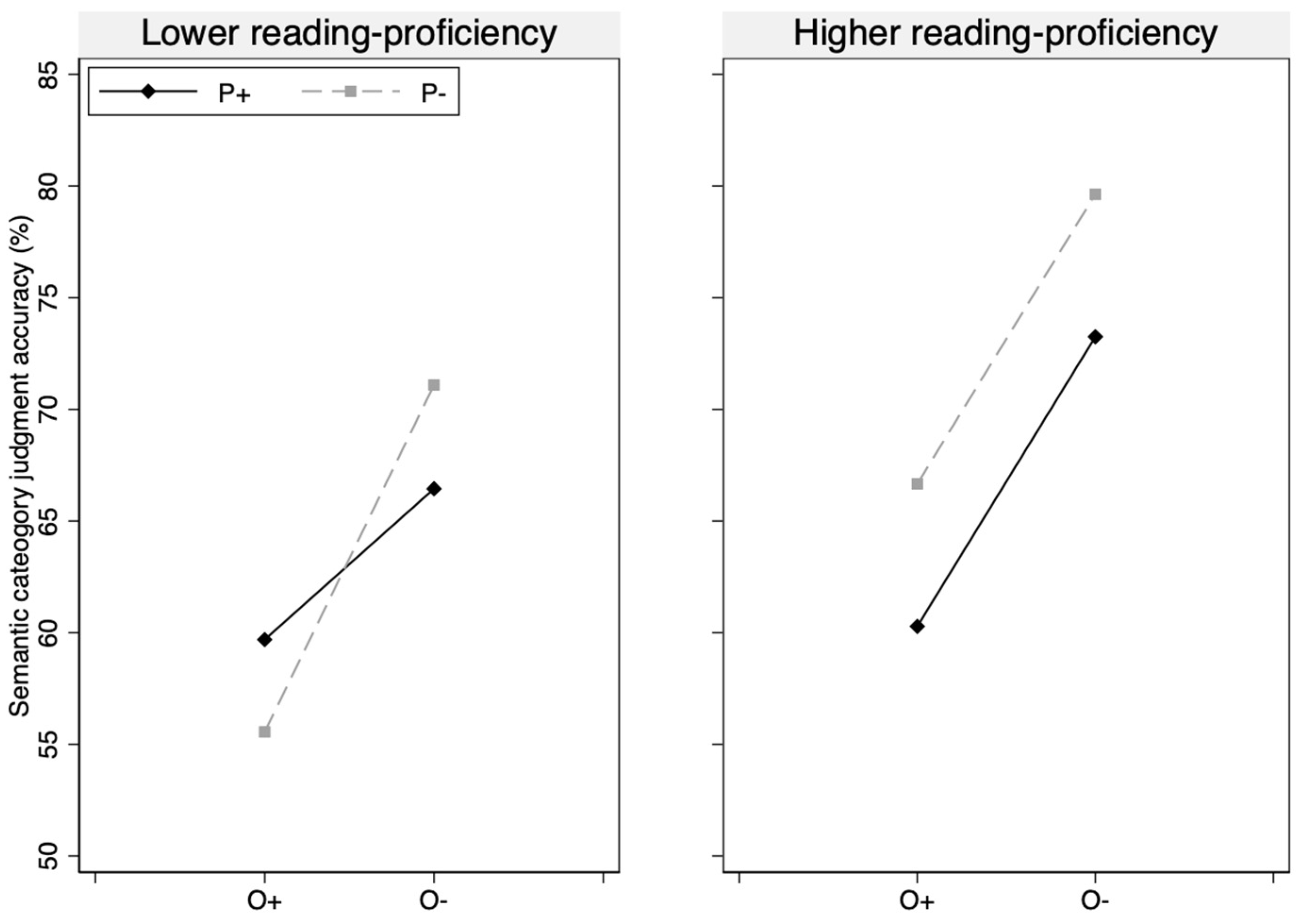
3.1.1. Accuracy Rates
3.1.2. Reaction Time
3.2. RQ2: Do the Chinese EFL Learners with Higher and Lower English Reading Proficiency Differ in Their Processing Skills of Phonological and Orthographic Information in English Word Meaning Retrieval?
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions, Implications, and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seidenberg, M.S. Beyond Orthographic Depth in Reading: Equitable Division of Labor. In Orthography, Phonology, Morphology, and Meaning; Frost, R., Katz, L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1992; Volume 94, pp. 85–118. ISBN 978-0-08-086748-9. [Google Scholar]
- Koda, K. Reading and Language Learning: Crosslinguistic Constraints on Second Language Reading Development. Lang. Learn. 2007, 57, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Koda, K. Linguistic Constraints on the Cross-Linguistic Variations in L2 Word Recognition. Read. Writ. 2022, 35, 1401–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, M.; Koda, K. The Role of Phonological Decoding in Second Language Word-Meaning Inference. Appl. Linguist. 2010, 31, 513–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride-Chang, C.; Suk-Han Ho, C. Predictors of Beginning Reading in Chinese and English: A 2-Year Longitudinal Study of Chinese Kindergartners. Sci. Stud. Read. 2005, 9, 117–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.T. English Orthography and Reading. TESOL Encycl. Engl. Lang. Teach. 2019, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Perfetti, C.A.; Fang, X.; Chang, L.-Y. Activation of L1 Orthography in L2 Word Reading: Constraints from Language and Writing System. Second Lang. Res. 2021, 37, 323–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koda, K. Development of Word Recognition in a Second Language. In Reading in a Second Language: Cognitive and Psycholinguistic Issues; Chen, X., Dronjic, V., Helms-Park, R., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 70–98. ISBN 978-1-315-88274-1. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, N.; Hou, F.; Jiang, X. Analytic Versus Holistic Recognition of Chinese Words Among L2 Learners. Mod. Lang. J. 2020, 104, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Yehudah, G.; Hirshorn, E.A.; Simcox, T.; Perfetti, C.A.; Fiez, J.A. Chinese-English Bilinguals Transfer L1 Lexical Reading Procedures and Holistic Orthographic Coding to L2 English. J. Neurolinguistics 2019, 50, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Koda, K.; Perfetti, C.A. Alphabetic and Nonalphabetic L1 Effects in English Word Identification: A Comparison of Korean and Chinese English L2 Learners. Cognition 2003, 87, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, C.K.; Hau, K.T.; Cheng, P.W.; Tan, L.H. Exploring Two-Wave Reciprocal Structural Relations Among Orthographic Knowledge, Phonological Sensitivity, and Reading and Spelling of English Words by Chinese Students. J. Educ. Psychol. 2005, 97, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Perfetti, C.A.; Liu, Y. Chinese–English Biliteracy Acquisition: Cross-Language and Writing System Transfer. Cognition 2005, 97, 67–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snowling, M.J.; Hulme, C. Evidence-Based Interventions for Reading and Language Difficulties: Creating a Virtuous Circle. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 2011, 81, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfetti, C. Lexical Quality Revisited. In Developmental Perspectives in Written Language and Literacy: In Honor of Ludo Verhoeven; Segers, E., van den Broek, P., Eds.; John Benjamins Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 51–67. ISBN 978-90-272-6515-9. [Google Scholar]
- Seidenberg, M.S.; McClelland, J.L. A Distributed, Developmental Model of Word Recognition and Naming. Psychol. Rev. 1989, 96, 523–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.Y.C.; Braze, D.; Kukona, A.; Johns, C.L.; Tabor, W.; Van Dyke, J.A.; Mencl, W.E.; Shankweiler, D.P.; Pugh, K.R.; Magnuson, J.S. Individual Differences in Subphonemic Sensitivity and Phonological Skills. J. Mem. Lang. 2019, 107, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, U.; Bryant, P. Phonological Skills and Learning to Read; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 1-317-44155-9. [Google Scholar]
- Gottardo, A.; Yan, B.; Siegel, L.S.; Wade-Woolley, L. Factors Related to English Reading Performance in Children with Chinese as a First Language: More Evidence of Cross-Language Transfer of Phonological Processing. J. Educ. Psychol. 2001, 93, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Yan, M.; Laubrock, J.; Shu, H. Lexical and Sublexical Phonological Effects in Chinese Silent and Oral Reading. Sci. Stud. Read. 2019, 23, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; McBride, C. How Do Phonological Processing Abilities Contribute to Early Chinese Reading and Mathematics? Educ. Psychol. 2020, 40, 893–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, A.; Araújo, S.; Morais, I.S.; Faísca, L. Reading and Reading-Related Skills in Adults with Dyslexia from Different Orthographic Systems: A Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Dyslexia 2020, 70, 339–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apel, K.; Henbest, V.S.; Masterson, J. Orthographic Knowledge: Clarifications, Challenges, and Future Directions. Read. Writ. 2019, 32, 873–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harm, M.W.; Seidenberg, M.S. Computing the Meanings of Words in Reading: Cooperative Division of Labor Between Visual and Phonological Processes. Psychol. Rev. 2004, 111, 662–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, C.; Pan, D.J.; Mohseni, F. Reading and Writing Words: A Cross-Linguistic Perspective. Sci. Stud. Read. 2022, 26, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltheart, M.; Rastle, K.; Perry, C.; Langdon, R.; Ziegler, J. DRC: A Dual Route Cascaded Model of Visual Word Recognition and Reading Aloud. Psychol. Rev. 2001, 108, 204–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, I.; Taylor, M. Writing and Literacy in Chinese, Korean and Japanese; Revised Edition; John Benjamins Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; ISBN 978-90-272-8576-8. [Google Scholar]
- Perfetti, C.A. The Universal Grammar of Reading. Sci. Stud. Read. 2003, 7, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Orden, G.C. A ROWS Is a ROSE: Spelling, Sound, and Reading. Mem. Cognit. 1987, 15, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, R.L.; Pickering, S.J. Phonological and Visual Similarity Effects in Chinese and English Language Users: Implications for the Use of Cognitive Resources in Short-Term Memory. Biling. Lang. Cogn. 2010, 13, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Geva, E. Spelling Performance of Chinese Children Using English as a Second Language: Lexical and Visual–Orthographic Processes. Appl. Psycholinguist. 2003, 24, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride-Chang, C.; Chung, K.K.H.; Tong, X. Copying Skills in Relation to Word Reading and Writing in Chinese Children with and without Dyslexia. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2011, 110, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siok, W.T.; Fletcher, P. The Role of Phonological Awareness and Visual-Orthographic Skills in Chinese Reading Acquisition. Dev. Psychol. 2001, 37, 886–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Perfetti, C.A. GraphCom: A Multidimensional Measure of Graphic Complexity Applied to 131 Written Languages. Behav. Res. Methods 2018, 50, 427–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, L.; Perfetti, C. Universals in Learning to Read across Languages and Writing Systems. Sci. Stud. Read. 2022, 26, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, S.; Snowling, M.J. Cognitive Profiles of Poor Readers of Kannada. Read. Writ. 2011, 24, 657–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, N. The Effects of First Language Orthographic Features on Second Language Reading in Text. Lang. Learn. 2003, 53, 207–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Shu, H.; Miller, K.; Yan, M. Reliance on Orthography and Phonology in Reading of Chinese: A Developmental Study. J. Res. Read. 2018, 41, 370–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-C.; Flores d’Arcais, G.B.; Cheung, S.-L. Orthographic and Phonological Activation in Recognizing Chinese Characters. Psychol. Res. 1995, 58, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leck, K.J.; Weekes, B.S.; Chen, M.J. Visual and Phonological Pathways to the Lexicon: Evidence from Chinese Readers. Mem. Cognit. 1995, 23, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Shu, H.; McCandliss, B.D.; Zevin, J.D. Orthographic Influences on Division of Labor in Learning to Read Chinese and English: Insights from Computational Modeling. Biling. Lang. Cogn. 2013, 16, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.G.; Guo, Q.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Yang, L. Multiple Pathways by Which Compounding Morphological Awareness Is Related to Reading Comprehension: Evidence from Chinese Second Graders. Read. Res. Q. 2020, 55, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.H.; Liu, H.-L.; Perfetti, C.A.; Spinks, J.A.; Fox, P.T.; Gao, J.-H. The Neural System Underlying Chinese Logograph Reading. NeuroImage 2001, 13, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikamatsu, N. Developmental Word Recognition: A Study of L1 English Readers of L2 Japanese. Mod. Lang. J. 2006, 90, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pae, T.-I. A Simultaneous Analysis of Relations Between L1 and L2 Skills in Reading and Writing. Read. Res. Q. 2019, 54, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koda, K. Insights into Second Language Reading: A Cross-Linguistic Approach; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; ISBN 978-1-139-52484-1. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, K. Kanji Recognition by Second Language Learners: Exploring Effects of First Language Writing Systems and Second Language Exposure. Mod. Lang. J. 2013, 97, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Share, D.L. On the Anglocentricities of Current Reading Research and Practice: The Perils of Overreliance on an “Outlier” Orthography. Psychol. Bull. 2008, 134, 584–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel de Abreu, P.M.J.; Gathercole, S.E. Executive and Phonological Processes in Second-Language Acquisition. J. Educ. Psychol. 2012, 104, 974–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Chen, B. Processing Morphologically Complex Words in Second-Language Learners: The Effect of Proficiency. Acta Psychol. 2014, 150, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, J. Writing Systems, Reading Processes, and Cross-Linguistic Influences. In Writing Systems, Reading Processes, and Cross-Lingusitic Influences; Pae, H.K., Ed.; John Benjamins Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 267–292. ISBN 978-90-272-6405-3. [Google Scholar]
- Chitiri, H.-F.; Willows, D.M. Bilingual Word Recognition in English and Greek. Appl. Psycholinguist. 1997, 18, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komori, S. Eigo Wo Bogoto Suru Chuujoukyuu Nihongo Gakushusha No Kanjigoi No Ninchi Nituite: Otonoeikyo (Kanji Recognition of Intermediate-High Learners of Japanese Whose First Language Is English: Sound Effect on Word Recognition). In Proceedings of the Nihongo Kyoiku Gakkai Shunki Taikai (The Conference of the Society for Teaching Japanese as a Foreign Language), Tokio, Japan, 2017; pp. 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-W.; Schallert, D. The Relative Contribution of L2 Language Proficiency and L1 Reading Ability to L2 Reading Performance: A Test of the Threshold Hypothesis in an EFL Context. TESOL Q. 1997, 31, 713–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade-Woolley, L.; Geva, E. Processing Novel Phonemic Contrasts in the Acquisition of L2 Word Reading. Sci. Stud. Read. 2000, 4, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongbo, Y.; Xiangdong, G.U. A Review of Testing a Nation—The Social and Educational Impact of the College English Test in China. Contemp. Foreign Lang. Stud. 2015, 15, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Preacher, K.J.; Rucker, D.D.; MacCallum, R.C.; Nicewander, W.A. Use of the Extreme Groups Approach: A Critical Reexamination and New Recommendations. Psychol. Methods 2005, 10, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torgesen, J.K.; Wagner, R.K.; Rashotte, C. Test of Word Reading Efficiency, 2nd ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Massaro, D.W.; Venezky, R.L.; Taylor, G.A. Orthographic Regularity, Positional Frequency, and Visual Processing of Letter Strings. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 1979, 108, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koda, K. Development of L2 Intraword Orthographic Sensitivity and Decoding Skills. Mod. Lang. J. 1999, 83, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.I. L1 Impacts on L2 Component Reading Skills, Word Skills, and Overall Reading Achievement. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hebart, M.N.; Dickter, A.H.; Kidder, A.; Kwok, W.Y.; Corriveau, A.; Van Wicklin, C.; Baker, C.I. THINGS: A Database of 1,854 Object Concepts and More than 26,000 Naturalistic Object Images. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, A.R.; Kane, M.J.; Bunting, M.F.; Hambrick, D.Z.; Wilhelm, O.; Engle, R.W. Working Memory Span Tasks: A Methodological Review and User’s Guide. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2005, 12, 769–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- StataCorp. Stata Statistical Software: Release Version 18; StataCorp: College Station, TX, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Seidenberg, M.S. Constraining Models of Word Recognition. Cognition 1985, 20, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehri, L.C. Orthographic Mapping in the Acquisition of Sight Word Reading, Spelling Memory, and Vocabulary Learning. Sci. Stud. Read. 2014, 18, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Measures | Lower Reading Proficiency Group | Higher Reading Proficiency Group | All Participants |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | (n = 43) | (n = 47) | (n = 133) |
| Reading 1 | 12.77 (1.67) | 21.04 (2.30) | 17.17 (3.82) |
| WMR 2 | 64.44 (5.48) | 67.43 (4.56) | 66.62 (4.75) |
| WMR RT 3 | 1009.54 (136.09) | 1001.28 (156.04) | 1004.18 (139.25) |
| OP 4 accuracy | 54.05% (9.00%) | 57.67% (7.49%) | 55.48% (8.12%) |
| OP RT | 939.29 (319.75) | 1020.23 (244.46) | 996.43 (279.90) |
| PP 5 accuracy | 79.86% (15.17%) | 86.53% (9.13%) | 83.42% (11.71%) |
| PP RT | 3833.47 (1954.87) | 3310.96 (1281.47) | 3457.58 (1577.71) |
| Working memory | 10.09 (2.33) | 10.23 (1.94) | 10.22 (2.04) |
| SCT 6 O+P+ accuracy | 59.69% (22.22%) | 60.28% (19.93%) | 58.65% (20.16%) |
| SCT O+P+ RT | 1228.88 (244.51) | 1256.33 (254.48) | 1257.86 (248.39) |
| SCT O+P− accuracy | 55.56% (22.49%) | 73.25% (15.93%) | 63.13% (20.29%) |
| SCT O+P− RT | 1210.45 (200.86) | 1256.33 (154.48) | 1257.86 (248.39) |
| SCT O−P+ accuracy | 66.45% (19.44%) | 73.25% (15.93%) | 70.68% (18.70%) |
| SCT O−P+ RT | 1188.04 (245.77) | 1225.49 (245.14) | 1230.46 (273.61) |
| SCT O−P− accuracy | 71.10% (17.77%) | 79.60% (15.93%) | 75.08% (17.90%) |
| SCT O−P− RT | 1243.73 (227.83) | 1319.75 (307.05) | 1254.79 (260.04) |
| 1. | 2. | 3. | 4. | 5. | 6. | 7. | 8. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. WMR 1 scores | -- | −0.212 | −0.205 | 0.296 * | 0.239 | 0.167 | 0.023 | 0.203 |
| 2. WMR (RT 2) | −0.031 | -- | −0.012 | −0.200 | 0.019 | −0.104 | 0.057 | −0.118 |
| 3. Reading 3 | 0.362 * | −0.110 | -- | −0.005 | −0.117 | 0.060 | −0.027 | −0.075 |
| 4. OP 4 accuracy | 0.120 | −0.122 | 0.139 | -- | 0.285 | 0.313 * | 0.058 | 0.225 |
| 5. OP RT | 0.184 | 0.066 | 0.052 | 0.621 *** | -- | 0.138 | −0.214 | 0.302 * |
| 6. PP 5 accuracy | 0.422 ** | −0.053 | 0.238 ** | 0.183 | 0.125 | -- | −0.182 | −0.306 * |
| 7. PP RT | −0.180 | 0.102 | −0.132 | −0.105 | −0.107 | −0.207 | -- | −0.070 |
| 8. Working memory | 0.351 * | −0.296 | 0.036 | 0.083 | 0.024 | −0.018 | −0.145 | -- |
| Model | R | R2 | ΔR2 | B | SE | β | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | 0.494 | 0.244 | 0.244 ** | |||||
| Working memory | 0.782 | 0.324 | 0.336 | 2.444 | 0.019 * | |||
| Reading 1 | 1.138 | 0.451 | 0.347 | 2.525 | 0.016 * | |||
| Step 2 | 0.632 | 0.399 | 0.155 ** | |||||
| Working memory | 0.813 | 0.293 | 0.345 | 2.778 | 0.008 * | |||
| Reading | 0.999 | 0.409 | 0.305 | 2.439 | 0.019 * | |||
| PP 2 | 14.315 | 4.514 | 0.396 | 3.171 | 0.003 ** |
| Model | R | R2 | ΔR2 | B | SE | β | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.296 | 0.088 | 0.088 * | ||||||
| OP 1 | 0.180 | 0.087 | 0.296 | 2.080 | 0.043 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Chen, T. The Role of Second Language Reading Proficiency in Moderating Second Language Word Recognition. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14020193
Li X, Chen T. The Role of Second Language Reading Proficiency in Moderating Second Language Word Recognition. Education Sciences. 2024; 14(2):193. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14020193
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaomeng, and Tianxu Chen. 2024. "The Role of Second Language Reading Proficiency in Moderating Second Language Word Recognition" Education Sciences 14, no. 2: 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14020193
APA StyleLi, X., & Chen, T. (2024). The Role of Second Language Reading Proficiency in Moderating Second Language Word Recognition. Education Sciences, 14(2), 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14020193





