Spatial Effects and Mechanisms of the Digital Economy and Industrial Structure on Urban Carbon Emissions: Evidence from 274 Chinese Cities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypotheses
2.1. The Mechanisms Through Which the DE Affects the CEI
2.2. The Spatial Spillover Effects of the DE on Regional CEI
2.3. The Mediating Effect of Industrial Structure Upgrading Between the DE and CEI
2.4. The Mediating Effect of Industrial Structure Advancement on the Relationship Between the DE and CEI
2.5. Threshold Effect of the DE in the Relationship Between the DE and CEI
3. Research Design and Method
3.1. Variables and Data Description
- 1.
- Variables and Data Description
- 2.
- Independent Variable
- 3.
- Steps for Entropy Weight Method
- (1)
- Dimensionless Processing:
- (2)
- Calculating the Proportion of the Indicator Value for the i-th Project under the j-th Indicator:
- (3)
- Calculating the Entropy Value for the j-th Indicator:
- (4)
- Calculating the Entropy Weight for the j-th Indicator:
- (5)
- Calculating the Indicator Evaluation Score:
- 4.
- Mediating Variable
- 5.
- Control Variable Setting
- 6.
- Data Description and Descriptive Statistical Analysis
- 7.
- Weight matrix involved in this paper
- (1)
- Spatial distance matrix and calculation formula:
- (2)
- Adjacency matrix:
- (3)
- Economic geography nesting matrix:
- (4)
- Economic distance spatial weight matrix:
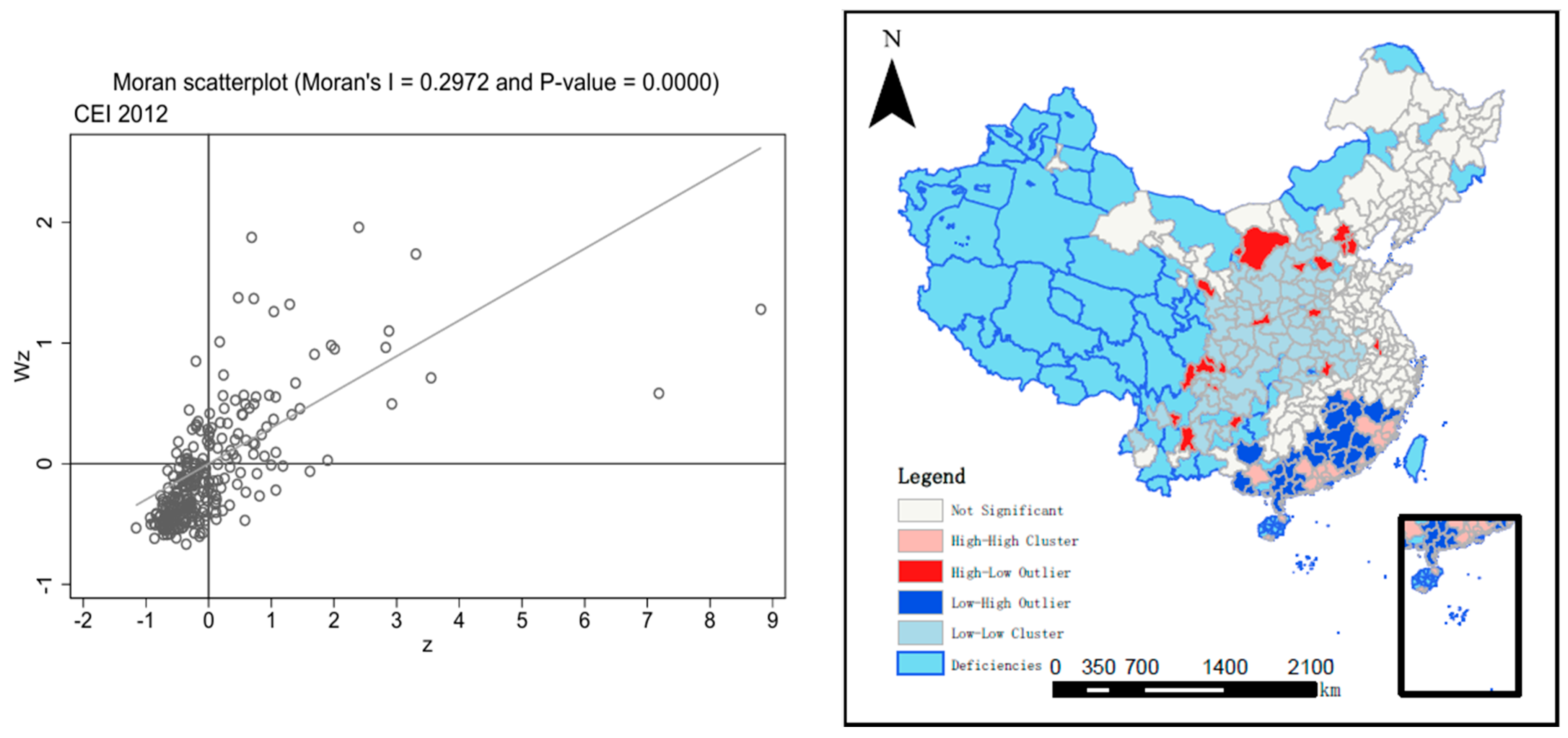
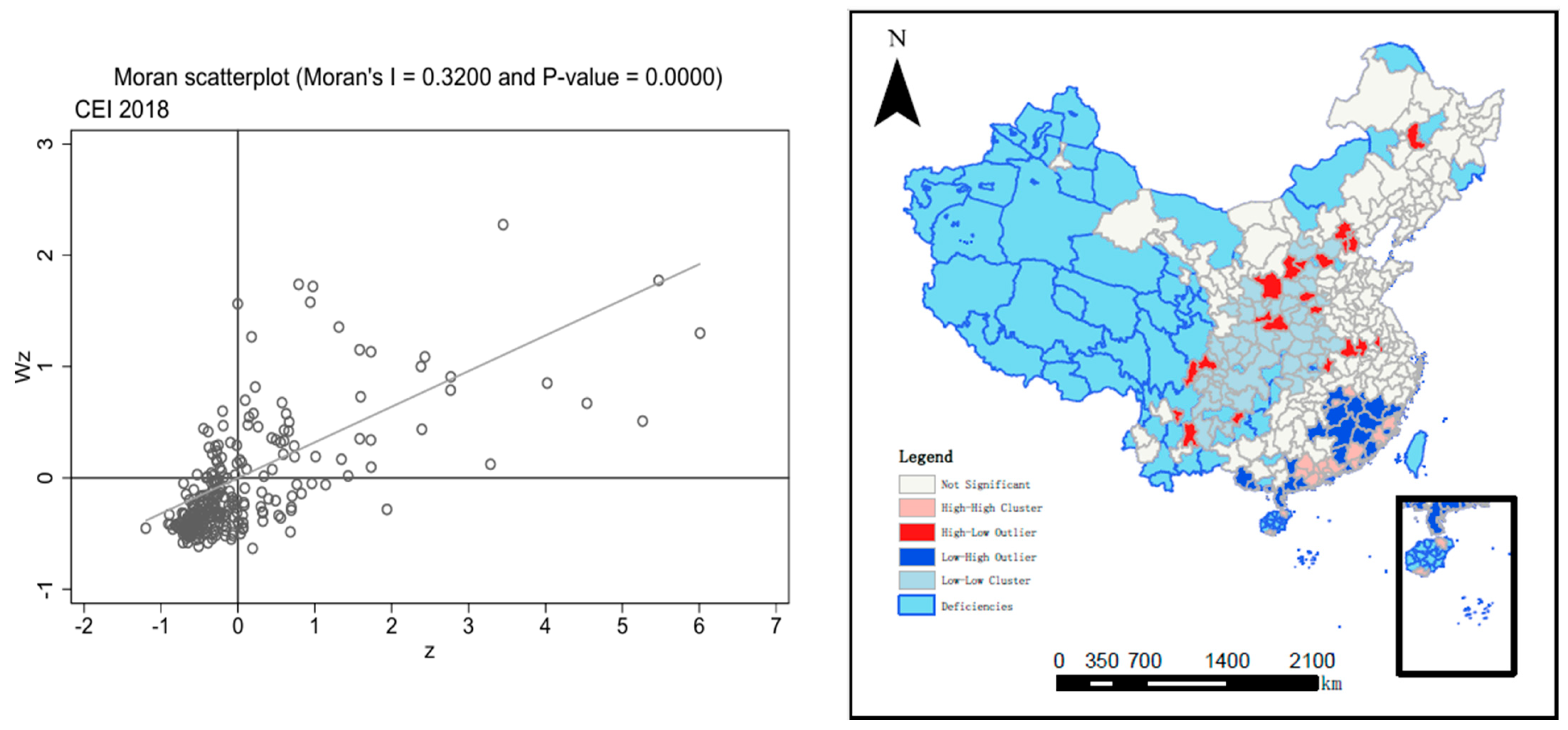
3.2. Spatial Autocorrelation Test of the CEI
3.3. Spatial Model Selection
3.4. Model Specification
3.4.1. Benchmark Model Specification
3.4.2. Spatial Durbin Model Specification
3.4.3. The Two-Region SDM Design
3.4.4. Mediation Effects Model
3.4.5. Threshold Model Design
4. Empirical Results Analysis and Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Basic Regression Results
4.2. Analysis of Spatial Empirical Results
4.2.1. Analysis of Spatial Durbin Regression Results
4.2.2. Spatial Durbin Decomposition Regression
4.2.3. The Decay Boundary of Spatial Spillover Effects
4.3. Robustness Check
4.4. Endogeneity Test
4.5. Heterogeneity Analysis
4.5.1. Eastern Cities
4.5.2. Central Cities
4.5.3. Western Cities
4.6. Further Differentiation Between Resource and Non-Resource Cities
4.7. Analysis of Intermediary Pathway Results
4.8. Analysis of Threshold Effects
5. Discussion, Conclusions, and Recommendations
5.1. Discussion
5.2. Conclusions
5.3. Recommendations
- (1)
- Promote regionally differentiated digital development strategies
- (2)
- Leverage resource-based cities as demonstration zones
- (3)
- Avoid overconcentration and diminishing returns of digital investment
- (4)
- Integrate digitalization with industrial upgrading and green finance
- (5)
- Encourage international cooperation and knowledge sharing
6. Limitations and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- An, Y., Zhou, D., Yu, J., Shi, X., & Wang, Q. (2021). Carbon emission reduction characteristics for China’s manufacturing firms: Implications for formulating carbon policies. Journal of Environmental Management, 284(4), 112055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, C. C., & Han, D. C. (2025). Can local government intervention promote corporate carbon neutral bond financing?—Intermediary effect based on regional innovation. Journal of Dalian Maritime University(Social Science Edition), 24(2), 82–91. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F. Z., & Jiang, G. H. (2023). The carbon reduction effect of the digital economy—Based on spatial panel data of 285 prefecture-level cities. Lanzhou Academic Journal, 5, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L. W., & Zhang, G. M. (2024). Research on the impact of digital financial inclusion and environmental regulation on industrial structure upgrading-based on spatial Durbin model analysis. PLoS ONE, 19(11), e0310720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y. M., Zhang, F. B., & Wang, X. H. (2025). Digital economy enabling low-carbon development—Spatial spillover and heterogeneity: Y. Ding et al. Empirical Economics, 69(2), 639–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F., Hu, M. Y., Gao, Y. J., Liu, Y. J., Zhu, J., & Pan, Y. L. (2022). How does digital economy affect carbon emissions? Evidence from global 60 countries. The Science of the Total Environment, 852, 158401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y. T., & Guan, S. (2023). The regionally heterogeneous impact of China’s environmental regulation on the transformation and upgrading of its industrial structure. Sustainability, 15(24), 16939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C. J., & Wang, C. G. (2024). Digitization and carbon emissions: How does the development of China’s digital economy affect carbon intensity? Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 31(18), 26895–26915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhorst, J. P. (2014). Spatial econometrics: From cross-sectional data to spatial panels. Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Elhorst, J. P., & Fréret, S. (2009). Evidence of political yardstick competition in France using a two-regime spatial Durbin model with fixed effects. Journal of Regional Science, 5, 931–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D. C., & Jia, M. Z. (2024). R&D Research on the impact of R&D resource mismatch on the efficiency of industrial green technology innovation: Based on the threshold effect of digital economy. Science Research Management, 45(6), 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, D., Yu, B. L., Hadachin, T., Dai, Y. J., Wang, Y., Zhang, S. N., & Long, R. Y. (2018). Drivers of carbon emission intensity change in China. Resources, Conservation & Recycling, 129, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C. H., Zheng, R. G., & Yu, D. F. (2011). An empirical study on the effects of Industrial Structure on economic growth and fluctuations in China. Economic Research Journal, 5(4), 16. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H., Xue, X., & Zhu, H. (2024). Developing digital dividends: Digital-economy-oriented indus-trial policy, digital technology innovation, and firms’ productivity. Applied Economics Letters, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H. P., & Zhang, L. (2021). The impact of digital inclusive financial development on the upgrading of industrial structure. Finance and Accounting Monthly, 3(9), 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R., Li, C., Yang, Y., Zhang, J., & Liu, K. (2023). Impact of digital economy development on carbon emission intensity in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region: A mechanism analysis based on industrial structure optimization and green innovation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 30(14), 41644–41664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P., & Liang, D. (2022). Does the low-carbon pilot policy improve the efficiency of urban carbon emissions: Quasi-natural experimental research based on low-carbon pilot cities. Journal of Natural Resources, 37(7), 1876–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B. E. (1999). Threshold effects in non-dynamic panels: Estimation, testing, and inference. Journal of Econometrics, 93(2), 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertwich, E. G. (2021). Increased carbon footprint of materials production driven by rise in investments. Nature Geoscience, 14(3), 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R., Zhang, S., & Wang, P. (2022). Key areas and pathways for carbon emissions reduction in Beijing for the “Dual Carbon” targets. Energy Policy, 164, 112873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W. B., Wang, Y. M., Yan, Y., Zhou, H. Y., Xu, L. Y., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, Y. Q. (2025). Digital economy, green finance, and carbon emissions: Evidence from China. Sustainability, 17(12), 5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, S. W., Wu, F. J., Shi, E. Y., Wu, X. H., & Du, M. Z. (2023). Does the digital economy promote the reduction of urban carbon emission intensity? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(4), 3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C. Y., & Zhou, W. S. (2024). Can digital economy development contribute to urban carbon emission reduction?—Empirical evidence from China. Journal of Environmental Management, 357, 120680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J. (2024). Impact of green finance on industrial structure upgrading: Implications for environmental sustainability in Chinese regions. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 31(9), 13063–13074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y. S., Li, F. P., & Li, X. (2022). Environmental regulation, digital inclusive finance and urban industrial upgrading-analysis based on spatial spillover effect and regulation effect. Inquiry into Economic Issues, 2022(1), 50–66. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z., & Wang, J. (2022). The dynamic impact of digital economy on carbon emission reduction: Evidence city-level empirical data in China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 351, 131570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C. Y. (2017). The study on the relationship between the tax burden and social consumption level in Xinjiang based on the panel threshold model under the background of “the belt and road”. West China Finance, 12(3), 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y. N., Chiu, Y. H., Chang, T. H., Lin, T. Y., & Chiu, S. Y. (2023). The impact of education level on residents’ carbon consumption in China. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 20(9), 9603–9618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, B., Guo, T. R., Wei, X., Kuang, M., & Jiang, L. (2023). Effects of digital economy on carbon emission intensity in Chinese cities: A life-cycle theory and the application of non-linear spatial panel smooth transition threshold model. Energy Policy, 183, 113792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B., Li, Y. K., Tian, X. Y., Sun, L. P., & Xiu, P. S. (2023). Can digital economy development contribute to the low-carbon transition? Evidence from the city level in China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(3), 2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, H. J., & Ryu, D. (2025). Does international trade moderate economic development’s impact on income inequality in the EU? Journal of International Financial Markets, Institutions and Money, 99, 102107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, E. M. (2003). Diffusion of innovations. In An integrated approach to communication theory and research (5th ed.). Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, S., Fan, M. T., & Yang, L. L. (2022). Economic restructuring, green technical progress, and low-carbon transition development in China: An empirical investigation based on the overall technology frontier and spatial spillover effect. Management World, 38(2), 46–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y. C., Tan, Z. S., Li, Q., & Xu, L. L. (2023). Can the digital economy promote the resilience of the tourism economy in the Yellow River Basin? Arid Land Geography, 46(10), 1704–1713. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, P., Williams, R., & Thomas, B. (2013). Are UK SMEs with active web sites more likely to achieve both innovation and growth? Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 20(4), 934–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittinghoff, E., Glidden, D. V., & Shiboski, S. C. (2012). Regression methods in biostatistics: Linear, logistic, survival, and repeated measures models. Springer Science & Business Media. [Google Scholar]
- Walenta-Bergmann, C., & Wi, T. (2024). The politics of subnational social policy: Social consumption versus social investment in Austria. Journal of European Social Policy, 34(4), 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., & Guo, D. (2023). Siphon and radiation effects of ICT agglomeration on green total factor productivity: Evidence from a spatial Durbin model. Energy Economics, 126, 106953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X., & Zhong, M. (2023). Can digital economy reduce carbon emission intensity? Empirical evidence from China’s smart city pilot policies. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 30(18), 51749–51769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijethunga, A. W. G. C. N., Rahman, M. M., & Sarker, T. (2025). Does financial development moderate the relationship between eco-nomic growth and environmental quality? Environmental and Sustainability Indicators, 27, 100728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooldridge, J. M. (2006). Introductory econometrics: A modern approach (3rd ed.). Thomson/South-Western, Mason. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, C., Zhang, Z. X., Shi, T., Yang, N., Shu, H., Chen, J., Mao, G. Z., Qi, Z. F., Rao, S., & Jiang, C. L. (2024). Climate synergistic benefits: A path to the beautiful China through total control of major air pollutants. Journal of Cleaner Production, 469, 143158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y. F., Wu, Y. Z., Qin, Y. L., & Fu, C. (2025). Mechanism and spatial spillover effect of the digital economy on carbon emission efficiency in Chinese provinces. Scientific Reports, 15(1), 19025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, M., Liu, X., & Luo, F. (2023). How does the development of urban agglomeration affect the electricity efficiency of resource-based cities?—An empirical research based on the fsQCA method. Socio-Economic Planning Sciences, 86, 101479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X. K., & Zhang, S. J. (2025). Carbon Emission Reduction Effect of Global Carbon Market: Market Mechanism and Administrative Intervention. Studies of International Finance, (5), 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X., Deng, Y., & Peng, L. (2022). Study on the impact of digital economy development on carbon emission intensity of urban agglomerations and its mechanism. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 30(12), 33142–33159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, R., Wang, C., Masron, T. A., & Ibrahim, H. (2025). Digital economy empowerment on carbon emission reduction: An analysis of spatial spillover effects based on temporal heterogeneity. Applied Economics, 57(35), 5359–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W., Liu, X., Wang, D., & Zhou, J. (2022). Digital economy and carbon emission performance: Evidence at China’s city level. Energy Policy, 165, 112927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. F., Cheng, K., Zou, Z. Z., & Wang, Z. B. (2025). The effect of digital economy development on carbon emission reduction—An empirical analysis based on 80 countries of the belt and road initiative. Sustainability, 17(3), 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. (2022). Analysis of China’s energy efficiency and influencing factors under carbon peaking and carbon neutrality goals. Journal of Cleaner Production, 370, 133604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z., Chen, L., Li, J., & Ding, S. Z. (2024). Digital economy development and carbon emission intensity-mechanisms and evidence from 72 countries. Scientific Reports, 14(1), 28459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T., Zhang, Z., & Liang, S. K. (2020). Digital economy, entrepreneurship, and high-quality economic development: Empirical evidence from urban China. Journal of Management World, 36(10), 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X. C., Jiang, M., & Zhou, Y. (2023). The impact of the digital economy on carbon emission intensity: Evidence from China. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J., Xiang, Y., & Tu, X. H. (2023). Digital economy, spatial spillover and carbon intensity: Concurrently on the threshold effect of human capital. Economic Research—Ekonomska Istraživanja, 36(2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X., Lu, Y., Yuan, J., Baninla, Y., Zhang, S., & Stenseth, N. C. (2020). Drivers of change in China’s energy-related CO2 emissions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, 117(1), 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q., Cheng, C., Fang, Z., Zhang, H., & Xu, Y. (2024). How does the development of the digital economy affect innovation output? Exploring mechanisms from the perspective of regional innovation systems. Structural Change and Economic Dynamics, 70, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, J. X., Xiao, S., Liu, S. S., & Chen, C. E. (2023). Passive sampling: A greener technique for the ‘dual carbon’ goal while implementing the action plan for controlling emerging pollutants. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol, 110, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Variable Name | Constituent Elements | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Economy Index | Inclusive Digital Finance Index | China City Statistical Yearbook |
| Number of Internet Users per 100 People | China City Statistical Yearbook | |
| Proportion of Workers in Information Transmission, Computer Services, and Software Industries | China City Statistical Yearbook | |
| Per Capita Telecommunications Volume (CNY in ten thousand) | China City Statistical Yearbook | |
| Number of Mobile Phone Users per 100 People | China City Statistical Yearbook |
| Variable | N | Mean | SD | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEI | 3288 | 0.099 | 0.092 | 0.004 | 0.892 |
| DE | 3288 | 0.345 | 0.333 | 0.006 | 2.885 |
| TC | 3288 | 2.310 | 0.144 | 1.821 | 2.835 |
| TCI | 3288 | 1.081 | 0.611 | 0.175 | 5.650 |
| GOV | 3288 | 0.201 | 0.101 | 0.044 | 0.916 |
| CON | 3288 | 0.384 | 0.109 | 0.001 | 1.013 |
| FDL | 3288 | 2.576 | 1.232 | 0.587 | 21.302 |
| PGDP | 3288 | 16.685 | 0.949 | 14.106 | 19.917 |
| EDU | 3288 | 0.176 | 0.039 | 0.036 | 0.356 |
| Year | Moran’s I | p-Value | Geary’s c | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 0.331 | 0.0000 | 0.204 | 0.025 |
| 2012 | 0.297 | 0.0000 | 0.223 | 0.015 |
| 2013 | 0.317 | 0.0000 | 0.211 | 0.016 |
| 2014 | 0.329 | 0.0000 | 0.213 | 0.0165 |
| 2015 | 0.337 | 0.0000 | 0.199 | 0.005 |
| 2016 | 0.371 | 0.0000 | 0.165 | 0.003 |
| 2017 | 0.320 | 0.0000 | 0.270 | 0.002 |
| 2018 | 0.319 | 0.0000 | 0.226 | 0.003 |
| 2019 | 0.348 | 0.0000 | 0.243 | 0.003 |
| 2020 | 0.348 | 0.0000 | 0.245 | 0.001 |
| 2021 | 0.332 | 0.0000 | 0.272 | 0.003 |
| 2022 | 0.449 | 0.0000 | 0.177 | 0.000 |
| Numerical Value | Numerical Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| LM-error | 1420.471 *** | R-LM-error | 1225.786 *** |
| LM-lag | 194.761 *** | R-LM-lag | 0.076 |
| LR-lrtest sdm_a sar_a | 55.52 *** | LR-lrtest sdm_a sem_a | 83.15 *** |
| wald-sdm | 21.4 *** | ||
| Hausman | 135.22 *** | ||
| Variables | VIF | 1/VIF |
|---|---|---|
| CEI | 2.24 | 0.447308 |
| GOV | 2.24 | 0.4473 |
| CON | 1.86 | 0.5368 |
| FDL | 1.46 | 0.6858 |
| PGDP2 | 2.85 | 0.3510 |
| EDU | 1.13 | 0.8848 |
| Mean VIF | 1.78 | |
| Variables | (1) | (2) |
|---|---|---|
| CEI | CEI | |
| DE | −0.038 *** (−7.88) | −0.114 *** (−5.44) |
| GOV | −0.070 (−0.90) | |
| CON | 0.229 *** (9.16) | |
| FDL | −0.025 *** (−3.36) | |
| PGDP2 | −0.123 *** (−9.93) | |
| EDU | −0.456 *** (−3.33) | |
| Constant | 0.112 *** (48.79) | 2.269 *** (9.87) |
| Individual Fixed | NO | NO |
| Time Fixed | NO | NO |
| Observations | 3288 | 3288 |
| Number of id | 274 | 274 |
| R-squared | 0.019 | 0.315 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEI | CEI | CEI | CEI | |
| DE | −0.030 *** (−3.02) | −0.123 *** (−4.90) | ||
| GOV | −0.069 ** (−2.37) | −0.269 *** (−3.75) | ||
| CON | 0.013 (1.17) | 0.068 ** (2.55) | ||
| FDL | −0.003 * (−1.86) | −0.006 * (−1.67) | ||
| PGDP | −0.025 *** (−3.64) | −0.054 *** (−3.32) | ||
| EDU | −0.206 *** (−5.06) | −0.443 *** (−4.05) | ||
| rho | 0.635 *** (25.06) | |||
| sigma2_e | 0.001 *** (39.72) | |||
| Individual Fixed | YES | |||
| Time Fixed | YES | |||
| Observations | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 |
| R-squared | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Number of id | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 |
| Variables | CEI | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect | |
| DE | −0.044 *** (−4.39) | −0.374 *** (−5.67) | −0.419 *** (−6.10) |
| GOV | −0.104 *** (−3.70) | −0.825 *** (−4.54) | −0.930 *** (−4.94) |
| CON | 0.023 ** (2.08) | 0.207 *** (3.049) | 0.230 *** (3.24) |
| FDL | −0.003 ** (−2.29) | −0.019 ** (−2.05) | −0.022 ** (−2.23) |
| PGDP | −0.0325 *** (−4.78) | −0.183 *** (−4.45) | −0.216 *** (−5.11) |
| EDU | −0.2671 *** (−6.31) | −1.490 *** (−5.08) | −1.757 *** (−5.66) |
| rho | 0.635 *** (25.057) | ||
| sigma2_e | 0.0012 *** (39.722) | ||
| Individual Fixed | YES | ||
| Time Fixed | YES | ||
| Observations | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 |
| R-squared | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Number of id | 274 | 274 | 274 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | CEI | CEI | CEI | CEI | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect |
| DE | −0.030 ** (−2.30) | −0.123 *** (−3.46) | −0.045 *** (−2.95) | −0.374 *** (−3.29) | −0.419 *** (−3.42) | ||
| GOV | −0.069 (−1.46) | −0.269 *** (−3.00) | −0.104 ** (−2.11) | −0.829 *** (−2.86) | −0.933 *** (−2.97) | ||
| CON | 0.013 (0.87) | 0.068 (1.51) | 0.024 (1.55) | 0.216 * (1.74) | 0.239 * (1.85) | ||
| FDL | −0.003 (−0.85) | −0.006 * (−1.70) | −0.003 (−1.06) | −0.020 (−1.61) | −0.023 (−1.58) | ||
| PGDP | −0.025 (−1.39) | −0.054 ** (−2.14) | −0.032 * (−1.66) | −0.186 ** (−2.23) | −0.218 ** (−2.32) | ||
| EDU | −0.206 * (−1.71) | −0.443 *** (−3.31) | −0.266 ** (−2.04) | −1.489 *** (−2.90) | −1.754 *** (−2.91) | ||
| rho | 0.635 *** (15.64) | ||||||
| sigma2_e | 0.001 *** (4.47) | ||||||
| Individual Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Time Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Observations | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 |
| R-squared | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Number of id | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | CEI | CEI | CEI | CEI | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect |
| DE | −0.040 *** (−4.12) | −0.128 *** (−4.60) | −0.052 *** (−4.99) | −0.307 *** (−5.13) | −0.359 *** (−5.64) | ||
| GOV | −0.118 *** (−4.10) | −0.146 * (−1.92) | −0.136 *** (−4.78) | −0.436 *** (−2.83) | −0.572 *** (−3.51) | ||
| CON | 0.024 ** (2.12) | 0.060 * (1.91) | 0.031 *** (2.71) | 0.157 ** (2.40) | 0.188 *** (2.67) | ||
| FDL | −0.004 ** (−2.45) | 0.001 (0.20) | −0.004 ** (−2.43) | −0.002 (−0.24) | −0.006 (−0.64) | ||
| PGDP | −0.031 *** (−4.80) | −0.060 *** (−3.52) | −0.038 *** (−5.50) | −0.159 *** (−4.33) | −0.197 *** (−5.00) | ||
| EDU | −0.249 *** (−5.92) | −0.594 *** (−4.79) | −0.307 *** (−7.12) | −1.481 *** (−5.63) | −1.788 *** (−6.37) | ||
| rho | 0.533 *** (18.80) | ||||||
| sigma2_e | 0.001 *** (39.86) | ||||||
| Individual Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Time Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Observations | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 |
| R-squared | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 |
| Number of id | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | CEI | CEI | CEI | CEI | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect |
| DE | −0.067 *** (−6.55) | −0.014 (−0.90) | −0.072 *** (−6.81) | −0.077 *** (−3.02) | −0.149 *** (−5.14) | ||
| GOV | −0.062 ** (−2.13) | −0.146 *** (−3.18) | −0.086 *** (−3.02) | −0.298 *** (−4.09) | −0.383 *** (−4.64) | ||
| CON | 0.020 (1.51) | −0.034 * (−1.74) | 0.018 (1.48) | −0.040 (−1.41) | −0.022 (−0.74) | ||
| FDL | −0.000 (−0.03) | −0.003 (−1.03) | −0.000 (−0.28) | −0.005 (−1.04) | −0.005 (−0.99) | ||
| PGDP | −0.063 *** (−7.34) | 0.027 *** (2.77) | −0.063 *** (−7.36) | −0.003 (−0.24) | −0.066 *** (−4.18) | ||
| EDU | −0.301 *** (−7.06) | −0.053 (−0.73) | −0.324 *** (−7.59) | −0.322 *** (−2.63) | −0.646 *** (−4.64) | ||
| rho | 0.464 *** (22.31) | ||||||
| sigma2_e | 0.001 *** (39.32) | ||||||
| Individual Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Time Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Observations | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 |
| R-squared | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 |
| Number of id | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | CEI | CEI | CEI | CEI | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect |
| DE | −0.018 ** (−2.37) | −0.066 *** (−3.32) | −0.025 *** (−3.13) | −0.165 *** (−3.90) | −0.190 *** (−4.29) | ||
| GOV | −0.055 ** (−2.40) | −0.092 (−1.55) | −0.067 *** (−3.06) | −0.266 ** (−2.20) | −0.333 *** (−2.67) | ||
| CON | 0.014 (1.58) | −0.040 * (−1.75) | 0.012 (1.42) | −0.066 (−1.41) | −0.054 (−1.10) | ||
| FDL | 0.000 (0.15) | −0.001 (−0.31) | 0.000 (0.07) | −0.002 (−0.26) | −0.002 (−0.23) | ||
| PGDP | −0.008 (−1.37) | −0.006 (−0.46) | −0.009 (−1.57) | −0.024 (−0.85) | −0.032 (−1.15) | ||
| EDU | −0.066 ** (−2.03) | −0.292 *** (−3.26) | −0.095 *** (−2.83) | −0.697 *** (−3.56) | −0.792 *** (−3.79) | ||
| rho | 0.555 *** (18.42) | ||||||
| sigma2_e | 0.001 *** (37.21) | ||||||
| Individual Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Time Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Observations | 2880 | 2880 | 2880 | 2880 | 2880 | 2880 | 2880 |
| R-squared | 0.044 | 0.044 | 0.044 | 0.044 | 0.044 | 0.044 | 0.044 |
| Number of id | 240 | 240 | 240 | 240 | 240 | 240 | 240 |
| Variables | 2sls | System-GMM |
|---|---|---|
| CEI | CEI | |
| L. CEI | 0.635 *** (33.62) | |
| DE | −0.110 *** (−4.13) | −0.120 *** (−8.10) |
| GOV | −0.135 *** (−3.56) | −0.292 *** (−7.17) |
| CON | 0.234 *** (15.40) | 0.253 *** (15.07) |
| FDL | −0.025 *** (−13.09) | −0.015 *** (−7.32) |
| PGDP | −0.141 *** (−20.55) | −0.119 *** (−17.16) |
| EDU | −0.593 *** (−9.27) | −0.588 *** (−7.89) |
| Constant | 2.160 *** (17.27) | |
| Kleibergen–Paap LM statistic | 945.768 | |
| p-value | 0.0000 | |
| Cragg–Donald Wald F statistic | 1441.134 | |
| AR(1)z and p-value | −6.6454 0.0000 | |
| AR(2)z and p-value | −0.84315 0.3991 | |
| Sargan test | 172 0.5423 | |
| Number of id | 274 | 274 |
| R-squared | 0.325 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | CEI | CEI | CEI | CEI | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect |
| DE | −0.138 *** (−3.05) | −0.403 *** (−3.94) | −0.197 *** (−3.92) | −0.969 *** (−4.27) | −1.166 *** (−4.63) | ||
| GOV | 0.133 (1.43) | −0.403 ** (−2.36) | 0.087 (0.98) | −0.679 ** (−2.10) | −0.592 * (−1.75) | ||
| CON | −0.079 *** (−3.22) | 0.017 (0.42) | −0.080 *** (−3.39) | −0.045 (−0.61) | −0.125 (−1.56) | ||
| FDL | −0.011 *** (−2.68) | −0.012 * (−1.81) | −0.013 *** (−3.11) | −0.035 ** (−2.51) | −0.048 *** (−2.99) | ||
| PGDP | −0.057 *** (−3.35) | −0.190 *** (−5.66) | −0.085 *** (−4.95) | −0.448 *** (−6.39) | −0.533 *** (−7.24) | ||
| EDU | −0.424 *** (−4.30) | −0.223 (−1.11) | −0.477 *** (−4.80) | −0.894 ** (−2.19) | −1.371 *** (−3.07) | ||
| rho | 0.536 *** (13.65) | ||||||
| sigma2_e | 0.002 *** (23.61) | ||||||
| Individual Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Time Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Observations | 1188 | 1188 | 1188 | 1188 | 1188 | 1188 | 1188 |
| R-squared | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.035 |
| Number of id | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | CEI | CEI | CEI | CEI | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect |
| DE | 0.002 (0.14) | −0.010 (−0.41) | 0.001 (0.12) | −0.015 (−0.40) | −0.013 (−0.33) | ||
| GOV | −0.069 ** (−2.20) | 0.020 (0.28) | −0.071 ** (−2.37) | −0.012 (−0.11) | −0.082 (−0.76) | ||
| CON | 0.021 * (1.77) | −0.011 (−0.41) | 0.022 ** (2.02) | −0.002 (−0.05) | 0.020 (0.53) | ||
| FDL | −0.000 (−0.31) | −0.000 (−0.11) | −0.000 (−0.34) | −0.001 (−0.13) | −0.001 (−0.20) | ||
| PGDP | −0.006 (−0.75) | 0.037 ** (2.39) | −0.003 (−0.45) | 0.053 ** (2.29) | 0.050 ** (2.16) | ||
| EDU | −0.095 ** (−2.26) | −0.166 * (−1.66) | −0.106 *** (−2.58) | −0.306 ** (−1.99) | −0.412 ** (−2.49) | ||
| rho | 0.382 *** (7.88) | ||||||
| sigma2_e | 0.000 *** (23.90) | ||||||
| Individual Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Time Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Observations | 1176 | 1176 | 1176 | 1176 | 1176 | 1176 | 1176 |
| R-squared | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.015 |
| Number of id | 98 | 98 | 98 | 98 | 98 | 98 | 98 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEI | CEI | CEI | CEI | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect | |
| DE | −0.032 *** (−3.13) | −0.056 ** (−2.39) | −0.035 *** (−3.33) | −0.081 *** (−2.74) | −0.116 *** (−3.84) | ||
| GOV | −0.054 (−1.52) | −0.303 *** (−3.45) | −0.069 ** (−2.03) | −0.403 *** (−3.76) | −0.472 *** (−4.17) | ||
| CON | 0.075 *** (3.74) | 0.031 (0.69) | 0.079 *** (4.10) | 0.068 (1.17) | 0.146 ** (2.33) | ||
| FDL | 0.010 ** (2.44) | 0.026 *** (2.93) | 0.011 *** (2.78) | 0.036 *** (3.29) | 0.047 *** (3.79) | ||
| PGDP | −0.004 (−0.39) | 0.008 (0.33) | −0.004 (−0.37) | 0.008 (0.27) | 0.004 (0.14) | ||
| EDU | −0.154 *** (−2.79) | −0.133 (−1.00) | −0.159 *** (−2.96) | −0.204 (−1.20) | −0.364 ** (−1.98) | ||
| rho | 0.238 *** (4.55) | ||||||
| sigma2_e | 0.001 *** (21.36) | ||||||
| Individual Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Time Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Observations | 924 | 924 | 924 | 924 | 924 | 924 | 924 |
| R-squared | 0.061 | 0.061 | 0.061 | 0.061 | 0.061 | 0.061 | 0.061 |
| Number of id | 77 | 77 | 77 | 77 | 77 | 77 | 77 |
| Variables | Economic Geography Matrix Results | Economic Geography Nested Matrix Results |
|---|---|---|
| ρ1 | 0.787 *** (32.710) | 3.362 *** (81.205) |
| ρ2 | 0.154 *** (3.579) | 1.192 *** (20.363) |
| ρ1 − ρ2 | 0.634 *** (13.323) | 2.170 *** (28.889) |
| DE | 0.019 ** (4.316) | 0.022 ** (5.244) |
| GOV | −0.003 (−0.153) | −0.089 *** (−6.910) |
| CON | −0.021 *** (−2.054) | −0.059 *** (−5.813) |
| FDL | 0.019 *** (19.274) | 0.023 *** (24.009) |
| PGDP | 0.017 *** (8.581) | 0.0029 *** (16.530) |
| EDU | −0.087 (0.5928) | −0.492 *** (16.069) |
| con | −0.016 *** (−7.116) | −0.004 * (−1.777) |
| w × DE | 0.005 (0.388) | −0.087 * (−1.867) |
| w × GOV | −0.084 *** (−2.156) | 0.631 *** (3.566) |
| w × CON | −0.005 (−0.175) | 0.096 (1.226) |
| w × FDL | −0.008 *** (−3.548) | −0.047 *** (−5.453) |
| w × PGDP | 0.015 *** (3.295) | −0.015 (−0.798) |
| w × EDU | 0.0004 (0.0007) | 0.955 *** (5.252) |
| Individual Fixed | NO | |
| Time Fixed | YES | |
| R2 | 0.6476 | 0.7033 |
| Observations | 3288 | |
| Number of id | 274 | |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TI | TI | TI | TI | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect | |
| DE | 0.069 *** (6.43) | −0.150 *** (−5.47) | 0.065 *** (5.98) | −0.172 *** (−4.85) | −0.107 *** (−3.00) | ||
| GOV | 0.022 (0.69) | −0.273 *** (−3.48) | 0.011 (0.38) | −0.348 *** (−3.51) | −0.336 *** (−3.41) | ||
| CON | 0.182 *** (14.68) | 0.018 (0.61) | 0.185 *** (15.87) | 0.084 ** (2.30) | 0.269 *** (7.32) | ||
| FDL | 0.006 *** (3.59) | 0.003 (0.71) | 0.006 *** (3.75) | 0.005 (1.12) | 0.011 ** (2.11) | ||
| PGDP2 | 0.032 *** (4.28) | −0.037 ** (−2.07) | 0.031 *** (4.21) | −0.038 * (−1.69) | −0.007 (−0.31) | ||
| EDU | 0.113 ** (2.53) | −0.385 *** (−3.23) | 0.102 ** (2.35) | −0.454 *** (−2.89) | −0.352 ** (−2.12) | ||
| rho | 0.248 *** (7.88) | ||||||
| sigma2_e | 0.002 *** (40.34) | ||||||
| Individual Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Time Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Observations | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 |
| R-squared | 0.456 | 0.456 | 0.456 | 0.456 | 0.456 | 0.456 | 0.456 |
| Number of id | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEI | CEI | CEI | CEI | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect | |
| TI | 0.092 *** (5.78) | 0.111 *** (2.70) | 0.110 *** (6.53) | 0.415 *** (4.31) | 0.526 *** (5.17) | ||
| DE | −0.035 *** (−3.59) | −0.113 *** (−4.47) | −0.050 *** (−5.25) | −0.331 *** (−5.39) | −0.381 *** (−6.02) | ||
| GOV | −0.065 ** (−2.26) | −0.262 *** (−3.64) | −0.094 *** (−3.41) | −0.748 *** (−4.31) | −0.841 *** (−4.71) | ||
| CON | −0.005 (−0.39) | 0.037 (1.33) | −0.001 (−0.09) | 0.085 (1.28) | 0.084 (1.20) | ||
| FDL | −0.003 ** (−2.34) | −0.007 ** (−2.01) | −0.004 *** (−2.90) | −0.022 ** (−2.31) | −0.026 ** (−2.56) | ||
| PGDP2 | −0.028 *** (−4.10) | −0.056 *** (−3.43) | −0.035 *** (−5.07) | −0.181 *** (−4.60) | −0.216 *** (−5.24) | ||
| EDU | −0.211 *** (−5.19) | −0.403 *** (−3.68) | −0.265 *** (−5.92) | −1.316 *** (−4.76) | −1.581 *** (−5.38) | ||
| rho | 0.616 *** (23.72) | ||||||
| sigma2_e | 0.001 *** (39.48) | ||||||
| Individual Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Time Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Observations | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 |
| R-squared | 0.019 | 0.019 | 0.019 | 0.019 | 0.019 | 0.019 | 0.019 |
| Number of id | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCI | TCI | TCI | TCI | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect | |
| DE | −0.226 *** (−4.14) | −0.634 *** (−4.54) | −0.240 *** (−4.36) | −0.807 *** (−4.80) | −1.047 *** (−6.28) | ||
| GOV | 1.227 *** (7.61) | −0.917 ** (−2.29) | 1.203 *** (7.85) | −0.840 * (−1.82) | 0.363 (0.80) | ||
| CON | 0.564 *** (8.97) | −0.321 ** (−2.14) | 0.565 *** (9.48) | −0.252 (−1.47) | 0.313 * (1.82) | ||
| FDL | 0.049 *** (6.22) | 0.111 *** (5.66) | 0.052 *** (6.77) | 0.143 *** (6.24) | 0.195 *** (7.88) | ||
| PGDP2 | −0.244 *** (−6.40) | −0.139 (−1.54) | −0.249 *** (−6.61) | −0.220 ** (−2.06) | −0.469 *** (−4.61) | ||
| EDU | 1.493 *** (6.58) | −1.330 ** (−2.20) | 1.475 *** (6.69) | −1.234 * (−1.67) | 0.241 (0.31) | ||
| rho | 0.179 *** (5.43) | ||||||
| sigma2_e | 0.039 *** (40.45) | ||||||
| Individual Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Time Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Observations | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 |
| R-squared | 0.061 | 0.061 | 0.061 | 0.061 | 0.061 | 0.061 | 0.061 |
| Number of id | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | CEI | CEI | CEI | CEI | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect |
| TCI | −0.000 (−0.08) | 0.049 *** (5.72) | 0.005 (1.47) | 0.121 *** (5.87) | 0.126 *** (5.78) | ||
| DE | −0.026 *** (−2.63) | −0.108 *** (−4.26) | −0.039 *** (−4.12) | −0.305 *** (−4.94) | −0.344 *** (−5.39) | ||
| GOV | −0.062 ** (−2.11) | −0.334 *** (−4.59) | −0.097 *** (−3.50) | −0.923 *** (−5.22) | −1.021 *** (−5.61) | ||
| CON | 0.016 (1.39) | 0.048 * (1.77) | 0.022 * (1.91) | 0.143 ** (2.22) | 0.165 ** (2.45) | ||
| FDL | −0.004 *** (−2.58) | −0.009 ** (−2.46) | −0.005 *** (−3.25) | −0.027 *** (−2.77) | −0.032 *** (−3.03) | ||
| PGDP2 | −0.023 *** (−3.30) | −0.048 *** (−2.96) | −0.029 *** (−4.07) | −0.154 *** (−3.94) | −0.183 *** (−4.44) | ||
| EDU | −0.200 *** (−4.87) | −0.468 *** (−4.27) | −0.260 *** (−5.81) | −1.462 *** (−5.29) | −1.721 *** (−5.88) | ||
| rho | 0.616 *** (23.80) | ||||||
| sigma2_e | 0.001 *** (39.49) | ||||||
| Individual Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Time Fixed | YES | ||||||
| Observations | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 | 3288 |
| R-squared | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 |
| Number of id | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 | 274 |
| Threshold Variables | Threshold Number | p-Value | Threshold Value | Boundary Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | 5% | 1% | ||||
| CE | 1 | 0.048 | 0.0326 | 27.6839 | 33.9259 | 43.6923 |
| Variables | (1) |
|---|---|
| CEI | |
| GOV | −0.066 * (−1.94) |
| CON | 0.226 *** (15.81) |
| FDL | −0.025 *** (−13.99) |
| PGDP2 | −0.120 *** (−24.54) |
| EDU | −0.430 *** (−7.51) |
| DE < 0.0326 | −2.028 *** (−5.70) |
| DE ≥ 0.0326 | −0.110 *** (−8.18) |
| Constant | 2.209 *** (24.94) |
| Observations | 3288 |
| Number of id | 274 |
| R-squared | 0.322 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; Chen, L.; Wang, H. Spatial Effects and Mechanisms of the Digital Economy and Industrial Structure on Urban Carbon Emissions: Evidence from 274 Chinese Cities. Economies 2025, 13, 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies13090263
Zhang G, Chen L, Wang H. Spatial Effects and Mechanisms of the Digital Economy and Industrial Structure on Urban Carbon Emissions: Evidence from 274 Chinese Cities. Economies. 2025; 13(9):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies13090263
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Guimei, Liuwu Chen, and Heyun Wang. 2025. "Spatial Effects and Mechanisms of the Digital Economy and Industrial Structure on Urban Carbon Emissions: Evidence from 274 Chinese Cities" Economies 13, no. 9: 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies13090263
APA StyleZhang, G., Chen, L., & Wang, H. (2025). Spatial Effects and Mechanisms of the Digital Economy and Industrial Structure on Urban Carbon Emissions: Evidence from 274 Chinese Cities. Economies, 13(9), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies13090263






