Abstract
This study proposes a novel approach to measuring phonetic distances among six Hailu Hakka vowels ([i, e, ɨ, a, u, o]) by applying Euclidean distance-based calculations from both articulatory and acoustic perspectives. By analyzing articulatory feature values and acoustic formant structures, vowel distances are systematically represented through linear vector arrangements. These measurements address ongoing debates regarding the central positioning of [ɨ], specifically whether it aligns more closely with front or back vowels and whether [a] or [ɑ] more accurately represents vowel articulation. This study also reassesses the validity of prior acoustic findings on Hailu Hakka vowels and evaluates the correspondence between articulatory normalization and acoustic formant-based models. Through the integration of articulatory and acoustic data, this research advances a replicable and theoretically grounded method for quantitative vowel analysis. The results not only refine phonetic classification within a Euclidean framework but also help resolve transcription inconsistencies in phonetic distance matrices. This study contributes to the growing field of quantitative phonetics by offering a systematic, multidimensional model applicable to both theoretical and experimental investigations of Taiwan Hailu Hakka.
1. Introduction
Quantifying the distance between single phones or between sequences of phones is utilized through different measurements, which are known as phonetic distances or phonological distances. To quantitatively measure phonetic distinctions between two separate and single phones is to compare the independent parameters such as tongue body advancement, tongue height, and tongue roundness in vowels, as well as place of articulation, manner of articulation, and voicing in consonants. Traditional methods in phonology and distance measures were adopted to calculate the sound constraints on phonological alternations (Gildea & Jurafsky, 1996) and phonotactic constraints (Frisch et al., 1997; Pierrehumbert, 1993). Cross-linguistic studies such as those by Wang et al. (2013) in English, Vakulenko (2019, 2021, 2023) in English and Ukrainian, and Do and Lai (2021) in Cantonese have assessed phonetic distances between speech sounds by adopting numerous approaches. Specifically, Wang et al. (2013) provided an important quantitative framework for articulatory vowel space analysis using Procrustes analysis and machine learning classification techniques. Vakulenko (2019, 2021, 2023) and Do and Lai (2021), on the other hand, explored methods for quantifying phonological distinctions. One such approach involves comparing the phonotactics or permissible sequences of phones found in lexical items.
In the past, a number of linguistic fields have provided different methods for calculating the distancing to solve the pronunciation–symbol mapping or to measure the unit similarity. In automatic speech recognition, the approach involved comparing reference symbols with hypothesized symbols using a formalization of the phone comparison procedure in distance measures to map for automatic text and speech processing (Fisher & Fiscus, 1993). In contemporary speech recognition and text-to-speech systems, a metric gauging the separation between two Gaussian distributions through their minds and covariance matrices was to adopt the Bhattacharyya distance (Hennig, 2010). In psycholinguistics, for spoken word recognition, phonological distance emerges as a pivotal factor in modeling phonological neighborhood density, indicating the extent to which a sound sequence overlaps with existing words in the lexicon via experimental paradigms (e.g., Luce et al., 2000; Luce & Pisoni, 1998) or speech errors (e.g., Vitevitch, 1997). In spoken word production, distance measures are computed to quantitatively measure the phonological and semantic distances in a string of symbols within lexical items (e.g., Allassonnière-Tang et al., 2024; Allassonnière-Tang & Wan, 2024). For the studies in bilingualism and diglossia, distance measures were assessed to quantify the similarity between languages and variations (e.g., Saiegh-Haddad, 2004). In dialectology, distance measures were employed to quantify the varieties between dialects (e.g., Heeringa, 2004; Heeringa et al., 2006; Nerbonne & Heeringa, 1997; Tang, 2009; Tang & van Heuven, 2015). In historical linguistics, distance measures are computed to aid in aligning and reconstructing cognate words (e.g., Oakes, 2000).
Phonetic comparison used to assess phonetic similarity between phones is commonly employed in computational phonology (Kondrak, 2003). However, the concept of phonetic similarity has historically been subjective and lacked a clear definition, which has promoted the adoption of machine-friendly algorithms (Kessler, 2005). Studies on the development of phonetic search algorithms across languages have found that the estimation of phonetic differences remained a challenging task (Jokisch & Hain, 2017). Because of the connection between the articulatory and acoustic characteristics of phones, one would naturally be curious about the basis for comparing articulatory models. The underlying assumption appears to be that a correct analysis will yield a distribution of vowel distances that more closely aligns with those derived from acoustic models.
To further understand the basis for phonetic distance estimation, it is important to consider the differing perspectives offered by the acoustic characteristics of vowels and vowel articulation diagrams. Acoustic representations relate to the physical properties of visualized speech signals, transforming into formant structures that reflect resonant frequencies corresponding to the shape of the vocal tract. This suggests that vowel phones with substantial differences in their formant frequencies are more likely to result in significant discretization of acoustic parameters. On the other hand, the vowel articulation diagram presented by the International Phonetic Association (2015) is closely tied to physiological structure, offering an idealized vowel chart that visually represents the relative positions of vowels based on articulatory features, particularly tongue and lip positioning. This suggests that vowel phones can be categorized into distinct articulation classes, each generating independent values. However, debates persist as to whether there is a highly significant correlation between acoustic characteristic properties and articulatory positions, especially regarding the anterior–posterior and high–low positions of the tongue. Based on the available vowel acoustic values and vowel articulation diagrams, it is generally predictable that acoustic parameters may offer more robust and precise measures for reliability and accuracy through computational modeling.
To measure the phonetic similarity of vowel phones, a metric approach will be needed to quantitively estimate the distinction as phonetic distances between the vowels. The technique used to measure the distance between phones is often known as Euclidean distance, which is a fundamental concept that measures the distance between coordinate points in a linear representation of a multi-dimensional space. Based on the acoustic characteristic properties and vowel articulatory diagram, Vakulenko (2019, 2021, 2023) adopted a novel formalism for quantifying phonetic distinctions between vowels by classifying those phones into different parameters (i.e., three parameters in vowels) in Euclidean distances, which then generated vectors between phones in articulatory space. In this method, the feature values of the vowel articulation diagram extracted from IPA charts are treated as independent parameters in the vocal tract. Vowels are typically examined from articulatory perspectives including tongue position, which refers to how the tongue is situated and shaped within the oral cavity during vowel production. The primary dimensions used to describe tongue position in vowels are relative height and backness and the roundness of lips. For the acoustic approach, the acoustic method has found extensive application in investigating the vowel quality of languages worldwide, as found in Ladefoged and Maddieson (1996). Utilizing acoustic analysis will provide a precise measurement to examine the quality of vowels by combining these dimensions as the modern acoustic analysis apparatus will convert the physical attributes of vowels into concrete digital numbers.
Building on Vakulenko’s two foundational studies, which applied Euclidean distance calculations to both acoustic vowel formant data and phonological feature matrices derived from IPA-based transcriptions to investigate vowel-pair distances in Ukrainian, the present study adopts a similarly dual-pronged approach. This framework facilitated direct comparisons between phonetic realizations and theoretical phonological representations, offering insights into the extent to which phonological models predict or align with actual speech production.
This study extends Vakulenko’s methodology by evaluating the consistency and predictive validity of his two test versions through the application of both empirical acoustic measurements and feature-based Euclidean distance metrics to vowel data from Hailu Hakka as spoken in Taiwan. Specifically, it integrates the 2021 method, which offers refined articulatory mapping for vowels, with the more comprehensive 2023 framework that facilitates phonological comparisons across a broader range of segmental categories, including consonants. These two approaches, grounded in a shared set of acoustic formant parameters and articulatory defined distinctive feature matrices (e.g., [±voiced], [±continuant]), provide complementary perspectives on segmental organization. Vakulenko (2021) demonstrated a high degree of consistency between the outcomes of these methods, thereby supporting the continued use of Euclidean measurements as a reliable formalism for calculating phonological distances.
In addition, this study engages with the theoretical complexities surrounding IPA-based phonemic transcription, recognizing that although IPA symbols are generally assumed to reflect phonetic grounding, their selection is often shaped by broader phonological considerations, including allophonic distribution, inventory symmetry, and interspeaker variation. In light of the limited availability of systematic phonetic data for Hailu Hakka, the analysis adopts IPA representations established in two foundational Taiwan-based studies, treating them as a phonetically motivated yet pragmatically constrained point of departure. This approach acknowledges that transcriptional practices must reconcile the demands of phonetic accuracy with the need for phonological coherence, particularly in cases where the surface realization of segments interacts with systemic organization. Rather than viewing transcriptional controversies as arising solely from mismatches between phonetic detail and symbol choice, this study situates such issues within the broader context of phonological structure, thereby adopting an integrated framework that draws on both acoustic evidence and theoretical modeling—segmental distances. Vakulenko (2021) also demonstrated that the two approaches yield highly consistent results, supporting the use of Euclidean measurements for calculating phonological distance. Based on this evidence, the current study adopts this formalism to compute segmental distances among vowels in Hailu Hakka as spoken in Taiwan.
The present study engages with the theoretical and practical complexities surrounding IPA-based phonemic transcription, particularly as they pertain to segmental analysis in underdocumented varieties such as Hailu Hakka. While IPA symbols are generally assumed to reflect phonetic grounding—especially in terms of acoustic or articulatory similarity—their selection is frequently influenced by broader phonological considerations, including allophonic distribution, inventory symmetry, and interspeaker variation. As Wan (1999) argues, the distinction between phonemic and phonetic representations often hinges on the analytical focus and contextual parameters of a given study, which can lead to divergent transcriptional outcomes even within a shared theoretical framework. In light of the limited availability of systematic phonetic data for Hailu Hakka, this study adopts the IPA representations proposed in two foundational Taiwan-based studies, treating them as a phonetically motivated yet pragmatically constrained foundation. This choice reflects an effort to balance phonetic precision with phonological coherence, recognizing that transcriptional practices must accommodate both the surface realization of speech sounds and their organization within a larger phonological system. Rather than attributing transcriptional controversies solely to mismatches between phonetic detail and symbol selection, this analysis situates such debates within the broader structural and functional dynamics of phonological organization. Within this framework, this study further adopts the formal methodology developed by Vakulenko (2021, 2023), which demonstrated a high degree of consistency between empirical acoustic data and feature-based phonological models using Euclidean distance calculations. By applying this dual approach that integrates formant-based measurements and phonological feature matrices, the present analysis seeks to compute segmental distances among vowels in Hailu Hakka and to evaluate the extent to which phonological models can account for observed patterns in vowel production. In doing so, it maintains a theoretically grounded yet empirically sensitive stance, addressing both the representational challenges of phonemic transcription and the methodological rigor required for cross-segmental comparison.1
The dialect Hailu Hakka is spoken in Hsinchu County of Taiwan, and there are only two acoustic reports presenting the acoustic vowel spaces of six vowels [i, e, ɨ, a, u, o] in the literature (Chung, 2017; Li, 2011). A small sample database from Li (2011) investigated 6 speakers (3 males, 3 females), and Chung (2017) examined 40 speakers (20 males, 20 females) in the study of Hailu Hakka vowels. The experimental results from these two acoustic reports revealed more concrete realities of Hakka vowels based on scientific analyses. Conventional classifications based on vowel articulation diagrams were to capture subtle differences in vowel qualities. Acoustic analysis, on the other hand, offers an objective and precise measurement for describing vowels by utilizing advanced acoustic equipment and converting the physical attributes into digital values. These two Hailu Hakka researchers provided more tangible insights into the characteristics of Hailu Hakka vowels. Linguistic questions emerge as to which scholar offers the highest level of acoustic accuracy. In addition, there is a question regarding the positioning, more advanced toward the close-central vowel [ɨ] or further back toward the close-back vowel [u] along the anterior–posterior tongue position, or whether it is located centrally close to the close-mid-central vowel [e] (Chung, 2017; Li, 2011; Luo, 1984, 2000). Researchers have observed that this apical (high central) vowel [ɨ] has been neutralized with the close front vowel [i] or transformed into the schwa [ə] or [e] in other dialects of Hakka (Chung, 2017). Finally, there is a debate over whether the open central [a] or the open back [ɑ] should be the appropriate symbol to precisely denote the tongue position in phonetic transcription within the context of the literature being examined.
Questions to be addressed involve the following: (1) To what extent do Vakulenko’s vowel distance tests yield consistent results when applied to Hailu Hakka vowel data? (2) How strongly do phonological (feature-based) Euclidean distances correlate with empirical formant-based measurements of Hailu Hakka vowel production, as reported in Li (2011) and Chung (2017)? (3) Can vowel spaces be systematically examined and validated across both articulatory and acoustic domains?
Rather than relying solely on spatial deformation metrics, this study incorporates a Euclidean distance-based analysis, following the vector design principles developed by Vakulenko (2021, 2023) to systematically quantify vowel separation. In the articulatory domain, vowel representations are constructed based on a distinctive feature matrix, focusing on key articulatory parameters such as tongue height, tongue advancement, and lip rounding. This feature-based approach allows for a more linguistically interpretable account of articulatory differentiation, linking articulatory gestures directly to underlying phonological structures. By integrating articulatory feature values and acoustic formant measurements within a unified Euclidean framework, this study seeks to capture the multi-dimensional nature of vowel organization and to offer a replicable model for cross-modal phonetic comparison.
The reason for adopting Vakulenko’s approach is to provide a direct comparison of the distances between individual vowel pairs. Vakulenko’s method is adopted as it offers a systematic numerical framework for representing pairwise comparisons between vowels. While many existing approaches rely on qualitative or categorical distinctions, Vakulenko’s model introduces quantifiable parameters derived from both phonological feature matrices and acoustic formant structures, thereby supporting a more integrated and empirically grounded analysis of vowel relationships. Building on the Euclidean distance methodology utilized in Vakulenko’s measurements (Vakulenko, 2021, 2023), this study aims to provide empirical results on both articulatory and acoustic approaches to the analysis of Hailu Hakka vowels. It quantitatively measures the phonetic distances among six Hailu Hakka vowels ([i, e, ɨ, a, u, o]) and seeks to address long-standing debated issues concerning vowel transcriptions in this variety. Moreover, this study further assesses the validity of two previous investigations (Chung, 2017; Li, 2011) through comparative measurements, offering a systematic evaluation of their findings.
2. Methodology
Vakulenko (2021, 2023) utilized the Euclidean formula to compare vowel coordinates encompassing articulatory and acoustic approaches. To decide the coordinate point values of transforming the coordinates between two n-dimensional vectors (e.g., x1, x2, …, xn, and y1, y2, …, yn), Vakulenko’s measurement set the coordinate values in vowel articulation diagram involving three key parameters such as tongue body advancement, tongue height, and lip roundness. For the acoustic approach, formant frequencies in Herz involving the first formant (F1) and the second formant (F2) structures are involved; the tongue height and tongue body advancement are inversely related to F1 and F2, respectively, in that the lower the F1 values are, the higher the tongue position is and the higher the F2 values are, the more advanced the tongue body is. The Euclidean formula is shown below2:
Following Vakulenko’s (2021, 2023) measurement where the vowel features are treated as linearly independent coordinates to quantify relevant phone coordinates, this study adopts a similar approach to assess articulatory contrast.
Three parameters in vowels can correspond to articulators such as horizontal tongue positions (ph), classified into three positions involving ‘front’, ‘central’, and ‘back’, vertical tongue position (pv), which is classified into seven grades, depending on mouth opening and closeness and advanced tongue root, and roundness (pr), including binary lip rounding, either [+round] or [−round]. The vector for each vowel feature is presented linearly, as provided in the following paragraphs.
In this measurement, the horizontal position feature has three grades (back, central, front), the vertical position feature has seven (open, …, close), and the roundness feature has two (rounded vs. unrounded). The vector values are assigned based on the corresponding subset positions. In a following study, Vakulenko (2023) provided a further advanced and refined measurement.
The disparities between these two tables stem from the requirement for a unified treatment of consonants and vowels. In Table 1, vectors for the vowels and consonants are measured separately, while in Table 2, Vakulenko’s approach is expanded to ensure equal treatment of vowels and consonants across all speech sounds. For more detailed and comprehensive parameters and vector assignments, please see Vakulenko (2021, 2023).

Table 1.
Vowel parameters (Vakulenko, 2021).

Table 2.
Vowel parameters revised (Vakulenko, 2023).
3. Phonetic Distances in Hailu Hakka Vowels
Based on Vakulenko’s measurements, the vectors generated from articulatory and acoustic approaches will be investigated in the six vowels of Hailu Hakka [i, e, a, ɨ, u, o]. The traditional Hakka linguists phonetically transcribed the six vowels as a close-front vowel, close-mid-front vowel, open-front vowel, close-central vowel, close-back vowel, and close-mid-back vowel for symmetrically phonological analysis. The debated vowel articulations involve the close-central and open-central vowel positions. The apical (high-central) vowel [ɨ] has undergone neutralization with the close-front vowel [i], shifted further back toward the close-back vowel [u], or been transformed into the schwa [ə] or the close-mid-central vowel [e]. While the apical vowel [ɨ] is traditionally sometimes classified as a syllabic consonant or even a sibilant due to its articulatory proximity to apical fricatives, this interpretation is particularly prevalent in traditional Chinese phonology, where [ɨ] is often analyzed as phonologically consonantal rather than vocalic. This interpretation fails to account for the phonetic and functional alignment of [ɨ] with canonical vowels. Acoustic evidence from Wan (1999, 2002) and Jeng (2011) demonstrates that [ɨ] exhibits vowel durations comparable to those of true vowels such as [i] and [u]. In addition, Wan and Jaeger (2003) provide psycho-phonological evidence from Taiwan Mandarin that further supports its vowel status. This indicates that [ɨ] functions more like a vowel than a consonant in terms of its acoustic properties. Duration is a particularly relevant metric in this context, as syllabic consonants, especially those based on fricatives, typically show shorter and less vowel-like timing and rarely serve as syllable nuclei in the same way as vowels. Furthermore, the classification of [ɨ] as a consonant tends to conflate articulatory similarity with phonological behavior. Although [ɨ] shares certain articulatory features with apical fricatives, it does not share phonological patterns with them. It consistently occupies the syllable nucleus, contrasts with other vowels in minimal pairs, and does not participate in consonant clusters in the way typical consonants do. These observations strongly support the analysis of [ɨ] as a vowel. In addition, framing the discussion as one rooted in present-day Mandarin rather than historical varieties is essential. While diachronic evidence may show that [ɨ] evolved from apical consonantal sources, the acoustic system treats it as a vowel. Hence, analysis should focus on its current phonological role, not its historical origins. Furthermore, there is debate over whether the tongue position in the open-central vowel [a] is more accurately represented as the open-back vowel [ɑ]. Quantitative evidence from the two approaches might offer different insights into re-examining the tongue body advancement and tongue height in the debated vowels.
Articulatory Approach
Table 3 lists of the vowel vectors in values show the phonetic distance between vowel pairs. The debated vowel questions are whether the open-central [a] or the open-back [ɑ] should be the right symbol in the precise tongue position and whether this occurs in Hailu Hakka.

Table 3.
Vowel distance in articulatory features (Vakulenko, 2021, 2023).
The table compares the measurement of vowel distances based on articulatory features using two different parameters resulting in different rankings. It is important to note that both the open-central [a] and the open-back [ɑ] are measured alongside other vowel pairs. In Vakulenko’s (2021) measurement, the shortest distance is between [i] and [e] or [o] and [u], while the longest distance occurs between [a] and [u]. In Vakulenko’s (2023) measurement, the shortest distance shifts to [i] and [ɨ], while [a] and [u] remain the pair with the longest distance between them. In this table, the open-central [a] and the open-back [ɑ] are calculated by distinct vectors when they are paired with different vowels. In the case of the open-central vowel [a], the most significant phonetic distance is observed between [a] and [u], whereas for the open-back vowel [ɑ], this gap remains consistent. The modified parameters will result in a slight alteration to the ranking order in mid vowels (Vakulenko, 2023).
The key differences between Vakulenko (2021) and Vakulenko (2023) in measuring phonetic distances can be summarized as follows: The refined version introduces a significantly smaller measurement scale than in the earlier version due to the incorporation of consonant features into the normalization techniques for vowel dimensions. These changes lead to a reconsideration of phonetic closeness. For instance, the [i]-[ɨ] pair is found to be more similar in the refined version, supporting a closer phonetic similarity. As a result, central vowels exhibit reduced distance values, reflecting a recalibrated phonetic distance framework. Consequently, the overall vowel space in Hailu Hakka appears more compressed. The major shift in the [i]-[ɨ] relationship suggests that the new measurement model aligns more closely with articulatory phonetics in Hailu Hakka. The refined model has a significantly lower standard deviation (0.0465) compared to the earlier one (0.2135), indicating that the distances between vowel pairs are more consistently distributed. A paired t-test confirms a highly significant difference between these two measurements (p < 0.0001), suggesting that the refinements are not due to random variation but represent a systematic and more uniform measurement system. Furthermore, correlation analysis reveals a very high Pearson correlation coefficient (0.9626) with a highly significant p-value (1.19 × 10−11), indicating a strong linear relationship between the two measurement systems. This suggests that while the overall scale of phonetic distances changed significantly in the refinement, the relative ranking of vowel distances remained consistent. In this case, whether the phonetic transcription is central [a] or back [ɑ] will not impact the shortest and longest distance in the ranking order. Samples of how these vowel pairs are calculated are provided as follows:
|[i]-[e]|
- a.
- (Vakulenko, 2021)
- b.
- (Vakulenko, 2023)
In this example, the vector of the phonetic distance between the vowels [i] and [e] is 0.1925, and for the modified version it is 0.0430.
|[o]-[u]|
- a.
- (Vakulenko, 2021)
- b.
- (Vakulenko, 2023)
Similarly, in this example, the vectors of the phonetic distance between the vowels [o] and [u] are 0.1925 and 0.0430, respectively. The results predict a consistent range of phonetic distances regardless of the different parameters utilized.
|[a]-[u]|
- a.
- (Vakulenko, 2021)
- b.
- (Vakulenko, 2023)
In this example, the vectors representing the phonetic distance between the vowels [a] and [u] are 0.8660, whereas in the modified version, the figure decreases to 0.1829.
|[ɑ]-[u]|
- a.
- (Vakulenko, 2021)
- b.
- (Vakulenko, 2023)
In this example, when the central vowel is considered as the back one, the vector of [ɑ] and [u] decreases to 0.1826 from 0.8165. In comparison to the earlier version, the refined one may not indicate a distinction. As seen in the previous ranking order, the tongue position of this particular vowel distinction does not impact the vowel distances much. In general, this measurement provides a better quantifying view of vowel space in Hailu Hakka. For instance, the vowel [o] is nearly 4.5 times closer than [a] to the vowel [u].
Since the values measured in the articulatory features provide a linearly normalized view, it is necessary to compare the acoustic values in the formant structures of vowels, which pertain to the resonant frequencies found in the acoustic qualities of vowel phones. These resonant frequencies result from the configurations of the vocal tract in the process of speech production, commonly labeled as F1 (the first formant structure), F2 (the second formant structure), etc. When differentiating the acoustic properties of vowels, F1 values, which are related to tongue vertical position (i.e., close, close-mid, open-mid, open), and F2 values, which are influenced by tongue position (front, central, back), are crucial in terms of the values. The lower the value of F1 is, the higher the tongue position is, and the lower the value of F2 is, the further place the tongue is in. In addition, the vowel [ɨ] in traditional analysis did not, in particular, belong to other specific vowel symbols, and Hakka phonologists would just question its tongue position being too central, so investigating the acoustic measurement is necessary.
Li (2011) and Chung (2017) examined the six vowels in Hailu Hakka and provided the following figures, respectively.
In this table, Li (2011) provides a list of all the informants’ F1 and F2 values along with their respective standard deviations. The F1 and F2 values for the six vowels in Hailu Hakka reveal important phonetic characteristics, including vowel height, backness, and distinctions among different speakers (male vs. female). It is evident that the high vowels [i] (289.46 Hz), [ɨ] (433.14 Hz), and [u] (444.81 Hz) have the lowest F1 values, confirming their high vowel status. In contrast, the low vowel [a] (1228.4 Hz) has the highest F1 value, reflecting its classification as a low vowel. The central vowel [a] also has the highest standard deviation, suggesting significant variation in its pronunciation across participants, potentially indicating dialectal variation between [a] and [ɑ].
Regarding F2, the front vowels [i] (2864.67 Hz) and [e] (2559.36 Hz) have high F2 values, confirming their front vowel status, whereas the back vowels [o] (1068.5 Hz) and [u] (740.59 Hz) have the lowest F2 values, indicating their back vowel positioning. In addition, [a] (1590.69 Hz) has a lower F2 value than expected for a front vowel, suggesting that it is central and slightly back rather than purely fronted. This supports the possibility that [ɑ] may be the more appropriate phonetic variant. The vowel [a] exhibits a high degree of variability in F1 (SD = 266.7 Hz) and F2 (SD = 328.0 Hz), indicating potential instability in its articulation. Its F2 value (1590.69 Hz) is closer to central vowels rather than a purely fronted vowel, further supporting a more central or back [ɑ]-like pronunciation rather than a strictly fronted [a]. This finding influences the phonetic transcription debate on whether Hailu Hakka should use [a] or [ɑ]. The classification of [ɨ] in Hailu Hakka remains complex. The F1 value of [ɨ] (433.14 Hz) is similar to [u] (444.81 Hz), suggesting that [ɨ] is a high central-back vowel. However, Vakulenko’s studies would have predicted a closer relationship between [i] and [ɨ] from articulatory perspectives. In terms of vowel variability, [a] has the highest standard deviation in both F1 (266.7) and F2 (328.0), suggesting instability in its pronunciation, while [ɨ] also shows moderate variability (F2 SD = 193.1 Hz). In contrast, [o] and [u] have the lowest standard deviations, suggesting that they are pronounced more consistently across speakers. Although gender differences in formant frequencies are expected, they do not significantly affect relative vowel positioning in the study. The vowels [ɨ] and [a] exhibit the most variation in articulation, supporting ongoing phonetic debates regarding their exact placement in the Hailu Hakka vowel system.
Moreover, although the F1/F2 ratio is not a direct measure of phonological distinctiveness, it remains a useful heuristic for analyzing vowel quality. F1 and F2 represent two independent acoustic dimensions that are reliably perceived by listeners, and their ratio can illuminate the interaction between vowel height (F1) and backness (F2). A greater difference in F1/F2 ratios between vowels may correspond to more distinct acoustic contrasts, while smaller differences may suggest closer articulatory or perceptual proximity. Importantly, vowels such as [a] and [u] are clearly phonologically distinct, and indeed, their F1/F2 ratios differ substantially, reflecting their articulatory distance; [a] is characterized by a high F1 and moderate F2, while [u] has a low F1 and very low F2. This sharp contrast is consistent with their positioning at opposite extremes of the vowel space. For example, the ongoing debate over [a] versus [ɑ] may be linked to the relatively high F1/F2 ratio of [a], supporting its interpretation as a low and potentially retracted vowel. Front vowels such as [i] and [e] typically exhibit lower F1/F2 ratios, consistent with their high and fronted articulatory positions. Back vowels like [u] and [o] also present low F1/F2 ratios but primarily due to extremely low F2 values rather than elevated F1.
The central vowel [ɨ] with an intermediate ratio, aligns well with its mid-to-high central articulation. While Li’s study offers valuable observations on these vowel contrasts, its conclusions are somewhat constrained by a limited sample size. Following the normalization method for format central tendency proposed in Vakulenko’s (2021) study on American English and Ukrainian vowels, the table below presents the mean formant frequencies (in Hz) of Hailu Hakka vowels, based on data from Li (2011) and Chung (2017).
Extracted the values from Table 4, the central point of maximum and minimum of F1 and F2 is provided in the following:
<F1HH(f)> = [F1HHmin(f) + F1HHmax(f)]/2 = [295.11 + 1596]/2 = 945.615 Hz
<F1HH(m)> = [F1HHmin(m) + F1HHmax(m)]/2 = [270.05 + 1058.32]/2 = 664.185 Hz
<F2HH(f)> = [F1HHmin(f) + F1HHmax(f)]/2 = [753.21 + 3257.02]/2 = 2005.115 Hz
<F2HH(m)> = [F2HHmin(m) + F2HHmax(m)]/2 = [692.27 + 2645.47]/2 = 1668.87 Hz

Table 4.
Mean F1 and F2 values (Hz) of 6 vowels in Hailu Hakka (Li, 2011).
Based on the aforementioned formula, Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6 show the average F1 and F2 frequency values for male and female speakers across the six Hailu Hakka vowels.

Table 5.
The mean value of formant frequencies of Hailu Hakka vowels (Hz) (Li, 2011).

Table 6.
Average values of F1 and F2 in Hailu Hakka (Hz) (Li, 2011).
Since F1 and F2 values do not vary significantly between males and females, the following presents the average values of the first two formants for the six Hailu Hakka vowels. To obtain normalized values for the first and second formants of the six Hailu Hakka vowels, Table 7 and Table 8 provide the vectors for each vowel.

Table 7.
Vectors of the first and second formants normalized to the six vowels in Hailu Hakka (Li, 2011).

Table 8.
Acoustic vectors (Li, 2011).
The phone distance is calculated from <f1> and <f2> as in the following formula:
The table displays the vectors derived from acoustic measurements in the vowel pairs. The shortest distance is observed between [o] and [u], and the pair [i] and [e] is the second shortest. In Vakulenko’s initial measurement (Vakulenko, 2021), the shortest distance is also found in the [o]-[u] pair and [i]-[e] pair, whereas in Vakulenko’s revised version (Vakulenko, 2023), the vowel pair [o]-[u] and [i]-[e] both become the second shortest. Regarding the acoustic vectors, the longest distance is observed in the [i]-[a] pair, but in both articulatory versions, this pair is situated at a middle distance. The longest distance in both articulatory versions is found in the [a]-[u] pair. The following presents the acoustic values and formulas in Chung’s (2017) study.
In this table, the data has already undergone descriptive statistical analysis, including mean, standard deviation (SD), minimum, and maximum values, without providing each informant’s individual F1 and F2 values. Therefore, a detailed statistical comparison with Li’s study cannot be fully conducted. However, Chung’s data shows slightly less variability in certain vowels, particularly for F2, although both studies present a similar SD range. Li’s findings seem to support greater vowel variability, particularly in the debated distinctions between the [a]-[ɑ] pair and the [i]-[ɨ] pair.
Extracting the values from Table 9, since F1 and F2 values are not presented for each informant, the midpoint between the maximum and minimum values of F1 and F2 is shown below:3
<F1HH(f)> = [F1HHmin(f) + F1HHmax(f)]/2 = [303 + 1120]/2 = 711.5 Hz
<F1HH(m)> = [F1HHmin(m) + F1HHmax(m)]/2 = [273 + 922]/2 = 597.5 Hz
<F2HH(f)> = [F1HHmin(f) + F1HHmax(f)]/2 = [804 + 2937]/2 = 1870.5 Hz
<F2HH(m)> = [F2HHmin(m) + F2HHmax(m)]/2 = [660 + 2569]/2 = 1614.5 Hz

Table 9.
Chung (2017).
Based on the aforementioned formula, Table 9, Table 10 and Table 11 show the average values of F1 and F2 frequencies between male and female speakers in six Hailu Hakka vowels.

Table 10.
The mean value of formant frequencies of Hailu Hakka vowels (Hz) (Chung, 2017).

Table 11.
Average values of F1 and F2 in Hailu Hakka (Hz) (Chung, 2017).
Since F1 and F2 values between males and females do not vary too much, the following shows the average values of the first two formants in the six Hailu Hakka vowels. To obtain the normalized values for the first and second formants of six Hailu Hakka vowels, Table 12 and Table 13 provide the vectors of each vowel.

Table 12.
Vectors of the first and second formants normalized to the six vowels in Hailu Hakka.

Table 13.
Acoustic vectors (Chung, 2017).
Figure 1 presents vowel distances based on articulatory and acoustic measurements.
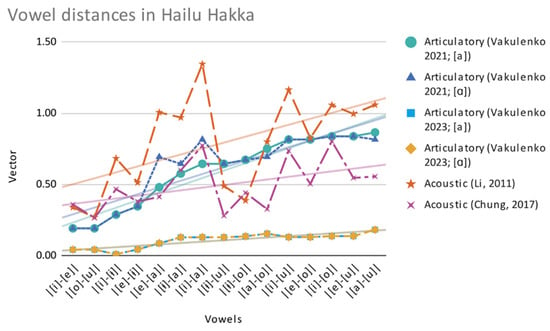
Figure 1.
Vowel distances in Hailu Hakka (Vakulenko, 2021, 2023; Li, 2011; Chung, 2017).
The figure presents vowel distance measurements in Hailu Hakka, comparing various methodologies (articulatory and acoustic) and data sources, including Vakulenko’s vector measurements from the earlier (Vakulenko, 2021) and the refined study (Vakulenko, 2023), as well as Li’s (2011) dataset and Chung’s (2017) dataset. To provide a more detailed examination of these measurements, separate figures are included in the Appendix A, illustrating the individual vowel distance comparisons for each methodological approach.
There are only two studies on the acoustic studies of the dialect Hailu Hakka, and these two both agree on the six-vowel distinction [i, e, ɨ, a, u, o]. Chung (2017) claimed that his study provides the most precise and robust acoustic measurement in Hailu Hakka by recruiting 40 participants and shows the downsides and insufficiency of Li’s (2011) measurement with 6 participants only. However, after conducting a two-tailed t-test, the results showed that there are no statistically significant differences between the two studies (p = 0.787). In Vakulenko’s (2021, 2023) studies, the apical (high central) vowel [ɨ] and the central/back vowel [a]/[ɑ] demonstrate no significant variance in articulatory methods, with the revised version displaying a relatively consistent slope across varying distances in Hailu Hakka vowels.
In Figure 2, the top panel displays normalized vowel distances based on articulatory models from Vakulenko (2021, 2023) and acoustic data from Li (2011) and Chung (2017). It presents the vowel-specific acoustic profiles across multiple speaker groups, illustrating raw formant values plotted across vowel categories. Clear variation is observed among the types, with certain vowels such as [a] showing systematically higher values and vowels like [i] and [u] showing lower values, consistent with their expected formant characteristics. The bottom panel depicts the same data following z-score normalization, which highlights relative deviations within each type. This transformation allows for clearer cross-type comparisons by removing baseline formant differences while preserving contrastive vowel patterns in a standardized scale.
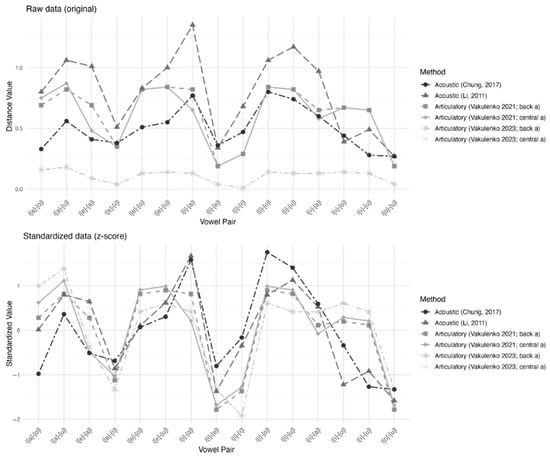
Figure 2.
Comparison of articulatory and acoustic vowel distances in Hailu Hakka (Chung, 2017; Li, 2011; Vakulenko, 2021, 2023).
Figure 3 presents vowel profiles for Hailu Hakka across six model configurations, segmented into acoustic and articulatory representations. The top row displays acoustic measurements derived from Chung (2017) and Li (2011), while the bottom row shows articulatory estimations based on Vakulenko’s models (Vakulenko, 2021, 2023). Each panel plots vowel categories along the x-axis and corresponding values on the y-axis to enable direct comparison across vowel types and modeling approaches. In each panel, the solid line represents the raw vowel-specific values, reflecting actual formant-based variation across vowel categories within either acoustic or articulatory data. The dotted line represents the z-score standardized values, highlighting relative deviations and allowing for comparisons across types on a normalized scale. This contrast enables observation of both the original vowel dispersion and its standardized counterpart within each configuration, supporting hypothesis testing by allowing researchers to assess how well articulatory model predictions align with empirical acoustic data and offering insight into the internal organization of the vowel system.
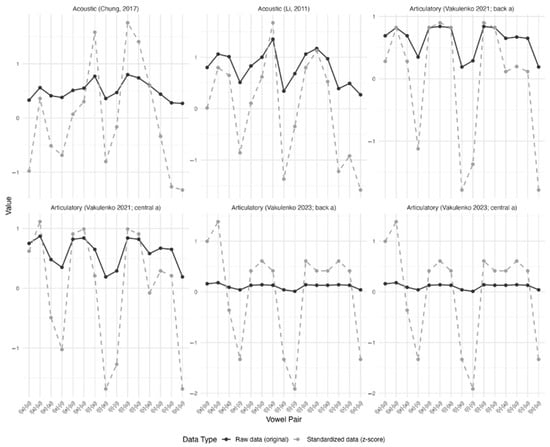
Figure 3.
Z-score standardized vowel distance distributions across acoustic and articulatory models (Chung, 2017; Li, 2011; Vakulenko, 2021, 2023).
Figure 4 presents a comprehensive visualization of z-score-standardized vowel distances, derived from both acoustic and articulatory models, using boxplots. The models are based on data from Chung (2017), Li (2011), and Vakulenko (2021, 2023). The distribution spread and median lines illustrate the variability and central tendency of vowel distances across models. These boxplots depict interquartile ranges (boxes), overall variability (whiskers), and outliers (dots), although no z-scores exceeded ±3, indicating the absence of extreme values and suggesting distributional consistency across models. No z-scores exceeding ±3 were observed in any dataset, indicating the absence of apparent outliers and suggesting a consistent distribution across all models.
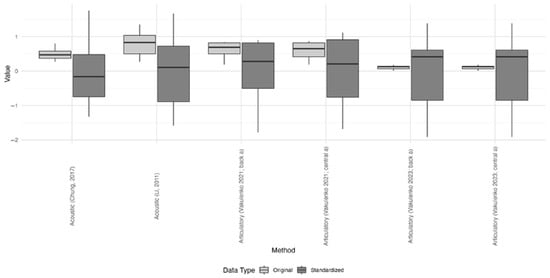
Figure 4.
Boxplot comparison of Z -score standardized vowel distances across acoustic and articulatory models (Chung, 2017; Li, 2011; Vakulenko, 2021, 2023).
Figure 5 presents a Pearson correlation matrix showing the pairwise relationships between vowel distance measurements derived from two acoustic models (Chung, 2017; Li, 2011) and five articulatory models based on Vakulenko (2021, 2023).
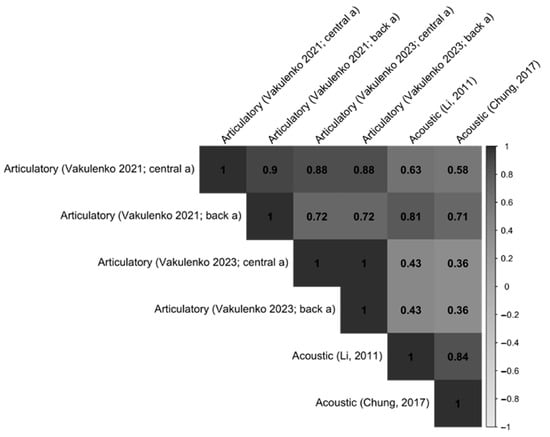
Figure 5.
Correlation matrix of vowel distances across acoustic and articulatory models (Vakulenko, 2021, 2023; Chung, 2017; Li, 2011).
Higher correlation values (closer to 1) indicate greater similarity in vowel distance distributions across models. In this heat map, the strongest correlation is observed between Vakulenko (2021) [a] and Vakulenko (2021) [ɑ], with a coefficient of 0.90. This is followed by the correlations between Vakulenko (2021) [a] and Vakulenko (2023) [a], and between Vakulenko (2021) [ɑ] and Vakulenko (2023) [ɑ], both with coefficients of 0.88. A moderate correlation is found with the acoustic formants reported in Li (2011) (r = 0.63), while the correlation with Chung (2017) is comparatively weaker, at 0.58. Strong correlations are consistently observed among articulatory models and between the two acoustic models. In contrast, correlations between acoustic and articulatory models tend to be moderate, reflecting both methodological consistency within modeling types and divergence across modeling approaches. In addition, Vakulenko (2021) [ɑ] shows strong correlations with Vakulenko (2023) [a] and Vakulenko (2023) [ɑ], both at r = 0.72. Interestingly, it also shows a higher correlation with Li (2011)’s acoustic data (r = 0.81), compared to its correlation with Chung (2017), which, while still moderate, is slightly lower at r = 0.71. Furthermore, Vakulenko (2023) [a] and Vakulenko (2023) [ɑ] display perfect correlation (r = 1.00), suggesting internal consistency within the 2023 articulatory model. However, Vakulenko (2023) [a] correlates only modestly with Li (2011) (r = 0.43) and even more weakly with Chung (2017) (r = 0.36). The correlation between Li (2011) and Chung (2017) is relatively strong at r = 0.84. In general, Vakulenko’s articulatory models exhibit a higher degree of consistency with the acoustic formants reported in Li (2011), as measured by vowel distance correlation.
Figure 6 presents vowel distance patterns across seven models, visualized through three phonological groupings: (1) peripheral versus non-peripheral vowels (left panel), (2) high versus low vowels (center panel), and (3) front versus back vowels (right panel). Each panel displays the mean vowel distance values for each category, based on data from two acoustic models, Li (2011) and Chung (2017), and four articulatory models from Vakulenko (2021, 2023). These comparisons highlight model-specific tendencies in how vowel subsets are distributed within the phonetic space of Hailu Hakka.
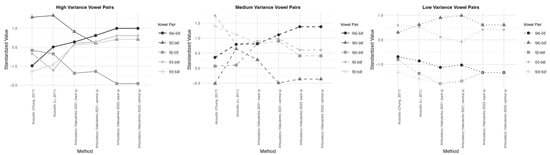
Figure 6.
Vowel distance distributions across models by vowel-pair groupings (Chung, 2017; Li, 2011; Vakulenko, 2021, 2023).
Within the high-variance group, the vowel pairs ([a]-[o], [i]-[a], [i]-[ɨ], [ɨ]-[o], [ɨ]-[u]) exhibit considerable fluctuations in distance values, reflecting inconsistencies in their spatial distribution. Closer inspection of the five vowel pairs across six models indicates that Vakulenko (2021) [ɑ] yields the most stable internal configuration. Li (2011) follows closely, maintaining relatively consistent distance values. Vakulenko (2023) [ɑ] and Vakulenko (2023) [a] display nearly identical patterns, while Chung (2017) stands out as the least consistent model in this group. In the medium-variance set ([a]-[u], [e]-[a], [e]-[o], [i]-[o], [i]-[u]), Vakulenko (2021) [a] emerges as the most stable, exhibiting the least fluctuation in vowel distances. Vakulenko (2021) [ɑ] and Li (2011) rank next in consistency, while Chung (2017) again shows the greatest degree of variation among models. Conversely, within the low-variance group ([e]-[ɨ], [e]-[u], [i]-[e], [ɨ]-[a], [o]-[u]), Chung (2017) presents the most stable vowel distributions, followed by Li (2011). In contrast, Vakulenko (2021) [a] and [ɑ] demonstrate increased variability, suggesting less internal consistency in their spatial vowel representation under this subset. In general, the model proposed by Li (2011) yields the most consistent values.
Although no statistically significant differences were observed among the six models in terms of average vowel-pair distances, the relative ranking and correlation patterns reveal notable methodological differences. In particular, there is a lack of strong consistency between articulatory and acoustic approaches. Articulatory models proposed by Vakulenko (2021, 2023) demonstrate a high degree of internal coherence and may serve as reliable references when internal consistency is the primary concern. In contrast, the methods developed by Li (2011) and Chung (2017), which show high intercorrelation and moderate alignment with some articulatory models, may more effectively reflect the empirical properties of acoustic data.
This study adopts six models of vowel distance computation, including three articulatory and three acoustic models, with the aim of examining how different theoretical frameworks represent phonetic distances between vowel pairs. The articulatory models follow the framework proposed by Vakulenko (2021, 2023), which quantifies articulatory distance based on the geometric configuration of speech gestures, and accounts for variation between central and back vowel realizations.
To examine the similarities and differences among the six models, pairwise Spearman rank correlations were computed. This approach evaluates how consistently the models rank vowel-pair distances, offering insights into their relative convergence or divergence. Spearman correlation analysis revealed more nuanced patterns. The Vakulenko (2021, 2023) models were highly correlated with each other (r > 0.87) and moderately with Li (2011) (r ≈ 0.63) but less so with Chung (2017) (r ≈ 0.58). Notably, the Vakulenko (2023) model exhibited weak and non-significant correlations with the acoustic models (p > 0.1), suggesting that it may primarily reflect an articulatory rather than acoustic structure.
Finally, analysis of individual vowel pairs revealed that pairs such as [i]-[ɨ], [a]-[o], and [ɨ]-[u] exhibited the highest variability across models. This suggests substantial discrepancies in how these models evaluate phonetic distance, possibly reflecting differing sensitivity to specific articulatory or acoustic features. Such differences may also stem from discontinuous distributions in phonetic space, warranting further investigation through experimental phonetic research.
The literature raises questions about which scholar provides the most accurate acoustic analysis and the specific positioning of the close-central vowel [ɨ]. These debates include whether [ɨ] is more aligned with the close-back vowel [u] along the anterior–posterior tongue axis or positioned closer to the close-mid-central vowel [e] (Chung, 2017; Li, 2011; Luo, 1984, 2000). Current findings suggest that the apical vowel [ɨ] is situated in the high-central tongue position, closer to the back vowel. Furthermore, while articulatory-based distinctive features indicate no significant difference between the open-central [a] and the open-back [ɑ] in representing tongue position, acoustic studies tend to show greater variability, ranging from central to back tongue positions, between the open-central [a] and the back [ɑ].
In conclusion, the refined version provides a general assessment of Hailu Hakka, whereas the earlier version, specifically designed for vowel analysis, presents larger vector distances, making it more effective in addressing long-standing phonetic controversies in Hailu Hakka. In addition, discrepancies between articulatory and acoustic measurements are observed across nearly all languages. Since the values measured in the articulatory features provide a linearly normalized view, it is necessary to compare the acoustic values in the formant structures of vowels, which pertain to the resonant frequencies found in the acoustic qualities of vowel phones. As Vakulenko has stated, experimental values derived from acoustic measurements tend to be more precise than phonological distinctive features based on articulatory theories. In this study, it is evident that despite the small sample size of only six speakers, the data effectively explain long-standing vowel-related debates in Hailu Hakka. In contrast, the dataset containing 40 speakers does not provide individual speaker distributions, and from the perspective of power statistics and inferential analysis, statistical testing cannot currently be performed.
4. Conclusions
This study aimed to develop a comprehensive and efficient technique for estimating and quantifying the phonetic distances between vowels in Hailu Hakka using both articulatory and acoustic approaches. It also evaluated various frameworks of acoustic parameters based on linear vectors that are generalized coordinates from Euclidean formalism (Vakulenko, 2021, 2023). The findings reveal that both acoustic and articulatory approaches yield similar coordinate values between vowels, supporting Vakulenko’s scientific view in which the theoretical model and findings align well with experimental phonetic results. In addition, this study further suggested that the acoustic method provides more reliable results due to the utilization of robust and precise acoustic parameters applicable across languages. Furthermore, the quantitative measurement demonstrated agreement between articulatory and acoustic regarding data values. Moreover, this study resolved the debated issue surrounding the existence of the close-central vowel [ɨ], indicating its phonetic transcription and its position between the close-front vowel [i] and the close-back vowel [u] in terms of anterior–posterior tongue position or tongue height. The data also indicate no difference in the articulatory method for the [a]/[ɑ] distinction, while the acoustic approaches show a preference for [ɑ]. In summary, adopting Euclidean distances in Vakulenko’s measurements (Vakulenko, 2021, 2023) yields scientific results on articulatory and acoustic approaches in Hailu Hakka vowels, quantitatively measuring the phonetic distances between six Hailu Hakka vowels [i, e, ɨ, a, u, o] and addressing long-standing debated issues on vowel transcriptions. Moreover, the validity of previous studies (Chung, 2017; Li, 2011) can be examined through these measurements for further comparison. Future studies may focus on refining other measurements such as Hamming and Manhattan distances. However, this study has limitations, including the absence of contrastive cues for fundamental frequency, duration, intonation, and voicing onset. In particular, languages like Mandarin exhibit a two-way contrast of aspiration for the plosives (i.e., [p] vs. [pʰ], [t] vs. [tʰ], [k] vs. [kʰ]) and affricates (i.e., [ts] vs. [tsʰ], [tʂ] vs. [tʂʰ] [tɕ] vs. [tɕʰ]), as well as a two-way contrast of voicing for the retroflex fricatives (i.e., [ʂ] vs. [ʐ]). Hailu Hakka does not have such a complex consonant inventory; however, introducing necessary weight coefficients and incorporating the formulated mechanism into such complex structures will be necessary. In addition, there are no reliable acoustic studies on Hailu Hakka consonants to date. It is hoped that future explorations of alternative methods will overcome these limitations and prove more effective in assessing phonetic distinctions. Previous studies by the two scholars generally offer efficient and thorough techniques for estimating and quantifying phonetic distances among distinct vowel phones.
Funding
This research was funded by the Hakka Affairs Council (98-C04) in Taiwan. The APC was funded by National Chengchi University, Taipei, Taiwan.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
I am grateful to the two anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments and constructive suggestions, which greatly improved the quality of this paper. I also thank the editors for their helpful guidance throughout the review process. I am especially indebted to Pu Yu for valuable assistance with the statistical analysis, and to Xiang Li and Yu Ching Tsai for their assistance during the preparation of this manuscript. I am deeply grateful to Hui-Ling Lai of the Department of English at National Chengchi University for her generous support, which was instrumental in the application process for the grant from the Hakka Affairs Council in Taiwan. I also would like to express my sincere gratitude to the Hakka Affairs Council (98-C04) in Taiwan for their financial support, which made this research possible. All remaining errors are my own.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
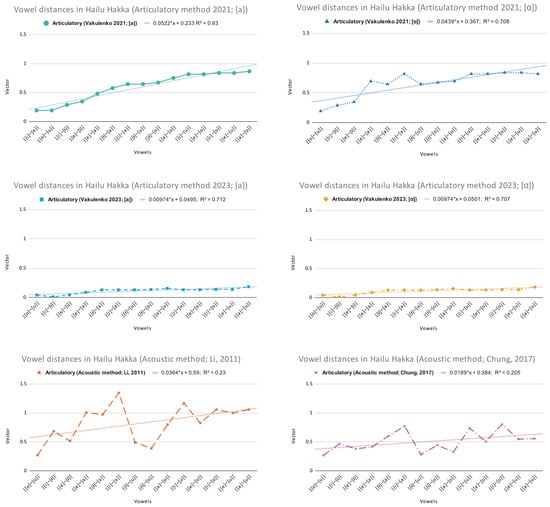
Figure A1.
Statistics for each measurement in Hailu Hakka (Vakulenko, 2021, 2023; Chung, 2017; Li, 2011).
Notes
| 1 | I am grateful to the reviewer for the insightful observation on the theoretical motivation behind the selection of IPA symbols. This point has prompted clarification in the current manuscript. |
| 2 | Each component of the vector is divided by the maximum vector length, corresponding to the square root of n, where n equals 3 for vowels. |
| 3 | The maximum and minimum observed values are estimated using the “2-sigma rule” of the “68–95–99.7 rule” based on the mean and standard deviation, as shown below:
Maximum Value (Upper Limit) = μ + 2σ (2) Minimum Value (Lower Limit): μ − 2σ.
|
References
- Allassonnière-Tang, M., & Wan, I. P. (2024). Revisiting the automatic prediction of lexical errors in Mandarin. Linguistics Vanguard, 10(1), 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allassonnière-Tang, M., Wan, I.-P., & Lee, C. (2024). Semantic and phonological distances in free word association tasks. In M. Dong, J.-F. Hong, J. Lin, & P. Jin (Eds.), Chinese lexical semantics (CLSW 2023) (Vol. 14515, pp. 91–100). Lecture notes in computer science. Springer Nature Singapore. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, R.-F. (2017). Acoustic studies on vowels of Hailu Hakka. Available online: https://cloud.hakka.gov.tw/details?p=11646 (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Do, Y., & Lai, R. K. Y. (2021). Accounting for lexical tones when modeling phonological distance. Language, 97(1), e39–e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, W. M., & Fiscus, J. G. (1993, April 27–30). Better alignment procedures for speech recognition evaluation. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing (Vol. 2, pp. 59–62), Minneapolis, MN, USA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, S., Broe, M., & Pierrehumbert, J. (1997). Similarity and phonotactics in Arabic. Rutgers Optimality Archive, 223, 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- Gildea, D., & Jurafsky, D. (1996). Learning bias and phonological-rule induction. Computational Linguistics, 22(4), 497–530. [Google Scholar]
- Heeringa, W. (2004). Measuring dialect pronunciation differences using Levenshtein distance [Doctoral dissertation, University of Groningen]. [Google Scholar]
- Heeringa, W., Gooskens, C., Nerbonne, J., & Kleiweg, P. (2006). Evaluation of string distance algorithms for dialectology. In J. Nerbonne, & E. Hinrichs (Eds.), Linguistic distances: Workshop at the joint conference of the international committee on computational linguistics and the association for computational linguistics (pp. 52–62). Association for Computational Linguistics. [Google Scholar]
- Hennig, C. (2010). Methods for merging Gaussian mixture components. Advances in Data Analysis and Classification, 4(1), 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Phonetic Association. (2015). IPA chart. Available online: http://www.internationalphoneticassociation.org/content/ipa-chart (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Jeng, J.-Y. (2011). Speech acoustics: The science of spoken sound. Psyche Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Jokisch, O., & Hain, H.-U. (2017). A trainable method for the phonetic similarity search in German proper names. In A. Karpov, R. Potapova, & I. Mporas (Eds.), Speech and computer (Vol. 10458, pp. 46–55). Lecture notes in computer science. Springer International Publishing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, B. (2005). Phonetic comparison algorithms. Transactions of the Philological Society, 103(2), 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrak, G. (2003). Phonetic alignment and similarity. Computers and the Humanities, 37(3), 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladefoged, P., & Maddieson, I. (1996). The sounds of the world’s languages. Blackwell. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C. W. (2011). An acoustic study of Hai-lu Hakka vowels [Master’s thesis, National Chengchi University]. [Google Scholar]
- Luce, P. A., Goldinger, S. D., Auer, E. T., & Vitevitch, M. S. (2000). Phonetic priming, neighborhood activation, and PARSYN. Perception & Psychophysics, 62(3), 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luce, P. A., & Pisoni, D. B. (1998). Recognizing spoken words: The neighborhood activation model. Ear and Hearing, 19(1), 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.-J. (1984). A study of the Sixian Hakka grammar [Doctoral dissertation, National Taiwan Normal University]. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.-J. (2000). The history of the Hakka community in Taiwan: Language aspect. Historical Records Committee of Taiwan Provincial Government. [Google Scholar]
- Nerbonne, J., & Heeringa, W. (1997). Measuring dialect distance phonetically. In Computational phonology: Third meeting of the ACL special interest group in computational phonology (pp. 11–18). Association for Computational Linguistics. Available online: https://aclanthology.org/W97-1102/ (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Oakes, M. P. (2000). Computer estimation of vocabulary in a protolanguage from word lists in four daughter languages. Journal of Quantitative Linguistics, 7(3), 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierrehumbert, J. (1993). Dissimilarity in the Arabic verbal roots. In Proceedings of north east linguistic society (NELS) (Vol. 23, pp. 367–381). University of Massachusetts. [Google Scholar]
- Saiegh-Haddad, E. (2004). The impact of phonemic and lexical distance on the phonological analysis of words and pseudowords in a diglossic context. Applied Psycholinguistics, 25(4), 495–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C. (2009). Mutual intelligibility of Chinese dialects: An experimental approach [Doctoral dissertation, University of Leiden]. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/1887/13963 (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Tang, C., & van Heuven, V. J. (2015). Predicting mutual intelligibility of Chinese dialects from multiple objective linguistic distance measures. Linguistics, 53(2), 285–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakulenko, M. O. (2019). Calculation of semantic distances between words: From synonymy to antonymy. Journal of Quantitative Linguistics, 26(2), 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakulenko, M. O. (2021). Calculation of phonetic distances between speech sounds. Journal of Quantitative Linguistics, 28(3), 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakulenko, M. O. (2023). Unified parametrization of phonetic features and numerical calculation of phonetic distances between speech sounds. Journal of Quantitative Linguistics, 30(1), 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitevitch, M. S. (1997). The neighborhood characteristics of malapropisms. Language and Speech, 40(3), 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, I.-P. (1999). Mandarin phonology: Evidence from speech errors [Doctoral dissertation, State University of New York]. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, I.-P. (2002). Alignments of prenuclear glides in Mandarin. Crane Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, I.-P., & Jaeger, J. (2003). The phonological representation of Mandarin vowels: A psycholinguistic study. Journal of East Asian Linguistics, 12(3), 205–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., Green, J. R., Samal, A., & Yunusova, Y. (2013). Articulatory distinctiveness of vowels and consonants: A data-driven approach. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 56(5), 1539–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).