Abstract
Agriculture is one of the sectors most susceptible to changes in climatic conditions. The impact is even stronger in Africa, where rain-fed agriculture is vital for daily subsistence, but where adaptive capacity is low. It is therefore crucial to increase the understanding of the actual climate change dynamics on agricultural productivity. This study examined the effects of changes in climatic variables such as rainfall and temperature on maize production in the Ejura-Sekyedumase Municipality, Ghana. Regression, chi-square and trend analyses were used to establish the relationship between climate variables (rainfall and temperature) and maize yield in the study area. This was supplemented with participatory household interviews with 120 farmers to understand the perception of farmers on rainfall and temperature patterns. The results from the study respondents and trend analysis show that rainfall is shorter in terms of duration and less predictable, whilst temperature has increased. The findings suggest that the general relationship between rainfall, temperature and maize yield is such that maize yield increased with increasing rainfall of the right amount and distribution pattern and decreased with increasing temperature. The study concludes that climate variability and/or change is evident in the study area and its effect on maize yield is severe.
1. Introduction
In spite of Ghana’s transition to service and industry sectors-led economy in recent years, agriculture is still very important to Ghana’s economy, contributing about 19.2 percent to the country’s GDP [1]. It is possible to achieve an agricultural growth rate of 6% as detailed in the Comprehensive African Agriculture Development Programme (CAADP) [2], but standing in the path to this possible achievement is a potential negative effect of climate variability and/or change [3]. Ghana’s agriculture is predominantly rain-fed and this makes the sector extremely vulnerable to the adverse impacts of climate change [4].
Agriculture is a major source of livelihood for millions of households in Ghana, where small-scale farmers dominate with 80% of domestic production. Studies have shown that, in the past forty years, Ghana has experienced changes in climatic conditions [5]. Since 1960, every ten years, there has been an increased average annual temperature by 1 °C [6]. Monthly rainfall has decreased by 2.4% during the period; however, rainfall amounts were particularly high [6]. Studies (e.g., [7]) suggest that changes in climatic variables such as rainfall and temperature will have a substantial impact on crop yield in Ghana. With the year 2000 as the baseline, findings by [7] showed that by 2050, the overall yield of rain-fed maize and rice will decrease by less than 25% and that of groundnuts above 25% as a result of climate change. This could affect the attainment of Sustainable Development Goal 2 relating to achieving food security for all by the year 2030. The impacts of climate change on maize production are compounded by interplay with other non-climatic factors such as high consumption patterns and complex land tenure issues that limit the adaptive capacity of farmers [8].
A study conducted in the Sahel [9] reported that farmers are aware of changes in climatic conditions such as rainfall and temperature. Similarly, in a World Bank study, [10] found that farmers in Africa perceived changes in rainfall and temperature. These findings are corroborated by a study conducted in Botswana, Ethiopia, Ghana and Malawi, where farmers reported perceived changes in rainfall [11]. Studies in the Ejura-Sekyedumase Municipality, the study area for this paper, report similar findings [12,13]. These perceived changes in climatic conditions, according to the farmers, affect maize yield [12]. Maize is the most important crop in Ghana in terms of the agricultural sector and food security [14]. It is a source of energy, vitamins and a negligible amount of protein for humans, and a major ingredient in feed formulation for livestock [15]. It leads in terms of area planted, and it is only second to cocoa in terms of commodity crop [14] and represents more than 50% of total cereal production in Ghana [16]. It is also the most widely consumed staple food in Ghana with increasing production since 1965 [17]. Maize production plays a vital role in food security for many poor households in Ghana [18] with a per capita consumption of over 100 kg while also serving as a cash crop [12].
The study area is one of the key food-producing areas in Ghana, and specifically maize production. Maize is a staple in Ghana, and how changing climate will affect its production is important to understand but very little has been studied [4,19]. To contribute to the adaptation of maize farmers in Ejura-Sekyedumae Municipality to changing climatic conditions requires that they are well-informed about the phenomenon and its adverse effect on their livelihoods. To address this, the study assessed the perception of farmers on rainfall and temperature patterns in the Ejura-Sekyedumae Municipality. The study further determined the extent of rainfall and temperature changes in the Ejura-Sekyedumae Municipality and the effect of rainfall and temperature variability on maize production in the Ejura-Sekyedumae Municipality. The study concludes that climate variability and/or change is evident in the study area and its effect on maize yield is severe. This paper contributes to the understanding of the effects of climate variability and/or change on maize production in the Ejura-Sekyredumase Municipality, Ghana. This evidence will provide the opportunity for policymakers to devise appropriate policy interventions to reduce the vulnerability of small-scale maize farmers to the adverse impacts of climate variability and/or change.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection and Description of the Study Area
The Ejura-Skyedumase Municipality leads in maize production in the Ashanti Region and is one of the leading producers in Ghana [20]. The municipality is located within longitudes 1°5″ W and 1°39″ W and latitudes 7°9″ N and 7°36″ N [21]. It experiences both savannah and forest climatic conditions with a bimodal type of rainfall in the Guinea Savannah and semi-deciduous forest agro-ecological zones. The average annual minimum and maximum temperatures are 21.4 °C (±0.4) and 31.2 °C (±0.5), respectively, with an average annual temperature of 26.30 °C [22]. The major season is April to June, whilst the minor season is September to November, with an average annual rainfall of 1430.0 mm [22]. The dry season ranges between November to April, and during this time, the North-East trade winds, popularly known as the Harmattan, blow dry and dusty air across the municipality [20]. The warmest months are between January and April, whilst the coolest months range between July and August [19]. The wet season is related to very high humidity, June records the highest relative humidity as high as 90% and February records relative humidity as low as 55%. The municipality is the driest in the Ashanti Region [20].
This study considered a questionnaire survey with farmers in three (3) communities in the study area, which were selected on the criteria that, the communities should have been or are being exposed to some sort of changes in climatic conditions. Based on the above criteria and local experts’ advice, Ejura, Dromankuma and Kyenkyenkura were selected for the study. Figure 1 presents Ghana with the study communities.
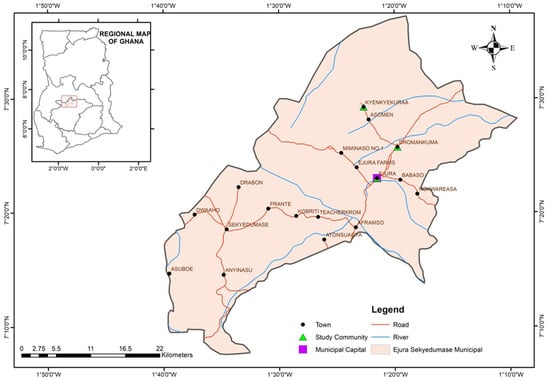
Figure 1.
Ghana showing study communities.
2.2. Household Surveys
Purposeful Random Sampling (PRS) was used to select one hundred and twenty (120) farmer households from the target communities and a semi-structured questionnaire administered to them. To avoid bias, in a household with more than one farmer, the questionnaire was administered to only one farmer. Each questionnaire took about twenty-five minutes to administer, and responses were recorded in writing and in audio and were later transcribed. Factors considered in the PRS included age, farming experience and gender in order to have a representation of the several social groups within each community and to ensure that people who were very knowledgeable on the theme of the research were interviewed.
The questionnaire was administered to forty (40) farmer households in each community in their homes. The questionnaire had a mix of close-ended questions with response options and open-ended questions to explore the answers of the respondents. The main questions administered were: (i) Have you perceived changes in rainfall and temperature? (ii) If you have perceived changes in rainfall and temperature, did it affect your maize crop? (iii) If the perceived changes affected your maize crop, did it lead to increase yield or decrease yield? (iv) If it led to decreased yield, in your opinion what accounted for the decrease in yield over the period? The survey data for the research were collected in June 2017.
2.3. Secondary Data Collection
Rainfall and temperature (minimum and maximum) data for the study area were obtained from the Ghana Meteorological Agency (GMet) in Accra covering the period between 2004 and 2015 for rainfall and 2004 and 2010 for temperature. The rainfall and temperature data were limited to 2004 to 2015 and 2004 to 2010, respectively, because data were available in those years at the time. Maize yield data for the study area were also obtained from the Ministry of Food and Agriculture (MoFA) covering the period between 2004 and 2015.
2.4. Data Analysis
A simple correlation method—rainfall, temperature and maize yield composite analysis—was used in order to examine the relationship between annual rainfall and maize yield and total average annual temperature and maize yield. Figures were used to describe and explore relationships of the variables used at the inter-annual time scale. Graphs were generated to deduce the trends.
Using average climate data (rainfall and temperature) between 1971 and 2000 as a baseline, the variance between the baseline and the annual rainfall and temperature data, respectively, were calculated. Regression and chi-square analysis were used to analyze annual rainfall and maize yield and total average annual temperature and maize yield to deduce the relationship between the variables used.
The equation for the linear regression is Y = b1 + b2X, where b1 is the intercept, and b2, the regression constant, X is the independent variable (total average annual rainfall/temperature), and Y, the dependent variable (annual maize yield). The responses by the farmers were coded and analyzed using SPSS (version 23). Tables and graphs were used to display the data in order to deduce the trends
3. Results
3.1. Farmers’ Perception of Climate Variability in the Study Area
As the focus of this study, farmers were asked whether they have over the years experienced variations that are perceived to be related to climatic changes. Table 1 summarizes the results where respondents indicated their knowledge or otherwise on the climatic variables. About 116 (96.7%) respondents indicated that they had noticed more rains in the past compared with now. The same number of respondents said they had noticed a decrease in total rainfall patterns in recent years compared with the past. The results show that 118 (98.3%) respondents said they had noticed changes in the duration of rainfall in recent years compared with the past. A total of 117 (97.5%) respondents indicated they had noticed changes in the onset of rains compared with the past and 110 (91.7%) noticed rainfall season has become shorter compared with the past.

Table 1.
Farmers’ perception of climate variability in Ejura-Sekeyedumase Municipality.
When asked whether rains come earlier compared with their childhood, 95 respondents representing 79.2% responded in the negative; however, when the same question was rephrased, 98 respondents, representing 81.7%, responded in the affirmative that, compared with their childhood, the rains come later. This is an indication that the respondents had noticed late rains in recent years. About 105 (87.5%) had noticed increased temperatures in recent times compared with the past, 95 (79.2%) had noticed increased wind storms in recent times compared with the past, whiles only 34 respondents, representing 28.3%, had noticed increased flooding compared with the past.
3.2. Inter-Annual Rainfall and Temperature Variability in the Study Area
The trend of annual rainfall (mm) from 2004 to 2015 in the study area is as shown in Figure 2. The highest annual rainfall was recorded in 2010 (1573.7 mm), which is above the study area’s average highest annual rainfall (1971–2000) of 1430.0 mm. The lowest annual rainfall was recorded in 2012 (1065.4 mm), which is below the study area’s average lowest annual rainfall (1971–2000). The pattern showed varied rainfall data.
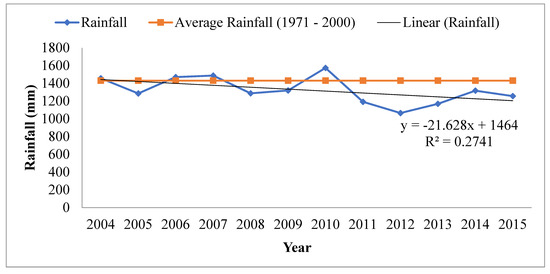
Figure 2.
Annual rainfall (mm) in Ejura-Sekyedumase Municipality (2004–2015); NB: average annual rainfall (1971–2000) for the municipality is 1430.0 mm.
Figure 3 indicates that there was high inter-annual rainfall variability in the study area, with 2011, 2013 and 2012 experiencing the highest reduction of 238.5 mm, 261.0 mm and 364.6 mm, respectively, below the study area’s average (1971–2000). With the exception of 2010, which experienced 143.7 mm of rainfall above the study area’s average (1971–2000), rainfall amount for 2004, 2006 and 2007 only varied from 26.7 mm to 57.5 mm above the study area’s average (1971–2000).
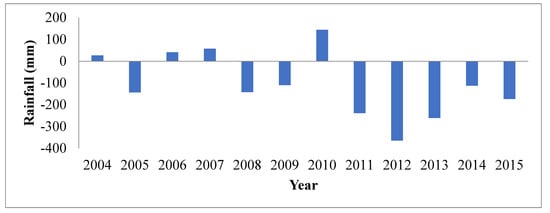
Figure 3.
Annual rainfall (mm) anomalies in Ejura-Sekyedumase Municipality (2004–2015); NB: average annual rainfall (1971–2000) for the municipality is 1430.0 mm.
Figure 4 shows the total average annual temperatures trend in the study area from 2004 to 2010. The highest total average annual temperature was recorded in 2010 (28.36 °C) and the lowest total average annual temperature was recorded in 2004 (24.80 °C).
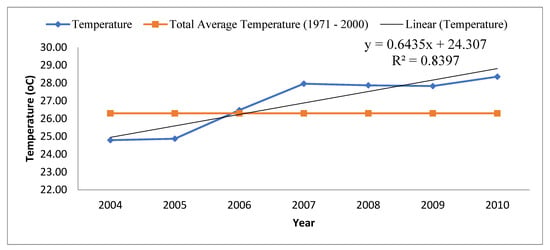
Figure 4.
Total average annual temperature (°C) trend in the Ejura-Sekyedumase Municipality (2004–2010); NB: total average annual temperature (1971–2000) for the municipality is 26.3 °C.
From Figure 5, the total average annual temperature departs from the study area’s average (1971–2000) of 26.30 °C. The total average annual temperature for 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009 and 2010 was higher than the study area’s average (1971–2000) with 2010 recording the highest departure of 2.06 °C.
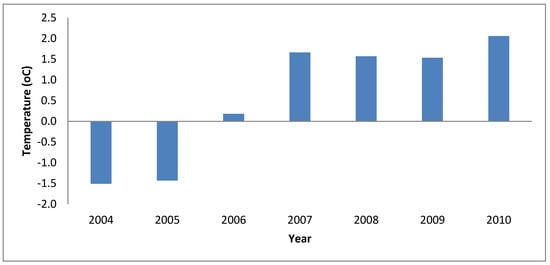
Figure 5.
Total average annual temperature (°C) anomalies in Ejura-Sekyedumase Municipality (2004–2010); NB: total average annual temperature (1971–2000) for the municipality is 26.3 °C.
3.3. Intra-Annual Variability of Rainfall in the Study Area
The trend of the total intra-annual variability of rainfall from 2004 to 2015 in the study area is as shown in Figure 6. The distribution of rainfall showed that in 2004, 2008, 2009, 2011, 2013, 2014 and 2015, the amount of rain received during the major rainy season (April–June) was higher than the minor rainy season (September–November).
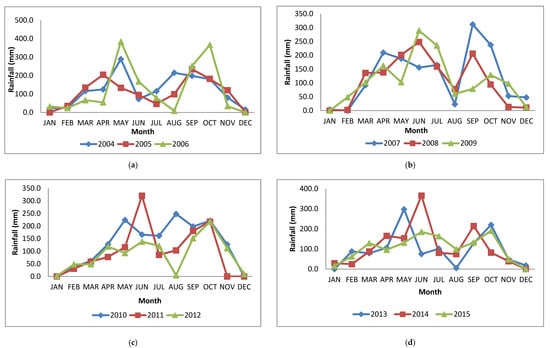
Figure 6.
(a–d): Intra-annual rainfall distribution in Ejura-Sekyedumase Municipality (2004–2015).
However, the trend was different in 2005, 2006, 2007, 2010 and 2012, where the amount of rain received in the minor season was higher than the amount received in the major season. It can be seen that lower amounts of rains in the major season were compensated for by higher amounts of rains during the minor season. In 2010, the highest amount of rainfall (248.3 mm) was recorded in August, which is outside the normal rainy season months in the study area. This accounts for why 2010 was the year with the highest annual rainfall (1573.7 mm). January and December were the months with predominantly less rainfall and in some cases no rainfall.
3.4. Relationship between Rainfall and Maize Yield
Figure 7 shows the relationship between annual rainfall and annual maize yield for 2004 to 2015 in the study area. As rainfall decreased from 1456.7 mm to 1286.2 mm in 2004 to 2005, maize yield also saw a decline from 1.4 t/Ha to 1.29 t/Ha. However, the trend changed in 2006 as maize yield decreased further to 1.22 t/Ha even though rainfall increased sharply to 1470.7 mm. Between 2006 and 2007, rainfall increased marginally, and maize yield also increased marginally and maintained a constant figure through 2008 and 2009 at 1.25 t/Ha; however, rainfall fluctuated moderately at 1287.8 mm and 1319.6 mm, respectively.
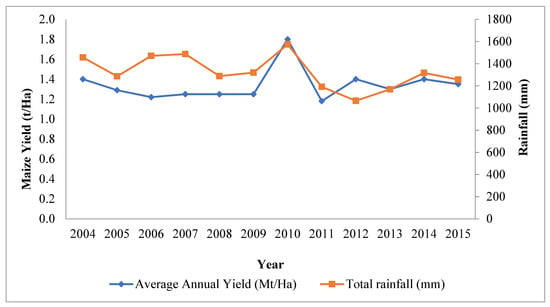
Figure 7.
Relationship between annual rainfall (mm) and annual maize yield (t/Ha).
The year 2010 recorded the highest maize yield of 1.8 t/Ha and at the same time recorded the highest rainfall of 1573.7 mm. The year 2011 recorded the lowest maize yield of 1.18 t/Ha, while 2012 recorded the lowest rainfall of 1065.4 mm for the study period. The trend for 2009, 2010, 2011, 2013, 2014 and 2015 is such that, maize yield increased with increasing rainfall and vice versa.
3.5. Relationship between Temperature and Maize Yield
Figure 8 shows the relationship between total average annual temperature and annual maize yield for 2004 to 2010 in the study area. As the temperature increased from 24.79 °C to 24.87 °C in 2004 and 2005, respectively, maize yield also decreased from 1.4 t/Ha to 1.29 t/Ha. A similar trend was observed in 2006 as temperature increased further to 26.48 °C maize yield saw a further decline to 1.22 t/Ha. The trend, however, changed in 2007 as there was a marginal increase in maize yield of 1.25 t/Ha, even though temperature increased sharply to 27.96 °C. The years 2008 and 2009 recorded the same maize yield as 2007, even though temperature declined marginally from 27.87 °C (2008) to 27.83 °C (2009). The year 2010 recorded the highest temperature of 28.36 °C as well as the highest maize yield of 1.8 t/Ha.
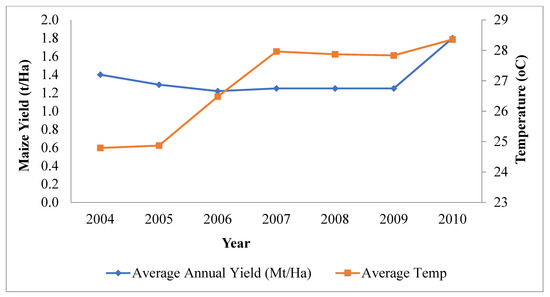
Figure 8.
Relationship between total average annual temperature (°C) and annual maize yield (t/Ha).
3.6. Regression for the Relationship between Rainfall and Maize Yield
From Table 2, annual maize yield = 0.762 + 4.378 × 10−4 (annual rainfall). The constant term (intercept) is indicative of the fact that the annual maize yield will be 0.762 metric tons per hectare if the annual rainfall was 0 mm. The slope of the line (4.378 × 10−4 also shows that an increase in the annual rainfall by 1 mm will increase the annual maize yield by 4.378 × 10−4 (0.0004378) metric tons per hectare. Thus, there is a slight positive relationship between annual rainfall and the annual maize yield.

Table 2.
Regression analysis of rainfall and temperature against maize yield.
From Table 2, the regression reported an R squared of 0.161. This means that annual rainfall (the independent variable) is able to account for approximately only 16.1% of the variations in the annual maize yield over the period. Indirectly, about 83.9% of the variations in the maize yield annually cannot be accounted for by the annual rainfall. These variations are caused by other factors that affect annual maize production, which are exogenous to the model (for example, fertilizer application and/or manure, use of improved varieties, improved technology, etc.) that could have various effects on the output of annual maize per hectare.
3.7. Regression for the Relationship between Temperature and Maize Yield
From Table 2, Annual maize yield = 0.513 - 0.031 (total average annual temperature). The constant term (intercept) is indicative of the fact that the annual maize yield will be 0.513 metric tons per hectare if the total average annual temperature was 0 °C. The slope of the line (−0.031) also shows that an increase in the total average annual temperature by 1 °C will decrease the annual maize yield by 0.031 metric tons per hectare. Thus, there is a negative relationship between the total average annual temperature and the annual maize yield.
From Table 2, the regression reported an R squared of 0.053. This means that the total average annual temperature is able to explain approximately 5.3% of the variations in the annual maize yield over the period. Implicitly, about 94.7% of the annual variations in the maize yield cannot be explained by the total average annual temperature. These variations are caused by other factors that affect annual maize production, which are exogenous to the model (for example, the use of improved seeds, the use of drought-resistant crops, and irrigation) which could have effects of diverse magnitudes on the output of annual maize yield per hectare.
4. Discussion
4.1. Perception of Rainfall and Temperature Changes in the Study Area
Farmers in the study area have observed changes in climatic conditions, particularly rainfall and temperature. A clear majority of the farmers reported that they have noticed a reduction in rainfall amount. This observation by the farmers is similar to results by [11], where they reported that 90% of respondents said that the rainfall amount had reduced compared to their childhood. Reference [23] reports that total annual rainfall is not decreasing; however, the amount recorded during the planting period has been decreasing in a study conducted in the Northern Savannah zone of Ghana. They concluded that, for this reason, many of the farmers reported noticing a decrease in rainfall amount. Reference [24] reports that the amount and distribution of rainfall within the planting season are more important than the total annual rainfall within the season. In terms of rainfall pattern, the number of respondents who noticed declining rainfall amount also noticed a change in the rainfall pattern. It was, however, not clear if this change means the rainfall pattern has become “erratic or unpredictable”.
Studies have shown that when farmers report noticing changes in rainfall pattern, they mean rainfall has become “more erratic” or “more unpredictable” compared to their past [11]. Almost all the farmers reported noticing changes in the duration of rainfall in recent times. These results support findings in other African countries by [11], which found that farmers in Malawi perceive the rainy period to be shorter now compared to the previously longer periods with heavy rainfall. Additionally, using 2000 as the baseline, they found that farmers in Ethiopia observed that the rains lasted longer than 3 months and with more precipitation at each rain event, which is now less than a week and provides less water. As was the case for the duration, it was almost unanimous among the farmers that the onset of the rainfall has changed. This finding corroborates results by [13] that over 90% of respondents were of the view that rainfall timing had changed, resulting in increased frequency of drought in the Ejura-Sekyedumase municipality. Our findings also corroborate that of [11], who reported that interviews across Malawi concluded that the rainy season now starts 1–1.5 months later.
Temperature, another climatic variable, was perceived to have increased in recent times compared to the past by a significant number of respondents. The authors of [23] reported similar findings, that about 80.2% of their survey respondents had the perception that the average temperature in their communities had increased in the past 30 years. Additionally, in a study by [25] in the Ejura-Sekyedumase municipality, results showed that about 92% of the respondents perceived increases in temperature.
4.2. Exploring the Extent of Climate Variability in the Study Area
Climate change and/or variability are projected to have serious environmental, economic and social impacts on Ghana [25]. It is expected to be severe for rural farmers whose livelihoods depend largely on climatic conditions, particularly rainfall. The extent of these impacts depends largely on awareness and the level of adaptation in response to climate change and/or variability [25]. Evidence from the household survey indicates that farmers are well aware of climate variability and by extension climate change and are employing on-farm and off-farm adaptation strategies to mitigate the impact on their livelihood. This finding is in line with results from studies by researchers in the study area (e.g., [12,13,26]).
The farmers’ awareness of climate variability is evidenced in their perception of changes in rainfall and temperature. In a study in the Northern Savannah zone of Ghana, farmers cited a decline in rainfall amounts and changes in planting time as evidence of climate change [23]. As planting is tied to the onset of the rains, farmers’ assertion that changes in planting time are evidence for climate change relates to the onset of the rain. This result resonates with the findings of this study. Additionally, reference [25] reports that farmers generally perceived climate change and/or variability in terms of erratic rainfall distribution, reduction in rainfall amounts, and increasing temperatures. The trend of annual rainfall from twelve-year data analyzed revealed that there was high inter-annual rainfall variability in the study area. The nature of this variability is similar to studies by [27] that inter-annual rainfall variability is a characteristic of sub-Sahara regions.
The variability of rainfall in the study area was not only between years but also within years. Such occurrence has a high probability to have substantial effects on crop production in the study area because the amount and frequency of precipitation determine the success or failure of crop production in a given year [28]. Additionally, the trend of seven-year data analyzed indicated that temperature was increasing with time. This confirms the World Bank’s finding that temperatures in Africa are becoming warmer in recent years [9]. Subjective approaches to the measurement of climate change have been criticized on the grounds that climate change is difficult to detect accurately based on personal experience [29]. Although farmers in the Ejura-Sekyedumase Municipality based their perceptions of changes in climatic variables on past weather conditions, their perceptions generally corresponded with the evidence of changes recorded by nearby weather monitoring stations.
4.3. Relationship between Rainfall and Maize Yield
The results suggest that the general relation between rainfall and maize yield is such that maize yield increases with increasing rainfall of the right amount and distribution pattern. The year 2010 recorded the highest maize yield and at the same time recorded the highest annual rainfall. The results show that 2010 not only recorded the highest rainfall amount but also the evenly distributed rainfall pattern for the study period, with August, a non-traditional rainy month, recording the highest amount of rainfall (248.3 mm) in that year. This indicates that rainfall in the right amount and distribution pattern is a critical factor for maize yield. This confirms the study by [30] that showed that the maize crop totally depends upon the amount and frequency of rainfall as well as its distribution on temporal and spatial scales.
In 2006, even though rainfall amount was considerably high, the maize yield was comparatively low. This might be due to the fact that if the amount of rainfall is above normal, it causes waterlogging and therefore affects maize production (Figure 6). This confirms the study by [31] showing that the correlation between rainfall variability and maize production indicated that as rainfall continues to increase above normal, the additional gain in maize production begins to diminish. It also confirms the study by [30] finding that maize requires a specific amount of water; an increase in rain enhances the yield up to certain limits beyond that threshold the grain yield decreases. Although 2012 recorded the lowest rainfall amount, it recorded a relatively high maize yield. This might be due to the fact that other factors, such as the use of improved seeds and fertilizer application, might have contributed to the boost in production in the year. This was confirmed by respondents who said that, with the advent of fertilizer, agro-chemicals, improved varieties, tractor services and new technologies, the yield was expected to be high but for climate variability and change.
Respondents in the study area highlighted that in years in which rainfall amount was low, maize yield decreases significantly. However, there are varying findings on the impact of rainfall on maize yield in the literature. The authors of [32] found that there is a significant positive correlation (p < 0.05) between maize yield and precipitation in Eastern United States. Reference [33] indicated that precipitation has negative effects on maize yields in the Middle East and parts of Northeast China. The authors of [34] also found a negative correlation between precipitations and maize yields in the northern plain of China. Reference [35] also shows that a 1 mm increase in precipitation decreases maize production by 0.02%. Findings by [36,37] revealed that maize plants tend to experience extreme sensitivity to water deficit during flowering to the beginning of the grain-filling phase. The authors of [11], in a study on how climate change impacts maize, reported that farmers suffer low yield in “bad years” as they are not able to harvest any grain at all in some seasons due to rainfall failure.
4.4. Relationship between Temperature and Maize Yield
The results suggest that the general relationship between temperature and maize yield is such that maize yield decreases with increasing temperature. However, in 2007, there was a marginal increase in maize yield, even though the temperature increased sharply. This can be explained by the fact that 2007 received a considerable amount of rainfall. Similarly, 2010 recorded the highest temperature value, yet it also recorded the highest maize yield value. This is because 2010 also recorded the highest rainfall amount as well. This is an indication that rainfall in the right amount and distribution pattern can mitigate the effect of temperature on maize yield.
Maize has been found to be one of the most sensitive crops to weather variations, in particular temperature [38]. Temperature seems to decrease maize yields: an increase by one standard deviation in temperature translates into a fall of about 1.4% in maize yields in the northern spring maize zone of China [39]. Generally, increased warming has a tendency to accelerate the loss of water from soil, thereby affecting maize growth from germination to vegetative growth and later grain filling [40]. In a study in the Shanxi Province in China, [41] found that a one percent increase in extreme-heat-degree days and consecutive-dry days result in a maize yield decline of 0.2% and 0.07%, respectively. They found further that, if all the historical temperatures in the villages are shifted up by 2 degrees Celsius, the total impacts of these extreme events would lead to a reduction in maize yield by over 30%. They concluded that the impacts may even be worse since they did not exclude the offset effect of adaptation measures adopted by farmers to combat these extreme events.
5. Conclusions
This paper builds on studies on climate change and implications of its variability on crop in Ghana [4,19] by analysing the effect of changes in climatic variables such as rainfall and temperature on maize yield in the Ejura-Sekyedumase municipality, Ghana. The research tried to authenticate farmers’ perceptions of climate variability with the real variations based on rainfall and temperature data (climate data) recorded from 2004 to 2015 (rainfall) and 2004 to 2010 (temperature).
This paper has confirmed that rainfall is less predictable, shorter in duration and reduced in amount, whilst temperature has become warmer, in recent years [6,42,43]. The paper further confirmed that rainfall in the right amount and distribution pattern is the most critical factor that affects crop (maize) production [30,44].
The paper revealed that the general relationship between rainfall, temperature and maize yield was such that, maize yield increased with increasing rainfall of the right amount and distribution pattern and decreased with increasing temperature. It is worth noting that, due to the limited availability of secondary data, the comparison between rainfall and maize yield spans for twelve (12) years, while that of temperature and maize yield spans for seven (7) years.
The results indicated that climate variability and/or change has adverse consequences on maize production. For example, erratic and unpredictable rainfall patterns, shorter rainfall duration and higher temperatures adversely affect maize yield. From the results, it can be concluded that climate change and/or variability is evident in the Ejura-Sekyedumase municipality, and its effects on maize yield are severe.
To this end, it is urgent to encourage interventions that improve the food production systems in the municipality so as to increase farmers’ ability to withstand the variability of rainfall. One strategy would be to finance agricultural research and extension and other methods to reduce food production losses associated with changes in climatic variables such as rainfall and temperature.
Finally, given the large doubts about future rainfall patterns, attention should be directed towards investments in support of water resources development and irrigation infrastructural development so as to restrict the impacts of food production losses.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and writing—original draft preparation, G.P.C.; supervision and writing—review and editing, P.A.-A.; writing—review and editing, B.A.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available and were collected from GMeT and MoFA in person.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- GSS. Quarterly Gross Domestic Product (QCDP), Third Quarter; Ghana Statistical Service: Accra, Ghana, 2018.
- Diao, X.; Thurlow, J.; Al-Hassan, R.M.B. Agriculture for Development in Ghana; Intl Food Policy Res Inst: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Deschenes, O.; Greenstone, M. The economic impacts of climate change: Evidence from agricultural output and random fluctuations in weather. Am. Econ. Rev. 2006, 97, 354–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwi-Agyei, P.; Fraser, E.D.; Dougill, A.J.; Stringer, L.C.; Simelton, E. Mapping the vulnerability of crop production to drought in Ghana using rainfall, yield and socioeconomic data. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 32, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyeman-Bonsu, W.; Minia, Z.; Dontwi, J.; Dontwi, I.K.; Buabeng, S.N.; Baffoe-Bonnie, B.; Yeboah, F.A.; Ofori, E.; Gyasi, E.A.; Karikari, O.; et al. Ghana Climate Change Impacts, Vulnerability and Adaptation Assessments; Allotey, J., Mensah, L., Eds.; Environmental Protection Agency: Accra, Ghana, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- GEPA. Ghana’s Second National Communication to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change; GEPA: Wuppertal, Germany, 2011.
- Nutsukpo, D.K.; Jalloh, A.; Zougmoré, R.B.; Nelson, G.C.; Thomas, T.S. West African Agriculture and Climate Change: Ghana Summary Note; Intl Food Policy Res Inst: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Antwi-Agyei, P.; Dougill, A.J.; Stringer, L.C. Land use policy impacts of land tenure arrangements on the adaptive capacity of marginalized groups: The case of Ghana’s Ejura Sekyedumase and Bongo districts. Land Use Policy 2015, 49, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertz, O.; Mbow, C.; Reenberg, A.; Diouf, A. Farmers’ perceptions of climate change and agricultural adaptation strategies in rural Sahel. Environ. Manag. 2009, 43, 804–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddison, D.J. The perception of and adaptation to climate change in Africa. In Policy Research Working Paper 4308; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; pp. 21–35. [Google Scholar]
- Simelton, E.; Claire, H.; Quinn, C.H.; Antwi-Agyei, P.; Batisani, N.; Dougill, A.J.; Dyer, J.; Evan, D.G.; Fraser, E.D.G.; Mkwambisi, D.; et al. African Farmers’ Perceptions of Erratic Rainfall; Sustainability Research Institute Paper No. 27; Working Paper No. 73; Centre for Climate Change Economics and Policy: Leeds, UK, 2011; pp. 70–79. [Google Scholar]
- Klutse, N.D.M.; Owusu, K.; Adukpo, D.C.; Nkrumah, F.; Quagraine, K.; Owusu, A.; Gutowski, W.J. Farmer’s observation on climate change impacts on maize (Zea mays) production in a selected agro-ecological zone in Ghana. Res. J. Agric. Environ. Manag. 2013, 2, 394–402. [Google Scholar]
- Kemausuor, F.; Dwamena, E.; Appiah, D.O. Assessment of farmers’ adaptation to climate change in Ghana; the Case of Ejura- Sekyeredumase District. J. Arts Humanit. 2012, 1, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- MiDA. Millennium Development Authority, Investment Opportunity Ghana, Maize, Soya and Rice Production. Available online: https://assets.mcc.gov/investmentopps/bom-ghana-english-grain.pd (accessed on 4 April 2017).
- Akowuah, J.O.; Mensah, L.D.; Chan, C.; Roskilly, A. Effects of practices of maize farmers and traders in Ghana on contamination of maize by aflatoxins: Case study of Ejura-Sekyeredumase Municipality. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 9, 1658–1666. [Google Scholar]
- Ragasa, C.; Takeshima, H.; Chapoto, A.; Kolavalli, S. Substituting for Rice Imports in Ghana; Intl Food Policy Res Inst: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. FAOSTAT: Statistical Databases. Available online: http://faostat.fao.org (accessed on 23 September 2013).
- MoFA. Agriculture in Ghana: 2010 Facts and Figures; MoFA: Tokyo, Japan, 2010; p. 53.
- Codjoe, S.N.A.; Owusu, G. Climate change/variability and food systems: Evidence from the Afram Plains, Ghana. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2011, 11, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MoFA. Available online: http://mofa.gov.gh/site/?page_id=857 (accessed on 4 April 2017).
- GSS. 2010 Population and Housing Census, District Analytical Report, Ejura-Sekyedumase Municipality; Ghana Statistical Service: Accra, Ghana, 2014.
- Codjoe, S.N.A. Effects of changes in population, household conditions and farming systems on agricultural land use in the volta river basin of Ghana, 1984–2000. Presented at Deutscher Tropentag, Gottingen, Germany, 8–10 October 2003; pp. 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Teye, J.K.; Yaro, J.A.; Bawakyillenuo, S. Local farmers’ experiences and perceptions of climate change in the Northern Savannah zone of Ghana. Int. J. Clim. Chang. Strateg. Manag. 2015, 7, 327–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCarthy, D.S.; Sommer, R.; Vlek, P.L.G. Modelling the impacts of contrasting nutrient and residue management practices on grain yield of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) in a semi-arid region of Ghana using APSIM. Field Crop. Res. 2009, 113, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosu-Mensah, B.Y.; Vlek, P.L.; MacCarthy, D.S. Farmers’ perception and adaptation to climate change: A case study of Sekyedumase district in Ghana. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2012, 14, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwi-Agyei, P.; Stringer, L.C.; Dougill, A.J. Livelihoods adaptation to climate variability: Insights from farming households in Ghana. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2014, 14, 1615–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiaensen, L.J. Down to Earth: Agriculture and Poverty Reduction in Africa; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nhemachena, C.; Hassan, R. Micro-Level Analysis of Farmers’ Adaption to Climate Change in Southern Africa; Intl Food Policy Res Inst: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, E.U. What shapes perceptions of climate change? WIREs Clim. Chang. 2010, 1, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, K.; Rasul, G. Rainfall variability and maize production over the Potohar Plateau of Pakistan. Pak. J. Meteorol. 2011, 8, 63–74. [Google Scholar]
- Magehema, A.O.; Changa, L.B.; Mkoma, S.L. Implication of rainfall variability on maize production in Morogoro, Tanzania. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 4, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Duiker, S.W.; Deng, L.; Fang, C.; Zeng, W. Influence of precipitation on maize yield in the Eastern United States. Sustainability 2015, 7, 5996–6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Huang, Y. Estimating the impacts of warming trends on wheat and maize in China from 1980 to 2008 based on county level data. Int. J. Climatol 2013, 33, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, E.; Xue, C. Climate and crop yields impacted by ENSO episodes on the North China Plain: 1956–2006. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2014, 14, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Takahashi, T.; Suzuki, N.; Kaiser, H.M. Impact of climate change on maize production in Northeast and Southwest China and risk mitigation strategies. Apcbee Procedia 2014, 8, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bergamaschi, H.; Dalmago, G.A.; Bergonci, J.I.; Bianchi, C.A.M.; Müller, A.G.; Comiran, F.; Heckler, B.M.M. Water supply in the critical period of maize and the grain production. Pesq Agrop Bras. 2004, 39, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlato, M.A.; Farenzena, H.; Fontana, D.C. Association between El Niño Southern Oscillation and corn yield in Rio Grande do Sul State. Pesq Agrop Bras. 2005, 40, 23–432. [Google Scholar]
- Schlenker, W.; Lobell, D.B. Robust negative impacts of climate change on African agriculture. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Maystadt, J. The impact of weather variations on maize yields and household income: Income diversification as adaptation in rural China. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2017, 42, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoyo, N.N.; Wakhungu, J.; Oteng, S. Effects of climate variability on maize yield in the arid and semi-arid lands of lower eastern Kenya. Agric. Food Secur. 2015, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Zhang, T.; de Bruin, K.; Glomrød, S.; Shi, Q. Extreme Weather Impacts on Maize Yield: The Case of Shanxi Province in China. Sustainability 2016, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacombe, G.; McCartney, M.; Forkuor, G. Drying climate in Ghana over the period 1960–2005: Evidence from the resampling-based Mann-Kendall test at local and regional levels. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2012, 57, 1594–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Economics of Adaptation to Climate Change: Ghana. Available online: http://climatechange.worldbank.org (accessed on 20 September 2013).
- Badolo, F.; Kinda, S.R. Climatic variability and food security in developing countries. Etudes Doc. 2014, 5, 43. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).