Abstract
The Persian walnut (Juglans regia L.) is the most grown nut tree crop in Central Europe. The aim was to study the full Hungarian walnut assortment with a distinct early spring phenology to detect the difference in phenolic profile in their green husks. Furthermore, the relationship between the presence and concentration of phenolic compounds and the tolerance/resistance of the observed cultivars to walnut bacterial blight was investigated. Examining the samples, significant differences were found between the concentrations of the different groups of phenolic compounds. Walnut blight immunity tests were also performed to clarify the role of phenolic compounds in the nut derived from a non-irrigated orchard. The Hungarian-bred local cultivars contained phenolic compounds in higher concentrations than the domesticated ones. There was a significant correlation between the budburst, as well as the pistillate flowers’ receptivity and the concentration of juglone. Cultivars with a low concentration of phenolic compounds were the most susceptible to walnut bacterial blight, except ‘Bonifác’.
1. Introduction
The Persian walnut (Juglans regia L.) is the most grown nut tree crop in Central Europe; its planting area and harvested yield are increasing annually in this region. All parts of the walnut such as leaves, green husk (mesocarp), pellicle, septum and kernel are rich in phytochemicals [1,2,3,4,5]. The nut is surrounded by the green husk that contains many bioactive compounds, such as polyphenols, which include flavonoids, [6,7], also known as phenolics [8,9,10], and pectin, glucans [5] and chlorophyll [11]. The phytochemicals have antimicrobial, antifungal and antioxidant activities [8,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19].
The phenolic compounds play an important role in the plant defence mechanisms against stress caused by many environmental factors and various pathogens [20]. They can inhibit the growth of mycelia and different bacteria up to 50%, but it is indicated that their inhibition effects depend on their concentration and the relationship between the juglone and phenolics present in the plant tissue [8,12,13,14,15,16,17,18].
The phenolic content and its profile vary in all walnut plant organs [21,22]. The quantity of the compounds depends on the soil and climatic conditions [5,23], while the cultivar [8,10,24,25,26,27], the sample period inside the growing season [28], the use of extracting solvent [18,29,30,31,32] and cultivation technology all affect the phenolic content.
In the green husk of walnut, one of the most important bioactive compounds from a chemical point of view is phenolics. The main groups of phenolics are hydroxybenzoic acids, hydroxycinnamic acids, flavonoids and naphthoquinones, which were detected in green husk samples [27,28]. Dihydroxybenzoic acid, gallic acid and syringic acid together with their derivatives are hydroxybenzoic acids, while coumaric acid, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, ferulic acid and its derivatives or esters are classified in the group of hydroxycinnamic acids. The group of flavonoids includes myricetin, quercetin and naringenin and/or their derivatives, while naphthoquinones include juglone with its different derivatives, which is a characteristic compound of unripe husks of the nuts [27,28].
Unfortunately, the green husk is mostly an agricultural waste, but this valuable organ has some uses as traditional alcoholic drinks [33,34,35], bottled fruits, jams [36,37] and cold-pressed oil [38,39,40] and some cosmetics [41,42] can also be made from it.
The phenolic compounds also play an important role in the defence against walnut blight caused by Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis. Gallic acid and juglone dominate in the nuts compared to the other phenolics [43]. The juglone concentration is usually higher in the green husk and nuts than in the leaves [44]. A negative correlation between juglone concentration and the susceptibility against walnut blight in the nuts was reported [45,46]. Juglone can be a discriminating biomarker for Xaj resistance [47,48] because the juglone concentration is smaller in the healthy areas than in the infected surfaces [49]. The resistance/tolerance of walnut cultivars against walnut bacterial blight does not depend on the density and breadth of stomas, the wax content of the leaves, leaf thickness, the thickness of the abaxial epidermis or the stratum corneum [50]. The inhibition effects of juglone depends on the isolation temperature too, as it has a negative correlation between antifungal activity and isolation temperature [18].
The aim of this study was to examine the full Hungarian walnut assortment, having a distinct early spring phenology, to detect the difference in phenolic profiles in their green husks. Furthermore, the relationship between the presence and concentration of phenolic compounds and tolerance/resistance of the observed cultivars to walnut bacterial blight at the stage of (finishing) completing nut size growth was investigated.
2. Results
Phenolic Compounds
In the green husk of walnuts one of the most important bioactive compounds is the phenolics. The studied cultivars were examined to detect the difference in concentration of total phenolics and the various compounds. The total phenolic content of the green husk in the samples ranged between 4420 and 5740 mg GAE/100 g dry matter (d.m.). A series of studies looked at the total phenolic content of the green husk, usually examining the samples in the context of antioxidant capacity. The present results are in line with data published by Soto-Madrid and co-workers [7] where the range of the total phenolic compounds was between 3117 and 10,601 mg GAE/100 g d.m. The research group of Soto-Maldonado [42] obtained the total polyphenol content as 1862.9 ± 72.4 mg GAE/100 g d.m., measured in the tested sample, while Oliveira and co-workers [8] determined the total phenolic content of the green husk of different cultivars and found that their concentration ranged from 32.61 mg/g of GAE (cv. ‘Mellanaise’) to 74.08 mg/g of GAE (cv. ‘Franquette’). Despite many applications, the Folin–Ciocalteu method [51] is only suitable for a rough estimate because, as Scalbert and co. [52] described, the molar absorbance or, instead, molar absorptivity per reactive group obtained for different compounds varies; in other words, the color generated by the different phenolic compounds depends on the molecular structure.
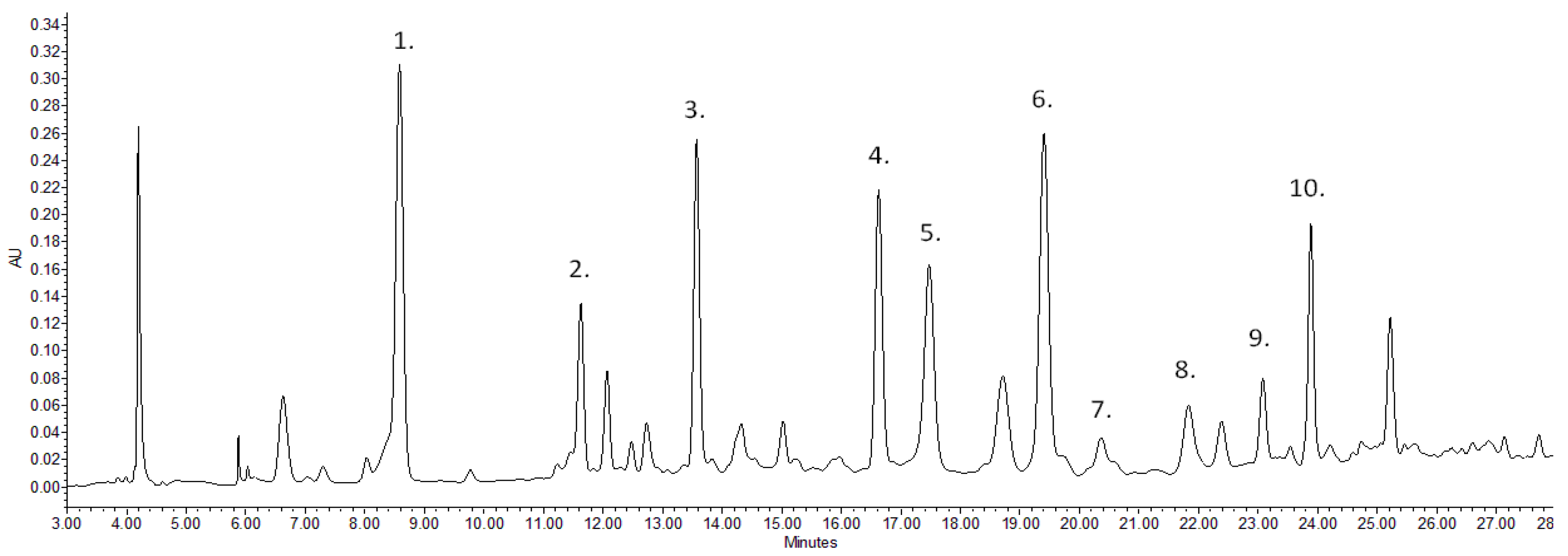
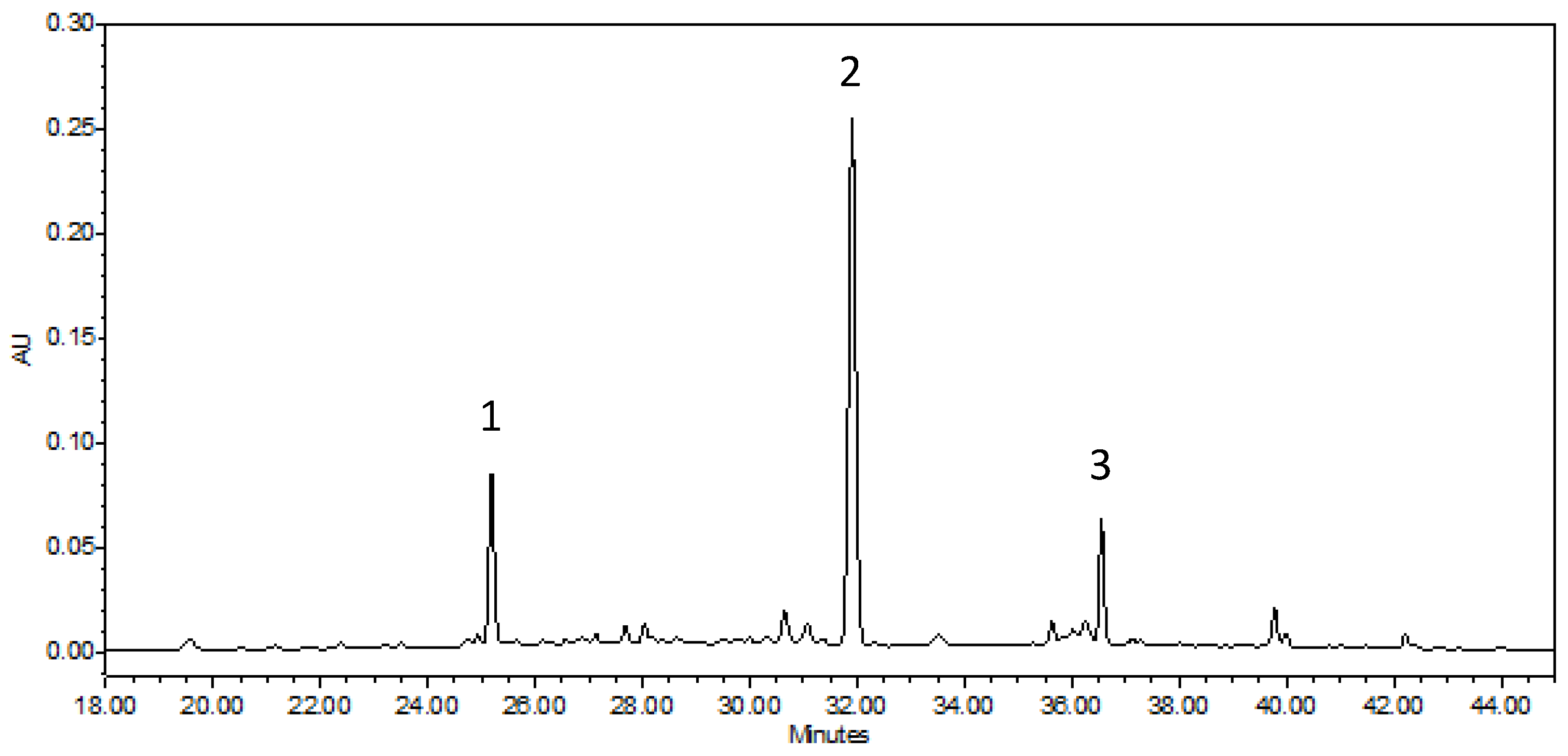
There is limited information in the scientific literature on detailed analysis of the walnut green husk; however, it can be important when we take into account the timings of the different developmental stages of the examined cultivars. When examining the cultivars, the concentration difference of the various compounds was also determined. Figure 1 and Figure 2 represent the chromatograms of the ‘Bonifác’ sample measured on a 280 nm wavelength for the main phenolic components and on 420 nm for juglone determination.
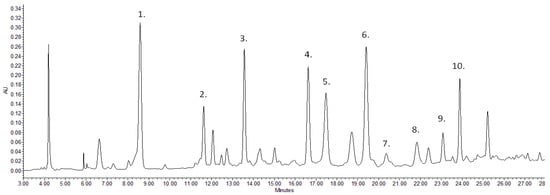
Figure 1.
Chromatogram of ‘Bonifác’ sample for the determination of the main identified phenolic components (λ = 280 nm; (1) gallic acid, (2) neochlorogenic acid, (3) p-coumaric acid, (4) syringic acid, (5) methylmirecitin derivative 1, (6) trihydroxyisoflavanone derivative, (7) quercetin-hexoside; (8) methylmirecitin derivative 2, (9) methoxynaringenin derivative, (10) quercetin-pentoside).
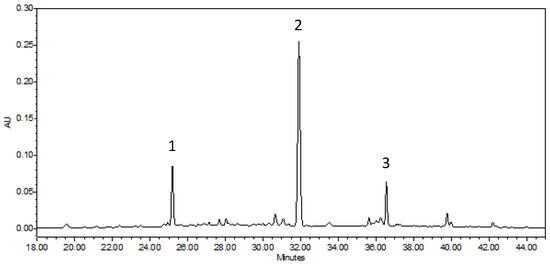
Figure 2.
Chromatogram of ‘Bonifác’ sample for the determination of juglone (λ = 420 nm).
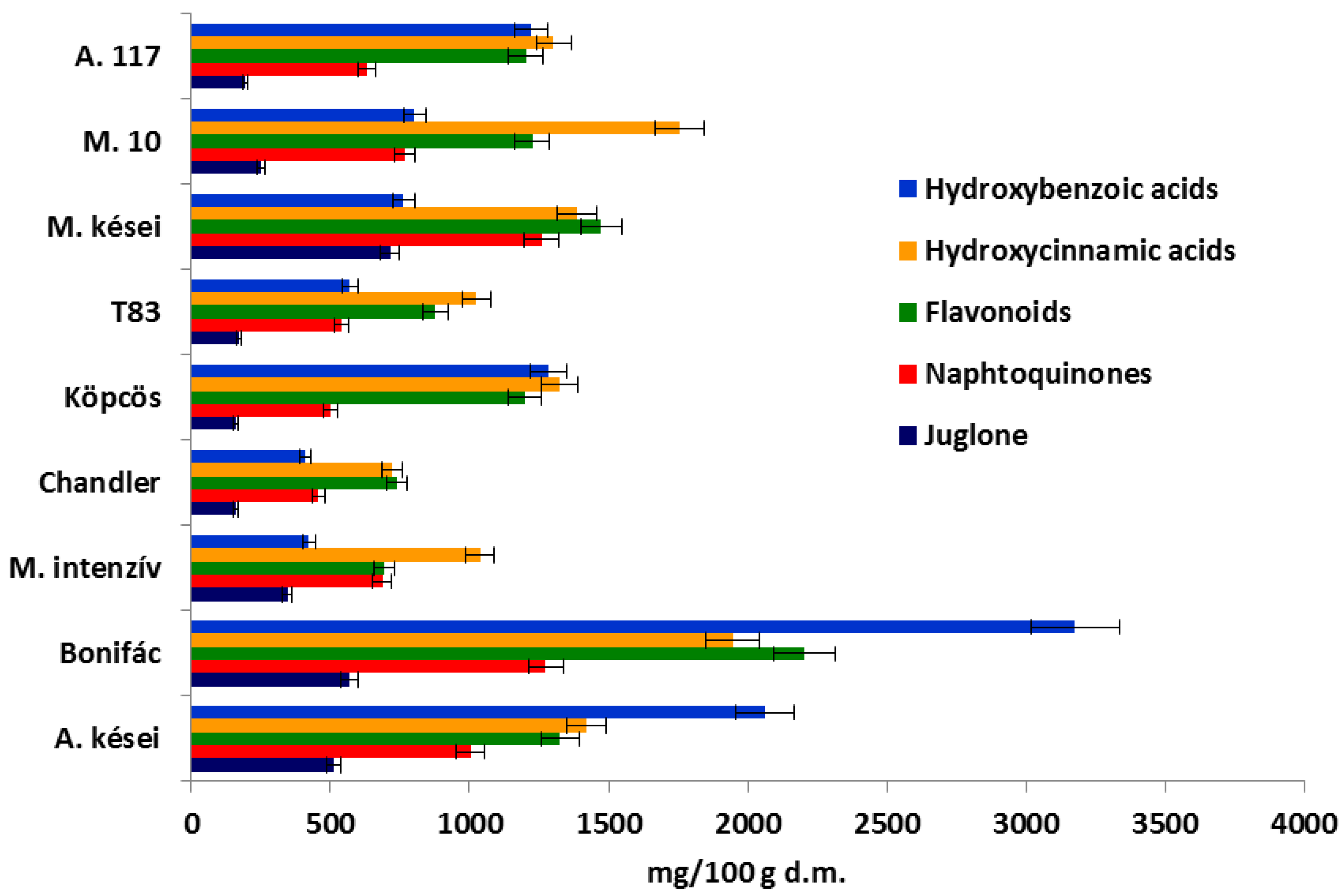
Examining the samples, significant differences were found between the concentrations of the different groups of phenolic compounds. In our measurements all components were calculated in rutin equivalent, except for the naphthoquinones calculated in the juglone equivalent. Figure 3 depicts the phenolic compound composition of the samples. The green husk of the ‘Alsószentiváni’-type samples contained the highest concentration of the components in question, especially ‘Bonifác’, in which the concentrations of hydroxybenzoic acids, hydroxycinnamic acids, flavonoids and naphthoquinones were 3176 mg/100 g d.m., 1947 mg/100 g d.m., 2203 mg/100 g d.m. and 1275 mg/100 g d.m., respectively. Comparing these results to the control ‘Chandler’, the total content of phenolics in the green husk was about 3.7 times higher in ‘Bonifác’. The total phenolics varied in the samples between 2329 and 8601 mg/100 g d.m.
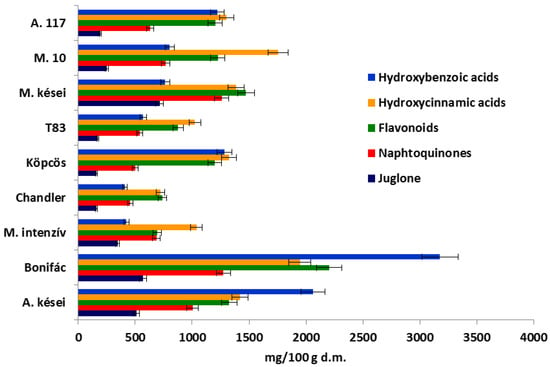
Figure 3.
Composition of phenolic compounds measured in the green husk of walnut samples (A.: Alsószentiváni, M.: Milotai).
The concentration of the hydroxybenzoic acids varied between 407 and 3176 mg/100 g d.m., with the samples with higher values being ‘Alsószentiváni 117’, ‘Alsószentiváni kései’, ‘Bonifác’ and ‘Köpcös’, 1220 mg/100 g d.m., 2063 mg/100 g d.m., 3176 mg/100 g d.m. and 1283 mg/100 g d.m., respectively. ‘Milotai 10′ and ‘Milotai kései’ contained 802 mg/100 g d.m. and 764 mg/100 g d.m., while ‘Milotai intenzív’ and ‘Chandler’ had the lowest values, 423 mg/100 g d.m. and 407 mg/100 g d.m., respectively. The content of hydroxycinnamic acids did not show such great differences; the concentration varied between 723 and 1947 mg/100 g d.m. In terms of flavonoids, a similar trend was seen; the concentration varied between 741 mg/100 g d.m. and 2203 mg/100 g d.m. The content of naphthoquinones was the highest in ‘Bonifác’ (1275 mg/100 g d.m.) and ‘Milotai kései’ (1260 mg/100 g d.m.). The lowest concentrations of this compound group were detected in ‘Köpcös’ (499 mg/100 g d.m.) and ‘Chandler’ (458 mg/100 g d.m.) (Figure 3).
3. Discussion
3.1. Phenolic Compounds and Early Spring Phenology
A higher concentration of phenolic compounds was detected in this trial compared to the data found in the literature [8,9,10,24,25,26,27,53]; whereas the mentioned authors collected their samples before ripening, our samples were collected during the lignification period in late June, when these components’ amounts reach their peak [28,51,53]. The juglone concentration measured in this trial was similar to the results of the research group from Slovenia [54]. This literature source also confirms that the locally bred cultivars can produce a higher concentration of compounds compared to the domesticated ones.
For juglone, several authors reported data that are consistent with our results. A research group [42] reported the amount of juglone was 169.1 mg/100 g d.m. and another research group [53] published values between 218 and 1404 mg/100 g d.m. depending on sampling time, while some researchers from Romania [10] found measurements between 20.56 and 42.78 mg/100 g from different varieties of mature walnut green husk. These results are in the same order of magnitude to ours, but, at the same time, they indicate the great variation due to the sampling time.
The ‘Alsószentiváni 117′, ‘Milotai 10′, ‘Tiszacsécsi 83′ and ‘Köpcös’ cultivars started their budburst and pistillate flowers’ receptivity almost at the same time as the control cultivar ‘Chandler’. The budburst of ‘Milotai intenzív’ was similar to the control, but it needed the longest period among the observed cultivars for the pistillate flowers to appear, 7 to 12 days after budburst. The budburst and pistillate flowers’ receptivity of ‘Bonifác’, ‘Milotai kései’ and ‘Alsószentiváni kései’ were 3 to 12 days and 7 to 17 days later than the control, respectively.
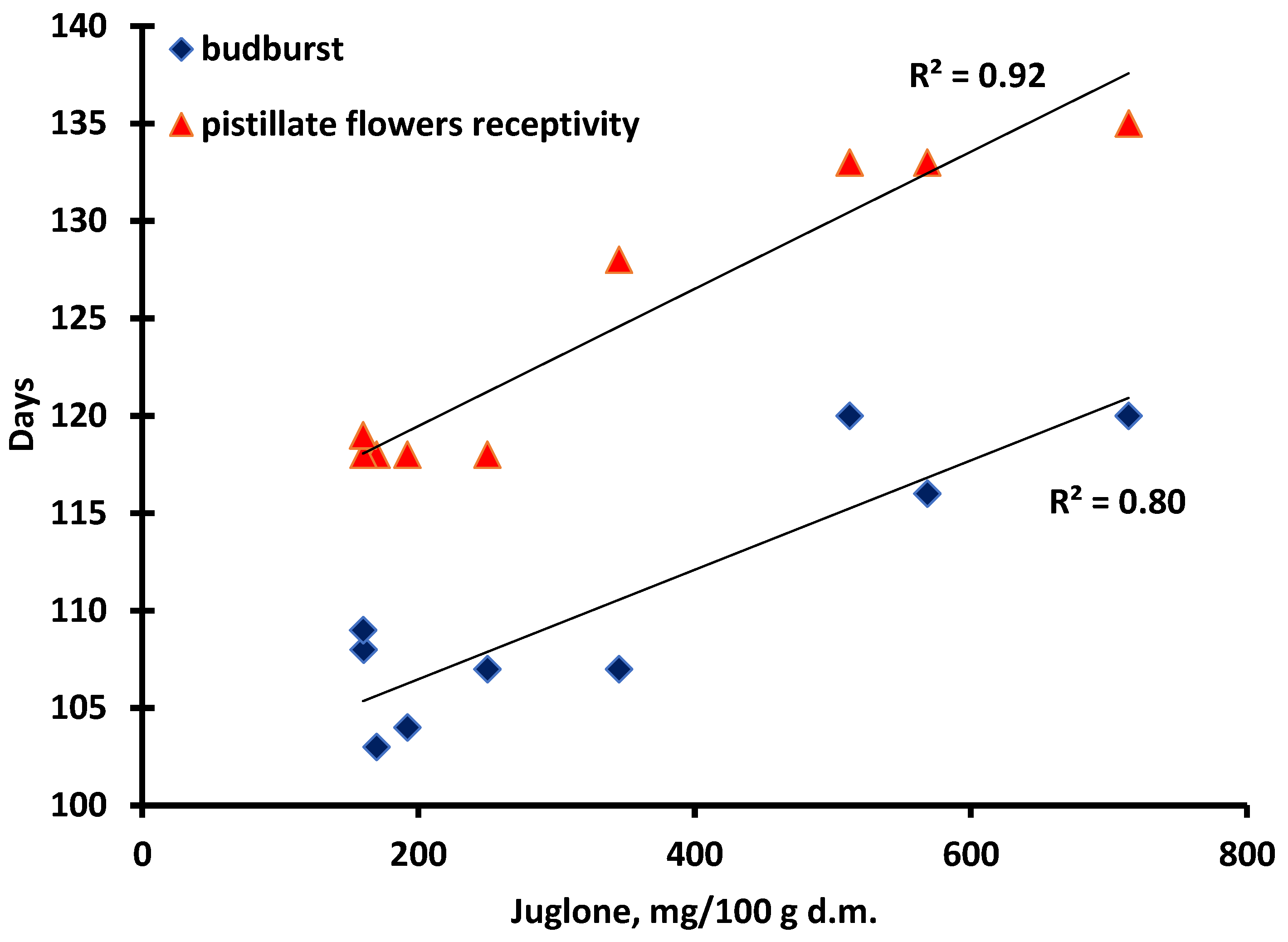
Furthermore, there were strong significant correlations between the budburst, as well as the pistillate flowers’ receptivity, and the concentration of juglone, where R2 was 0.80 and 0.92, respectively (Figure 4.). The lowest values were measured in samples that were the earliest in their pistillate flowers’ receptivity, namely, ‘Alsószentiváni 117’ (192 mg/100 g d.m.), ‘Milotai 10’ (250 mg/100 g d.m.), ‘Tiszacsécsi 83’ (170 mg/100 g d.m.), ‘Köpcös’ (160 mg/100 g d.m.) and ‘Chandler’ (160 mg/100 g d.m.). (Figure 3.) The ‘Alsószentiváni kései’, ‘Bonifác’, ‘Milotai intenzív’ and ‘Milotai kései’ cultivars reached a similar state of development about 10–15 days later, and the juglone content was measured much higher (512 mg/100 g d.m., 568 mg/100 g d.m., 345 mg/100 g d.m. and 714 mg/100 g d.m., respectively) compared to those varieties, which had earlier budburst and blossom (Figure 3.).
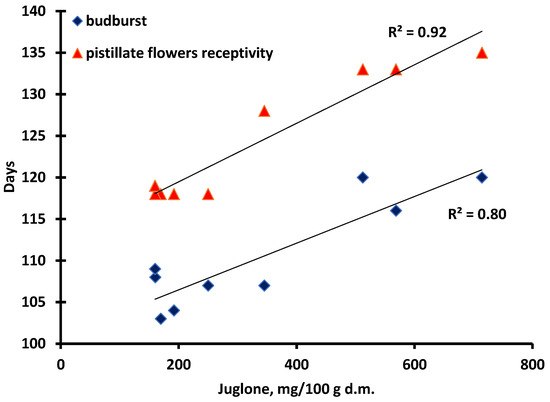
Figure 4.
Correlation between the budburst and pistillate flowers’ receptivity and the concentration of juglone.
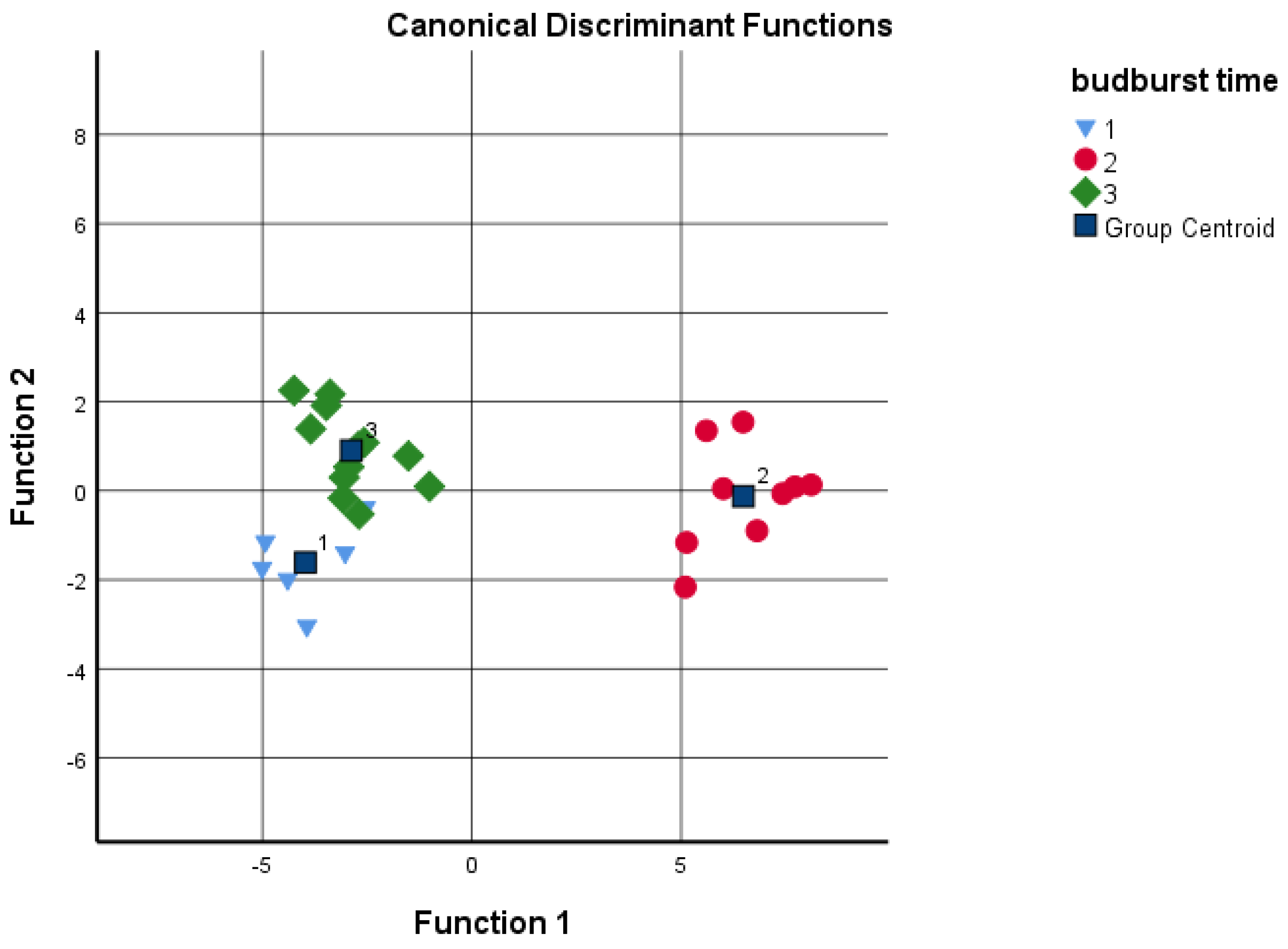
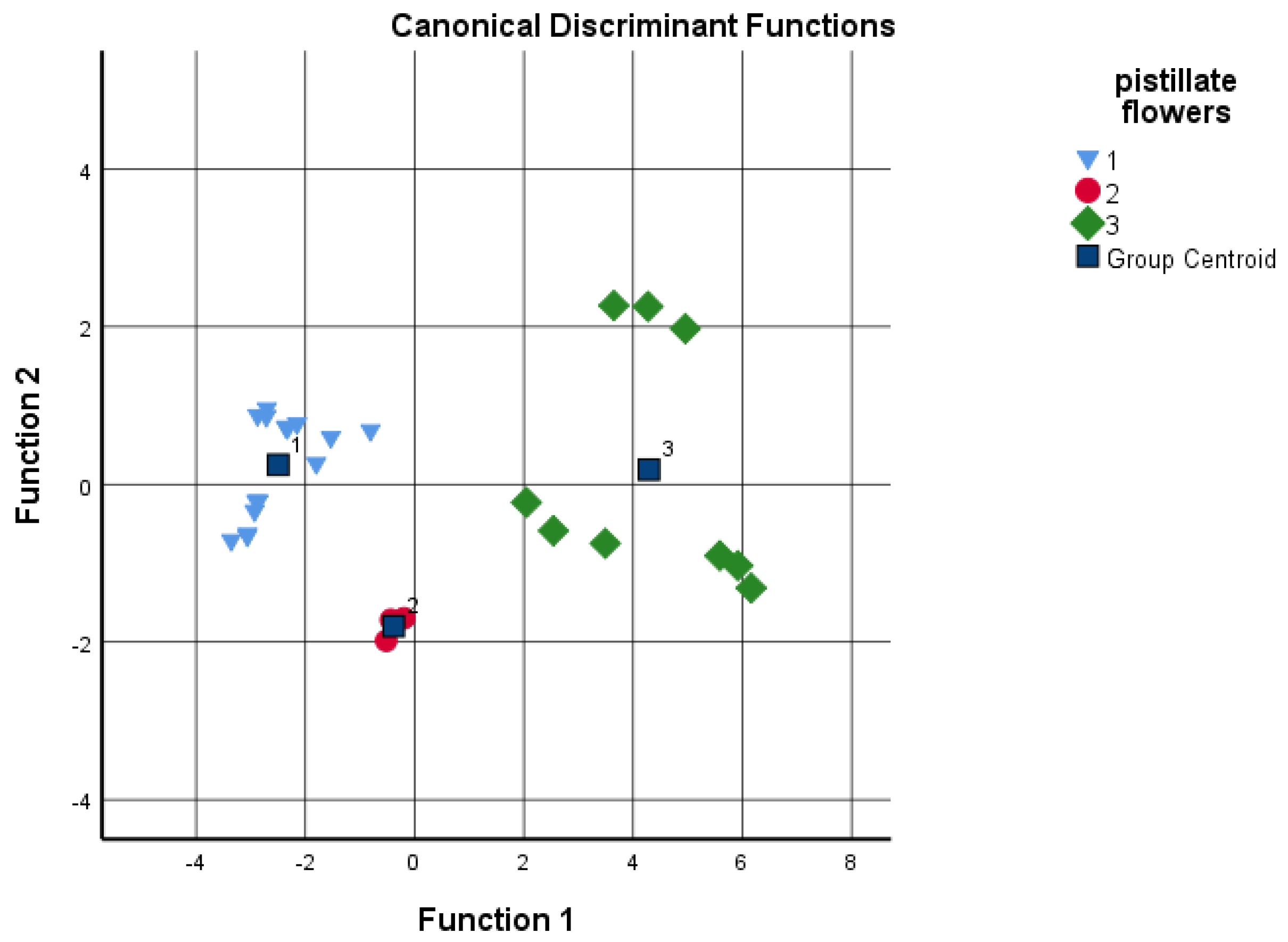
Discriminant analysis was performed to determine if the different cultivars could be distinguished according to the grouping variables, such as budburst and pistillate flowers’ receptivity based on the given analytical tests. The sums of the four data groups and juglone concentration were used as independents (Figure 5 and Figure 6). Based on the results, the date of the budburst is less indicative than the pistillate flowers’ receptivity. When analyzing the results, the discriminant analysis could not distinguish between ‘Milotai 10′, ‘Milotai intenzív’, ‘Köpcös’ and ‘Chandler’, as they were very similar in the time of budburst (107–109 calendar days) but differed in analytical values. When using all five data series for discriminant analysis, 89% of the original grouped cases were correctly classified. In contrast, when the data of pistillate flowers’ receptivity was used for the discriminant analysis, it was found that the amount of flavonoids, naphthoquinones and juglone as variables already ensured the correct classification of 100% of the original grouped cases.
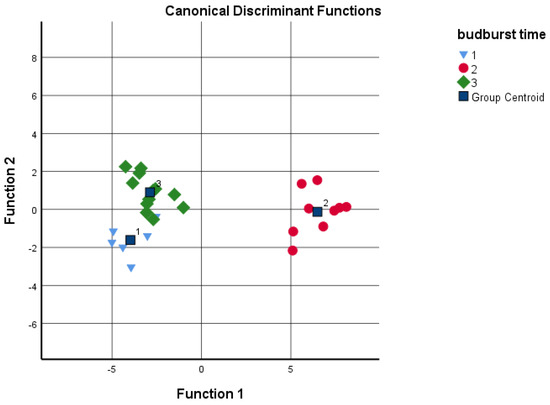
Figure 5.
Discriminant analysis by budburst time as a grouping variable; 1—early: 103–104 days; 2—medium: 107–109 days; late: 116–120 days (independents: sum of hydroxybenzoic acids, hydroxycinnamic acids, flavonoids and naphthoquinones, as well as juglone concentration).
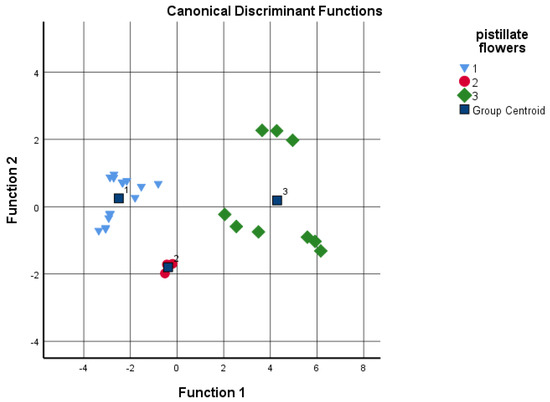
Figure 6.
Discriminant analysis by pistillate flowers’ receptivity time as a grouping variable; 1-early: 118–119 days; 2-medium: 128 days; late: 133–135 days (independents: sum of flavonoids and naphthoquinones, as well as juglone concentration).
Table 1 contains the correlations between early spring phenology and the observed phenolic compounds. The naphthoquinones correlated well to the budburst (0.70) and the blossom time (0.78). Interestingly there was a strong correlation between the budburst and the blossom of the pistillate flowers (0.79), as without a shoot, it is not possible for the female flower to develop.

Table 1.
Correlation matrix of measured parameters and observed characteristics (R2) *.
3.2. Tolerance/Susceptivity to Xanthomonas Arboricola pv. Juglandis
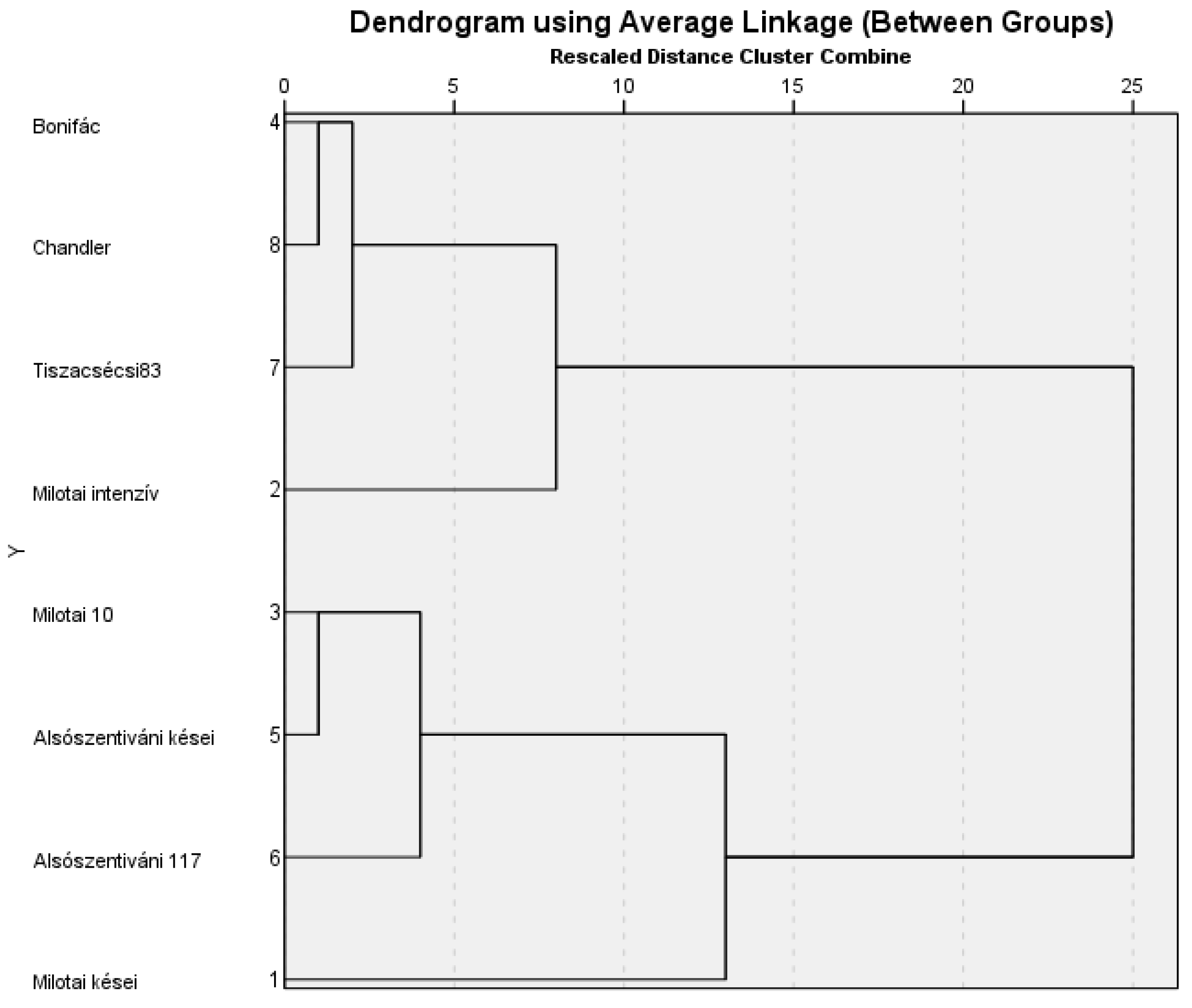
The dendrogram, containing the diameter of the necrotic spots and the disease rate values, differentiated the cultivars belonging to certain susceptibility groups. In 2020, the susceptibility/resistance of cultivars showed significant differences. Based on the statistical evaluation of the data, ‘Milotai intenzív’ proved to have a high susceptibility (hS), while susceptibility (S) was detected for ‘Bonifác’, ‘Tiszacsécsi 83’, ‘Alsószentiváni kései’, ‘Milotai 10’ and ‘Chandler’. Moderately susceptible cultivars were ‘Milotai kései’ and ‘Alsószentiváni 117’. The origin of the Hungarian walnut cultivars did not relate with their susceptibility to walnut blight (Figure 7).
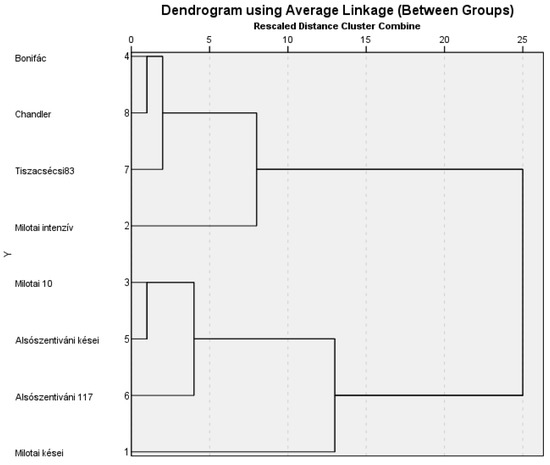
Figure 7.
Dendrogram of Hungarian-bred walnut cultivars from the point of view of their susceptibility to walnut blight.
In previous research a linkage between the polyphenols content and resistance to walnut bacterial blight was determined [28]. A strong correlation between the high polyphenols content and resistance to walnut blight was observed in this study. The current results confirmed this statement, except in the case of cultivar ‘Bonifác’. This cultivar contained the highest concentration of phenolic compounds, but its nuts were susceptible to walnut blight (Figure 7) as described in the cultivars’ description [55]. In addition to the phenolic compounds, there are more factors, e.g., protein profile of the green husk [56], to determine the susceptibility of a genotype against walnut blight. Little research about the susceptivity of ‘Alsószentivani 117′ and its hybrids to walnut blight is known, and further research needs to investigate this. Based on the artificial infections, the varieties with late budburst usually had better resistance to walnut blight due to them having a higher amount of phenolic compounds (Figure 3 and Figure 7). However, a high concentration of phenolic compounds does not only link to resistance. Some cultivars with an early budburst can also have good resistance, such as ’BD6’ [57]. This conclusion confirms other research results [45,46,47,48,54] that there is a negative correlation between juglone concentration and the susceptibility of the walnut genotypes and cultivars to blight.
The concentration and composition of phenolic compounds in the green husk of walnuts change significantly during crop development; thus a detailed kinetic study would be very important.
Evaluating the results, it is concluded that the concentration of phenolic compounds of the most susceptible cultivars, ‘Milotai intenzív’ ‘Tiszacsécsi 83’ and ‘Chandler’, was the lowest during the measurements.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
The trial was conducted at the Experimental Fields of the Hungarian University of Agriculture and Life Sciences Research Centre for Fruit Growing (GPS coordinates: 47°20′11.44″ N 18°51′53.42″ E). The trial was planted in spring 1990 on chernozem soil with high lime (pH = 8, total lime content in the top 60 cm layer 5%) and humus content (2.3–2.5%). Considering the Arany-type cohesion index [58] the KA = 40 refers to medium compactness. Meteorological conditions of the site are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Meteorological data during the data collection 2020.
The entire Hungarian walnut assortment (‘Alsószentiváni 117′, ‘Milotai 10′, ‘Tiszacsécsi 83′ selected from the local Hungarian population; ‘Milotai intenzív’, ‘Milotai kései℗’(kései refers to its late leafing time) crossbred between ‘Milotai 10’ and ‘Pedro’; ‘Alsószentiváni kései℗’, ‘Bonifác℗’ crossbred between ‘Alsószentiváni 117’ and ‘Pedro’), found on the Hungarian National Variety List, was established in the trial. All are state-registered cultivars for Hungarian and neighboring countries’ (e.g., Slovakia, Romania, Serbia, Croatia, Slovenia and Austria) production. Another genotype (possible candidate) for the rootstock ‘Köpcös’ was added to the trial. The control of this trial was the US-bred ‘Chandler’, with detailed phenological descriptions in Table 3.

Table 3.
Detailed phenological descriptions of the examined walnut cultivars in this study [55].
The trees were grafted on selected Juglans regia seedlings, and planted 10 × 10 m in the row and between the rows. The grafted trees were trained as a central leader canopy, with 5 trees replicated of each, and the trial was not irrigated.
4.2. Phenological Stages
All the phenological stages were recorded as indicated in the Ctifl scheme [59]. The corresponding stages when the data was collected, were the budburst stage of ‘Cf’; the start of pistillate flowers’ receptivity, the stage of ‘Ff2’. Thus the start of pistillate receptivity period was considered when the stigmas in the earliest pistillate flowers became receptive onwards. The data were recorded within two to three day intervals, usually in the morning.
4.3. Sample Collection and Preparation
The samples were collected late June, on the 181st day of 2020, during lignification of the nut shell. The time of budburst and pistillate flowers’ receptivity in days of each samples is summarized in Table 4. During sample collection, the following periods were taken from the pistillate flowers’ receptivity until the sample collection: for ‘Alsószentiváni 117’, ‘Milotai 10’, ‘Tiszacsécsi 83’, ‘Köpcös’ 63 days, for ‘Chandler’ 62 days, for Milotai intenzív’ 53 days, for ‘Alsószentiváni kései’ and ‘Bonifác’ 48 days, as well as 45 days for ‘Milotai kései’. The collected nuts were immediately delivered to the laboratory where ten nuts of every sample type sample were peeled with a 2 mm width blade kitchen peeler and the green husk was lyophilized. The dried samples were ground to fine powder and stored hermetically sealed at 4 °C until analysis.

Table 4.
The time of budburst and pistillate flowers’ receptivity in calendar days starting from 1st January.
4.4. Chemicals
Standards used for identification and quantification of phenolic compounds were gallic acid, syringic acid, catechin, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, quercetin, rutin (quercetin-3-O-rutinoside), hyperoside (quercetin-3-O-galactoside), kaempherol, juglone (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany), ferulic acid and ellagic acid (Fluka-Honeywell, Charlotte, NC, USA). HPLC/MS grade acetonitrile and formic acid, analytical grade methanol and acetic acid were purchased from Avantor (Radnor, PA, USA). The bidistilled water was filtered through a 0.45 µm nylon membrane.
4.5. Total Phenolic Content
Total phenolic content was determined by the Folin–Ciocalteu’s photometric method [53]. Fifty mg of green husk was extracted in 10 mL of 80% methanol, left for 24 h. After 30 min shaking at 25 °C the mixture was filtered. One hundred µL of the filtrate was mixed with 3.7 mL distilled water, 0.5 mL Folin–Ciocalteu reagent and 2 mL 20% Na2CO3 solution and filled up to 10 mL with distilled water. Samples were left in the dark for 30 min at room temperature; the absorbance was measured by spectrophotometer (UY-160 A, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) at 750 nm against blank sample (4.75 mL distilled water and 0.25 mL Folin–Ciocalteu reagent). Total phenolic content was calculated according to a calibration curve prepared with gallic acid in 0–0.5 mg/mL concentration range (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA).
4.6. Phenolic Compounds’ Determination by HPLC-ESI-DAD
One hundred mg of dried green husks were placed in a test tube and 10 mL of the extraction solvent (bidistilled water/2% acetic acid in methanol, 30/70) added. Mixtures were sonicated (AU 65, ArgoLab, Carpi, Italy) for 20 min at room temperature. After centrifugation (5000 rpm, 20 min; Digicen 21, Orto Alresa, Madrid, Spain), the supernatant was filtered through a 0.45 µm PVDF syringe filter before HPLC injection and analysed on the same day.
A Waters Alliance system (Waters, Milford, (CT), USA) consisting of a Model e2695 separation module with Model 2998 photodiode array (PDA) detector operated by Empower software (Waters, Milford, (CT), USA) was used for the determination of the phenolic compounds. The separation was carried out using a Sphinx 5 μm 250 × 4.6 mm column (Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany) by gradient elution. The mobile phase was (A) 0.1% formic acid in bidistilled water and (B) 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile. The gradient elution program: 0–9 min, 5–20% B; 9–16 min, 20–22% B; 16–25 min, 22–50% B; 25–28 min 50% B; 28–40 min, 50–100% B; 40–43 min, 100% B; 43–45 min, 100–5% B; 45–50 min, 5% B. The injected volume was 20 µL and the flow rate was 0.7 mL/min. Data acquisition of PDA proceeded with the range of 200–600 nm and the detection wavelengths were at 280, 320, 355 and 420 nm.
The HPLC system was coupled to a Model Acquity Mass (QDa) detector (Waters, Milford, (CT), USA). The mass spectrometry conditions were set as both negative and positive modes: electrospray ionization (ESI) was used as a source, mass spectra in the m/z range from 100 to 1000 were obtained and probe temperature was adjusted to 600 °C (default). In positive ion mode the cone voltage was set to 15 V and capillary voltage was 1.5 kV. In negative ion mode those were 50 V and 0.8 kV, respectively.
Identification of phenolic compounds was achieved by comparing their spectral characteristic, retention times, measured mass (m/z) and fragmentation pattern. In addition, the previously published literature [26,60,61,62] and internet databases [63,64,65] were applied. The quantification of the identified phenolic compounds was based on calibration curve of rutin at 280, 320 and 355 nm as rutin gives an easily measurable signal at these wavelengths, and juglone at 420 nm.
4.7. Walnut Blight Immunity Test
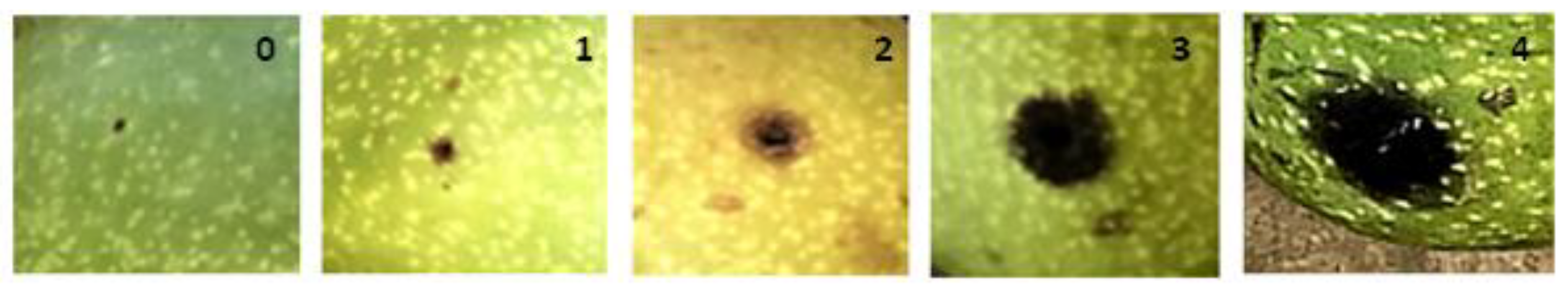
The susceptibility test was carried out based on the methods [66,67] using 10 immature green nuts from every individual, collected in 2020. For the artificial infection a mixture of 3 Xaj strains was used, isolated from naturally infected walnut nuts from four different locations in Hungary (Vecsés, Karád, Balatonbolgár and Zánka). Before infection of immature nuts, isolates were either inoculated into the intercellular tissue of tobacco leaf (‘White Burley’) or were inoculated in immature nuts for confirmation capability of them to induce hypersensitive tissue necrosis and also aggressiveness to produce disease symptoms. The mixture of the three strains was used for the infection after the virulence test. Before the infection the fruit surface was disinfected with alcohol. Two inoculations of 20 μL bacterial suspension were performed in exocarp for each nut, thus the 10 nuts per cultivar with 2 inoculations each were tested. Sterile distilled water (SDW) was injected into the 10 immature nuts for every cultivar as control negative treatment. After the infection, the nuts were incubated in transparent plastic boxes for 7 days at a temperature of 26–28 °C, with over 90–95% relative humidity. Temperature and RH% were monitored by a micro-sensor placed into one of the plastic boxes. The disease severity was recorded on a scale from 0 to 4 (Figure 8), from the least to the most, based on the diameter and depth of necrosis reached on the 7th day: 0—no symptoms; 1—less than 2.0 mm, superficial and small spots on the inoculation point; 2—blackening on the inoculation point of nut by 2.1 mm to 3 mm; 3—blackening on the inoculation point of nut by 3.1 mm to 4 mm; 4—blackening on the inoculation point of nut more than 4.1 mm; see legend of Figure 8.
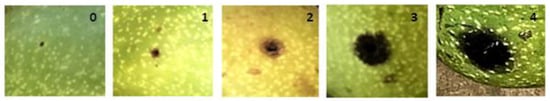
Figure 8.
Evaluation of susceptibility, scale (0–4). 0—no symptoms; 1—less than 2.0 mm, superficial and small spots on the inoculation point; 2—blackening on the inoculation point of nut by 2.1 mm to 2.6 mm; 3—blackening on the inoculation point of nut by 2.7 mm to 3.1 mm; 4—blackening on the inoculation point of nut more than 4.1 mm.
Four groups were formed: Moderately Resistant (MR) ≤ 2 mm; Moderately Susceptible (MS) 2.1–3 mm; Susceptible (S) 3.1–4 mm; Highly Susceptible (HS) ≤ 4.1 mm. The test was performed using the same cultivars as for chemical analysis except for ‘Köpcös’.
4.8. Statistical Analysis
The data derived from compositional analyses and the immunity test were evaluated using the SPSS software (IBM SPSS 27.0, Chicago, IL, USA). Discriminant analysis was carried out based on the results of analytical measurements. Relationships between the observed traits in the correlation matrix were calculated by Pearson correlation coefficient. For the immunity test the statistical analyses were determined based on the sample size, distribution analysis (Kolmogorov–Smirnov test) and t-test. It was accepted on the p ≤ 95% confidence level. A hierarchical cluster analysis based on one-year data regarding the diameter and disease rate was conducted in order to classify the cultivars into susceptibility groups. The results were represented in a dendrogram (Figure 7). Values represent the mean and standard deviation of three replicates from each sample.
5. Conclusions
The research groups from Slovenia [28,54] indicated in their study that the concentration of phenolics in the walnut crop varies with time inside the growing season. It can be assumed that the concentration and composition of phenolic compounds in the green husk of walnuts also change significantly during crop development; thus, a detailed kinetic study would be very important in the future [54].
The concentration of phenolic compounds varied by cultivars [8,10,24,25,26,27]; it was higher in the locally-bred cultivars compared to the foreign-bred ‘Chandler’, grown and collected among Hungarian climatic conditions. The phenolic compounds inhibited the artificial Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis infection on the surface of the green husk. This effect had a strong correlation with the high phenolics’ concentration, except on ‘Bonifác’.
Naphthoquinones showed strong correlations between budburst and blossom time, which are related to their yearly fluctuation; the earlier the budburst and blossom, the earlier their peak concentration can be reached [54]. The cultivars with late budburst and blossom time are the best for growers due to their lower susceptibility to walnut blight as described in some previous papers [68,69,70]. Fortunately, there is a strong correlation between the budburst and blossom time (0.79) too, as described by breeders [68,69,70].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.B., N.A., É.L.-K. and A.V.; methodology, G.B., N.A., É.L.-K. and A.V.; software, G.B., N.A., É.L.-K., M.B., A.F. and A.V.; validation, G.B., N.A., É.L.-K., M.B., A.F. and A.V.; formal analysis, N.A., É.L.-K., M.B. and A.V.; investigation, N.A., É.L.-K., M.B. and A.V.; resources, G.B., N.A., É.L.-K., M.B. and A.V.; data curation, G.B., N.A., É.L.-K., M.B., A.F. and A.V.; writing—original draft preparation, G.B., N.A., É.L.-K., M.B. and A.V.; writing—review and editing, G.B., N.A., É.L.-K., M.B. and A.V.; visualization, G.B., N.A., É.L.-K. and A.V.; supervision, G.B. and N.A.; project administration, G.B.; funding acquisition, G.B. and A.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by ‘Research of Nut Tree Species’ (17K0200017), of the Research Centre of Fruit Growing, at the Hungarian University of Agriculture and Life Sciences. This project was supported by the János Bolyai Research Scholarship of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences (bo_671_20).
Data Availability Statement
All data were collected from the published research papers.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks go to Alina Ratiu for her assistance in data collection.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rahimipanah, M.; Hamedi, M.; Mirzapour, M. Antioxidant activity and phenolic contents of Persian walnut (Juglans regia L.) green husk extract. Afr. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 4, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Nadaf, A.H.; Bastoni, H.M.; Hamdan, D.F. Microwave-assisted efficient extraction of phenolics from Juglans regia L.: Pellicle; kernel unripe fruits; and leaves in different solvents. Int. J. Green Pharm. 2018, 3, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marius, R.E.; Gheldiu, A.-M.; Moldovan, A.M.C.; Popa, D.-S.; Tomuta, I.; Vlase, L. Process Optimization for Improved Phenolic Compounds Recovery from Walnut (Juglans regia L.) Septum: Phytochemical Profile and Biological Activities. Molecules 2018, 11, 2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquaviva, R.; D’Angeli, F.; Malfa, G.A.; Ronsisvalle, S.; Garozzo, A.; Stivala, A.; Ragusa, S.; Nicolosi, D.; Salmeri, M.; Genovese, C. Antibacterial and anti-biofilm activities of walnut pellicle extract (Juglans regia L.) against coagulase-negative staphylococci. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 12, 2076–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Torre, C.; Caputo, P.; Plastina, P.; Cione, E.; Fazio, A. Green Husk of Walnuts (Juglans regia L.) from Southern Italy as a Valuable Source for the Recovery of Glucans and Pectins. Fermentation 2021, 7, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croitoru, A.; Ficai, D.; Craciun, L.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E. Evaluation and Exploitation of Bioactive Compounds of Walnut, Juglans regia. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 2, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Madrid, D.; Gutiérrez-Cutiño, M.; Pozo-Martínez, J.; Zúñiga-López, M.C.; Olea-Azar, C.; Matiacevich, S. Dependence of the Ripeness Stage on the Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Walnut (Juglans regia L.) Green Husk Extracts from Industrial By-Products. Molecules 2021, 10, 2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, I.; Sousa, A.; Ferreira, I.C.; Bento, A.; Estevinho, L.; Pereira, J.A. Total phenols, antioxidant potential and antimicrobial activity of walnut (Juglans regia L.) green husks. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 7, 2326–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.; Ferreira, P.J.; Mendes, V.S.; Silva, R.; Pereira, J.A.; Jerónimo, C.; Silva, B.M. Human cancer cell antiproliferative and antioxidant activities of Juglans regia L. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 1, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosmulesscu, S.N.; Trandafir, I.; Achim, G.; Botu, M.; Baciu, A.; Gruia, M. Phenolics of Green Husk in Mature Walnut Fruits. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. 2010, 1, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovici, C.; Gîtin, L.; Alexe, P. Characterization of walnut (Juglans regia L.) green husk extract obtained by supercritical carbon dioxide fluid extraction. J. Food Packag. Sci. Tech. Technol. 2012, 1, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C.-B.; Wu, S.-Z.; Li, G.-Q.; Jia, C.-H.; Chang, L.-X. Anti-fungal activity of walnut green husk extracts. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 722–724, 755. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.X.; He, K.Z.; Pu, Q. Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of extracts from walnut green husks. Ying Yong Yu Huan Jing Sheng Wu Xue Bao 2014, 1, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salejda, A.; Janiewicz, U.; Korzeniowska, M.; Kolniak-Ostek, J.; Grazyna, K. Effect of walnut green husk addition on some quality properties of cooked sausages. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 61, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panth, N.; Paudel, K.R.; Karki, R. Phytochemical profile and biological activity of Juglans regia. J. Integr. Med. 2016, 5, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wianowska, D.; Garbaczewska, S.; Cieniecka-Roslonkiewicz, A.; Dawidowicz, A.L.; Jankowska, A. Comparison of antifungal activity of extracts from different Juglans regia cultivars and juglone. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 100, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi-Kiakhani, M.; Tehrani-Bagha, A.; Gharanjig, K.; Hashemi, E. Use of Pomegranate peels and Walnut Green husks as the green antimicrobial agents to reduce the consumption of inorganic nanoparticles on wool yarns. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 231, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wianowska, D.; Garbaczewska, S.; Cieniecka-Roslonkiewicz, A.; Dawidowicz, A.; Typek, R.; Kielczewska, A. Influence of the Extraction Conditions on the Antifungal Properties of Walnut Green Husk Isolates. Anal. Lett. 2020, 53, 1970–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, S.; Nouri, M.; Baghi, M. The effect of adding walnut green husk extract on antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of ketchup. J. Food Bioprocess Eng. 2020, 2, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Medic, A.; Jakopič, J.; Hudina, M.; Solar, A.; Veberic, R. Identification and quantification of major phenolic constituents in Juglans regia L. leaves: Healthy vs. infected leaves with Xanthomonas campestris pv. juglandis using HPLC-MS/MS. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2022, 34, 101890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colarič, M.; Veberic, R.; Solar, A.; Hudina, M.; Stampar, F. Phenolic Acids, Syringaldehyde, and Juglone in Fruits of Different Cultivars of Juglans regia L. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 6390–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hama, J.; Anwar, R.; Rashid, R.; Mohammed, N.; Thoss, V. The Diversity of Phenolic Compounds along Defatted Kernel, Green Husk and Leaves of Walnut (Juglans regia L.). Anal. Chem. Lett. 2016, 1, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, G.; Yousef, G.; Abdollah, E.; Seyed, M.N.; Seyed, F.N.; Mohammad, A.E.; Fereshteh, P. Influence of environmental factors on antioxidant activity, phenol and flavonoids contents of walnut (Juglans regia L.) green husks. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Cosmulescu, S.; Trandafir, I.; Achim, G.; Baciu, A. Juglone Content in Leaf and Green Husk of Five Walnut (Juglans regia L.) Cultivars. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. 2011, 39, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, V.; Jamei, R.; Heidari, R.; Esfahlan, A.J. Antiradical activity of different parts of Walnut (Juglans regia L.) fruit as a function of genotype. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2404–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, F.; Dehganiasl, M.; Heidari, R.; Rezaee, R.; Darvishzadeh, R. Genotype impact on antioxidant potential of hull and kernel in Persian walnut (Juglans regia L.). Int. Food Res. J. 2018, 25, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Jahanban-Esfahlan, A.; Ostadrahimi, A.; Tabibiazar, M.; Amarowicz, R. A Comprehensive Review on the Chemical Constituents and Functional Uses of Walnut (Juglans spp.) Husk. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakopic, J.; Solar, A.; Colaric, M.; Hudina, M.; Veberic, R.; Stampar, F. The influence of ethanol concentration on content of total and individual phenolics in walnut alcoholic drink. Acta Aliment. 2008, 37, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakopic, J.; Veberic, R. Extraction of phenolic compounds from green walnut fruits in different solvents. Acta Agric. Slov. 2009, 93, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Agulló, A.; Pereira, E.; Freire, M.S.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B.; González-Álvarez, J.; Pereira, J.A. Influence of solvent on the antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of walnut (Juglans regia L.) green husk extracts. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 42, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwaseun, R.A.; Nour, H.A.; Chinonso, I.U. Extraction of phenolic compounds: A review. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakopic, J.; Colaric, M.; Veberic, R.; Hudina, M.; Solar, A.; Stampar, F. How much do cultivar and preparation time influence on phenolics content in walnut liqueur? Food Chem. 2007, 104, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosmulescu, S.; Trandafir, I.; Nour, V.; Ionica, M.; Tutulescu, F. Phenolics content, antioxidant activity and color of green walnut extracts for preparing walnut liquor. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. 2014, 42, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uğurlu, S.; Okumuş, E.; Bakkalbaşı, E. Reduction of Bitterness in Green Walnuts By Conventional And Ultrasound-Assisted Maceration. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 66, 105094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binici, H.; Şat, İ.; Aoudeh, E. Nutritional Composition and Health Benefits of Walnut and its Products. Atatürk Üniversitesi Ziraat Fakültesi Derg. 2021, 52, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cindrić, I.; Zeiner, M.; Hlebec, D. Mineral Composition of Elements in Walnuts and Walnut Oils. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosso, A.; Asensio, C.; Nepote, V.; Grosso, N. Antioxidant Activity Displayed by Phenolic Compounds Obtained from Walnut Oil Cake used for Walnut Oil Preservation. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2018, 95, 1409–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabrenović, B.B.; Natić, M.; Dabić Zagorac, D.; Meland, M.; Fotirić Akšić, M. Bioactive Phytochemicals from Walnut (Juglans spp.) Oil Processing By-Products. In Bioactive Phytochemicals from Vegetable Oil and Oilseed Processing By-Products; Ramadan Hassanien, M.F., Ed.; Reference Series in Phytochemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiki, T.; Najafpour, G.D.; Hosseini, M. Evaluation of antimicrobial and dyeing properties of walnut (Juglans regia L.) green husk extract for cosmetics. Color. Technol. 2018, 134, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiantos, J.; Vagelas, I.K.; Rumbos, C.I.; Chatzaki, A.; Rouskas, D.; Gravanis, F.T. Evaluation of resistance of cultivated walnut varieties and selections to Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis in Greece. In Proceedings of the COST873 Management Committee Meeting, Athens, Greece, 15 May 2008; Available online: http://www.cost873.ch/uploads/files/GRXajSheetWalnut.pdf (accessed on 26 April 2020).
- Han, M.M.; Shi, S.Y.; Wang, F.; Pang, M.X.; Qu, C.; Qi, J.H. Extraction and Dyeing Propertie of Juglone from Walnut Green Husk. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 199, 042008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Maldonado, C.; Vergara-Castro, M.; Jara-Quezada, J.; Caballero-Valdés, E.; Müller-Pavez, A.; Zúñiga-Hansen, M.E.; Altamirano, C. Polyphenolic extracts of walnut (Juglans regia) green husk containing juglone inhibit the growth of HL-60 cells and induce apoptosis. Electronic. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 39, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frutos, D.; Ortega, G. Search for Juglans regia genotypes resistant/tolerant to Xanthomonas arboricola pv. Juglandis in the framework of COST Action 873. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 94, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.A.; Oliveira, I.; Sousa, A.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Ferreres, F.; Bento, A.; Seabra, R.; Estevinho, L. Walnut (Juglans regia L.) leaves: Phenolic com-pounds, antibacterial activity and antioxidant potential of different cultivars. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 2287–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matias, J.; Jakopic, J.; Solar, A.; Rovira, M.; Aletà, N. Walnut varietal patterns of polyphenol contents. In Proceedings of the Cost 873, WG3/WG4 Joint Meeting, Murcia, Spain, 23–25 October 2007; Available online: http://www.cost873.ch/_uploads/_files/m_Matias_2007_10.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Matias, J.; Aletà, N.; Rovira, C.; Moragrega, C. Phenoliccomposition in Juglans regia Commercial Cultivars. Relationship with Blight Susceptibility. In Proceedings of the Annual Cost 873 Meeting, Cetara, Italy, 26–29 October 2009; Available online: http://www.cost873.ch/_uploads/_files/JMatias_Walnut-Phenolics_Italy_1.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Solar, A.; Jakopic, J.; Veberic, R.; Stampar, F. Phenolic compounds as a potential marker of walnut resistance against Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis. In Proceedings of the Cost 873, WG3/WG4 Joint Meeting, Murcia, Spain, 23–25 October 2007; Available online: https://www.cost873.ch/_up_loads/_files/m_Solar_murcia (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Dirlewanger, E. Genetic mapping and MAS of resistancegenes in stone fruit and nut trees at INRA. In Proceedings of the Cost 873 STF Meeting, Barcelona, Spain, 2010; Available online: https://www.cost873.ch/_uploads/_files/EDirlewanger_GeneticMappingPeach (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Solar, A.; Jakopic, J.; Mikulic-Petkovsěk, M.; Veberic, R.; Dreo, T.; Zadravec, P.; Stampar, F. Validation of polyphenol contents as biochemical markers for walnut blight (Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis resistance. In Proceedings of the Cost 873, WG and Management Committee Meeting, Athens, Greece, 20–23 October 2008; Available online: http://www.cost873.ch/_uploads/_files/m_Athens_Abstracts_FinalBook.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Yang, H. Resistance evaluation of walnut (Juglans spp.) against Xanthomonas arboricola and the correlation between leaf structure and resistance. For. Pathol. 2021, 51, e12659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1999, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar]
- Scalbert, A.; Monties, B.; Janin, G. Tannins in Wood: Comparison of Different Estimation Methods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1989, 5, 1324–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stampar, F.; Solar, A.; Hudina, M.; Veberic, R.; Colaric, M. Traditional walnut liqueur—Cocktail of phenolics. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solar, A.; Colarič, M.; Usenik, V.; Stampar, F. Seasonal variations of selected flavonoids, phenolic acids, and quinones in annual shoots of common walnut (Juglans regia L.). Plant Sci. 2006, 170, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szentiványi, P.; Kállay, T. (Eds.) Dió [Walnut]. In Diófajták Leírása [Description of Walnut Cultivars]; Mezőgazda Kiadó: Budapest, Hungary, 2006; pp. 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Sagawa, H.D.C.; de Assis, A.B.R.; Zaini, P.A.; Wilmarth, P.A.; Phinney, B.S.; Moreira, L.M.; Dandekar, A.M. Proteome Analysis of Walnut Bacterial Blight Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujdosó, G.; Fodor, A.; Végh, A. BD6 walnut. Hortscience 2020, 8, 1393–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobos, E.; Bialko, T.; Micheli, E.; Kobra, J. Legacy soil data harmonization and database development. In Digital Soil Mapping; Boettinger, J.L., Howell, D.W., Moore, A.C., Hartemink, A.E., Kienast-Brown, S., Eds.; Progress in Soil Science; Springer: Dordrecht, Germany, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 215–223. [Google Scholar]
- Germain, E.; Prunet, J.-P.; Garcin, A. Le Noyer [The walnut]. In Biologie Florale [Flower Biology]; Centr’Imprim: Issoudun, France, 1999; pp. 43–56. [Google Scholar]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. Method Enzymol. 1999, 299, 152–178. [Google Scholar]
- Nour, V.; Trandafir, I.; Cosmulescu, S. HPLC Determination of Phenolic Acids, Flavonoids and Juglone in Walnut Leaves. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2012, 51, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, J.-H.; Du, X.-W.; Sun, G.-D.; Dong, W.-T.; Wang, W.-M. Identification and characterization of major constituents in Juglans mandshurica using ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-ESI-Q-TOF/MS). Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 7, 525–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phenol-Explorer. Available online: https://phenol-explorer.eu/ (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- MassBank of North America. Available online: https://mona.fiehnlab.ucdavis.edu/ (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Ozaktan, H.; Erdal, M.; Akkopru, A.; Aslan, E. Evaluation of susceptibility of some walnut cultivars to Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis by immature nut test. In Proceedings of the COST873 Management Committee Meeting, Athens, Greece, 20–23 October 2008; Available online: https://www.cost873.ch/uploads/files/GRXapFactSheetWalnut.pdf (accessed on 26 April 2020).
- Solar, A.; Jakopič, J.; Veberic, R.; Stampar, F. Correlations between Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis severity and endogenous juglone and phenolic acids in walnut. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 94, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botu, M.; Tudor, M.; Papachatzis, A. Evaluation of some walnut cultivars with different bearing habits in the ecological conditions of Oltenia—Romania. Acta Hortic. 2010, 861, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujdosó, G.; Izsépi, F.; Szügyiné Bartha, K.; Varjas, V.; Szentiványi, P. Persian walnut breeding program at Naric Fruticulture Research Institute in Hungary. Acta Hortic. 2020, 1280, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solar, A.; Stampar, F. Evaluation of some perspective walnut genotypes in Slovenia. Acta Hortic. 2005, 705, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).