Abstract
Travel times in urban road networks are highly stochastic. However, most existing travel time estimation methods only estimate the mean travel times, while ignoring travel time variances. To this end, this paper proposes a robust travel time distribution estimation method to estimate both the mean and variance of travel times by using emerging low-frequency floating car data. Different from the existing studies, the path travel time distribution in this study is formulated as the sum of the deterministic link travel times and stochastic turning delays at intersections. Using this formulation, distinct travel time delays for different turning movements at the same intersection can be well captured. In this study, a speed estimation algorithm is developed to estimate the deterministic link travel times, and a distribution estimation algorithm is proposed to estimate the stochastic turning delays. Considering the low sampling rate of the floating car data, a weighted moving average algorithm is further developed for a robust estimation of the path travel time distribution. A real-world case study in Wuhan, China is carried out to validate the applicability of the proposed method. The results of the case study show that the proposed method can obtain a reliable and accurate estimation of path travel time distribution in congested urban road networks.
1. Introduction
In recent years, urban road networks in many countries are becoming more congested [1]. To alleviate traffic congestions, increasing attention has been given to developing intelligent transportation systems (ITS), with the aim to best use existing transportation networks through various advanced information technologies. The accurate and robust estimation of travel time information is critical to many ITS applications. The provision of updated travel time information enables travelers to make informed path choice decisions to avoid congested sites [2,3,4]. Moreover, the updated travel time information allows for network operators to evaluate network performance, and to identify bottlenecks for proactively deploying effective controls so as to improve overall traffic conditions [5,6].
During the last few decades, various technologies have been developed to collect real-time travel time information [7,8]. Existing data collection techniques could be roughly classified into two categories: fixed traffic detection systems; and, floating car systems [9,10]. The fixed traffic detection systems employ conventional stationary detectors, such as loop detectors, installed at specific locations of road segments. These stationary detectors can continuously record every travel speed and traffic volume for all vehicles passing through the road segment with detectors. Because of their high installation and maintenance cost, stationary detectors are generally installed at only freeways or a few major roads. Thus, fixed traffic detector systems tend to have a small spatial coverage. Floating car systems are an emerging data collection technique, due to the recent advances in positioning and wireless communication techniques. The floating car system typically makes use of a large fleet of probe vehicles (e.g., thousands of taxis in a city), equipped with global positioning system (GPS) devices. The locations and speeds of moving probe vehicles are collected at a certain time interval to estimate travel time. The floating car systems are able to collect real-time travel time information for any part of the network where probe vehicles move. Due to the low operational cost and large spatial coverage, floating car data (FCD) recently has become a major data source for travel time estimation studies, as well as many ITS applications.
Travel time estimation methods have been intensively studied in the existing literature [10]. Many effective methods have been proposed to estimate the mean travel times in freeways based on stationary detectors, including statistical methods and analytical methods [11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. These travel time estimation methods for freeways, however, cannot be easily applied to urban road networks, mainly due to the following two reasons. Firstly, as mentioned above, stationary detectors are generally deployed at a few major roads, and are thus insufficient for estimating travel times in large-scale urban road networks. Secondly, travel times in congested urban road networks are highly stochastic, largely caused by the interruptions of signal controls at intersections. Many empirical studies have found that the stochastic nature of travel times in urban road networks have had a significant impact on travelers’ route choice behavior [4]. The reliability of travel times has been recognized by network operators as one of the most important performance indicators. Nevertheless, the existing methods for estimating mean travel times in freeways ignore travel time variances, and thus are inadequate for estimating actual traffic conditions in urban road networks. Therefore, it is necessary to develop new methods for estimating both the mean and the variation of travel times (i.e., travel time distributions) in urban road networks using FCD.
In recent years, much attention has been given to developing travel time estimation methods based on the FCD [1,11,15,17,18,19,20,21]. Herring [17] used FCD to estimate and predict traffic states, rather than link travel times. Sanaullah [19] used FCD to study the influence of vehicle penetration rates, data sampling frequencies, vehicle coverage on the links, and time window lengths on the accuracy of link travel time. Zheng [20] proposed a three-layer ANN model to estimate urban link travel times for individual probe vehicle data. Tang [21] presented a method to estimate travel time based on low-frequency FCD. These travel time estimation methods based on FCD could provide effective mean travel times for a large-scale road networks, but travel time variances are still ignored.
To the best of our knowledge, only a few methods based on FCD have been developed to estimate travel time distributions in urban road networks. Jenelius [1] presented a statistical model to estimate travel time in urban road networks based on low-frequency FCD. Both the mean travel time and 95% confidence intervals were given. Jenelius [22] analyzed the estimation of path travel time distributions based on probe vehicle data sampled by time and space, and highlighted the difference between them. Rahmani [15] developed a non-parametric method for route travel time distribution estimation using low-frequency FCD. The 25th, 50th, and 75th percentile values of the estimated travel time distributions were used to compare with that of the observed travel time distributions.
Along the line of previous work, this study proposes a robust method to estimate travel time distributions in urban road networks by using low-frequency FCD. Different from previous work, the path travel time distribution in this study is formulated as the sum of deterministic link travel times, and stochastic turning delays at intersections. Using this formulation, distinct travel time delays for different turning movements at the same intersection can be well captured. For example, left turns in China or USA (or right turns in the UK) are generally much more difficult than forward movements. The main contributions of this paper are summarized as follows.
Firstly, an effective method is proposed to estimate path travel time distributions based on low-frequency FCD. In this study, the path travel time distribution in this study is formulated as the sum of the deterministic link travel times and stochastic turning delays at intersections. A robust speed estimation algorithm based on the degree of central tendency is proposed to estimate deterministic link travel times. A distribution estimation algorithm is proposed to estimate the stochastic turning delays. Based on the arrival time of the intersection, α-discrete approximation method [23] is utilized to generate the path travel time distribution.
Secondly, a weighted moving average algorithm is proposed to smooth deterministic link travel time and stochastic turning delays. Considering the low level of market penetration and the low sampling rate of probe vehicles, the sample size of FCD may not be sufficient in some time intervals. Thus, this method can provide a robust estimation and obtain reliable results.
Thirdly, to illustrate the applicability of the proposed method, a comprehensive case study is carried out using FCD from the Wuhan network. Two new indexes are employed to evaluate the accuracy of the estimated path travel time distributions. The experimental results show that the proposed method can obtain a reliable and accurate estimation of path travel time distribution in congested urban road networks.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Problem statement of travel time distribution estimation is introduced in Section 2. The proposed method to estimate travel time distribution is presented in Section 3. A case study using real-world FCD collected at Wuhan, China is reported in Section 4. Conclusions and recommendations for further research are given in Section 5.
2. Problem Statement
A road network can be represented as a directed graph , consisting of a set of nodes , a set of directed links , and a set of allowed movements . Each node is a geographical location representing a network intersection, which can be either signalized or non-signalized [24]. A link is defined to be the road section from its tail node to head node . Its length is denoted by , and its travel time, denoted by , is represented to be deterministic but varying with time of day. Each element represents an allowed movement from tail link to head link , passing through node . A movement means that this movement is restricted in the road network (e.g., no U-turn). A movement is assumed to have no physical distance, but it associates with a stochastic turning delay, denoted by , varying with different probe vehicles and time of day. In this study, different movements (e.g., left-turn, through, and right-turn movements in Figure 1) at the same node can have distinct turning delays.
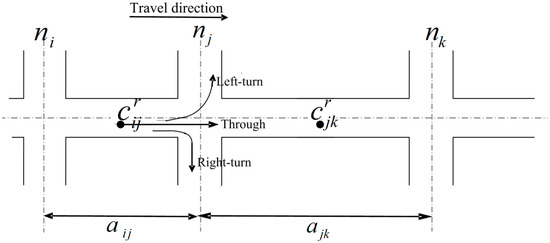
Figure 1.
An illustrative example of road network.
Let be a selected path from origin to destination . The path travel time, denoted by , is the sum of the related link travel times and turning delays along the path as
where and are the arrival times at link and node respectively. As both arrival time and turning delays are stochastic time-dependent variables, the path travel time is also a random variable conditionally depending on arrival times, link travel times and turning delays along the path.
In this study, trajectories of probe vehicles (i.e., FCD) are adopted to estimate the path travel time distribution, , as well as associated link travel times and turning delay distributions along the path. As shown in Figure 1, the trajectory of probe vehicle consists of a set of GPS sampling points, . Each GPS sampling point compromises of a set of attributes, including time stamp , instantaneous speed , and geographic location in terms of latitude and longitude. This geographical location can be equivalently represented by a network location using the linear reference system in terms of a link and a relative location [7]. For example, indicates sampling point is located at the middle of the link . As illustrated in Figure 1, there are two GPS sampling points, and , at adjacent links and . The time difference between these two sampling points is the vehicle’s experienced travel time, which can be decomposed into two components: (1) deterministic travel times at these two network links, , (2) and a stochastic turning delay , experienced for movement . Given a trajectory set of probe vehicles during the same time interval, the observation set of link travel times and turning delay distributions can be generated. In next section, a robust method is proposed to estimate the path travel time distributions based on the observation set generated from FCD.
3. The Proposed Method
In this section, a robust method to estimate path travel time distribution using low-frequency FCD is proposed. Figure 2 shows the framework of this proposed method. After collecting the FCD, a basic work should be done first. Due to GPS measurement errors and digital map geometric errors, the GPS locations may not appear on the network links. Thus, a map-matching (MM) procedure is required to precisely match these FCD onto network links. Then, link travel time is estimated as a deterministic value considering the reliability of the collected speed data. Next, the estimation of turning delay distribution is presented. Afterward, a weighted moving average method is adopted in this study to smooth the travel time of each interval to provide a reliable and robust estimation of travel time distribution. Finally, path travel time distribution or interval is estimated.
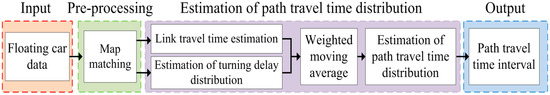
Figure 2.
Framework of the proposed method.
3.1. Link Travel Time Estimation
The link travel time is calculated as the ratio of link length and speed (), where, is the maximum speed of link . To ensure the reliability of the maximum speed, the sampling speed of all vehicles on link are sorted in ascending order. The last several sampling speeds are weighted to calculate the maximum link speed as follows.
where is the speed of sampling point of probe vehicle on the link during the period of interest. denotes the weight of the corresponding GPS sampling speed .
In this study, it is postulated that the vehicles far from the intersections are less likely to be interrupted by signal timing. Following this postulation, the concept of degree of central tendency is introduced to calculate the weight parameter . The degree of central tendency indicates that the degree of a sampling point from the midpoint of link, and can be obtained by the following formula:
Only when the GPS sampling points are on the middle of the link, that is, equals to 0.5, the degree of central tendency is equal 1, which means that the GPS sampling point is fairly reliable based on the hypothesis.
3.2. Estimation of Turning Delay Distribution
This step is to estimate the turning delay distribution for different turning movements. For the probe vehicle, these can be categorized into two types: (I) there is at least one sampling point from the same probe vehicle on each link; (II) at least one full link is existing between the two consecutive sampling points from the same probe vehicle as shown in Figure 3.
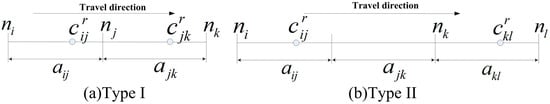
Figure 3.
The locations of two consecutive sampling points of the probe vehicle.
3.2.1. Turning Delay Estimation for Type I
Figure 4 shows an illustration of sparsely sampling GPS data on the links for Type I. As shown in Figure 4, given the probe vehicle, its locations at tail link and head link are recorded at time instance and respectively. It should be noted that if several GPS points are recorded in the same link, the GPS point with the largest central tendency degree (blue points) is selected. It can reduce error caused by sampling points being too close to the intersection. As shown in the blue area of Figure 4, the difference () of these two time stamps and is the experienced travel time between two sampling points.
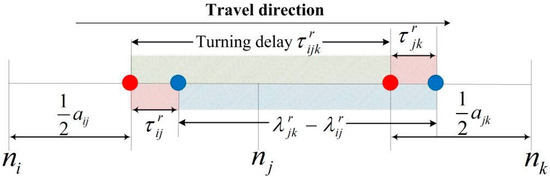
Figure 4.
An illustration of sparsely sampling global positioning system (GPS) data on the links for Type I.
In Figure 4, the red points represent the midpoints of the links, whose degree of central tendency is equal 1. However, the sampling points cannot be exactly in the middle of the links as there are still acceleration (or deceleration) times arriving at the intersection and leaving from the midpoints. In this study, vehicles are assumed to accelerate to a maximum speed or decelerate to current speed uniformly. and (the red areas shown in Figure 4) represent these acceleration (or deceleration) times at tail link and head link, respectively. Based on the fundamental formulas and inferences of uniformly accelerated rectilinear motion, these acceleration (or deceleration) times are calculated as
In addition, the relationship between the sampling points (blue points) and midpoints (red points) has a certain influence on the calculation of travel time between the two consecutive midpoints. For example, in Figure 4, should be included in the travel time, while should be excluded. Therefore, sign function is introduced to describe this situation as follows.
Following the travel direction in Figure 4, when the sampling point is on the right side of the midpoint (e.g., ), . Also, when the sampling points are accurately located in the midpoints, is equal to 0, which means that there is no acceleration (or deceleration) times.
The turning delay (denoted by , the green area in Figure 4), experienced when the vehicle passes through the turning movement , can be estimated by subtracting free-flow travel time from the total travel time as shown below:
The first two terms in Equation (7) are the estimated travel time with delays. In the third term, the vehicle is travelling at a constant speed on head link and on tail link , while the delay due to queuing, acceleration, and deceleration is included in the turning delay.
3.2.2. Turning Delay Estimation for Type II
For Type II, the question is how to reallocate travel delay into individual intersections only based on the GPS-equipped FCD. Some models have been developed to decompose travel times by Hellinga [25] and Zheng [20]. However, considering the algorithm’s complexity and efficiency, a more simple and effective method is put forward.
There are two intersections between two sampling points as shown in Figure 5. Similar to Type I, the turning delays (denoted as ) for these two intersections can be estimated as
where and can be calculated similarly with Equations (4) and (5).
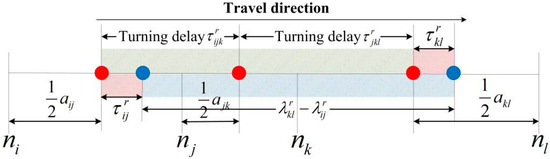
Figure 5.
An illustration of sparsely sampling GPS data on the links for Type II.
The question is how to reallocate turning delays into each intersection. The traffic condition in the middle link is likely to be free flow, since the sampling interval is quite short. The allocation coefficients are the function of travel speed, link free-flow speed, link length, and the relative location of sampling points on the link. However, to simply to the algorithm, it is assumed that the delays passing through the upstream and downstream intersections are proportional to the length between the two midpoints. Hence, the allocated delays of intersections and are calculated accordingly as followings:
3.2.3. Delay Distribution of Different Turning Movements
Three kinds of turning movements are defined when probe vehicles go through the road intersection, that is, through-movement, left-turn movement, and right-turn movement [18]. With the obtained turning delays, , for all probe vehicles during the same time interval, the turning delay distribution, , can be fitted. In general, the turning delay obeys Normal, Lognormal, or Gamma distribution. In this paper, the best-fitted distribution is chosen as the type of turning delay distribution. Therefore, the turning delay distribution may change with different intersections and time intervals. It is much more reasonable in highly stochastic urban road networks.
3.3. The Weighted Moving Average Method
As probe vehicles generally have a low level of market penetration (e.g., 3%) and a low sampling rate (e.g., 2 min), the sample size of FCD may not be sufficient in some time intervals. The smoothing methods, such as the moving average method, Savitzky–Golay smoothing, roughness penalty smoothing, and Kernel smoothing are a commonly used techniques to address this issue. In the previous studies, smoothing methods are generally employed to obtain a robust estimation of mean travel times. In this study, the conventional moving average method is extended to obtain a robust estimation of bot mean and variances of travel times. The moving average method is adopted due to its simplicity and effectiveness [26,27]. Let and be the estimated link travel time at time interval and link travel time at time interval . Using the weighted moving average method, the estimated link travel time at time interval , denoted by can be calculated by
where is the adaptive smoothing factor, which depends on a sensitivity parameter and the number of probe vehicles passing link during the time interval .
This weighted moving average method is further extended to improve the turning delay distribution. Let and be the estimated travel time distribution at time intervals and using the weighted moving average method, and be the mean and standard deviation (STD) of the turning delay distribution at time interval . The estimated travel delay distribution can be calculated by
where is the adaptive smoothing factor. is the number of probe vehicles through the turning movement during time interval . and are the estimated mean and STD of the turning delay distribution at time interval and , respectively. After processing the results with the weighted moving average method, estimated travel delays can be quite reliable.
3.4. Estimation of Path Travel Time Distribution
Let the mean and STD of path travel time distribution be and , respectively. They can be expressed as
where is the travel time covariance between the and intersections along the path.
In the application of ITS, the provision of travel time distribution to road users may be meaningless. It seems more reasonable to provide the confidence interval (CI) based on the estimated travel time distribution. Given a confidence level , the covers the range of probable travel times travelers may encounter, where and correspond to the lower and upper bounds of a CI.
4. Case Study
The performance of the proposed model is investigated using numerical experiments. This section describes the experimental setup and discusses the experimental results.
4.1. Test Site and Data Collection
A real-world case study is reported in this section to demonstrate the applicability of the proposed distribution estimation method of turning delay and path travel time. The probe vehicle system in Wuhan, China is adopted for this case study. This probe vehicle system utilizes 11,245 taxis as probe vehicles, and the sampling time interval is about 40 s. 80% of the collected data are used to construct a model, and the rest of the data are test data. To validate performance of the proposed method, a major road (or path) from ‘Wuhan University’ to ‘Wuchang Railway Station’ (as shown in Figure 6) was selected as the study path. This selected path consists of eight links and seven intersections, and its travel distance is 5.8 km. Travel times are estimated at 15-min interval from the morning peak to evening peak (07:00–22:00) of a typical weekday on 17 September 2009 (Thursday).
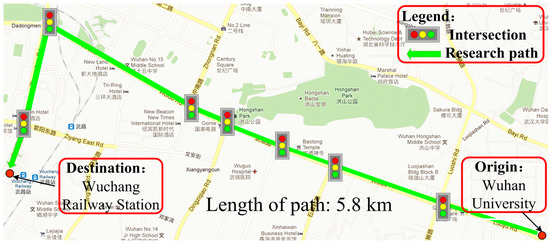
Figure 6.
Location of study path in Wuhan, China.
In this paper, the MM and the path inference algorithm [28] are used. Chen et al., take into account the projection distance, network topology, and the shortest path comprehensively to determine the best candidate link. The proposed method is competitive with the existing FCD–MM algorithms with respect to both MM accuracy and computational performance.
Many studies assume that travel times follow for normal distribution [23,29]. Moreover, lognormal distribution is also a reasonable alternative. In congested urban road networks, travel times however are highly stochastic due to the fluctuations in traffic demand and supply, traffic control, and drivers’ varying behaviors, etc. Thus, the type of travel time distribution may be quite different at different locations in different periods. Based on these current studies, the path travel time and turning delay distribution are usually fitted with several classical distributions, namely normal distribution, lognormal distribution, and gamma distribution [30,31]. According to the Chi-square test, the best-fit results of turning delay distributions are shown in Table 1. On the whole, the lognormal distribution is superior to the other two distributions at a 5% significance level. More than 50% of the distributions follow lognormal distribution, and the same results can be found in off-peak periods. In the morning and evening peak, the percentage of lognormal distribution decreases slightly, but is still dominant. The results show that normal distribution cannot describe a certain skew and long tail distribution [16]. In conclusion, the assumption that all turning delay distributions obey the same distribution is unreasonable.

Table 1.
Best-fit results for three types of turning delay distributions at 5% significant level.
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
To quantify the accuracy assessment, two widely accepted metrics, namely, mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) and root mean square error (RMSE), were adopted to evaluate the accuracy of the estimated mean of path travel time distribution,
where and are the estimated and observed mean values of path travel times at time interval , and is the number of time intervals during the period of interest. Smaller and indicate a higher accuracy of the estimated mean path travel time.
The MAPE and RMSE concepts were extended to evaluate the accuracy of the estimated STD of the path travel time as followings,
where and are the estimated and observed STDs of path travel times at time interval .
For many transportation applications, it is meaningful to construct a travel time interval at a given confidence level from the estimated or predicted travel time distribution [32,33]. The accuracy of travel time interval represents the integrated accuracy of both the estimated mean and STD. Two metrics were adopted to evaluate these accuracies: probability outside of the predicted (estimated) time interval (POPI), and the probability outside of the observed time interval (POOI) [34]. The POPI measures the percentage of observed data, or observed travel time interval outside of the estimated travel time interval, while the POOI measures the percentage of estimated distribution outside of the observed travel time interval.
Let represent the estimated travel time interval. The lower and upper bounds are and , respectively, at confidence level , where is the inverse cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the estimated path travel time distribution. Similarly, the observed travel time interval is expressed as . and , respectively, which denote the lower and upper bounds of the observed travel time interval, at a confidence level of , where is the inverse of the CDF of the observed path travel time distribution. Let be the intersection between the estimated and observed travel time intervals. and are the lower and upper bounds of the intersection, respectively. For a certain time interval, and if .
In mathematical terms, POPI is defined as follows,
where denotes the CDF of the estimated travel time distribution. The POPI value ranges from 0 to 1. The smaller POPI indicates capture of larger proportion of observed data, i.e., higher accuracy of the estimated travel time interval. As noted by Shi [34], this POPI metric is very useful, but tends to exhibit bias for situations of wide travel time intervals due to large STD errors.
As an alternative, the POOI measures the percentage of estimated distribution outside of the observed travel time interval. denotes the CDF of the estimated travel time distribution. Accordingly, POOI can be defined as
The POOI value also ranges from 0 to 1. The larger POOI value indicates the lower accuracy of the estimated travel time interval, because the larger proportion of estimated travel time interval is outside of the observed travel time interval. Therefore, these POPI and POOI matrices are complementary to evaluate the accuracy of the estimated path travel time interval.
4.3. Experimental Results and Analysis
This section reports the experimental results of the case study. In the proposed method, the sensitive parameter in Equations (12) and (15) was set as 0.2, which is initially recommended by Dion and Rakha [26], Tam and Lam [27].
Figure 7a shows the path travel times estimated by the proposed method against the observed path travel times. The coefficient of determination (R2) is 0.90, which reflects the accuracy of the estimated path travel times. It implies that 90% of the estimated path travel times are well fitted with the observed travel times on the study path during the period of interest. Moreover, the cumulative frequency distribution of the absolute percentage errors of the path travel times is depicted in Figure 7b. It can be seen that half of the estimated travel times on the selected path are within 3% errors, whereas at least 90% of the estimated path travel times are within 8% errors. The estimation errors of the travel times on the selected path are all less than 13% in the study periods (as the red star shows). The proposed path travel time estimation method provided a reliable and accurate estimation of mean travel time, , throughout the period of interest, with . In summary, the performance of the proposed algorithm for urban travel time estimation is shown to be satisfactory.
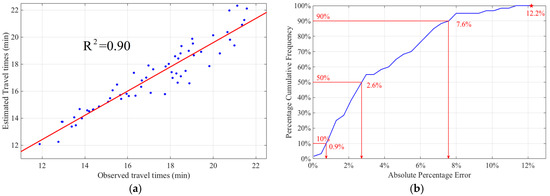
Figure 7.
(a) Accuracy of the proposed algorithm in the fifteen-hour survey period; (b) Cumulative frequency distribution of the estimated errors of the mean path travel times.
The upper and lower bounds of the estimated and observed path travel time intervals are given in Figure 8. In this paper, the confidence level is equal to 80% (i.e., ) due to two main reasons. On one hand, the travel time interval is determined by the level of confidence. Very narrow travel time intervals with a low confidence level are not reliable, while very wide travel time intervals with a high confidence level are not practically very useful. On the other hand, 10th and 90th percentile values of travel time distribution are usually used as the lower and upper bounds of travel time interval in the existing studies [35,36,37,38]. In Figure 8, the constructed travel time intervals for both of the estimated and observed travel time distributions are shown in red and blue dotted lines, respectively. POPI and POOI metrics are also calculated for an 80% confidence level. Observed data from the field survey, shown in green dots, were only used for accuracy validation. As shown in the figure, the estimated travel time intervals can cover most observed data well during the period of interest. The proposed path travel time estimation method provided a reliable and accurate estimation of mean travel time, , throughout the period of interest, with . However, the relatively large indicates that the proposed method has a bigger bias in estimation of path travel time distribution STD, , for the period of interest. This highlights the challenge of accurately estimating in congested road networks. One major reason may be the difficulty of estimating of the population using biased and sparse samples. The RMSEs of the mean and STD are 0.85 and 0.95 min, respectively. This indicates that the mean and STD of the estimated and observed path travel time distributions fluctuate within 1 min.
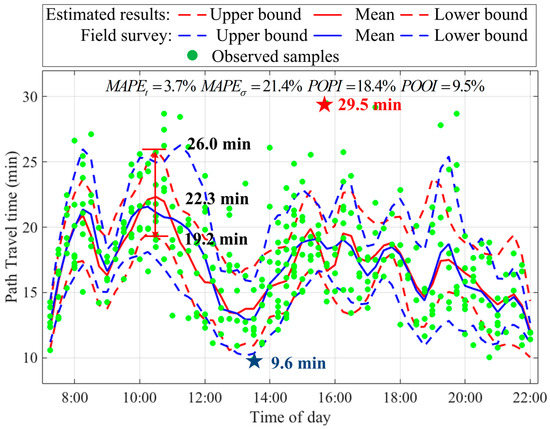
Figure 8.
The estimated and observed path travel time distributions during the period of interest.
In terms of the accuracy of the estimated travel time interval, POPI is 18.4%, somewhat better than the target (20%), which indicates that a high proportion (81.6%) of observation data was well covered by the estimated path travel time interval. It can also be seen from the figure that the estimated interval was not too wide, given the relatively large STD error. POOI is equal to 9.5%, which is much smaller than the target (20%). Overall, the STD was underestimated, because the observation samples were relatively sparse. Thus, the POPI and POOI metrics demonstrate that the proposed method could obtain accurate and robust estimations of the path travel time interval (i.e., path travel time distribution).
It can be observed from Figure 8 that the mean path travel time is stable, varying only from 12.1 min to 22.3 min. A lucky traveler may only require 9.6 min (as the blue star shows), while an unlucky one may even spend 29.5 min for the same trip (as the red star shows). For example, travelers want to take the train at 10:30 and set aside 10 min to check in, which means that travelers should arrive at Wuchang Railway Station at 10:20. The estimated mean travel time is 22.3 min, and the STD is 2.8 min. Based on the distribution of path travel times, travelers would choose appropriate departure times based on their attitudes of on-time arrival. Risk-seeking travelers (on-time arrival probability is lower than 50%) tended to assign a small travel time budget for their trips. When , risk-seeking travelers were assigned only 19.2 min travel time budget, which was 13.9% less than the expected travel time. However, the observed travel time was 21.6 min, and this was 2.4 min larger than the assigned travel time, which meant that risk-seeking travelers were almost late for their train. When , the risk-averse travelers started their trips at 9:54, and this travel time budget was about 4.4 min larger than the expected travel time, that is, more time should be set aside to ensure a higher probability of on-time arrival. Therefore, it is necessary to provide not only the mean path travel time but also the variation of travel time distribution to travelers, so that they can make an informed trip planning decision.
The study demonstrated through Chi-square tests that the assumption of lognormal distribution is consistent with field travel time observations, and that lognormal distribution is representative of urban travel times under both light and heavy traffic conditions.
5. Conclusions and Further Studies
Provision of link or path travel time distribution information is a crucial requirement for travelers to make reliable route choice decisions incorporating travel time uncertainty. With advances in information and communication technologies (ICT), floating car systems, such as probe vehicles, are widely used in congested urban road networks. These floating car data collected from floating car systems are beneficial for robust and accurate estimation of travel time distribution information.
This paper addressed the problem of estimating travel time distribution in congested urban road networks using low-frequency FCD. In this study, the link travel time was modeled as a deterministic variable without consideration of interruptions caused by signal timing at intersections. Such interruptions due to signal timing were considered in delays of different turning movements at intersections. In this way, turning delays of different turning movements (through, right turn, and left turn) were modeled as random variables and fixed into lognormal distribution, which was consistent with field travel time observations validated through Chi-square tests. In addition, a weighted moving average method was proposed to provide a reliable and robust estimation of link travel time and turning delay distribution, considering that a sample size of FCD may be not sufficient. A speed estimation algorithm using the degree of central tendency instead of coverage proportion is presented to estimate the link travel time. A -discrete approximation method is utilized to generate the path travel time distribution.
A case study using real-world FCD collected in Wuhan, China was carried out to demonstrate the applicability of the proposed travel time estimation method. The results of the case study indicated that the lognormal distribution could provide a satisfied fitting for path travel time distribution, and turning delay distribution in congested urban road networks. Also, the results validated that the proposed method could obtain robust and accurate estimation of path travel time distribution over the whole period of interest. Compared with the observed travel time distribution, the estimation errors were quite low with respect to and metrics.
In the future study, the existing research can be extended in the following ways. First, travel times in this study were assumed to follow lognormal distributions for all time periods. However, several previous studies have found that the travel times in congested road networks could be better represented by normal, gamma, or Burr distributions [39]. These distributions may be suitable for different time periods. Second, fusing traffic data from multiple sources to estimate or predict travel time distribution is also a significant challenge [34]. Last but not the least, travel time distributions were estimated in this study for the current time interval. Extension of the proposed method to the problem of short-term travel time distribution prediction is another interesting topic for further study.
Acknowledgments
The work described in this paper was supported by research grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41231171 and 41571149), the Research Institute for Sustainable Urban Development of the Hong Kong Polytechnic University (No. 1-ZVEW), and the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (No. 2016CFB568).
Author Contributions
Chaoyang Shi, Bi Yu Chen and Qingquan Li provided the idea of this study; Chaoyang Shi implemented the proposed method, carried out the case study, and wrote the manuscript; and, Bi Yu Chen and Qingquan Li made important comments and suggestions on the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jenelius, E.; Koutsopoulos, H.N. Travel time estimation for urban road networks using low frequency probe vehicle data. Transp. Res. B Methodol. 2013, 53, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Y.; Lam, W.H.K.; Sumalee, A.; Li, Q.Q.; Shao, H.; Fang, Z.X. Finding reliable shortest paths in road networks under uncertainty. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2013, 13, 123–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Y.; Li, Q.Q.; Lam, W.H.K. Finding the k reliable shortest paths under travel time uncertainty. Transp. Res. B Methodol. 2016, 94, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhou, X. Optimizing on-time arrival probability and percentile travel time for elementary path finding in time-dependent transportation networks: Linear mixed integer programming reformulations. Transp. Res. B Methodol. 2017, 96, 68–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Sumalee, A.; Maruyama, T. Dynamic marginal cost, access control, and pollution charge: A comparison of bottleneck and whole link models. J. Adv. Transp. 2012, 46, 191–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ma, W.; Liu, Y.; Han, K. Optimal operation of freeway weaving segment with combination of lane assignment and on-ramp signal control. Transp. A 2016, 12, 413–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Y.; Yuan, H.; Li, Q.Q.; Shaw, S.L.; Lam, W.H.K.; Chen, X. Spatiotemporal data model for network time geographic analysis in the era of big data. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2016, 30, 1041–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Shan, J.; Shao, Z.; Zhou, X.; Yao, Y. Geomatics for smart cities: Concept, key techniques, and applications. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2013, 16, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, A.; Chung, E.; Dumont, A.G. Fusing loop detector and probe vehicle data to estimate travel time statistics on signalized urban networks. Comput. Aided Civ. Inf. 2011, 26, 433–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, U.; Mendiburu, A.; Alvarez, M.; Lozano, J.A. A review of travel time estimation and forecasting for Advanced Traveller Information Systems. Transp. A 2015, 11, 119–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevlian, R.; Rajagopal, R. Travel Time Estimation Using Floating Car Data; Cornell University Library: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Simroth, A.; Zahle, H. Travel time prediction using floating car data applied to logistics planning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2011, 12, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.S. A Study of Travel Time Modeling via Time Series Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Conference on Control Applications, Toronto, ON, Canada, 28–31 August 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hofleitner, A.; Herring, R.; Abbeel, P.; Bayen, A. Learning the dynamics of arterial traffic from probe data using a dynamic Bayesian network. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2012, 13, 1679–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, M.; Jenelius, E.; Koutsopoulos, H.N. Non-parametric estimation of route travel time distributions from low-frequency floating car data. Transp. Res. C Emerg. Technol. 2015, 58, 343–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susilawati, S.; Taylor, M.A.P.; Somenahalli, S.V.C. Distributions of travel time variability on urban roads. J. Adv. Transp. 2013, 47, 720–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, R.; Hofleitner, A.; Abbeel, P.; Bayen, A. Estimating arterial traffic conditions using sparse probe data. Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC). In Proceedings of the 2010 13th International IEEE Conference, Funchal, Portugal, 19–22 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.C.; Lu, F.; Zhou, L.; Duan, Y.Y. Computing turn delay in city road network with GPS collected trajectories. In Proceedings of the 2011 international workshop on Trajectory data mining and analysis, Beijing, China, 18 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sanaullah, I.; Quddus, M.; Enoch, M. Developing travel time estimation methods using sparse GPS data. J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 20, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.F.; Henk, V.Z. Urban link travel time estimation based on sparse probe vehicle data. Transp. Res. C Emerg. Technol. 2012, 31, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Kan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Huang, F.; Li, Q. Travel time estimation at intersections based on low-frequency spatial-temporal GPS trajectory big data. Cart. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2016, 43, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenelius, E.; Koutsopoulos, H.N. Probe vehicle data sampled by time or space: Consistent travel time allocation and estimation. Transp. Res. B Methodol. 2015, 71, 120–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Y.; Shi, C.; Zhang, J.; Lam, W.H.; Li, Q.Q.; Xiang, S. Most reliable path-finding algorithm for maximizing on-time arrival probability. Transp. B 2016, 5, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Y.; Lam, W.H.; Sumalee, A.; Li, Q.; Tam, M.L. Reliable shortest path problems in stochastic time-dependent networks. J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2014, 18, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellinga, B.; Izadpanah, P.; Takada, H.; Fu, L.P. Decomposing travel times measured by probe-based traffic monitoring systems to individual road segments. Transp. Res. C Emerg. Technol. 2008, 16, 768–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dion, F.; Rakha, H. Estimating dynamic roadway travel times using automatic vehicle identification data for low sampling rates. Transp. Res. B Methodol. 2006, 40, 745–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, M.L.; Lam, W.H.K. Using automatic vehicle identification data for travel time estimation in Hong Kong. Transportmetrica 2008, 4, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Y.; Yuan, H.; Li, Q.Q.; Lam, W.H.K.; Shaw, S.L.; Yan, K. Map matching algorithm for large-scale low-frequency floating car data. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomax, T.; Schrank, D.; Turner, S.; Margiotta, R. Selecting Travel Reliability Measures; Texas Transportation Institute Monograph: College Station, TX, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Rakha, H.; El-Shawarby, I.; Arafeh, M.; Dion, F. Estimating path travel-time reliability. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference, Toronto, ON, Canada, 17–20 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kaparias, I.; Bell, M.G.H.; Belzner, H. A new measure of travel time reliability for in-vehicle navigation systems. J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2008, 12, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, A.; Mazloumi, E.; Nahavandi, S.; Creighton, D.; Van Lint, J.W.C. A genetic algorithm-based method for improving quality of travel time prediction intervals. Transp. Res. C Emerg. Technol. 2011, 19, 1364–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, A.; Mazloumi, E.; Nahavandi, S.; Creighton, D.; Van Lint, J.W.C. Prediction intervals to account for uncertainties in travel time prediction. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2011, 12, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.Y.; Chen, B.Y.; Lam, W.H.K.; Li, Q.Q. Heterogeneous data fusion method to estimate travel time distributions in congested road networks. Transp. Res. B Methodol. 2017. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Rose, G. Incorporating uncertainty into short-term travel time predictions. Transp. Res. C Emerg. Technol. 2011, 19, 1006–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazloumi, E.; Currie, G.; Sarvi, M. Assessing measures of transit travel time variability and reliability using AVL data. In Proceedings of the 87th Transportation Research Board Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 13–17 January 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mazloumi, E.; Currie, G.; Rose, G. Using GPS data to gain insight into public transport travel time variability. J. Transp. Eng. 2010, 136, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirimoglu, M.; Geroliminis, N. Experienced travel time prediction for congested freeways. Transp. Res. B Methodol. 2013, 53, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.A.P. Susilawati. Modelling travel time reliability with the burr distribution. Proc. -Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 54, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).