Abstract
Several studies attempt to describe changes in the spatial patterns of forests over time, resorting to the comparison of landscape pattern indices (LPI), but new methods for quantifying landscape differences in a statistical context are necessary. In this paper, we quantified and assessed the statistical significance of the forests pattern changes, which have occurred since the end of WWII in Central Italy (Isernia). To do this; based on the proportion of forest cover (pi) and contagion (H) of three land cover maps (1954–1981–2006); we generated 100 forest maps with predictable results through the midpoint displacement algorithm. Then, for both observed and simulated maps, we computed a set of LPI (number of patches, cohesion, largest forest patch index and area weighted mean shape index) and we derived their empirical distributions; finally, we compared the empirical distributions using the non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test. Our results show significant changes in the spatial pattern of forests and underline the process of natural forest re-growth, which, in the area, is constrained by “remnants” of traditional activities. The adopted approach could be extended to a large ensemble of landscapes and spatial scales and could become a standard procedure when comparing patterns in time.
1. Introduction
Landscapes change in both structure and function [1] and said dynamism is mainly driven by changes in management practices responding to social, political and economic forces [2]. The analysis of temporal and spatial changes represents one of the most challenging problems in landscape ecology. Describing changes in different land cover types through time may be crucial, both for preserving biological diversity and related ecosystem services, and for developing general landscape models, which are useful in ecosystem management and environmental policies [3,4]. The current state of landscape patterns in the world is mainly the result of centuries of evolution in land use [5]. For instance, temperate forests in mountain and hilly landscapes of Europe are currently distributed in a mosaic, which is derived not only from centuries of extensive forest exploitation, but also from agriculture and cattle farming [6,7,8], followed by a recent, spontaneous reforestation process, which occurred after the World War II rural exodus and the consequent abandonment of traditional agricultural practices [9,10,11,12,13,14].
The quantitative, spatial and temporal analysis of natural forest re-growth in abandoned farmlands has acquired increasing relevance due to the effects of forest expansion on many important ecosystem functions [11]. For example, forest expansion affects hydrological cycles and soil dynamics [15], climate [16,17] and biodiversity [11,18,19] at different scales. Several landscape metrics have been developed to quantify forest patterns in terms of space and time, most of which have been tested on grid-based thematic maps [5,20,21,22]. Studies aimed at quantifying forest distribution frequently employ landscape pattern indices (LPI) to measure changes in both forest cover and pattern. Changes over time are assessed by many authors simply through the comparison of LPI [23,24,25]. Current research suggests that the comparison of raw LPI values should be avoided [26], since they are sensitive to scale [27], land cover proportions [28], spatial resolution [29,30], spatial extent [31] and land-cover misclassification [32]. New methods for comparing LPI values may be useful in order to add statistical context to landscape pattern analysis [27,33]. As at present it is possible to clearly identify and quantify the differences between any two given dates, the statistical significance of the observed changes remains the most important and complex challenge with which to deal [28,34]. In order to enrich landscape pattern analysis with statistical significance, new methods for comparing and testing LPI values have been proposed [34,35,36]. In ecological research, at the landscape scale, replication cannot be considered, and consequently, distribution, expected values and variance are not available; ecologists who want to perform statistically robust comparisons of landscapes among different maps must rely upon simulations based on computer-generated models able to reproduce an expected pattern, which shares statistical properties with an empirical pattern of interest [34,35,37].
Among the spatial models developed in landscape ecology, the neutral models (NLMs) are those able to produce an expected pattern in the absence of specific landscape processes [21,38,39,40,41,42], providing a baseline in order to evaluate the influence of landscape heterogeneity on ecological processes and vice versa [42]. The first neutral model in landscape ecology was the simple random map developed from percolation theory [39,43] and created by randomly assigning habitats to a proportion, pi, of a grid map [39]. Subsequently, the evolution of NLMs followed the development of fractal methods applied to percolation maps [42]. The second generation of NLMs were hierarchical, random landscapes, generated by fractal curdling [44]. Both the above-mentioned NLMs assume a complete spatial independence from the habitat (or cells in a map) throughout a landscape. Since, in real-life landscapes, habitats usually show a certain degree of spatial contagion, another fractal algorithm, specifically the “midpoint displacement algorithm” [45] has been proposed, giving way to a third generation of NLMs, whose surfaces exhibit continuous environmental variability. Successively, many attempts to test their usefulness in various fields of research have been made. The NLMs based on the midpoint displacement algorithm have been used to assess the effect of landscape fragmentation on population distribution [46], dispersal success of communities [47], insect movement patterns [48] and biodiversity [49]. They were also used to model the diffusion of contamination in aquatic environments [38], the influence of correlated spatial patterns on species coexistence of plant communities [50] and the spatial pattern of disturbance [51] at different scales [52,53]. Although, initially, many NLMs were theoretically applied [54], several efforts toward modeling complex landscapes and testing their differences using neutral fractals have been made [35,55,56]; therefore, we are confident that such an approach can be applied to landscape comparison over time, while carrying out a statistical significance assessment.
Considering the aforementioned points, the present work aims to describe forest cover dynamics in the hilly landscapes of Central Italy in the last 60 years, analyzing the spatial pattern of temperate forest patches of the area surrounding a small city in a rural European setting in detail (Isernia municipality). In particular, we focus on two questions:
- (1)
- How did the spatial pattern of temperate forests change over time (1954–1981–2006)?
- (2)
- Is the spatial pattern change of these forests significantly different over time?
To properly handle such an issue, on one hand, we used a set of landscape pattern indices to describe the forest spatial pattern dynamics and, on the other hand, we compared LPI of real and simulated landscapes to assess the statistical significance of any possible differences. In order to simulate fractal maps, we chose the midpoint displacement algorithm, because it looks very promising for modeling the natural reforestation process, which occurs in many hilly landscapes, as it is able to represent continuous autocorrelated pattern variations [40]. In particular, this fractal NLM allows, through the variation of both proportion and spatial contagion, the obtaining of different levels of habitat aggregation and patchiness [57]. In order to better understand the dynamics of forest fragments and to offer the basis for pinpointing specific conservation actions and forest management strategies for temperate forests in Europe, a multi-temporal analysis, which takes into account the statistical significance of differences in landscape, should be implemented.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Area
Isernia (Central Italy) was selected for our analysis (Figure 1), because the abandonment of traditional rural activities in this area, along with recent developments in infrastructure, appear to have caused changes in land cover, which are typical of small cities in many areas of Italy and other Mediterranean countries [58]. Furthermore, the municipality of Isernia represents a pilot study area of a larger project aimed at analyzing the landscape dynamics of rural areas, which have occurred since the end of World War II in Central Italy. Isernia covers ca. 68 ha and, at present, consists of a small continuous urban area (22,000 inhabitants) surrounded by a hilly landscape with agricultural, semi-natural and natural land cover types: olive groves, crop fields, complex cultivation patterns and broad-leaved forests (mainly Quercuspubescens and Quercuscerris woodlands). Although these forests are very important from a conservation point of view (“Pannonian-Balkanic turkey oak-sessile oak forests” according to “Habitat Directive” EEC 43/92), no protected areas exist in Isernia. Altitudes range from 291 m above mean sea level (a.m.s.l.) to 906 m a.m.s.l., and the climate is temperate [12]. During the last half century, almost 50% of the territory has changed, mainly due to an evolution in landscape management trends: agricultural intensification in the alluvial plains and abandonment of traditional land use activities on the reliefs and less accessible areas [58]. In 1955, the study area was characterized by widespread agricultural lands accompanied by natural and semi-natural vegetation patches of broadleaved forests, thickets and pastures. On the contrary, more recently, broad-leaved forest cover increased in less accessible and hilly areas, substituting shrub lands, part of pre-existing grasslands and olive groves [58].
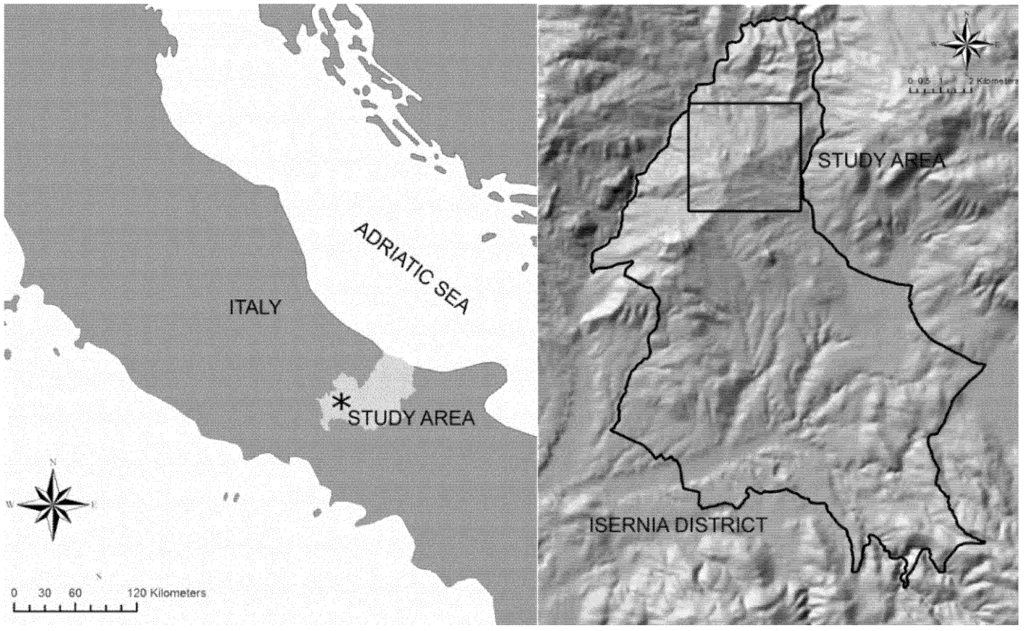
Figure 1.
Map showing the Isernia district (Italy) and the location of the study area.
Figure 1.
Map showing the Isernia district (Italy) and the location of the study area.
2.2. Data Analysis
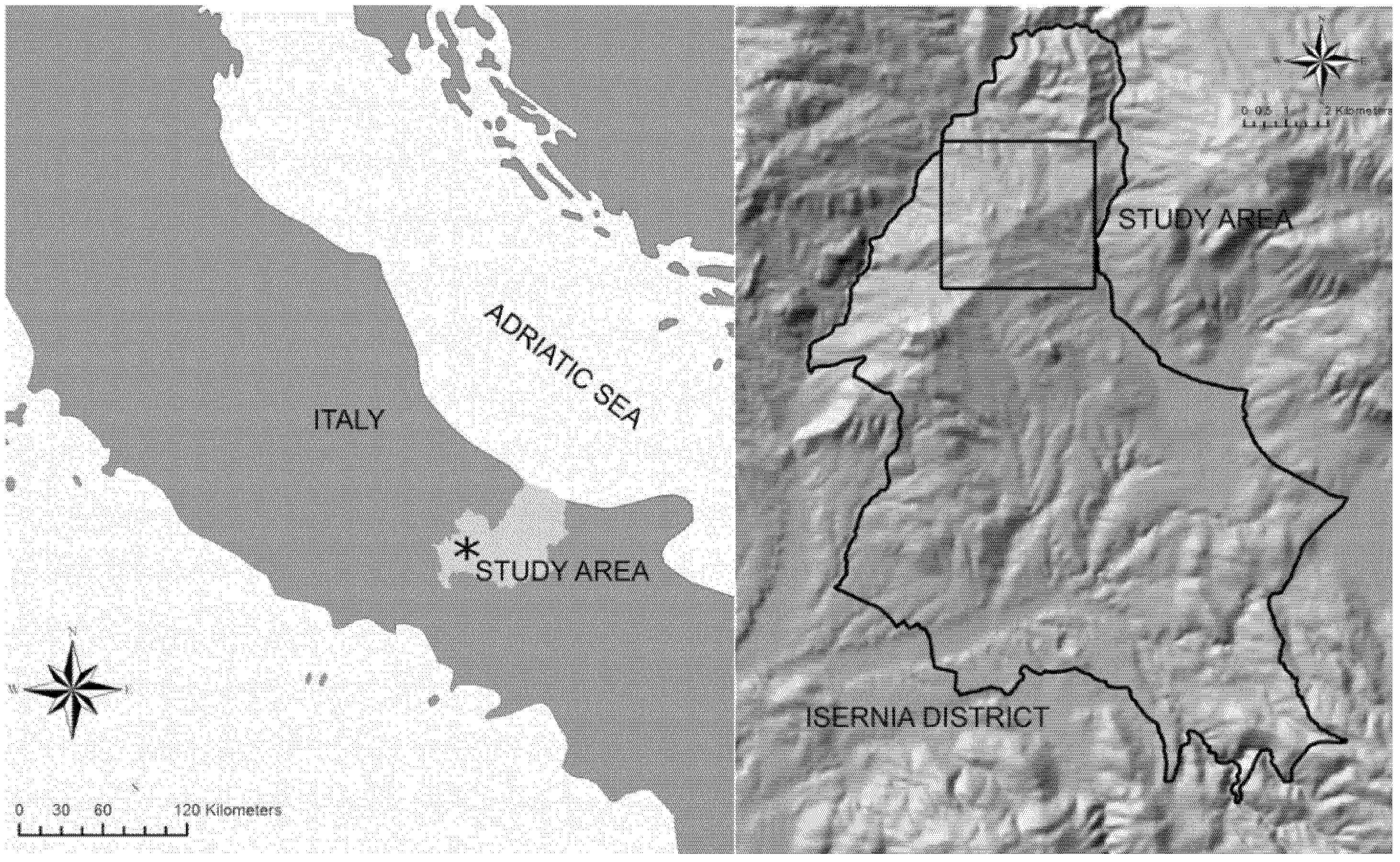
We analyzed the spatial pattern of forests and assessed the significance of the observed differences over time, following the general framework proposed by Remmel and Csillag [35], as described in Figure 2.
2.2.1. Data Preparation
Three land cover maps, relative to the years 1954, 1981 [58] and 2006 (1:25,000), derived from aerial photographs, were used to perform the landscape pattern analysis at the regional scale (see Acosta et al. [58]).
Due to the fact that the midpoint displacement algorithms can generate only square maps [55], we delineated a representative (approximately 20% of hilly sectors of Isernia) 256 × 256 pixel square area, which was used to extract the same geographical window from each map to be compared in time (Figure 3). Next, land cover maps were rasterized with a spatial resolution of 10 m and reclassified in two categories: broadleaved oak forests and other cover types (arable land, permanent crops, pastures, shrub and herbaceous vegetation).
Figure 2.
Proposed framework for comparing and testing differences of forest pattern over time.
Figure 2.
Proposed framework for comparing and testing differences of forest pattern over time.
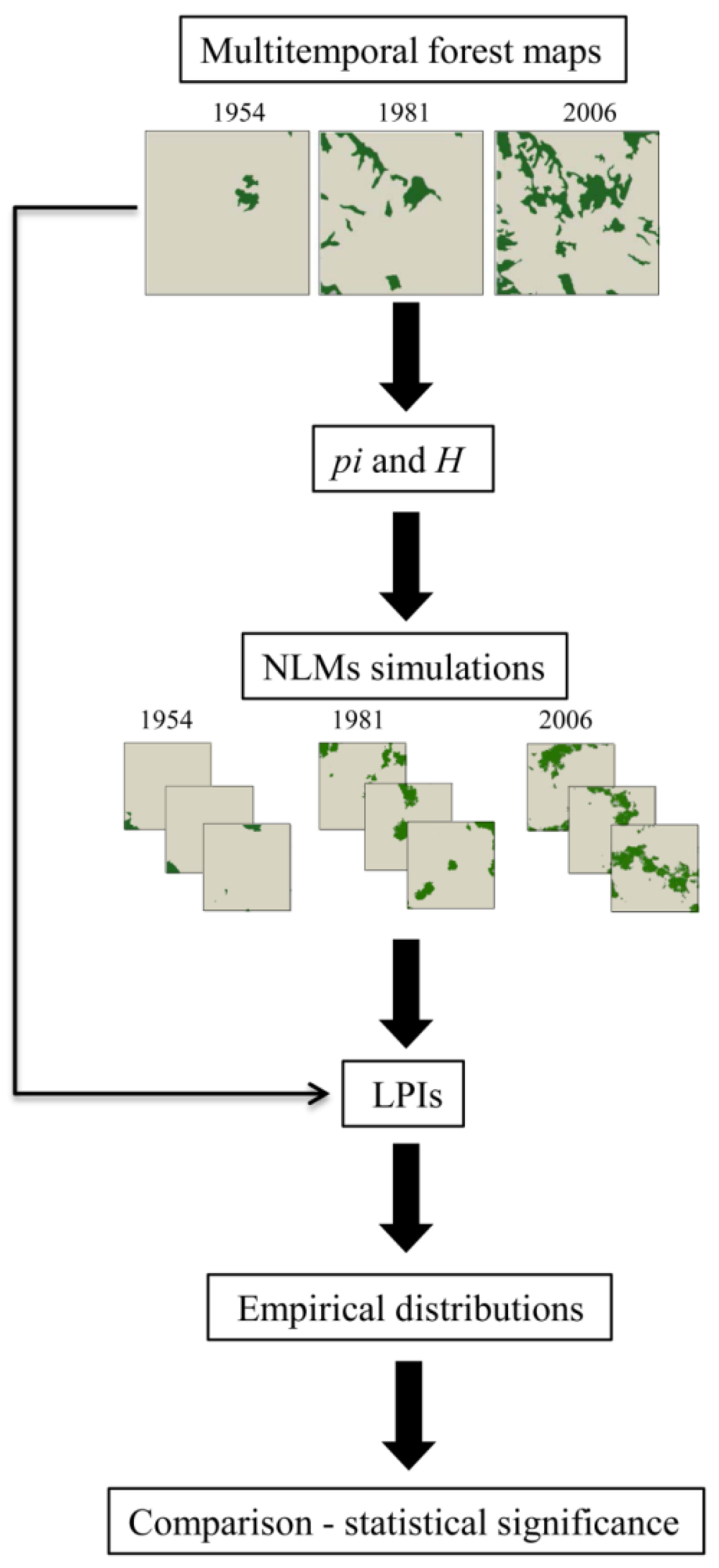
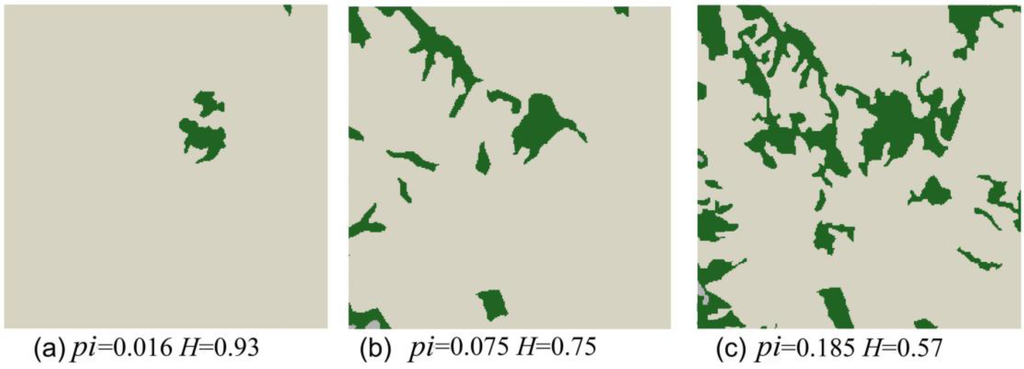
Figure 3.
Three forest cover maps extracted from a multitemporal dataset of Isernia, Italy. Each image is 256 × 256 pixels, with a spatial resolution of 10 m. The binary classification separates oak forest (dark green) from other cover types (arable land, permanent crops, pastures, shrub and herbaceous vegetation—soft grey). pi indicates the proportion of forest cover; H is the autocorrelation of the map. (a) = 1954; (b) = 1981; (c) = 2006.
Figure 3.
Three forest cover maps extracted from a multitemporal dataset of Isernia, Italy. Each image is 256 × 256 pixels, with a spatial resolution of 10 m. The binary classification separates oak forest (dark green) from other cover types (arable land, permanent crops, pastures, shrub and herbaceous vegetation—soft grey). pi indicates the proportion of forest cover; H is the autocorrelation of the map. (a) = 1954; (b) = 1981; (c) = 2006.
2.2.2. NLM
Firstly, two parameters necessary for running the NLM simulations were calculated for each date (1954, 1981 and 2006): proportion of forest cover (pi) and contagion (H). pi is given by the number of forested cells in relation with the total number of cells present in the landscape and ranges between 0 (no forest cover) and 1 (whole landscape covered by forests). H, or contagion [59], describes the adjacencies of forest “cells” and ranges from 0, when forest distribution is maximally disaggregated (no adjacencies among cells of the same class), to 100, when landscape is totally covered by forests (only forest-to-forest adjacencies). Next, for each above mentioned map, we generated 100 maps using the public domain software Qrule [57], freely available on-line (http://www.al.umces.edu/faculty/bobgardner.html). Fractal landscapes were generated using the midpoint displacement algorithm [45], as described in With [60] and With et al. [46]. In short, for each simulation, a three-dimensional fractal surface with roughness controlled by H was created by the midpoint displacement algorithm; then, every fractal surface was sectioned at the appropriate elevation to create a two-dimensional landscape map with the requisite amount of forest given by pi. Finally, in order to avoid the “salt and pepper” artifact commonly present in fractal maps [55] and to make simulated maps comparable with real landscapes [56], we deleted all the patches smaller than the minimum mapping unit of the original maps [61]. The removal of small patches didn’t significantly affect the proportion of forest cover (pi reduction < 0.5%).
2.2.3. LPI Calculation
To analyze the spatial pattern of forests through time, a set of landscape pattern indices on both real and simulated maps was calculated by using FRAGSTATS 4.0 [62]. After recording the total number of patches of forest (NP), we focused on the other three class landscape metrics, which had been previously reported as ecologically meaningful [22,63] and have been proven to be useful in describing patch spatial structure in a forested landscape context [64,65,66,67,68,69]: largest forest patch index (LFP), area weighted mean shape index (AWMSI) and patch cohesion index (COHESION). NP and LFP were selected, because they are related to forest fragmentation [33,66,67,70], defined as the breaking up of one large forest area into many smaller patches [71]. The largest forest patch index (LFP) quantifies the percentage of total landscape area comprised by the largest forest patch. As the diminution of LFP over time is one of the most effective metrics for measuring forest fragmentation [67], its increment could be an effective indicator for describing the reverse process [72,73]. AWMSI [74] measures the complexity of patch shape compared to a standard shape that, in raster format, attains its minimum value (AWMSI = 1) for squares. AWMSI values increase for more irregular and elongated shapes. We chose AWMSI, because of its capacity to distinguish between big, round-shaped patches, characteristic of well-preserved forests, and small, irregular patches, which often dominate in disturbed landscapes (for a review, see Haines-Young and Chopping [64]). COHESION measures the physical connectedness of forests and is commonly used for describing habitat connectivity [75,76]. In conditions of natural forest re-growth, an increment in time of landscape cohesion and connectivity could be expected [69]. COHESION, which ranges between 0 and 100, is minimal when the proportion of the forested landscape decreases and becomes increasingly subdivided and less physically connected. On the other hand, COHESION increases as the proportion of the landscape covered by forests increases (see McGarigal and Marks [74] for details).
2.2.4. Comparing Observed and Simulated LPI
By computing the selected LPI (NP, LFP, AWSI and COHESION) on simulated landscapes, their empirical distributions (sensu Fortin et al. [77]) for each date were obtained. First, we verified the ability of the midpoint displacement algorithm to produce plausible patterns and underlying processes by generating scatterplots that include LPI derived from both real and simulated maps (Figure 4). In particular, the following LPI-based two-parameter spaces were built: NP vs. COHESION and LFP vs. AWMSI. Then, we quantified the differences of LPI among the three dates (1954, 1981 and 2006) by performing a Kruskal-Wallis test, followed by a Mann-Whitney post-hoc pairwise test.
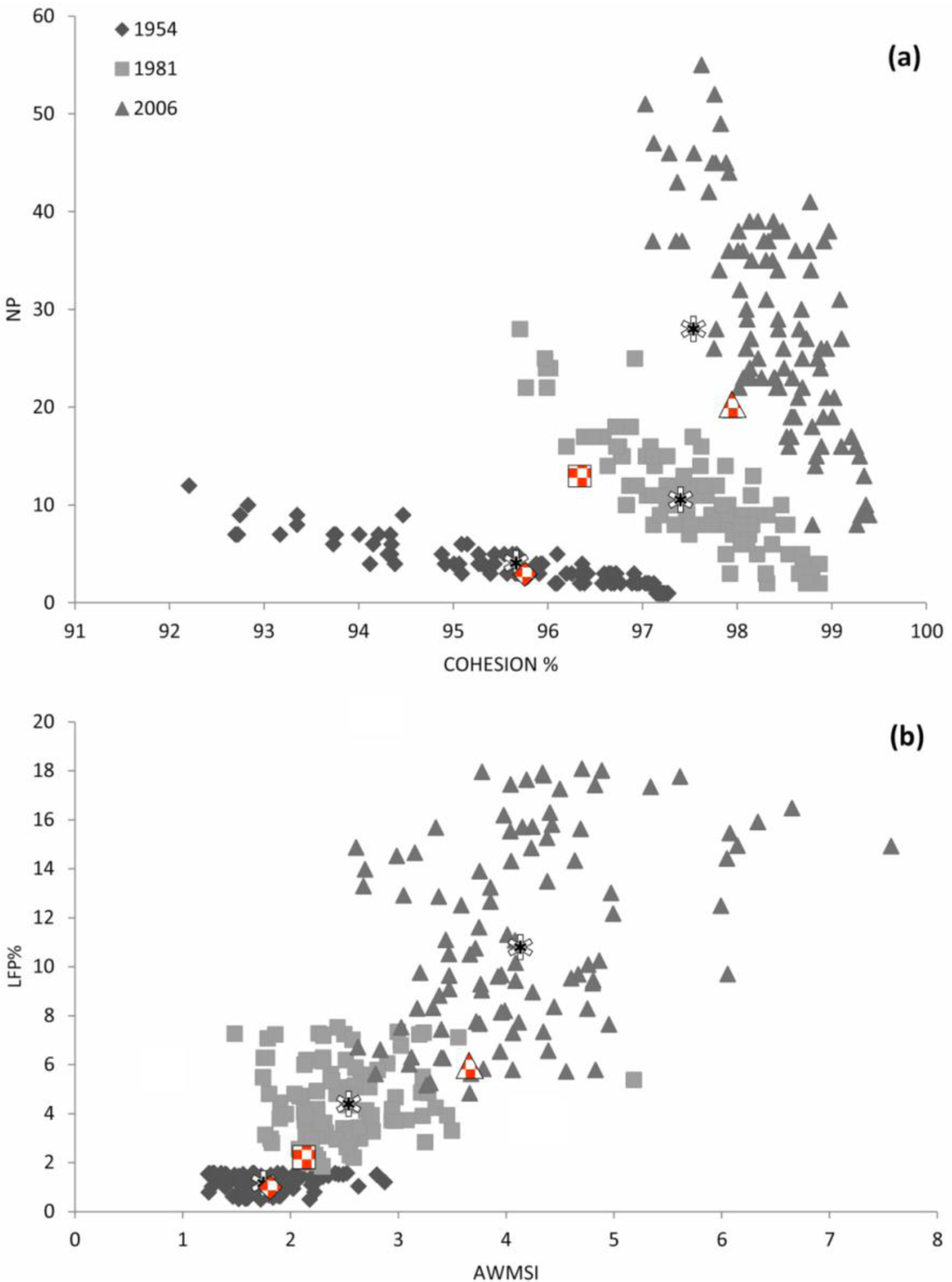
Figure 4.
Scatter plots among two paired combinations of observed landscape pattern indices (LPI) values for simulated landscapes (N = 100; 1954, 1981 and 2006): (a) total number of patches of forest (NP) vs. COHESION and (b) LFP vs. weighted mean shape index (AWMSI). Asterisks indicate the mean values, and red symbols show the position of real landscapes within the empirical distribution derived from simulated landscapes (in grey scale).
Figure 4.
Scatter plots among two paired combinations of observed landscape pattern indices (LPI) values for simulated landscapes (N = 100; 1954, 1981 and 2006): (a) total number of patches of forest (NP) vs. COHESION and (b) LFP vs. weighted mean shape index (AWMSI). Asterisks indicate the mean values, and red symbols show the position of real landscapes within the empirical distribution derived from simulated landscapes (in grey scale).
3. Results and Discussion
The analysis of the 1954, 1986 and 2006 maps shows consistent changes on both the abundance and spatial distribution of forests (Figure 3). During the last 60 years, the proportion of forests increased from pi = 0.016 in 1954 to pi = 0.185 in 2006, as the spatial contagion decreased from H = 0.93 (1954) to H = 0.57 (2006). From the post-war until the end of the analyzed period, we observed the natural spread of forests, a phenomenon that characterizes the large scale dynamics of oak woodlands in many hilly and mountainous landscapes of the Italian peninsula [14,58,68,78]. In Mediterranean areas, the socio-economic post- World War II changes led to a decline of the number of people involved in traditional agricultural and grazing activities [78,79,80,81,82]. Consequently, natural re-growth of forests took place in abandoned lands [58,83].
The rate of forest spread, which in the first time span (1954–1981) was of 5.9%, increased to 11% in the second one (1982–2006) and is in contrast with previous studies, which pointed out an overall decrease in the rate change of secondary successions over time [84,85,86], because of the occupation of the most suitable sites during the first stages of colonization. In our case, in fact, the slow and gradual cessation of farmland practices, the persistence of agricultural activities [58] and the overexploited conditions of soil in abandoned farms slowed down the establishment and growth of woody vegetation [68,86]. Instead, the observed increment of forest expansion rate after 1981 is probably related to two main factors: (i) the consistent abandonment of agricultural practices occurring in Isernia during this period [58], which provided new areas to be colonized and; (ii) the presence of nuclei of forest regrowth, which ecologically facilitated landscape evolution towards a more natural condition.
In Figure 4, scatter plots showing both the position of real and simulated landscapes within the LPI-based two-parameter space (NP vs. COHESION and LFP vs. AWMSI) are reported. It is important to note that real landscapes (red symbols) fall inside the simulated landscapes scatter cloud (grey symbols). Despite the fact that many authors stress the limits of NLMs to capture the structure of real landscapes [87], the use of the midpoint displacement algorithm has provided a reliable set of simulated maps, which adequately describe the spatial pattern of forests through time (Figure 4). The fact that all the LPI calculated from real landscapes fall within the area of the respective distribution, obtained from simulated landscapes, contrasts with previous works, which state the merely theoretical value of such simulations [42,54]. It is important to note that the midpoint displacement algorithm constitutes the starting point for modeling more realistic and complicated scenarios of landscape change [38,40,60]. In our case, we obtained landscapes with several degrees of patchiness and spatial aggregation, by tuning the parameters that control landscape simulations (pi = proportion of forest cover and H = forest spatial autocorrelation), of the values observed in the different maps. A significant change in all LPI values was observed when analyzing the spatial pattern of forests (Kruskal-Wallis test, p < 0.01). In particular, the number of forest patches (NP) significantly increased by about 66% (3–13) from 1954 to 1981 and by about 61% (13–20) from 1981 to 2006, resulting in an overall 87% (3–20) increase for the entire period (1954–2006). The significant rise in the number of patches, caused by the establishment of several new nuclei of young forests into abandoned farmlands [68], characterizes the former stages of natural colonization of abandoned lands in Mediterranean ecosystems [70,78,79,80,88,89]. Contemporarily, we also detected a significant increment in the percentage of landscape occupied by the largest forest patch: in 1954, the percentage of landscape occupied by the largest forest patch was 1.17% (S.E. ± 0.034), while it significantly increased both in 1981 (4.47%, S.E. ± 0.16) and 2006 (11.26%, S.E. ± 0.39). This is mainly due to the enlargement, over time, of existing vast nuclei and their coalescence with contiguous ones [14,68,78,79,80,88,89,90]. During the advanced phases of spontaneous regeneration in Mediterranean areas, forest cover tends to evolve into a more homogeneous distribution, with a general decrease in the number of patches [14,68,90] derived from the expansion and coalescence of the numerous small pioneering forest patches into a few larger ones. In contrast with the general trend observed inside a natural reserve in Tuscany, where the protection regime allowed for a complete regeneration of forests [68], in the analyzed territory (where no conservation or protection constraints exist), only a partial forest re-growth occurred. Indeed, as evident in other Mediterranean landscapes [83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90], many “remnants” of the traditional activities in Molise hilly landscapes are still present and constrain the distribution and natural spread of forests. Over the three “sampling dates”, the shape of forest patches (AWMSI) significantly increased, ranging from 1.74 (S.E. ± 0.035) in 1954 to 2.48 (S.E. ± 0.052) in 1981, with a further increase in 2006 (4.13, S.E. ± 0.091). In terms of COHESION, there was a significant increase of the physical connection of forest patches. In particular, the COHESION index was 95.69% (S.E. ± 0.14) in 1954 and increased to 97.54% (S.E. ± 0.075) in 1981, reaching 97.96% (S.E. ± 0.056) in 2006. As previously described in Mediterranean landscapes, the re-colonization of oak forests in Molise occurred with an increment over time of shape complexity (AWMSI) [83,91] and connectivity (COHESION) values [78,82]. Immediately after the abandonment of traditional agricultural practices, the fine-grained pattern, which characterizes landscapes affected by long-established agriculture, formed by small regularly shaped and isolated patches, was progressively replaced by a more coarsely grained pattern, which results in large, irregularly shaped forest patches [83,91].
4. Conclusions
The observed increment in extension and the significant changes in spatial distribution of forests suggest that the analyzed area underwent an intense process of natural re-colonization, which has slowly begun after World War II and which is still in progress. The phenomenon we observed could be considered as reforestation (sensu Sitzia et al. [69]), that is, the natural reestablishment of a forested landscape on disused agricultural lands following farm abandonment [70] in regions where the potential natural vegetation (sensu Zerbe [92]) is a forest. The presence of many (NP) irregular patches (AWMSI), with increasing values of connectivity (COHESION) and patch dimension (LFP), underlines a transitional stage of forest re-growth.
Although the accurate description of the huge ecological consequences of such transformations is beyond the scope of this work, we can point out possible effects, such as an increment in true forest species [93,94], a stronger connectivity for forest vertebrates [76,95], an improvement in CO2 sink services [96], regulation of water drainage [97] and landslide prevention [98].
The NLMs effectively modeled the pattern of forests over time at a specific spatial resolution and could be also very useful for exploring future scenarios, responding in this way to the urgent need to predict natural reforestation process [86]. Simulation models could also help to better understand how natural re-growth varies in space and time and its effects on landscape function [71]. In particular, predicting the pattern of forest expansion is extremely important, because of its possible effects on many key ecosystem functions [99,100]. For instance, the pattern of forest expansion affects watershed services [15,101,102], biodiversity [11,18,19] and climate at different scales [16,17].
Many of the insights and conclusions obtained in this study have been facilitated by the statistical framework provided by the utilization of NLMs. In particular, the application of the midpoint displacement algorithm:
- (1)
- allows for modeling a reliable set of maps, which adequately describe the spatial pattern of forests through time and which can be directly compared with real landscapes [56];
- (2)
- generates a set of landscape replications, which account for the most relevant information;
- (3)
- defines the landscape expectations, which allows the statistical comparison of patterns through time [29,47,48].
It is important to note that the obtained results are strongly dependent on both the specific type of landscape and the chosen spatio-temporal scale. Since, by tuning the scale of analysis, the observed patterns and the underlying processes become finer or coarser, a sound study of landscape evolution over time should include the spatio-temporal scale [103]. Therefore, such an approach could be extended across a large ensemble of landscapes [37,55] and spatio-temporal scales [52,53], thus providing relevant indications as to the changes in landscape structure over time and all the ecological and cultural consequences linked to this issue [99].
Furthermore, statistical analysis could become a standard method when comparing maps [20], especially in change detection procedures, so that a sound basis for developing efficient management policies of forests could be provided.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge Mita Drius for the careful and critical reading of the draft, Angela Pitassi for the language review, as well as two anonymous referees for helping to improve the original version of the manuscript.
References and Notes
- Turner, M.G.; Gardner, R.H.; O’Neill, R.V. Landscape Ecology in Theory and Practice; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, C.P.; Sharpe, D.M.; Guntenspergen, G.R.; Stearns, F.; Yang, Z. Methods for Analyzing Temporal Changes in Landscape Pattern. In Quantitative Methods in Landscape Ecology; Turner, M.G., Gardner, R.H., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 173–198. [Google Scholar]
- Franklin, J.F. Lessons from old-growth: Fueling controversy and providing direction. J. Forest 1993, 91, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, N.L.; Bartuska, A.M.; Brown, J.H.; Carpenter, S.; D’Antonio, C.; Francis, R.; Franklin, J.F.; MacMahon, J.A.; Noss, R.F.; Parsons, D.J.; et al. The report of the Ecological Society of America Committee on the scientific basis for ecosystem management. Ecol. Appl. 1996, 6, 665–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienast, F. Analysis of historic landscape patterns with a Geographical Information System—A methodological outline. Landscape Ecol. 1993, 8, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekmann, M.; Eilertsen, O.; Fremstad, E.; Lawesson, J.E.; Aude, E. Beech forest communities in the Nordic countries—A multivariate analysis. Plant Ecol. 1999, 140, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson, A.L.; Östlund, L. Retrospective gap analysis in a Swedish boreal forest landscape using historical data. Forest Ecol. Manage. 2001, 147, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, L.; Fipaldini, M.; Marignani, M.; Blasi, C. Effects of fragmentation on vascular plant diversity in a Mediterranean forest archipelago. Plant. Biosyst. 2010, 144, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, D.; Crabtree, J.R.; Wiesinger, G.; Dax, T.; Stamou, N.; Fleury, P.; Gutierrez Lazpita, J.; Gibon, A. Agricultural abandonment in mountain areas of Europe: Environmental consequences and policy response. J. Environ. Manage. 2000, 59, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antrop, M. Landscape change and the urbanization process in Europe. Landscape Urban Plan. 2004, 67, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudel, T.K.; Coomes, O.T.; Moran, E.; Achard, F.; Angelsen, A.; Xu, J.; Lambin, E. Forest transitions: Towards a global understanding of land use change. Global Environ. Change. 2005, 15, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carranza, M.L.; Acosta, A.; Ricotta, C. Analyzing landscape diversity in time: The use of Rènyi’s generalized entropy function. Ecol. Indic. 2007, 7, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gils, H.; Batsukh, O.; Rossiter, D.; Munthali, W.; Liberatoscioli, E. Forecasting the pattern and pace of Fagus forest expansion in Majella National Park, Italy. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2008, 11, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracchetti, L.; Carotenuto, L.; Catorci, A. Land-cover changes in a remote area of central Apennines (Italy) and management directions. Landscape Urban Plan. 2012, 104, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, R.A.; Richter, D.D.; Pattanayak, S.; Sharma, N.P. Ecological and economic analysis of watershed protection in Eastern Madagascar. J. Environ. Manage. 1997, 49, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, R.A.; Skole, D.L.; Nobre, C.A.; Hackler, J.L.; Lawrence, K.T.; Chomentowski, W.H. Annual fluxes of carbon from deforestation and regrowth in the Brazilian Amazon. Nature 2000, 403, 301–304. [Google Scholar]
- Nabuurs, G.J.; Schelhaas, M.-J.; Mohren, G.M.J.; Field, C.B. Temporal evolution of the European forest sector carbon sink from 1950 to 1999. Glob. Change Biol. 2003, 9, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrig, L. Effects of habitat fragmentation on biodiversity. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. S. 2003, 34, 487–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estreguil, C.; Mouton, C. Measuring and Reporting on Forest Landscape Pattern, Fragmentation and Connectivity in Europe: Methods and Indicators; EUR 23841 EN; European Commision Joint Research Center, Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, R.V.; Krummel, J.R.; Gardner, R.H.; Sugihara, G.; Jackson, B.; de Angelis, D.L.; Milne, B.T.; Turner, M.G.; Zygmunt, B.; Christensen, S.W.; et al. Indices of landscape pattern. Landscape Ecol. 1988, 1, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.G. Landscape ecology: The effect of pattern on process. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. S. 1989, 20, 171–197. [Google Scholar]
- Ritters, K.H.; O’Neill, R.V.; Hunsaker, C.T.; Wickham, J.D.; Yankee, D.H.; Timmins, S.P.; Jones, B.K.; Jackson, B.L. A factor analysis of landscape pattern and structure metrics. Landscape Ecol. 1995, 10, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessburg, P.F.; Smith, B.G.; Salter, R.B. Detecting change in forest spatial patterns from reference conditions. Ecol. Appl. 1999, 9, 1232–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohn, R.; Hao, Y. Landscape metric performance in analyzing two decades of deforestation in the Amazon Basin of Rondonia, Brazil. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.G.; Person, S.M.; Bolstad, P.; Wear, D.N. Effects of land-cover change on spatial pattern of forest communities in the Southern Appalachian Mountains (USA). Landscape Ecol. 2003, 18, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergel, S.E. New Direction in Landscape Pattern Analysis and Linkages with Remote Sensing. In Understanding Forest Disturbance and Spatial Pattern: Remote Sensing and GIS Approaches; Wulder, M.A., Franklin, S.E., Eds.; Taylor and Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 173–208. [Google Scholar]
- Cullinan, V.I; Thomas, M. A comparison of quantitative methods for examining landscape pattern and scale. Landscape Ecol. 1992, 7, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, E.J.; Parker, G.R. Relationships between landcover proportion and indexes of landscape spatial pattern. Landscape Ecol. 1992, 7, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, J.D.; Riitters, K.H. Sensitivity of landscape metrix to pixel size. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 3585–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchini, D. Resolution problems in calculating landscape metrics. J.Spat. Sci. 2005, 50, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, S.; Martínez-Millán, J. Sensitivity of lanscape pattern metrics to map spatial extent. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sensing 2001, 67, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, J.D.; O’Neill, R.V.; Riitters, K.H.; Wade, T.G.; Jones, K.B. Sensitivity of selected landscape pattern metrics to land-cover misclassification and differences in land-cover caomposition. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sensing 1997, 63, 397–402. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.A.; Nelson, T.A.; Wulder, M.A. Characterizing forest fragmentation: Distinguishing change in composition from configuration. Appl. Geogr. 2010, 30, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boots, B.; Csillag, F. Categorical maps, comparisons, and confidence. J. Geogr. Syst. 2006, 8, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmel, T.K.; Csillag, F. When are two landscape pattern indices significantly different? J. Geogr. Syst. 2003, 5, 331–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csillag, F.; Boots, B. A framework for statistical inferential decisions in spatial pattern analysis. Can. Geogr. 2005, 49, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keitt, T.H. Spectral representation of neutral landscapes. Landscape Ecol. 2000, 15, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, S.M.; Gardner, R.H. Neutral Models: Useful Tools for Understanding Landscape Patterns. In Wildlife and Landscape Ecology: Effects of Pattern and Scale; Bisonette, J.A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 215–230. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, R.H.; Milne, B.T.; Turner, M.G.; O’Neill, R.V. Neutral models for the analysis of broad-scale landscape pattern. Landscape Ecol. 1987, 1, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, B.T. Spatial aggregation and neutral models in fractal landscapes. Am. Naturalist 1992, 139, 32–57. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, R.V.; Gardner, R.H.; Turner, M.G. A hierarchical neutral model for landscape analysis. Landscape Ecol. 1992, 7, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- With, K.A.; King, A.W. The use and misuse of neutral landscape models in ecology. Oikos 1997, 79, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, D.; Aharony, A. Introduction to Percolation Theory, 2nd ed; CRC Press Inc.: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Mandelbrot, B.B. The Fractal Geometry of Nature; W. H. Freeman and Company Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Saupe, D. Algorithms for Random Fractals. In The Science of Fractal Images; Peitgen, H.O., Saupe, D., Barnsley, M.F., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 71–113. [Google Scholar]
- With, K.A.; Gardner, R.H.; Turner, M.G. Landscape connectivity and population distributions in heterogeneous environments. Oikos 1997, 78, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- With, K.A.; King, A.W. Dispersal success on fractal landscapes: A consequence of lacunarity thresholds. Landscape Ecol. 1999, 14, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- With, K.A.; Cadaret, S.J.; Davis, C. Movement responses to patch structure in experimental fracta landscapes. Ecology 1999, 80, 1340–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- With, K.A.; King, A.W. The effect of landscape structure on community self-organization and critical biodiversity. Ecol. Model. 2004, 179, 349–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.W. The coexistence of species in fractal landscapes. Am. Naturalist 1992, 139, 375–397. [Google Scholar]
- Moloney, K.A.; Levin, S.A. The effects of disturbance architecture on landscape-level population dynamics. Ecology 1996, 77, 375–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurlini, G.; Riitters, K.H.; Zaccarelli, N.; Petrosillo, I. Patterns of disturbances at multiple scales in real and simulated landscapes. Landscape Ecol. 2007, 22, 705–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccarelli, N.; Petrosillo, I.; Zurlini, G.; Riitters, K.H. Source/Sink Patterns of Disturbance and Cross-Scale Mismatches in a Panarchy of Social-Ecological Landscapes. Available online: http://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol13/iss1/art26/ (accessed on 5 February 2013).
- Ricotta, C.; Carranza, M.L.; Avena, G.; Blasi, C. Are potential natural vegetation maps a meaningful alternative to neutral landscape models? Appl. Veg. Sci. 2002, 5, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargrove, W.; Hoffman, F.M.; Schwartz, P.M. A Fractal Landscape Realizer for Generating Synthetic Maps. Available online: http://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol6/iss1/art2/ (accessed on 25 September 2012).
- Neel, M.C.; McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.A. Behavior of class-level landscape metrics across gradients of class aggregation and area. Landscape Ecol. 2004, 19, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, R.H. RULE: A Program for the Generation of Random Maps and the Analysis of Spatial Patterns. In Landscape Ecological Analysis: Issues and Applications; Klopatek, J.M., Gardner, R.H., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 280–303. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta, A.; Carranza, M.L.; Giancola, M. Landscape change and ecosystem classification in a municipal district of a small city (Isernia, Central Italy). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2005, 108, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Reynolds, J.F. A new contagion index to quantify spatial patterns of landscapes. Landscape Ecol. 1993, 8, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- With, K.A. The applications of neutral landscape models in conservation biology. Conserv. Biol. 1997, 11, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Saura, S. Effects of minimum mapping unit on land cover data spatial configuration and composition. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 4853–4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.A.; Ene, E. FRAGSTATS V. 4. Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Categorical and Continuous Maps. Available online: http://www.umass.edu/landeco/research/fragstats/fragstats.html (accessed on 20 September 2012).
- Schindler, S.; Poirazidis, K.; Wrbka, T. Towards a core set of landscape metrics for biodiversity assessments: A case study from Dadia National Park, Greece. Ecol. Indic. 2008, 8, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines-Young, R.; Chopping, M. Quantifying landscape structure: A review of landscape indices and their application to forested landscapes. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 1996, 20, 418–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, S.; Martínez-Millán, J. Landscape patterns simulation with a modified random cluster methods. Landscape Ecol. 2000, 15, 661–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenteras, D.; Gast, F.; Villareal, H. Andean forest fargmentation and the representativeness of protected natural areas in the esatern Andes, Colombia. Biol. Conserv. 2003, 113, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batistella, M.; Robeson, S.; Moran, E.F. Settlement design, forest fragmentation, and landscape change in Rondonia, Amazonia. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sensing 2003, 69, 805–812. [Google Scholar]
- Rocchini, D.; Perry, G.L.W.; Salerno, M.; Maccherini, S.; Chiarucci, A. Landscape change and the dynamics of open formations in a natural reserve. Landscape Urban Plan. 2006, 77, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitzia, T.; Semenzato, P.; Trentanovi, G. Natural reforestation is changing spatial patterns of rural mountain and hill landscapes: A global overview. Forest Ecol. Manage. 2010, 259, 1354–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, R.T.T. Some general principles of landscape and regional ecology. Landscape Ecol. 1995, 10, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, R.T.T.; Godron, M. Landscape Ecology; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzsimmons, M. Effects of deforestation and reforestation on landscape spatial structure in boreal Saskatchewan, Canada. Forest Ecol. Manage. 2003, 174, 577–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southworth, J.; Nagendra, H.; Carlson, L.A.; Tucker, C. Assessing the impact of Celaque National Park on forest fragmentation in western Honduras. Appl. Geogr. 2004, 24, 303–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarigal, K.; Marks, B. FRAGSTATS, Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Quantifying Landscape Structure; PNW-GTR-351; US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Research Station: Portland, OR, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Schumaker, N.H. Using landscape indices to predict habitat connectivity. Ecology 1996, 77, 1210–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opdam, P.; Verboom, J.; Pouwels, R. Landscape cohesion: an index for the conservation potential of landscapes for biodiversity. Landscape Ecol. 2003, 18, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, M.-J.; Boots, B.; Csillag, F. On the role of spatial stochastic models in understanding landscape indices in ecology. Oikos 2003, 102, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torta, G. Consequences of Rural Abandonment in a Northern Apennines Landscape (Tuscany, Italy). In Recent Dynamics of the Mediterranean Vegetation and Landscape; Mazzoleni, S., di Martino, P., Strumia, S., Buonanno, M., Bellelli, M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2005; pp. 157–165. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzoleni, S.; Martino, P.D.; Strumia, S.; Buonanno, M.; Bellelli, M. Recent Changes of Coastal and Sub-Mountain Vegetation Landscape in Campania and Molise Regions in Southern Italy. In Recent Dynamics of the Mediterranean Vegetation and Landscape; Mazzoleni, S., di Pasquale, G., Mulligan, M., di Martino, P., Rego, F., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2005; pp. 143–155. [Google Scholar]
- Globevnik, L.; Kaligarič, M.; Sovinc, A. Forest Cover Progression, Land-Use and Socio-Economic Changes on the Edge of the Mediterranean. In Recent Dynamics of the Mediterranean Vegetation and Landscape; Mazzoleni, S., di Pasquale, G., Mulligan, M., di Martino, P., Rego, F., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2005; pp. 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Lasanta-Martínez, T.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Cuadrat-Prats, J.M. Mountain Mediterranean landscape evolution caused by the abandonment of traditional primary activities: A study of the Spanish Central Pyrenees. Appl. Geogr. 2005, 25, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirado, M.; Pino, J.; Rodà, F.; Basnou, C. Quercus and Pinus cover are determined by landscape structure and dynamics in peri-urban Mediterranean forest patches. Plant Ecol. 2007, 194, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, W.; Stortelder, A. Vanishing Tuscan Landscapes: Landscape Ecology of a Submediterranean-Montane Area (Solano Basin, Tuscany, Italy); Pudoc Scientific Publishers: Wageningen, NL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Myster, R.W.; Malahy, M.P. Is there a middle way between permanent plots and chronosequences? Can. J. Forest Res. 2008, 38, 3133–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myster, R.W.; Pickett, S.T.A. A comparison of rate of succession over 18 Yr in 10 contrasting old fields. Ecology 1994, 75, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pueyo, Y.; Beguería, S. Modelling the rate of secondary succession after farmland abandonment in a Mediterranean mountain area. Landscape Urban Plan. 2007, 83, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, H.S.; Wang, X.; Bu, R.; Hu, Y.; Chang, Y. Evaluating the effectiveness of neutral landscape models to represent a real landscape. Landscape Urban Plan. 2004, 69, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatoni, T.; Médail, F.; Roche, P.; Barbero, M. The Impact of Changes in Land Use on Ecological Patterns in Provence (Mediterranean France). In Recent Dynamics of the Mediterranean Vegetation and Landscape; Mazzoleni, S., di Pasquale, G., Mulligan, M., di Martino, P., Rego, F., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2005; pp. 105–120. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho-Silva, J.L.; Castro Rego, F.; Castelbranco Silveira, S.; Cardoso Gonçalves, C.P.; Machado, C.A. Rural Changes and Landscape in Serra da Malcata, Central East of Portugal. In Recent Dynamics of the Mediterranean Vegetation and Landscape; Mazzoleni, S., di Pasquale, G., Mulligan, M., di Martino, P., Rego, F., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2005; pp. 189–200. [Google Scholar]
- Geri, F.; Rocchini, D.; Chiarucci, A. Landscape metrics and topographical determinants of large-scale forest dynamics in a Mediterranean landscape. Landscape Urban Plan. 2010, 95, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertacchi, A.; Onnis, A. Changes in the Forested Agricultural Landscape of the Pisan Hills (Tuscany, Italy). In Recent Dynamics of the Mediterranean Vegetation and Landscape; Mazzoleni, S., di Pasquale, G., Mulligan, M., di Martino, P., Rego, F., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2005; pp. 167–178. [Google Scholar]
- Zerbe, S. Potential natural vegetation: Validity and applicability in landscape planning and nature conservation. Appl. Veg. Sci. 1998, 1, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, A.; Diekmann, M. Effects of life-history traits on responses of plant species to forest fragmentation. Conserv. Biol. 2005, 19, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carranza, M.L.; Frate, L.; Paura, B. Structure, ecology and plant richness patterns in fragmented beech forests. Plant Ecol. Divers. 2012, 5, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortelliti, A.; Amori, G.; Capizzi, D.; Cervone, C.; Fagiani, S.; Pollini, B.; Boitani, L. Independent effects of habitat loss, habitat fragmentation and structural connectivity on the distribution of two arboreal rodents. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 48, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, W.L.; Ostertag, R.; Lugo, A.E. The potential for carbon sequestration through reforestation of abandoned tropical agricultural and pasture lands. Restor. Ecol. 2000, 8, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Hairsine, P.B.; Arancibia, J.P.; Dowling, T.I. Reforestation, water availability and stream salinity: A multi-scale analysis in the Murray-Darling Basin, Australia. Forest Ecol. Manage. 2007, 251, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathurst, J.C.; Bovolo, C.I.; Cisneros, F. Modelling the effect of forest cover on shallow landslides at the river basin scale. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellrich, M.; Baur, P.; Koch, B.; Zimmermann, N.E. Agricultural land abandonment and natural forest re-growth in the Swiss mountains: A spatially explicit economic analysis. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 118, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, S.; Fürst, C.; Koschke, L.; Makeschin, F. A contribution towards a transfer of the ecosystem service concept to landscape planning using landscape metrics. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 21, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, J.; Aronson, J. Biology and Wildlife of the Mediterranean Region; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wainwright, J.; Thornes, J.B. Environmental Issues in the Mediterranean Processes and Perspectives from the Past and Present; Rutledge: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zurlini, G.; Petrosillo, I.; Jones, K.B.; Zaccarelli, N. Highlighting order and disorder in social-ecological landscapes to foster adaptive capacity and sustainability. Landscape Ecol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
