Abstract
Georeferenced data are crucial for addressing societal spatial challenges, as most corporate and governmental information is location-compatible. However, many open-source solutions lack automation in geocoding while ensuring quality. This study evaluates the functionalities of various R packages and their integration with external APIs for converting postal addresses into geographic coordinates. Among the fifteen R methods/packages reviewed, tidygeocoder stands out for its versatility, though discrepancies in processing times and missing values vary by provider. The accuracy was assessed by proximity to original dataset coordinates (Madrid street map) using a sample of 15,000 addresses. The results indicate significant variability in performance: MapQuest was the fastest, ArcGIS the most accurate, and Nominatim had the highest number of missing values. To address these issues, an alternative web scraping methodology is proposed, substantially reducing the error rates and missing values, but raising potential legal concerns. This comparative analysis highlights the strengths and limitations of different geocoding tools, facilitating better integration of geographic information into datasets for researchers and social agents.
1. Introduction
In the era of digitalization and connectivity, the use of data is the cornerstone of the technological revolution. Huge amounts of data are generated around the world every second, from financial transactions and health records to social media posts and online purchases [1]. The reduction in the prices of storage systems and technological advances has facilitated the storage, processing, and analysis of this huge amount of data, (potentially) offering a powerful tool for companies, governments, and institutions. However, data alone cannot add value. They must be adequate and of sufficient quality, with a double objective: (i) to facilitate adequate decision-making [2,3]; and (ii) to generate transparency, trust, and knowledge, enabling society to be more efficient [4].
In recent years, initiatives related to offering open data and the reuse of information have increased considerably [5,6]. But having data is not enough. Steps must be taken to ensure the quality and accessibility of the data, as well as the interoperability of the systems used for the data collection, storage, and processing [7]. Clear standards and protocols must, therefore, be established to guarantee the quality of the data and facilitate their use and reuse by the scientific community and other stakeholders [8].
Much of the data that are currently being generated are unstructured data that (may) contain the location of a certain event, obtained from sensors and mobile devices with positioning systems. In contrast, much of the (structured) data available in open data repositories, compatible with spatial information, are not georeferenced. In fact, it is estimated that half of the data openly available do not have geographic information [9], possibly because incorporating the spatial component can be a more complex and costly process than simply collecting information on an object or topic.
The importance of spatial data lies in the data’s ability to provide a deeper and more detailed understanding of the world around us [10]. Data are used in a wide variety of applications, from urban planning and transportation to natural disaster management and precision agriculture [11]. Knowing what is happening, and where, is extremely relevant for various social and economic agents, with this being the second category of data most reused and consulted by companies in the EU [12]. For this reason, it is of great interest to the scientific community, and to society in general, to have tools and techniques that make it possible to elaborate/complete/improve datasets with spatial information.
Despite their usefulness, however, spatial data present some common problems and difficulties. One of the biggest challenges is the complexity of data collection and processing. The number and variety of spatial data sources available can be overwhelming, and data processing and analysis can be costly and time consuming. Some of the problems that the researcher usually encounters (when using location data) are related to: (i) missing values; (ii) precision in the coordinates; and (iii) the absence in the metadata of the Coordinate Reference System (CRS) used [13].
The objective of this paper is to propose methods and tools that enable quality datasets to be built/improved that include the spatial component. Specifically, two techniques are proposed to obtain geographic coordinates from postal addresses (geocoding): one based on the use of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), and another based on the automated extraction of data from websites (web scraping). In both cases, R statistical software [14] is used (version 4.3.2), as this is a free tool widely used in research [15].
2. Related Work
Geocoding, geolocation, or address matching is defined as the action of attributing geographic coordinates (latitude, longitude) to one or more events, using the postal address as a reference [16]. This technique allows researchers and other economic and social agents to carry out analyses and identify patterns based on spatial information. It is a technique that has its uses in multiple areas and fields of research; for example, in: (i) market analysis, where the behavior and trends of various agents can be analyzed according to their geographical location [17]; (ii) tourism, in identifying the behavior patterns of tourists to optimize the offer of certain services [18]; (iii) logistics and transportation, in identifying the locations of distribution centers and facilitating the optimization of routes [19]; (iv) emergency services, to obtain the location of an emergency quickly and accurately [20]; (v) urbanism, in assisting with urban development planning and improving the quality of life of citizens [21]; and (vi) scientific research, in facilitating the study of spatial patterns and the interactions of natural phenomena, as well as carrying out epidemiological analyses [22].
Geocoding has become a widely used technique, both for performing multiple spatial analyses and for decision-making [23]. Various authors refer to geocoding as a powerful tool that enables complex spatial analysis, highlighting the added value that the spatial component brings to datasets. Präger et al. [24] highlight the usefulness of the online geocoding services of Google and OpenStreetMap (OSM) in the detection of factors that promote obesity, concluding that its validity is reasonable, and that it can be used in diabetes surveillance. Chopin and Caneppele [25] use geocoding to carry out an exploratory analysis of mobility between aggressors and victims in crimes of child abuse in France. McIntire et al. [26] geocodes the addresses of 10,750 patients with prostate cancer in the state of Pennsylvania (USA) to create a composite index that identifies the neighborhoods with the highest incidence of the disease. Geocoding also becomes especially relevant in data obtained from social media. Ref. [27] tackled the challenge of geocoding non-geotagged tweets from location-based social networks, proposing a privacy-preserving geocoding method, P-GENT, which ensures privacy while maintaining a high accuracy and utility of the social media data for spatial analysis.
Given the diversity of the geocoding services available, it is crucial to systematically evaluate their output, so as to ensure that decision-makers are relying on the most accurate and reliable data. While some previous work has focused on assessing the accuracy of these services [28,29], there is a need for more in-depth evaluations considering a broader range of current service providers and their evolving technologies. This could lead to a better understanding of their respective strengths and limitations, ultimately enhancing the precision of geocoding applications across different fields.
Due to the growing interest that geocoding is arousing in various economic and social fields, there is now a wide range of methods that address this issue from different perspectives [30,31,32,33,34]. One of the most widely used tools is a web map viewer which, due to its appealing presentation and easy access, allows any citizen to quickly obtain the geographic coordinates of practically any postal address. While there are many options, such as Bing Maps, Here Map, MapQuest, or Waze Map [35], the most used option is Google Maps, with 80% of the market share worldwide [36].
Web map viewers are a perfectly valid option when working with just a few addresses. However, when the goal is to obtain hundreds or thousands of locations, automating the process is essential. Below are two methods that automate the process of obtaining coordinates from postal addresses.
3. Materials and Methods
This section details the systematic approach used to enrich datasets with geospatial information, utilizing various geocoding tools. Our methodology encompasses several steps, starting from the initial data input, through the variable selection and address compilation, to the application of the geocoding processes using different R packages and geocoding service providers. Figure 1 outlines the sequence of operations performed, including decisions on the use of APIs or web scraping based on the effectiveness of the initial geocoding results. Section 3.1 and Section 3.2 further elaborate on the specific tools and techniques employed, illustrating our comprehensive approach to ensuring the accuracy and utility of the geospatial data obtained.

Figure 1.
Flowchart of the data enrichment process using geocoding and web scraping techniques.
3.1. Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)
APIs help to significantly smooth out these automation processes, allowing for applications and/or computer systems to be connected with extensive and updated databases of geographic information [37,38]. Some examples of APIs that allow for geocoding processes to be carried out are: (i) Google Maps Geocoding API; (ii) OpenCage Geocoding API; (iii) HERE Geocoding & Search API; (iv) Bing Maps API; (v) Esri ArcGIS REST APIs–Geocoding Services; (vi) Mapbox Geocoding API; (vii) TomTom Geocoding API; (viii) MapQuest Geocoding API; and (ix) Nominatim (free and open source geocoding API using data from OpenStreetMap).
Many of the existing geocoding APIs can be managed using R. This is currently one of the most widely used programming languages in data analysis, and can facilitate massive data collection and subsequent processing. Table 1 shows the correspondence between different geocoding APIs and some R packages that facilitate their use.

Table 1.
Correspondence of geocoding APIs and R packages.
Two of the most prominent R packages shown in Table 1 are ggmap [39] and tidygeocoder [40]; the first for being the one that was downloaded the most times from the CRAN repository during 2023 (see Table 2), and the second for offering great versatility, since it can work with all of the aforementioned APIs.

Table 2.
The number of times each R package was downloaded from the CRAN repository during 2023. Source: compiled by the authors, based on the results reported by the cranlogs R package.
While APIs simplify the process of geocoding, every provider sets specific limitations on the utilization of their service without incurring costs. For instance, accessing the Google, Bing, or HERE APIs requires users to first register and acquire a personal key (API-KEY). Table 3 presents the various features and conditions for the free use of each API, detailing the requirements and the extent of the free access provided by these platforms.

Table 3.
Characteristics and conditions of use of different geocoding APIs.
Since there are different options (R packages) that enable geocoding processes to be carried out, a comparison of their effectiveness would be useful. To do this, we use a large dataset (the street map of Madrid), which contains more than two hundred thousand observations (postal addresses) and 20 variables [41]. These variables include road type (VIA_CLASE), street name (VIA_NOMBRE, VIA_NOMBRE_ACENTOS), house number (NUMERO), type of numbering (TIPO_NDP), and unique identifiers for the road (COD_VIA) and house number (COD_NDP). Additionally, the dataset comprises the district (DISTRITO) and neighborhood codes (BARRIO), postal codes (COD_POSTAL), and geographical coordinates in both the ED50 (UTMX_ED, UTMY_ED) and ETRS89 (UTMX_ETRS, UTMY_ETRS, LATITUD, LONGITUD) geodetic systems. It also includes the angle of the house number signage relative to the building facade (ANGULO_ROTULACION).
This dataset enables two actions to be completed: (i) obtaining coordinates from postal addresses; and (ii) determining the geographic distances between the coordinates obtained in the geocoding process and those provided in the dataset itself. A random sample (n = 15,000) of postal addresses is selected, and the different R packages under analysis in this paper are tested. Given the usage limitations outlined in Table 3, the sample is divided into 100 subsamples (S1 to S100) of 150 observations each.
The versatility of the tidygeocoder R package is scrutinized, emphasizing its support for up to 13 different geocoding services. Nine methods (service providers) have been selected, applying this function across 150 subsamples. The geocoding process is conducted using the package’s geo() function, showcasing its extensive capabilities. Similarly, six alternative R packages are analyzed, each with a function developed to geocode using a single service provider: (i) ggmap [42] for Google Maps Geocoding API; (ii) hereR [43] for HERE Geocoding & Search API; (iii) mapquestr [44] for MapQuest Geocoding API; (iv) tmaptools [45]; (v) opencage [46]; and (vi) mapboxapi [47] for the Mapbox Geocoding API. All tests were conducted using the same computer, with the following specifications: 3.30 GHz processor speed and 8 GB of RAM.
Knowing the speed of the process (computation time) and the success/error rate (number of missing values) for each package and method (service provider) allows the researcher to select the appropriate option for the task in hand. However, this is not enough; the reliability of the data is also a fundamental characteristic. For this reason, we consider it appropriate to audit the results obtained, calculating the Euclidean distance between the coordinates obtained in the geocoding process and the coordinates included in the dataset used, implementing the st_distance() function of the sf package [48]. This verification process, in addition to providing confidence to the end user, fulfils one of the purposes of this document: to generate (sets of) quality data.
3.2. Automated Data Extraction from Websites (Web Scraping)
The use of R packages that interact with geolocation service APIs has proven to be an efficient option for geocoding postal addresses and obtaining geographic coordinates quickly. However, in some cases, the results are seen to be unreliable, which gives rise to the need to explore other alternatives. One such alternative is the promising strategy of web scraping on web map viewers. This technique offers the possibility of extracting geographic information directly from online platforms, which expands the data sources available for geocoding. Also, by getting data directly from map viewers, dependency on third-party geolocation service providers can be reduced, which helps increase autonomy in the geocoding process. In this section we explore in detail the use of web scraping as a valuable tool for obtaining coordinates from postal addresses, offering a reliable and complementary alternative to the methods presented in the previous section.
The widespread use of the Internet, together with different platforms, both private and open source, allows any agent to locate a specific postal address on the map and, consequently, to obtain its geographic coordinates. Online map viewers, such as Google Maps, have become very popular and useful tools nowadays, due to their appealing presentation, easy access, and the large amount of geographic information they provide. In addition to Google Maps, there are other options, such as Bing Maps, HERE WeGo, OpenStreetMap, and many others, each with their own interface, but with a similar appearance. These map viewers allow users to locate postal addresses, explore remote locations around the world, and plan routes. They also make it possible to search for and obtain geographic coordinates from postal addresses. However, as we mentioned at the beginning of the paper, this process carried out manually fulfils its objective for specific enquiries, but it is not efficient when multiple coordinates are needed.
A possible solution to this problem is to use web scraping techniques, which enable information to be extracted from web pages, their HTML code scanned, and data extraction patterns generated [49]. These techniques can be implemented in R with the rvest [50] and RSelenium [51] R packages, among others, although there are notable differences between them. On the one hand, rvest enables the extraction of data from web pages through static web scraping; that is, selecting elements of a web page using CSS and XPath selectors [52]. On the other hand, with RSelenium, the user can connect with web pages that require interaction to extract data. RSelenium uses a Selenium server [53] to control a web browser and perform tasks, such as clicking buttons, filling in forms, or browsing different pages. In this way, data can be extracted from web pages that require interaction.
The proposed method consists of automating the sequential scheme, represented in Figure 2, by implementing various functions of the RSelenium package. To verify the operation of this procedure, and purely for academic purposes, we develop an R script that allows the described sequence to be carried out (see the Supplementary Materials).
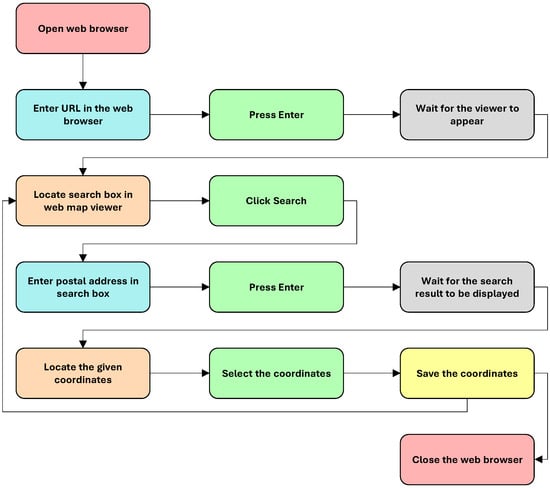
Figure 2.
Sequential diagram of the manual retrieval process to obtain coordinates from a web map viewer.
When using web scraping techniques, it is essential to include pauses in the script, allowing the browser to perform certain actions, such as opening pages and loading content, before continuing. When defining a sequential system, in which the user must wait until one step is finished to start the next, several issues must be considered, such as the need for a certain web page to be fully loaded before interacting with its content. In fact, since this procedure is based on interacting with specific elements of the web, such as clicking buttons or filling in forms, the possible limitations of the equipment/computer system used (internet connection speed, etc.) should also be considered.
4. Results
This section presents the results obtained from applying the methodology outlined in the previous section. Following the procedures and analyses described, we have systematically evaluated the performance, accuracy, and limitations of various geocoding services. The outcomes of these evaluations, including computational times, the incidence of missing values, and overall efficiency of each method, are detailed in this part of the paper. The results are crucial for understanding the practical implications of choosing one geocoding service over another, as they provide concrete data on performance metrics and reliability across different platforms.
Table 4 shows the computing times for the subsample and method (service provider) used, as well as the missing values (number of non-geocoded addresses, from here on NA). As can be seen, MapQuest is the fastest method, with an average of 2.099 s per subsample (314.86 s for the 15,000 observations), while the slowest methods are OSM and OpenCage, with a computation time of 139.641 and 104.805 s per subsample, respectively. Regarding missing values, OSM is the method with the highest error rate, at 3.1% (466 NAs), followed by HERE, with 0.95% (142 NAs).

Table 4.
Time and number of NAs (in brackets) using tidygeocoder R package.
Complementing the previous information, we analyze other R packages that enable geocoding by implementing some of the methods presented in the first column of Table 4. The ggmap and hereR packages present results like those obtained with the “Google” and “HERE” methods of tidygeocoder. In the case of the mapquestr package, the computation times are much higher than those obtained with the “MapQuest” method. The method tmaptools halves the computation times of the “OSM” method, but maintains the same number of missing values (NA). The opencage package reports computation times higher than those obtained by the “OpenCage” method. The opposite occurs with the mapboxapi package, which reduces the computing times of the Mapbox service used in tidygeocoder by more than 60% (see Table 5).

Table 5.
Time and number of NAs (in brackets) using different R packages.
To audit the results obtained, we have compared geocoded coordinates with the original data. Table 6 shows the median of the Euclidean distances obtained for each subsample analyzed and for each of the 15 methods used (M1–M15). The median is used instead of the average, to avoid the distortions produced by the extreme values caused by geocoding errors that report greater distances with respect to the coordinates offered in the original dataset. M9 is the method that best replicates the coordinates provided in the Madrid street map. The M3, M11 and M12 methods also offer results with a high degree of accuracy, giving an average distance within less than 2 m.

Table 6.
Median of the Euclidean distance, in meters, between the coordinates included in the original dataset and those obtained by geocoding for each subsample and method.
Based on the distance between the coordinates obtained by geocoding and the coordinates included in the original dataset, the methods M5, M6, M13 and M14 are seen to be the ones that return the greatest discrepancies in distances. This is mainly due to detection/interpretation errors by the municipality. For example, for the first subsample (S1), the methods M5 and M13 (Nominatim service), in addition to not geocoding three postal addresses (see Table 4 and Table 5), impute ten locations to municipalities other than Madrid (see the red dots on the left panel of Figure 3). Of these ten points, nine are located in towns close to the Spanish capital, within the Community of Madrid itself (lightly brown-colored area), while another point is located in the American continent, specifically in Mexico City. Similar errors occur with the M6 and M14 (OpenCage) methods. In this case, all of the postal addresses of S1 are geocoded, but the results are not as accurate as one would hope (see the black dots in the right panel of Figure 3). Twenty-five locations are outside the municipal boundaries of Madrid, two of which are positioned again in Mexico City. The green dots indicate the coordinates offered in the original dataset, corresponding to the 150 postal addresses in the subsample.

Figure 3.
Graphic representation of the geographic coordinates corresponding to the postal addresses of the S1 subsample: (a) coordinates obtained by geocoding (methods M5 and M13) are in red; (b) coordinates obtained with the M6 and M14 methods are in black. Coordinates included in the original dataset are shown in green (both panels). In brown, the Autonomous Community of Madrid; in white, the Municipality of Madrid.
Regarding the use of web scraping techniques, the following results have been obtained. On the one hand, in terms of accuracy and missing values, the proposed method matches the performance of APIs, as it can retrieve the same coordinates reported by the R packages explored in this document. On the other hand, as expected, the time taken to obtain the coordinates is substantially longer than that reported by the R packages, largely due to the waiting times that must be introduced into the algorithm to allow the browser to load the necessary data. Despite this, this method significantly reduces the time and effort required to manually collect geographical data.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
In a world where georeferenced data offers substantial added value, most freely available databases lack spatial information. This study provides a comparative analysis of geocoding techniques to address this gap, focusing on API management through R packages and web scraping methods. Our findings highlight the significant variability in performance across different methods.
We evaluated fifteen geocoding methods using tidygeocoder and other R packages, noting computation times, missing values, and accuracy relative to the original dataset coordinates. Key outcomes include: (i) computation time: MapQuest emerged as the fastest method, averaging 2.099 s per subsample, significantly quicker than others like OSM and OpenCage, which took over 100 s; (ii) missing values: Nominatim (OSM) had the highest error rate, with an average of 3.107% missing values per subsample, while most methods, including Google and Bing, had negligible missing values; (iii) accuracy: ArcGIS was the most accurate, with an average Euclidean distance of 0.0025 m from the original coordinates, outperforming others like OpenCage, which had an average error of 483.547 m.
The results equip researchers and social agents with insights to select the most suitable geocoding method based on their needs. The significant outcome of this study is the identification of MapQuest as the fastest tool, ArcGIS as the most accurate, and the caution against using Nominatim for high-precision tasks due to its higher error rates.
Web scraping techniques were proposed as an alternative, demonstrating reduced error rates and missing values compared to some API-based methods. However, this approach raises potential legal and ethical concerns, and requires adaptation to specific platforms.
Future research could develop an R package to automate the geocoding method selection based on specific criteria, potentially integrating machine learning techniques to predict the methods’ performance. This advancement would further enhance the integration of spatial data into existing and new databases, offering substantial economic and social benefits.
By providing a detailed comparative analysis, this research aids in making informed decisions about geocoding approaches, ultimately facilitating better integration of geographic information into datasets across various research settings needs.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijgi13060170/s1, Table S1: Time and number of NAs using tidygeocoder R package; Table S2: Time and number of NAs using different R packages; Table S3: Median of the Euclidean distance, in meters, between the coordinates included in the original dataset and those obtained by geocoding for each subsample and method; File S4: Web scraping R script.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Virgilio Pérez; methodology, Virgilio Pérez and Cristina Aybar; software, Virgilio Pérez; validation, Virgilio Pérez; formal analysis, Cristina Aybar; investigation, Virgilio Pérez and Cristina Aybar; data curation, Cristina Aybar; writing—original draft preparation, Virgilio Pérez; writing—review and editing, Virgilio Pérez and Cristina Aybar; visualization, Virgilio Pérez; supervision, Cristina Aybar; funding acquisition, Virgilio Pérez and Cristina Aybar. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Department of Education, Universities, and Employment of Valencian Government [grant numbers AICO/2021/257, CIAICO/2023-GVRTE/2023/4572860] and Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities [grant number PID2021-128228NB-I00].
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Shreyas, M.; Tyagi, A. The World with Future Technologies (Post-COVID-19): Open Issues, Challenges, and the Road Ahead. Intelligent Interactive Multimedia Systems for e-Healthcare Applications; Springer: Auburn, AL, USA, 2022; pp. 411–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, M.A.; López-Ayuso, B.; Paniagua, E.; Cadenas, J.M. Una revisión de la Cadena Datos-Información-Conocimiento desde el Pragmatismo de Peirce. Doc. Cienc. Inf. 2015, 38, 153–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Curto-Rodríguez, R. Análisis multidimensional de los portales de datos abiertos autonómicos españoles. Rev. Española Doc. Científica 2021, 44, e284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, V. Aproximaciones Metodológicas para la Obtención de Bases de Datos de Calidad. Instrumentos de Análisis del Cambio Económico y Social. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Valencia, Valencia, Spain, 2023. Available online: https://roderic.uv.es/handle/10550/85100 (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Peset, F.; Aleixandre, R.; Blasco, Y.; Ferrer, A. Datos abiertos de investigación. Camino recorrido y cuestiones pendientes. An. Doc. 2017, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pérez, V.; Aybar, C.; Pavía, J.M. Spanish electoral archive. SEA database. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Foerster, T.; Yue, P. The Geoprocessing Web. Comput. Geosci. 2012, 47, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abella, A.; Ortiz, M.; Pablos-Heredero, C. Indicadores de calidad de datos abiertos: El caso del portal de datos abiertos de Barcelona. Prof. Inf. 2018, 27, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abella, A.; Ortiz, M.; Pablos-Heredero, C.; García-Luna, D. La Reutilización de Datos Abiertos III; ESIC: Madrid, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.; Torgo, L.; Bifet, A. A Survey on Spatio-temporal Data Analytics Systems. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 54, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, I.; Ramírez, E. Potencialidades y limitaciones de los datos inspire de catastro para la cartografía y caracterización de la edificación rural. Aplicación a la provincia de Sevilla. GeoFocus. Rev. Int. Cienc. Tecnol. 2019, 23, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Data Portal. Reusing Open Data; EU Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrienko, G.; Andrienko, N.; Fuchs, G. Understanding movement data quality. J. Locat. Based Serv. 2016, 10, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sardareh, A.S.; Brown, G.; Denny, P. Comparing four contemporary statistical software tools for introductory data science and statistics in the social sciences. Teach. Stat. 2021, 43, S157–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prener, C.G.; Fox, B. Creating open source composite geocoders: Pitfalls and oportunities. Trans. GIS 2021, 25, 1868–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchuente, D.; Nyawa, S. Real estate price estimation in French cities using geocoding and machine learning. Ann. Oper. Res. 2022, 308, 571–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiliç, B.; Gulgen, F. Accuracy and similarity aspects in online geocoding services: A comparative evaluation for Google and Bing Maps. Int. J. Eng. Geosci. 2020, 5, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumedah, G. Address points of landmarks and paratransit services as a credible reference database for geocoding. Trans. GIS 2021, 25, 1027–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Mao, H.; Wang, Y.; Rae, C.; Shaw, W. Hyper-resolution monitoring of urban flooding with social media and crowdsourcing data. Comput. Geosci. 2018, 111, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, U.; Shamsi, M.; Bohacek, M.; Purcell, K.; Hoare, K.; Mangina, E.; O’Donnell, J. A data-driven approach for multi-scale GIS-based building energy modeling for analysis, planning and support decision making. Appl. Energy 2020, 279, 115834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnee, E.; Tripathy, S.; Schinasi, L.; Shmool, J.; Sheffield, P.; Holguin, F.; Clougherty, J. Geocoding Error, Spatial Uncertainty, and Implications for Exposure Assessment and Environmental Epidemiology. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Stefanakis, E. What3Words Geocoding Extensions. J. Geovis. Spat. Anal. 2018, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Präger, M.; Kurz, C.; Böhm, J.; Laxy, M.; Maier, W. Using data from online geocoding services for the assessment of environmental obesogenic factors: A feasibility study. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2019, 18, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopin, J.; Caneppele, S. Geocoding child sexual abuse: An explorative analysis on journey to crime and to victimization from French police data. Child Abus. Negl. 2019, 91, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntire, R.; Keith, S.; Boamah, M.; Leader, A.; Glanz, K.; Klassen, A.; Zeigler, C. A Prostate Cancer Composite Score to Identify High Burden Neighborhoods. Prev. Med. 2018, 112, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Sinnott, R.; Nepal, S. P-GENT: Privacy-Preserving Geocoding of Non-Geotagged Tweets. In Proceedings of the 17th IEEE International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications, New York, NY, USA, 1–3 August 2018; pp. 972–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roongpiboonsopit, D.; Karimi, H.A. Comparative evaluation and analysis of online geocoding services. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 1081–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra Requena, R.; Martínez-Llario, J.C.; Lorenzo-Sáez, E.; Coll-Aliaga, E. Development of an Algorithm to Evaluate the Quality of Geolocated Addresses in Urban Areas. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, S.E.; Strauss, B.; Miranda, M.L. Geocoding Large Population-Level Administrative Datasets at Highly Resolved Spatial Scales. Trans. GIS 2014, 18, 586–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, T.; Dede-Bamfo, N.; Dahal, K. Geographic disparity of positional errors and matching rate of residential addresses among geocoding solutions. Ann. GIS 2016, 22, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, E.; Danjou, A.; Clavel-Chapelon, F.; Boutron-Ruault, M.; Dossus, L.; Fervers, B. Accuracy of two geocoding methods for geographic information system-based exposure assessment in epidemiological studies. Environ. Health 2017, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Claridades, A.R.; Lee, J. Improving a Street-Based Geocoding Algorithm Using Machine Learning Techniques. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Kang, M.; Wu, Y.; Du, Q.; Liu, T. A deep learning architecture for semantic address matching. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2020, 34, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horbinski, T.; Cybulski, P. Similarities of global web mapping services functionality in the context of responsive web design. Geod. Cartogr. 2018, 67, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, C.G. One Map to Rule Them All: Google Maps and Quasi-Sovereign Power in International Legal Disputes. Hastings Sci. Technol. Law J. 2023, 14, 67–122. [Google Scholar]
- Kiliç, B.; Hacar, M.; Gulgen, F. Effects of reverse geocoding on OpenStreetMap tag quality assessment. Trans. GIS 2023, 27, 1599–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H. Describing the APIs comprehensively: Obtaining the holistic representations from multiple modalities data for different tasks. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2023, 158, 107188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahle, D.; Wickham, H. ggmap: Spatial Visualization with ggplot2. R J. 2013, 5, 144–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambon, J.; Hernangómez, D.; Belanger, C.; Possenriede, D. tidygeocoder: An R package for geocoding. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 65, 3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid City Council. Callejero Oficial del Ayuntamiento de Madrid. Available online: https://datos.madrid.es/portal/site/egob (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Kahle, D.; Wickham, H.; Jackson, S.; Korpela, M. ggmap: Spatial Visualization with ggplot2; R Package Version 4.0.0. 2023. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=ggmap (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Unterfinger, M.; Possenriede, D. hereR: ‘sf’-Based Interface to the ‘HERE’ REST APIs; R Package Version 1.0.0. 2023. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=hereR (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Chiou, E. mapquestr: R Interface to Interact with (Parts of) the MapQuest APIs; R Package Version 0.1.0. 2023. Available online: https://github.com/chiouey/mapquestr/ (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Tennekes, M. tmaptools: Thematic Map Tools; R Package Version 3.1.1. 2021. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=tmaptools (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Possenriede, D.; Sadler, J.; Salmon, M.; Ross, N.; Russ, J.; Silge, J. opencage: Geocode with the OpenCage API; R Package Version 0.2.2. 2021. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=opencage (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Walker, K.; Pousson, E.; North, A.; McBain, M. mapboxapi: R Interface to ‘Mapbox’ Web Services; R Package Version 0.5.3. 2022. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=mapboxapi (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Pebesma, E. Simple Features for R: Standardized Support for Spatial Vector Data. R J. 2018, 10, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo, D.; Saavedra, D. Web Scraping de los Perfiles y Publicaciones de una Afiliación en Google Scholar utilizando Aplicaciones Web e implementando un Algoritmo en R. In Proceedings of the 4th Internacional Congress AmITIC, Popayán, Colombia, 6 September 2017; Available online: https://ridda2.utp.ac.pa/handle/123456789/1689 (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Wickham, H. rvest: Easily Harvest (Scrape) Web Pages; R Package Version 1.0.4. 2024. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=rvest (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Harrison, J. RSelenium: R Bindings for Selenium WebDriver; R Package Version 1.7.9. 2022. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=RSelenium (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Parvez, M.S.; Agah-Tasneem, K.S.; Rajendra, S.; Bodke, K. Analysis of Different Web Data Extraction Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Smart City and Emerging Technology (ICSCET), Mumbai, India, 5 May 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Z. Remote Control Server. In Selenium WebDriver Recipes in C#, 2nd ed.; Zhan, Z., Ed.; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).